|
Sauropsida
Sauropsida (Greek language, Greek for "lizard faces") is a clade of amniotes, broadly equivalent to the Class (biology), class Reptile, Reptilia, though typically used in a broader sense to also include extinct stem-group relatives of modern reptiles and birds (which, as theropod dinosaurs, are nested within reptiles as more closely related to crocodilians than to lizards or turtles).Gauthier J.A. (1994): ''The diversification of the amniotes''. In: D.R. Prothero and R.M. Schoch (ed.) Major Features of Vertebrate Evolution: 129–159. Knoxville, Tennessee: The Paleontological Society. The most popular definition states that Sauropsida is the Sister group, sibling taxon to Synapsida, the other clade of amniotes which includes mammals as its only modern representatives. Although early synapsids have historically been referred to as "mammal-like reptiles", all synapsids are more closely related to mammals than to any modern reptile. Sauropsids, on the other hand, include all amniotes m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesosauria
Mesosaurs ("middle lizards") were a group of small aquatic reptiles that lived during the early Permian period (Cisuralian), roughly Geologic time scale, 299 to 270 million years ago. Mesosaurs were the first known aquatic reptiles, having apparently returned to an aquatic lifestyle from more terrestrial ancestors. It is uncertain which and how many terrestrial traits these ancestors displayed; recent research cannot establish with confidence if the first amniotes were fully terrestrial, or only amphibious. Most authors consider mesosaurs to have been aquatic, although adult animals may have been amphibious, rather than completely aquatic, as indicated by their moderate skeletal adaptations to a semiaquatic lifestyle.Pablo Nuñez Demarco et al. Was Mesosaurus a Fully Aquatic Reptile? Front. Ecol. Evol, published online July 27, 2018; doi: 10.3389/fevo.2018.00109 Similarly, their affinities are uncertain; they may have been among the most basal sauropsids or among the most basal p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
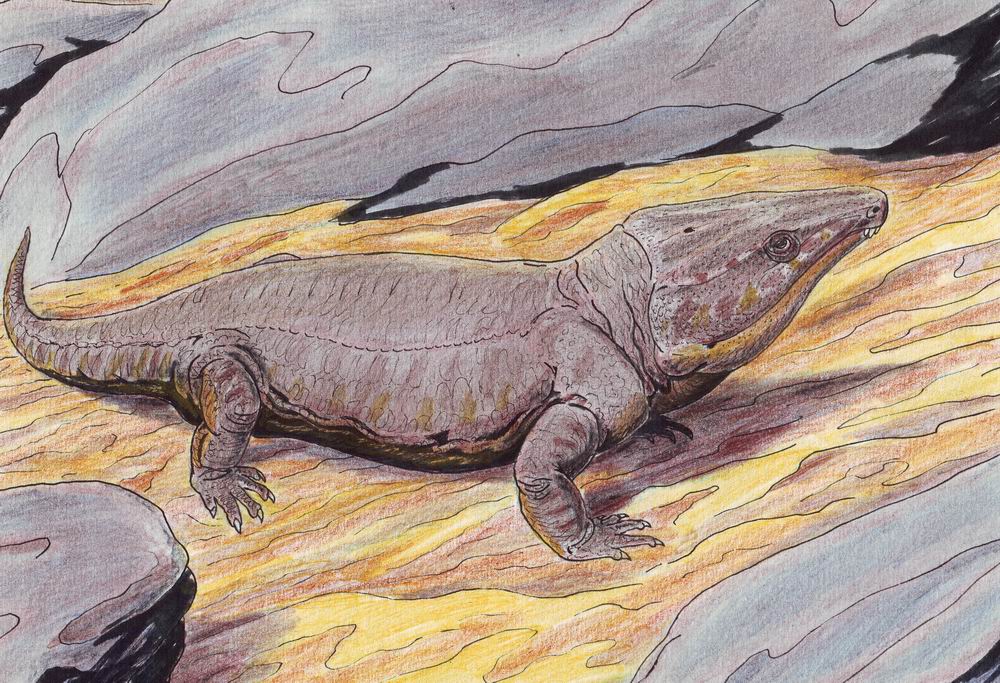
Mesosaur
Mesosaurs ("middle lizards") were a group of small aquatic reptiles that lived during the early Permian period ( Cisuralian), roughly 299 to 270 million years ago. Mesosaurs were the first known aquatic reptiles, having apparently returned to an aquatic lifestyle from more terrestrial ancestors. It is uncertain which and how many terrestrial traits these ancestors displayed; recent research cannot establish with confidence if the first amniotes were fully terrestrial, or only amphibious. Most authors consider mesosaurs to have been aquatic, although adult animals may have been amphibious, rather than completely aquatic, as indicated by their moderate skeletal adaptations to a semiaquatic lifestyle.Pablo Nuñez Demarco et al. Was Mesosaurus a Fully Aquatic Reptile? Front. Ecol. Evol, published online July 27, 2018; doi: 10.3389/fevo.2018.00109 Similarly, their affinities are uncertain; they may have been among the most basal sauropsids or among the most basal parareptiles (in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parareptile
Parareptilia ("near-reptiles") is an extinct group of Basal (phylogenetics), basal Sauropsida, sauropsids ("Reptile, reptiles"), traditionally considered the sister taxon to Eureptilia (the group that likely contains all living reptiles and birds). Parareptiles first arose near the end of the Carboniferous, Carboniferous period and achieved their highest diversity during the Permian, Permian period. Several ecological innovations were first accomplished by parareptiles among reptiles. These include the first reptiles to return to marine ecosystems (mesosaurs), the first Bipedalism, bipedal reptiles (Bolosauridae, bolosaurids such as ''Eudibamus''), the first reptiles with advanced hearing systems (Nycteroleteridae, nycteroleterids and others), and the first large herbivorous reptiles (the pareiasaurs). The only parareptiles to survive into the Triassic, Triassic period were the Procolophonoidea, procolophonoids, a group of small generalists, omnivores, and herbivores. The largest f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parareptilia
Parareptilia ("near-reptiles") is an extinct group of basal sauropsids (" reptiles"), traditionally considered the sister taxon to Eureptilia (the group that likely contains all living reptiles and birds). Parareptiles first arose near the end of the Carboniferous period and achieved their highest diversity during the Permian period. Several ecological innovations were first accomplished by parareptiles among reptiles. These include the first reptiles to return to marine ecosystems (mesosaurs), the first bipedal reptiles ( bolosaurids such as '' Eudibamus''), the first reptiles with advanced hearing systems ( nycteroleterids and others), and the first large herbivorous reptiles (the pareiasaurs). The only parareptiles to survive into the Triassic period were the procolophonoids, a group of small generalists, omnivores, and herbivores. The largest family of procolophonoids, the procolophonids, rediversified in the Triassic, but subsequently declined and became extinct by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Captorhinidae
Captorhinidae is an extinct family of tetrapods, traditionally considered primitive Reptile, reptiles, known from the late Carboniferous to the Late Permian. They had a cosmopolitan distribution across Pangea. Description Captorhinids are a clade of small to very large lizard-like animals that date from the Late Carboniferous through the Permian. Their skulls were much stronger than those of their relatives, the protorothyridids, and had teeth that were better able to deal with tough plant material. The postcranial skeleton is similar to those of seymouriamorphs and diadectomorphs; these animals were grouped together with the captorhinids in the order Cotylosauria as the first reptiles in the early 20th century, but are now usually regarded as Stem group, stem-amniotes no closer to reptiles than to mammals. Captorhinids have broad, robust skulls that are generally triangular in shape when seen in dorsal view. The premaxillae are characteristically downturned. The largest captorh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Captorhinid
Captorhinidae is an extinct family of tetrapods, traditionally considered primitive reptiles, known from the late Carboniferous to the Late Permian. They had a cosmopolitan distribution across Pangea. Description Captorhinids are a clade of small to very large lizard-like animals that date from the Late Carboniferous through the Permian. Their skulls were much stronger than those of their relatives, the protorothyridids, and had teeth that were better able to deal with tough plant material. The postcranial skeleton is similar to those of seymouriamorphs and diadectomorphs; these animals were grouped together with the captorhinids in the order Cotylosauria as the first reptiles in the early 20th century, but are now usually regarded as stem-amniotes no closer to reptiles than to mammals. Captorhinids have broad, robust skulls that are generally triangular in shape when seen in dorsal view. The premaxillae are characteristically downturned. The largest captorhinid, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orovenator
''Orovenator'' is an extinct genus of diapsid from Lower Permian ( Artinskian stage) deposits of Oklahoma, United States. It is known from two partial skulls from the Richards Spur locality in Oklahoma. The holotype OMNH 74606 consists of a partial skull preserving snout and mandible, and the referred specimen, OMNH 74607, a partial skull preserving the skull roof, vertebrae and palatal elements. It was first named by Robert R. Reisz, Sean P. Modesto and Diane M. Scott in 2011 and the type species is ''Orovenator mayorum''. The generic name means "mountain", ''oro'', in Greek in reference to the Richards Spur locality, which was mountainous during the Permian period and "hunter", ''venator'', in Latin. The specific name honours Bill and Julie May. ''Orovenator'' is the oldest and most basal neodiapsid to date. A 2018 redescription by David Ford and Roger Benson found that ''Orovenator'' shared many similarities with varanopids, a group of reptile-like tetrapo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varanopidae
Varanopidae is an extinct family (biology), family of amniotes known from the Late Carboniferous to Middle Permian that resembled monitor lizards (with the name of the group deriving from the monitor lizard genus ''Varanus'') and may have filled a similar niche. Typically, they are considered to be relatively Basal (phylogenetics), basal Synapsida, synapsids (and thus more closely related to mammals than to reptiles), although some studies from the late 2010s recovered them being taxonomically closer to diapsid reptiles, recent studies from the early 2020s support their traditional placement as synapsids on the basis of high degree of bone labyrinth ossification, maxillary canal morphology and phylogenetic analyses. A varanopid from the late Middle Permian Pristerognathus Assemblage Zone, ''Pristerognathus'' Assemblage Zone (Capitanian) is the youngest known varanopid and the last member of the "pelycosaur" group of synapsids. Thus, Varanopidae vanishes from the fossil record at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
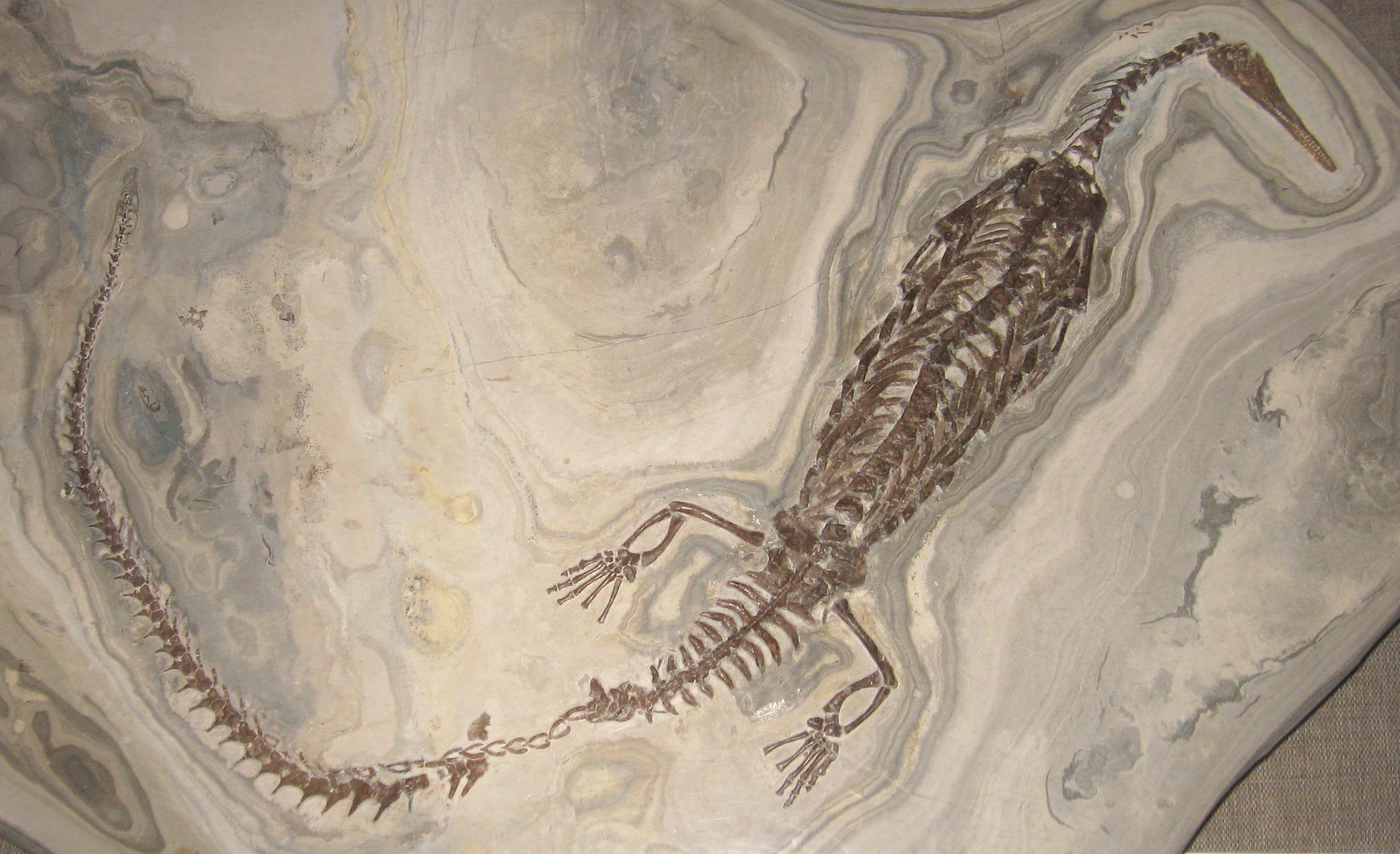
Mesosaurus
''Mesosaurus'' (meaning "middle lizard") is an extinct genus of reptile from the Early Permian of southern Africa and South America. Along with it, the genera '' Brazilosaurus'' and '' Stereosternum'', it is a member of the family Mesosauridae and the order Mesosauria. ''Mesosaurus'' was long thought to have been one of the first marine reptiles, although new data suggests that at least those of Uruguay inhabited a hypersaline water body, rather than a typical marine environment. In any case, it had many adaptations to a fully aquatic lifestyle. It is usually considered to have been anapsid, although Friedrich von Huene considered it to be a synapsid. Recent study of Mesosauridae phylogeny places the group as either the basal most clade within Parareptilia or the basal most clade within Sauropsida (with the latter being the less supported position) despite the skull of ''Mesosaurus'' possessing the "Synapsid condition" of one temporal fenestra. Discovery and naming The ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recumbirostra
Recumbirostra is a clade of tetrapods which lived during the Carboniferous and Permian periods. They are thought to have had a fossorial (burrowing) lifestyle and the group includes both short-bodied and long-bodied snake-like forms. At least one species, the long-bodied molgophid '' Nagini mazonense,'' lost its forelimbs entirely. Recumbirostra includes the families Pantylidae, Gymnarthridae, Ostodolepidae, Rhynchonkidae and Brachystelechidae, with additional families such as Microbrachidae and Molgophidae being included by some authors. Brachystelechidae and Molgophidae have also been grouped together in the suggested clade Chthonosauria. Recumbirostra was erected as a clade in 2007 to include many of the taxa traditionally grouped in " Microsauria", which has since been shown to be a paraphyletic or polyphyletic grouping. Like other "microsaurs", the recumbirostrans have traditionally been considered to be members of the subclass Lepospondyli; however, many phylogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acleistorhinidae
Acleistorhinidae is an extinct family of Late Carboniferous and Early Permian-aged ( Moscovian to Kungurian stage) parareptiles. It is defined as a node based clade including the last common ancestor of '' Acleistorhinus pteroticus'' and '' Colobomycter pholeter'' and all its descendants. Acleistorhinids are most diverse from the Richards Spur locality of the Early Permian of Oklahoma. Richards Spur acleistorhinids include '' Acleistorhinus'', '' Colobomycter'', '' Delorhynchus'', '' Feeserpeton'' and '' Klastomycter''. Other taxa include '' Carbonodraco'' from the Late Carboniferous of Ohio and '' Karutia'' from the Early Permian of Brazil. Acleistorhinidae is commonly considered a subgroup of lanthanosuchoids, related to taxa such as '' Chalcosaurus'', '' Lanthaniscus'' and '' Lanthanosuchus''. However, a re-examination of parareptile phylogeny conducted by Cisneros ''et al.'' (2021) argued that lanthanosuchids were not closely related to acleistorhinids. The phylogenetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millerettidae
Millerettidae is an extinct family of parareptiles from the Middle Permian to the Late Permian period ( Capitanian - Changhsingian stages) of South Africa. The millerettids were small insectivores and probably resembled modern lizards in appearance and lifestyle. The following cladogram shows the phylogenetic In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical dat ... position of the Millerettidae, from Ruta ''et al.'', 2011. References External linksBerkeley University information. Permian reptiles Prehistoric reptiles of Africa Guadalupian first appearances Lopingian extinctions Prehistoric reptile families {{Permian-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |