Dinosaur Hunting on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Dinosaurs are a diverse group of
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of
 Using one of the above definitions, dinosaurs can be generally described as
Using one of the above definitions, dinosaurs can be generally described as
 A detailed assessment of archosaur interrelations by
A detailed assessment of archosaur interrelations by  A variety of other skeletal features are shared by dinosaurs. However, because they either are common to other groups of archosaurs or were not present in all early dinosaurs, these features are not considered to be synapomorphies. For example, as
A variety of other skeletal features are shared by dinosaurs. However, because they either are common to other groups of archosaurs or were not present in all early dinosaurs, these features are not considered to be synapomorphies. For example, as
 Scholarly descriptions of what would now be recognized as dinosaur bones first appeared in the late 17th century in England. Part of a bone, now known to have been the femur of a ''
Scholarly descriptions of what would now be recognized as dinosaur bones first appeared in the late 17th century in England. Part of a bone, now known to have been the femur of a '' Between 1815 and 1824, the Rev
Between 1815 and 1824, the Rev
 New revelations were supported by an increase in dinosaur discoveries. Major new dinosaur discoveries have been made by paleontologists working in previously unexplored regions, including India, South America, Madagascar, Antarctica, and most significantly China. Across theropods, sauropodomorphs, and ornithischians, the number of named genera began to increase exponentially in the 1990s. In 2008 over 30 new species of dinosaurs were named each year. At least sauropodomorphs experienced a further increase in the number of named species in the 2010s, with an average of 9.3 new species having been named each year between 2009 and 2020. As a consequence, more sauropodomorphs were named between 1990 and 2020 than in all previous years combined. These new localities also led to improvements in overall specimen quality, with new species being increasingly named not on scrappy fossils but on more complete skeletons, sometimes from multiple individuals. Better specimens also led to new species being invalidated less frequently. Asian localities have produced the most complete theropod specimens, while North American localities have produced the most complete sauropodomorph specimens.
Prior to the dinosaur renaissance, dinosaurs were mostly classified using the traditional rank-based system of
New revelations were supported by an increase in dinosaur discoveries. Major new dinosaur discoveries have been made by paleontologists working in previously unexplored regions, including India, South America, Madagascar, Antarctica, and most significantly China. Across theropods, sauropodomorphs, and ornithischians, the number of named genera began to increase exponentially in the 1990s. In 2008 over 30 new species of dinosaurs were named each year. At least sauropodomorphs experienced a further increase in the number of named species in the 2010s, with an average of 9.3 new species having been named each year between 2009 and 2020. As a consequence, more sauropodomorphs were named between 1990 and 2020 than in all previous years combined. These new localities also led to improvements in overall specimen quality, with new species being increasingly named not on scrappy fossils but on more complete skeletons, sometimes from multiple individuals. Better specimens also led to new species being invalidated less frequently. Asian localities have produced the most complete theropod specimens, while North American localities have produced the most complete sauropodomorph specimens.
Prior to the dinosaur renaissance, dinosaurs were mostly classified using the traditional rank-based system of
 Dinosaur fossils are not limited to bones, but also include imprints or mineralized remains of skin coverings, organs, and other tissues. Of these, skin coverings based on
Dinosaur fossils are not limited to bones, but also include imprints or mineralized remains of skin coverings, organs, and other tissues. Of these, skin coverings based on
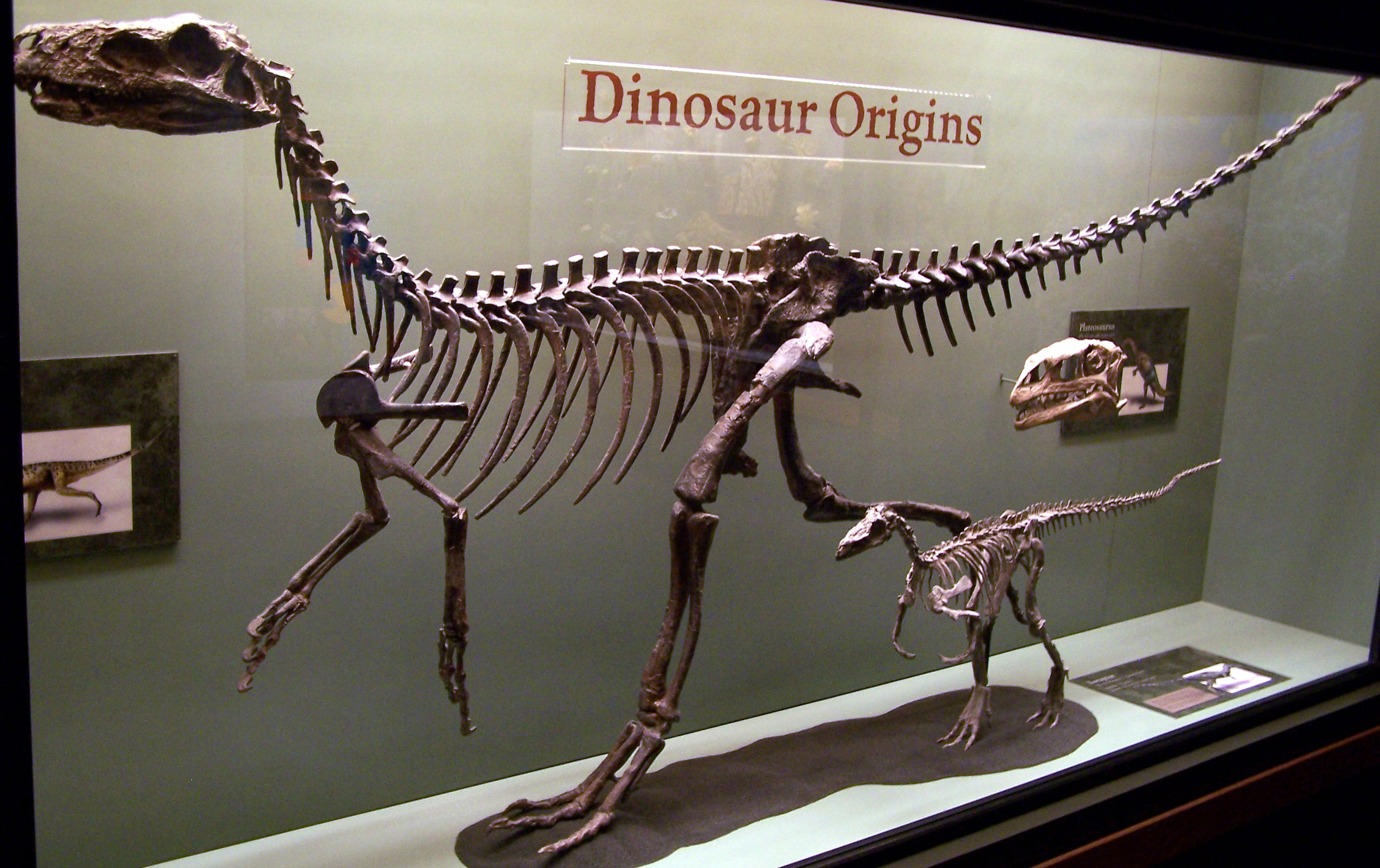 Dinosaurs diverged from their archosaur ancestors during the Middle to Late Triassic epochs, roughly 20 million years after the devastating
Dinosaurs diverged from their archosaur ancestors during the Middle to Late Triassic epochs, roughly 20 million years after the devastating
 Dinosaur evolution after the Triassic followed changes in vegetation and the location of continents. In the Late Triassic and Early Jurassic, the continents were connected as the single landmass
Dinosaur evolution after the Triassic followed changes in vegetation and the location of continents. In the Late Triassic and Early Jurassic, the continents were connected as the single landmass
 Dinosaurs are a diverse group of
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocepha ...
s of the clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach t ...
Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic
The Triassic ( ; sometimes symbolized 🝈) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.5 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.4 Mya. The Triassic is t ...
period
Period may refer to:
Common uses
* Period (punctuation)
* Era, a length or span of time
*Menstruation, commonly referred to as a "period"
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Period (music), a concept in musical composition
* Periodic sentence (o ...
, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago
Million years ago, abbreviated as Mya, Myr (megayear) or Ma (megaannum), is a unit of time equal to (i.e. years), or approximately 31.6 teraseconds.
Usage
Myr is in common use in fields such as Earth science and cosmology. Myr is also used w ...
(mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is ...
is a subject of active research. They became the dominant terrestrial vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
s after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event
The Triassic–Jurassic (Tr-J) extinction event (TJME), often called the end-Triassic extinction, marks the boundary between the Triassic and Jurassic periods, . It represents one of five major extinction events during the Phanerozoic, profoundly ...
201.3 mya and their dominance continued throughout the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. ...
and Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
periods. The fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserve ...
record shows that bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
s are feathered dinosaur
A feathered dinosaur is any species of dinosaur possessing feathers. That includes all species of birds, and in recent decades evidence has accumulated that many non-avian dinosaur species also possessed feathers in some shape or form. The exte ...
s, having evolved from earlier theropods
Theropoda (; from ancient Greek , (''therion'') "wild beast"; , (''pous, podos'') "foot"">wiktionary:ποδός"> (''pous, podos'') "foot" is one of the three major groups (clades) of dinosaurs, alongside Ornithischia and Sauropodom ...
during the Late Jurassic
The Late Jurassic is the third Epoch (geology), epoch of the Jurassic Period, and it spans the geologic time scale, geologic time from 161.5 ± 1.0 to 143.1 ± 0.8 million years ago (Ma), which is preserved in Upper Jurassic stratum, strata.Owen ...
epoch
In chronology and periodization, an epoch or reference epoch is an instant in time chosen as the origin of a particular calendar era. The "epoch" serves as a reference point from which time is measured.
The moment of epoch is usually decided b ...
, and are the only dinosaur lineage known to have survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event
The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) extinction event, also known as the K–T extinction, was the extinction event, mass extinction of three-quarters of the plant and animal species on Earth approximately 66 million years ago. The event cau ...
approximately 66 mya. Dinosaurs can therefore be divided into avian dinosaurs—bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
s—and the extinct non-avian dinosaurs, which are all dinosaurs other than birds.
Dinosaurs are varied from taxonomic
280px, Generalized scheme of taxonomy
Taxonomy is a practice and science concerned with classification or categorization. Typically, there are two parts to it: the development of an underlying scheme of classes (a taxonomy) and the allocation ...
, morphological and ecological
Ecology () is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms and their environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere levels. Ecology overlaps with the closely re ...
standpoints. Birds
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
, at over 11,000 living species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
, are among the most diverse groups of vertebrates. Using fossil evidence, paleontologists
Paleontology, also spelled as palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of the life of the past, mainly but not exclusively through the study of fossils. Paleontologists use fossils as a means to classify organisms, measure geolo ...
have identified over 900 distinct genera
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial s ...
and more than 1,000 different species of non-avian dinosaurs. Dinosaurs are represented on every continent by both extant
Extant or Least-concern species, least concern is the opposite of the word extinct. It may refer to:
* Extant hereditary titles
* Extant literature, surviving literature, such as ''Beowulf'', the oldest extant manuscript written in English
* Exta ...
species (birds) and fossil remains. Through most of the 20th century, before birds were recognized as dinosaurs, most of the scientific community believed dinosaurs to have been sluggish and cold-blooded. Most research conducted since the 1970s, however, has indicated that dinosaurs were active animals with elevated metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the co ...
s and numerous adaptations for social interaction. Some were herbivorous
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically evolved to feed on plants, especially upon vascular tissues such as foliage, fruits or seeds, as the main component of its diet. These more broadly also encompass animals that eat n ...
, others carnivorous
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose nutrition and energy requirements are met by consumption of animal tissues (mainly mu ...
. Evidence suggests that all dinosaurs were egg-laying, and that nest
A nest is a structure built for certain animals to hold Egg (biology), eggs or young. Although nests are most closely associated with birds, members of all classes of vertebrates and some invertebrates construct nests. They may be composed of ...
-building was a trait shared by many dinosaurs, both avian and non-avian.
While dinosaurs were ancestrally bipedal
Bipedalism is a form of terrestrial locomotion where an animal moves by means of its two rear (or lower) limbs or legs. An animal or machine that usually moves in a bipedal manner is known as a biped , meaning 'two feet' (from Latin ''bis'' ...
, many extinct
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
groups included quadrupedal
Quadrupedalism is a form of Animal locomotion, locomotion in which animals have four legs that are used to weight-bearing, bear weight and move around. An animal or machine that usually maintains a four-legged posture and moves using all four l ...
species, and some were able to shift between these stances. Elaborate display structures such as horns or crests are common to all dinosaur groups, and some extinct groups developed skeletal
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of most animals. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is a rigid outer shell that holds up an organism's shape; the endoskeleton, a rigid internal fram ...
modifications such as bony armor and spines. While the dinosaurs' modern-day surviving avian lineage (birds) are generally small due to the constraints of flight, many prehistoric dinosaurs (non-avian and avian) were large-bodied—the largest sauropod
Sauropoda (), whose members are known as sauropods (; from '' sauro-'' + '' -pod'', 'lizard-footed'), is a clade of saurischian ('lizard-hipped') dinosaurs. Sauropods had very long necks, long tails, small heads (relative to the rest of their b ...
dinosaurs are estimated to have reached lengths of and heights of and were the largest land animals of all time. The misconception that non-avian dinosaurs were uniformly gigantic is based in part on preservation bias
Taphonomy is the study of how organisms decay and become fossilized or preserved in the paleontological record. The term ''taphonomy'' (from Greek , 'burial' and , 'law') was introduced to paleontology in 1940 by Soviet scientist Ivan Efremov ...
, as large, sturdy bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
s are more likely to last until they are fossilized. Many dinosaurs were quite small, some measuring about in length.
The first dinosaur fossils were recognized in the early 19th century, with the name "dinosaur" (meaning "terrible lizard") being coined by Sir Richard Owen
Sir Richard Owen (20 July 1804 – 18 December 1892) was an English biologist, comparative anatomy, comparative anatomist and paleontology, palaeontologist. Owen is generally considered to have been an outstanding naturalist with a remarkabl ...
in 1842 to refer to these "great fossil lizards". Since then, mounted fossil dinosaur skeletons have been major attractions at museums worldwide, and dinosaurs have become an enduring part of popular culture. The large sizes of some dinosaurs, as well as their seemingly monstrous and fantastic nature, have ensured their regular appearance in best-selling books and films, such as the ''Jurassic Park
''Jurassic Park'', later referred to as ''Jurassic World'', is an American science fiction media franchise created by Michael Crichton, centered on a disastrous attempt to create a theme park of De-extinction#Cloning, cloned dinosaurs. It bega ...
'' franchise. Persistent public enthusiasm for the animals has resulted in significant funding for dinosaur science, and new discoveries are regularly covered by the media.
Definition
Underphylogenetic nomenclature
Phylogenetic nomenclature is a method of nomenclature for taxa in biology that uses phylogenetic definitions for taxon names as explained below. This contrasts with the traditional method, by which taxon names are defined by a '' type'', which c ...
, dinosaurs are usually defined as the group consisting of the most recent common ancestor
A most recent common ancestor (MRCA), also known as a last common ancestor (LCA), is the most recent individual from which all organisms of a set are inferred to have descended. The most recent common ancestor of a higher taxon is generally assu ...
(MRCA) of ''Triceratops
''Triceratops'' ( ; ) is a genus of Chasmosaurinae, chasmosaurine Ceratopsia, ceratopsian dinosaur that lived during the late Maastrichtian age of the Late Cretaceous Period (geology), period, about 68 to 66 million years ago on the island ...
'' and modern birds (Neornithes), and all its descendants. It has also been suggested that Dinosauria be defined with respect to the MRCA of ''Megalosaurus
''Megalosaurus'' (meaning "great lizard", from Ancient Greek, Greek , ', meaning 'big', 'tall' or 'great' and , ', meaning 'lizard') is an extinct genus of large carnivorous theropod dinosaurs of the Middle Jurassic Epoch (Bathonian stage, 166 ...
'' and ''Iguanodon
''Iguanodon'' ( ; meaning 'iguana-tooth'), named in 1825, is a genus of iguanodontian dinosaur. While many species found worldwide have been classified in the genus ''Iguanodon'', dating from the Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous, Taxonomy (bi ...
'', because these were two of the three genera cited by Richard Owen when he recognized the Dinosauria. Both definitions cover the same known genera: Dinosauria = Ornithischia
Ornithischia () is an extinct clade of mainly herbivorous dinosaurs characterized by a pelvic structure superficially similar to that of birds. The name ''Ornithischia'', or "bird-hipped", reflects this similarity and is derived from the Greek ...
+ Saurischia
Saurischia ( , meaning "reptile-hipped" from the Greek ' () meaning 'lizard' and ' () meaning 'hip joint') is one of the two basic divisions of dinosaurs (the other being Ornithischia), classified by their hip structure. Saurischia and Ornithi ...
. This includes major groups such as ankylosauria
Ankylosauria is a group of herbivorous dinosaurs of the clade Ornithischia. It includes the great majority of dinosaurs with armor in the form of bony osteoderms, similar to turtles. Ankylosaurs were bulky quadrupeds, with short, powerful limbs ...
ns (armored herbivorous quadrupeds), stegosauria
Stegosauria is a group of Herbivore, herbivorous ornithischian dinosaurs that lived during the Jurassic and early Cretaceous Period (geology), periods. Stegosaurian fossils have been found mostly in the Northern Hemisphere (North America, Europe a ...
ns (plated herbivorous quadrupeds), ceratopsia
Ceratopsia or Ceratopia ( or ; Ancient Greek, Greek: "horned faces") is a group of herbivore, herbivorous, beaked dinosaurs that thrived in what are now North America, Asia and Europe, during the Cretaceous Period (geology), Period, although ance ...
ns (bipedal or quadrupedal herbivores with neck frill
A neck frill is the relatively extensive margin seen on the back of the heads of reptiles with either a bony support such as those present on the skulls of dinosaurs of the suborder Marginocephalia or a cartilaginous one as in the frill-nec ...
s), pachycephalosauria
Pachycephalosauria (; from Greek παχυκεφαλόσαυρος for 'thick headed lizards') is a clade of ornithischian dinosaurs. Along with Ceratopsia, it makes up the clade Marginocephalia. With the exception of two species, most pachyceph ...
ns (bipedal herbivores with thick skulls), ornithopod
Ornithopoda () is a clade of ornithischian dinosaurs, called ornithopods (). They represent one of the most successful groups of herbivorous dinosaurs during the Cretaceous. The most primitive members of the group were bipedal and relatively sm ...
s (bipedal or quadrupedal herbivores including " duck-bills"), theropod
Theropoda (; from ancient Greek , (''therion'') "wild beast"; , (''pous, podos'') "foot"">wiktionary:ποδός"> (''pous, podos'') "foot" is one of the three major groups (clades) of dinosaurs, alongside Ornithischia and Sauropodom ...
s (mostly bipedal carnivores and birds), and sauropodomorphs
Sauropodomorpha ( ; from Greek, meaning "lizard-footed forms") is an extinct clade of long-necked, herbivorous, saurischian dinosaurs that includes the sauropods and their ancestral relatives. Sauropods generally grew to very large sizes, had lo ...
(mostly large herbivorous quadrupeds with long necks and tails).
Birds are the sole surviving dinosaurs. In traditional taxonomy
image:Hierarchical clustering diagram.png, 280px, Generalized scheme of taxonomy
Taxonomy is a practice and science concerned with classification or categorization. Typically, there are two parts to it: the development of an underlying scheme o ...
, birds were considered a separate class
Class, Classes, or The Class may refer to:
Common uses not otherwise categorized
* Class (biology), a taxonomic rank
* Class (knowledge representation), a collection of individuals or objects
* Class (philosophy), an analytical concept used d ...
that had evolved from dinosaurs, a distinct superorder
Order () is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between family and class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized ...
. However, most contemporary paleontologists reject the traditional style of classification based on anatomical similarity, in favor of phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical dat ...
taxonomy based on deduced ancestry, in which each group is defined as all descendants of a given founding genus. Birds belong to the dinosaur subgroup Maniraptora
Maniraptora is a clade of coelurosaurian dinosaurs which includes the birds and the non-avian dinosaurs that were more closely related to them than to ''Ornithomimus velox''. It contains the major subgroups Avialae, Dromaeosauridae, Troodontidae, ...
, which are coelurosaurs
Coelurosauria (; from Greek, meaning "hollow-tailed lizards") is the clade containing all theropod dinosaurs more closely related to birds than to carnosaurs.
Coelurosauria is a subgroup of theropod dinosaurs that includes compsognathids, tyran ...
, which are theropods, which are saurischians.
Research by Matthew G. Baron, David B. Norman, and Paul M. Barrett in 2017 suggested a radical revision of dinosaurian systematics. Phylogenetic analysis by Baron ''et al.'' recovered the Ornithischia as being closer to the Theropoda than the Sauropodomorpha, as opposed to the traditional union of theropods with sauropodomorphs. This would cause sauropods and kin to fall outside traditional dinosaurs, so they re-defined Dinosauria as the last common ancestor of ''Triceratops horridus'', ''Passer domesticus
The house sparrow (''Passer domesticus'') is a bird of the sparrow family Passeridae, found in most parts of the world. It is a small bird that has a typical length of and a mass of . Females and young birds are coloured pale brown and grey, ...
'' and '' Diplodocus carnegii'', and all of its descendants, to ensure that sauropods and kin remain included as dinosaurs. They also resurrected the clade Ornithoscelida
Ornithoscelida () is a proposed clade that includes various major groupings of dinosaurs. An order Ornithoscelida was originally proposed by Thomas Henry Huxley but later abandoned in favor of Harry Govier Seeley's division of Dinosauria into ...
to refer to the group containing Ornithischia and Theropoda. "A version of this article appears in print on March 28, 2017, on Page D6 of the New York edition with the headline: Shaking Up the Dinosaur Family Tree."
General description
 Using one of the above definitions, dinosaurs can be generally described as
Using one of the above definitions, dinosaurs can be generally described as archosaur
Archosauria () or archosaurs () is a clade of diapsid sauropsid tetrapods, with birds and crocodilians being the only extant taxon, extant representatives. Although broadly classified as reptiles, which traditionally exclude birds, the cladistics ...
s with hind limbs held erect beneath the body. Other prehistoric animals, including pterosaur
Pterosaurs are an extinct clade of flying reptiles in the order Pterosauria. They existed during most of the Mesozoic: from the Late Triassic to the end of the Cretaceous (228 million to 66 million years ago). Pterosaurs are the earli ...
s, mosasaur
Mosasaurs (from Latin ''Mosa'' meaning the 'Meuse', and Ancient Greek, Greek ' meaning 'lizard') are an extinct group of large aquatic reptiles within the family Mosasauridae that lived during the Late Cretaceous. Their first fossil remains wer ...
s, ichthyosaur
Ichthyosauria is an order of large extinct marine reptiles sometimes referred to as "ichthyosaurs", although the term is also used for wider clades in which the order resides.
Ichthyosaurians thrived during much of the Mesozoic era; based on fo ...
s, plesiosaurs
The Plesiosauria or plesiosaurs are an Order (biology), order or clade of extinct Mesozoic marine reptiles, belonging to the Sauropterygia.
Plesiosaurs first appeared in the latest Triassic Period (geology), Period, possibly in the Rhaetian st ...
, and ''Dimetrodon
''Dimetrodon'' ( or ; ) is an extinct genus of sphenacodontid synapsid that lived during the Cisuralian (Early Permian) Epoch (geology), epoch of the Permian period, around 295–272 million years ago. With most species measuring long and ...
'', while often popularly conceived of as dinosaurs, are not taxonomically classified as dinosaurs. Pterosaurs are distantly related to dinosaurs, being members of the clade Ornithodira
Avemetatarsalia (meaning "bird metatarsals") is a clade of diapsid reptiles containing all archosaurs more closely related to birds than to crocodilians. The two most successful groups of avemetatarsalians were the dinosaurs and pterosaurs. Di ...
. The other groups mentioned are, like dinosaurs and pterosaurs, members of Sauropsida
Sauropsida (Greek language, Greek for "lizard faces") is a clade of amniotes, broadly equivalent to the Class (biology), class Reptile, Reptilia, though typically used in a broader sense to also include extinct stem-group relatives of modern repti ...
(the reptile and bird clade), except ''Dimetrodon'' (which is a synapsid
Synapsida is a diverse group of tetrapod vertebrates that includes all mammals and their extinct relatives. It is one of the two major clades of the group Amniota, the other being the more diverse group Sauropsida (which includes all extant rept ...
). None of them had the erect hind limb posture characteristic of true dinosaurs.
Dinosaurs were the dominant terrestrial vertebrates of the Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era is the Era (geology), era of Earth's Geologic time scale, geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Period (geology), Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of archosaurian r ...
Era
An era is a span of time.
Era or ERA may also refer to:
* Era (geology), a subdivision of geologic time
* Calendar era
Education
* Academy of European Law (German: '), an international law school
* ERA School, in Melbourne, Australia
* E ...
, especially the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. Other groups of animals were restricted in size and niches; mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s, for example, rarely exceeded the size of a domestic cat and were generally rodent-sized carnivores of small prey. Dinosaurs have always been recognized as an extremely varied group: over 900 non-avian dinosaur genera have been confidently identified (2018) with 1124 species (2016). Estimates put the total number of dinosaur genera preserved in the fossil record at 1850, nearly 75% still undiscovered, and the number that ever existed (in or out of the fossil record) at 3,400. A 2016 estimate put the number of dinosaur species living in the Mesozoic at 1,543–2,468, compared to the number of modern-day birds (avian dinosaurs) at 10,806 species.
Extinct dinosaurs, as well as modern birds, include genera that are herbivorous and others carnivorous, including seed-eaters, fish-eaters, insectivores, and omnivores. While dinosaurs were ancestrally bipedal (as are all modern birds), some evolved into quadrupeds, and others, such as ''Anchisaurus
''Anchisaurus'' is a genus of basal sauropodomorph dinosaur. It lived during the Early Jurassic Period, and its fossils have been found in the red sandstone of the Upper Portland Formation, Northeastern United States, which was deposited fro ...
'' and ''Iguanodon'', could walk as easily on two or four legs. Cranial modifications like horns and crests are common dinosaurian traits, and some extinct species had bony armor. Although the best-known genera are remarkable for their large size, many Mesozoic dinosaurs were human-sized or smaller, and modern birds are generally small in size. Dinosaurs today inhabit every continent, and fossils show that they had achieved global distribution by the Early Jurassic
The Early Jurassic Epoch (geology), Epoch (in chronostratigraphy corresponding to the Lower Jurassic series (stratigraphy), Series) is the earliest of three epochs of the Jurassic Period. The Early Jurassic starts immediately after the Triassic� ...
epoch at latest. Modern birds inhabit most available habitats, from terrestrial to marine, and there is evidence that some non-avian dinosaurs (such as ''Microraptor
''Microraptor'' (Greek language, Greek, μικρός, ''mīkros'': "small"; Latin language, Latin, ''raptor'': "one who seizes") is a genus of small, four-winged dromaeosaurid dinosaurs. Numerous well-preserved fossil specimens have been recovere ...
'') could fly or at least glide, and others, such as spinosaurids
Spinosauridae (or spinosaurids) is a clade or family of tetanuran theropod dinosaurs comprising ten to seventeen known genera. Spinosaurid fossils have been recovered worldwide, including Africa, Europe, South America, and Asia. Their remains have ...
, had semiaquatic
In biology, being semi-aquatic refers to various macroorganisms that live regularly in both aquatic and terrestrial environments. When referring to animals, the term describes those that actively spend part of their daily time in water (in ...
habits.
Distinguishing anatomical features
While recent discoveries have made it more difficult to present a universally agreed-upon list of their distinguishing features, nearly all dinosaurs discovered so far share certain modifications to the ancestral archosaurian skeleton, or are clearly descendants of older dinosaurs showing these modifications. Although some later groups of dinosaurs featured further modified versions of these traits, they are considered typical for Dinosauria; the earliest dinosaurs had them and passed them on to their descendants. Such modifications, originating in the most recent common ancestor of a certain taxonomic group, are called thesynapomorphies
In phylogenetics, an apomorphy (or derived trait) is a novel character or character state that has evolved from its ancestral form (or plesiomorphy). A synapomorphy is an apomorphy shared by two or more taxa and is therefore hypothesized to ...
of such a group.
Sterling Nesbitt
Sterling Nesbitt (born March 25, 1982, in Mesa, Arizona) is an American paleontologist best known for his work on the origin and early evolutionary patterns of archosaurs. He is currently an associate professor at Virginia Tech in the Departme ...
confirmed or found the following twelve unambiguous synapomorphies, some previously known:
* In the skull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
, a supratemporal fossa (excavation) is present in front of the supratemporal fenestra
Temporal fenestrae are openings in the temporal region of the skull of some amniotes, behind the orbit (eye socket). These openings have historically been used to track the evolution and affinities of reptiles. Temporal fenestrae are commonly (al ...
, the main opening in the rear skull roof
* Epipophyses
Epipophyses are bony projections of the cervical vertebrae found in archosauromorphs, particularly dinosaurs (including some basal birds). These paired processes sit above the postzygapophyses on the rear of the vertebral neural arch. Their m ...
, obliquely backward-pointing processes on the rear top corners of the anterior (front) neck vertebra
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spina ...
e behind the atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of world map, maps of Earth or of a continent or region of Earth. Advances in astronomy have also resulted in atlases of the celestial sphere or of other planets.
Atlases have traditio ...
and axis
An axis (: axes) may refer to:
Mathematics
*A specific line (often a directed line) that plays an important role in some contexts. In particular:
** Coordinate axis of a coordinate system
*** ''x''-axis, ''y''-axis, ''z''-axis, common names ...
, the first two neck vertebrae
* Apex of a deltopectoral crest (a projection on which the deltopectoral muscles attach) located at or more than 30% down the length of the humerus
The humerus (; : humeri) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius (bone), radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extrem ...
(upper arm bone)
* Radius
In classical geometry, a radius (: radii or radiuses) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its Centre (geometry), center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The radius of a regular polygon is th ...
, a lower arm bone, shorter than 80% of humerus length
* Fourth trochanter
The fourth trochanter is a shared characteristic common to archosaurs. It is a protrusion on the posterior-medial side of the middle of the femur shaft that serves as a muscle attachment, mainly for the '' musculus caudofemoralis longus'', the m ...
(projection where the caudofemoralis The caudofemoralis (from the Latin ''cauda'', tail and ''femur'', thighbone) is a muscle found in the pelvic limb of mostly all animals possessing a tail. It is thus found in nearly all tetrapods.
Location
The caudofemoralis spans plesiomorphica ...
muscle attaches on the inner rear shaft) on the femur
The femur (; : femurs or femora ), or thigh bone is the only long bone, bone in the thigh — the region of the lower limb between the hip and the knee. In many quadrupeds, four-legged animals the femur is the upper bone of the hindleg.
The Femo ...
(thigh bone) is a sharp flange
* Fourth trochanter asymmetrical, with distal, lower, margin forming a steeper angle to the shaft
* On the astragalus
Astragalus may refer to:
* ''Astragalus'' (plant), a large genus of herbs and small shrubs
*Astragalus (bone)
The talus (; Latin for ankle or ankle bone; : tali), talus bone, astragalus (), or ankle bone is one of the group of foot bones known ...
and calcaneum
In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus (; from the Latin ''calcaneus'' or ''calcaneum'', meaning heel; : calcanei or calcanea) or heel bone is a bone of the tarsus of the foot which constitutes the heel. In some other animals, it is t ...
, upper ankle bones, the proximal articular facet, the top connecting surface, for the fibula
The fibula (: fibulae or fibulas) or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. ...
occupies less than 30% of the transverse width of the element
* Exoccipitals (bones at the back of the skull) do not meet along the midline on the floor of the endocranial cavity, the inner space of the braincase
* In the pelvis, the proximal articular surfaces of the ischium
The ischium (; : is ...
with the ilium and the pubis are separated by a large concave surface (on the upper side of the ischium a part of the open hip joint is located between the contacts with the pubic bone and the ilium)
* Cnemial crest The cnemial crest is a crestlike prominence located at the front side of the head of the tibiotarsus or tibia in the legs of many mammals and reptiles (including birds and other dinosaurs). The main extensor muscle of the thigh
In anatomy, the ...
on the tibia
The tibia (; : tibiae or tibias), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two Leg bones, bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outsi ...
(protruding part of the top surface of the shinbone) arcs anterolaterally (curves to the front and the outer side)
* Distinct proximodistally oriented (vertical) ridge present on the posterior face of the distal end of the tibia (the rear surface of the lower end of the shinbone)
* Concave articular surface for the fibula of the calcaneum (the top surface of the calcaneum, where it touches the fibula, has a hollow profile)
Nesbitt found a number of further potential synapomorphies and discounted a number of synapomorphies previously suggested. Some of these are also present in silesaurids
Silesauridae is an extinct family of Triassic dinosauriforms. It is most commonly considered to be a clade of non-dinosaur dinosauriforms, and the sister group of dinosaurs. Some studies have instead suggested that most or all silesaurids compr ...
, which Nesbitt recovered as a sister group to Dinosauria, including a large anterior trochanter, metatarsals II and IV of subequal length, reduced contact between ischium and pubis, the presence of a cnemial crest on the tibia and of an ascending process on the astragalus, and many others.
diapsid
Diapsids ("two arches") are a clade of sauropsids, distinguished from more primitive eureptiles by the presence of two holes, known as temporal fenestrae, in each side of their skulls. The earliest traditionally identified diapsids, the araeosc ...
s, dinosaurs ancestrally had two pairs of Infratemporal fenestra
Temporal fenestrae are openings in the temporal region of the skull of some amniotes, behind the orbit (eye socket). These openings have historically been used to track the evolution and affinities of reptiles. Temporal fenestrae are commonly (al ...
e (openings in the skull behind the eyes), and as members of the diapsid group Archosauria, had additional openings in the snout
A snout is the protruding portion of an animal's face, consisting of its nose, mouth, and jaw. In many animals, the structure is called a muzzle, Rostrum (anatomy), rostrum, beak or proboscis. The wet furless surface around the nostrils of the n ...
and lower jaw. Additionally, several characteristics once thought to be synapomorphies are now known to have appeared before dinosaurs, or were absent in the earliest dinosaurs and independently evolved by different dinosaur groups. These include an elongated scapula
The scapula (: scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side ...
, or shoulder blade; a sacrum
The sacrum (: sacra or sacrums), in human anatomy, is a triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1S5) between ages 18 and 30.
The sacrum situates at the upper, back part of the pelvic cavity, ...
composed of three or more fused vertebrae (three are found in some other archosaurs, but only two are found in ''Herrerasaurus
''Herrerasaurus'' is likely a genus of saurischian dinosaur from the Late Triassic period. Measuring long and weighing around , this genus was one of the earliest dinosaurs from the fossil record. Its name means "Herrera's lizard", after the ...
''); and a perforate acetabulum
The acetabulum (; : acetabula), also called the cotyloid cavity, is a wikt:concave, concave surface of the pelvis. The femur head, head of the femur meets with the pelvis at the acetabulum, forming the Hip#Articulation, hip joint.
Structure
The ...
, or hip socket, with a hole at the center of its inside surface (closed in '' Saturnalia tupiniquim'', for example). Another difficulty of determining distinctly dinosaurian features is that early dinosaurs and other archosaurs from the Late Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch (geology), epoch of the Triassic geologic time scale, Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between annum, Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch a ...
epoch are often poorly known and were similar in many ways; these animals have sometimes been misidentified in the literature.
Dinosaurs stand with their hind limbs erect in a manner similar to most modern mammals, but distinct from most other reptiles, whose limbs sprawl out to either side. This posture is due to the development of a laterally facing recess in the pelvis (usually an open socket) and a corresponding inwardly facing distinct head on the femur. Their erect posture enabled early dinosaurs to breathe easily while moving, which likely permitted stamina and activity levels that surpassed those of "sprawling" reptiles. Erect limbs probably also helped support the evolution
Evolution is the change in the heritable Phenotypic trait, characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, re ...
of large size by reducing bending stresses on limbs. Some non-dinosaurian archosaurs, including rauisuchia
"Rauisuchia" is a paraphyletic group of mostly large and carnivorous Triassic archosaurs. Rauisuchians are a category of archosaurs within a larger group called Pseudosuchia, which encompasses all archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians ...
ns, also had erect limbs but achieved this by a "pillar-erect" configuration of the hip joint, where instead of having a projection from the femur insert on a socket on the hip, the upper pelvic bone was rotated to form an overhanging shelf.
History of study
Pre-scientific history
Dinosaur fossils have been known for millennia, although their true nature was not recognized. The Chinese considered them to bedragon
A dragon is a Magic (supernatural), magical legendary creature that appears in the folklore of multiple cultures worldwide. Beliefs about dragons vary considerably through regions, but European dragon, dragons in Western cultures since the Hi ...
bones and documented them as such. For example, '' Huayang Guo Zhi'' (), a gazetteer
A gazetteer is a geographical dictionary or wikt:directory, directory used in conjunction with a map or atlas.Aurousseau, 61. It typically contains information concerning the geographical makeup, social statistics and physical features of a co ...
compiled by Chang Qu
Chang Qu (291–361), courtesy name Daojiang, was a Chinese historian of the Cheng-Han dynasty during the Sixteen Kingdoms period and the Jin dynasty (266–420). Chang Qu is best known for his magnum opus, the '' Chronicles of Huayang'' or ''Re ...
() during the Western Jin Dynasty
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
* Western, New York, a town in the US
* Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
* Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that ...
(265–316), reported the discovery of dragon bones at Wucheng in Sichuan
Sichuan is a province in Southwestern China, occupying the Sichuan Basin and Tibetan Plateau—between the Jinsha River to the west, the Daba Mountains to the north, and the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau to the south. Its capital city is Cheng ...
Province. Villagers in central China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
have long unearthed fossilized "dragon bones" for use in traditional medicines. In Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
, dinosaur fossils were generally believed to be the remains of giant
In folklore, giants (from Ancient Greek: ''wiktionary:gigas, gigas'', cognate wiktionary:giga-, giga-) are beings of humanoid appearance, but are at times prodigious in size and strength or bear an otherwise notable appearance. The word ''gia ...
s and other biblical
The Bible is a collection of religious texts that are central to Christianity and Judaism, and esteemed in other Abrahamic religions such as Islam. The Bible is an anthology (a compilation of texts of a variety of forms) biblical languages ...
creatures.
Early dinosaur research
 Scholarly descriptions of what would now be recognized as dinosaur bones first appeared in the late 17th century in England. Part of a bone, now known to have been the femur of a ''
Scholarly descriptions of what would now be recognized as dinosaur bones first appeared in the late 17th century in England. Part of a bone, now known to have been the femur of a ''Megalosaurus
''Megalosaurus'' (meaning "great lizard", from Ancient Greek, Greek , ', meaning 'big', 'tall' or 'great' and , ', meaning 'lizard') is an extinct genus of large carnivorous theropod dinosaurs of the Middle Jurassic Epoch (Bathonian stage, 166 ...
'', was recovered from a limestone quarry at Cornwell near Chipping Norton
Chipping Norton is a market town and Civil parishes in England, civil parish in the Cotswolds in the West Oxfordshire district of Oxfordshire, England, about south-west of Banbury and north-west of Oxford. The United Kingdom Census 2011, 201 ...
, Oxfordshire, in 1676. The fragment was sent to Robert Plot
Robert Plot (13 December 1640 – 30 April 1696) was an English naturalist and antiquarian who was the first professor of chemistry at the University of Oxford and the first keeper of the Ashmolean Museum.
Early life and education
Born in Bor ...
, Professor of Chemistry at the University of Oxford
The University of Oxford is a collegiate university, collegiate research university in Oxford, England. There is evidence of teaching as early as 1096, making it the oldest university in the English-speaking world and the List of oldest un ...
and first curator of the Ashmolean Museum
The Ashmolean Museum of Art and Archaeology () on Beaumont Street in Oxford, England, is Britain's first public museum. Its first building was erected in 1678–1683 to house the cabinet of curiosities that Elias Ashmole gave to the University ...
, who published a description in his ''The Natural History of Oxford-shire'' (1677). He correctly identified the bone as the lower extremity of the femur of a large animal, and recognized that it was too large to belong to any known species. He therefore concluded it to be the femur of a huge human, perhaps a Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
or another type of giant featured in legends. Edward Lhuyd
Edward Lhuyd (1660– 30 June 1709), also known as Edward Lhwyd and by other spellings, was a Welsh scientist, geographer, historian and antiquary. He was the second Keeper of the University of Oxford's Ashmolean Museum, and published the firs ...
, a friend of Sir Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton () was an English polymath active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author. Newton was a key figure in the Scientific Revolution and the Enlightenment that followed. His book (''Mathe ...
, published ''Lithophylacii Britannici ichnographia'' (1699), the first scientific treatment of what would now be recognized as a dinosaur. In it he described and named a sauropod tooth
A tooth (: teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tea ...
, " Rutellum impicatum", that had been found in Caswell, near Witney
Witney is a market town on the River Windrush in West Oxfordshire in the county of Oxfordshire, England. It is west of Oxford.
History
The Toponymy, place-name "Witney" is derived from the Old English for "Witta's island". The earliest kno ...
, Oxfordshire.
 Between 1815 and 1824, the Rev
Between 1815 and 1824, the Rev William Buckland
William Buckland Doctor of Divinity, DD, Royal Society, FRS (12 March 1784 – 14 August 1856) was an English theologian, geologist and paleontology, palaeontologist.
His work in the early 1820s proved that Kirkdale Cave in North Yorkshire h ...
, the first Reader of Geology at the University of Oxford, collected more fossilized bones of ''Megalosaurus'' and became the first person to describe a non-avian dinosaur in a scientific journal
In academic publishing, a scientific journal is a periodical publication designed to further the progress of science by disseminating new research findings to the scientific community. These journals serve as a platform for researchers, schola ...
. The second non-avian dinosaur genus to be identified, ''Iguanodon
''Iguanodon'' ( ; meaning 'iguana-tooth'), named in 1825, is a genus of iguanodontian dinosaur. While many species found worldwide have been classified in the genus ''Iguanodon'', dating from the Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous, Taxonomy (bi ...
'', was purportedly discovered in 1822 by Mary Ann Mantell, the wife of English geologist Gideon Mantell
Gideon Algernon Mantell Membership of the Royal College of Surgeons, MRCS Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS (3 February 1790 – 10 November 1852) was an English obstetrician, geologist and paleontology, palaeontologist. His attempts to reconstr ...
, though this is disputed and some historians say Gideon had acquired remains years earlier. Gideon Mantell recognized similarities between his fossils and the bones of modern iguana
''Iguana'' (, ) is a genus of herbivorous lizards that are native to tropical areas of Mexico, Central America, South America, and the Caribbean. The genus was first described by Austrian naturalist Josephus Nicolaus Laurenti, J.N. Laurenti in ...
s and published his findings in 1825.
The study of these "great fossil lizards" soon became of great interest to European and American scientists, and in 1842 the English paleontologist Sir Richard Owen coined the term "dinosaur", using it to refer to the "distinct tribe or sub-order of Saurian Reptiles" that were then being recognized in England and around the world. The term is derived . Though the taxonomic name has often been interpreted as a reference to dinosaurs' teeth, claws, and other fearsome characteristics, Owen intended it also to evoke their size and majesty. Owen recognized that the remains that had been found so far, ''Iguanodon'', ''Megalosaurus'' and ''Hylaeosaurus
''Hylaeosaurus'' ( ; Greek: / "belonging to the forest" and / "lizard") is a herbivorous ankylosaurian dinosaur that lived about 136 million years ago, in the late Valanginian stage of the early Cretaceous period of England. It was found i ...
'', shared distinctive features, and so decided to present them as a distinct taxonomic group. As clarified by British geologist and historian Hugh Torrens, Owen had given a presentation about fossil reptiles to the British Association for the Advancement of Science in 1841, but reports of the time show that Owen did not mention the word "dinosaur", nor recognize dinosaurs as a distinct group of reptiles in his address. He introduced the Dinosauria only in the revised text version of his talk published in April 1842. With the backing of Prince Albert
Prince Albert most commonly refers to:
*Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (1819–1861), consort of Queen Victoria
*Albert II, Prince of Monaco (born 1958), present head of state of Monaco
Prince Albert may also refer to:
Royalty
* Alb ...
, the husband of Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in January 1901. Her reign of 63 year ...
, Owen established the Natural History Museum, London
The Natural History Museum in London is a museum that exhibits a vast range of specimens from various segments of natural history. It is one of three major museums on Exhibition Road in South Kensington, the others being the Science Museum (Lo ...
, to display the national collection of dinosaur fossils and other biological and geological exhibits.
Discoveries in North America
In 1858,William Parker Foulke
William Parker Foulke (1816–1865) discovered the first full dinosaur skeleton in North America ('' Hadrosaurus foulkii'', which means "Foulke's big lizard") in Haddonfield, New Jersey, in 1858.
Born in Philadelphia, and a descendant of Welsh ...
discovered the first known American dinosaur, in marl
Marl is an earthy material rich in carbonate minerals, Clay minerals, clays, and silt. When Lithification, hardened into rock, this becomes marlstone. It is formed in marine or freshwater environments, often through the activities of algae.
M ...
pits in the small town of Haddonfield, New Jersey
Haddonfield is a borough (New Jersey), borough located in Camden County, New Jersey, Camden County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey. As of the 2020 United States census, the borough's population was 12,550, an increase of 957 (+8.3%) from the ...
. (Although fossils had been found before, their nature had not been correctly discerned.) The creature was named ''Hadrosaurus foulkii
''Hadrosaurus'' (; ) is a genus of hadrosaurid ornithopod dinosaurs that lived in North America during the Late Cretaceous Period in what is now the Woodbury Formation in New Jersey about 83.6 to 77.9 Ma. The holotype specimen was found in fluv ...
''. It was an extremely important find: ''Hadrosaurus'' was one of the first nearly complete dinosaur skeletons found (the first The First or The 1st may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Albums
* The 1st (album), ''The 1st'' (album), by Willow, 2017
* The First (Shinee album), ''The First'' (Shinee album), 2011
* The First (single album), by NCT Dream, 2017
Television
* T ...
was in 1834, in Maidstone, England), and it was clearly a bipedal creature. This was a revolutionary discovery as, until that point, most scientists had believed dinosaurs walked on four feet, like other lizards. Foulke's discoveries sparked a wave of interests in dinosaurs in the United States, known as dinosaur mania.
Dinosaur mania was exemplified by the fierce rivalry between Edward Drinker Cope
Edward Drinker Cope (July 28, 1840 – April 12, 1897) was an American zoologist, paleontology, paleontologist, comparative anatomy, comparative anatomist, herpetology, herpetologist, and ichthyology, ichthyologist. Born to a wealthy Quaker fam ...
and Othniel Charles Marsh
Othniel Charles Marsh (October 29, 1831 – March 18, 1899) was an American professor of paleontology. A prolific fossil collector, Marsh was one of the preeminent paleontologists of the nineteenth century. Among his legacies are the discovery or ...
, both of whom raced to be the first to find new dinosaurs in what came to be known as the Bone Wars
The Bone Wars, also known as the Great Dinosaur Rush, was a period of intense and ruthlessly competitive fossil hunting and discovery during the Gilded Age of American history, marked by a heated rivalry between Edward Drinker Cope (of the Aca ...
. This fight between the two scientists lasted for over 30 years, ending in 1897 when Cope died after spending his entire fortune on the dinosaur hunt. Many valuable dinosaur specimens were damaged or destroyed due to the pair's rough methods: for example, their diggers often used dynamite
Dynamite is an explosive made of nitroglycerin, sorbents (such as powdered shells or clay), and Stabilizer (chemistry), stabilizers. It was invented by the Swedish people, Swedish chemist and engineer Alfred Nobel in Geesthacht, Northern German ...
to unearth bones. Modern paleontologists would find such methods crude and unacceptable, since blasting easily destroys fossil and stratigraphic evidence. Despite their unrefined methods, the contributions of Cope and Marsh to paleontology were vast: Marsh unearthed 86 new species of dinosaur and Cope discovered 56, a total of 142 new species. Cope's collection is now at the American Museum of Natural History
The American Museum of Natural History (AMNH) is a natural history museum on the Upper West Side of Manhattan in New York City. Located in Theodore Roosevelt Park, across the street from Central Park, the museum complex comprises 21 interconn ...
in New York City, while Marsh's is at the Peabody Museum of Natural History
The Peabody Museum of Natural History at Yale University (also known as the Yale Peabody Museum of Natural History or the Yale Peabody Museum) is one of the oldest, largest, and most prolific university natural history museums in the world. It ...
at Yale University
Yale University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in New Haven, Connecticut, United States. Founded in 1701, Yale is the List of Colonial Colleges, third-oldest institution of higher education in the United Stat ...
.
"Dinosaur renaissance" and beyond
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
caused a pause in palaeontological research; after the war, research attention was also diverted increasingly to fossil mammals rather than dinosaurs, which were seen as sluggish and cold-blooded. At the end of the 1960s, however, the field of dinosaur research experienced a surge in activity that remains ongoing. Several seminal studies led to this activity. First, John Ostrom
John Harold Ostrom (February 18, 1928 – July 16, 2005) was an American paleontologist who revolutionized the modern understanding of dinosaurs. Ostrom's work inspired what his pupil Robert T. Bakker has termed a " dinosaur renaissance".
Begin ...
discovered the bird-like dromaeosaurid
Dromaeosauridae () is a family (biology), family of feathered coelurosaurian Theropoda, theropod dinosaurs. They were generally small to medium-sized feathered carnivores that flourished in the Cretaceous period (geology), Period. The name Drom ...
theropod ''Deinonychus
''Deinonychus'' ( ; ) is a genus of Dromaeosauridae, dromaeosaurid Theropoda, theropod dinosaur with one described species, ''Deinonychus antirrhopus''. This species, which could grow up to long, lived during the early Cretaceous Period (ge ...
'' and described it in 1969. Its anatomy indicated that it was an active predator that was likely warm-blooded, in marked contrast to the then-prevailing image of dinosaurs. Concurrently, Robert T. Bakker
Robert Thomas Bakker (born March 24, 1945) is an American paleontologist who helped reshape modern theories about dinosaurs, particularly by adding support to the theory that some dinosaurs were endothermic (warm-blooded). Along with his mentor ...
published a series of studies that likewise argued for active lifestyles in dinosaurs based on anatomical and ecological evidence (see ), which were subsequently summarized in his 1986 book '' The Dinosaur Heresies''.
 New revelations were supported by an increase in dinosaur discoveries. Major new dinosaur discoveries have been made by paleontologists working in previously unexplored regions, including India, South America, Madagascar, Antarctica, and most significantly China. Across theropods, sauropodomorphs, and ornithischians, the number of named genera began to increase exponentially in the 1990s. In 2008 over 30 new species of dinosaurs were named each year. At least sauropodomorphs experienced a further increase in the number of named species in the 2010s, with an average of 9.3 new species having been named each year between 2009 and 2020. As a consequence, more sauropodomorphs were named between 1990 and 2020 than in all previous years combined. These new localities also led to improvements in overall specimen quality, with new species being increasingly named not on scrappy fossils but on more complete skeletons, sometimes from multiple individuals. Better specimens also led to new species being invalidated less frequently. Asian localities have produced the most complete theropod specimens, while North American localities have produced the most complete sauropodomorph specimens.
Prior to the dinosaur renaissance, dinosaurs were mostly classified using the traditional rank-based system of
New revelations were supported by an increase in dinosaur discoveries. Major new dinosaur discoveries have been made by paleontologists working in previously unexplored regions, including India, South America, Madagascar, Antarctica, and most significantly China. Across theropods, sauropodomorphs, and ornithischians, the number of named genera began to increase exponentially in the 1990s. In 2008 over 30 new species of dinosaurs were named each year. At least sauropodomorphs experienced a further increase in the number of named species in the 2010s, with an average of 9.3 new species having been named each year between 2009 and 2020. As a consequence, more sauropodomorphs were named between 1990 and 2020 than in all previous years combined. These new localities also led to improvements in overall specimen quality, with new species being increasingly named not on scrappy fossils but on more complete skeletons, sometimes from multiple individuals. Better specimens also led to new species being invalidated less frequently. Asian localities have produced the most complete theropod specimens, while North American localities have produced the most complete sauropodomorph specimens.
Prior to the dinosaur renaissance, dinosaurs were mostly classified using the traditional rank-based system of Linnaean taxonomy
Linnaean taxonomy can mean either of two related concepts:
# The particular form of biological classification (taxonomy) set up by Carl Linnaeus, as set forth in his ''Systema Naturae'' (1735) and subsequent works. In the taxonomy of Linnaeus th ...
. The renaissance was also accompanied by the increasingly widespread application of cladistics
Cladistics ( ; from Ancient Greek 'branch') is an approach to Taxonomy (biology), biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups ("clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesiz ...
, a more objective method of classification based on ancestry and shared traits, which has proved tremendously useful in the study of dinosaur systematics and evolution. Cladistic analysis, among other techniques, helps to compensate for an often incomplete and fragmentary fossil record. Reference books summarizing the state of dinosaur research, such as David B. Weishampel
Professor David Bruce Weishampel (born November 16, 1952) is an American palaeontologist in the Center for Functional Anatomy and Evolution at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. Weishampel received his Ph.D. in Geology from the Univer ...
and colleagues' ''The Dinosauria
''The Dinosauria'' is an encyclopedia on dinosaurs, edited by paleontologists David B. Weishampel, Peter Dodson, and Halszka Osmólska. It has been published in two editions by the University of California Press, with the first edition in 1990 ...
'', made knowledge more accessible and spurred further interest in dinosaur research. The release of the first and second editions of ''The Dinosauria'' in 1990 and 2004, and of a review paper by Paul Sereno
Paul Callistus Sereno (born October 11, 1957) is a professor of paleontology at the University of Chicago who has discovered several new dinosaur species on several continents, including at sites in Inner Mongolia, Argentina, Morocco and Niger. ...
in 1998, were accompanied by increases in the number of published phylogenetic tree
A phylogenetic tree or phylogeny is a graphical representation which shows the evolutionary history between a set of species or taxa during a specific time.Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA. In ...
s for dinosaurs.
Soft tissue and molecular preservation
 Dinosaur fossils are not limited to bones, but also include imprints or mineralized remains of skin coverings, organs, and other tissues. Of these, skin coverings based on
Dinosaur fossils are not limited to bones, but also include imprints or mineralized remains of skin coverings, organs, and other tissues. Of these, skin coverings based on keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. It is the key structural material making up Scale (anatomy), scales, hair, Nail (anatomy), nails, feathers, horn (anatomy), horns, claws, Hoof, hoove ...
proteins are most easily preserved because of their cross-link
In chemistry and biology, a cross-link is a bond or a short sequence of bonds that links one polymer chain to another. These links may take the form of covalent bonds or ionic bonds and the polymers can be either synthetic polymers or natural ...
ed, hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the chemical property of a molecule (called a hydrophobe) that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water. In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, thu ...
molecular structure. Fossils of keratin-based skin coverings or bony skin coverings are known from most major groups of dinosaurs. Dinosaur fossils with scaly skin impressions have been found since the 19th century. Samuel Beckles discovered a sauropod forelimb with preserved skin in 1852 that was incorrectly attributed to a crocodile; it was correctly attributed by Marsh in 1888 and subject to further study by Reginald Hooley in 1917. Among ornithischians, in 1884 Jacob Wortman found skin impressions on the first known specimen of ''Edmontosaurus annectens
''Edmontosaurus annectens'' (meaning "connected lizard from Edmonton"), often colloquially and historically known as ''Anatosaurus'' (meaning "duck lizard"), is a species of flat-headed Saurolophinae, saurolophine hadrosaurid dinosaur from the la ...
'', which were largely destroyed during the specimen's excavation. Owen and Hooley subsequently described skin impressions of ''Hypsilophodon
''Hypsilophodon'' (; meaning "high-crested tooth") is a neornithischian dinosaur genus from the Early Cretaceous period of England. It has traditionally been considered an early member of the group Ornithopoda, but recent research has put this ...
'' and ''Iguanodon'' in 1885 and 1917. Since then, scale impressions have been most frequently found among hadrosaurids, where the impressions are known from nearly the entire body across multiple specimens.
Starting from the 1990s, major discoveries of exceptionally preserved fossils in deposits known as conservation Lagerstätte
A Fossil-Lagerstätte (, from ''Lager'' 'storage, lair' '' Stätte'' 'place'; plural ''Lagerstätten'') is a sedimentary deposit that preserves an exceptionally high amount of palaeontological information. ''Konzentrat-Lagerstätten'' preserv ...
n contributed to research on dinosaur soft tissues. Chiefly among these were the rocks that produced the Jehol (Early Cretaceous) and Yanliao (Mid-to-Late Jurassic) biotas of northeastern China, from which hundreds of dinosaur specimens bearing impressions of feather-like structures (both closely related to birds and otherwise, see ) have been described by Xing Xu and colleagues. In living reptiles and mammals, pigment-storing cellular structures known as melanosome
A melanosome is an organelle found in animal cells and is the site for synthesis, storage and transport of melanin, the most common light-absorbing pigment found in the animal kingdom. Melanosomes are responsible for color and photoprotectio ...
s are partially responsible for producing colouration. Both chemical traces of melanin
Melanin (; ) is a family of biomolecules organized as oligomers or polymers, which among other functions provide the pigments of many organisms. Melanin pigments are produced in a specialized group of cells known as melanocytes.
There are ...
and characteristically shaped melanosomes have been reported from feathers and scales of Jehol and Yanliao dinosaurs, including both theropods and ornithischians. This has enabled multiple full-body reconstructions of dinosaur colouration, such as for ''Sinosauropteryx
''Sinosauropteryx'' (meaning "Chinese reptilian wing") is an extinct genus of coelurosaurian theropod dinosaurs. Described in 1996, it was the first dinosaur taxon outside of Avialae (birds and their immediate relatives) to be found with eviden ...
'' and ''Psittacosaurus
''Psittacosaurus'' ( ; "parrot lizard") is a genus of extinct ceratopsian dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous of what is now Asia, existing between 125 and 105 million years ago. It is notable for being the most species-rich non-avian dinosaur ...
'' by Jakob Vinther and colleagues, and similar techniques have also been extended to dinosaur fossils from other localities. (However, some researchers have also suggested that fossilized melanosomes represent bacterial remains.) Stomach contents in some Jehol and Yanliao dinosaurs closely related to birds have also provided indirect indications of diet and digestive system anatomy (e.g., crops
A crop is a plant that can be grown and harvested extensively for profit or subsistence. In other words, a crop is a plant or plant product that is grown for a specific purpose such as food, fibre, or fuel.
When plants of the same species a ...
). More concrete evidence of internal anatomy has been reported in ''Scipionyx
''Scipionyx'' ( ) was a genus of theropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous Pietraroja Formation of Italy, around 113 mya (unit), million years ago.
There is only one fossil known of ''Scipionyx'', discovered in 1981 by an amateur paleontolog ...
'' from the Pietraroja Plattenkalk
The Pietraroia Plattenkalk is a Cretaceous geologic Formation (geology), formation located in the Italy, Italian municipality of Pietraroja,
of Italy. It preserves portions of the intestines, colon, liver, muscles, and windpipe.
Concurrently, a line of work led by Mary Higby Schweitzer
Mary Higby Schweitzer is an American paleontologist at North Carolina State University, who led the groups that discovered the remains of blood cells in dinosaur fossils and later discovered soft tissue remains in the ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' specime ...
, Jack Horner Jack Horner may refer to:
*"Little Jack Horner", a nursery rhyme
People
* Jack Horner (activist) (born 1922), Australian author and activist in the Aboriginal-Australian Fellowship
* Jack Horner (baseball) (1863–1910), American professional ba ...
, and colleagues reported various occurrences of preserved soft tissues and proteins within dinosaur bone fossils. Various mineralized structures that likely represented red blood cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), referred to as erythrocytes (, with -''cyte'' translated as 'cell' in modern usage) in academia and medical publishing, also known as red cells, erythroid cells, and rarely haematids, are the most common type of blood cel ...
s and collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix of the connective tissues of many animals. It is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up 25% to 35% of protein content. Amino acids are bound together to form a trip ...
fibres had been found by Schweitzer and others in tyrannosaurid
Tyrannosauridae (or tyrannosaurids, meaning "tyrant lizards") is a family of coelurosaurian theropod dinosaurs that comprises two subfamilies containing up to fifteen genera, including the eponymous ''Tyrannosaurus''. The exact number of genera ...
bones as early as 1991. However, in 2005, Schweitzer and colleagues reported that a femur of ''Tyrannosaurus
''Tyrannosaurus'' () is a genus of large theropod dinosaur. The type species ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' ( meaning 'king' in Latin), often shortened to ''T. rex'' or colloquially t-rex, is one of the best represented theropods. It lived througho ...
'' preserved soft, flexible tissue within, including blood vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (bi ...
s, bone matrix, and connective tissue (bone fibers) that had retained their microscopic structure. This discovery suggested that original soft tissues could be preserved over geological time, with multiple mechanisms having been proposed. Later, in 2009, Schweitzer and colleagues reported that a ''Brachylophosaurus
''Brachylophosaurus'' ( or ) is a genus of hadrosaurid dinosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous period of western North America. It was first named in 1953 by Charles Mortram Sternberg for a skull and skeleton he discovered in 1936 in th ...
'' femur preserved similar microstructures, and immunohistochemical
Immunohistochemistry is a form of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens in cells and tissue, by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. Albert Hewett ...
techniques (based on antibody
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as pathogenic bacteria, bacteria and viruses, includin ...
binding) demonstrated the presence of proteins such as collagen, elastin
Elastin is a protein encoded by the ''ELN'' gene in humans and several other animals. Elastin is a key component in the extracellular matrix of gnathostomes (jawed vertebrates). It is highly Elasticity (physics), elastic and present in connective ...
, and laminin
Laminins are a family of glycoproteins of the extracellular matrix of all animals. They are major constituents of the basement membrane, namely the basal lamina (the protein network foundation for most cells and organs). Laminins are vital to bi ...
. Both specimens yielded collagen protein sequences that were viable for molecular phylogenetic analyses, which grouped them with birds as would be expected. The extraction of fragmentary DNA has also been reported for both of these fossils, along with a specimen of ''Hypacrosaurus
''Hypacrosaurus'' (meaning "near the highest lizard"
''. In 2015, Sergio Bertazzo and colleagues reported the preservation of collagen fibres and red blood cells in eight Cretaceous dinosaur specimens that did not show any signs of exceptional preservation, indicating that soft tissue may be preserved more commonly than previously thought. Suggestions that these structures represent bacterial reek υπο-, ''hypo-'' = less + ακρος, ''akros'', high
Reek may refer to:
Places
* Reek, Netherlands, a village in the Dutch province of North Brabant
* Croagh Patrick, a mountain in the west of Ireland nicknamed "The Reek"
People
* Nikolai Reek (1890–1942), Estonian military commander
* Salme Ree ...
because it was almost but not quite as large as ''Tyrannosaurus'') is an extinct genus of hadrosaurid, duckbill dinosaur simila ...biofilm
A biofilm is a Syntrophy, syntrophic Microbial consortium, community of microorganisms in which cell (biology), cells cell adhesion, stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy ext ...
s have been rejected, but cross-contamination remains a possibility that is difficult to detect.
Evolutionary history
Origins and early evolution
 Dinosaurs diverged from their archosaur ancestors during the Middle to Late Triassic epochs, roughly 20 million years after the devastating
Dinosaurs diverged from their archosaur ancestors during the Middle to Late Triassic epochs, roughly 20 million years after the devastating Permian–Triassic extinction event
The Permian–Triassic extinction event (also known as the P–T extinction event, the Late Permian extinction event, the Latest Permian extinction event, the End-Permian extinction event, and colloquially as the Great Dying,) was an extinction ...
wiped out an estimated 96% of all marine species and 70% of terrestrial vertebrate species approximately 252 million years ago. The oldest dinosaur fossils known from substantial remains date to the Carnian
The Carnian (less commonly, Karnian) is the lowermost stage (stratigraphy), stage of the Upper Triassic series (stratigraphy), Series (or earliest age (geology), age of the Late Triassic Epoch (reference date), Epoch). It lasted from 237 to 227.3 ...
epoch of the Triassic period and have been found primarily in the Ischigualasto
Ischigualasto Provincial Park (), also called ''Valle de la Luna'' ("Valley of the Moon" or "Moon Valley"), due to its moon-like appearance, is a provincial protected area in the north-east of San Juan Province, north-western Argentina, limiting ...
and Santa Maria Formation
The Santa Maria Formation is a sedimentary rock formation found in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. It is primarily Carnian in age (Late Triassic), and is notable for its fossils of cynodonts, " rauisuchian" pseudosuchians, and early dinosaurs and othe ...
s of Argentina and Brazil, and the Pebbly Arkose Formation
The Pebbly Arkose Formation is a Late Triassic geologic Formation (geology), formation found in southern Africa.
Geology Description
The formation comprises mainly coarse, arkosic sandstones.
Extent
The Pebbly Arkose Formation is found in ...
of Zimbabwe.
The Ischigualasto Formation (radiometrically dated
Radiometric dating, radioactive dating or radioisotope dating is a technique which is used to date materials such as rocks or carbon, in which trace radioactive impurities were selectively incorporated when they were formed. The method compares t ...
at 231–230 million years old) has produced the early saurischian ''Eoraptor
''Eoraptor'' () is a genus of small, lightly built, Basal (phylogenetics), basal sauropodomorpha, sauropodomorph dinosaur. One of the earliest-known dinosaurs and one of the earliest sauropodomorphs, it lived approximately 231 to 228 million yea ...
'', originally considered a member of the Herrerasauridae
Herrerasauridae is a family of carnivorous dinosaurs, possibly basal to either theropods or even all of saurischians, or even their own branching from Dracohors, separate from Dinosauria altogether. They are among the oldest known dinosaurs, ...
but now considered to be an early sauropodomorph, along with the herrerasaurids ''Herrerasaurus'' and ''Sanjuansaurus
''Sanjuansaurus'' (" San Juan Province lizard") is a genus of herrerasaurid dinosaur from the Late Triassic (Carnian) Ischigualasto Formation of the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin in northwestern Argentina.
Discovery
''Sanjuansaurus'' was ...
'', and the sauropodomorphs '' Chromogisaurus'', ''Eodromaeus
''Eodromaeus'' (meaning "dawn runner") is an extinct genus of probable basal (phylogenetics), basal theropod dinosaurs from the Late Triassic of Argentina. Like many other of the earliest-known dinosaurs, it hails from the Carnian-age (~230 Ma) I ...
'', and '' Panphagia''. ''Eoraptor'' likely resemblance to the common ancestor
Common descent is a concept in evolutionary biology applicable when one species is the ancestor of two or more species later in time. According to modern evolutionary biology, all living beings could be descendants of a unique ancestor commonl ...
of all dinosaurs suggests that the first dinosaurs would have been small, bipedal predators
Predation is a biological interaction in which one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill ...
. The Santa Maria Formation (radiometrically dated to be older, at 233.23 million years old) has produced the herrerasaurids ''Gnathovorax
''Gnathovorax'' is a genus of herrerasaurid saurischian dinosaur from the Santa Maria Formation in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. The type and only species is ''Gnathovorax cabreirai'', described by Pacheco ''et al.'' in 2019.
The type specimen com ...
'' and ''Staurikosaurus
''Staurikosaurus'' (Pronounced /ˌstɔɹ̠ikoʊˈsɔɹ̠ʌs/, '' STOR-ree-koh-SOR-ruhs''; "Southern Cross lizard") is a genus of herrerasaurid dinosaur from the Late Triassic of Brazil, found in the Santa Maria Formation.
Description
Colber ...
'', along with the sauropodomorphs '' Bagualosaurus'', ''Buriolestes
''Buriolestes'' is a genus of early sauropodomorph dinosaurs from the Late Triassic Santa Maria Formation of the Paraná Basin in southern Brazil. It contains a single species, ''B. schultzi'', named in 2016. The type specimen was found alongsid ...
'', '' Guaibasaurus'', ''Macrocollum
''Macrocollum'' is a genus of unaysauridae, unaysaurid sauropodomorph dinosaur that lived during the Late Triassic period (geology), period (early Norian) in what is now Brazil. It is one of the oldest dinosaurs known.
Discovery and naming
''Mac ...
'', ''Nhandumirim
''Nhandumirim'' (meaning "small Rhea (bird), rhea" in the Tupi language) is a genus of basal Sauropodomorpha, sauropodomorph dinosaur from the Carnian age of Late Triassic Brazil. It is currently considered a Saturnaliidae, saturnaliid sauropodom ...
'', '' Pampadromaeus'', ''Saturnalia'', and ''Unaysaurus
''Unaysaurus'' is a genus of unaysauridae, unaysaurid sauropodomorpha, sauropodomorph herbivore dinosaur. Discovered in southern Brazil, in the geopark of Paleorrota, in 1998, and announced in a press conference on Thursday, December 3, 2004, it ...
''. The Pebbly Arkose Formation, which is of uncertain age but was likely comparable to the other two, has produced the sauropodomorph ''Mbiresaurus
''Mbiresaurus'' (meaning " Mbire reptile") is an extinct genus of basal sauropodomorph dinosaur from the Late Triassic (Carnian) Pebbly Arkose Formation of Zimbabwe. The genus contains a single species, ''Mbiresaurus raathi'', known from a near ...
'', along with an unnamed herrerasaurid.
Less well-preserved remains of the sauropodomorphs ''Jaklapallisaurus
''Jaklapallisaurus'' is a genus of unaysaurid sauropodomorph dinosaur. It lived during the Late Triassic period (late Norian to earliest Rhaetian) in what is now Telangana, central India.The genus is monotypic, only including the species ''Jakl ...
'' and ''Nambalia
''Nambalia'' is a genus of basal sauropodomorph dinosaur. It lived during the Late Triassic period (late Norian to earliest Rhaetian) in what is now Telangana, central India. It is known from the holotype ISI R273, parts 1–3, partially arti ...
'', along with the early saurischian ''Alwalkeria
''Alwalkeria'' (; "for Alick Walker") is an extinct genus of basal saurischian dinosaur from the Late Triassic Lower Maleri Formation of India.
Discovery and naming
''Alwalkeria'' was originally named ''Walkeria maleriensis'' by Sankar Chatte ...
'', are known from the Upper Maleri and Lower Maleri Formation
The Lower Maleri Formation is a sedimentary geological formation, rock formation found in Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, India. It is the lowermost member of the Pranhita–Godavari Basin. It is of late Carnian to early Norian age (Upper Triassi ...
s of India. The Carnian-aged Chañares Formation
The Chañares Formation is a Carnian-age geologic formation of the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin, located in La Rioja Province, Argentina. It is characterized by drab-colored fine-grained volcaniclastic claystones, siltstones, and sandstones ...
of Argentina preserves primitive, dinosaur-like ornithodirans such as ''Lagosuchus
''Lagosuchus'' is an extinct genus of avemetatarsalian archosaur from the Late Triassic of Argentina. The type species of ''Lagosuchus'', ''Lagosuchus talampayensis'', is based on a small partial skeleton recovered from the early Carnian-age Cha ...
'' and ''Lagerpeton
''Lagerpeton'' is a genus of lagerpetid avemetatarsalian, comprising a single species, ''L. chanarensis''. First described from the Chañares Formation of Argentina by A. S. Romer in 1971, ''Lagerpeton'' anatomy is somewhat incompletely k ...
'' in Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
, making it another important site for understanding dinosaur evolution. These ornithodirans support the model of early dinosaurs as small, bipedal predators. Dinosaurs may have appeared as early as the Anisian
In the geologic timescale, the Anisian is the lower stage (stratigraphy), stage or earliest geologic age, age of the Middle Triassic series (stratigraphy), series or geologic epoch, epoch and lasted from million years ago until million years ag ...
epoch of the Triassic, approximately 243 million years ago, which is the age of ''Nyasasaurus
''Nyasasaurus'' (meaning " Lake Nyasa lizard") is an extinct genus of avemetatarsalian archosaur from the putatively Middle Triassic Manda Formation of Tanzania that may be the earliest known dinosaur. The type species ''Nyasasaurus parringtoni'' ...
'' from the Manda Formation
The Manda Formation (also known as the Manda Beds) is a Middle Triassic (Anisian?) or possibly Late Triassic (Carnian?) Formation (stratigraphy), geologic formation in Tanzania. It preserves fossils of many terrestrial vertebrates from the Triassi ...
of Tanzania. However, its known fossils are too fragmentary to identify it as a dinosaur or only a close relative. The referral of the Manda Formation to the Anisian is also uncertain. Regardless, dinosaurs existed alongside non-dinosaurian ornithodirans for a period of time, with estimates ranging from 5–10 million years to 21 million years.
When dinosaurs appeared, they were not the dominant terrestrial animals. The terrestrial habitats were occupied by various types of archosauromorphs
Archosauromorpha (Greek language, Greek for "ruling lizard forms") is a clade of diapsid reptiles containing all reptiles more closely related to archosaurs (such as crocodilians and dinosaurs, including birds) than to Lepidosauria, lepidosaurs ( ...
and therapsids, like cynodont
Cynodontia () is a clade of eutheriodont therapsids that first appeared in the Late Permian (approximately 260 Megaannum, mya), and extensively diversified after the Permian–Triassic extinction event. Mammals are cynodonts, as are their extin ...
s and rhynchosaur
Rhynchosaurs are a group of extinct herbivorous Triassic archosauromorph reptiles, belonging to the order Rhynchosauria. Members of the group are distinguished by their triangular skulls and elongated, beak like premaxillary bones. Rhynchosaurs ...
s. Their main competitors were the pseudosuchians
Pseudosuchia, from Ancient Greek ψεύδος (''pseúdos)'', meaning "false", and σούχος (''soúkhos''), meaning "crocodile" is one of two major divisions of Archosauria, including living crocodilians and all archosaurs more closely relat ...
, such as aetosaur
Aetosaurs () are heavily armored reptiles belonging to the extinct order (biology), order Aetosauria (; from Ancient Greek, Greek, (aetos, "eagle") and (, "lizard")). They were medium- to large-sized Omnivore, omnivorous or Herbivore, herbivor ...
s, ornithosuchids and rauisuchians, which were more successful than the dinosaurs. Most of these other animals became extinct in the Triassic, in one of two events. First, at about 215 million years ago, a variety of basal archosauromorphs, including the protorosaurs, became extinct. This was followed by the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event (about 201 million years ago), that saw the end of most of the other groups of early archosaurs, like aetosaurs, ornithosuchids, phytosaur
Phytosaurs (Φυτόσαυροι in Greek, meaning 'plant lizard') are an extinct group of large, mostly semiaquatic Late Triassic archosauriform or basal archosaurian reptiles. Phytosaurs belong to the order Phytosauria and are sometimes ref ...
s, and rauisuchians. Rhynchosaurs and dicynodont
Dicynodontia is an extinct clade of anomodonts, an extinct type of non-mammalian therapsid. Dicynodonts were herbivores that typically bore a pair of tusks, hence their name, which means 'two dog tooth'. Members of the group possessed a horny, t ...
s survived (at least in some areas) at least as late as early –mid Norian
The Norian is a division of the Triassic geological period, Period. It has the rank of an age (geology), age (geochronology) or stage (stratigraphy), stage (chronostratigraphy). It lasted from ~227.3 to Mya (unit), million years ago. It was prec ...
and late Norian or earliest Rhaetian
The Rhaetian is the latest age (geology), age of the Triassic period (geology), Period (in geochronology) or the uppermost stage (stratigraphy), stage of the Triassic system (stratigraphy), System (in chronostratigraphy). It was preceded by the N ...
stage
Stage, stages, or staging may refer to:
Arts and media Acting
* Stage (theatre), a space for the performance of theatrical productions
* Theatre, a branch of the performing arts, often referred to as "the stage"
* ''The Stage'', a weekly Brit ...
s, respectively, and the exact date of their extinction
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
is uncertain. These losses left behind a land fauna of crocodylomorphs
Crocodylomorpha is a group of pseudosuchian archosaurs that includes the crocodilians and their extinct relatives. They were the only members of Pseudosuchia to survive the end-Triassic extinction. Extinct crocodylomorphs were considerably more ...
, dinosaurs, mammals, pterosaurians, and turtle
Turtles are reptiles of the order (biology), order Testudines, characterized by a special turtle shell, shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Crypt ...
s. The first few lines of early dinosaurs diversified through the Carnian and Norian stages of the Triassic, possibly by occupying the niches of the groups that became extinct. Also notably, there was a heightened rate of extinction during the Carnian pluvial event
The Carnian pluvial episode (CPE), often called the Carnian pluvial event, was a period of major change in global climate that coincided with significant changes in Earth's biota both in the sea and on land. It occurred during the latter part of ...
.
Evolution and paleobiogeography
 Dinosaur evolution after the Triassic followed changes in vegetation and the location of continents. In the Late Triassic and Early Jurassic, the continents were connected as the single landmass
Dinosaur evolution after the Triassic followed changes in vegetation and the location of continents. In the Late Triassic and Early Jurassic, the continents were connected as the single landmass Pangaea
Pangaea or Pangea ( ) was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous period approximately 335 mi ...
, and there was a worldwide dinosaur fauna mostly composed of coelophysoid
Coelophysoidea is an extinct clade of theropod dinosaurs common during the Late Triassic and Early Jurassic periods. They were widespread geographically, probably living on all continents. Coelophysoids were all slender, carnivorous forms with a ...
carnivores and early sauropodomorph herbivores. Gymnosperm
The gymnosperms ( ; ) are a group of woody, perennial Seed plant, seed-producing plants, typically lacking the protective outer covering which surrounds the seeds in flowering plants, that include Pinophyta, conifers, cycads, Ginkgo, and gnetoph ...
plants (particularly conifer
Conifers () are a group of conifer cone, cone-bearing Spermatophyte, seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the phylum, division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a sin ...
s), a potential food source, radiated in the Late Triassic. Early sauropodomorphs did not have sophisticated mechanisms for processing food in the mouth, and so must have employed other means of breaking down food farther along the digestive tract. The general homogeneity of dinosaurian faunas continued into the Middle and Late Jurassic, where most localities had predators consisting of ceratosauria
Ceratosaurs are members of the clade Ceratosauria, a group of dinosaurs defined as all theropods sharing a more recent common ancestor with '' Ceratosaurus'' than with birds. The oldest known ceratosaur, '' Saltriovenator'', dates to the earlies ...
ns, megalosauroids, and allosauroids, and herbivores consisting of stegosaurian ornithischians and large sauropods. Examples of this include the Morrison Formation
The Morrison Formation is a distinctive sequence of Upper Jurassic sedimentary rock found in the western United States which has been the most fertile source of dinosaur fossils in North America. It is composed of mudstone, sandstone, siltston ...
of North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
and Tendaguru Beds of Tanzania. Dinosaurs in China show some differences, with specialized metriacanthosaurid
Metriacanthosauridae (Greek for "moderately-spined lizards") is an extinct family of allosauroid theropod dinosaurs that lived in Europe and Asia from the Middle Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous. The family is split into two subgroups: Metriacant ...
theropods and unusual, long-necked sauropods like ''Mamenchisaurus
''Mamenchisaurus'' ( , or spelling pronunciation ) is an extinct genus of sauropod dinosaurs known for their remarkably long necks which made up nearly half the total body length. Numerous species have been assigned to the genus; however, the val ...
''. Ankylosaurians and ornithopods were also becoming more common, but primitive sauropodomorphs had become extinct. Conifers and pteridophyte
A pteridophyte is a vascular plant (with xylem and phloem) that reproduces by means of spores. Because pteridophytes produce neither flowers nor seeds, they are sometimes referred to as " cryptogams", meaning that their means of reproduction is ...
s were the most common plants. Sauropods, like earlier sauropodomorphs, were not oral processors, but ornithischians were evolving various means of dealing with food in the mouth, including potential cheek
The cheeks () constitute the area of the face below the eyes and between the nose and the left or right ear. ''Buccal'' means relating to the cheek. In humans, the region is innervated by the buccal nerve. The area between the inside of th ...
-like organs to keep food in the mouth, and jaw motions to grind food. Another notable evolutionary event of the Jurassic was the appearance of true birds, descended from maniraptoran coelurosaurians.
By the Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous (geochronology, geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphy, chronostratigraphic name) is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 143.1 ...
and the ongoing breakup of Pangaea, dinosaurs were becoming strongly differentiated by landmass. The earliest part of this time saw the spread of ankylosaurians, iguanodontia
Ornithopoda () is a clade of ornithischian dinosaurs, called ornithopods (). They represent one of the most successful groups of herbivorous dinosaurs during the Cretaceous. The most primitive members of the group were bipedal and relatively sm ...
ns, and brachiosaurids
The Brachiosauridae ("arm lizards", from Greek ''brachion'' (βραχίων) = "arm" and ''sauros'' = "lizard") are a family or clade of herbivorous, quadrupedal sauropod dinosaurs. Brachiosaurids had long necks that enabled them to access the le ...
through Europe, North America, and northern Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
. These were later supplemented or replaced in Africa by large spinosaurid and carcharodontosaurid
Carcharodontosauridae (carcharodontosaurids; from the Greek καρχαροδοντόσαυρος, ''carcharodontósauros'': "shark-toothed lizards") is a group of carnivorous theropod dinosaurs. In 1931, Ernst Stromer named Carcharodontosauridae ...
theropods, and rebbachisaurid
Rebbachisauridae is a Family (biology), family of sauropod dinosaurs known from fragmentary fossil remains from the Cretaceous of South America, Africa, North America, Europe and possibly Central Asia.
Taxonomy
In 1990 sauropod specialist Jack M ...
and titanosauria
Titanosaurs (or titanosaurians; members of the group Titanosauria) were a diverse group of Sauropoda, sauropod dinosaurs, including genera from all seven continents. The titanosaurs were the last surviving group of long-necked sauropods, with tax ...
n sauropods, also found in South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
. In Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
, maniraptoran coelurosaurians like dromaeosaurids, troodontids
Troodontidae is a clade of bird-like theropod dinosaurs from the Late Jurassic to Late Cretaceous. During most of the 20th century, troodontid fossils were few and incomplete and they have therefore been allied, at various times, with many dinos ...
, and oviraptorosauria
Oviraptorosaurs ("egg thief lizards") are a group of feathered maniraptoran dinosaurs from the Cretaceous Period (geology), Period of what are now Asia and North America. They are distinct for their characteristically short, beaked, parrot-like s ...
ns became the common theropods, and ankylosaurids
Ankylosauridae () is a family of armored dinosaurs within Ankylosauria, and is the sister group to Nodosauridae. The oldest known ankylosaurids date to around 122 million years ago and went extinct 66 million years ago during the Cretaceous–Pal ...
and early ceratopsians like ''Psittacosaurus'' became important herbivores. Meanwhile, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
was home to a fauna of basal ankylosaurians, hypsilophodont
Hypsilophodontidae (or Hypsilophodontia) is a traditionally used family of ornithopod dinosaurs, generally considered invalid today. It historically included many small bodied bipedal neornithischian taxa from around the world, and spanning from ...
s, and iguanodontians. The stegosaurians appear to have gone extinct at some point in the late Early Cretaceous or early Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the more recent of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''cre ...
. A major change in the Early Cretaceous, which would be amplified in the Late Cretaceous, was the evolution of flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (). The term angiosperm is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek words (; 'container, vessel') and (; 'seed'), meaning that the seeds are enclosed with ...
s. At the same time, several groups of dinosaurian herbivores evolved more sophisticated ways to orally process food. Ceratopsians developed a method of slicing with teeth stacked on each other in batteries, and iguanodontians refined a method of grinding with dental batteries
Dinosaur teeth have been studied since 1822 when Mary Ann Mantell (1795-1869) and her husband Gideon Algernon Mantell, Dr Gideon Algernon Mantell (1790-1852) discovered an ''Iguanodon'' tooth in Sussex in England. Unlike Mammal tooth, mammal teeth ...
, taken to its extreme in hadrosaurids. Some sauropods also evolved tooth batteries, best exemplified by the rebbachisaurid ''Nigersaurus
''Nigersaurus'' () is a genus of rebbachisaurid sauropod dinosaur that lived during the middle Cretaceous period, about 115 to 105 million years ago. It was discovered in the Elrhaz Formation in an area called Gadoufaoua, in Niger. Fossils o ...
''.
There were three general dinosaur faunas in the Late Cretaceous. In the northern continents of North America and Asia, the major theropods were tyrannosaurids and various types of smaller maniraptoran theropods, with a predominantly ornithischian herbivore assemblage of hadrosaurids, ceratopsians, ankylosaurids, and pachycephalosaurians. In the southern continents that had made up the now-splitting supercontinent Gondwana
Gondwana ( ; ) was a large landmass, sometimes referred to as a supercontinent. The remnants of Gondwana make up around two-thirds of today's continental area, including South America, Africa, Antarctica, Australia (continent), Australia, Zea ...
, abelisaurids
Abelisauridae (meaning "Abel's lizards") is a family (biology), family (or clade) of ceratosaurian theropod dinosaurs. Abelisaurids thrived during the Cretaceous Period (geology), period, on the ancient southern supercontinent of Gondwana, and ...
were the common theropods, and titanosaurian sauropods the common herbivores. Finally, in Europe, dromaeosaurids, rhabdodontid iguanodontians, nodosaurid
Nodosauridae is a family of ankylosaurian dinosaurs known from the Late Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous periods in what is now Asia, Europe, North America, and possibly South America. While traditionally regarded as a monophyletic clade as the s ...
ankylosaurians, and titanosaurian sauropods were prevalent. Flowering plants were greatly radiating, with the first grasses appearing by the end of the Cretaceous. Grinding hadrosaurids and shearing ceratopsians became very diverse across North America and Asia. Theropods were also radiating as herbivores or omnivore
An omnivore () is an animal that regularly consumes significant quantities of both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize t ...
s, with therizinosaur
Therizinosaurs (; once called segnosaurs) are an extinct group of large herbivorous theropod dinosaurs whose fossils have been mainly discovered from Cretaceous deposits in Asia and North America. Potential fragmentary remains have also been foun ...
ians and ornithomimosauria
Ornithomimosauria ("bird-mimic lizards") are theropod dinosaurs which bore a superficial resemblance to the modern-day ostrich. They were fast, omnivorous or herbivorous dinosaurs from the Cretaceous Period of Laurasia (now Asia, Europe and No ...
ns becoming common.
The Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, which occurred approximately 66 million years ago at the end of the Cretaceous, caused the extinction of all dinosaur groups except for the neornithine birds. Some other diapsid groups, including crocodilia
Crocodilia () is an order of semiaquatic, predatory reptiles that are known as crocodilians. They first appeared during the Late Cretaceous and are the closest living relatives of birds. Crocodilians are a type of crocodylomorph pseudosuchia ...
ns, dyrosaurs, sebecosuchia
Sebecosuchia (meaning "Sobek crocodiles") is an extinct group of mesoeucrocodylian crocodyliforms that includes the families Sebecidae and Baurusuchidae. The group was long thought to have first appeared in the Late Cretaceous with the baurusu ...
ns, turtles, lizard
Lizard is the common name used for all Squamata, squamate reptiles other than snakes (and to a lesser extent amphisbaenians), encompassing over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most Island#Oceanic isla ...
s, snake
Snakes are elongated limbless reptiles of the suborder Serpentes (). Cladistically squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales much like other members of the group. Many species of snakes have s ...
s, sphenodontians, and choristodera
Choristodera (from the Greek χωριστός ''chōristos'' + δέρη ''dérē'', 'separated neck') is an extinct order of semiaquatic diapsid reptiles that ranged from the Middle Jurassic, or possibly Triassic, to the Miocene (168 to 20 or p ...
ns, also survived the event.
The surviving lineages of neornithine birds, including the ancestors of modern ratite
Ratites () are a polyphyletic group consisting of all birds within the infraclass Palaeognathae that lack keels and cannot fly. They are mostly large, long-necked, and long-legged, the exception being the kiwi, which is also the only nocturnal ...
s, ducks and chickens, and a variety of waterbirds
A water bird, alternatively waterbird or aquatic bird, is a bird that lives on or around water. In some definitions, the term ''water bird'' is especially applied to birds in freshwater ecosystems, although others make no distinction from seabi ...
, diversified rapidly at the beginning of the Paleogene
The Paleogene Period ( ; also spelled Palaeogene or Palæogene) is a geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Neogene Period Ma. It is the fir ...
period, entering ecological niche
In ecology, a niche is the match of a species to a specific environmental condition.
Three variants of ecological niche are described by
It describes how an organism or population responds to the distribution of Resource (biology), resources an ...
s left vacant by the extinction of Mesozoic dinosaur groups such as the arboreal enantiornithine
The Enantiornithes, also known as enantiornithines or enantiornitheans in literature, are a group of extinct avialans ("birds" in the broad sense), the most abundant and diverse group known from the Mesozoic era. Almost all retained teeth and c ...
s, aquatic hesperornithines, and even the larger terrestrial theropods (in the form of ''Gastornis
''Gastornis'' is an extinct genus of large, flightless birds that lived during the mid-Paleocene to mid-Eocene epochs of the Paleogene period. Most fossils have been found in Europe, and some species typically referred to the genus are known fr ...
'', eogruiids, bathornithids
Bathornithidae is an extinct family of birds from the Eocene to Miocene of North America. Part of Cariamiformes, they are related to the still extant seriemas and the extinct Phorusrhacidae. They were likely similar in habits, being terrestria ...
, ratites, geranoidids, mihirungs, and "terror bird
Phorusrhacids, colloquially known as terror birds, are an extinct family of large carnivorous, mostly flightless birds that were among the largest apex predators in South America during the Cenozoic era. Their definitive fossil records range from ...
s"). It is often stated that mammals out-competed the neornithines for dominance of most terrestrial niches but many of these groups co-existed with rich mammalian faunas for most of the Cenozoic
The Cenozoic Era ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterized by the dominance of mammals, insects, birds and angiosperms (flowering plants). It is the latest of three g ...
Era. Terror birds and bathornithids occupied carnivorous guilds alongside predatory mammals, and ratites are still fairly successful as midsized herbivores; eogruiids similarly lasted from the Eocene
The Eocene ( ) is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (Ma). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes ...
to Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch (geology), epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.33 to 2.58
Collectively, dinosaurs as a clade are divided into two primary branches, Saurischia and Ornithischia. Saurischia includes those taxa sharing a more recent common ancestor with birds than with Ornithischia, while Ornithischia includes all
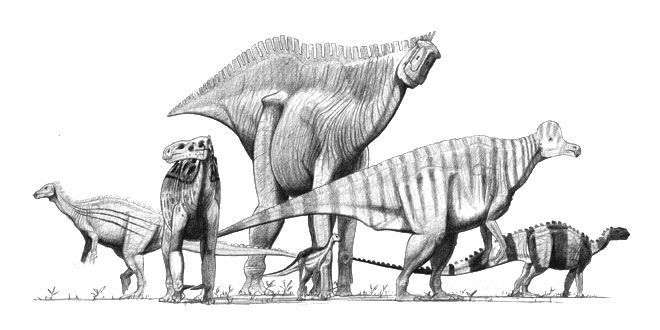
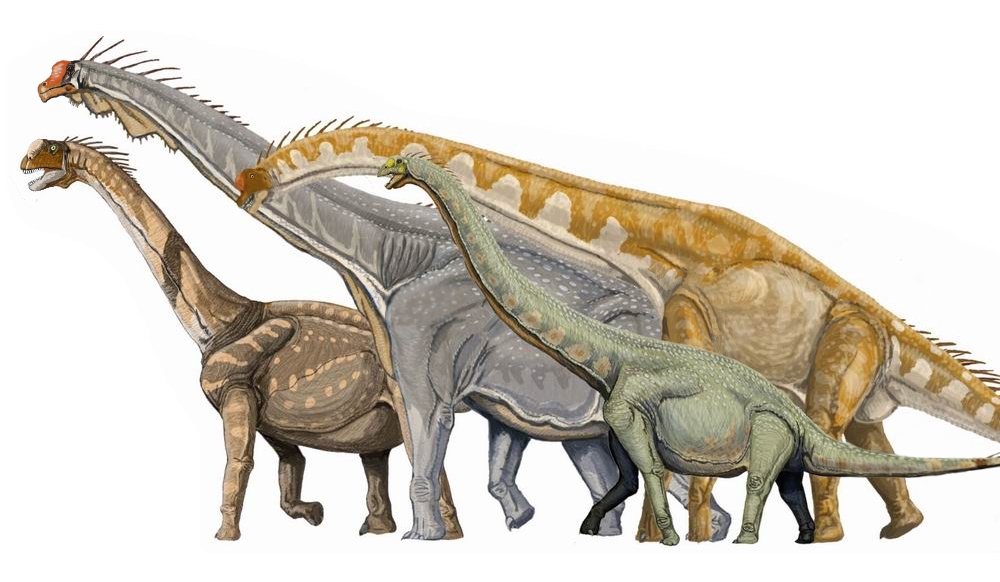 The following is a simplified classification of dinosaur groups based on their evolutionary relationships, and those of the main dinosaur groups Theropoda, Sauropodomorpha and Ornithischia, compiled by Justin Tweet. Further details and other hypotheses of classification may be found on individual articles.
*Dinosauria
**†
The following is a simplified classification of dinosaur groups based on their evolutionary relationships, and those of the main dinosaur groups Theropoda, Sauropodomorpha and Ornithischia, compiled by Justin Tweet. Further details and other hypotheses of classification may be found on individual articles.
*Dinosauria
**†
 Current evidence suggests that dinosaur average size varied through the Triassic, Early Jurassic, Late Jurassic and Cretaceous. Predatory theropod dinosaurs, which occupied most terrestrial carnivore niches during the Mesozoic, most often fall into the category when sorted by estimated weight into categories based on
Current evidence suggests that dinosaur average size varied through the Triassic, Early Jurassic, Late Jurassic and Cretaceous. Predatory theropod dinosaurs, which occupied most terrestrial carnivore niches during the Mesozoic, most often fall into the category when sorted by estimated weight into categories based on
 The tallest and heaviest dinosaur known from good skeletons is '' Giraffatitan brancai'' (previously classified as a species of ''
The tallest and heaviest dinosaur known from good skeletons is '' Giraffatitan brancai'' (previously classified as a species of '' There were larger dinosaurs, but knowledge of them is based entirely on a small number of fragmentary fossils. Most of the largest herbivorous specimens on record were discovered in the 1970s or later, and include the massive ''Argentinosaurus'', which may have weighed and reached lengths of ; some of the longest were the long ''Diplodocus hallorum'' (formerly ''Seismosaurus''), the long ''
There were larger dinosaurs, but knowledge of them is based entirely on a small number of fragmentary fossils. Most of the largest herbivorous specimens on record were discovered in the 1970s or later, and include the massive ''Argentinosaurus'', which may have weighed and reached lengths of ; some of the longest were the long ''Diplodocus hallorum'' (formerly ''Seismosaurus''), the long ''
 Many modern birds are highly social, often found living in flocks. There is general agreement that some behaviors that are common in birds, as well as in crocodilians (closest living relatives of birds), were also common among extinct dinosaur groups. Interpretations of behavior in fossil species are generally based on the pose of skeletons and their Habitat (ecology), habitat, computer simulations of their biomechanics, and comparisons with modern animals in similar ecological niches.
The first potential evidence for herding or Flocking (behavior), flocking as a widespread behavior common to many dinosaur groups in addition to birds was the 1878 discovery of 31 ''Iguanodon'', ornithischians that were then thought to have perished together in Bernissart, Belgium, after they fell into a deep, flooded sinkhole and drowned. Other mass-death sites have been discovered subsequently. Those, along with multiple trackways, suggest that gregarious behavior was common in many early dinosaur species. Trackways of hundreds or even thousands of herbivores indicate that duck-billed (hadrosaurids) may have moved in great herds, like the American bison or the African springbok. Sauropod tracks document that these animals traveled in groups composed of several different species, at least in Oxfordshire, England, although there is no evidence for specific herd structures. Congregating into herds may have evolved for defense, for Bird migration, migratory purposes, or to provide protection for young. There is evidence that many types of slow-growing dinosaurs, including various theropods, sauropods, ankylosaurians, ornithopods, and ceratopsians, formed aggregations of immature individuals. One example is a site in Inner Mongolia that has yielded remains of over 20 ''Sinornithomimus'', from one to seven years old. This assemblage is interpreted as a social group that was trapped in mud. The interpretation of dinosaurs as gregarious has also extended to depicting carnivorous theropods as pack hunters working together to bring down large prey. However, this lifestyle is uncommon among modern birds, crocodiles, and other reptiles, and the taphonomy, taphonomic evidence suggesting mammal-like pack hunting in such theropods as ''Deinonychus'' and ''
Many modern birds are highly social, often found living in flocks. There is general agreement that some behaviors that are common in birds, as well as in crocodilians (closest living relatives of birds), were also common among extinct dinosaur groups. Interpretations of behavior in fossil species are generally based on the pose of skeletons and their Habitat (ecology), habitat, computer simulations of their biomechanics, and comparisons with modern animals in similar ecological niches.
The first potential evidence for herding or Flocking (behavior), flocking as a widespread behavior common to many dinosaur groups in addition to birds was the 1878 discovery of 31 ''Iguanodon'', ornithischians that were then thought to have perished together in Bernissart, Belgium, after they fell into a deep, flooded sinkhole and drowned. Other mass-death sites have been discovered subsequently. Those, along with multiple trackways, suggest that gregarious behavior was common in many early dinosaur species. Trackways of hundreds or even thousands of herbivores indicate that duck-billed (hadrosaurids) may have moved in great herds, like the American bison or the African springbok. Sauropod tracks document that these animals traveled in groups composed of several different species, at least in Oxfordshire, England, although there is no evidence for specific herd structures. Congregating into herds may have evolved for defense, for Bird migration, migratory purposes, or to provide protection for young. There is evidence that many types of slow-growing dinosaurs, including various theropods, sauropods, ankylosaurians, ornithopods, and ceratopsians, formed aggregations of immature individuals. One example is a site in Inner Mongolia that has yielded remains of over 20 ''Sinornithomimus'', from one to seven years old. This assemblage is interpreted as a social group that was trapped in mud. The interpretation of dinosaurs as gregarious has also extended to depicting carnivorous theropods as pack hunters working together to bring down large prey. However, this lifestyle is uncommon among modern birds, crocodiles, and other reptiles, and the taphonomy, taphonomic evidence suggesting mammal-like pack hunting in such theropods as ''Deinonychus'' and '' The crests and frills of some dinosaurs, like the marginocephalians, theropods and Lambeosaurinae, lambeosaurines, may have been too fragile to be used for active defense, and so they were likely used for sexual or aggressive displays, though little is known about dinosaur mating and territory (animal), territorialism. Head wounds from bites suggest that theropods, at least, engaged in active aggressive confrontations.
From a behavioral standpoint, one of the most valuable dinosaur fossils was discovered in the Gobi Desert in 1971. It included a ''Velociraptor'' attacking a ''Protoceratops'', providing evidence that dinosaurs did indeed attack each other. Additional evidence for attacking live prey is the partially healed tail of an ''Edmontosaurus'', a hadrosaurid dinosaur; the tail is damaged in such a way that shows the animal was bitten by a tyrannosaur but survived. Cannibalism (zoology), Cannibalism amongst some species of dinosaurs was confirmed by tooth marks found in Madagascar in 2003, involving the theropod ''Majungasaurus''.
Comparisons between the sclerotic ring, scleral rings of dinosaurs and modern birds and reptiles have been used to infer daily activity patterns of dinosaurs. Although it has been suggested that most dinosaurs were active during the day, these comparisons have shown that small predatory dinosaurs such as dromaeosaurids, ''Juravenator'', and ''Megapnosaurus'' were likely nocturnal. Large and medium-sized herbivorous and omnivorous dinosaurs such as ceratopsians, sauropodomorphs, hadrosaurids, ornithomimosaurs may have been cathemeral, active during short intervals throughout the day, although the small ornithischian ''Agilisaurus'' was inferred to be Diurnality, diurnal.
Based on fossil evidence from dinosaurs such as ''Oryctodromeus'', some ornithischian species seem to have led a partially fossorial (burrowing) lifestyle. Many modern birds are arboreal (tree climbing), and this was also true of many Mesozoic birds, especially the enantiornithines. While some early bird-like species may have already been arboreal as well (including dromaeosaurids) such as ''Microraptor'') most non-avialan dinosaurs seem to have relied on land-based locomotion. A good understanding of how dinosaurs moved on the ground is key to models of dinosaur behavior; the science of biomechanics, pioneered by Robert McNeill Alexander, has provided significant insight in this area. For example, studies of the forces exerted by muscles and gravity on dinosaurs' skeletal structure have investigated how fast dinosaurs could run, whether diplodocids could create sonic booms via whip-like tail snapping, and whether sauropods could float.
The crests and frills of some dinosaurs, like the marginocephalians, theropods and Lambeosaurinae, lambeosaurines, may have been too fragile to be used for active defense, and so they were likely used for sexual or aggressive displays, though little is known about dinosaur mating and territory (animal), territorialism. Head wounds from bites suggest that theropods, at least, engaged in active aggressive confrontations.
From a behavioral standpoint, one of the most valuable dinosaur fossils was discovered in the Gobi Desert in 1971. It included a ''Velociraptor'' attacking a ''Protoceratops'', providing evidence that dinosaurs did indeed attack each other. Additional evidence for attacking live prey is the partially healed tail of an ''Edmontosaurus'', a hadrosaurid dinosaur; the tail is damaged in such a way that shows the animal was bitten by a tyrannosaur but survived. Cannibalism (zoology), Cannibalism amongst some species of dinosaurs was confirmed by tooth marks found in Madagascar in 2003, involving the theropod ''Majungasaurus''.
Comparisons between the sclerotic ring, scleral rings of dinosaurs and modern birds and reptiles have been used to infer daily activity patterns of dinosaurs. Although it has been suggested that most dinosaurs were active during the day, these comparisons have shown that small predatory dinosaurs such as dromaeosaurids, ''Juravenator'', and ''Megapnosaurus'' were likely nocturnal. Large and medium-sized herbivorous and omnivorous dinosaurs such as ceratopsians, sauropodomorphs, hadrosaurids, ornithomimosaurs may have been cathemeral, active during short intervals throughout the day, although the small ornithischian ''Agilisaurus'' was inferred to be Diurnality, diurnal.
Based on fossil evidence from dinosaurs such as ''Oryctodromeus'', some ornithischian species seem to have led a partially fossorial (burrowing) lifestyle. Many modern birds are arboreal (tree climbing), and this was also true of many Mesozoic birds, especially the enantiornithines. While some early bird-like species may have already been arboreal as well (including dromaeosaurids) such as ''Microraptor'') most non-avialan dinosaurs seem to have relied on land-based locomotion. A good understanding of how dinosaurs moved on the ground is key to models of dinosaur behavior; the science of biomechanics, pioneered by Robert McNeill Alexander, has provided significant insight in this area. For example, studies of the forces exerted by muscles and gravity on dinosaurs' skeletal structure have investigated how fast dinosaurs could run, whether diplodocids could create sonic booms via whip-like tail snapping, and whether sauropods could float.
 A 2009 review indicated that non-avians used visual displays and possibly non-vocal sounds, such as hissing, jaw-grinding or -clapping, splashing, and wing-beating (possible in winged maniraptoran dinosaurs). Other researchers have countered that vocalizations also exist in turtles, the closest relatives of archosaurs, suggesting that the trait is ancestral to their lineage. In addition, vocal communication in dinosaurs is indicated by the development of advanced hearing in nearly all major groups. Hence the syrinx may have supplemented and then replaced the larynx as a vocal organ, without a "silent period" in bird evolution.
In 2023, a fossilized larynx was described, from a specimen of the ankylosaurid ''Pinacosaurus''. The structure was composed of cricoid cartilage, cricoid and arytenoid cartilages, similar to those of non-avian reptiles; but the mobile cricoid–arytenoid joint and long arytenoid cartilages would have allowed air-flow control similar to that of birds, and thus could have made bird-like vocalizations. In addition, the cartilages were ossification, ossified, implying that laryngeal ossification is a feature of some non-avian dinosaurs. A 2016 study concludes that some dinosaurs may have produced closed-mouth vocalizations, such as cooing, hooting, and booming. These occur in both reptiles and birds and involve inflating the esophagus or tracheal pouches. Such vocalizations evolved independently in extant archosaurs numerous times, following increases in body size. The crests of some hadrosaurids and the nasal chambers of ankylosaurids may have been acoustic resonance, resonators.
A 2009 review indicated that non-avians used visual displays and possibly non-vocal sounds, such as hissing, jaw-grinding or -clapping, splashing, and wing-beating (possible in winged maniraptoran dinosaurs). Other researchers have countered that vocalizations also exist in turtles, the closest relatives of archosaurs, suggesting that the trait is ancestral to their lineage. In addition, vocal communication in dinosaurs is indicated by the development of advanced hearing in nearly all major groups. Hence the syrinx may have supplemented and then replaced the larynx as a vocal organ, without a "silent period" in bird evolution.
In 2023, a fossilized larynx was described, from a specimen of the ankylosaurid ''Pinacosaurus''. The structure was composed of cricoid cartilage, cricoid and arytenoid cartilages, similar to those of non-avian reptiles; but the mobile cricoid–arytenoid joint and long arytenoid cartilages would have allowed air-flow control similar to that of birds, and thus could have made bird-like vocalizations. In addition, the cartilages were ossification, ossified, implying that laryngeal ossification is a feature of some non-avian dinosaurs. A 2016 study concludes that some dinosaurs may have produced closed-mouth vocalizations, such as cooing, hooting, and booming. These occur in both reptiles and birds and involve inflating the esophagus or tracheal pouches. Such vocalizations evolved independently in extant archosaurs numerous times, following increases in body size. The crests of some hadrosaurids and the nasal chambers of ankylosaurids may have been acoustic resonance, resonators.
 All dinosaurs laid Amniote, amniotic eggs. Dinosaur eggs were usually laid in a nest. Most species create somewhat elaborate nests which can be cups, domes, plates, beds scrapes, mounds, or burrows. Some species of modern bird have no nests; the cliff-nesting Common murre, common guillemot lays its eggs on bare rock, and male emperor penguins keep eggs between their body and feet. Primitive birds and many non-avialan dinosaurs often lay eggs in communal nests, with males primarily incubating the eggs. While modern birds have only one functional oviduct and lay one egg at a time, more primitive birds and dinosaurs had two oviducts, like crocodiles. Some non-avialan dinosaurs, such as ''Troodon'', exhibited iterative laying, where the adult might lay a pair of eggs every one or two days, and then ensured simultaneous hatching by delaying Broodiness#Broodiness in non-avian animals, brooding until all eggs were laid.
When laying eggs, females grow a special type of bone between the hard outer bone and the Bone marrow, marrow of their limbs. This medullary bone, which is rich in calcium, is used to make eggshells. A discovery of features in a ''Tyrannosaurus'' skeleton provided evidence of medullary bone in extinct dinosaurs and, for the first time, allowed paleontologists to establish the sex of a fossil dinosaur specimen. Further research has found medullary bone in the carnosaur ''Allosaurus'' and the ornithopod ''Tenontosaurus''. Because the line of dinosaurs that includes ''Allosaurus'' and ''Tyrannosaurus'' diverged from the line that led to ''Tenontosaurus'' very early in the evolution of dinosaurs, this suggests that the production of medullary tissue is a general characteristic of all dinosaurs.
All dinosaurs laid Amniote, amniotic eggs. Dinosaur eggs were usually laid in a nest. Most species create somewhat elaborate nests which can be cups, domes, plates, beds scrapes, mounds, or burrows. Some species of modern bird have no nests; the cliff-nesting Common murre, common guillemot lays its eggs on bare rock, and male emperor penguins keep eggs between their body and feet. Primitive birds and many non-avialan dinosaurs often lay eggs in communal nests, with males primarily incubating the eggs. While modern birds have only one functional oviduct and lay one egg at a time, more primitive birds and dinosaurs had two oviducts, like crocodiles. Some non-avialan dinosaurs, such as ''Troodon'', exhibited iterative laying, where the adult might lay a pair of eggs every one or two days, and then ensured simultaneous hatching by delaying Broodiness#Broodiness in non-avian animals, brooding until all eggs were laid.
When laying eggs, females grow a special type of bone between the hard outer bone and the Bone marrow, marrow of their limbs. This medullary bone, which is rich in calcium, is used to make eggshells. A discovery of features in a ''Tyrannosaurus'' skeleton provided evidence of medullary bone in extinct dinosaurs and, for the first time, allowed paleontologists to establish the sex of a fossil dinosaur specimen. Further research has found medullary bone in the carnosaur ''Allosaurus'' and the ornithopod ''Tenontosaurus''. Because the line of dinosaurs that includes ''Allosaurus'' and ''Tyrannosaurus'' diverged from the line that led to ''Tenontosaurus'' very early in the evolution of dinosaurs, this suggests that the production of medullary tissue is a general characteristic of all dinosaurs.
 Another widespread trait among modern birds (but see below in regards to fossil groups and extant megapodes) is parental care for young after hatching. Jack Horner (paleontologist), Jack Horner's 1978 discovery of a ''Maiasaura'' ("good mother lizard") nesting ground in Montana demonstrated that parental care continued long after birth among ornithopods. A specimen of the oviraptoridae, oviraptorid ''Citipati, Citipati osmolskae'' was discovered in a Chicken#Broodiness, chicken-like brooding position in 1993, which may indicate that they had begun using an insulating layer of feathers to keep the eggs warm. An embryo of the basal sauropodomorph ''Massospondylus'' was found without teeth, indicating that some parental care was required to feed the young dinosaurs. Trackways have also confirmed parental behavior among ornithopods from the Isle of Skye in northwestern Scotland.
However, there is ample evidence of precociality or Precociality#Superprecociality, superprecociality among many dinosaur species, particularly theropods. For instance, non-Euornithes, ornithuromorph birds have been abundantly demonstrated to have had slow growth rates, megapode-like egg burying behavior and the ability to fly soon after birth. Both ''Tyrannosaurus'' and ''Troodon'' had juveniles with clear superprecociality and likely occupying different ecological niches than the adults. Superprecociality has been inferred for sauropods.
Genital structures are unlikely to fossilize as they lack scales that may allow preservation via pigmentation or residual calcium phosphate salts. In 2021, the best preserved specimen of a dinosaur's cloacal vent exterior was described for ''Psittacosaurus'', demonstrating lateral swellings similar to crocodylian musk glands used in social displays by both sexes and pigmented regions which could also reflect a signalling function. However, this specimen on its own does not offer enough information to determine whether this dinosaur had sexual signalling functions; it only supports the possibility. Cloacal visual signalling can occur in either males or females in living birds, making it unlikely to be useful to determine sex for extinct dinosaurs.
Another widespread trait among modern birds (but see below in regards to fossil groups and extant megapodes) is parental care for young after hatching. Jack Horner (paleontologist), Jack Horner's 1978 discovery of a ''Maiasaura'' ("good mother lizard") nesting ground in Montana demonstrated that parental care continued long after birth among ornithopods. A specimen of the oviraptoridae, oviraptorid ''Citipati, Citipati osmolskae'' was discovered in a Chicken#Broodiness, chicken-like brooding position in 1993, which may indicate that they had begun using an insulating layer of feathers to keep the eggs warm. An embryo of the basal sauropodomorph ''Massospondylus'' was found without teeth, indicating that some parental care was required to feed the young dinosaurs. Trackways have also confirmed parental behavior among ornithopods from the Isle of Skye in northwestern Scotland.
However, there is ample evidence of precociality or Precociality#Superprecociality, superprecociality among many dinosaur species, particularly theropods. For instance, non-Euornithes, ornithuromorph birds have been abundantly demonstrated to have had slow growth rates, megapode-like egg burying behavior and the ability to fly soon after birth. Both ''Tyrannosaurus'' and ''Troodon'' had juveniles with clear superprecociality and likely occupying different ecological niches than the adults. Superprecociality has been inferred for sauropods.
Genital structures are unlikely to fossilize as they lack scales that may allow preservation via pigmentation or residual calcium phosphate salts. In 2021, the best preserved specimen of a dinosaur's cloacal vent exterior was described for ''Psittacosaurus'', demonstrating lateral swellings similar to crocodylian musk glands used in social displays by both sexes and pigmented regions which could also reflect a signalling function. However, this specimen on its own does not offer enough information to determine whether this dinosaur had sexual signalling functions; it only supports the possibility. Cloacal visual signalling can occur in either males or females in living birds, making it unlikely to be useful to determine sex for extinct dinosaurs.
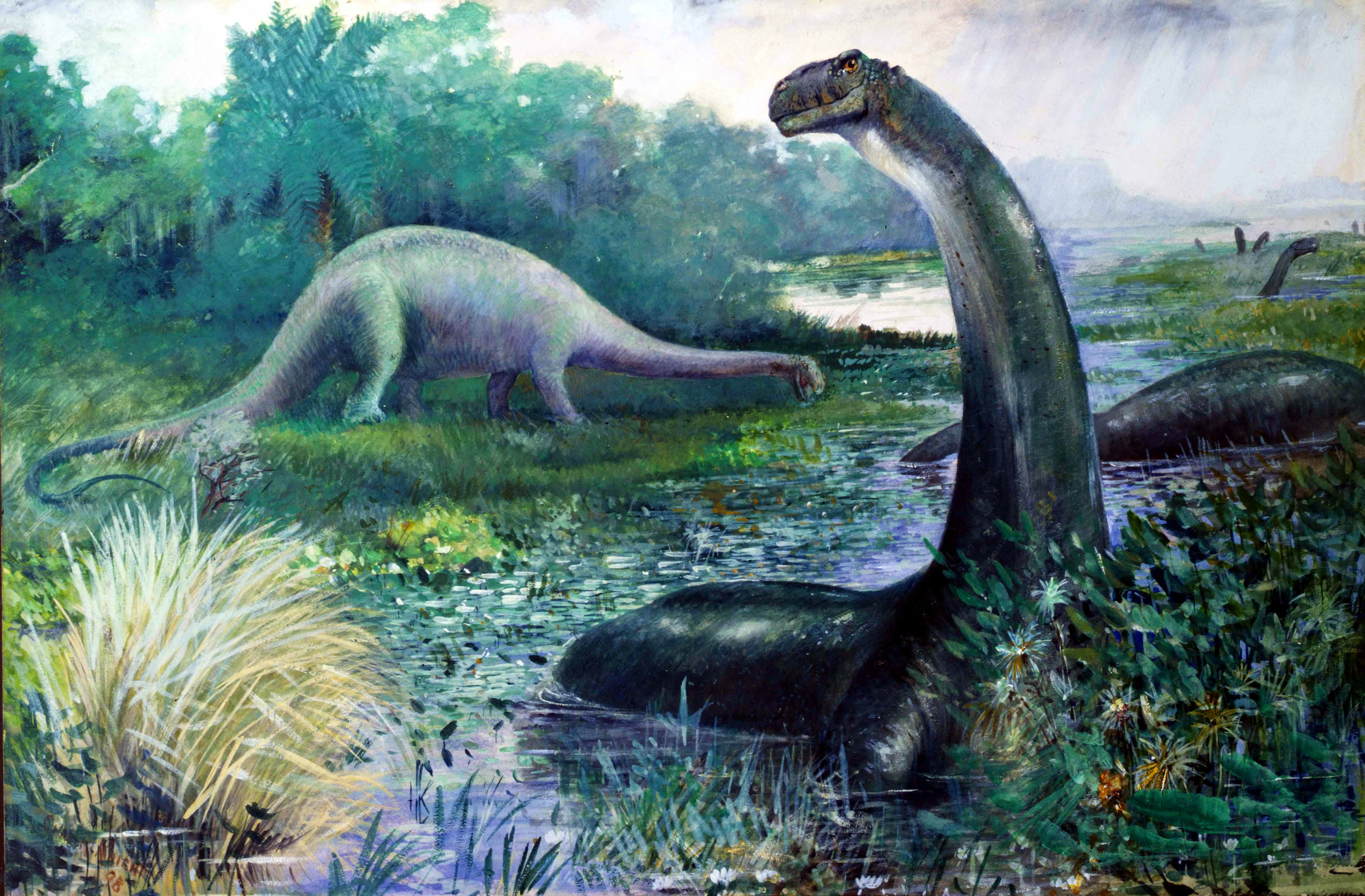 After non-avian dinosaurs were discovered, paleontologists first posited that they were ectothermic. This was used to imply that the ancient dinosaurs were relatively slow, sluggish organisms, even though many modern reptiles are fast and light-footed despite relying on external sources of heat to regulate their body temperature. The idea of dinosaurs as ectothermic remained a prevalent view until
After non-avian dinosaurs were discovered, paleontologists first posited that they were ectothermic. This was used to imply that the ancient dinosaurs were relatively slow, sluggish organisms, even though many modern reptiles are fast and light-footed despite relying on external sources of heat to regulate their body temperature. The idea of dinosaurs as ectothermic remained a prevalent view until  In saurischian dinosaurs, higher metabolisms were supported by the evolution of the avian respiratory system, characterized by an extensive system of air sacs that extended the lungs and invaded many of the bones in the skeleton, making them hollow. Such respiratory systems, which may have appeared in the earliest saurischians, would have provided them with more oxygen compared to a mammal of similar size, while also having a larger resting tidal volume and requiring a lower breathing frequency, which would have allowed them to sustain higher activity levels. The rapid airflow would also have been an effective cooling mechanism, which in conjunction with a lower metabolic rate would have prevented large sauropods from overheating. These traits may have enabled sauropods to grow quickly to gigantic sizes. Sauropods may also have benefitted from their size—their small surface area to volume ratio meant that they would have been able to thermoregulate more easily, a phenomenon termed gigantothermy.
Like other reptiles, dinosaurs are primarily uricotelic, that is, their kidneys extract nitrogenous wastes from their bloodstream and excrete it as uric acid instead of urea or ammonia via the ureters into the intestine. This would have helped them to conserve water. In most living species, uric acid is excreted along with feces as a semisolid waste. However, at least some modern birds (such as hummingbirds) can be facultatively ammonotelic, excreting most of the nitrogenous wastes as ammonia. This material, as well as the output of the intestines, emerges from the cloaca. In addition, many species regurgitate Pellet (ornithology), pellets, and fossil pellets are known as early as the Jurassic from ''Anchiornis''.
The size and shape of the brain can be partly reconstructed based on the surrounding bones. In 1896, Marsh calculated ratios between brain weight and body weight of seven species of dinosaurs, showing that the brain of dinosaurs was proportionally smaller than in today's crocodiles, and that the brain of ''Stegosaurus'' was smaller than in any living land vertebrate. This contributed to the widespread public notion of dinosaurs as being sluggish and extraordinarily stupid. Harry Jerison, in 1973, showed that proportionally smaller brains are expected at larger body sizes, and that brain size in dinosaurs was not smaller than expected when compared to living reptiles. Later research showed that relative brain size progressively increased during the evolution of theropods, with the highest intelligence – comparable to that of modern birds – calculated for the troodontid ''Troodon''.
In saurischian dinosaurs, higher metabolisms were supported by the evolution of the avian respiratory system, characterized by an extensive system of air sacs that extended the lungs and invaded many of the bones in the skeleton, making them hollow. Such respiratory systems, which may have appeared in the earliest saurischians, would have provided them with more oxygen compared to a mammal of similar size, while also having a larger resting tidal volume and requiring a lower breathing frequency, which would have allowed them to sustain higher activity levels. The rapid airflow would also have been an effective cooling mechanism, which in conjunction with a lower metabolic rate would have prevented large sauropods from overheating. These traits may have enabled sauropods to grow quickly to gigantic sizes. Sauropods may also have benefitted from their size—their small surface area to volume ratio meant that they would have been able to thermoregulate more easily, a phenomenon termed gigantothermy.
Like other reptiles, dinosaurs are primarily uricotelic, that is, their kidneys extract nitrogenous wastes from their bloodstream and excrete it as uric acid instead of urea or ammonia via the ureters into the intestine. This would have helped them to conserve water. In most living species, uric acid is excreted along with feces as a semisolid waste. However, at least some modern birds (such as hummingbirds) can be facultatively ammonotelic, excreting most of the nitrogenous wastes as ammonia. This material, as well as the output of the intestines, emerges from the cloaca. In addition, many species regurgitate Pellet (ornithology), pellets, and fossil pellets are known as early as the Jurassic from ''Anchiornis''.
The size and shape of the brain can be partly reconstructed based on the surrounding bones. In 1896, Marsh calculated ratios between brain weight and body weight of seven species of dinosaurs, showing that the brain of dinosaurs was proportionally smaller than in today's crocodiles, and that the brain of ''Stegosaurus'' was smaller than in any living land vertebrate. This contributed to the widespread public notion of dinosaurs as being sluggish and extraordinarily stupid. Harry Jerison, in 1973, showed that proportionally smaller brains are expected at larger body sizes, and that brain size in dinosaurs was not smaller than expected when compared to living reptiles. Later research showed that relative brain size progressively increased during the evolution of theropods, with the highest intelligence – comparable to that of modern birds – calculated for the troodontid ''Troodon''.
 Feathers are one of the most recognizable characteristics of modern birds, and a trait that was also shared by several non-avian dinosaurs. Based on the current distribution of fossil evidence, it appears that feathers were an ancestral dinosaurian trait, though one that may have been selectively lost in some species. Direct fossil evidence of feathers or feather-like structures has been discovered in a diverse array of species in many non-avian dinosaur groups, both among saurischians and ornithischians. Simple, branched, feather-like structures are known from Heterodontosauridae, heterodontosaurids, primitive neornithischians, and theropods, and primitive ceratopsians. Evidence for true, vaned feathers similar to the flight feathers of modern birds has been found only in the theropod subgroup Maniraptora, which includes oviraptorosaurs, troodontids, dromaeosaurids, and birds. Feather-like structures known as Pterosaur#Pycnofibers, pycnofibres have also been found in pterosaurs.
However, researchers do not agree regarding whether these structures share a common origin between lineages (i.e., they are homology (biology), homologous), or if they were the result of widespread experimentation with skin coverings among ornithodirans. If the former is the case, filaments may have been common in the ornithodiran lineage and evolved before the appearance of dinosaurs themselves. Research into the genetics of American alligators has revealed that crocodylian
Feathers are one of the most recognizable characteristics of modern birds, and a trait that was also shared by several non-avian dinosaurs. Based on the current distribution of fossil evidence, it appears that feathers were an ancestral dinosaurian trait, though one that may have been selectively lost in some species. Direct fossil evidence of feathers or feather-like structures has been discovered in a diverse array of species in many non-avian dinosaur groups, both among saurischians and ornithischians. Simple, branched, feather-like structures are known from Heterodontosauridae, heterodontosaurids, primitive neornithischians, and theropods, and primitive ceratopsians. Evidence for true, vaned feathers similar to the flight feathers of modern birds has been found only in the theropod subgroup Maniraptora, which includes oviraptorosaurs, troodontids, dromaeosaurids, and birds. Feather-like structures known as Pterosaur#Pycnofibers, pycnofibres have also been found in pterosaurs.
However, researchers do not agree regarding whether these structures share a common origin between lineages (i.e., they are homology (biology), homologous), or if they were the result of widespread experimentation with skin coverings among ornithodirans. If the former is the case, filaments may have been common in the ornithodiran lineage and evolved before the appearance of dinosaurs themselves. Research into the genetics of American alligators has revealed that crocodylian
 Large meat-eating dinosaurs had a complex system of air sacs similar to those found in modern birds, according to a 2005 investigation led by Patrick M. O'Connor. The lungs of theropod dinosaurs (carnivores that walked on two legs and had bird-like feet) likely pumped air into hollow sacs in their skeletons, as is the case in birds. "What was once formally considered unique to birds was present in some form in the ancestors of birds", O'Connor said. In 2008, scientists described ''Aerosteon, Aerosteon riocoloradensis'', the skeleton of which supplies the strongest evidence to date of a dinosaur with a bird-like breathing system. CT scanning of ''Aerosteons fossil bones revealed evidence for the existence of air sacs within the animal's body cavity.
Large meat-eating dinosaurs had a complex system of air sacs similar to those found in modern birds, according to a 2005 investigation led by Patrick M. O'Connor. The lungs of theropod dinosaurs (carnivores that walked on two legs and had bird-like feet) likely pumped air into hollow sacs in their skeletons, as is the case in birds. "What was once formally considered unique to birds was present in some form in the ancestors of birds", O'Connor said. In 2008, scientists described ''Aerosteon, Aerosteon riocoloradensis'', the skeleton of which supplies the strongest evidence to date of a dinosaur with a bird-like breathing system. CT scanning of ''Aerosteons fossil bones revealed evidence for the existence of air sacs within the animal's body cavity.

 The Alvarez hypothesis, bolide impact hypothesis, first brought to wide attention in 1980 by Walter Alvarez, Luis Walter Alvarez, Luis Alvarez, and colleagues, attributes the K-Pg extinction event to a bolide (extraterrestrial projectile) impact. Alvarez and colleagues proposed that a sudden increase in iridium levels, recorded around the world in rock deposits at the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary, was direct evidence of the impact. Shocked quartz, indicative of a strong shockwave emanating from an impact, was also found worldwide. The actual impact site remained elusive until a Chicxulub crater, crater measuring wide was discovered in the Yucatán Peninsula of southeastern Mexico, and was publicized in a 1991 paper by Alan R. Hildebrand, Alan Hildebrand and colleagues. Now, the bulk of the evidence suggests that a bolide wide impacted the Yucatán Peninsula 66 million years ago, forming this crater and creating a "kill mechanism" that triggered the extinction event.
Within hours, the Chicxulub impact would have created immediate effects such as earthquakes, tsunamis, and a global firestorm that likely killed unsheltered animals and started wildfires. However, it would also have had longer-term consequences for the environment. Within days, sulfate aerosols released from rocks at the impact site would have contributed to acid rain and ocean acidification. Soot aerosols are thought to have spread around the world over the ensuing months and years; they would have cooled the surface of the Earth by reflecting thermal radiation, and greatly slowed photosynthesis by blocking out sunlight, thus creating an impact winter. (This role was ascribed to sulfate aerosols until experiments demonstrated otherwise.) The cessation of photosynthesis would have led to the collapse of food webs depending on leafy plants, which included all dinosaurs save for grain-eating birds.
The Alvarez hypothesis, bolide impact hypothesis, first brought to wide attention in 1980 by Walter Alvarez, Luis Walter Alvarez, Luis Alvarez, and colleagues, attributes the K-Pg extinction event to a bolide (extraterrestrial projectile) impact. Alvarez and colleagues proposed that a sudden increase in iridium levels, recorded around the world in rock deposits at the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary, was direct evidence of the impact. Shocked quartz, indicative of a strong shockwave emanating from an impact, was also found worldwide. The actual impact site remained elusive until a Chicxulub crater, crater measuring wide was discovered in the Yucatán Peninsula of southeastern Mexico, and was publicized in a 1991 paper by Alan R. Hildebrand, Alan Hildebrand and colleagues. Now, the bulk of the evidence suggests that a bolide wide impacted the Yucatán Peninsula 66 million years ago, forming this crater and creating a "kill mechanism" that triggered the extinction event.
Within hours, the Chicxulub impact would have created immediate effects such as earthquakes, tsunamis, and a global firestorm that likely killed unsheltered animals and started wildfires. However, it would also have had longer-term consequences for the environment. Within days, sulfate aerosols released from rocks at the impact site would have contributed to acid rain and ocean acidification. Soot aerosols are thought to have spread around the world over the ensuing months and years; they would have cooled the surface of the Earth by reflecting thermal radiation, and greatly slowed photosynthesis by blocking out sunlight, thus creating an impact winter. (This role was ascribed to sulfate aerosols until experiments demonstrated otherwise.) The cessation of photosynthesis would have led to the collapse of food webs depending on leafy plants, which included all dinosaurs save for grain-eating birds.
 By human standards, dinosaurs were creatures of fantastic appearance and often enormous size. As such, they have captured the popular imagination and become an enduring part of human culture. The entry of the word "dinosaur" into the common vernacular reflects the animals' cultural importance: in English, "dinosaur" is commonly used to describe anything that is impractically large, obsolete, or bound for extinction.
Public enthusiasm for dinosaurs first developed in Victorian era, Victorian England, where in 1854, three decades after the first scientific descriptions of dinosaur remains, a menagerie of lifelike Crystal Palace dinosaurs, dinosaur sculptures was unveiled in London's Crystal Palace Park. The Crystal Palace dinosaurs proved so popular that a strong market in smaller replicas soon developed. In subsequent decades, dinosaur exhibits opened at parks and Natural history museum, museums around the world, ensuring that successive generations would be introduced to the animals in an immersive and exciting way. The enduring popularity of dinosaurs, in its turn, has resulted in significant public funding for dinosaur science, and has frequently spurred new discoveries. In the United States, for example, the competition between museums for public attention led directly to the Bone Wars of the 1880s and 1890s, during which a pair of feuding paleontologists made enormous scientific contributions.
The popular preoccupation with dinosaurs has ensured their appearance in literature, film, and other Media (communication), media. Beginning in 1852 with a passing mention in Charles Dickens ''Bleak House'', dinosaurs have been featured in large numbers of fictional works. Jules Verne's 1864 novel ''Journey to the Center of the Earth'', Arthur Conan Doyle, Sir Arthur Conan Doyle's 1912 book ''The Lost World (Doyle novel), The Lost World'', the 1914 animated film ''Gertie the Dinosaur'' (featuring the first animated dinosaur), the iconic 1933 motion picture, film ''King Kong (1933 film), King Kong'', the 1954 ''Godzilla (1954 film), Godzilla'' and its many sequels, the best-selling 1990 novel ''Jurassic Park (novel), Jurassic Park'' by Michael Crichton and its 1993 Jurassic Park (film), film adaptation are just a few notable examples of dinosaur appearances in fiction. Authors of general-interest non-fiction works about dinosaurs, including some prominent paleontologists, have often sought to use the animals as a way to educate readers about science in general. Dinosaurs are ubiquitous in advertising; numerous Company (law), companies have referenced dinosaurs in printed or televised advertisements, either in order to sell their own products or in order to characterize their rivals as slow-moving, dim-witted, or obsolete.
By human standards, dinosaurs were creatures of fantastic appearance and often enormous size. As such, they have captured the popular imagination and become an enduring part of human culture. The entry of the word "dinosaur" into the common vernacular reflects the animals' cultural importance: in English, "dinosaur" is commonly used to describe anything that is impractically large, obsolete, or bound for extinction.
Public enthusiasm for dinosaurs first developed in Victorian era, Victorian England, where in 1854, three decades after the first scientific descriptions of dinosaur remains, a menagerie of lifelike Crystal Palace dinosaurs, dinosaur sculptures was unveiled in London's Crystal Palace Park. The Crystal Palace dinosaurs proved so popular that a strong market in smaller replicas soon developed. In subsequent decades, dinosaur exhibits opened at parks and Natural history museum, museums around the world, ensuring that successive generations would be introduced to the animals in an immersive and exciting way. The enduring popularity of dinosaurs, in its turn, has resulted in significant public funding for dinosaur science, and has frequently spurred new discoveries. In the United States, for example, the competition between museums for public attention led directly to the Bone Wars of the 1880s and 1890s, during which a pair of feuding paleontologists made enormous scientific contributions.
The popular preoccupation with dinosaurs has ensured their appearance in literature, film, and other Media (communication), media. Beginning in 1852 with a passing mention in Charles Dickens ''Bleak House'', dinosaurs have been featured in large numbers of fictional works. Jules Verne's 1864 novel ''Journey to the Center of the Earth'', Arthur Conan Doyle, Sir Arthur Conan Doyle's 1912 book ''The Lost World (Doyle novel), The Lost World'', the 1914 animated film ''Gertie the Dinosaur'' (featuring the first animated dinosaur), the iconic 1933 motion picture, film ''King Kong (1933 film), King Kong'', the 1954 ''Godzilla (1954 film), Godzilla'' and its many sequels, the best-selling 1990 novel ''Jurassic Park (novel), Jurassic Park'' by Michael Crichton and its 1993 Jurassic Park (film), film adaptation are just a few notable examples of dinosaur appearances in fiction. Authors of general-interest non-fiction works about dinosaurs, including some prominent paleontologists, have often sought to use the animals as a way to educate readers about science in general. Dinosaurs are ubiquitous in advertising; numerous Company (law), companies have referenced dinosaurs in printed or televised advertisements, either in order to sell their own products or in order to characterize their rivals as slow-moving, dim-witted, or obsolete.
Internet Archive
Retrieved 2019-10-19. * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * "Reprint of papers published in a special volume of Modern geology [v. 18 (Halstead memorial volume), 1993], with five additional contributions.--Pref." * *
taxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and ...
sharing a more recent common ancestor with ''Triceratops'' than with Saurischia. Anatomically, these two groups can be distinguished most noticeably by their pelvic
The pelvis (: pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of an anatomical trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis or pelvic skeleton).
...
structure. Early saurischians—"lizard-hipped", from the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
' () meaning "lizard" and ' () meaning "hip joint"—retained the hip structure of their ancestors, with a pubis bone directed cranially
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provi ...
, or forward. This basic form was modified by rotating the pubis backward to varying degrees in several groups (''Herrerasaurus'', therizinosauroids, dromaeosaurids, and birds). Saurischia includes the theropods (exclusively bipedal and with a wide variety of diets) and sauropodomorphs (long-necked herbivores which include advanced, quadrupedal groups).
By contrast, ornithischians—"bird-hipped", from the Greek ''ornitheios'' (ὀρνίθειος) meaning "of a bird" and ''ischion'' (ἰσχίον) meaning "hip joint"—had a pelvis that superficially resembled a bird's pelvis: the pubic bone was oriented caudally (rear-pointing). Unlike birds, the ornithischian pubis also usually had an additional forward-pointing process. Ornithischia includes a variety of species that were primarily herbivores.
Despite the terms "bird hip" (Ornithischia) and "lizard hip" (Saurischia), birds are not part of Ornithischia. Birds instead belong to Saurischia, the "lizard-hipped" dinosaurs—birds evolved from earlier dinosaurs with "lizard hips".
Taxonomy

 The following is a simplified classification of dinosaur groups based on their evolutionary relationships, and those of the main dinosaur groups Theropoda, Sauropodomorpha and Ornithischia, compiled by Justin Tweet. Further details and other hypotheses of classification may be found on individual articles.
*Dinosauria
**†
The following is a simplified classification of dinosaur groups based on their evolutionary relationships, and those of the main dinosaur groups Theropoda, Sauropodomorpha and Ornithischia, compiled by Justin Tweet. Further details and other hypotheses of classification may be found on individual articles.
*Dinosauria
**†Ornithischia
Ornithischia () is an extinct clade of mainly herbivorous dinosaurs characterized by a pelvic structure superficially similar to that of birds. The name ''Ornithischia'', or "bird-hipped", reflects this similarity and is derived from the Greek ...
("bird-hipped"; diverse bipedal and quadrupedal herbivores)
***†Heterodontosauridae
Heterodontosauridae is a family (biology), family of ornithischian dinosaurs that were likely among the most Basal (phylogenetics), basal (primitive) members of the group. Their phylogenetic placement is uncertain but they are most commonly fou ...
(small herbivores/omnivores with prominent canine-like teeth)
****†Thyreophora
Thyreophora ("shield bearers", often known simply as "armored dinosaurs") is a group of armored ornithischian dinosaurs that lived from the Early Jurassic until the end of the Cretaceous.
Thyreophorans are characterized by the presence of bod ...
(armored dinosaurs; bipeds and quadrupeds)
*****†Stegosauria
Stegosauria is a group of Herbivore, herbivorous ornithischian dinosaurs that lived during the Jurassic and early Cretaceous Period (geology), periods. Stegosaurian fossils have been found mostly in the Northern Hemisphere (North America, Europe a ...
(spikes and plates as primary armor)
*****†Ankylosauria
Ankylosauria is a group of herbivorous dinosaurs of the clade Ornithischia. It includes the great majority of dinosaurs with armor in the form of bony osteoderms, similar to turtles. Ankylosaurs were bulky quadrupeds, with short, powerful limbs ...
(scute
A scute () or scutum (Latin: ''scutum''; plural: ''scuta'' "Scutum (shield), shield") is a bony external plate or scale overlaid with horn, as on the shell of a turtle, the skin of crocodilians, and the feet of Bird anatomy#Scales, birds. The ter ...
s as primary armor)
******†Parankylosauria
Parankylosauria is a group of Basal (phylogenetics), basal ankylosaurian dinosaurs known from the Cretaceous of South America, Antarctica, and Australia. It is thought the group split from other ankylosaurs during the mid-Jurassic period, despite ...
(small, southern ankylosaurs with macuahuitl
A macuahuitl () is a weapon, a wooden sword with several embedded obsidian blades. The name is derived from the Nahuatl language and means "hand-wood". Its sides are embedded with prismatic blades traditionally made from obsidian, which is c ...
-like tails)
******†Nodosauridae
Nodosauridae is a family of ankylosaurian dinosaurs known from the Late Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous periods in what is now Asia, Europe, North America, and possibly South America. While traditionally regarded as a monophyletic clade as the ...
(mostly spiky, club-less ankylosaurs)
******†Ankylosauridae
Ankylosauridae () is a family of armored dinosaurs within Ankylosauria, and is the sister group to Nodosauridae. The oldest known ankylosaurids date to around 122 million years ago and went extinct 66 million years ago during the Cretaceous–Pal ...
(characterized by flat scutes)
****†Neornithischia
Neornithischia ("new ornithischians") is a clade of the dinosaur order Ornithischia. It is the sister group of the Thyreophora within the clade Genasauria. Neornithischians are united by having a thicker layer of asymmetrical enamel on the insi ...
("new ornithischians")
*****†Thescelosauridae
Thescelosauridae is a clade of neornithischians from the Cretaceous of East Asia and North America. The group was originally used as a name by Charles M. Sternberg in 1937, but was not formally defined until 2013, where it was used by Brown and ...
("wondrous lizards")
*****† Marginocephalia (characterized by a cranial growth)
******†Pachycephalosauria
Pachycephalosauria (; from Greek παχυκεφαλόσαυρος for 'thick headed lizards') is a clade of ornithischian dinosaurs. Along with Ceratopsia, it makes up the clade Marginocephalia. With the exception of two species, most pachyceph ...
(bipeds with domed or knobby growth on skulls)
******†Ceratopsia
Ceratopsia or Ceratopia ( or ; Ancient Greek, Greek: "horned faces") is a group of herbivore, herbivorous, beaked dinosaurs that thrived in what are now North America, Asia and Europe, during the Cretaceous Period (geology), Period, although ance ...
(bipeds and quadrupeds; many had neck frills and horns)
*******†Chaoyangsauridae
Chaoyangsauridae is a family of ceratopsian dinosaurs. They are among the earliest known marginocephalian dinosaurs, with remains dating to about 160 million years ago, during the Late Jurassic period. Members of this group had sharp beaks for s ...
(small, frill-less basal ceratopsians)
*******†Leptoceratopsidae
Leptoceratopsidae is an extinct family (biology), family of neoceratopsian dinosaurs from Asia, North America and possibly Europe. Leptoceratopsids resembled, and were closely related to, other neoceratopsians, such as the family (biology), famil ...
(little to no frills, hornless, with robust jaws)
********†Protoceratopsidae
Protoceratopsidae is a family of basal (primitive) ceratopsians from the Late Cretaceous period. Although ceratopsians have been found all over the world, protoceratopsids are only definitively known from Cretaceous strata in Asia, with most spec ...
(basal ceratopsians with small frills and stubby horns)
*********†Ceratopsidae
Ceratopsidae (sometimes spelled Ceratopidae) is a family of ceratopsian dinosaurs including ''Triceratops'', ''Centrosaurus'', and ''Styracosaurus''. All known species were quadrupedal herbivores from the Upper Cretaceous. All but one species are k ...
(large, elaborately ornamented ceratopsians)
*****†Ornithopoda
Ornithopoda () is a clade of ornithischian dinosaurs, called ornithopods (). They represent one of the most successful groups of herbivorous dinosaurs during the Cretaceous. The most primitive members of the group were bipedal and relatively sm ...
(various sizes; bipeds and quadrupeds; evolved a method of chewing using skull flexibility and numerous teeth)
******†Hypsilophodontidae
Hypsilophodontidae (or Hypsilophodontia) is a traditionally used family (biology), family of ornithopod dinosaurs, generally considered invalid today. It historically included many small bodied bipedal neornithischian taxa from around the world, ...
(small European neornithischians)
******†Rhabdodontomorpha
Rhabdodontomorpha is a clade of basal iguanodont dinosaurs. This group was named in 2016 in the context of the description, based on Spanish findings of an early member of the Rhabdodontidae. A cladistic analysis was conducted in which it was f ...
(with distinctive dentition)
******†Elasmaria
Elasmaria is a clade of Ornithopoda, ornithopods known from Cretaceous deposits in the former Gondwana (South America, Antarctica, Australia, and possibly Africa) that contains many bipedal ornithopods that were previously considered Hypsilophodo ...
(mostly southern ornithopods with mineralized plates along the ribs; may be thescelosaurids)
******†Dryosauridae
Dryosauridae was a family of primitive iguanodonts, first proposed by Milner & Norman in 1984. They are known from Middle Jurassic to Early Cretaceous rocks of Africa, Europe, and North America.
Dryosauridae was first proposed in 1984 by Britis ...
(mid-sized, small headed)
*******†Ankylopollexia
Ankylopollexia is an extinct clade of ornithischian dinosaurs that lived from the Late Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous. It is a derived clade of iguanodontian ornithopods and contains the subgroup Styracosterna. The name stems from the Greek wo ...
(early members mid-sized, stocky)
********† Hadrosauromorpha (hadrosaurids and their closest relatives)
*********†Hadrosauridae
Hadrosaurids (), also hadrosaurs or duck-billed dinosaurs, are members of the ornithischian family Hadrosauridae. This group is known as the duck-billed dinosaurs for the flat duck-bill appearance of the bones in their snouts. The ornithopod fam ...
("duck-billed dinosaurs"; often with crests)
**Saurischia
Saurischia ( , meaning "reptile-hipped" from the Greek ' () meaning 'lizard' and ' () meaning 'hip joint') is one of the two basic divisions of dinosaurs (the other being Ornithischia), classified by their hip structure. Saurischia and Ornithi ...
***†Herrerasauridae
Herrerasauridae is a family of carnivorous dinosaurs, possibly basal to either theropods or even all of saurischians, or even their own branching from Dracohors, separate from Dinosauria altogether. They are among the oldest known dinosaurs, ...
(early bipedal carnivores)
***†Sauropodomorpha
Sauropodomorpha ( ; from Greek, meaning "lizard-footed forms") is an extinct clade of long-necked, herbivorous, saurischian dinosaurs that includes the sauropods and their ancestral relatives. Sauropods generally grew to very large sizes, had lo ...
(herbivores with small heads, long necks, and long tails)
****†Unaysauridae
Unaysauridae is a clade of basal sauropodomorphs from the Late Triassic of India and Brazil.
Diagnosis and systematics
Unaysauridae was defined by Müller ''et al.'' (2018) as the most inclusive clade including ''Unaysaurus tolentinoi'', but no ...
(primitive, strictly bipedal "prosauropods")
****†Plateosauria
Sauropodomorpha ( ; from Greek, meaning "lizard-footed forms") is an extinct clade of long-necked, herbivorous, saurischian dinosaurs that includes the sauropods and their ancestral relatives. Sauropods generally grew to very large sizes, had lo ...
(diverse; bipeds and quadrupeds)
*****†Massopoda
Sauropodomorpha ( ; from Greek, meaning "lizard-footed forms") is an extinct clade of long-necked, herbivorous, saurischian dinosaurs that includes the Sauropoda, sauropods and their ancestral relatives. Sauropods generally grew to very large siz ...
("heavy feet")
******†Massospondylidae
Massospondylidae is a family (biology), family of early massopod dinosaurs that existed in Asia, Africa, North America, South America and AntarcticaHellert, Spencer M. "A New Basal Sauropodomorph from The Early Jurassic Hanson Formation of Antarc ...
(long-necked, primitive sauropodomorphs)
******†Riojasauridae
Riojasauridae is an extinct family of sauropodomorph dinosaurs from the Late Triassic Period (late Carnian to Norian Ages). It contains the genera ''Riojasaurus'' and '' Eucnemesaurus''. The Riojasauridae is considered a stem taxon, and is defin ...
(large, primitive sauropodomorphs)
*******†Sauropoda
Sauropoda (), whose members are known as sauropods (; from ''wikt:sauro-, sauro-'' + ''wikt:-pod, -pod'', 'lizard-footed'), is a clade of saurischian ('lizard-hipped') dinosaurs. Sauropods had very long necks, long tails, small heads (relative t ...
(very large and heavy; quadrupedal)
********†Lessemsauridae
Lessemsauridae is a clade (family) of early sauropodiform dinosaurs that lived in the Triassic and Jurassic of Argentina, South Africa and possibly Lesotho. A phylogenetic analysis performed by Apaldetti and colleagues in 2018 recovered a new cl ...
(gigantic yet lacking several weight-saving adaptations)
********†Eusauropoda
Eusauropoda (meaning "True Lizard Foot") is a derived clade of sauropod dinosaurs. Eusauropods represent the node-based group that includes all descendant sauropods starting with the basal eusauropods of '' Shunosaurus'', and possibly '' Barapas ...
("true sauropods")
*********†Turiasauria
Turiasauria is an unranked clade of eusauropod dinosaurs known from Middle Jurassic to Early Cretaceous deposits in Europe, North America, and Africa.
Description
Turiasauria was originally erected by Royo-Torres et al. (2006) to include '' Tur ...
(often large, widespread sauropods)
*********†Neosauropoda
Neosauropoda is a clade within Dinosauria, coined in 1986 by Argentina, Argentine paleontologist José Bonaparte and currently described as ''Saltasaurus loricatus'', ''Diplodocus longus'', and all animals directly descended from their most recent ...
("new sauropods"; columnar limbs)
**********†Diplodocoidea
Diplodocoidea is a superfamily of sauropod dinosaurs, which included some of the longest animals of all time, including slender giants like ''Supersaurus'', ''Diplodocus'', ''Apatosaurus'', and ''Amphicoelias''. Most had very long necks and long, ...
(skulls and tails elongated; teeth typically narrow and pencil-like)
***********†Rebbachisauridae
Rebbachisauridae is a family of sauropod dinosaurs known from fragmentary fossil remains from the Cretaceous of South America, Africa, North America, Europe and possibly Central Asia.
Taxonomy
In 1990 sauropod specialist Jack McIntosh included t ...
(short-necked, low-browsing diplodocoids often with high backs)
************†Dicraeosauridae
Dicraeosauridae is a Family (biology), family of Diplodocoidea, diplodocoid sauropods who are the sister group to Diplodocidae. Dicraeosaurids are a part of the Flagellicaudata, along with Diplodocidae. Dicraeosauridae includes genera such as ''A ...
(small, short-necked diplodocoids with enlarged cervical and dorsal vertebrae)
************†Diplodocidae
Diplodocids, or members of the family Diplodocidae ("double beams"), are a group of sauropod dinosaurs. The family includes some of the longest creatures ever to walk the Earth, including '' Diplodocus'' and '' Supersaurus'', some of which may ha ...
(extremely long-necked)
**********†Macronaria
Macronaria is a clade of sauropod dinosaurs. Macronarians are named after the large diameter of the nasal opening of their skull, known as the external naris, which exceeded the size of the orbit, the skull opening where the eye is located (hence ...
(boxy skulls; spoon- or pencil-shaped teeth)
***********†Brachiosauridae
The Brachiosauridae ("arm lizards", from Greek ''brachion'' (βραχίων) = "arm" and ''sauros'' = "lizard") are a family or clade of herbivorous, quadrupedal sauropod dinosaurs. Brachiosaurids had long necks that enabled them to access the le ...
(long-necked, long-armed macronarians)
***********†Somphospondyli
Somphospondyli is an extinct clade of titanosauriformes, titanosauriform sauropods that lived from the Late Jurassic until the end of the Late Cretaceous, comprising all titanosauriforms more closely related to Titanosauria proper than Brachiosau ...
("porous vertebrae")
************†Euhelopodidae
Euhelopodidae is a family of sauropod dinosaurs of disputed membership and affinities, which contains '' Euhelopus'' and its close relatives. Most proposed euhelopodids are from East Asia.
Euhelopodidae was first recognized by Carl Wiman in 1929 ...
(stocky, mostly Asian)
************†Diamantinasauria
Diamantinasauria is an extinct clade of somphospondylan titanosauriform sauropod dinosaurs with close affinities to the Titanosauria, known from the early Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian-Turonian) of South America and Australia. It was named by Poro ...
(horse-like skulls; restricted to the Southern Hemisphere; may be titanosaurs)
************†Titanosauria
Titanosaurs (or titanosaurians; members of the group Titanosauria) were a diverse group of Sauropoda, sauropod dinosaurs, including genera from all seven continents. The titanosaurs were the last surviving group of long-necked sauropods, with tax ...
(diverse; stocky, with wide hips; most common in the Late Cretaceous of southern continents)
***Theropoda
Theropoda (; from ancient Greek iktionary:θηρίον, , (''therion'') "wild beast"; wiktionary:πούς, , wiktionary:ποδός, (''pous, podos'') "foot" is one of the three major groups (Clade, clades) of Dinosaur, dinosaurs, alon ...
(carnivorous)
****†Coelophysoidea
Coelophysoidea is an extinct clade of theropod dinosaurs common during the Late Triassic and Early Jurassic periods. They were widespread geographically, probably living on all continents. Coelophysoids were all slender, carnivorous forms with a ...
(early theropods; includes ''Coelophysis
''Coelophysis'' ( Traditional English pronunciation of Latin, traditionally; or , as heard more commonly in recent decades) is a genus of coelophysid Theropoda, theropod dinosaur that lived Approximation, approximately 215 to 201.4 million y ...
'' and close relatives)
****†Ceratosauria
Ceratosaurs are members of the clade Ceratosauria, a group of dinosaurs defined as all theropods sharing a more recent common ancestor with '' Ceratosaurus'' than with birds. The oldest known ceratosaur, '' Saltriovenator'', dates to the earlies ...
(generally elaborately horned carnivores that existed from the Jurassic to Cretaceous periods, originally included Coelophysoidea)
*****†Abelisauridae
Abelisauridae (meaning "Abel's lizards") is a family (or clade) of ceratosaurian theropod dinosaurs. Abelisaurids thrived during the Cretaceous period, on the ancient southern supercontinent of Gondwana, and today their fossil remains are fou ...
(large abelisauroids with short arms and oftentimes elaborate facial ornamentation)
*****†Noasauridae
Noasauridae is an extinct family of theropod dinosaurs belonging to the group Ceratosauria. They were closely related to the short-armed Abelisauridae, abelisaurids, although most noasaurids had much more traditional body types generally simila ...
(diverse, generally light theropods; may include several obscure taxa)
****Tetanurae
Tetanurae (/ˌtɛtəˈnjuːriː/ or "stiff tails") is a clade that includes most Theropoda, theropod dinosaurs, including Megalosauroidea, megalosauroids, Allosauroidea, allosauroids, and Coelurosauria, coelurosaurs (which includes Tyrannosauroi ...
(stiff-tailed dinosaurs)
*****†Megalosauroidea
Megalosauroidea (meaning 'great/big lizard forms') is a superfamily (or clade) of tetanuran theropod dinosaurs that lived from the Middle Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous period. The group is defined as '' Megalosaurus bucklandii'' and all taxa ...
(early group of large carnivores)
******†Piatnitzkysauridae
Piatnitzkysauridae is an extinct family of megalosauroid or basal allosauroid dinosaurs. It only consists of three to four known dinosaur genera: '' Condorraptor'', '' Marshosaurus'', '' Piatnitzkysaurus and'' possibly '' Xuanhanosaurus.'' The ...
(small basal megalosauroids endemic to the Americas)
******†Megalosauridae
Megalosauridae is a monophyletic Family (taxonomy), family of Carnivore, carnivorous theropod dinosaurs within the group Megalosauroidea. Appearing in the Middle Jurassic, megalosaurids were among the first major radiation of large theropod dino ...
(large megalosauroids with powerful arms and hands)
******†Spinosauridae
Spinosauridae (or spinosaurids) is a clade or Family (taxonomy), family of tetanuran theropod dinosaurs comprising ten to seventeen known genera. Spinosaurid fossils have been recovered worldwide, including Africa, Europe, South America, and Asia. ...
(crocodile-like, semiaquatic carnivores)
*****†Carnosauria
Carnosauria is an extinct group of carnivorous theropod dinosaurs that lived during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods.
While Carnosauria was historically considered largely synonymous with Allosauroidea, some recent studies have revived Ca ...
(large meat-eating dinosaurs; megalosauroids sometimes included)
******†Metriacanthosauridae
Metriacanthosauridae (Greek for "moderately-spined lizards") is an extinct family of allosauroid theropod dinosaurs that lived in Europe and Asia from the Middle Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous. The family is split into two subgroups: Metriacan ...
(primitive Asian allosauroids)
******†Allosauridae
Allosauridae is an extinct family of medium to large bipedal, carnivorous allosauroid theropod dinosaurs from the Late Jurassic. Allosauridae is a fairly old taxonomic group, having been first named by the American paleontologist Othniel Cha ...
(''Allosaurus
''Allosaurus'' ( ) is an extinct genus of theropod dinosaur that lived 155 to 145 million years ago during the Late Jurassic period ( Kimmeridgian to late Tithonian ages). The first fossil remains that could definitively be ascribed to th ...
'' and its very closest relatives)
******†Carcharodontosauridae
Carcharodontosauridae (carcharodontosaurids; from the Greek καρχαροδοντόσαυρος, ''carcharodontósauros'': "shark-toothed lizards") is a group of carnivorous theropod dinosaurs. In 1931, Ernst Stromer named Carcharodontosaurida ...
(robust allosauroids; includes some of the largest purely terrestrial carnivores)
*****Coelurosauria
Coelurosauria (; from Greek, meaning "hollow-tailed lizards") is the clade containing all theropod dinosaurs more closely related to birds than to carnosaurs.
Coelurosauria is a subgroup of theropod dinosaurs that includes compsognathids, tyra ...
(feathered theropods, with a range of body sizes and niches)
******†Megaraptora
Megaraptora is a clade of carnivorous theropod dinosaurs. Its derived members, the Megaraptoridae are noted for their large hand claws and powerfully-built forelimbs, which are usually reduced in size in other large theropods. Although undoubt ...
? (theropods with large hand claws; potentially tyrannosauroids or neovenatorids)
******†Tyrannosauroidea
Tyrannosauroidea (meaning 'tyrant lizard forms') is a superfamily (or clade) of coelurosaurian theropod dinosaurs that includes the family Tyrannosauridae as well as more basal relatives. Tyrannosauroids lived on the Laurasian supercontinent ...
(mostly large, primitive coelurosaurs)
*******†Proceratosauridae
Proceratosauridae is a family or clade of tyrannosauroid theropod dinosaurs from the Middle Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous.
Distinguishing features
Unlike the advanced tyrannosaurids but similar to primitive tyrannosauroids like '' Dilong ...
(tyrannosauroids with head crests)
*******†Tyrannosauridae
Tyrannosauridae (or tyrannosaurids, meaning "tyrant lizards") is a family of coelurosaurian theropod dinosaurs that comprises two subfamilies containing up to fifteen genera, including the eponymous ''Tyrannosaurus''. The exact number of genera ...
(''Tyrannosaurus
''Tyrannosaurus'' () is a genus of large theropod dinosaur. The type species ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' ( meaning 'king' in Latin), often shortened to ''T. rex'' or colloquially t-rex, is one of the best represented theropods. It lived througho ...
'' and close relatives)
******†Ornithomimosauria
Ornithomimosauria ("bird-mimic lizards") are theropod dinosaurs which bore a superficial resemblance to the modern-day ostrich. They were fast, omnivorous or herbivorous dinosaurs from the Cretaceous Period of Laurasia (now Asia, Europe and No ...
(small-headed, mostly toothless, omnivorous or possible herbivores)
*******†Ornithomimidae
Ornithomimidae (meaning "bird-mimics") is an extinct family of theropod dinosaurs which bore a superficial resemblance to modern ostriches. Ornithomimids were fast, omnivorous or herbivorous dinosaurs known mainly from the Late Cretaceous Period ...
(very ostrich-like dinosaurs)
******Maniraptora
Maniraptora is a clade of coelurosaurian dinosaurs which includes the birds and the non-avian dinosaurs that were more closely related to them than to ''Ornithomimus velox''. It contains the major subgroups Avialae, Dromaeosauridae, Troodontidae, ...
(dinosaurs with pennaceous feathers)
*******†Alvarezsauroidea
Alvarezsauroidea (from the Argentine historian, writer and physician Gregorio Álvarez) is a group of small maniraptoran dinosaurs. The group was first formally proposed by Choiniere and colleagues in 2010, to contain the family Alvarezsauridae ...
(small hunters with reduced forelimbs)
********†Alvarezsauridae
Alvarezsauridae is a family of small, long-legged dinosaurs. Although originally thought to represent the earliest known flightless birds, they are now thought to be an early diverging branch of maniraptoran theropods. Alvarezsaurids were highly ...
(insectivores with only one enlarged digit)
*******†Therizinosauria
Therizinosaurs (; once called segnosaurs) are an extinct group of large herbivorous Theropoda, theropod dinosaurs whose fossils have been mainly discovered from Cretaceous deposits in Asia and North America. Potential fragmentary remains have als ...
(tall, long-necked theropods; omnivores and herbivores)
********†Therizinosauridae
Therizinosauridae (meaning 'scythe lizards')Translated paper
is an extinct family of derive ...
(sloth-like herbivores, often with enlarged claws)
*******†is an extinct family of derive ...
Oviraptorosauria
Oviraptorosaurs ("egg thief lizards") are a group of feathered maniraptoran dinosaurs from the Cretaceous Period (geology), Period of what are now Asia and North America. They are distinct for their characteristically short, beaked, parrot-like s ...
(omnivorous, beaked dinosaurs)
********†Caudipteridae
Caudipteridae is an extinct family of oviraptorosaurian dinosaurs known from the Early Cretaceous of China. Found in the Yixian and Jiufotang Formations, the group existed between 125 and 120 million years ago. Distinguishing characteristics of ...
(bird-like, basal oviraptorosaurs)
********†Caenagnathidae
Caenagnathidae is a family of derived caenagnathoid dinosaurs from the Cretaceous of North America and Asia. They are a member of the Oviraptorosauria, and relatives of the Oviraptoridae. Like other oviraptorosaurs, caenagnathids had specialize ...
(toothless oviraptorosaurs known from North America and Asia)
********†Oviraptoridae
Oviraptoridae is a group of bird-like, herbivorous and omnivorous maniraptoran dinosaurs. Oviraptorids are characterized by their toothless, parrot-like beaks and, in some cases, elaborate crests. They were generally small, measuring between one ...
(characterized by two bony projections at the back of the mouth; exclusive to Asia)
********Paraves
Paraves are a widespread group of theropod dinosaurs that originated in the Middle Jurassic period. In addition to the extinct dromaeosauridae, dromaeosaurids, troodontidae, troodontids, Anchiornithidae, anchiornithids, and possibly the scansor ...
(avialans and their closest relatives)
*********†Scansoriopterygidae
Scansoriopterygidae (meaning "climbing wings") is an extinct family (biology), family of climbing and gliding maniraptoran dinosaurs. Scansoriopterygids are known from five well-preserved fossils, representing four species, unearthed in the Tiaoj ...
(small tree-climbing theropods with membranous wings)
*********†Deinonychosauria
Deinonychosauria is a clade of paravian dinosaurs which lived from the Late Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous periods. Fossils have been found across the globe in North America, Europe, Africa, Asia, South America, and Antarctica,Case, J.A., Marti ...
(toe-clawed dinosaurs; may not form a natural group)
**********†Archaeopterygidae
Archaeopterygidae is a group of paravian dinosaurs, known from the latest Jurassic and earliest Cretaceous of Europe. In most current classifications, it contains only the genera ''Archaeopteryx'' and ''Wellnhoferia''. As its name suggests, ''Pro ...
(small, winged theropods or primitive birds)
**********†Troodontidae
Troodontidae is a clade of bird-like theropod dinosaurs from the Late Jurassic to Late Cretaceous. During most of the 20th century, troodontid fossils were few and incomplete and they have therefore been allied, at various times, with many dinos ...
(omnivores; enlarged brain cavities)
**********†Dromaeosauridae
Dromaeosauridae () is a family of feathered coelurosaurian theropod dinosaurs. They were generally small to medium-sized feathered carnivores that flourished in the Cretaceous Period. The name Dromaeosauridae means 'running lizards', from ...
("raptors")
**********†Unenlagiidae
Unenlagiidae is a proposed family of eumaniraptoran paravians that includes the subfamilies Unenlagiinae and possibly Halszkaraptorinae. Fossils of both subfamilies have been found in both Gondwanan and Laurasian deposits. The biology of the g ...
(piscivores; may be dromaeosaurids)
*********Avialae
Avialae ("bird wings") is a clade containing the only living dinosaurs, the birds, and their closest relatives. It is usually defined as all theropod dinosaurs more closely related to birds (Aves) than to Deinonychosauria, deinonychosaurs, though ...
(modern birds and extinct relatives)
Paleobiology
Knowledge about dinosaurs is derived from a variety of fossil and non-fossil records, including fossilized bones,feces
Feces (also known as faeces American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, or fæces; : faex) are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the ...
, trackway
Historic roads (or historic trails in the US and Canada) are paths or routes that have historical importance due to their use over a period of time. Examples exist from prehistoric times until the early 20th century. They include ancient track ...
s, gastrolith
A gastrolith, also called a stomach stone or gizzard stone, is a rock held inside a gastrointestinal tract. Gastroliths in some species are retained in the muscular gizzard and used to grind food in animals lacking suitable grinding teeth. In ...
s, feather
Feathers are epidermal growths that form a distinctive outer covering, or plumage, on both avian (bird) and some non-avian dinosaurs and other archosaurs. They are the most complex integumentary structures found in vertebrates and an exa ...
s, impressions of skin, internal organ
In a multicellular organism, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to a ...
s and other soft tissue
Soft tissue connective tissue, connects and surrounds or supports internal organs and bones, and includes muscle, tendons, ligaments, Adipose tissue, fat, fibrous tissue, Lymphatic vessel, lymph and blood vessels, fasciae, and synovial membranes.� ...
s. Many fields of study contribute to our understanding of dinosaurs, including physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge whi ...
(especially biomechanics
Biomechanics is the study of the structure, function and motion of the mechanical aspects of biological systems, at any level from whole organisms to Organ (anatomy), organs, Cell (biology), cells and cell organelles, using the methods of mechani ...
), chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules a ...
, biology
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, History of life, origin, evolution, and ...
, and the Earth science
Earth science or geoscience includes all fields of natural science related to the planet Earth. This is a branch of science dealing with the physical, chemical, and biological complex constitutions and synergistic linkages of Earth's four spheres ...
s (of which paleontology
Paleontology, also spelled as palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of the life of the past, mainly but not exclusively through the study of fossils. Paleontologists use fossils as a means to classify organisms, measure ge ...
is a sub-discipline). Two topics of particular interest and study have been dinosaur size and behavior.
Size
order of magnitude
In a ratio scale based on powers of ten, the order of magnitude is a measure of the nearness of two figures. Two numbers are "within an order of magnitude" of each other if their ratio is between 1/10 and 10. In other words, the two numbers are ...
, whereas recent
The Holocene () is the current geological epoch, beginning approximately 11,700 years ago. It follows the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene together form the Qu ...
predatory carnivoran mammals peak in the category. The mode
Mode ( meaning "manner, tune, measure, due measure, rhythm, melody") may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* MO''D''E (magazine), a defunct U.S. women's fashion magazine
* ''Mode'' magazine, a fictional fashion magazine which is the setting fo ...
of Mesozoic dinosaur body masses is between . This contrasts sharply with the average size of Cenozoic mammals, estimated by the National Museum of Natural History
The National Museum of Natural History (NMNH) is a natural history museum administered by the Smithsonian Institution, located on the National Mall in Washington, D.C., United States. It has free admission and is open 364 days a year. With 4.4 ...
as about .
The sauropods were the largest and heaviest dinosaurs. For much of the dinosaur era, the smallest sauropods were larger than anything else in their habitat, and the largest was an order of magnitude more massive than anything else that has since walked the Earth. Giant prehistoric mammals such as ''Paraceratherium
''Paraceratherium'' is an extinct genus of hornless rhinocerotoids belonging to the family Paraceratheriidae. It is one of the largest terrestrial mammals that has ever existed and lived from the early to late Oligocene epoch (34–23 ...
'' (the largest land mammal ever) were dwarfed by the giant sauropods, and only modern whales approach or surpass them in size. There are several proposed advantages for the large size of sauropods, including protection from predation, reduction of energy use, and longevity, but it may be that the most important advantage was dietary. Large animals are more efficient at digestion than small animals, because food spends more time in their digestive systems. This also permits them to subsist on food with lower nutritive value than smaller animals. Sauropod remains are mostly found in rock formations interpreted as dry or seasonally dry, and the ability to eat large quantities of low-nutrient browse would have been advantageous in such environments.
Largest and smallest
Scientists will probably never be certain of the largest and smallest dinosaurs to have ever existed. This is because only a tiny percentage of animals were ever fossilized and most of these remain buried in the earth. Few non-avian dinosaur specimens that are recovered are complete skeletons, and impressions of skin and other soft tissues are rare. Rebuilding a complete skeleton by comparing the size and morphology of bones to those of similar, better-known species is an inexact art, and reconstructing the muscles and other organs of the living animal is, at best, a process of educated guesswork.Brachiosaurus
''Brachiosaurus'' () is a genus of sauropod dinosaur that lived in North America during the Late Jurassic, about . It was first Species description, described by American paleontologist Elmer S. Riggs in 1903 in paleontology, 1903 from fossi ...
''). Its remains were discovered in Tanzania between 1907 and 1912. Bones from several similar-sized individuals were incorporated into the skeleton now mounted and on display at the Museum für Naturkunde
The Natural History Museum () is a natural history museum located in Berlin, Germany. It exhibits a vast range of specimens from various segments of natural history and in such domain it is one of three major museums in Germany alongside Naturm ...
in Berlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population withi ...
; this mount is tall and long, and would have belonged to an animal that weighed between and kilograms ( and lb). The longest complete dinosaur is the long ''Diplodocus'', which was discovered in Wyoming
Wyoming ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States, Western United States. It borders Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho t ...
in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
and displayed in Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, United States, and its county seat. It is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania#Municipalities, second-most populous city in Pennsylvania (after Philadelphia) and the List of Un ...
's Carnegie Museum of Natural History
The Carnegie Museum of Natural History (abbreviated as CMNH) is a natural history museum in the Oakland (Pittsburgh), Oakland neighborhood of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. It was founded by List of people from the Pittsburgh metropolitan area, Pit ...
in 1907. The longest dinosaur known from good fossil material is ''Patagotitan
''Patagotitan'' is a genus of titanosaurian sauropoda, sauropod dinosaur from the Cerro Barcino Formation in Chubut Province, Patagonia, Argentina. The genus contains a single species known from at least six young adult individuals, ''Patagotita ...
'': the skeleton mount in the American Museum of Natural History in New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
is long. The Museo Municipal Carmen Funes in Plaza Huincul
Plaza Huincul is a small city in Neuquen province, with a population of around 13,000 people, located in southwestern Argentina. It is approximately south-west from the capital, Buenos Aires. Plaza Huincul is located in the middle of the desert ...
, Argentina, has an ''Argentinosaurus
''Argentinosaurus'' (meaning "lizard from Argentina") is a genus of giant sauropod dinosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous Period (geology), period in what is now Argentina. Although it is only known from fragmentary remains, ''Argentinos ...
'' reconstructed skeleton mount that is long.
 There were larger dinosaurs, but knowledge of them is based entirely on a small number of fragmentary fossils. Most of the largest herbivorous specimens on record were discovered in the 1970s or later, and include the massive ''Argentinosaurus'', which may have weighed and reached lengths of ; some of the longest were the long ''Diplodocus hallorum'' (formerly ''Seismosaurus''), the long ''
There were larger dinosaurs, but knowledge of them is based entirely on a small number of fragmentary fossils. Most of the largest herbivorous specimens on record were discovered in the 1970s or later, and include the massive ''Argentinosaurus'', which may have weighed and reached lengths of ; some of the longest were the long ''Diplodocus hallorum'' (formerly ''Seismosaurus''), the long ''Supersaurus
''Supersaurus'' (meaning "super lizard") is a genus of diplodocid sauropod dinosaur that lived in North America during the Late Jurassic period. The type species, ''S. vivianae'', was first discovered by Vivian Jones of Delta, Colorado, in the ...
'', and long ''Patagotitan''; and the tallest, the tall ''Sauroposeidon
''Sauroposeidon'' ( ; meaning "lizard earthquake deity, god", after the Greek god Poseidon) is a genus of sauropod dinosaur known from several incomplete specimens including a bone bed and fossilized trackways that have been found in the U.S. st ...
'', which could have reached a sixth-floor window. There were a few dinosaurs that was considered either the heaviest and longest. The most famous one include '' Amphicoelias fragillimus'', known only from a now lost partial vertebral neural arch
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal ...
described in 1878. Extrapolating from the illustration of this bone, the animal may have been long and weighed . However, recent research have placed ''Amphicoelias'' from the long, gracile diplodocid to the shorter but much stockier rebbachisaurid. Now renamed as ''Maraapunisaurus
''Maraapunisaurus'' is a controversial genus of sauropod dinosaur from the Late Jurassic Morrison Formation of western North America. Originally named ''Amphicoelias fragillimus'', it has sometimes been estimated to be the Dinosaur size, largest ...
'', this sauropod now stands as much as long and weigh as much as . Another contender of this title includes '' Bruhathkayosaurus'', a controversial taxon that was recently confirmed to exist after archived photos were uncovered. ''Bruhathkayosaurus'' was a titanosaur and would have most likely weighed more than even ''Marrapunisaurus''. Recent size estimates in 2023 have placed this sauropod reaching lengths of up to long and a colossal weight range of around , if these upper estimates up true, ''Bruhathkayosaurus'' would have rivaled the ''blue whale
The blue whale (''Balaenoptera musculus'') is a marine mammal and a baleen whale. Reaching a maximum confirmed length of and weighing up to , it is the largest animal known ever to have existed. The blue whale's long and slender body can ...
'' and ''Perucetus colossus
''Perucetus'' is an extinct genus of an early whale from Peru that lived during the Bartonian age of the middle Eocene. ''Perucetus'' is the largest Eocene whale, with length estimates varying from to . It was initially claimed to have rivaled ...
'' as one of the largest animals to have ever existed.
The largest carnivorous dinosaur was ''Spinosaurus
''Spinosaurus'' (; ) is a genus of large spinosaurid theropod dinosaurs that lived in what now is North Africa during the Cenomanian faunal stage, stage of the Late Cretaceous Period (geology), period, about 100 to 94 annum, million year ...
'', reaching a length of and weighing . Other large carnivorous theropods included ''Giganotosaurus
''Giganotosaurus'' ( ) is a genus of large theropod dinosaur that lived in what is now Argentina, during the early Cenomanian age of the Late Cretaceous period (geology), period, approximately 99.6 to 95 million years ago. The holotype specim ...
'', ''Carcharodontosaurus
''Carcharodontosaurus'' (; ) is a genus of large carnivorous theropod dinosaur that lived in Northwest Africa from about 100 to 94 million years ago during the Cenomanian age of the Cretaceous. Two teeth of the genus, now lost, were first des ...
'', and ''Tyrannosaurus''. ''Therizinosaurus
''Therizinosaurus'' (; meaning 'scythe lizard') is a genus of very large therizinosaurid dinosaurs that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period in what is now the Nemegt Formation around 70 million years ago. It contains a single speci ...
'' and ''Deinocheirus
''Deinocheirus'' ( ) is a genus of large ornithomimosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous around 70 million years ago. In 1965, a pair of large arms, shoulder girdles, and a few other bones of a new dinosaur were first discovered in the ...
'' were among the tallest of the theropods. The largest ornithischian dinosaur was probably the hadrosaurid ''Shantungosaurus giganteus
''Shantungosaurus'' (meaning "''Shandong Lizard''") is a genus of very large saurolophine hadrosaurid dinosaur found in the Late Cretaceous Wangshi Group of the Shandong Peninsula in China, containing a single species, ''Shantungosaurus giganteu ...
'' which measured . The largest individuals may have weighed as much as .
The smallest dinosaur known is the bee hummingbird
The bee hummingbird, zunzuncito or Helena hummingbird (''Mellisuga helenae'') is a species of hummingbird, native to the island of Cuba in the Caribbean. It is the smallest known bird. The bee hummingbird feeds on nectar of flowers and bugs foun ...
, with a length of only and mass of around . The smallest known non-avialan
Avialae ("bird wings") is a clade containing the only living dinosaurs, the birds, and their closest relatives. It is usually defined as all theropod dinosaurs more closely related to birds (Aves) than to deinonychosaurs, though alternative defi ...
dinosaurs were about the size of pigeon
Columbidae is a bird family consisting of doves and pigeons. It is the only family in the order Columbiformes. These are stout-bodied birds with small heads, relatively short necks and slender bills that in some species feature fleshy ceres. ...
s and were those theropods most closely related to birds. For example, ''Anchiornis huxleyi
''Anchiornis'' is a genus of small, four-winged paravian dinosaurs, with only one known species, the type species ''Anchiornis huxleyi'', named for its similarity to modern birds. The Latin name ''Anchiornis'' derives from a Greek word meaning " ...
'' is currently the smallest non-avialan dinosaur described from an adult specimen, with an estimated weight of and a total skeletal length of . The smallest herbivorous non-avialan dinosaurs included '' Microceratus'' and '' Wannanosaurus'', at about long each.
Behavior
 Many modern birds are highly social, often found living in flocks. There is general agreement that some behaviors that are common in birds, as well as in crocodilians (closest living relatives of birds), were also common among extinct dinosaur groups. Interpretations of behavior in fossil species are generally based on the pose of skeletons and their Habitat (ecology), habitat, computer simulations of their biomechanics, and comparisons with modern animals in similar ecological niches.
The first potential evidence for herding or Flocking (behavior), flocking as a widespread behavior common to many dinosaur groups in addition to birds was the 1878 discovery of 31 ''Iguanodon'', ornithischians that were then thought to have perished together in Bernissart, Belgium, after they fell into a deep, flooded sinkhole and drowned. Other mass-death sites have been discovered subsequently. Those, along with multiple trackways, suggest that gregarious behavior was common in many early dinosaur species. Trackways of hundreds or even thousands of herbivores indicate that duck-billed (hadrosaurids) may have moved in great herds, like the American bison or the African springbok. Sauropod tracks document that these animals traveled in groups composed of several different species, at least in Oxfordshire, England, although there is no evidence for specific herd structures. Congregating into herds may have evolved for defense, for Bird migration, migratory purposes, or to provide protection for young. There is evidence that many types of slow-growing dinosaurs, including various theropods, sauropods, ankylosaurians, ornithopods, and ceratopsians, formed aggregations of immature individuals. One example is a site in Inner Mongolia that has yielded remains of over 20 ''Sinornithomimus'', from one to seven years old. This assemblage is interpreted as a social group that was trapped in mud. The interpretation of dinosaurs as gregarious has also extended to depicting carnivorous theropods as pack hunters working together to bring down large prey. However, this lifestyle is uncommon among modern birds, crocodiles, and other reptiles, and the taphonomy, taphonomic evidence suggesting mammal-like pack hunting in such theropods as ''Deinonychus'' and ''
Many modern birds are highly social, often found living in flocks. There is general agreement that some behaviors that are common in birds, as well as in crocodilians (closest living relatives of birds), were also common among extinct dinosaur groups. Interpretations of behavior in fossil species are generally based on the pose of skeletons and their Habitat (ecology), habitat, computer simulations of their biomechanics, and comparisons with modern animals in similar ecological niches.
The first potential evidence for herding or Flocking (behavior), flocking as a widespread behavior common to many dinosaur groups in addition to birds was the 1878 discovery of 31 ''Iguanodon'', ornithischians that were then thought to have perished together in Bernissart, Belgium, after they fell into a deep, flooded sinkhole and drowned. Other mass-death sites have been discovered subsequently. Those, along with multiple trackways, suggest that gregarious behavior was common in many early dinosaur species. Trackways of hundreds or even thousands of herbivores indicate that duck-billed (hadrosaurids) may have moved in great herds, like the American bison or the African springbok. Sauropod tracks document that these animals traveled in groups composed of several different species, at least in Oxfordshire, England, although there is no evidence for specific herd structures. Congregating into herds may have evolved for defense, for Bird migration, migratory purposes, or to provide protection for young. There is evidence that many types of slow-growing dinosaurs, including various theropods, sauropods, ankylosaurians, ornithopods, and ceratopsians, formed aggregations of immature individuals. One example is a site in Inner Mongolia that has yielded remains of over 20 ''Sinornithomimus'', from one to seven years old. This assemblage is interpreted as a social group that was trapped in mud. The interpretation of dinosaurs as gregarious has also extended to depicting carnivorous theropods as pack hunters working together to bring down large prey. However, this lifestyle is uncommon among modern birds, crocodiles, and other reptiles, and the taphonomy, taphonomic evidence suggesting mammal-like pack hunting in such theropods as ''Deinonychus'' and ''Allosaurus
''Allosaurus'' ( ) is an extinct genus of theropod dinosaur that lived 155 to 145 million years ago during the Late Jurassic period ( Kimmeridgian to late Tithonian ages). The first fossil remains that could definitively be ascribed to th ...
'' can also be interpreted as the results of fatal disputes between feeding animals, as is seen in many modern diapsid predators.
 The crests and frills of some dinosaurs, like the marginocephalians, theropods and Lambeosaurinae, lambeosaurines, may have been too fragile to be used for active defense, and so they were likely used for sexual or aggressive displays, though little is known about dinosaur mating and territory (animal), territorialism. Head wounds from bites suggest that theropods, at least, engaged in active aggressive confrontations.
From a behavioral standpoint, one of the most valuable dinosaur fossils was discovered in the Gobi Desert in 1971. It included a ''Velociraptor'' attacking a ''Protoceratops'', providing evidence that dinosaurs did indeed attack each other. Additional evidence for attacking live prey is the partially healed tail of an ''Edmontosaurus'', a hadrosaurid dinosaur; the tail is damaged in such a way that shows the animal was bitten by a tyrannosaur but survived. Cannibalism (zoology), Cannibalism amongst some species of dinosaurs was confirmed by tooth marks found in Madagascar in 2003, involving the theropod ''Majungasaurus''.
Comparisons between the sclerotic ring, scleral rings of dinosaurs and modern birds and reptiles have been used to infer daily activity patterns of dinosaurs. Although it has been suggested that most dinosaurs were active during the day, these comparisons have shown that small predatory dinosaurs such as dromaeosaurids, ''Juravenator'', and ''Megapnosaurus'' were likely nocturnal. Large and medium-sized herbivorous and omnivorous dinosaurs such as ceratopsians, sauropodomorphs, hadrosaurids, ornithomimosaurs may have been cathemeral, active during short intervals throughout the day, although the small ornithischian ''Agilisaurus'' was inferred to be Diurnality, diurnal.
Based on fossil evidence from dinosaurs such as ''Oryctodromeus'', some ornithischian species seem to have led a partially fossorial (burrowing) lifestyle. Many modern birds are arboreal (tree climbing), and this was also true of many Mesozoic birds, especially the enantiornithines. While some early bird-like species may have already been arboreal as well (including dromaeosaurids) such as ''Microraptor'') most non-avialan dinosaurs seem to have relied on land-based locomotion. A good understanding of how dinosaurs moved on the ground is key to models of dinosaur behavior; the science of biomechanics, pioneered by Robert McNeill Alexander, has provided significant insight in this area. For example, studies of the forces exerted by muscles and gravity on dinosaurs' skeletal structure have investigated how fast dinosaurs could run, whether diplodocids could create sonic booms via whip-like tail snapping, and whether sauropods could float.
The crests and frills of some dinosaurs, like the marginocephalians, theropods and Lambeosaurinae, lambeosaurines, may have been too fragile to be used for active defense, and so they were likely used for sexual or aggressive displays, though little is known about dinosaur mating and territory (animal), territorialism. Head wounds from bites suggest that theropods, at least, engaged in active aggressive confrontations.
From a behavioral standpoint, one of the most valuable dinosaur fossils was discovered in the Gobi Desert in 1971. It included a ''Velociraptor'' attacking a ''Protoceratops'', providing evidence that dinosaurs did indeed attack each other. Additional evidence for attacking live prey is the partially healed tail of an ''Edmontosaurus'', a hadrosaurid dinosaur; the tail is damaged in such a way that shows the animal was bitten by a tyrannosaur but survived. Cannibalism (zoology), Cannibalism amongst some species of dinosaurs was confirmed by tooth marks found in Madagascar in 2003, involving the theropod ''Majungasaurus''.
Comparisons between the sclerotic ring, scleral rings of dinosaurs and modern birds and reptiles have been used to infer daily activity patterns of dinosaurs. Although it has been suggested that most dinosaurs were active during the day, these comparisons have shown that small predatory dinosaurs such as dromaeosaurids, ''Juravenator'', and ''Megapnosaurus'' were likely nocturnal. Large and medium-sized herbivorous and omnivorous dinosaurs such as ceratopsians, sauropodomorphs, hadrosaurids, ornithomimosaurs may have been cathemeral, active during short intervals throughout the day, although the small ornithischian ''Agilisaurus'' was inferred to be Diurnality, diurnal.
Based on fossil evidence from dinosaurs such as ''Oryctodromeus'', some ornithischian species seem to have led a partially fossorial (burrowing) lifestyle. Many modern birds are arboreal (tree climbing), and this was also true of many Mesozoic birds, especially the enantiornithines. While some early bird-like species may have already been arboreal as well (including dromaeosaurids) such as ''Microraptor'') most non-avialan dinosaurs seem to have relied on land-based locomotion. A good understanding of how dinosaurs moved on the ground is key to models of dinosaur behavior; the science of biomechanics, pioneered by Robert McNeill Alexander, has provided significant insight in this area. For example, studies of the forces exerted by muscles and gravity on dinosaurs' skeletal structure have investigated how fast dinosaurs could run, whether diplodocids could create sonic booms via whip-like tail snapping, and whether sauropods could float.
Communication
Modern birds Animal communication, communicate by visual and auditory signals, and the wide diversity of visual display structures among fossil dinosaur groups, such as horns, frills, crests, sails, and feathers, suggests that visual communication has always been important in dinosaur biology. Reconstruction of the plumage color of ''Anchiornis'' suggest the importance of color in visual communication in non-avian dinosaurs. Vocalization in non-avian dinosaurs is less certain. In birds, the larynx plays no role in sound production. Instead, birds vocalize with a novel organ, the Syrinx (bird anatomy), syrinx, farther down the trachea. The earliest remains of a syrinx were found in a specimen of the duck-like ''Vegavis, Vegavis iaai'' dated 69 –66 million years ago, and this organ is unlikely to have existed in non-avian dinosaurs. A 2009 review indicated that non-avians used visual displays and possibly non-vocal sounds, such as hissing, jaw-grinding or -clapping, splashing, and wing-beating (possible in winged maniraptoran dinosaurs). Other researchers have countered that vocalizations also exist in turtles, the closest relatives of archosaurs, suggesting that the trait is ancestral to their lineage. In addition, vocal communication in dinosaurs is indicated by the development of advanced hearing in nearly all major groups. Hence the syrinx may have supplemented and then replaced the larynx as a vocal organ, without a "silent period" in bird evolution.
In 2023, a fossilized larynx was described, from a specimen of the ankylosaurid ''Pinacosaurus''. The structure was composed of cricoid cartilage, cricoid and arytenoid cartilages, similar to those of non-avian reptiles; but the mobile cricoid–arytenoid joint and long arytenoid cartilages would have allowed air-flow control similar to that of birds, and thus could have made bird-like vocalizations. In addition, the cartilages were ossification, ossified, implying that laryngeal ossification is a feature of some non-avian dinosaurs. A 2016 study concludes that some dinosaurs may have produced closed-mouth vocalizations, such as cooing, hooting, and booming. These occur in both reptiles and birds and involve inflating the esophagus or tracheal pouches. Such vocalizations evolved independently in extant archosaurs numerous times, following increases in body size. The crests of some hadrosaurids and the nasal chambers of ankylosaurids may have been acoustic resonance, resonators.
A 2009 review indicated that non-avians used visual displays and possibly non-vocal sounds, such as hissing, jaw-grinding or -clapping, splashing, and wing-beating (possible in winged maniraptoran dinosaurs). Other researchers have countered that vocalizations also exist in turtles, the closest relatives of archosaurs, suggesting that the trait is ancestral to their lineage. In addition, vocal communication in dinosaurs is indicated by the development of advanced hearing in nearly all major groups. Hence the syrinx may have supplemented and then replaced the larynx as a vocal organ, without a "silent period" in bird evolution.
In 2023, a fossilized larynx was described, from a specimen of the ankylosaurid ''Pinacosaurus''. The structure was composed of cricoid cartilage, cricoid and arytenoid cartilages, similar to those of non-avian reptiles; but the mobile cricoid–arytenoid joint and long arytenoid cartilages would have allowed air-flow control similar to that of birds, and thus could have made bird-like vocalizations. In addition, the cartilages were ossification, ossified, implying that laryngeal ossification is a feature of some non-avian dinosaurs. A 2016 study concludes that some dinosaurs may have produced closed-mouth vocalizations, such as cooing, hooting, and booming. These occur in both reptiles and birds and involve inflating the esophagus or tracheal pouches. Such vocalizations evolved independently in extant archosaurs numerous times, following increases in body size. The crests of some hadrosaurids and the nasal chambers of ankylosaurids may have been acoustic resonance, resonators.
Reproductive biology
 Another widespread trait among modern birds (but see below in regards to fossil groups and extant megapodes) is parental care for young after hatching. Jack Horner (paleontologist), Jack Horner's 1978 discovery of a ''Maiasaura'' ("good mother lizard") nesting ground in Montana demonstrated that parental care continued long after birth among ornithopods. A specimen of the oviraptoridae, oviraptorid ''Citipati, Citipati osmolskae'' was discovered in a Chicken#Broodiness, chicken-like brooding position in 1993, which may indicate that they had begun using an insulating layer of feathers to keep the eggs warm. An embryo of the basal sauropodomorph ''Massospondylus'' was found without teeth, indicating that some parental care was required to feed the young dinosaurs. Trackways have also confirmed parental behavior among ornithopods from the Isle of Skye in northwestern Scotland.
However, there is ample evidence of precociality or Precociality#Superprecociality, superprecociality among many dinosaur species, particularly theropods. For instance, non-Euornithes, ornithuromorph birds have been abundantly demonstrated to have had slow growth rates, megapode-like egg burying behavior and the ability to fly soon after birth. Both ''Tyrannosaurus'' and ''Troodon'' had juveniles with clear superprecociality and likely occupying different ecological niches than the adults. Superprecociality has been inferred for sauropods.
Genital structures are unlikely to fossilize as they lack scales that may allow preservation via pigmentation or residual calcium phosphate salts. In 2021, the best preserved specimen of a dinosaur's cloacal vent exterior was described for ''Psittacosaurus'', demonstrating lateral swellings similar to crocodylian musk glands used in social displays by both sexes and pigmented regions which could also reflect a signalling function. However, this specimen on its own does not offer enough information to determine whether this dinosaur had sexual signalling functions; it only supports the possibility. Cloacal visual signalling can occur in either males or females in living birds, making it unlikely to be useful to determine sex for extinct dinosaurs.
Another widespread trait among modern birds (but see below in regards to fossil groups and extant megapodes) is parental care for young after hatching. Jack Horner (paleontologist), Jack Horner's 1978 discovery of a ''Maiasaura'' ("good mother lizard") nesting ground in Montana demonstrated that parental care continued long after birth among ornithopods. A specimen of the oviraptoridae, oviraptorid ''Citipati, Citipati osmolskae'' was discovered in a Chicken#Broodiness, chicken-like brooding position in 1993, which may indicate that they had begun using an insulating layer of feathers to keep the eggs warm. An embryo of the basal sauropodomorph ''Massospondylus'' was found without teeth, indicating that some parental care was required to feed the young dinosaurs. Trackways have also confirmed parental behavior among ornithopods from the Isle of Skye in northwestern Scotland.
However, there is ample evidence of precociality or Precociality#Superprecociality, superprecociality among many dinosaur species, particularly theropods. For instance, non-Euornithes, ornithuromorph birds have been abundantly demonstrated to have had slow growth rates, megapode-like egg burying behavior and the ability to fly soon after birth. Both ''Tyrannosaurus'' and ''Troodon'' had juveniles with clear superprecociality and likely occupying different ecological niches than the adults. Superprecociality has been inferred for sauropods.
Genital structures are unlikely to fossilize as they lack scales that may allow preservation via pigmentation or residual calcium phosphate salts. In 2021, the best preserved specimen of a dinosaur's cloacal vent exterior was described for ''Psittacosaurus'', demonstrating lateral swellings similar to crocodylian musk glands used in social displays by both sexes and pigmented regions which could also reflect a signalling function. However, this specimen on its own does not offer enough information to determine whether this dinosaur had sexual signalling functions; it only supports the possibility. Cloacal visual signalling can occur in either males or females in living birds, making it unlikely to be useful to determine sex for extinct dinosaurs.
Physiology
Because both modern crocodilians and birds have four-chambered hearts (albeit modified in crocodilians), it is likely that this is a trait shared by all archosaurs, including all dinosaurs. While all modern birds have high metabolisms and are endothermic ("warm-blooded"), a vigorous debate has been ongoing since the 1960s regarding how far back in the dinosaur lineage this trait extended. Various researchers have supported dinosaurs as being endothermic, ectothermic ("cold-blooded"), or somewhere in between. An emerging consensus among researchers is that, while different lineages of dinosaurs would have had different metabolisms, most of them had higher metabolic rates than other reptiles but lower than living birds and mammals, which is termed mesothermy by some. Evidence from crocodiles and their extinct relatives suggests that such elevated metabolisms could have developed in the earliest archosaurs, which were the common ancestors of dinosaurs and crocodiles. After non-avian dinosaurs were discovered, paleontologists first posited that they were ectothermic. This was used to imply that the ancient dinosaurs were relatively slow, sluggish organisms, even though many modern reptiles are fast and light-footed despite relying on external sources of heat to regulate their body temperature. The idea of dinosaurs as ectothermic remained a prevalent view until
After non-avian dinosaurs were discovered, paleontologists first posited that they were ectothermic. This was used to imply that the ancient dinosaurs were relatively slow, sluggish organisms, even though many modern reptiles are fast and light-footed despite relying on external sources of heat to regulate their body temperature. The idea of dinosaurs as ectothermic remained a prevalent view until Robert T. Bakker
Robert Thomas Bakker (born March 24, 1945) is an American paleontologist who helped reshape modern theories about dinosaurs, particularly by adding support to the theory that some dinosaurs were endothermic (warm-blooded). Along with his mentor ...
, an early proponent of dinosaur endothermy, published an influential paper on the topic in 1968. Bakker specifically used anatomical and ecological evidence to argue that sauropods, which had hitherto been depicted as sprawling aquatic animals with their tails dragging on the ground, were endotherms that lived vigorous, terrestrial lives. In 1972, Bakker expanded on his arguments based on energy requirements and predator-prey ratios. This was one of the seminal results that led to the dinosaur renaissance.
One of the greatest contributions to the modern understanding of dinosaur physiology has been histology, paleohistology, the study of microscopic tissue structure in dinosaurs. From the 1960s forward, Armand de Ricqlès suggested that the presence of fibrolamellar bone—bony tissue with an irregular, fibrous texture and filled with blood vessels—was indicative of consistently fast growth and therefore endothermy. Fibrolamellar bone was common in both dinosaurs and pterosaurs, though not universally present. This has led to a significant body of work in reconstructing growth curve (biology), growth curves and modeling the evolution of growth rates across various dinosaur lineages,For examples of this work conducted on different dinosaur lineages, see
*
*
*
*
*
* which has suggested overall that dinosaurs grew faster than living reptiles. Other lines of evidence suggesting endothermy include the presence of feathers and other types of body coverings in many lineages (see ); more consistent ratios of the isotope oxygen-18 in bony tissue compared to ectotherms, particularly as latitude and thus air temperature varied, which suggests stable internal temperatures (although these ratios can be altered during fossilization); and the discovery of South Polar region of the Cretaceous#Dinosaurs, polar dinosaurs, which lived in Australia, Antarctica, and Alaska when these places would have had cool, temperate climates.
 In saurischian dinosaurs, higher metabolisms were supported by the evolution of the avian respiratory system, characterized by an extensive system of air sacs that extended the lungs and invaded many of the bones in the skeleton, making them hollow. Such respiratory systems, which may have appeared in the earliest saurischians, would have provided them with more oxygen compared to a mammal of similar size, while also having a larger resting tidal volume and requiring a lower breathing frequency, which would have allowed them to sustain higher activity levels. The rapid airflow would also have been an effective cooling mechanism, which in conjunction with a lower metabolic rate would have prevented large sauropods from overheating. These traits may have enabled sauropods to grow quickly to gigantic sizes. Sauropods may also have benefitted from their size—their small surface area to volume ratio meant that they would have been able to thermoregulate more easily, a phenomenon termed gigantothermy.
Like other reptiles, dinosaurs are primarily uricotelic, that is, their kidneys extract nitrogenous wastes from their bloodstream and excrete it as uric acid instead of urea or ammonia via the ureters into the intestine. This would have helped them to conserve water. In most living species, uric acid is excreted along with feces as a semisolid waste. However, at least some modern birds (such as hummingbirds) can be facultatively ammonotelic, excreting most of the nitrogenous wastes as ammonia. This material, as well as the output of the intestines, emerges from the cloaca. In addition, many species regurgitate Pellet (ornithology), pellets, and fossil pellets are known as early as the Jurassic from ''Anchiornis''.
The size and shape of the brain can be partly reconstructed based on the surrounding bones. In 1896, Marsh calculated ratios between brain weight and body weight of seven species of dinosaurs, showing that the brain of dinosaurs was proportionally smaller than in today's crocodiles, and that the brain of ''Stegosaurus'' was smaller than in any living land vertebrate. This contributed to the widespread public notion of dinosaurs as being sluggish and extraordinarily stupid. Harry Jerison, in 1973, showed that proportionally smaller brains are expected at larger body sizes, and that brain size in dinosaurs was not smaller than expected when compared to living reptiles. Later research showed that relative brain size progressively increased during the evolution of theropods, with the highest intelligence – comparable to that of modern birds – calculated for the troodontid ''Troodon''.
In saurischian dinosaurs, higher metabolisms were supported by the evolution of the avian respiratory system, characterized by an extensive system of air sacs that extended the lungs and invaded many of the bones in the skeleton, making them hollow. Such respiratory systems, which may have appeared in the earliest saurischians, would have provided them with more oxygen compared to a mammal of similar size, while also having a larger resting tidal volume and requiring a lower breathing frequency, which would have allowed them to sustain higher activity levels. The rapid airflow would also have been an effective cooling mechanism, which in conjunction with a lower metabolic rate would have prevented large sauropods from overheating. These traits may have enabled sauropods to grow quickly to gigantic sizes. Sauropods may also have benefitted from their size—their small surface area to volume ratio meant that they would have been able to thermoregulate more easily, a phenomenon termed gigantothermy.
Like other reptiles, dinosaurs are primarily uricotelic, that is, their kidneys extract nitrogenous wastes from their bloodstream and excrete it as uric acid instead of urea or ammonia via the ureters into the intestine. This would have helped them to conserve water. In most living species, uric acid is excreted along with feces as a semisolid waste. However, at least some modern birds (such as hummingbirds) can be facultatively ammonotelic, excreting most of the nitrogenous wastes as ammonia. This material, as well as the output of the intestines, emerges from the cloaca. In addition, many species regurgitate Pellet (ornithology), pellets, and fossil pellets are known as early as the Jurassic from ''Anchiornis''.
The size and shape of the brain can be partly reconstructed based on the surrounding bones. In 1896, Marsh calculated ratios between brain weight and body weight of seven species of dinosaurs, showing that the brain of dinosaurs was proportionally smaller than in today's crocodiles, and that the brain of ''Stegosaurus'' was smaller than in any living land vertebrate. This contributed to the widespread public notion of dinosaurs as being sluggish and extraordinarily stupid. Harry Jerison, in 1973, showed that proportionally smaller brains are expected at larger body sizes, and that brain size in dinosaurs was not smaller than expected when compared to living reptiles. Later research showed that relative brain size progressively increased during the evolution of theropods, with the highest intelligence – comparable to that of modern birds – calculated for the troodontid ''Troodon''.
Origin of birds
The possibility that dinosaurs were the ancestors of birds was first suggested in 1868 by Thomas Henry Huxley. After the work of Gerhard Heilmann in the early 20th century, the Scientific theory, theory of birds as dinosaur descendants was abandoned in favor of the idea of them being descendants of generalized Thecodontia, thecodonts, with the key piece of evidence being the supposed lack of clavicles in dinosaurs. However, as later discoveries showed, clavicles (or a single fused furcula, wishbone, which derived from separate clavicles) were not actually absent; they had been found as early as 1924 in ''Oviraptor'', but misidentified as an interclavicle. In the 1970s, John Ostrom revived the dinosaur–bird theory, which gained momentum in the coming decades with the advent of cladistic analysis, and a great increase in the discovery of small theropods and early birds. Of particular note have been the fossils of the Jehol Biota, where a variety of theropods and early birds have been found, often with feathers of some type. Birds share over a hundred distinct anatomical features with theropod dinosaurs, which are now generally accepted to have been their closest ancient relatives. They are most closely allied with maniraptoran coelurosaurs. A minority of scientists, most notably Alan Feduccia and Larry Martin, have proposed other evolutionary paths, including revised versions of Heilmann's basal archosaur proposal, or that maniraptoran theropods are the ancestors of birds but themselves are not dinosaurs, only convergent evolution, convergent with dinosaurs.Feathers
 Feathers are one of the most recognizable characteristics of modern birds, and a trait that was also shared by several non-avian dinosaurs. Based on the current distribution of fossil evidence, it appears that feathers were an ancestral dinosaurian trait, though one that may have been selectively lost in some species. Direct fossil evidence of feathers or feather-like structures has been discovered in a diverse array of species in many non-avian dinosaur groups, both among saurischians and ornithischians. Simple, branched, feather-like structures are known from Heterodontosauridae, heterodontosaurids, primitive neornithischians, and theropods, and primitive ceratopsians. Evidence for true, vaned feathers similar to the flight feathers of modern birds has been found only in the theropod subgroup Maniraptora, which includes oviraptorosaurs, troodontids, dromaeosaurids, and birds. Feather-like structures known as Pterosaur#Pycnofibers, pycnofibres have also been found in pterosaurs.
However, researchers do not agree regarding whether these structures share a common origin between lineages (i.e., they are homology (biology), homologous), or if they were the result of widespread experimentation with skin coverings among ornithodirans. If the former is the case, filaments may have been common in the ornithodiran lineage and evolved before the appearance of dinosaurs themselves. Research into the genetics of American alligators has revealed that crocodylian
Feathers are one of the most recognizable characteristics of modern birds, and a trait that was also shared by several non-avian dinosaurs. Based on the current distribution of fossil evidence, it appears that feathers were an ancestral dinosaurian trait, though one that may have been selectively lost in some species. Direct fossil evidence of feathers or feather-like structures has been discovered in a diverse array of species in many non-avian dinosaur groups, both among saurischians and ornithischians. Simple, branched, feather-like structures are known from Heterodontosauridae, heterodontosaurids, primitive neornithischians, and theropods, and primitive ceratopsians. Evidence for true, vaned feathers similar to the flight feathers of modern birds has been found only in the theropod subgroup Maniraptora, which includes oviraptorosaurs, troodontids, dromaeosaurids, and birds. Feather-like structures known as Pterosaur#Pycnofibers, pycnofibres have also been found in pterosaurs.
However, researchers do not agree regarding whether these structures share a common origin between lineages (i.e., they are homology (biology), homologous), or if they were the result of widespread experimentation with skin coverings among ornithodirans. If the former is the case, filaments may have been common in the ornithodiran lineage and evolved before the appearance of dinosaurs themselves. Research into the genetics of American alligators has revealed that crocodylian scute
A scute () or scutum (Latin: ''scutum''; plural: ''scuta'' "Scutum (shield), shield") is a bony external plate or scale overlaid with horn, as on the shell of a turtle, the skin of crocodilians, and the feet of Bird anatomy#Scales, birds. The ter ...
s do possess feather-keratins during embryonic development, but these keratins are not expressed by the animals before hatching. The description of feathered dinosaurs has not been without controversy in general; perhaps the most vocal critics have been Alan Feduccia and Theagarten Lingham-Soliar, who have proposed that some purported feather-like fossils are the result of the decomposition of collagenous fiber that underlaid the dinosaurs' skin, and that maniraptoran dinosaurs with vaned feathers were not actually dinosaurs, but convergent with dinosaurs. However, their views have for the most part not been accepted by other researchers, to the point that the scientific nature of Feduccia's proposals has been questioned.
''Archaeopteryx'' was the first fossil found that revealed a potential connection between dinosaurs and birds. It is considered a transitional fossil, in that it displays features of both groups. Brought to light just two years after Charles Darwin's seminal ''On the Origin of Species'' (1859), its discovery spurred the nascent debate between proponents of evolutionary biology and creationism. This early bird is so dinosaur-like that, without a clear impression of feathers in the surrounding rock, at least one specimen was mistaken for the small theropod ''Compsognathus''. Since the 1990s, a number of additional feathered dinosaurs have been found, providing even stronger evidence of the close relationship between dinosaurs and modern birds. Many of these specimens were unearthed in the lagerstätten of the Jehol Biota. If feather-like structures were indeed widely present among non-avian dinosaurs, the lack of abundant fossil evidence for them may be due to the fact that delicate features like skin and feathers are seldom preserved by fossilization and thus often absent from the fossil record.
Skeleton
Because feathers are often associated with birds, feathered dinosaurs are often touted as the missing link between birds and dinosaurs. However, the multiple skeletal features also shared by the two groups represent another important line of evidence for paleontologists. Areas of the skeleton with important similarities include the neck, pubis, wrist (semi-lunate carpal), arm and Shoulder girdle, pectoral girdle, furcula (wishbone), and Keel (bird anatomy), breast bone. Comparison of bird and dinosaur skeletons through cladistic analysis strengthens the case for the link.Soft anatomy
 Large meat-eating dinosaurs had a complex system of air sacs similar to those found in modern birds, according to a 2005 investigation led by Patrick M. O'Connor. The lungs of theropod dinosaurs (carnivores that walked on two legs and had bird-like feet) likely pumped air into hollow sacs in their skeletons, as is the case in birds. "What was once formally considered unique to birds was present in some form in the ancestors of birds", O'Connor said. In 2008, scientists described ''Aerosteon, Aerosteon riocoloradensis'', the skeleton of which supplies the strongest evidence to date of a dinosaur with a bird-like breathing system. CT scanning of ''Aerosteons fossil bones revealed evidence for the existence of air sacs within the animal's body cavity.
Large meat-eating dinosaurs had a complex system of air sacs similar to those found in modern birds, according to a 2005 investigation led by Patrick M. O'Connor. The lungs of theropod dinosaurs (carnivores that walked on two legs and had bird-like feet) likely pumped air into hollow sacs in their skeletons, as is the case in birds. "What was once formally considered unique to birds was present in some form in the ancestors of birds", O'Connor said. In 2008, scientists described ''Aerosteon, Aerosteon riocoloradensis'', the skeleton of which supplies the strongest evidence to date of a dinosaur with a bird-like breathing system. CT scanning of ''Aerosteons fossil bones revealed evidence for the existence of air sacs within the animal's body cavity.
Behavioral evidence
Fossils of the troodonts ''Mei long, Mei'' and ''Sinornithoides'' demonstrate that some dinosaurs slept with their heads tucked under their arms. This behavior, which may have helped to keep the head warm, is also characteristic of modern birds. Several Deinonychosauria, deinonychosaur and oviraptorosaur specimens have also been found preserved on top of their nests, likely brooding in a bird-like manner. The ratio between egg volume and body mass of adults among these dinosaurs suggest that the eggs were primarily brooded by the male and that the young were highly precocial, similar to many modern ground-dwelling birds. Some dinosaurs are known to have used gizzard stones like modern birds. These stones are swallowed by animals to aid digestion and break down food and hard fibers once they enter the stomach. When found in association with fossils, gizzard stones are called gastroliths.Extinction of major groups
All non-avian dinosaurs and most lineages of birds became extinct in a extinction event, mass extinction event, called the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, Cretaceous–Paleogene (K-Pg) extinction event, at the end of the Cretaceous period. Above the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary, which has been dated to 66.038 ± 0.025 million years ago, fossils of non-avian dinosaurs disappear abruptly; the absence of dinosaur fossils was historically used to assign rocks to the ensuing Cenozoic. The nature of the event that caused this mass extinction has been extensively studied since the 1970s, leading to the development of two mechanisms that are thought to have played major roles: an extraterrestrial impact event in the Yucatán Peninsula, along with flood basalt volcanism in India. However, the specific mechanisms of the extinction event and the extent of its effects on dinosaurs are still areas of ongoing research. Alongside dinosaurs, many other groups of animals became extinct: pterosaurs, marine reptiles such as mosasaurs and plesiosaurs, several groups of mammals, ammonoidea, ammonites (nautilus-like Mollusca, mollusks), rudists (reef-building bivalvia, bivalves), and various groups of marine plankton. In all, approximately 47% of genera and 76% of species on Earth became extinct during the K-Pg extinction event. The relatively large size of most dinosaurs and the low diversity of small-bodied dinosaur species at the end of the Cretaceous may have contributed to their extinction; the extinction of the bird lineages that did not survive may also have been caused by a dependence on forest habitats or a lack of adaptations to seed predation, eating seeds for survival.Pre-extinction diversity
Just before the K-Pg extinction event, the number of non-avian dinosaur species that existed globally has been estimated at between 628 and 1078. It remains uncertain whether the diversity of dinosaurs was in gradual decline before the K-Pg extinction event, or whether dinosaurs were actually thriving prior to the extinction. Rock formations from the Maastrichtian epoch, which directly preceded the extinction, have been found to have lower diversity than the preceding Campanian epoch, which led to the prevailing view of a long-term decline in diversity. However, these comparisons did not account either for varying preservation potential between rock units or for different extents of exploration and excavation. In 1984, Dale Russell carried out an analysis to account for these biases, and found no evidence of a decline; another analysis by David Fastovsky and colleagues in 2004 even showed that dinosaur diversity continually increased until the extinction, but this analysis has been rebutted. Since then, different approaches based on statistics and mathematical models have variously supported either a sudden extinction or a gradual decline. End-Cretaceous trends in diversity may have varied between dinosaur lineages: it has been suggested that sauropods were not in decline, while ornithischians and theropods were in decline.Impact event
 The Alvarez hypothesis, bolide impact hypothesis, first brought to wide attention in 1980 by Walter Alvarez, Luis Walter Alvarez, Luis Alvarez, and colleagues, attributes the K-Pg extinction event to a bolide (extraterrestrial projectile) impact. Alvarez and colleagues proposed that a sudden increase in iridium levels, recorded around the world in rock deposits at the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary, was direct evidence of the impact. Shocked quartz, indicative of a strong shockwave emanating from an impact, was also found worldwide. The actual impact site remained elusive until a Chicxulub crater, crater measuring wide was discovered in the Yucatán Peninsula of southeastern Mexico, and was publicized in a 1991 paper by Alan R. Hildebrand, Alan Hildebrand and colleagues. Now, the bulk of the evidence suggests that a bolide wide impacted the Yucatán Peninsula 66 million years ago, forming this crater and creating a "kill mechanism" that triggered the extinction event.
Within hours, the Chicxulub impact would have created immediate effects such as earthquakes, tsunamis, and a global firestorm that likely killed unsheltered animals and started wildfires. However, it would also have had longer-term consequences for the environment. Within days, sulfate aerosols released from rocks at the impact site would have contributed to acid rain and ocean acidification. Soot aerosols are thought to have spread around the world over the ensuing months and years; they would have cooled the surface of the Earth by reflecting thermal radiation, and greatly slowed photosynthesis by blocking out sunlight, thus creating an impact winter. (This role was ascribed to sulfate aerosols until experiments demonstrated otherwise.) The cessation of photosynthesis would have led to the collapse of food webs depending on leafy plants, which included all dinosaurs save for grain-eating birds.
The Alvarez hypothesis, bolide impact hypothesis, first brought to wide attention in 1980 by Walter Alvarez, Luis Walter Alvarez, Luis Alvarez, and colleagues, attributes the K-Pg extinction event to a bolide (extraterrestrial projectile) impact. Alvarez and colleagues proposed that a sudden increase in iridium levels, recorded around the world in rock deposits at the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary, was direct evidence of the impact. Shocked quartz, indicative of a strong shockwave emanating from an impact, was also found worldwide. The actual impact site remained elusive until a Chicxulub crater, crater measuring wide was discovered in the Yucatán Peninsula of southeastern Mexico, and was publicized in a 1991 paper by Alan R. Hildebrand, Alan Hildebrand and colleagues. Now, the bulk of the evidence suggests that a bolide wide impacted the Yucatán Peninsula 66 million years ago, forming this crater and creating a "kill mechanism" that triggered the extinction event.
Within hours, the Chicxulub impact would have created immediate effects such as earthquakes, tsunamis, and a global firestorm that likely killed unsheltered animals and started wildfires. However, it would also have had longer-term consequences for the environment. Within days, sulfate aerosols released from rocks at the impact site would have contributed to acid rain and ocean acidification. Soot aerosols are thought to have spread around the world over the ensuing months and years; they would have cooled the surface of the Earth by reflecting thermal radiation, and greatly slowed photosynthesis by blocking out sunlight, thus creating an impact winter. (This role was ascribed to sulfate aerosols until experiments demonstrated otherwise.) The cessation of photosynthesis would have led to the collapse of food webs depending on leafy plants, which included all dinosaurs save for grain-eating birds.
Deccan Traps
At the time of the K-Pg extinction, the Deccan Traps flood basalts of India were actively erupting. The eruptions can be separated into three phases around the K-Pg boundary, two prior to the boundary and one after. The second phase, which occurred very close to the boundary, would have extruded 70 to 80% of the volume of these eruptions in intermittent pulses that occurred around 100,000 years apart. Greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide would have been released by this volcanic activity, resulting in climate change through temperature perturbations of roughly but possibly as high as . Like the Chicxulub impact, the eruptions may also have released sulfate aerosols, which would have caused acid rain and global cooling. However, due to large error margins in the dating of the eruptions, the role of the Deccan Traps in the K-Pg extinction remains unclear. Before 2000, arguments that the Deccan Traps eruptions—as opposed to the Chicxulub impact—caused the extinction were usually linked to the view that the extinction was gradual. Prior to the discovery of the Chicxulub crater, the Deccan Traps were used to explain the global iridium layer; even after the crater's discovery, the impact was still thought to only have had a regional, not global, effect on the extinction event. In response, Luis Alvarez rejected volcanic activity as an explanation for the iridium layer and the extinction as a whole. Since then, however, most researchers have adopted a more moderate position, which identifies the Chicxulub impact as the primary progenitor of the extinction while also recognizing that the Deccan Traps may also have played a role. Walter Alvarez himself has acknowledged that the Deccan Traps and other ecological factors may have contributed to the extinctions in addition to the Chicxulub impact. Some estimates have placed the start of the second phase in the Deccan Traps eruptions within 50,000 years after the Chicxulub impact. Combined with mathematical modelling of the seismic waves that would have been generated by the impact, this has led to the suggestion that the Chicxulub impact may have triggered these eruptions by increasing the permeability of the mantle plume underlying the Deccan Traps. Whether the Deccan Traps were a major cause of the extinction, on par with the Chicxulub impact, remains uncertain. Proponents consider the climatic impact of the sulfur dioxide released to have been on par with the Chicxulub impact, and also note the role of flood basalt volcanism in other mass extinctions like the Permian-Triassic extinction event. They consider the Chicxulub impact to have worsened the ongoing climate change caused by the eruptions. Meanwhile, detractors point out the sudden nature of the extinction and that other pulses in Deccan Traps activity of comparable magnitude did not appear to have caused extinctions. They also contend that the causes of different mass extinctions should be assessed separately. In 2020, Alfio Chiarenza and colleagues suggested that the Deccan Traps may even have had the opposite effect: they suggested that the long-term warming caused by its carbon dioxide emissions may have dampened the impact winter from the Chicxulub impact.Possible Paleocene survivors
Non-avian dinosaur remains have occasionally been found above the K-Pg boundary. In 2000, Spencer G. Lucas, Spencer Lucas and colleagues reported the discovery of a single hadrosaur right femur in the San Juan Basin of New Mexico, and described it as evidence of Paleocene dinosaurs. The rock unit in which the bone was discovered has been dated to the early Paleocene epoch, approximately 64.8 million years ago. If the bone was not deposition (geology), re-deposited by weathering action, it would provide evidence that some dinosaur populations survived at least half a million years into the Cenozoic. Other evidence includes the presence of dinosaur remains in the Hell Creek Formation up to above the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary, representing 40,000 years of elapsed time. This has been used to support the view that the K-Pg extinction was gradual. However, these supposed Paleocene dinosaurs are considered by many other researchers to be reworked fossil, reworked, that is, washed out of their original locations and then reburied in younger sediments. The age estimates have also been considered unreliable.Cultural depictions
 By human standards, dinosaurs were creatures of fantastic appearance and often enormous size. As such, they have captured the popular imagination and become an enduring part of human culture. The entry of the word "dinosaur" into the common vernacular reflects the animals' cultural importance: in English, "dinosaur" is commonly used to describe anything that is impractically large, obsolete, or bound for extinction.
Public enthusiasm for dinosaurs first developed in Victorian era, Victorian England, where in 1854, three decades after the first scientific descriptions of dinosaur remains, a menagerie of lifelike Crystal Palace dinosaurs, dinosaur sculptures was unveiled in London's Crystal Palace Park. The Crystal Palace dinosaurs proved so popular that a strong market in smaller replicas soon developed. In subsequent decades, dinosaur exhibits opened at parks and Natural history museum, museums around the world, ensuring that successive generations would be introduced to the animals in an immersive and exciting way. The enduring popularity of dinosaurs, in its turn, has resulted in significant public funding for dinosaur science, and has frequently spurred new discoveries. In the United States, for example, the competition between museums for public attention led directly to the Bone Wars of the 1880s and 1890s, during which a pair of feuding paleontologists made enormous scientific contributions.
The popular preoccupation with dinosaurs has ensured their appearance in literature, film, and other Media (communication), media. Beginning in 1852 with a passing mention in Charles Dickens ''Bleak House'', dinosaurs have been featured in large numbers of fictional works. Jules Verne's 1864 novel ''Journey to the Center of the Earth'', Arthur Conan Doyle, Sir Arthur Conan Doyle's 1912 book ''The Lost World (Doyle novel), The Lost World'', the 1914 animated film ''Gertie the Dinosaur'' (featuring the first animated dinosaur), the iconic 1933 motion picture, film ''King Kong (1933 film), King Kong'', the 1954 ''Godzilla (1954 film), Godzilla'' and its many sequels, the best-selling 1990 novel ''Jurassic Park (novel), Jurassic Park'' by Michael Crichton and its 1993 Jurassic Park (film), film adaptation are just a few notable examples of dinosaur appearances in fiction. Authors of general-interest non-fiction works about dinosaurs, including some prominent paleontologists, have often sought to use the animals as a way to educate readers about science in general. Dinosaurs are ubiquitous in advertising; numerous Company (law), companies have referenced dinosaurs in printed or televised advertisements, either in order to sell their own products or in order to characterize their rivals as slow-moving, dim-witted, or obsolete.
By human standards, dinosaurs were creatures of fantastic appearance and often enormous size. As such, they have captured the popular imagination and become an enduring part of human culture. The entry of the word "dinosaur" into the common vernacular reflects the animals' cultural importance: in English, "dinosaur" is commonly used to describe anything that is impractically large, obsolete, or bound for extinction.
Public enthusiasm for dinosaurs first developed in Victorian era, Victorian England, where in 1854, three decades after the first scientific descriptions of dinosaur remains, a menagerie of lifelike Crystal Palace dinosaurs, dinosaur sculptures was unveiled in London's Crystal Palace Park. The Crystal Palace dinosaurs proved so popular that a strong market in smaller replicas soon developed. In subsequent decades, dinosaur exhibits opened at parks and Natural history museum, museums around the world, ensuring that successive generations would be introduced to the animals in an immersive and exciting way. The enduring popularity of dinosaurs, in its turn, has resulted in significant public funding for dinosaur science, and has frequently spurred new discoveries. In the United States, for example, the competition between museums for public attention led directly to the Bone Wars of the 1880s and 1890s, during which a pair of feuding paleontologists made enormous scientific contributions.
The popular preoccupation with dinosaurs has ensured their appearance in literature, film, and other Media (communication), media. Beginning in 1852 with a passing mention in Charles Dickens ''Bleak House'', dinosaurs have been featured in large numbers of fictional works. Jules Verne's 1864 novel ''Journey to the Center of the Earth'', Arthur Conan Doyle, Sir Arthur Conan Doyle's 1912 book ''The Lost World (Doyle novel), The Lost World'', the 1914 animated film ''Gertie the Dinosaur'' (featuring the first animated dinosaur), the iconic 1933 motion picture, film ''King Kong (1933 film), King Kong'', the 1954 ''Godzilla (1954 film), Godzilla'' and its many sequels, the best-selling 1990 novel ''Jurassic Park (novel), Jurassic Park'' by Michael Crichton and its 1993 Jurassic Park (film), film adaptation are just a few notable examples of dinosaur appearances in fiction. Authors of general-interest non-fiction works about dinosaurs, including some prominent paleontologists, have often sought to use the animals as a way to educate readers about science in general. Dinosaurs are ubiquitous in advertising; numerous Company (law), companies have referenced dinosaurs in printed or televised advertisements, either in order to sell their own products or in order to characterize their rivals as slow-moving, dim-witted, or obsolete.
See also
* Dinosaur diet and feeding * Evolutionary history of life * Lists of dinosaur-bearing stratigraphic units * List of dinosaur genera * List of bird genera * List of birds * List of informally named dinosaurs * List of films featuring dinosaursNotes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * The 5th edition of the book is available from thInternet Archive
Retrieved 2019-10-19. * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * "Reprint of papers published in a special volume of Modern geology [v. 18 (Halstead memorial volume), 1993], with five additional contributions.--Pref." * *
Further reading
* * * . * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Dinosaur Carnian first appearances Dinosaurs, Extant Late Triassic first appearances Taxa named by Richard Owen