|
Pangaea
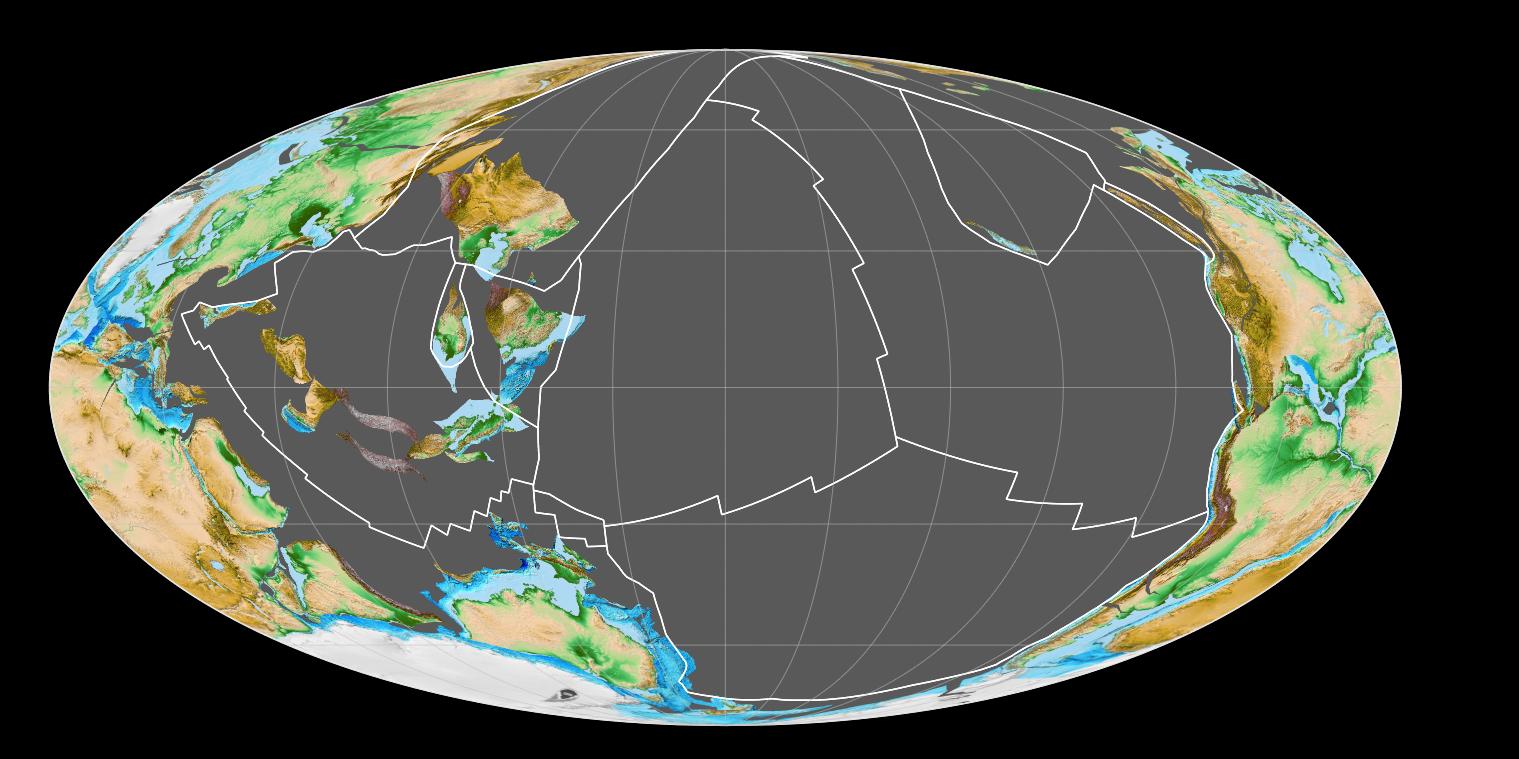
Pangaea or Pangea ( ) was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous period approximately 335 million years ago, and began to break apart about 200 million years ago, at the end of the Triassic and beginning of the Jurassic. Pangaea was C-shaped, with the bulk of its mass stretching between Earth's northern and southern polar regions and surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa and the Paleo-Tethys and subsequent Tethys Oceans. Pangaea is the most recent supercontinent to have existed and was the first to be reconstructed by geologists. Origin of the concept The name "Pangaea" is derived from Ancient Greek ''pan'' (, "all, entire, whole") and '' Gaia'' or Gaea (, " Mother Earth, land"). The first to suggest that the continents were once joined and later separated may have been Abraham Ortelius in 1596. The concept that the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pangaea 200Ma
Pangaea or Pangea ( ) was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia (continent), Siberia during the Carboniferous period approximately 335 million years ago, and began to break apart about 200 million years ago, at the end of the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, Triassic and beginning of the Jurassic. Pangaea was C-shaped, with the bulk of its mass stretching between Earth's northern and southern polar regions and surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa and the Paleo-Tethys Ocean, Paleo-Tethys and subsequent Tethys Oceans. Pangaea is the most recent supercontinent to have existed and was the first to be reconstructed by geologists. Origin of the concept The name "Pangaea" is derived from Ancient Greek ''pan'' (, "all, entire, whole") and ''Gaia (mythology), Gaia'' or Gaea (, "Mother goddess, Mother Earth, land"). The first to suggest that the con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pangaea (mountain)
Pangaea or Pangea ( ) was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous period approximately 335 million years ago, and began to break apart about 200 million years ago, at the end of the Triassic and beginning of the Jurassic. Pangaea was C-shaped, with the bulk of its mass stretching between Earth's northern and southern polar regions and surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa and the Paleo-Tethys and subsequent Tethys Oceans. Pangaea is the most recent supercontinent to have existed and was the first to be reconstructed by geologists. Origin of the concept The name "Pangaea" is derived from Ancient Greek ''pan'' (, "all, entire, whole") and ''Gaia'' or Gaea (, " Mother Earth, land"). The first to suggest that the continents were once joined and later separated may have been Abraham Ortelius in 1596. The concept that the cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euramerica
Laurasia () was the more northern of two large landmasses that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from around ( Mya), the other being Gondwana. It separated from Gondwana (beginning in the late Triassic period) during the breakup of Pangaea, drifting further north after the split and finally broke apart with the opening of the North Atlantic Ocean 56 Mya. The name is a portmanteau of Laurentia and Eurasia. Laurentia, Avalonia, Baltica, and a series of smaller terranes, collided in the Caledonian orogeny c. 400 Mya to form Laurussia. Laurussia then collided with Gondwana to form Pangaea. Kazakhstania and Siberia were then added to Pangaea 290–300 Mya to form Laurasia. Laurasia finally became an independent continental mass when Pangaea broke up into Gondwana and Laurasia. Terminology and origin of the concept Laurentia, the Palaeozoic core of North America and continental fragments that now make up part of Europe, collided with Baltica and Aval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is the assembly of most or all of Earth's continent, continental blocks or cratons to form a single large landmass. However, some geologists use a different definition, "a grouping of formerly dispersed continents", which leaves room for interpretation and is easier to apply to Precambrian times. To separate supercontinents from other groupings, a limit has been proposed in which a continent must include at least about 75% of the continental crust then in existence in order to qualify as a supercontinent. Moving under the forces of plate tectonics, supercontinents have assembled and dispersed multiple times in the geologic past. According to modern definitions, a supercontinent does not exist today; the closest is the current Afro-Eurasian landmass, which covers approximately 57% of Earth's total land area. The last period in which the continental landmasses were near to one another was 336 to 175 million years ago, forming the supercontinent Pangaea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gondwana
Gondwana ( ; ) was a large landmass, sometimes referred to as a supercontinent. The remnants of Gondwana make up around two-thirds of today's continental area, including South America, Africa, Antarctica, Australia (continent), Australia, Zealandia, Arabian Peninsula, Arabia, and the Indian subcontinent. Gondwana was formed by the Accretion (geology), accretion of several cratons (large stable blocks of the Earth's crust), beginning with the East African Orogeny, the collision of India and Geography of Madagascar, Madagascar with East Africa, and culminating in with the overlapping Brasiliano orogeny, Brasiliano and Kuunga orogeny, Kuunga orogenies, the collision of South America with Africa, and the addition of Australia and Antarctica, respectively. Eventually, Gondwana became the largest piece of continental crust of the Paleozoic Era, covering an area of some , about one-fifth of the Earth's surface. It fused with Laurasia during the Carboniferous to form Pan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era is the Era (geology), era of Earth's Geologic time scale, geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Period (geology), Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of archosaurian reptiles such as the dinosaurs, and of Gymnosperm, gymnosperms such as cycads, ginkgoaceae and Araucariaceae, araucarian conifers; a hot Greenhouse and icehouse earth, greenhouse climate; and the tectonic break-up of Pangaea. The Mesozoic is the middle of the three eras since Cambrian explosion, complex life evolved: the Paleozoic, the Mesozoic, and the Cenozoic. The era began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, the largest mass extinction in Earth's history, and ended with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, another mass extinction whose victims included the non-avian dinosaurs, Pterosaur, pterosaurs, Mosasaur, mosasaurs, and Plesiosaur, plesiosaurs. The Mesozoic was a time of significant tectonic, climatic, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleozoic
The Paleozoic ( , , ; or Palaeozoic) Era is the first of three Era (geology), geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Beginning 538.8 million years ago (Ma), it succeeds the Neoproterozoic (the last era of the Proterozoic Eon) and ends 251.9 Ma at the start of the Mesozoic Era. The Paleozoic is subdivided into six period (geology), geologic periods (from oldest to youngest), Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous and Permian. Some geological timescales divide the Paleozoic informally into early and late sub-eras: the Early Paleozoic consisting of the Cambrian, Ordovician and Silurian; the Late Paleozoic consisting of the Devonian, Carboniferous and Permian. The name ''Paleozoic'' was first used by Adam Sedgwick (1785–1873) in 1838 to describe the Cambrian and Ordovician periods. It was redefined by John Phillips (geologist), John Phillips (1800–1874) in 1840 to cover the Cambrian to Permian periods. It is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek ''palaiós'' (π� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the second and middle period of the Mesozoic, Mesozoic Era as well as the eighth period of the Phanerozoic, Phanerozoic Eon and is named after the Jura Mountains, where limestone strata from the period were first identified. The start of the Jurassic was marked by the major Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, associated with the eruption of the Central Atlantic magmatic province, Central Atlantic Magmatic Province (CAMP). The beginning of the Toarcian Age started around 183 million years ago and is marked by the Toarcian Oceanic Anoxic Event, a global episode of Anoxic event, oceanic anoxia, ocean acidification, and elevated global temperatures associated with extinctions, likely caused by the eruption of the Kar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superocean
A superocean is an ocean that surrounds a supercontinent. It is less commonly defined as any ocean larger than the current Pacific Ocean. Named global superoceans include Mirovia, which surrounded the supercontinent Rodinia, and Panthalassa, which surrounded the supercontinent Pangaea. Pannotia and Columbia, along with landmasses before Columbia (such as Ur and Kenorland), were also surrounded by superoceans. As surface water moves unobstructed east to west in superoceans, it tends to warm from the exposure to sunlight so that the western edge of the ocean is warmer than the eastern. Additionally, seasonal changes in temperature, which would have been significantly more rapid inland, probably caused powerful monsoons. In general, however, the mechanics of superoceans are not well understood. List of superoceans * Nealbara/Gyrosia ( Vaalbara/ Ur) (4.404–1.071 Ga) * Lerova ( Kenorland) (2.523–1.805 Ga) * Atlanta-Pacifica Ocean (Atlic Ocean) ( Columbia) (1.41–1.065 Ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleo-Tethys Ocean
The Paleo-Tethys or Palaeo-Tethys Ocean was an ocean located along the northern margin of the paleocontinent Gondwana that started to open during the Middle Cambrian, grew throughout the Paleozoic, and finally closed during the Late Triassic; existing for about 400 million years. Paleo-Tethys was a precursor to the Tethys Ocean (also called the Neo-Tethys), which was located between Gondwana and the Hunic terranes (continental fragments that broke off Gondwana and moved north). It opened as the Proto-Tethys Ocean subducted under these terranes and closed as the Cimmerian terranes (that also broke-off Gondwana and moved north) gave way to the Tethys Ocean. Confusingly, the Neo-Tethys is sometimes defined as the ocean south of a hypothesized mid-ocean ridge separating Greater India from Asia, in which case the ocean between Cimmeria and this hypothesized ridge is called the Meso-Tethys, i.e., the "Middle-Tethys". The so-called Hunic terranes are divided into the ''European H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panthalassa
Panthalassa, also known as the Panthalassic Ocean or Panthalassan Ocean (from Greek "all" and "sea"), was the vast superocean that encompassed planet Earth and surrounded the supercontinent Pangaea, the latest in a series of supercontinents in the history of Earth. During the Paleozoic–Mesozoic transition ( 250 ), the ocean occupied almost 70% of Earth's surface, with the supercontinent Pangaea taking up the remaining one third. The original, ancient ocean floor has now completely disappeared because of the continuous subduction along the continental margins on its circumference. Panthalassa is also referred to as the Paleo-Pacific ("old Pacific") or Proto-Pacific because the Pacific Ocean is a direct continuation of Panthalassa. Formation The supercontinent Rodinia began to break up 870–845 probably as a consequence of a superplume caused by mantle slab avalanches along the margins of the supercontinent. In a second episode 750 the western half of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tethys Ocean
The Tethys Ocean ( ; ), also called the Tethys Sea or the Neo-Tethys, was a prehistoric ocean during much of the Mesozoic Era and early-mid Cenozoic Era. It was the predecessor to the modern Indian Ocean, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Eurasian inland marine basins (primarily represented today by the Black Sea and Caspian Sea). During the early Mesozoic, as Pangaea broke up, the Tethys Ocean was defined as the ocean located between the ancient continents of Gondwana and Laurasia. After the opening of the Indian and Atlantic oceans during the Cretaceous Period and the breakup of these continents over the same period, it came to be defined as the ocean bordered by the continents of Africa, Eurasia, India, and Australasia. During the early-mid Cenozoic, the Indian, African, Australian and Arabian plates moved north and collided with the Eurasian plate, which created new borders to the ocean, a land barrier to the flow of currents between the Indian and Mediterranean basins, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |