|
Ankylosauridae
Ankylosauridae () is a family of armored dinosaurs within Ankylosauria, and is the sister group to Nodosauridae. The oldest known ankylosaurids date to around 122 million years ago and went extinct 66 million years ago during the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. These animals were mainly herbivorous and were obligate quadrupeds, with leaf-shaped teeth and robust, scute-covered bodies. Ankylosaurids possess a distinctly domed and short snout, wedge-shaped osteoderms on their skull, scutes along their torso, and a tail club. Ankylosauridae is exclusively known from the Northern Hemisphere, with specimens found in North America, Europe, and Asia. The first discoveries within this family were of the genus ''Ankylosaurus'', by Peter Kaiser and Barnum Brown in Montana in 1906. Brown went on to name Ankylosauridae and the subfamily Ankylosaurinae in 1908. Anatomy Ankylosaurids are stout, solidly built, armoured dinosaurs. They possess accessory ossifications on cranial bones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
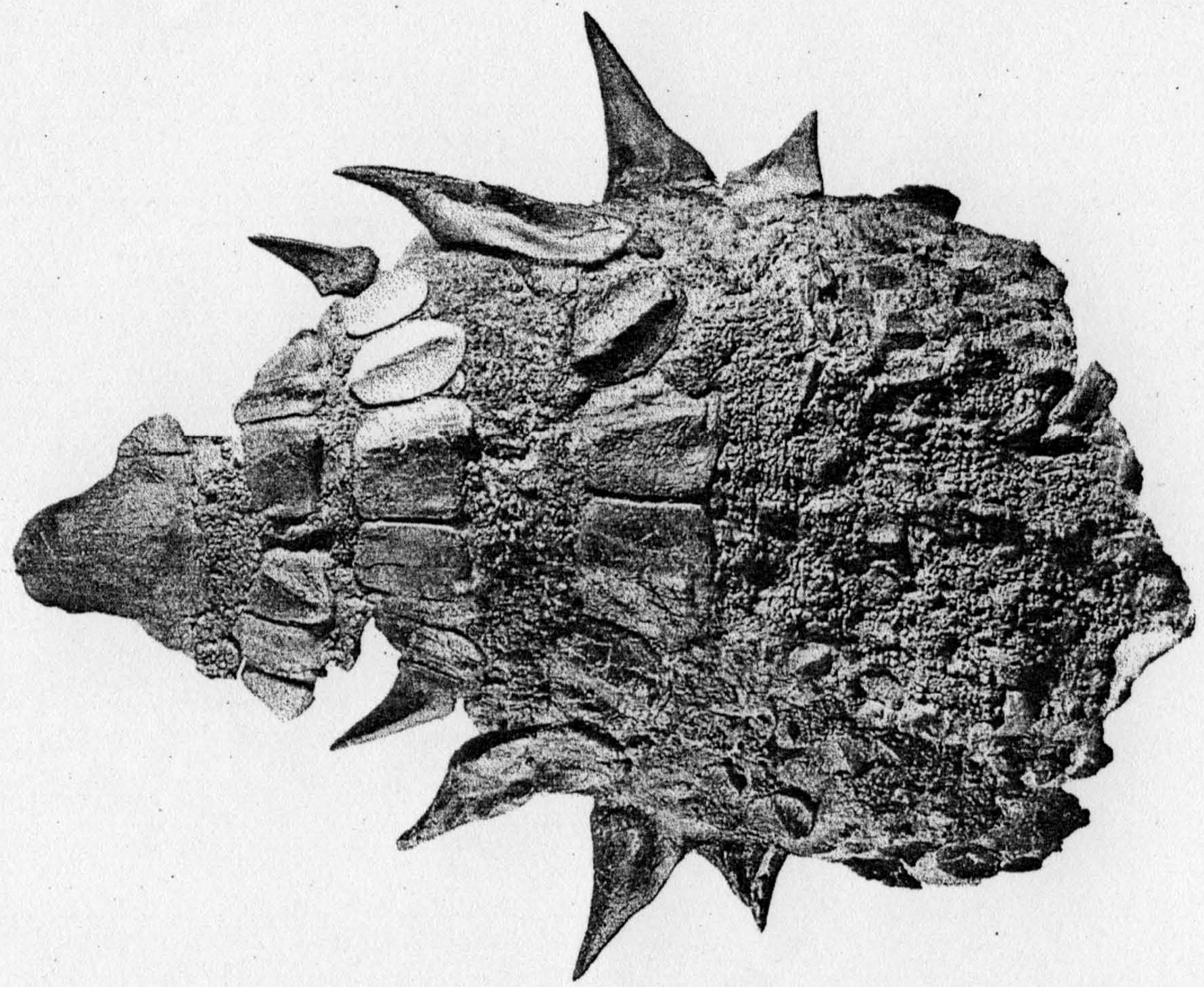
Ankylosaurus Tail Terminology
''Ankylosaurus'' is a genus of Thyreophora, armored dinosaur. Its fossils have been found in geological formations dating to the very end of the Cretaceous Period (geology), Period, about 68–66 million years ago, in western North America, making it among the last of the non-avian dinosaurs. It was named by Barnum Brown in 1908; it is Monotypic taxon, monotypic, containing only ''A. magniventris''. The Binomial nomenclature, generic name means "fused" or "bent lizard", and the specific name means "great belly". A handful of specimens have been excavated to date, but a complete skeleton has not been discovered. Though other members of Ankylosauria are represented by more extensive fossil material, ''Ankylosaurus'' is often considered the archetype, archetypal member of its group, despite having some unusual features. Possibly the largest known Ankylosauridae, ankylosaurid, ''Ankylosaurus'' is estimated to have been between long and to have weighed between . It was Quadrupedal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankylosaurus Magniventris
''Ankylosaurus'' is a genus of armored dinosaur. Its fossils have been found in geological formations dating to the very end of the Cretaceous Period, about 68–66 million years ago, in western North America, making it among the last of the non-avian dinosaurs. It was named by Barnum Brown in 1908; it is monotypic, containing only ''A. magniventris''. The generic name means "fused" or "bent lizard", and the specific name means "great belly". A handful of specimens have been excavated to date, but a complete skeleton has not been discovered. Though other members of Ankylosauria are represented by more extensive fossil material, ''Ankylosaurus'' is often considered the archetypal member of its group, despite having some unusual features. Possibly the largest known ankylosaurid, ''Ankylosaurus'' is estimated to have been between long and to have weighed between . It was quadrupedal, with a broad, robust body. It had a wide, low skull, with two horns pointing backward from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankylosauria
Ankylosauria is a group of herbivorous dinosaurs of the clade Ornithischia. It includes the great majority of dinosaurs with armor in the form of bony osteoderms, similar to turtles. Ankylosaurs were bulky quadrupeds, with short, powerful limbs. They are known to have first appeared in North Africa during the Middle Jurassic, and persisted until the end of the Late Cretaceous. The two main families of ankylosaurians, Nodosauridae and Ankylosauridae primarily originated from the Northern Hemisphere (North America, Europe and Asia), but the more basal Parankylosauria originated from southern Gondwana (South America, Australia and Antarctica) during the Cretaceous. Ankylosauria was first named by Henry Fairfield Osborn in 1923.Osborn, H. F. (1923). "Two Lower Cretaceous dinosaurs of Mongolia." ''American Museum Novitates'', 95: 1–1/ref> In the Linnaean classification system, the group is usually considered either a suborder or an infraorder. It is contained within the group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
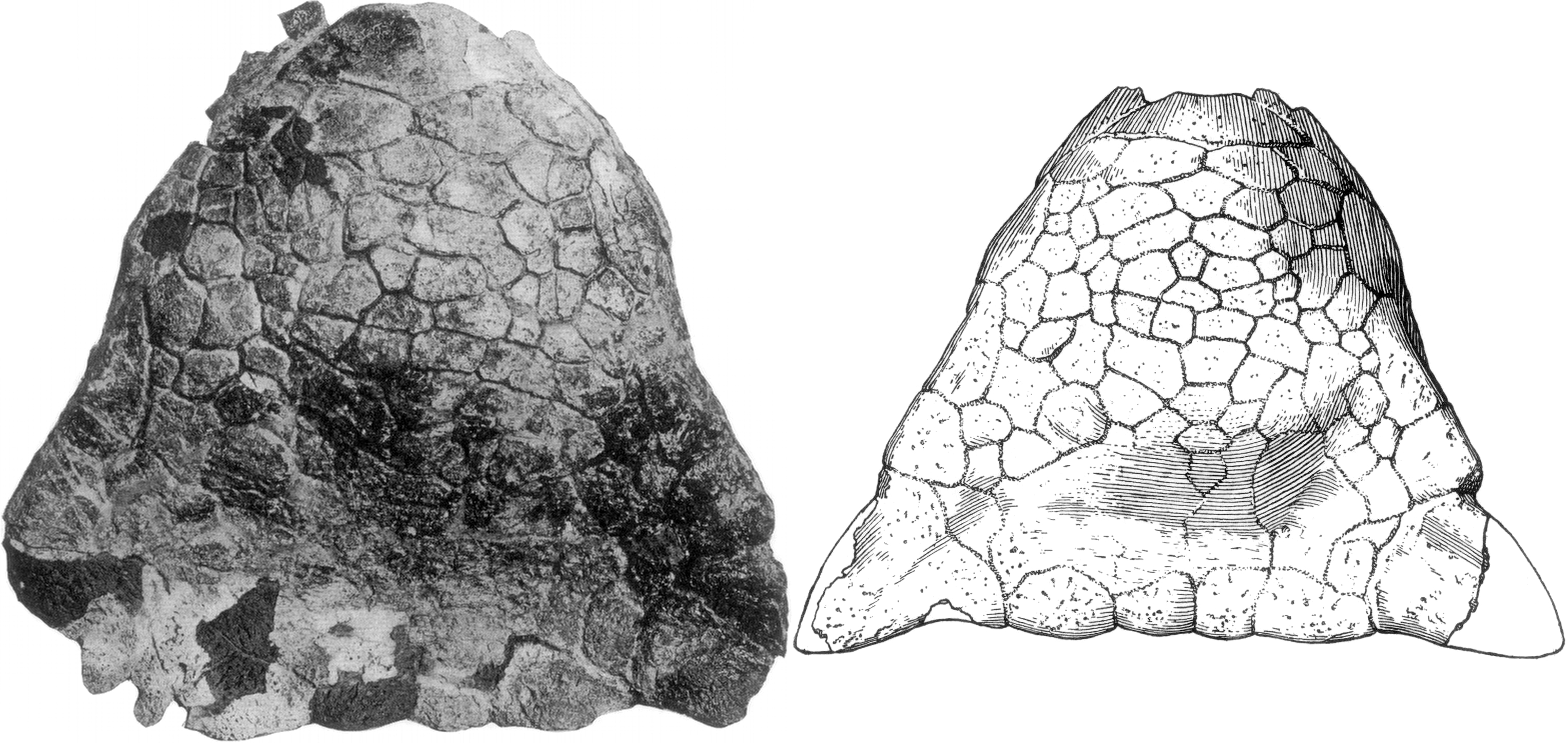
Shamosaurus
''Shamosaurus'' is an extinct genus of herbivorous basal ankylosaurid ankylosaur from Early Cretaceous (Aptian to Albian stage) deposits of Höövör, Mongolia. Discovery and naming In 1977, a Soviet-Mongolian expedition discovered the skeleton of an unknown ankylosaurian at the Hamrin-Us site in Dornogovi Province. This was the first discovery of an ankylosaur in the Lower Cretaceous of Mongolia.T.A. Tumanova, 1983, "Pervyy ankilozavr iz nizhnego mela Mongolii", In: L.P. Tatarinov, R. Barsbold, E. Vorobyeva, B. Luvsandanzan, B.A. Trofimov, Yu. A. Reshetov, & M.A. Shishkin (eds.), ''Iskopayemyye reptilii mongolii''. Trudy Sovmestnaya Sovetsko-Mongol'skaya Paleontologicheskaya Ekspeditsiya 24: 110-118 In 1983, Tatyana Tumanova named and described the type species ''Shamosaurus scutatus''. The generic name is derived from Mandarin ''sha mo'', "sand desert", the Chinese name for the Gobi. The specific name means "protected by a shield" in Latin, a reference to the body armour. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gobisaurus
''Gobisaurus'' is an extinct genus of herbivorous basal ankylosaurid ankylosaur from the Lower Cretaceous of China (''Nei Mongol Zizhiqu''). The genus is monotypic, containing only the species ''Gobisaurus domoculus''. Discovery and naming The Sino-Soviet Expeditions (1959–1960) discovered an ankylosaurian skeleton in the Gobi Desert of Inner Mongolia near Moartu, in the region of the Alashan Desert. The find was largely neglected until fossils were selected for a travelling exhibition touring the globe between 1990 and 1997, in the context of the China-Canada Dinosaur Project. The postcranial skeleton could not be located but the skull was displayed, informally labelled "Gobisaurus", at the time a ''nomen nudum''. In 2001, Matthew K. Vickaryous, Anthony P. Russell, Philip John Currie and Zhao Xijin named and described the type species ''Gobisaurus domoculus''. The generic name means "Gobi (Desert) lizard," referring to its provenance. The specific name means "hidden f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cedarpelta
''Cedarpelta'' is an extinct genus of basal ankylosaurid dinosaur from Utah that lived during the Late Cretaceous period (Cenomanian to lower Turonian stage, 98.2 to 93 Ma) in what is now the Mussentuchit Member of the Cedar Mountain Formation. The type and only species, ''Cedarpelta bilbeyhallorum'', is known from multiple specimens including partial skulls and postcranial material. It was named in 2001 by Kenneth Carpenter, James Kirkland, Don Burge, and John Bird. ''Cedarpelta'' has an estimated length of 7 metres (23 feet) and weight of 5 tonnes (11,023 lbs). The skull of ''Cedarpelta'' lacks extensive cranial ornamentation and is one of the only known ankylosaurs with individual skull bones that are not completely fused together. Discovery and naming The partial remains of an ankylosaur were discovered by Evan Hall and Sue Ann Bilbey at the CEM site near the Price River in Carbon County, Utah while they were visiting an excavation in the surrounding area.Carpenter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aletopelta
''Aletopelta'' (; meaning 'wanderer shield') is a monospecific genus of basal ankylosauridae, ankylosaurid dinosaur from Southern California that lived during the Late Cretaceous (upper Campanian stage, 75.5 Ma) in what is now the Point Loma Formation. The type and only species, ''Aletopelta coombsi'', is known from a partial skeleton preserving osteoderms. It was originally described in 1996 by W. P. Coombs, Jr. and T.A. Deméré before being named in 2001 by Tracy Ford and James I. Kirkland, James Kirkland. ''Aletopelta'' has an estimated size of 5 metres (16 feet) and weight of 2 tonnes (4,409 lbs). The holotype formed a miniature reef and was scavenged upon by invertebrates and sharks. Discovery and naming In 1987, construction work was done on the College Boulevard near Carlsbad, California, Carlsbad at the Californian coast. While paleontologically surveying the work, Bradford Riney noted that a skeleton had been uncovered by a ditch dug for a sewage pipe. Within days, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bissektipelta
''Bissektipelta'' (meaning " Bissekty shield") is a genus of ankylosaurine thyreophoran dinosaurs that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous in what is now the Bissekty Formation of Uzbekistan. ''Bissektipelta'' is a monospecific genus, containing only the type species ''B. archibaldi''. History of discovery In September 1998, the joint Uzbek-Russian-British-American-Project excavated the braincase of an ankylosaur. In 2002, Alexandr Averianov, based on this find, named a second species of the genus '' Amtosaurus'': ''Amtosaurus archibaldi''. The specific name honours James David Archibald, leading the URBAC (Uzbekistan, Russia, Britain, America, & Canada) project that performed the excavation. The holotype specimen, ZIN PH 1/6, was collected from the Bissekty Formation, dating from the late Turonian- Coniacian, of Dzharakuduk. It consists of a well-preserved, fully ossified braincase with a partial skull roof, along with isolated teeth and osteoderms. In 2004, Jolyon Pari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huaxiazhoulong
''Huaxiazhoulong '' is an extinct genus of ankylosaurid dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous (Campanian) Tangbian Formation of Jiangxi Province, China. The genus contains a single species, ''H. shouwen'', known from a partial skeleton. Discovery and naming The ''Huaxiazhoulong'' holotype specimen, JPM-N000, was discovered in 1986 in sediments of the Tangbian Formation in Longxi village of Guangchang County in Fuzhou Municipality of Jiangxi Province, southern China. It was subsequently collected by the Guangchang County Museum, and it is now deposited at the Jiangxi Provincial Museum. The specimen is largely complete and well-preserved, comprising nine dorsal vertebrae, a sacral vertebra, most of the caudal vertebrae including the co-ossified tail "handle" and club, several ribs, the scapulocoracoids, the sternum, both forelimbs with three metacarpals, both hindlimbs with four metatarsals, most of the pelvic girdle, and three isolated osteoderms. In 2024, Zhu et al. des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chuanqilong
''Chuanqilong'' (meaning "legendary dragon") is a monospecific genus of basal ankylosaurid dinosaur from the Liaoning Province, China that lived during the Early Cretaceous (late Barremian to Aptian stage, 122.0 to 118.9 Ma) in what is now the Jiufotang Formation. The type and only species, ''Chuanqilong chaoyangensis'', is known from a nearly complete skeleton with a skull of a juvenile individual. It was described in 2014 by Fenglu Han, Wenjie Zheng, Dongyu Hu, Xing Xu, and Paul M. Barrett. ''Chuanqilong'' shows many similarities with '' Liaoningosaurus'' and may represent a later ontogenetic stage of the taxon. ''Chuanqilong'' was a medium-sized ankylosaur, with an estimated length of 4.5 metres (14.8 feet), although it has been suggested that it would have been larger due to the immature age of the type specimen. It had a triangular skull and a neck that was protected by bands of osteoderms known as cervical half rings. The rest of the body was covered in osteoderms and ossic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nodosauridae
Nodosauridae is a family of ankylosaurian dinosaurs known from the Late Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous periods in what is now Asia, Europe, North America, and possibly South America. While traditionally regarded as a monophyletic clade as the sister taxon to the Ankylosauridae, some analyses recover it as a paraphyletic grade leading to the ankylosaurids. Description Nodosaurids, like their sister group the ankylosaurids, were heavily armored dinosaurs adorned with rows of bony armor nodules and spines (osteoderms), which were covered in keratin sheaths. Ankylosaurians were small- to large-sized, heavily built, quadrupedal, herbivorous dinosaurs, possessing small, leaf-shaped teeth. Unlike ankylosaurids, nodosaurids lacked mace-like tail clubs and instead had more flexible tail tips. Many nodosaurids had spikes projecting outward from their shoulders. One particularly well-preserved nodosaurid "mummy", the holotype of '' Borealopelta markmitchelli'', preserves a nearly comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |