The heart is a muscular
organ
Organ and organs may refer to:
Biology
* Organ (biology), a group of tissues organized to serve a common function
* Organ system, a collection of organs that function together to carry out specific functions within the body.
Musical instruments
...
found in
human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
s and other
animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, ...
s. This organ pumps
blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells.
Blood is com ...
through the
blood vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (bi ...
s. The heart and blood vessels together make the
circulatory system
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart ...
.
The pumped blood carries
oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
and
nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
s to the tissue, while carrying
metabolic waste
Metabolic wastes or excrements are substances left over from metabolic processes (such as cellular respiration) which cannot be used by the organism (they are surplus or toxic), and must therefore be excreted. This includes nitrogen compounds ...
such as
carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
to the
lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their ...
s. In
human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
s, the heart is approximately the size of a closed
fist
A fist is the shape of a hand when the fingers are bent inward against the palm and held there tightly. To make or clench a fist is to fold the fingers tightly into the center of the palm and then to clamp the thumb over the middle phalanges; i ...
and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the
chest
The thorax (: thoraces or thoraxes) or chest is a part of the anatomy of mammals and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen.
In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main di ...
, called the
mediastinum
The mediastinum (from ;: mediastina) is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is a region that contains vital organs and structures within the thorax, mainly the heart and its vessels, the eso ...
.
In humans, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right
atria
Atria may refer to:
Science
*Atrium (heart) (plural: atria), an anatomical structure of the heart
*Atria (genus), a flatworm genus in the family Dendrocoelidae
* Atria (star) or Alpha Trianguli Australis, a star in the constellation Triangulum Aus ...
and lower left and right
ventricles.
Commonly, the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the
right heart
The heart is a muscular organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the tiss ...
and their left counterparts as the
left heart
The heart is a muscular organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the tissue ...
. In a healthy heart, blood flows one way through the heart due to
heart valve
A heart valve is a biological one-way valve that allows blood to flow in one direction through the chambers of the heart. A mammalian heart usually has four valves. Together, the valves determine the direction of blood flow through the heart. Hea ...
s, which prevent
backflow
Backflow is a term in plumbing for an unwanted flow of water in the reverse direction. It can be a serious health risk for the contamination of potable water supplies with foul water. In the most obvious case, a toilet flush cistern and its wate ...
.
The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the
pericardium
The pericardium (: pericardia), also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong inelastic connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), ...
, which also contains a small amount of
fluid
In physics, a fluid is a liquid, gas, or other material that may continuously motion, move and Deformation (physics), deform (''flow'') under an applied shear stress, or external force. They have zero shear modulus, or, in simpler terms, are M ...
. The wall of the heart is made up of three layers:
epicardium
The pericardium (: pericardia), also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong inelastic connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), a ...
,
myocardium
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle or myocardium) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, the others being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the wall o ...
, and
endocardium
The endocardium (: endocardia) is the innermost layer of tissue that lines the chambers of the heart. Its cells are embryologically and biologically similar to the endothelial cells that line blood vessels. The endocardium also provides prot ...
.
The heart pumps blood with a
rhythm
Rhythm (from Greek , ''rhythmos'', "any regular recurring motion, symmetry") generally means a " movement marked by the regulated succession of strong and weak elements, or of opposite or different conditions". This general meaning of regular r ...
determined by a group of
pacemaker cells
350px, Image showing the cardiac pacemaker or SA node, the primary pacemaker within the electrical conduction system of the heart
The cardiac pacemaker is the heart's natural rhythm generator. It employs pacemaker Cell (biology), cells that ...
in the
sinoatrial node
The sinoatrial node (also known as the sinuatrial node, SA node, sinus node or Keith–Flack node) is an ellipse, oval shaped region of special cardiac muscle in the upper back wall of the right atrium made up of Cell (biology), cells known as pa ...
. These generate an electric current that causes the heart to contract, traveling through the
atrioventricular node
The atrioventricular node (AV node, or Aschoff-Tawara node) electrically connects the heart's atria and ventricles to coordinate beating in the top of the heart; it is part of the electrical conduction system of the heart. The AV node lies at the ...
and along the
conduction system of the heart
The cardiac conduction system (CCS, also called the electrical conduction system of the heart) transmits the signals generated by the sinoatrial node – the heart's pacemaker, to cause the heart muscle to contract, and pump blood through the bo ...
. In humans, deoxygenated blood enters the heart through the right atrium from the
superior
Superior may refer to:
*Superior (hierarchy), something which is higher in a hierarchical structure of any kind
Places
* Superior (proposed U.S. state), an unsuccessful proposal for the Upper Peninsula of Michigan to form a separate state
*Lak ...
and
inferior venae cavae and passes to the right ventricle. From here, it is pumped into
pulmonary circulation
The pulmonary circulation is a division of the circulatory system in all vertebrates. The circuit begins with deoxygenated blood returned from the body to the right atrium of the heart where it is pumped out from the right ventricle to the lun ...
to the
lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their ...
s, where it receives oxygen and gives off carbon dioxide. Oxygenated blood then returns to the left atrium, passes through the left ventricle and is pumped out through the
aorta
The aorta ( ; : aortas or aortae) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the Ventricle (heart), left ventricle of the heart, branching upwards immediately after, and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits at ...
into
systemic circulation
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a organ system, system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of ...
, traveling through
arteries
An artery () is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in ...
,
arteriole
An arteriole is a small-diameter blood vessel in the microcirculation that extends and branches out from an artery and leads to capillary, capillaries.
Arterioles have vascular smooth muscle, muscular walls (usually only one to two layers of smoo ...
s, and
capillaries
A capillary is a small blood vessel, from 5 to 10 micrometres in diameter, and is part of the microcirculation system. Capillaries are microvessels and the smallest blood vessels in the body. They are composed of only the tunica intima (the in ...
—where
nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
s and other substances are exchanged between blood vessels and cells, losing oxygen and gaining carbon dioxide—before being returned to the heart through
venule
A venule is a very small vein in the microcirculation that allows blood to return from the capillary beds to drain into the venous system via increasingly larger veins. Post-capillary venules are the smallest of the veins with a diameter of ...
s and
vein
Veins () are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and feta ...
s. The adult heart beats at a
resting rate close to 72 beats per minute.
Exercise
Exercise or workout is physical activity that enhances or maintains fitness and overall health. It is performed for various reasons, including weight loss or maintenance, to aid growth and improve strength, develop muscles and the cardio ...
temporarily increases the rate, but lowers it in the long term, and is good for heart health.
Cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina, heart attack), heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumati ...
s were the most common cause of death globally as of 2008, accounting for 30% of all human deaths.
Of these more than three-quarters are a result of
coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), or ischemic heart disease (IHD), is a type of cardiovascular disease, heart disease involving Ischemia, the reduction of blood flow to the cardiac muscle due to a build-up ...
and
stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemor ...
.
Risk factors include:
smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is combusted, and the resulting smoke is typically inhaled to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream of a person. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, whi ...
, being
overweight
Being overweight is having more body fat than is optimally healthy. Being overweight is especially common where food supplies are plentiful and lifestyles are sedentary.
, excess weight reached epidemic proportions globally, with more than ...
, little exercise,
high cholesterol
Hypercholesterolemia, also called high cholesterol, is the presence of high levels of cholesterol in the blood. It is a form of hyperlipidemia (high levels of lipids in the blood), hyperlipoproteinemia (high levels of lipoproteins in the blood), ...
,
high blood pressure
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms itself. It is, however, a major ri ...
, and poorly controlled
diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
, among others. Cardiovascular diseases do not frequently have symptoms but may cause
chest pain
Chest pain is pain or discomfort in the chest, typically the front of the chest. It may be described as sharp, dull, pressure, heaviness or squeezing. Associated symptoms may include pain in the shoulder, arm, upper abdomen, or jaw, along with n ...
or
shortness of breath
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that con ...
. Diagnosis of heart disease is often done by the taking of a
medical history
The medical history, case history, or anamnesis (from Greek: ἀνά, ''aná'', "open", and μνήσις, ''mnesis'', "memory") of a patient is a set of information the physicians collect over medical interviews. It involves the patient, and ev ...
,
listening
Listening is the act of attention, paying attention to sounds. It includes listening to the sounds of Natural environment, nature, listening to music, and perhaps most importantly, Interpersonal communication, interpersonal listening, i.e. liste ...
to the
heart-sounds with a
stethoscope
The stethoscope is a medicine, medical device for auscultation, or listening to internal sounds of an animal or human body. It typically has a small disc-shaped resonator that is placed against the skin, with either one or two tubes connected t ...
, as well as with
ECG
Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), a recording of the heart's electrical activity through repeated cardiac cycles.
It is an electrogram of the heart which is a graph of voltage versus time of ...
, and
echocardiogram
Echocardiography, also known as cardiac ultrasound, is the use of ultrasound to examine the heart. It is a type of medical imaging, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound. The visual image formed using this technique is called an echo ...
which uses
ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply ...
.
Specialists who focus on diseases of the heart are called
cardiologists
Cardiology () is the study of the heart. Cardiology is a branch of medicine that deals with disorders of the heart and the cardiovascular system. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery di ...
, although many specialties of medicine may be involved in treatment.
Structure

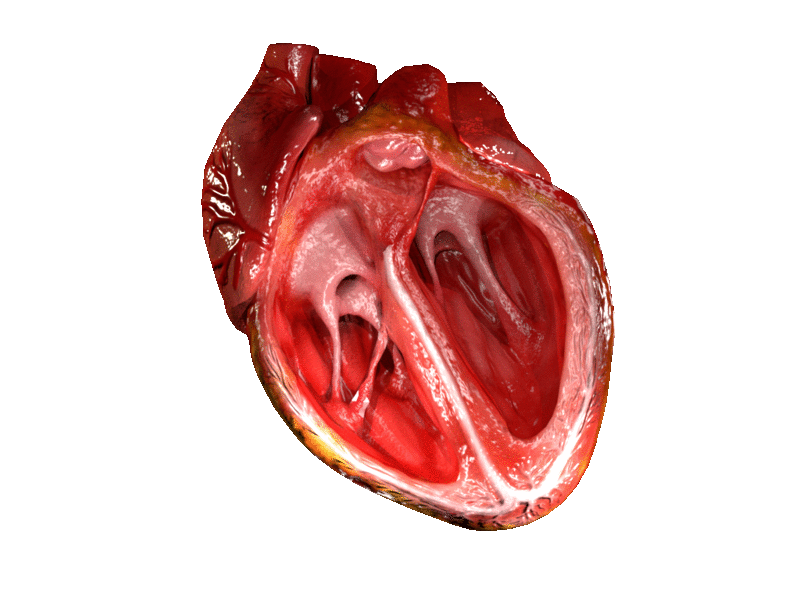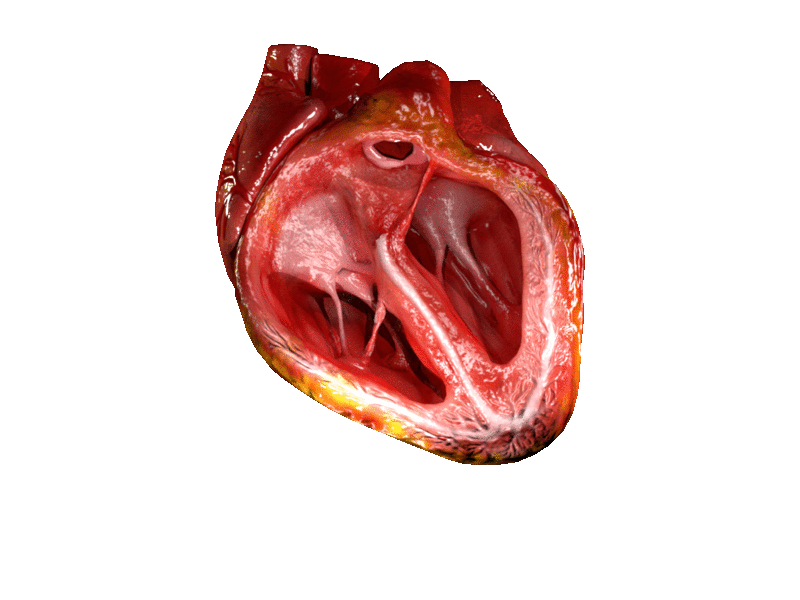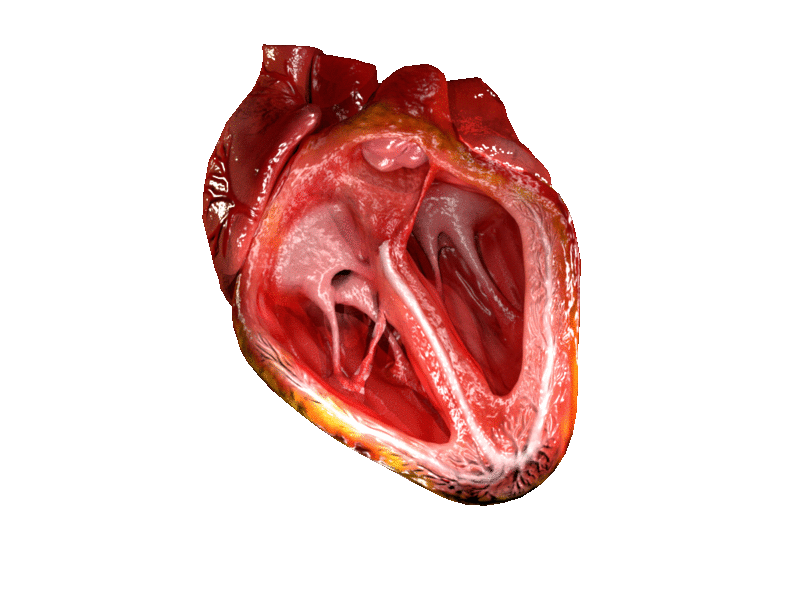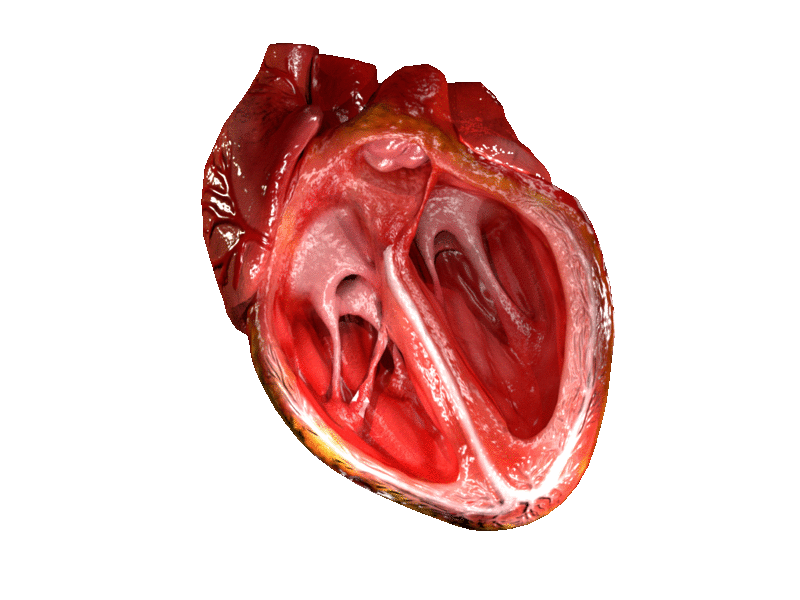
Location and shape

The human heart is situated in the
mediastinum
The mediastinum (from ;: mediastina) is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is a region that contains vital organs and structures within the thorax, mainly the heart and its vessels, the eso ...
, at the level of
thoracic vertebrae
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebra (anatomy), vertebrae of intermediate size between the ce ...
T5–
T8. A double-membraned sac called the
pericardium
The pericardium (: pericardia), also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong inelastic connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), ...
surrounds the heart and attaches to the mediastinum. The back surface of the heart lies near the
vertebral column
The spinal column, also known as the vertebral column, spine or backbone, is the core part of the axial skeleton in vertebrates. The vertebral column is the defining and eponymous characteristic of the vertebrate. The spinal column is a segmente ...
, and the front surface, known as the sternocostal surface, sits behind the
sternum
The sternum (: sternums or sterna) or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major bl ...
and
rib cartilages.
The upper part of the heart is the attachment point for several large blood vessels—the
venae cavae
In anatomy, the ''venae cavae'' (; ''vena cava'' ; ) are two large veins (great vessels) that return deoxygenated blood from the body into the heart. In humans they are the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava, and both empty into the ...
,
aorta
The aorta ( ; : aortas or aortae) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the Ventricle (heart), left ventricle of the heart, branching upwards immediately after, and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits at ...
and
pulmonary trunk
A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the ''main pulmonary artery'' or ''pulmonary trunk'' from the heart, and t ...
. The upper part of the heart is located at the level of the third costal cartilage.
The lower tip of the heart, the apex, lies to the left of the sternum (8 to 9 cm from the
midsternal line
The midsternal line is used to describe a part of the surface anatomy of the anterior thorax. The midsternal line runs vertical down the middle of the sternum.
It can be interpreted as a component of the median plane
Whether in reference to th ...
) between the junction of the fourth and fifth ribs near their
articulation with the costal cartilages.
The largest part of the heart is usually slightly offset to the left side of the chest (
levocardia). In a rare congenital disorder (
dextrocardia
Dextrocardia () is a rare congenital condition in which the apex of the heart is located on the right side of the body, rather than the more typical placement towards the left. There are two main types of dextrocardia: dextrocardia of embryonic ...
) the heart is offset to the right side and is felt to be on the left because the
left heart
The heart is a muscular organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the tissue ...
is stronger and larger, since it pumps to all body parts. Because the heart is between the
lungs
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory syste ...
, the left lung is smaller than the right lung and has a cardiac notch in its border to accommodate the heart.
The heart is cone-shaped, with its base positioned upwards and tapering down to the apex.
An adult heart has a mass of 250–350 grams (9–12 oz). The heart is often described as the size of a fist: 12 cm (5 in) in length, 8 cm (3.5 in) wide, and 6 cm (2.5 in) in thickness,
although this description is disputed, as the heart is likely to be slightly larger. Well-trained
athlete
An athlete is most commonly a person who competes in one or more sports involving physical strength, speed, power, or endurance. Sometimes, the word "athlete" is used to refer specifically to sport of athletics competitors, i.e. including track ...
s can have much larger hearts due to the effects of exercise on the heart muscle, similar to the response of skeletal muscle.
Chambers

The heart has four chambers, two upper
atria
Atria may refer to:
Science
*Atrium (heart) (plural: atria), an anatomical structure of the heart
*Atria (genus), a flatworm genus in the family Dendrocoelidae
* Atria (star) or Alpha Trianguli Australis, a star in the constellation Triangulum Aus ...
, the receiving chambers, and two lower
ventricles, the discharging chambers. The atria open into the ventricles via the
atrioventricular valve
A heart valve is a biological one-way valve that allows blood to flow in one direction through the chambers of the heart. A mammalian heart usually has four valves. Together, the valves determine the direction of blood flow through the heart. Hear ...
s, present in the
atrioventricular septum. This distinction is visible also on the surface of the heart as the
coronary sulcus
The coronary sulcus (also called coronary groove, auriculoventricular groove, atrioventricular groove, AV groove) is a Sulcus (morphology), groove on the surface of the heart at the base of right auricle that separates the Atrium (heart), atria fr ...
. There is an ear-shaped structure in the upper right atrium called the
right atrial appendage
The atrium (; : atria) is one of the two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular mitral and tricuspid heart valves.
...
, or auricle, and another in the upper left atrium, the
left atrial appendage
The atrium (; : atria) is one of the two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular mitral and tricuspid heart valves.
T ...
. The right atrium and the right ventricle together are sometimes referred to as the
right heart
The heart is a muscular organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the tiss ...
. Similarly, the left atrium and the left ventricle together are sometimes referred to as the
left heart
The heart is a muscular organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the tissue ...
. The ventricles are separated from each other by the
interventricular septum
The interventricular septum (IVS, or ventricular septum, or during development septum inferius) is the stout wall separating the ventricle (heart), ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart, from one another.
The interventricular septum is di ...
, visible on the surface of the heart as the
anterior longitudinal sulcus
The anterior interventricular sulcus (or anterior longitudinal sulcus) is one of two grooves separating the ventricles of the heart (the other being the posterior interventricular sulcus). They can also be known as paraconal interventricular gr ...
and the
posterior interventricular sulcus
The posterior interventricular sulcus or posterior longitudinal sulcus is one of the two grooves separating the ventricles of the heart (the other being the anterior interventricular sulcus). They can be known as subsinosal interventricular groo ...
.
The
fibrous
Fiber (spelled fibre in British English; from ) is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often inco ...
cardiac skeleton
In cardiology, the cardiac skeleton, also known as the fibrous skeleton of the heart, is a high-density homogeneous structure of connective tissue that forms and anchors the valves of the heart, and influences the forces exerted by and through the ...
gives structure to the heart. It forms the atrioventricular septum, which separates the atria from the ventricles, and the fibrous rings, which serve as bases for the four
heart valve
A heart valve is a biological one-way valve that allows blood to flow in one direction through the chambers of the heart. A mammalian heart usually has four valves. Together, the valves determine the direction of blood flow through the heart. Hea ...
s. The cardiac skeleton also provides an important boundary in the heart's electrical conduction system since collagen cannot conduct
electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwel ...
. The interatrial septum separates the atria, and the interventricular septum separates the ventricles.
The interventricular septum is much thicker than the interatrial septum since the ventricles need to generate greater pressure when they contract.
Valves
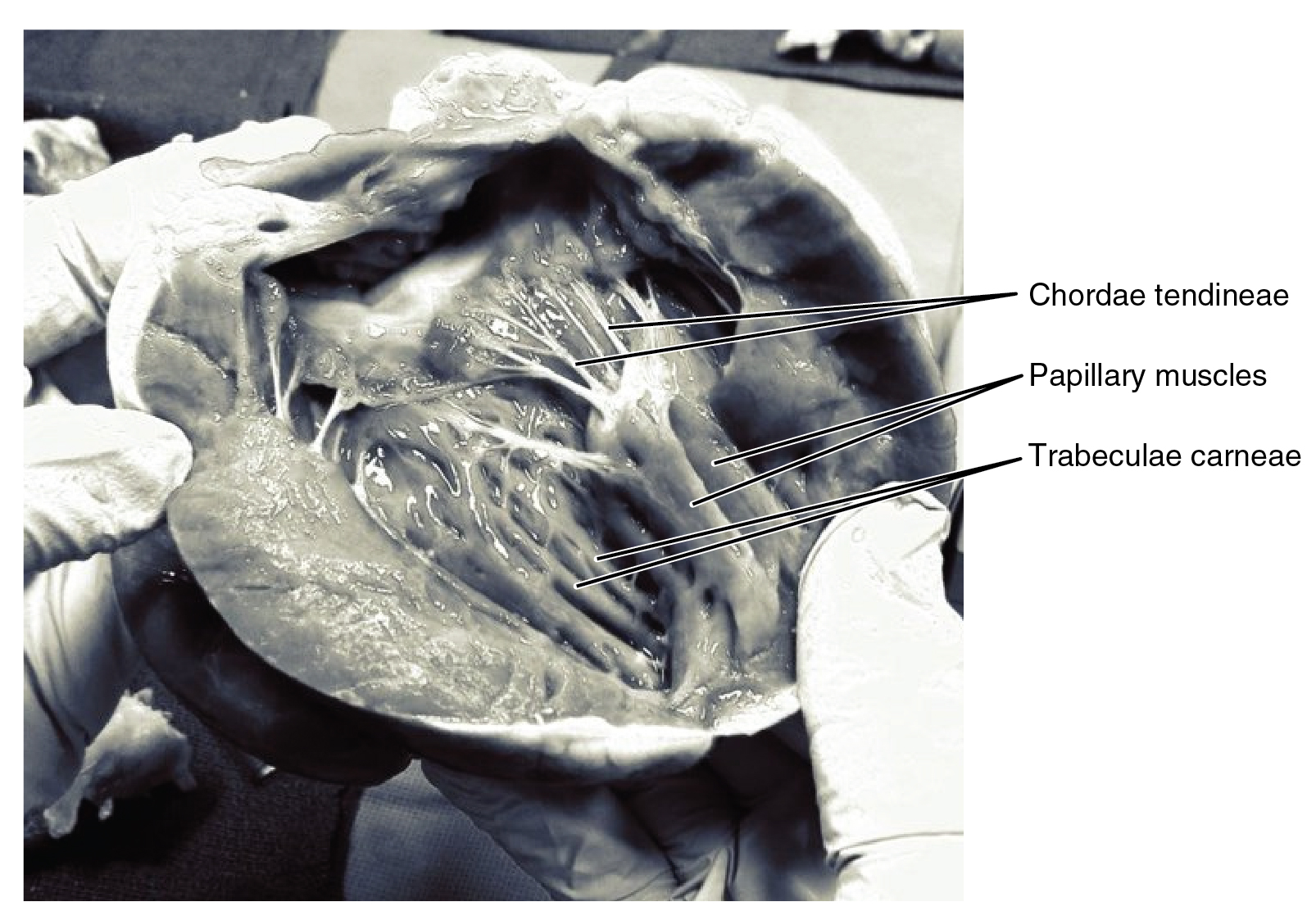
The heart has four valves, which separate its chambers. One valve lies between each atrium and ventricle, and one valve rests at the exit of each ventricle.
[
The valves between the atria and ventricles are called the atrioventricular valves. Between the right atrium and the right ventricle is the ]tricuspid valve
The tricuspid valve, or right atrioventricular valve, is on the right dorsal side of the mammalian heart, at the superior portion of the right ventricle. The function of the valve is to allow blood to flow from the right atrium to the right vent ...
. The tricuspid valve has three cusps, which connect to chordae tendinae
The chordae tendineae (: chorda tendinea) or tendinous cords, colloquially known as the heart strings, are inelastic cords of fibrous connective tissue that connect the papillary muscles to the tricuspid valve and the mitral valve in the heart. ...
and three papillary muscle
The papillary muscles are muscles located in the ventricles of the heart. They attach to the cusps of the atrioventricular valves (also known as the mitral and tricuspid valves) via the chordae tendineae and contract to prevent inversion or ...
s named the anterior, posterior, and septal muscles, after their relative positions. The mitral valve
The mitral valve ( ), also known as the bicuspid valve or left atrioventricular valve, is one of the four heart valves. It has two Cusps of heart valves, cusps or flaps and lies between the atrium (heart), left atrium and the ventricle (heart), ...
lies between the left atrium and left ventricle. It is also known as the bicuspid valve due to its having two cusps, an anterior and a posterior cusp. These cusps are also attached via chordae tendinae to two papillary muscles projecting from the ventricular wall.
The papillary muscles extend from the walls of the heart to valves by cartilaginous connections called chordae tendinae. These muscles prevent the valves from falling too far back when they close. During the relaxation phase of the cardiac cycle, the papillary muscles are also relaxed and the tension on the chordae tendineae is slight. As the heart chambers contract, so do the papillary muscles. This creates tension on the chordae tendineae, helping to hold the cusps of the atrioventricular valves in place and preventing them from being blown back into the atria.pulmonary valve
The pulmonary valve (sometimes referred to as the pulmonic valve) is a valve of the heart that lies between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery, and has three cusps. It is one of the four valves of the heart and one of the two semiluna ...
is located at the base of the pulmonary artery
A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the ''main pulmonary artery'' or ''pulmonary trunk'' from the heart, and ...
. This has three cusps which are not attached to any papillary muscles. When the ventricle relaxes blood flows back into the ventricle from the artery and this flow of blood fills the pocket-like valve, pressing against the cusps which close to seal the valve. The semilunar aortic valve
The aortic valve is a valve in the heart of humans and most other animals, located between the left ventricle and the aorta. It is one of the four valves of the heart and one of the two semilunar valves, the other being the pulmonary valve. ...
is at the base of the aorta
The aorta ( ; : aortas or aortae) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the Ventricle (heart), left ventricle of the heart, branching upwards immediately after, and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits at ...
and also is not attached to papillary muscles. This too has three cusps which close with the pressure of the blood flowing back from the aorta.
Right heart
The right heart consists of two chambers, the right atrium and the right ventricle, separated by a valve, the tricuspid valve
The tricuspid valve, or right atrioventricular valve, is on the right dorsal side of the mammalian heart, at the superior portion of the right ventricle. The function of the valve is to allow blood to flow from the right atrium to the right vent ...
.vein
Veins () are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and feta ...
s, the superior
Superior may refer to:
*Superior (hierarchy), something which is higher in a hierarchical structure of any kind
Places
* Superior (proposed U.S. state), an unsuccessful proposal for the Upper Peninsula of Michigan to form a separate state
*Lak ...
and inferior venae cavae
In anatomy, the ''venae cavae'' (; ''vena cava'' ; ) are two large veins (great vessels) that return deoxygenated blood from the body into the heart. In humans they are the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava, and both empty into the ...
. A small amount of blood from the coronary circulation also drains into the right atrium via the coronary sinus
The coronary sinus () is the largest vein of the heart. It drains over half of the deoxygenated blood from the heart muscle into the right atrium. It begins on the backside of the heart, in between the left atrium, and left ventricle; it begi ...
, which is immediately above and to the middle of the opening of the inferior vena cava.pectinate muscle
The pectinate muscles (musculi pectinati) are parallel muscular ridges in the walls of the atria of the heart.
Structure
Behind the crest (crista terminalis) of the right atrium the internal surface is smooth. Pectinate muscles make up the par ...
s, which are also present in the right atrial appendage
The atrium (; : atria) is one of the two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular mitral and tricuspid heart valves.
...
.trabeculae carneae
The trabeculae carneae (columnae carneae or meaty ridges) are rounded or irregular muscular columns which project from the inner surface of the right and left ventricle of the heart.Moore, K.L., & Agur, A.M. (2007). ''Essential Clinical Anatomy: ...
, ridges of cardiac muscle covered by endocardium. In addition to these muscular ridges, a band of cardiac muscle, also covered by endocardium, known as the moderator band reinforces the thin walls of the right ventricle and plays a crucial role in cardiac conduction. It arises from the lower part of the interventricular septum and crosses the interior space of the right ventricle to connect with the inferior papillary muscle.pulmonary trunk
A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the ''main pulmonary artery'' or ''pulmonary trunk'' from the heart, and t ...
, into which it ejects blood when contracting. The pulmonary trunk branches into the left and right pulmonary arteries that carry the blood to each lung. The pulmonary valve lies between the right heart and the pulmonary trunk.
Left heart
The left heart has two chambers: the left atrium and the left ventricle, separated by the mitral valve
The mitral valve ( ), also known as the bicuspid valve or left atrioventricular valve, is one of the four heart valves. It has two Cusps of heart valves, cusps or flaps and lies between the atrium (heart), left atrium and the ventricle (heart), ...
.pulmonary vein
The pulmonary veins are the veins that transfer Blood#Oxygen transport, oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. The largest pulmonary veins are the four ''main pulmonary veins'', two from each lung that drain into the left atrium of the h ...
s. The left atrium has an outpouching called the left atrial appendage
The atrium (; : atria) is one of the two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular mitral and tricuspid heart valves.
T ...
. Like the right atrium, the left atrium is lined by pectinate muscles
The pectinate muscles (musculi pectinati) are parallel muscular ridges in the walls of the atria of the heart.
Structure
Behind the crest (crista terminalis) of the right atrium the internal surface is smooth. Pectinate muscles make up the pa ...
. The left atrium is connected to the left ventricle by the mitral valve.trabeculae carneae
The trabeculae carneae (columnae carneae or meaty ridges) are rounded or irregular muscular columns which project from the inner surface of the right and left ventricle of the heart.Moore, K.L., & Agur, A.M. (2007). ''Essential Clinical Anatomy: ...
, but there is no moderator band. The left ventricle pumps blood to the body through the aortic valve and into the aorta. Two small openings above the aortic valve carry blood to the heart muscle
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle or myocardium) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, the others being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the wall of ...
; the left coronary artery
The left coronary artery (LCA, also known as the left main coronary artery, or left main stem coronary artery) is a coronary artery that arises from the aorta above the left cusp of the aortic valve, and supplies blood to the left side of the ...
is above the left cusp of the valve, and the right coronary artery
In the coronary circulation, blood supply of the heart, the right coronary artery (RCA) is an artery originating above the right cusp of the aortic valve, at the Aortic sinus, right aortic sinus in the heart. It travels down the right coronary su ...
is above the right cusp.
Wall
 The heart wall is made up of three layers: the inner
The heart wall is made up of three layers: the inner endocardium
The endocardium (: endocardia) is the innermost layer of tissue that lines the chambers of the heart. Its cells are embryologically and biologically similar to the endothelial cells that line blood vessels. The endocardium also provides prot ...
, middle myocardium
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle or myocardium) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, the others being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the wall o ...
and outer epicardium
The pericardium (: pericardia), also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong inelastic connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), a ...
. These are surrounded by a double-membraned sac called the pericardium.
The innermost layer of the heart is called the endocardium. It is made up of a lining of simple squamous epithelium
A simple squamous epithelium, also known as pavement epithelium and tessellated epithelium, is a single layer of flattened, polygonal cells in contact with the basal lamina (one of the two layers of the basement membrane) of the epithelium. This ...
and covers heart chambers and valves. It is continuous with the endothelium
The endothelium (: endothelia) is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the r ...
of the veins and arteries of the heart, and is joined to the myocardium with a thin layer of connective tissue.endothelins
Endothelins are peptides with receptors and effects in many body organs. Endothelin constricts blood vessels and raises blood pressure. The endothelins are normally kept in balance by other mechanisms, but when overexpressed, they contribute ...
, may also play a role in regulating the contraction of the myocardium.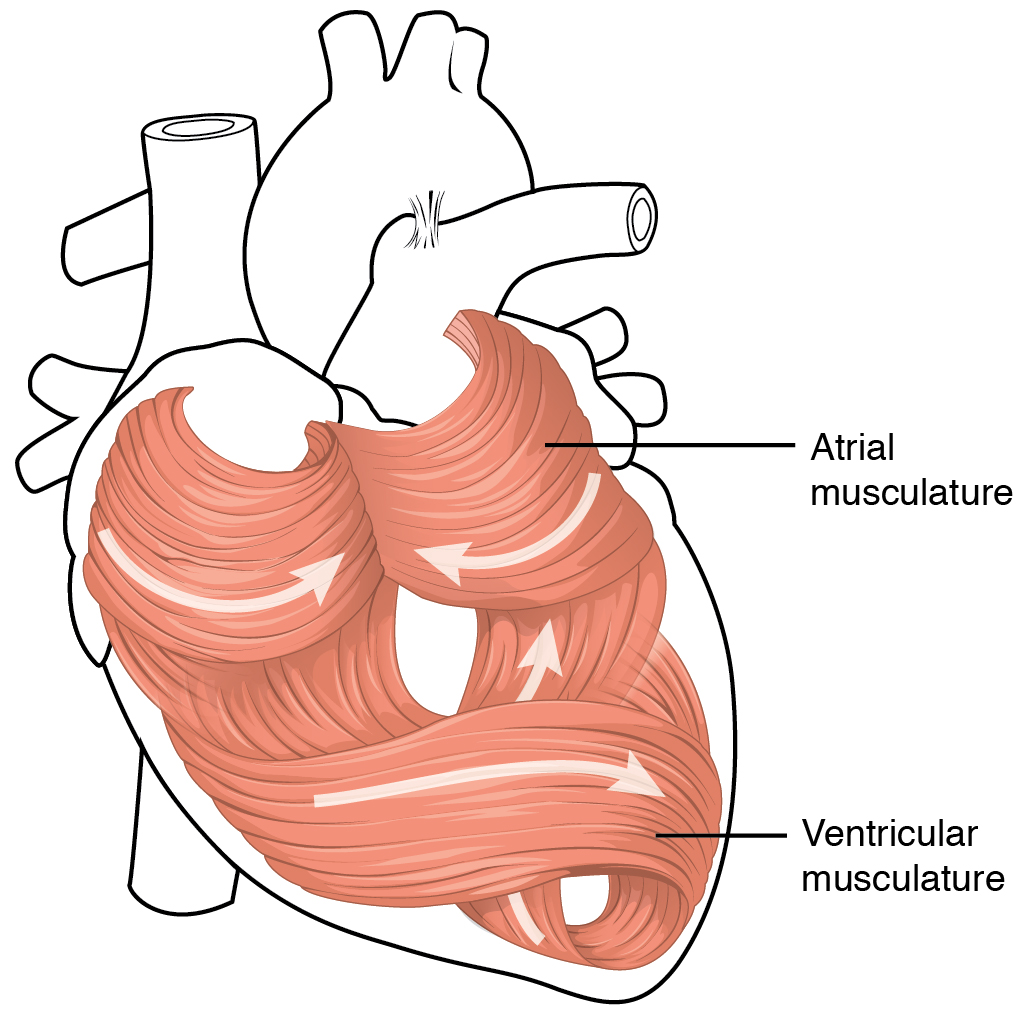 The middle layer of the heart wall is the myocardium, which is the
The middle layer of the heart wall is the myocardium, which is the cardiac muscle
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle or myocardium) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, the others being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the wall o ...
—a layer of involuntary striated muscle tissue
Striated muscle tissue is a muscle tissue that features repeating functional units called sarcomeres. Under the microscope, sarcomeres are visible along muscle fibers, giving a striated appearance to the tissue. The two types of striated muscle a ...
surrounded by a framework of collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix of the connective tissues of many animals. It is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up 25% to 35% of protein content. Amino acids are bound together to form a trip ...
. The cardiac muscle pattern is elegant and complex, as the muscle cells swirl and spiral around the chambers of the heart, with the outer muscles forming a figure 8 pattern around the atria and around the bases of the great vessels and the inner muscles, forming a figure 8 around the two ventricles and proceeding toward the apex. This complex swirling pattern allows the heart to pump blood more effectively.muscle cells
A muscle cell, also known as a myocyte, is a mature contractile cell in the muscle of an animal. In humans and other vertebrates there are three types: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac (cardiomyocytes). A skeletal muscle cell is long and threadli ...
which have the ability to contract easily, and pacemaker cells
350px, Image showing the cardiac pacemaker or SA node, the primary pacemaker within the electrical conduction system of the heart
The cardiac pacemaker is the heart's natural rhythm generator. It employs pacemaker Cell (biology), cells that ...
of the conducting system. The muscle cells make up the bulk (99%) of cells in the atria and ventricles. These contractile cells are connected by intercalated disc
Intercalated discs or lines of Eberth are microscopic identifying features of cardiac muscle. Cardiac muscle consists of individual heart muscle cells (cardiomyocytes) connected by intercalated discs to work as a single functional Syncytium#Cardia ...
s which allow a rapid response to impulses of action potential
An action potential (also known as a nerve impulse or "spike" when in a neuron) is a series of quick changes in voltage across a cell membrane. An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific Cell (biology), cell rapidly ri ...
from the pacemaker cells. The intercalated discs allow the cells to act as a syncytium
A syncytium (; : syncytia; from Greek: σύν ''syn'' "together" and κύτος ''kytos'' "box, i.e. cell") or symplasm is a multinucleate cell that can result from multiple cell fusions of uninuclear cells (i.e., cells with a single nucleus), i ...
and enable the contractions that pump blood through the heart and into the major arteries.myofibril
A myofibril (also known as a muscle fibril or sarcostyle) is a basic rod-like organelle of a muscle cell. Skeletal muscles are composed of long, tubular cells known as Skeletal muscle#Skeletal muscle cells, muscle fibers, and these cells contain ...
s which gives them limited contractibility. Their function is similar in many respects to neuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural net ...
s.autorhythmicity
Unlike the action potential in skeletal muscle, skeletal muscle cells, the cardiac action potential is not initiated by nervous activity. Instead, it arises from a group of specialized cells known as pacemaker cells, that have automatic action pot ...
, the unique ability to initiate a cardiac action potential at a fixed rate—spreading the impulse rapidly from cell to cell to trigger the contraction of the entire heart.actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of ...
, myosin
Myosins () are a Protein family, family of motor proteins (though most often protein complexes) best known for their roles in muscle contraction and in a wide range of other motility processes in eukaryotes. They are adenosine triphosphate, ATP- ...
, tropomyosin
Tropomyosin is a two-stranded alpha-helical, coiled coil protein found in many animal and fungal cells. In animals, it is an important component of the muscular system which works in conjunction with troponin to regulate muscle contraction. It ...
, and troponin
Troponin, or the troponin complex, is a complex of three regulatory proteins (troponin C, troponin I, and troponin T) that are integral to muscle contraction in skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle, but not smooth muscle. Measurements of cardiac-spe ...
. They include MYH6
Myosin heavy chain, α isoform (MHC-α) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MYH6'' gene. This isoform is distinct from the ventricular/slow myosin heavy chain isoform, MYH7, referred to as MHC-β. MHC-α isoform is expressed predomin ...
, ACTC1
ACTC1 encodes cardiac muscle alpha actin. This isoform differs from the alpha actin that is expressed in skeletal muscle, ACTA1. Alpha cardiac actin is the major protein of the thin filament in cardiac sarcomeres, which are responsible for muscle ...
, TNNI3
Troponin I, cardiac muscle is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TNNI3'' gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that ...
, CDH2
Cadherin-2 also known as Neural cadherin (N-cadherin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CDH2'' gene. CDH2 has also been designated as CD325 ( cluster of differentiation 325).
Cadherin-2 is a transmembrane protein expressed in mult ...
and PKP2
Plakophilin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PKP2'' gene. Plakophilin 2 is expressed in skin and cardiac muscle, where it functions to link cadherins to intermediate filaments in the cytoskeleton. In cardiac muscle, plakophilin- ...
. Other proteins expressed are MYH7
Myosin-7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MYH7'' gene.
It is the myosin heavy chain beta (MHC-β) isoform (slow twitch) expressed primarily in the heart, but also in skeletal muscles (type I fibers). This isoform is distinct from ...
and LDB3
LIM domain binding 3 (LDB3), also known as Z-band alternatively spliced PDZ-motif (ZASP), is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''LDB3'' gene. ZASP belongs to the Enigma subfamily of proteins and stabilizes the sarcomere (the basic units ...
that are also expressed in skeletal muscle.
Pericardium
The pericardium is the sac that surrounds the heart. The tough outer surface of the pericardium is called the fibrous membrane. This is lined by a double inner membrane called the serous membrane that produces pericardial fluid
Pericardial fluid is the serous fluid secreted by the Serous membrane, serous layer of the pericardium into the pericardial cavity. The pericardium consists of two layers, an outer fibrous layer and the inner serous layer. This serous layer has t ...
to lubricate the surface of the heart. The part of the serous membrane attached to the fibrous membrane is called the parietal pericardium, while the part of the serous membrane attached to the heart is known as the visceral pericardium. The pericardium is present in order to lubricate its movement against other structures within the chest, to keep the heart's position stabilised within the chest, and to protect the heart from infection.
Coronary circulation
 Heart tissue, like all cells in the body, needs to be supplied with
Heart tissue, like all cells in the body, needs to be supplied with oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
, nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
s and a way of removing metabolic waste
Metabolic wastes or excrements are substances left over from metabolic processes (such as cellular respiration) which cannot be used by the organism (they are surplus or toxic), and must therefore be excreted. This includes nitrogen compounds ...
s. This is achieved by the coronary circulation, which includes arteries
An artery () is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in ...
, vein
Veins () are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and feta ...
s, and lymphatic vessels
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph vessel ...
. Blood flow through the coronary vessels occurs in peaks and troughs relating to the heart muscle's relaxation or contraction.left main coronary artery
The left coronary artery (LCA, also known as the left main coronary artery, or left main stem coronary artery) is a coronary artery that arises from the aorta above the left cusp of the aortic valve, and supplies blood to the left side of the ...
and the right coronary artery
In the coronary circulation, blood supply of the heart, the right coronary artery (RCA) is an artery originating above the right cusp of the aortic valve, at the Aortic sinus, right aortic sinus in the heart. It travels down the right coronary su ...
. The left main coronary artery splits shortly after leaving the aorta into two vessels, the left anterior descending
The left anterior descending artery (LAD, or anterior descending branch), also called anterior interventricular artery (IVA, or anterior interventricular branch of left coronary artery) is a branch of the left coronary artery. It supplies the ante ...
and the left circumflex artery
The circumflex branch of left coronary artery (also known as the left circumflex artery or circumflex artery) is a branch of the left coronary artery. It winds around the left side of the heart along the atrioventricular groove (coronary sulc ...
. The left anterior descending artery supplies heart tissue and the front, outer side, and septum of the left ventricle. It does this by branching into smaller arteries—diagonal and septal branches. The left circumflex supplies the back and underneath of the left ventricle. The right coronary artery supplies the right atrium, right ventricle, and lower posterior sections of the left ventricle. The right coronary artery also supplies blood to the atrioventricular node (in about 90% of people) and the sinoatrial node (in about 60% of people). The right coronary artery runs in a groove at the back of the heart and the left anterior descending artery runs in a groove at the front. There is significant variation between people in the anatomy of the arteries that supply the heart. The arteries divide at their furthest reaches into smaller branches that join at the edges of each arterial distribution.coronary sinus
The coronary sinus () is the largest vein of the heart. It drains over half of the deoxygenated blood from the heart muscle into the right atrium. It begins on the backside of the heart, in between the left atrium, and left ventricle; it begi ...
is a large vein that drains into the right atrium, and receives most of the venous drainage of the heart. It receives blood from the great cardiac vein
The great cardiac vein (left coronary vein) is a vein of the heart. It begins at the apex of the heart and ascends along the anterior interventricular sulcus before joining the oblique vein of the left atrium to form the coronary sinus upon the p ...
(receiving the left atrium and both ventricles), the posterior cardiac vein
Posterior may refer to:
* Posterior (anatomy), the end of an organism opposite to anterior
** Buttocks, as a euphemism
* Posterior horn (disambiguation)
* Posterior probability
The posterior probability is a type of conditional probability that ...
(draining the back of the left ventricle), the middle cardiac vein
The middle cardiac vein commences at the apex of the heart. It passes posteriorly along the inferior interventricular sulcus to end at the coronary sinus near the sinus' termination.
Structure
Origin
The middle cardiac vein commences at the ...
(draining the bottom of the left and right ventricles), and small cardiac vein The small cardiac vein, also known as the right coronary vein, is a coronary vein that drains parts of the right atrium and right ventricle of the heart. Despite its size, it is one of the major drainage vessels for the heart.
Anatomy
Course
...
s. The anterior cardiac veins
The anterior cardiac veins (or anterior veins of right ventricle) are a variable number of small veins (usually 2-5) which drain blood from the anterior portion of the right ventricle into the right atrium.
Anatomy
The right marginal vein fr ...
drain the front of the right ventricle and drain directly into the right atrium.plexus
In anatomy, a plexus (from the Latin term for 'braid') is a branching network of blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, or nerves. The nerves are typically axons outside the central nervous system.
The standard plural form in English is plexuses. Al ...
es exist beneath each of the three layers of the heart. These networks collect into a main left and a main right trunk, which travel up the groove between the ventricles that exists on the heart's surface, receiving smaller vessels as they travel up. These vessels then travel into the atrioventricular groove, and receive a third vessel which drains the section of the left ventricle sitting on the diaphragm. The left vessel joins with this third vessel, and travels along the pulmonary artery and left atrium, ending in the inferior tracheobronchial node
The tracheobronchial lymph nodes are lymph nodes that are located around the division of trachea and main bronchi.
Structure
These lymph nodes form four main groups including paratracheal, tracheobronchial, bronchopulmonary and pulmonary nodes ...
. The right vessel travels along the right atrium and the part of the right ventricle sitting on the diaphragm. It usually then travels in front of the ascending aorta and then ends in a brachiocephalic node.
Nerve supply
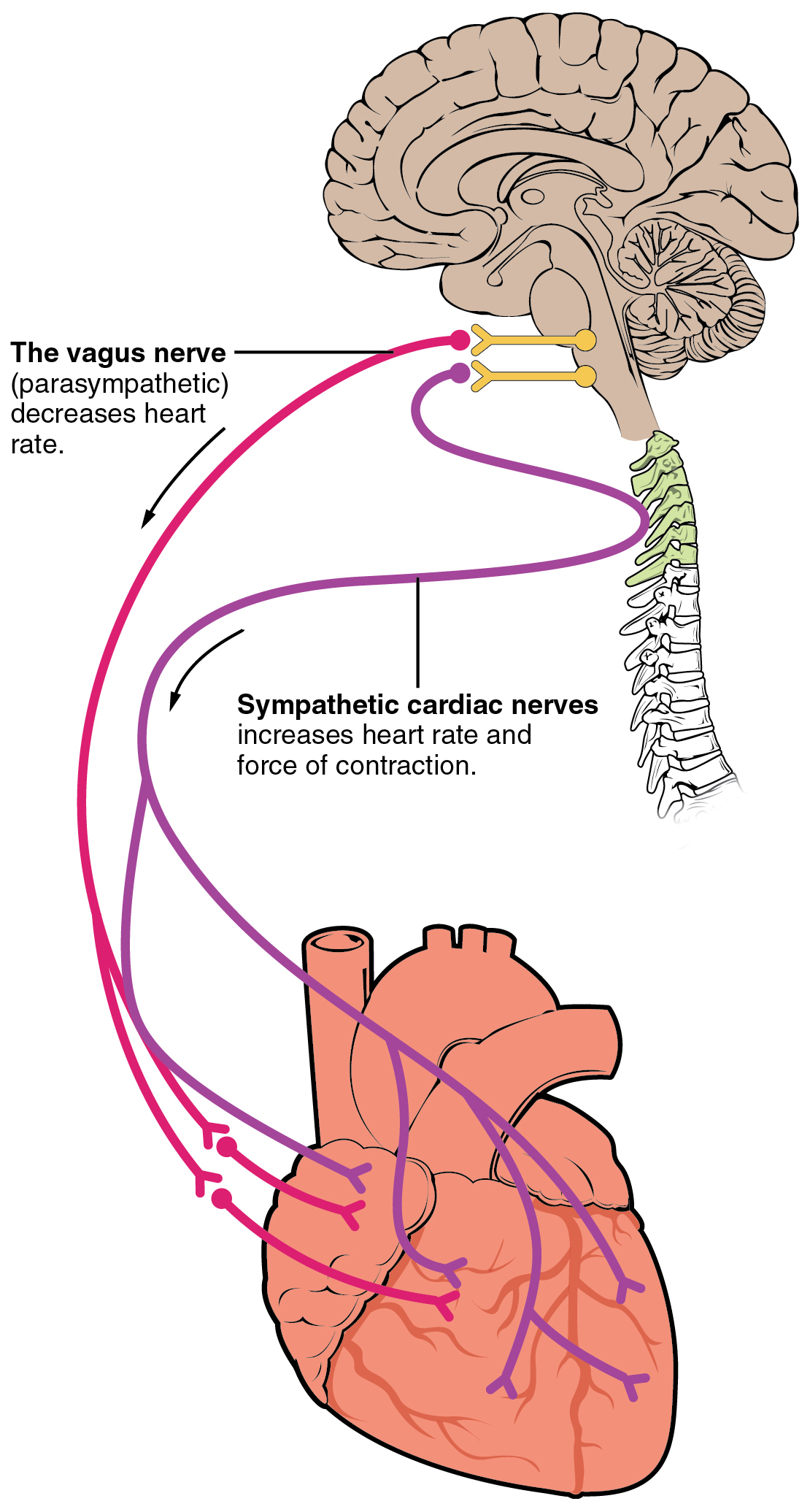 The heart receives nerve signals from the
The heart receives nerve signals from the vagus nerve
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve (CN X), plays a crucial role in the autonomic nervous system, which is responsible for regulating involuntary functions within the human body. This nerve carries both sensory and motor fibe ...
and from nerves arising from the sympathetic trunk
The sympathetic trunk (sympathetic chain, gangliated cord) is a paired bundle of nerve fibers that run from the base of the skull to the coccyx. It is a major component of the sympathetic nervous system.
Structure
The sympathetic trunk lies just ...
. These nerves act to influence, but not control, the heart rate. Sympathetic nerves
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS or SANS, sympathetic autonomic nervous system, to differentiate it from the somatic nervous system) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the parasympathetic nervous sy ...
also influence the force of heart contraction. Signals that travel along these nerves arise from two paired cardiovascular centres in the medulla oblongata
The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involun ...
. The vagus nerve of the parasympathetic nervous system
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system.
The autonomic nervous system is responsible for regulat ...
acts to decrease the heart rate, and nerves from the sympathetic trunk
The sympathetic trunk (sympathetic chain, gangliated cord) is a paired bundle of nerve fibers that run from the base of the skull to the coccyx. It is a major component of the sympathetic nervous system.
Structure
The sympathetic trunk lies just ...
act to increase the heart rate.cardiac plexus
The cardiac plexus is a plexus of nerves situated at the base of the heart that innervates the heart.
Structure
The cardiac plexus is divided into a superficial part, which lies in the concavity of the aortic arch, and a deep part, between the ao ...
.brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is conti ...
and provides parasympathetic stimulation to a large number of organs in the thorax and abdomen, including the heart. The nerves from the sympathetic trunk emerge through the T1–T4 thoracic ganglia
The thoracic ganglia are paravertebral ganglia. The thoracic portion of the sympathetic trunk typically has 12 thoracic ganglia. Emerging from the ganglia are thoracic splanchnic nerves (the cardiopulmonary, the greater, lesser, and least splanch ...
and travel to both the sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes, as well as to the atria and ventricles. The ventricles are more richly innervated by sympathetic fibers than parasympathetic fibers. Sympathetic stimulation causes the release of the neurotransmitter norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic compound, organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and human body, body as a hormone, neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. The ...
(also known as noradrenaline
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and body as a hormone, neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. The name "noradrenaline" (from ...
) at the neuromuscular junction
A neuromuscular junction (or myoneural junction) is a chemical synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber.
It allows the motor neuron to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.
Muscles require innervation to ...
of the cardiac nerves. This shortens the repolarisation period, thus speeding the rate of depolarisation and contraction, which results in an increased heart rate. It opens chemical or ligand-gated sodium and calcium ion channels, allowing an influx of positively charged ions.
Development
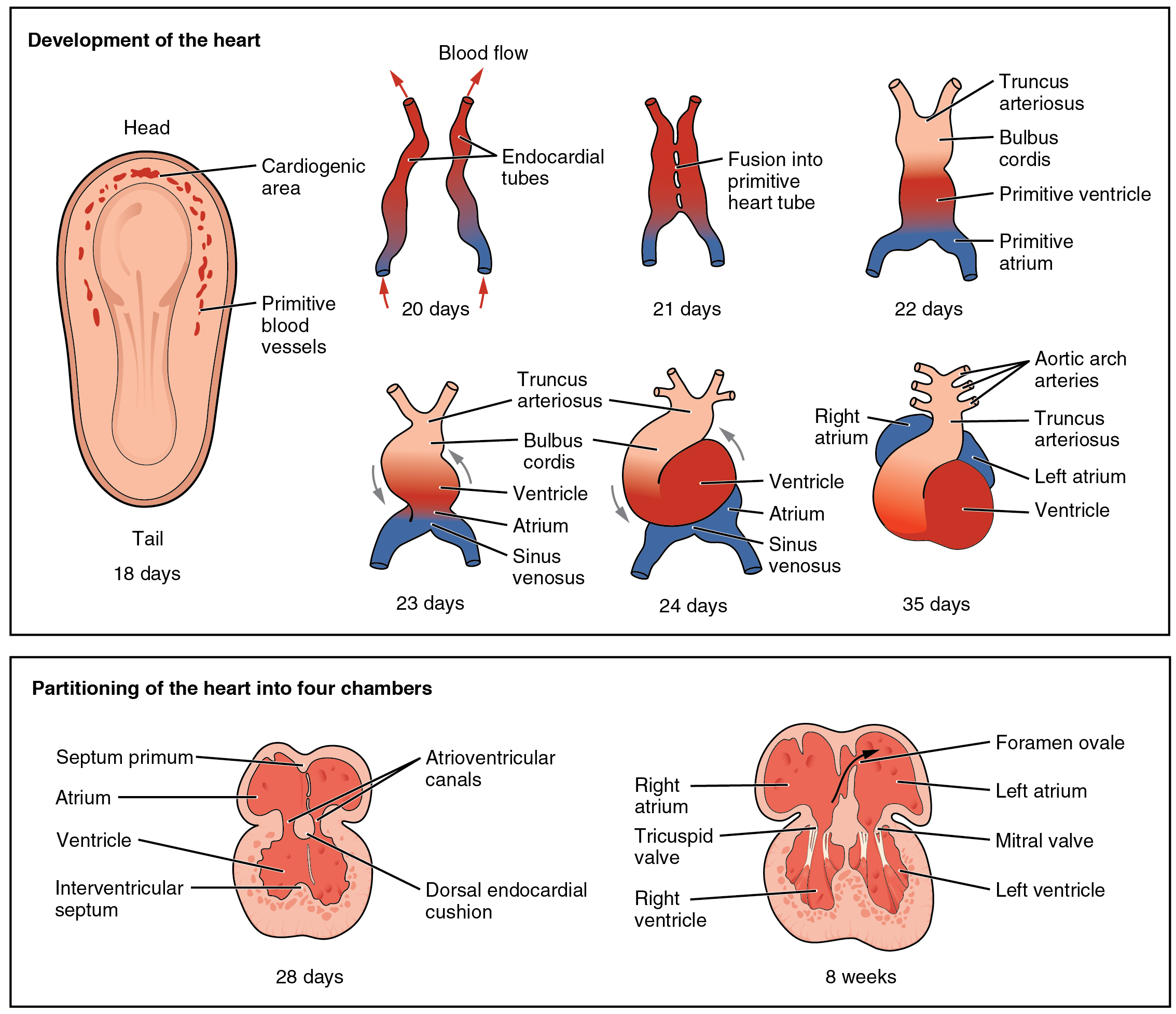 The heart is the first functional organ to develop and starts to beat and pump blood at about three weeks into
The heart is the first functional organ to develop and starts to beat and pump blood at about three weeks into embryogenesis
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male ...
. This early start is crucial for subsequent embryonic and prenatal development
Prenatal development () involves the development of the embryo and of the fetus during a viviparous animal's gestation. Prenatal development starts with fertilization, in the germinal stage of embryonic development, and continues in fetal de ...
.
The heart derives from splanchnopleuric mesenchyme
In the anatomy of an embryo, the splanchnopleuric mesenchyme is a structure created during embryogenesis when the lateral mesodermal germ layer splits into two layers. The inner (or splanchnic) layer adheres to the endoderm, and with it forms th ...
in the neural plate which forms the cardiogenic region
The heart is a muscular organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the tissue ...
. Two endocardial tubes The endocardial tubes are paired regions in the embryo that appear in its ventral pole by the middle of the third week of gestation and consist of precursor cells for the development of the embryonic heart. The endocardial heart tubes derive from t ...
form here that fuse to form a primitive heart tube known as the tubular heart
The tubular heart or primitive heart tube is the earliest stage of heart development. The heart is the first organ to develop during human embryonic development.
From the inflow to the outflow, the tubular heart consists of sinus venosus, primit ...
. Between the third and fourth week, the heart tube lengthens, and begins to fold to form an S-shape within the pericardium. This places the chambers and major vessels into the correct alignment for the developed heart. Further development will include the formation of the septa and the valves and the remodeling of the heart chambers. By the end of the fifth week, the septa are complete, and by the ninth week, the heart valves are complete.septum primum
During heart development of a human embryo, the single primitive atrium becomes divided into right and left by a , the septum primum. The septum primum () grows downward into the single atrium.
Development
The gap below it is known as the os ...
that previously acted as a valve closes the foramen ovale and establishes the typical cardiac circulation pattern. A depression in the surface of the right atrium remains where the foramen ovale was, called the fossa ovalis.embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sp ...
nic heart begins beating at around 22 days after conception (5 weeks after the last normal menstrual period, LMP). It starts to beat at a rate near to the mother's which is about 75–80 beats per minute
Beat, beats, or beating may refer to:
Common uses
* Assault, inflicting physical harm or unwanted physical contact
* Battery (crime), a criminal offense involving unlawful physical contact
* Battery (tort), a civil wrong in common law of in ...
(bpm). The embryonic heart rate then accelerates and reaches a peak rate of 165–185 bpm early in the early 7th week (early 9th week after the LMP).[DuBose, T.J. (1996) ''Fetal Sonography'', pp. 263–274; Philadelphia: WB Saunders ] After 9 weeks (start of the fetal
A fetus or foetus (; : fetuses, foetuses, rarely feti or foeti) is the unborn offspring of a viviparous animal that develops from an embryo. Following the embryonic stage, the fetal stage of development takes place. Prenatal development is a ...
stage) it starts to decelerate, slowing to around 145 (±25) bpm at birth. There is no difference in female and male heart rates before birth.
Physiology
Blood flow
 The heart functions as a pump in the
The heart functions as a pump in the circulatory system
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart ...
to provide a continuous flow of blood throughout the body. This circulation consists of the systemic circulation
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a organ system, system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of ...
to and from the body and the pulmonary circulation
The pulmonary circulation is a division of the circulatory system in all vertebrates. The circuit begins with deoxygenated blood returned from the body to the right atrium of the heart where it is pumped out from the right ventricle to the lun ...
to and from the lungs. Blood in the pulmonary circulation exchanges carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
for oxygen in the lungs through the process of respiration
Respiration may refer to:
Biology
* Cellular respiration, the process in which nutrients are converted into useful energy in a cell
** Anaerobic respiration, cellular respiration without oxygen
** Maintenance respiration, the amount of cellul ...
. The systemic circulation then transports oxygen to the body and returns carbon dioxide and relatively deoxygenated blood to the heart for transfer to the lungs.right heart
The heart is a muscular organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the tiss ...
collects deoxygenated blood from two large veins, the superior
Superior may refer to:
*Superior (hierarchy), something which is higher in a hierarchical structure of any kind
Places
* Superior (proposed U.S. state), an unsuccessful proposal for the Upper Peninsula of Michigan to form a separate state
*Lak ...
and inferior venae cavae
In anatomy, the ''venae cavae'' (; ''vena cava'' ; ) are two large veins (great vessels) that return deoxygenated blood from the body into the heart. In humans they are the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava, and both empty into the ...
. Blood collects in the right and left atrium continuously.diaphragm
Diaphragm may refer to:
Anatomy
* Thoracic diaphragm, a thin sheet of muscle between the thorax and the abdomen
* Pelvic diaphragm or pelvic floor, a pelvic structure
* Urogenital diaphragm or triangular ligament, a pelvic structure
Other
* Diap ...
and empties into the upper back part of the right atrium. The inferior vena cava drains the blood from below the diaphragm and empties into the back part of the atrium below the opening for the superior vena cava. Immediately above and to the middle of the opening of the inferior vena cava is the opening of the thin-walled coronary sinus.coronary sinus
The coronary sinus () is the largest vein of the heart. It drains over half of the deoxygenated blood from the heart muscle into the right atrium. It begins on the backside of the heart, in between the left atrium, and left ventricle; it begi ...
returns deoxygenated blood from the myocardium to the right atrium. The blood collects in the right atrium. When the right atrium contracts, the blood is pumped through the tricuspid valve
The tricuspid valve, or right atrioventricular valve, is on the right dorsal side of the mammalian heart, at the superior portion of the right ventricle. The function of the valve is to allow blood to flow from the right atrium to the right vent ...
into the right ventricle. As the right ventricle contracts, the tricuspid valve closes and the blood is pumped into the pulmonary trunk through the pulmonary valve. The pulmonary trunk divides into pulmonary arteries and progressively smaller arteries throughout the lungs, until it reaches capillaries
A capillary is a small blood vessel, from 5 to 10 micrometres in diameter, and is part of the microcirculation system. Capillaries are microvessels and the smallest blood vessels in the body. They are composed of only the tunica intima (the in ...
. As these pass by alveoli
Alveolus (; pl. alveoli, adj. alveolar) is a general anatomical term for a concave cavity or pit.
Uses in anatomy and zoology
* Pulmonary alveolus, an air sac in the lungs
** Alveolar cell or pneumocyte
** Alveolar duct
** Alveolar macrophage
* M ...
carbon dioxide is exchanged for oxygen. This happens through the passive process of diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical p ...
.
In the left heart
The heart is a muscular organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the tissue ...
, oxygenated blood is returned to the left atrium via the pulmonary veins. It is then pumped into the left ventricle through the mitral valve
The mitral valve ( ), also known as the bicuspid valve or left atrioventricular valve, is one of the four heart valves. It has two Cusps of heart valves, cusps or flaps and lies between the atrium (heart), left atrium and the ventricle (heart), ...
and into the aorta through the aortic valve for systemic circulation. The aorta is a large artery that branches into many smaller arteries, arteriole
An arteriole is a small-diameter blood vessel in the microcirculation that extends and branches out from an artery and leads to capillary, capillaries.
Arterioles have vascular smooth muscle, muscular walls (usually only one to two layers of smoo ...
s, and ultimately capillaries. In the capillaries, oxygen and nutrients from blood are supplied to body cells for metabolism, and exchanged for carbon dioxide and waste products.venule
A venule is a very small vein in the microcirculation that allows blood to return from the capillary beds to drain into the venous system via increasingly larger veins. Post-capillary venules are the smallest of the veins with a diameter of ...
s and veins that ultimately collect in the superior and inferior vena cavae, and into the right heart.
Cardiac cycle
 The cardiac cycle is the sequence of events in which the heart contracts and relaxes with every heartbeat. The period of time during which the ventricles contract, forcing blood out into the aorta and main pulmonary artery, is known as
The cardiac cycle is the sequence of events in which the heart contracts and relaxes with every heartbeat. The period of time during which the ventricles contract, forcing blood out into the aorta and main pulmonary artery, is known as systole
Systole ( ) is the part of the cardiac cycle during which some chambers of the heart contract after refilling with blood. Its contrasting phase is diastole, the relaxed phase of the cardiac cycle when the chambers of the heart are refilling ...
, while the period during which the ventricles relax and refill with blood is known as diastole
Diastole ( ) is the relaxed phase of the cardiac cycle when the chambers of the heart are refilling with blood. The contrasting phase is systole when the heart chambers are contracting. Atrial diastole is the relaxing of the atria, and ventricul ...
. The atria and ventricles work in concert, so in systole when the ventricles are contracting, the atria are relaxed and collecting blood. When the ventricles are relaxed in diastole, the atria contract to pump blood to the ventricles. This coordination ensures blood is pumped efficiently to the body.mitral
The mitral valve ( ), also known as the bicuspid valve or left atrioventricular valve, is one of the four heart valves. It has two Cusps of heart valves, cusps or flaps and lies between the atrium (heart), left atrium and the ventricle (heart), ...
and tricuspid
The tricuspid valve, or right atrioventricular valve, is on the right dorsal side of the mammalian heart, at the superior portion of the right ventricle. The function of the valve is to allow blood to flow from the right atrium to the right vent ...
valves. After the ventricles have completed most of their filling, the atria contract, forcing further blood into the ventricles and priming the pump. Next, the ventricles start to contract. As the pressure rises within the cavities of the ventricles, the mitral and tricuspid valves are forced shut. As the pressure within the ventricles rises further, exceeding the pressure with the aorta and pulmonary arteries, the aortic and pulmonary valves open. Blood is ejected from the heart, causing the pressure within the ventricles to fall. Simultaneously, the atria refill as blood flows into the right atrium through the superior and inferior vena cava
The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart. It is formed by the joining of the right and the left common iliac veins, usually at the level of the ...
e, and into the left atrium through the pulmonary veins. Finally, when the pressure within the ventricles falls below the pressure within the aorta and pulmonary arteries, the aortic and pulmonary valves close. The ventricles start to relax, the mitral and tricuspid valves open, and the cycle begins again.
Cardiac output
 Cardiac output (CO) is a measurement of the amount of blood pumped by each ventricle (stroke volume) in one minute. This is calculated by multiplying the stroke volume (SV) by the beats per minute of the heart rate (HR). So that: CO = SV x HR.
Cardiac output (CO) is a measurement of the amount of blood pumped by each ventricle (stroke volume) in one minute. This is calculated by multiplying the stroke volume (SV) by the beats per minute of the heart rate (HR). So that: CO = SV x HR.body surface area
In physiology and medicine, the body surface area (BSA) is the measured or calculated surface area of a human body. For many clinical purposes, BSA is a better indicator of metabolic mass than body weight because it is less affected by abnormal ad ...
and is called the cardiac index
The cardiac index (CI) is a hemodynamic measure that represents the cardiac output (CO) of an individual divided by their body surface area (BSA), expressed in liters per minute per square meter (L/min/m2). This parameter provides a more accurate ...
.
The average cardiac output, using an average stroke volume of about 70mL, is 5.25 L/min, with a normal range of 4.0–8.0 L/min.echocardiogram
Echocardiography, also known as cardiac ultrasound, is the use of ultrasound to examine the heart. It is a type of medical imaging, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound. The visual image formed using this technique is called an echo ...
and can be influenced by the size of the heart, physical and mental condition of the individual, sex
Sex is the biological trait that determines whether a sexually reproducing organism produces male or female gametes. During sexual reproduction, a male and a female gamete fuse to form a zygote, which develops into an offspring that inheri ...
, contractility
Contractility refers to the ability for self- contraction, especially of the muscles or similar active biological tissue
*Contractile ring in cytokinesis
*Contractile vacuole
*Muscle contraction
**Myocardial contractility
*See contractile cell fo ...
, duration of contraction, preload and afterload
Afterload is the pressure that the heart must work against to eject blood during systole (ventricular contraction). Afterload is proportional to the average arterial pressure. As aortic and pulmonary pressures increase, the afterload increases on ...
.Afterload
Afterload is the pressure that the heart must work against to eject blood during systole (ventricular contraction). Afterload is proportional to the average arterial pressure. As aortic and pulmonary pressures increase, the afterload increases on ...
, or how much pressure the heart must generate to eject blood at systole, is influenced by vascular resistance
Vascular resistance is the resistance that must be overcome for blood to flow through the circulatory system. The resistance offered by the systemic circulation is known as the systemic vascular resistance or may sometimes be called by another ter ...
. It can be influenced by narrowing of the heart valves (stenosis
Stenosis () is the abnormal narrowing of a blood vessel or other tubular organ or structure such as foramina and canals. It is also sometimes called a stricture (as in urethral stricture).
''Stricture'' as a term is usually used when narrowing ...
) or contraction or relaxation of the peripheral blood vessels.inotropes
An inotrope or inotropic is a drug or any substance that alters the force or energy of muscular contractions. Negatively inotropic agents weaken the force of muscular contractions. Positively inotropic agents increase the strength of muscular co ...
.life support
Life support comprises the treatments and techniques performed in an emergency in order to support life after the failure of one or more vital organs. Healthcare providers and emergency medical technicians are generally certified to perform bas ...
, particularly in intensive care unit
An intensive care unit (ICU), also known as an intensive therapy unit or intensive treatment unit (ITU) or critical care unit (CCU), is a special department of a hospital or health care facility that provides intensive care medicine.
An inten ...
s. Inotropes that increase the force of contraction are "positive" inotropes, and include sympathetic agents such as adrenaline
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
, noradrenaline
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and body as a hormone, neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. The name "noradrenaline" (from ...
and dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. It is an amine synthesized ...
.calcium channel blocker
Calcium channel blockers (CCB), calcium channel antagonists or calcium antagonists are a group of medications that disrupt the movement of calcium () through calcium channels. Calcium channel blockers are used as antihypertensive drugs, i.e., as ...
s.
Electrical conduction
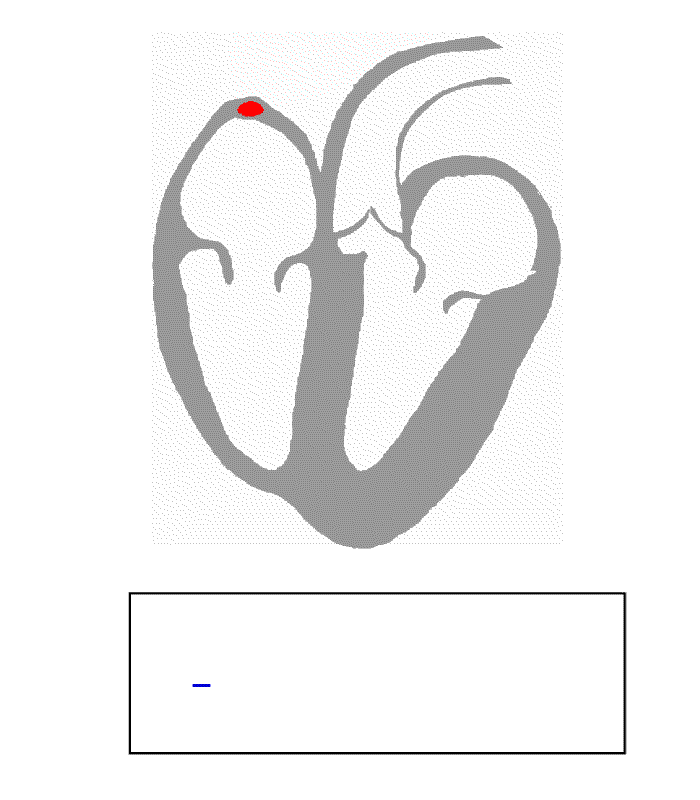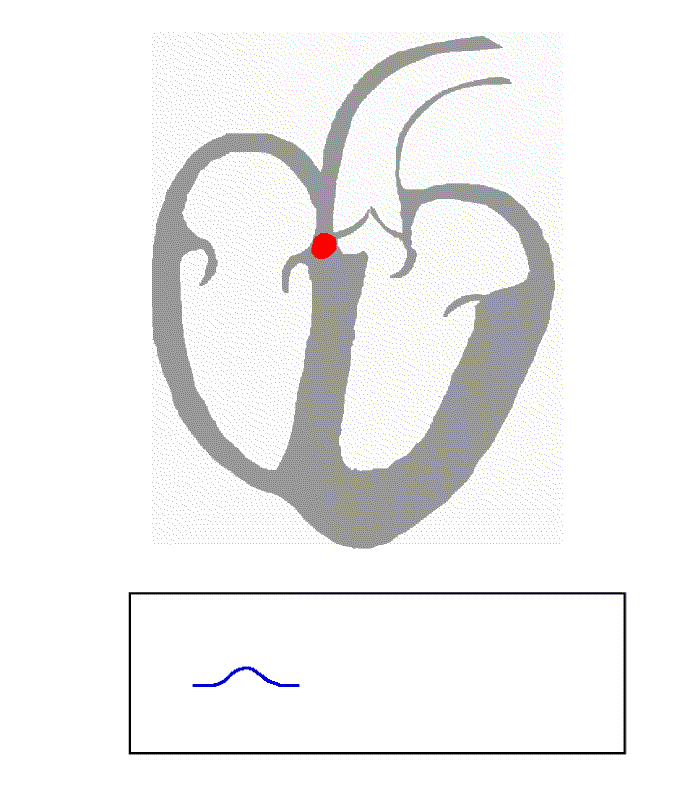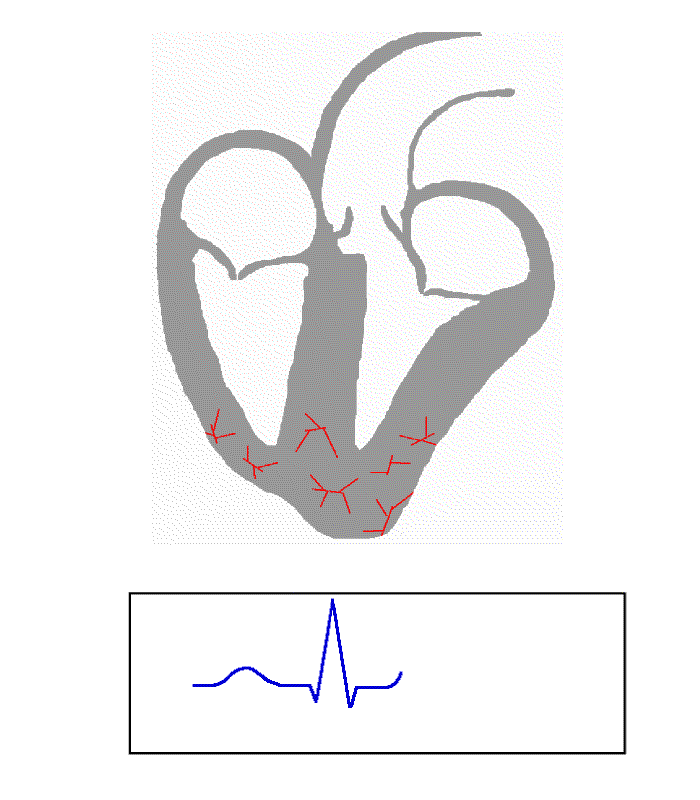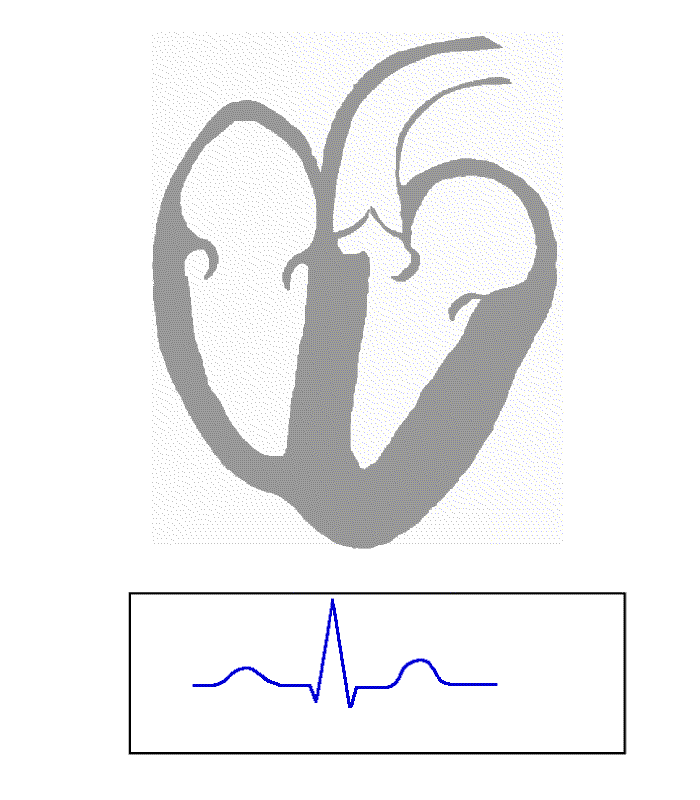 The normal rhythmical heart beat, called
The normal rhythmical heart beat, called sinus rhythm
A sinus rhythm is any cardiac rhythm in which depolarisation of the cardiac muscle begins at the sinus node. It is necessary, but not sufficient, for normal electrical activity within the heart. On the electrocardiogram (ECG), a sinus rhythm ...
, is established by the heart's own pacemaker, the sinoatrial node
The sinoatrial node (also known as the sinuatrial node, SA node, sinus node or Keith–Flack node) is an ellipse, oval shaped region of special cardiac muscle in the upper back wall of the right atrium made up of Cell (biology), cells known as pa ...
(also known as the sinus node or the SA node). Here an electrical signal is created that travels through the heart, causing the heart muscle to contract. The sinoatrial node is found in the upper part of the right atrium
The atrium (; : atria) is one of the two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular mitral and tricuspid heart valves.
...
near to the junction with the superior vena cava. The electrical signal generated by the sinoatrial node travels through the right atrium in a radial way that is not completely understood. It travels to the left atrium via Bachmann's bundle
In the heart's conduction system, Bachmann's bundle (also called the Bachmann bundle or the interatrial band) is a branch of the anterior internodal tract that resides on the inner wall of the left atrium. It is a broad band of cardiac muscle ...
, such that the muscles of the left and right atria contract together. The signal then travels to the atrioventricular node
The atrioventricular node (AV node, or Aschoff-Tawara node) electrically connects the heart's atria and ventricles to coordinate beating in the top of the heart; it is part of the electrical conduction system of the heart. The AV node lies at the ...
. This is found at the bottom of the right atrium in the atrioventricular septum, the boundary between the right atrium and the left ventricle. The septum is part of the cardiac skeleton
In cardiology, the cardiac skeleton, also known as the fibrous skeleton of the heart, is a high-density homogeneous structure of connective tissue that forms and anchors the valves of the heart, and influences the forces exerted by and through the ...
, tissue within the heart that the electrical signal cannot pass through, which forces the signal to pass through the atrioventricular node only.bundle of His
The bundle of His (BH) or His bundle (HB) ( "hiss"Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spiral bound Version'. Cengage Learning; 2016. . pp. 129–.) is a collection of heart muscle cells specialized for electrical conduction. As part of ...
to left and right bundle branches
The bundle branches, or Tawara branches, transmit cardiac action potentials (electrical signals) from the bundle of His to Purkinje fibers in heart ventricles. They are offshoots of the bundle of His and are important to the electrical conduc ...
through to the ventricles of the heart. In the ventricles the signal is carried by specialized tissue called the Purkinje fibers
The Purkinje fibers, named for Jan Evangelista Purkyně, ( ; ; Purkinje tissue or subendocardial branches) are located in the inner ventricular walls of the heart, just beneath the endocardium in a space called the subendocardium. The Purki ...
which then transmit the electric charge to the heart muscle.
275px, Conduction system of the heart
Heart rate
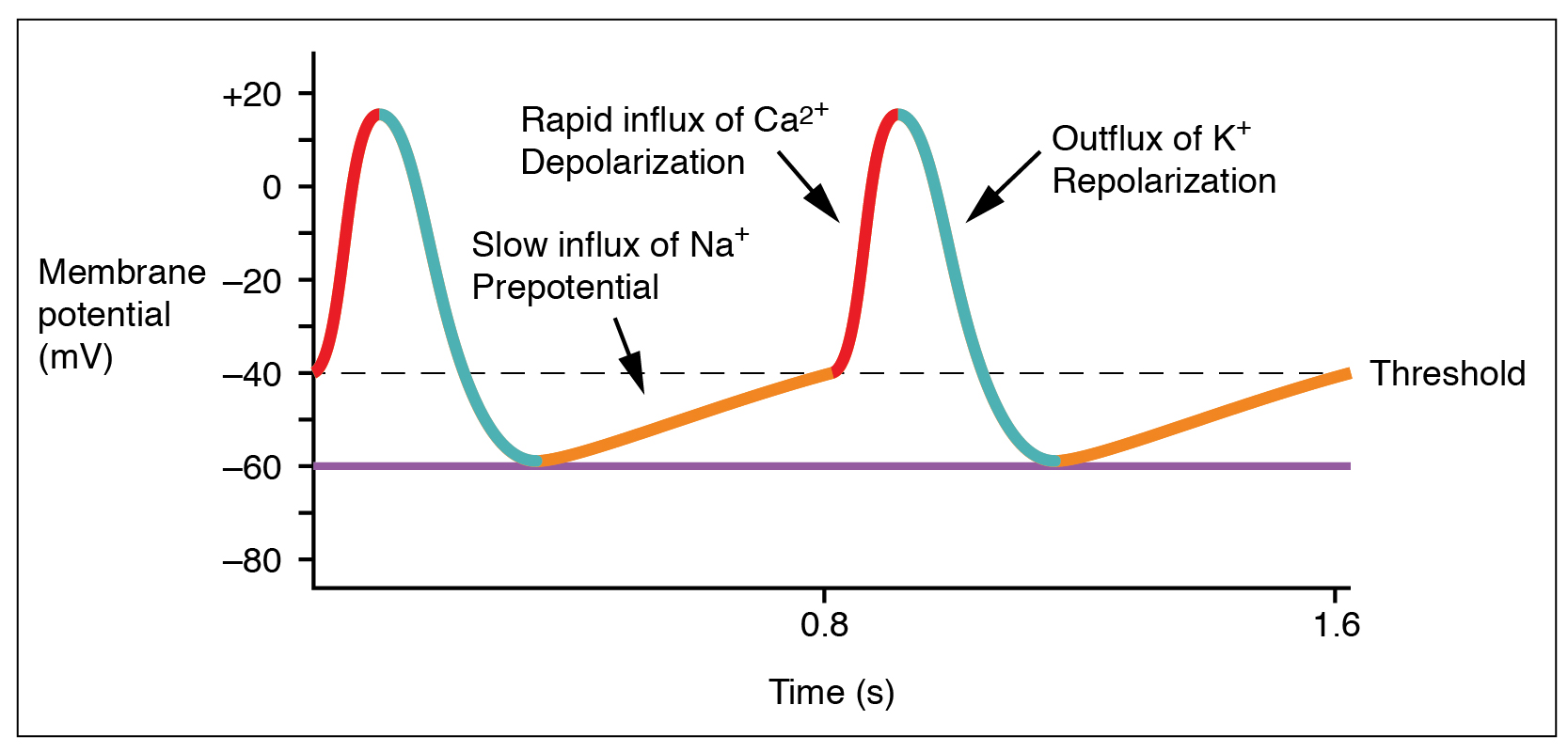 The normal
The normal resting heart rate
Heart rate is the frequency of the heartbeat measured by the number of contractions of the heart per minute (''beats per minute'', or bpm). The heart rate varies according to the body's physical needs, including the need to absorb oxygen and ...
is called the sinus rhythm
A sinus rhythm is any cardiac rhythm in which depolarisation of the cardiac muscle begins at the sinus node. It is necessary, but not sufficient, for normal electrical activity within the heart. On the electrocardiogram (ECG), a sinus rhythm ...
, created and sustained by the sinoatrial node
The sinoatrial node (also known as the sinuatrial node, SA node, sinus node or Keith–Flack node) is an ellipse, oval shaped region of special cardiac muscle in the upper back wall of the right atrium made up of Cell (biology), cells known as pa ...
, a group of pacemaking cells found in the wall of the right atrium. Cells in the sinoatrial node do this by creating an action potential
An action potential (also known as a nerve impulse or "spike" when in a neuron) is a series of quick changes in voltage across a cell membrane. An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific Cell (biology), cell rapidly ri ...
. The cardiac action potential
Unlike the action potential in skeletal muscle cells, the cardiac action potential is not initiated by nervous activity. Instead, it arises from a group of specialized cells known as pacemaker cells, that have automatic action potential generati ...
is created by the movement of specific electrolyte
An electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity through the movement of ions, but not through the movement of electrons. This includes most soluble Salt (chemistry), salts, acids, and Base (chemistry), bases, dissolved in a polar solven ...
s into and out of the pacemaker cells. The action potential then spreads to nearby cells.
When the sinoatrial cells are resting, they have a negative charge on their membranes. A rapid influx of sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the peri ...
ions causes the membrane's charge to become positive; this is called depolarisation
In biology, depolarization or hypopolarization is a change within a cell, during which the cell undergoes a shift in electric charge distribution, resulting in less negative charge inside the cell compared to the outside. Depolarization is esse ...
and occurs spontaneously.calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ...
ions then begin to enter the cell, shortly after which potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to ...
begins to leave it. All the ions travel through ion channels
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of ...
in the membrane of the sinoatrial cells. The potassium and calcium start to move out of and into the cell only once it has a sufficiently high charge, and so are called voltage-gated
Voltage-gated ion channels are a class of transmembrane proteins that form ion channels that are activated by changes in a cell's electrical membrane potential near the channel. The membrane potential alters the conformation of the channel prot ...
. Shortly after this, the calcium channels close and potassium channels
Potassium channels are the most widely distributed type of ion channel found in virtually all organisms. They form potassium-selective pores that span cell membranes. Potassium channels are found in most cell types and control a wide variety of ...
open, allowing potassium to leave the cell. This causes the cell to have a negative resting charge and is called repolarisation. When the membrane potential reaches approximately −60 mV, the potassium channels close and the process may begin again.troponin C
Troponin C is a protein which is part of the troponin complex. It contains four calcium-binding EF hands, although different isoforms may have fewer than four functional calcium-binding subdomains. It is a component of thin filaments, along ...
in the troponin complex
Troponin, or the troponin complex, is a complex of three regulatory proteins (troponin C, troponin I, and troponin T) that are integral to muscle contraction in skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle, but not smooth muscle. Measurements of cardiac-sp ...
to enable contraction
Contraction may refer to:
Linguistics
* Contraction (grammar), a shortened word
* Poetic contraction, omission of letters for poetic reasons
* Elision, omission of sounds
** Syncope (phonology), omission of sounds in a word
* Synalepha, merged ...
of the cardiac muscle, and separate from the protein to allow relaxation.newborn
In common terminology, a baby is the very young offspring of adult human beings, while infant (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'baby' or 'child') is a formal or specialised synonym. The terms may also be used to refer to Juvenile (orga ...
can be 129 beats per minute (bpm) and this gradually decreases until maturity. An athlete's heart rate can be lower than 60 bpm. During exercise the rate can be 150 bpm with maximum rates reaching from 200 to 220 bpm.
Influences
The normal sinus rhythm
A sinus rhythm is any cardiac rhythm in which depolarisation of the cardiac muscle begins at the sinus node. It is necessary, but not sufficient, for normal electrical activity within the heart. On the electrocardiogram (ECG), a sinus rhythm ...
of the heart, giving the resting heart rate, is influenced by a number of factors. The cardiovascular centres in the brainstem control the sympathetic and parasympathetic influences to the heart through the vagus nerve and sympathetic trunk.baroreceptor
Baroreceptors (or archaically, pressoreceptors) are stretch receptors that sense blood pressure. Thus, increases in the pressure of blood vessel triggers increased action potential generation rates and provides information to the central nervous s ...
s, sensing the stretching of blood vessels and chemoreceptor
A chemoreceptor, also known as chemosensor, is a specialized sensory receptor which transduces a chemical substance ( endogenous or induced) to generate a biological signal. This signal may be in the form of an action potential, if the chemorece ...
s, sensing the amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood and its pH. Through a series of reflexes these help regulate and sustain blood flow.aortic sinus
An aortic sinus, also known as a sinus of Valsalva, is one of the anatomic dilations of the ascending aorta, which occurs just above the aortic valve. These widenings are between the wall of the aorta and each of the three cusps of the aortic va ...
, carotid bodies
The carotid body is a small cluster of peripheral chemoreceptor cells and supporting sustentacular cells situated at the bifurcation of each common carotid artery in its tunica externa.
The carotid body detects changes in the composition of arte ...
, the venae cavae, and other locations, including pulmonary vessels and the right side of the heart itself. Baroreceptors fire at a rate determined by how much they are stretched, which is influenced by blood pressure, level of physical activity, and the relative distribution of blood. With increased pressure and stretch, the rate of baroreceptor firing increases, and the cardiac centers decrease sympathetic stimulation and increase parasympathetic stimulation. As pressure and stretch decrease, the rate of baroreceptor firing decreases, and the cardiac centers increase sympathetic stimulation and decrease parasympathetic stimulation.Bainbridge reflex
The Bainbridge reflex (or Bainbridge effect or atrial reflex) is a cardiovascular reflex causing an increase in heart rate in response to increased stretching of the wall of the right atrium and/or the inferior vena cava as a result of increased ...
, associated with varying rates of blood flow to the atria. Increased venous return stretches the walls of the atria where specialized baroreceptors are located. However, as the atrial baroreceptors increase their rate of firing and as they stretch due to the increased blood pressure, the cardiac center responds by increasing sympathetic stimulation and inhibiting parasympathetic stimulation to increase heart rate. The opposite is also true.basal metabolic rate
Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest.. In other words it is the energy required by body organs to perform normal It is reported in energy units per unit time ranging from watt ( ...
, and even a person's emotional state can all affect the heart rate. High levels of the hormones epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
, norepinephrine, and thyroid hormone
File:Thyroid_system.svg, upright=1.5, The thyroid system of the thyroid hormones triiodothyronine, T3 and T4
rect 376 268 820 433 Thyroid-stimulating hormone
rect 411 200 849 266 Thyrotropin-releasing hormone
rect 297 168 502 200 Hypothalamus
r ...
s can increase the heart rate. The levels of electrolytes including calcium, potassium, and sodium can also influence the speed and regularity of the heart rate; low blood oxygen, low blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of Circulatory system, circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term ...
and dehydration
In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water that disrupts metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds intake, often resulting from excessive sweating, health conditions, or inadequate consumption of water. Mild deh ...
may increase it.
Clinical significance
Diseases
Cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina, heart attack), heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumati ...
s, which include diseases of the heart, are the leading cause of death worldwide.high-income countries
A high-income economy is defined by the World Bank as a country with a gross national income per capita of US$14,005 or more in 2023, calculated using the Atlas method. While the term "high-income" is often used interchangeably with "First World" ...
.cardiologist
Cardiology () is the study of the heart. Cardiology is a branch of medicine that deals with disorders of the heart and the cardiovascular system. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery di ...
s. Many other medical professionals are involved in treating diseases of the heart, including doctors
Doctor, Doctors, The Doctor or The Doctors may refer to:
Titles and occupations
* Physician, a medical practitioner
* Doctor (title), an academic title for the holder of a doctoral-level degree
** Doctorate
** List of doctoral degrees awarded b ...
, cardiothoracic surgeons, intensivist
An intensivist, also known as a critical care doctor, is a medical practitioner who specializes in the care of critically ill patients, most often in the intensive care unit (ICU). Intensivists can be internists or internal medicine sub-special ...
s, and allied health practitioners including physiotherapist
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is a healthcare profession, as well as the care provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through patient education, physical intervention, disease preventio ...
s and dietician
A dietitian, medical dietitian, or dietician is an expert in identifying and treating disease-related malnutrition and in conducting medical nutrition therapy, for example designing an enteral tube feeding regimen or mitigating the effects of ...
s.
Ischemic heart disease
Coronary artery disease, also known as ischemic heart disease, is caused by atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis, characterized by development of abnormalities called lesions in walls of arteries. This is a chronic inflammatory disease involving many different cell types and is driven by eleva ...
—a build-up of fatty material along the inner walls of the arteries. These fatty deposits known as atherosclerotic plaques narrow the coronary arteries, and if severe may reduce blood flow to the heart.angina
Angina, also known as angina pectoris, is chest pain or pressure, usually caused by insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle (myocardium). It is most commonly a symptom of coronary artery disease.
Angina is typically the result of parti ...
) or breathlessness during exercise or even at rest. The thin covering of an atherosclerotic plaque can rupture, exposing the fatty centre to the circulating blood. In this case a clot or thrombus can form, blocking the artery, and restricting blood flow to an area of heart muscle causing a myocardial infarction (a heart attack) or unstable angina
In dynamical systems instability means that some of the outputs or internal states increase with time, without bounds. Not all systems that are not stable are unstable; systems can also be marginally stable or exhibit limit cycle behavior ...
. In the worst case this may cause cardiac arrest
Cardiac arrest (also known as sudden cardiac arrest CA is when the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating. When the heart stops beating, blood cannot properly Circulatory system, circulate around the body and the blood flow to the ...
, a sudden and utter loss of output from the heart. Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi ...
, high blood pressure
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms itself. It is, however, a major ri ...
, uncontrolled diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
, smoking and high cholesterol
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body Tissue (biology), tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in Animal fat, animal fats and oils.
Cholesterol is biosynthesis, biosynthesized by all anima ...
can all increase the risk of developing atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease.
Heart failure
Heart failure is defined as a condition in which the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the demands of the body.heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome caused by an impairment in the heart's ability to Cardiac cycle, fill with and pump blood.
Although symptoms vary based on which side of the heart is affected, HF ...
may experience breathlessness especially when lying flat, as well as ankle swelling, known as peripheral oedema
Peripheral edema is edema (accumulation of fluid causing swelling) in tissues perfused by the peripheral vascular system, usually in the lower limbs. In the most dependent parts of the body (those hanging distally), it may be called dependent ede ...
. Heart failure is the result of many diseases affecting the heart, but is most commonly associated with ischemic heart disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), or ischemic heart disease (IHD), is a type of heart disease involving the reduction of blood flow to the cardiac muscle due to a build-up of atheromatous plaque in the ...
, valvular heart disease
Valvular heart disease is any cardiovascular disease process involving one or more of the four valves of the heart (the aortic and mitral valves on the left side of heart and the pulmonic and tricuspid valves on the right side of heart). The ...
, or high blood pressure. Less common causes include various cardiomyopathies
Cardiomyopathy is a group of primary diseases of the heart muscle. Early on there may be few or no symptoms. As the disease worsens, shortness of breath, feeling tired, and swelling of the legs may occur, due to the onset of heart failure. An ...
. Heart failure is frequently associated with weakness of the heart muscle in the ventricles (systolic heart failure), but can also be seen in patients with heart muscle that is strong but stiff (diastolic heart failure). The condition may affect the left ventricle (causing predominantly breathlessness), the right ventricle (causing predominantly swelling of the legs and an elevated jugular venous pressure
The jugular venous pressure (JVP, sometimes referred to as ''jugular venous pulse'') is the indirectly observed pressure over the venous system via visualization of the internal jugular vein. It can be useful in the differentiation of different f ...
), or both ventricles. Patients with heart failure are at higher risk of developing dangerous heart rhythm disturbances or arrhythmias
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. Essentially, this is anything but normal sinus rhythm. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats ...
.
Cardiomyopathies
Cardiomyopathies are diseases affecting the muscle of the heart. Some cause abnormal thickening of the heart muscle (hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM, or HOCM when obstructive) is a condition in which muscle tissues of the heart become thickened without an obvious cause. The parts of the heart most commonly affected are the interventricular septum and the ...
), some cause the heart to abnormally expand and weaken (dilated cardiomyopathy
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a condition in which the heart becomes enlarged and cannot pump blood effectively. Symptoms vary from none to feeling tired, leg swelling, and shortness of breath. It may also result in chest pain or fainting. C ...
), some cause the heart muscle to become stiff and unable to fully relax between contractions (restrictive cardiomyopathy
Restrictive cardiomyopathy (RCM) is a form of cardiomyopathy in which the walls of the heart are rigid (but not thickened). Thus the heart is restricted from stretching and filling with blood properly. It is the least common of the three original s ...
) and some make the heart prone to abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy
Arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy (ACM) is an inherited heart disease.
ACM is caused by genetic defects of parts of the cardiac muscle known as desmosomes, areas on the surface of muscle cells which link them together. The desmosomes are composed ...
). These conditions are often genetic and can be inherited, but some such as dilated cardiomyopathy may be caused by damage from toxins such as alcohol. Some cardiomyopathies such as hypertrophic cardiomopathy are linked to a higher risk of sudden cardiac death, particularly in athletes.
Valvular heart disease
Healthy heart valves allow blood to flow easily in one direction, and prevent it from flowing in the other direction. A diseased heart valve may have a narrow opening (stenosis
Stenosis () is the abnormal narrowing of a blood vessel or other tubular organ or structure such as foramina and canals. It is also sometimes called a stricture (as in urethral stricture).
''Stricture'' as a term is usually used when narrowing ...
), that restricts the flow of blood in the forward direction. A valve may otherwise be leaky, allowing blood to leak in the reverse direction ( regurgitation). Valvular heart disease may cause breathlessness, blackouts, or chest pain, but may be asymptomatic and only detected on a routine examination by hearing abnormal heart sounds or a heart murmur
Heart murmurs are unique heart sounds produced when blood flows across a heart valve or blood vessel. This occurs when turbulent blood flow creates a sound loud enough to hear with a stethoscope. The sound differs from normal heart sounds by th ...
. In the developed world, valvular heart disease is most commonly caused by degeneration secondary to old age, but may also be caused by infection of the heart valves (endocarditis
Endocarditis is an inflammation of the inner layer of the heart, the endocardium. It usually involves the heart valves. Other structures that may be involved include the interventricular septum, the chordae tendineae, the mural endocardium, o ...
). In some parts of the world rheumatic heart disease
Valvular heart disease is any cardiovascular disease process involving one or more of the four valves of the heart (the aortic and mitral valves on the left side of heart and the pulmonic and tricuspid valves on the right side of heart). The ...
is a major cause of valvular heart disease, typically leading to mitral or aortic stenosis and caused by the body's immune system reacting to a streptococcal
''Streptococcus'' is a genus of gram-positive spherical bacteria that belongs to the family Streptococcaceae, within the order Lactobacillales (lactic acid bacteria), in the phylum Bacillota. Cell division in streptococci occurs along a single ...
throat infection.
Cardiac arrhythmias
While in the healthy heart, waves of electrical impulses originate in the sinus node
The sinoatrial node (also known as the sinuatrial node, SA node, sinus node or Keith–Flack node) is an oval shaped region of special cardiac muscle in the upper back wall of the right atrium made up of cells known as pacemaker cells. The sin ...
before spreading to the rest of the atria, the atrioventricular node
The atrioventricular node (AV node, or Aschoff-Tawara node) electrically connects the heart's atria and ventricles to coordinate beating in the top of the heart; it is part of the electrical conduction system of the heart. The AV node lies at the ...
, and finally the ventricles (referred to as a normal sinus rhythm
A sinus rhythm is any cardiac rhythm in which depolarisation of the cardiac muscle begins at the sinus node. It is necessary, but not sufficient, for normal electrical activity within the heart. On the electrocardiogram (ECG), a sinus rhythm ...
), this normal rhythm can be disrupted. Abnormal heart rhythms or arrhythmias may be asymptomatic or may cause palpitations, blackouts, or breathlessness. Some types of arrhythmia such as atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (AF, AFib or A-fib) is an Heart arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia) characterized by fibrillation, rapid and irregular beating of the Atrium (heart), atrial chambers of the heart. It often begins as short periods ...
increase the long term risk of stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemor ...
.bradycardia
Bradycardia, also called bradyarrhythmia, is a resting heart rate under 60 beats per minute (BPM). While bradycardia can result from various pathological processes, it is commonly a physiological response to cardiovascular conditioning or due ...
or bradyarrhythmia. This may be caused by an abnormally slow sinus node or damage within the cardiac conduction system (heart block
Heart block (HB) is a disorder in the heart's rhythm due to a fault in the natural pacemaker. This is caused by an obstruction – a block – in the electrical conduction system of the heart. Sometimes a disorder can be inherited. Despite the ...
).tachycardia
Tachycardia, also called tachyarrhythmia, is a heart rate that exceeds the normal resting rate. In general, a resting heart rate over 100 beats per minute is accepted as tachycardia in adults. Heart rates above the resting rate may be normal ...
or tachyarrhythmia. These arrhythmias can take many forms and can originate from different structures within the heart—some arise from the atria (e.g. atrial flutter
Atrial flutter (AFL) is a common abnormal heart rhythm that starts in the atrial chambers of the heart. When it first occurs, it is usually associated with a fast heart rate and is classified as a type of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT). ...
), some from the atrioventricular node (e.g. AV nodal re-entrant tachycardia) whilst others arise from the ventricles (e.g. ventricular tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia (V-tach or VT) is a cardiovascular disorder in which fast heart rate occurs in the ventricles of the heart. Although a few seconds of VT may not result in permanent problems, longer periods are dangerous; and multiple ...
). Some tachyarrhythmias are caused by scarring within the heart (e.g. some forms of ventricular tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia (V-tach or VT) is a cardiovascular disorder in which fast heart rate occurs in the ventricles of the heart. Although a few seconds of VT may not result in permanent problems, longer periods are dangerous; and multiple ...
), others by an irritable focus (e.g. focal atrial tachycardia
Atrial tachycardia is a type of heart rhythm problem in which the heart's electrical impulse comes from an ectopic pacemaker (that is, an abnormally located cardiac pacemaker) in the upper chambers ( atria) of the heart, rather than from the sin ...
), while others are caused by additional abnormal conduction tissue that has been present since birth (e.g. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome). The most dangerous form of heart racing is ventricular fibrillation
Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib or VF) is an abnormal heart rhythm in which the Ventricle (heart), ventricles of the heart Fibrillation, quiver. It is due to disorganized electrical conduction system of the heart, electrical activity. Ventricula ...
, in which the ventricles quiver rather than contract, and which if untreated is rapidly fatal.
Pericardial disease
The sac which surrounds the heart, called the pericardium, can become inflamed in a condition known as pericarditis
Pericarditis () is inflammation of the pericardium, the fibrous sac surrounding the heart. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp chest pain, which may also be felt in the shoulders, neck, or back. The pain is typically less severe whe ...
. This condition typically causes chest pain that may spread to the back, and is often caused by a viral infection (glandular fever
A gland is a cell or an organ in an animal's body that produces and secretes different substances that the organism needs, either into the bloodstream or into a body cavity or outer surface. A gland may also function to remove unwanted substances ...
, cytomegalovirus
''Cytomegalovirus'' (CMV) (from ''cyto-'' 'cell' via Greek - 'container' + 'big, megalo-' + -''virus'' via Latin 'poison') is a genus of viruses in the order '' Herpesvirales'', in the family '' Herpesviridae'', in the subfamily '' Betaherp ...
, or coxsackievirus
Coxsackieviruses are a few related enteroviruses that belong to the ''Picornaviridae'' family of viral envelope, nonenveloped, linear, positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses, as well as its genus ''Enterovirus'', which also includes poliovi ...
). Fluid can build up within the pericardial sac, referred to as a pericardial effusion
A pericardial effusion is an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pericardial cavity. The pericardium is a two-part membrane surrounding the heart: the outer fibrous Connective tissue, connective membrane and an inner two-layered serous membrane ...
. Pericardial effusions often occur secondary to pericarditis, kidney failure, or tumours, and frequently do not cause any symptoms. However, large effusions or effusions which accumulate rapidly can compress the heart in a condition known as cardiac tamponade
Cardiac tamponade, also known as pericardial tamponade (), is a compression of the heart due to pericardial effusion (the build-up of pericardial fluid in the pericardium, sac around the heart). Onset may be rapid or gradual. Symptoms typically i ...
, causing breathlessness and potentially fatal low blood pressure. Fluid can be removed from the pericardial space for diagnosis or to relieve tamponade using a syringe in a procedure called pericardiocentesis
Pericardiocentesis (PCC), also called pericardial tap, is a medical procedure where fluid is aspirated from the pericardium (the sac enveloping the heart).
Anatomy and physiology
The pericardium is a fibrous sac surrounding the heart composed o ...
.
Congenital heart disease
Some people are born with hearts that are abnormal and these abnormalities are known as congenital heart defects. They may range from the relatively minor (e.g. patent foramen ovale
Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a congenital heart defect in which blood flows between the atria (upper chambers) of the heart. Some flow is a normal condition both pre-birth and immediately post-birth via the foramen ovale; however, when this d ...
, arguably a variant of normal) to serious life-threatening abnormalities (e.g. hypoplastic left heart syndrome
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) is a rare congenital heart defect in which the left side of the heart is severely underdeveloped and incapable of supporting the systemic circulation. It is estimated to account for 2-3% of all congenital hea ...
). Common abnormalities include those that affect the heart muscle that separates the two side of the heart (a "hole in the heart", e.g. ventricular septal defect
A ventricular septal defect (VSD) is a defect in the ventricular septum, the wall dividing the left and right ventricles of the heart. It's a common heart problem present at birth ( congenital heart defect). The extent of the opening may vary ...
). Other defects include those affecting the heart valves (e.g. congenital aortic stenosis), or the main blood vessels that lead from the heart (e.g. coarctation of the aorta
Coarctation of the aorta (CoA) is a congenital condition whereby the aorta is narrow, usually in the area where the ductus arteriosus ( ligamentum arteriosum after regression) inserts. The word ''coarctation'' means "pressing or drawing toget ...
). More complex syndromes are seen that affect more than one part of the heart (e.g. Tetralogy of Fallot
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF), formerly known as Steno-Fallot tetralogy, is a congenital heart defect characterized by four specific cardiac defects. Classically, the four defects are:
* Pulmonary stenosis, which is narrowing of the exit from the r ...
).
Some congenital heart defects allow blood that is low in oxygen that would normally be returned to the lungs to instead be pumped back to the rest of the body. These are known as cyanotic congenital heart defects and are often more serious. Major congenital heart defects are often picked up in childhood, shortly after birth, or even before a child is born (e.g. transposition of the great arteries
Transposition of the great vessels (TGV) is a group of congenital heart defects involving an abnormal spatial arrangement of any of the great vessels: superior and/or inferior venae cavae, pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins, and aorta. Congenit ...
), causing breathlessness and a lower rate of growth. More minor forms of congenital heart disease may remain undetected for many years and only reveal themselves in adult life (e.g., atrial septal defect
Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a congenital heart defect in which blood flows between the atrium (heart), atria (upper chambers) of the heart. Some flow is a normal condition both pre-birth and immediately post-birth via the Foramen ovale (heart) ...
).
Channelopathies
Channelopathies
Channelopathies are a group of diseases caused by the dysfunction of ion channel subunits or their interacting proteins. These diseases can be inherited or acquired by other disorders, drugs, or toxins. Mutations in genes encoding ion channels, wh ...
can be categorized based on the organ system they affect. In the cardiovascular system, the electrical impulse required for each heart beat is provided by the electrochemical gradient
An electrochemical gradient is a gradient of electrochemical potential, usually for an ion that can move across a membrane. The gradient consists of two parts:
* The chemical gradient, or difference in Concentration, solute concentration across ...
of each heart cell. Because the beating of the heart depends on the proper movement of ions across the surface membrane, cardiac ion channelopathies form a major group of heart diseases. Cardiac ion channelopathies may explain some of the cases of sudden death syndrome
Sudden death syndrome (SDS), a disease in soybean plants, quickly spread across the southern United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North Ameri ...
and sudden arrhythmic death syndrome
Sudden arrhythmic death syndrome (SADS) is a sudden unexpected death of adolescents and adults caused by a cardiac arrest. However, the exact cause of the cardiac arrest, and thus the exact cause of death, is unknown. These deaths occur mainly ...
.Long QT syndrome
Long QT syndrome (LQTS) is a condition affecting repolarization (relaxing) of the heart after a heartbeat, giving rise to an abnormally lengthy QT interval. It results in an increased risk of an irregular heartbeat which can result in fainti ...
(LQTS) – Mostly hereditary. On EKG can be observed as longer corrected QT interval (QTc). Characterized by fainting, sudden, life-threatening heart rhythm disturbances – Torsades de pointes
''Torsades de pointes, torsade de pointes'' or ''torsades des pointes'' (TdP; also called ''torsades'') (, , translated as "twisting of peaks") is a specific type of abnormal heart rhythm that can lead to sudden cardiac death. It is a polymorph ...
type ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation and risk of sudden cardiac death.
* Short QT syndrome
Short QT syndrome (SQT) is a very rare genetics, genetic disease of the electrical system of the heart, and is associated with an increased risk of Heart arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythms and sudden cardiac death. The syndrome gets its name from ...
.
* Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia
Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT) is an inherited genetic disorder that predisposes those affected to potentially life-threatening abnormal heart rhythms or arrhythmias. The arrhythmias seen in CPVT typically occur du ...
(CPVT).
* Progressive cardiac conduction defect
Progressive cardiac conduction defect (PCCD) is a hereditary cardiac condition marked by a progressive delay in impulse conduction via the His-Purkinje system, resulting in right or left bundle branch block (RBBB or LBBB), syncope, and occasional ...
(PCCD).
* Early repolarisation syndrome (BER) – common in younger and active people, especially men, because it is affected by higher testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting se ...
levels, which cause increased potassium currents, which further causes an elevation of the J-point
The QRS complex is the combination of three of the graphical deflections seen on a typical electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). It is usually the central and most visually obvious part of the tracing. It corresponds to the depolarization of the ri ...
on the EKG. In very rare cases, it can lead to ventricular fibrillation and death.
* Brugada syndrome – a genetic disorder characterized by an abnormal EKG and is one of the most common causes of sudden cardiac death in young men.
Diagnosis
Heart disease is diagnosed by the taking of a medical history
The medical history, case history, or anamnesis (from Greek: ἀνά, ''aná'', "open", and μνήσις, ''mnesis'', "memory") of a patient is a set of information the physicians collect over medical interviews. It involves the patient, and ev ...
, a cardiac examination
In medicine, the cardiac examination, also precordial exam, is performed as part of a physical examination, or when a patient presents with chest pain suggestive of a cardiovascular pathology. It would typically be modified depending on the ind ...
, and further investigations, including blood test
A blood test is a medical laboratory, laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle, or via fingerprick. Multiple tests for specific blood components, such as a glucose ...
s, echocardiogram
Echocardiography, also known as cardiac ultrasound, is the use of ultrasound to examine the heart. It is a type of medical imaging, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound. The visual image formed using this technique is called an echo ...
s, electrocardiograms
Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), a recording of the heart's electrical activity through repeated cardiac cycles.
It is an electrogram of the heart which is a graph of voltage versus time of ...
, and imaging
Imaging is the representation or reproduction of an object's form; especially a visual representation (i.e., the formation of an image).
Imaging technology is the application of materials and methods to create, preserve, or duplicate images.
...
. Other invasive procedures such as cardiac catheterisation
Cardiac catheterization (heart cath) is the insertion of a catheter into a chamber or vessel of the heart. This is done both for diagnostic and interventional purposes.
A common example of cardiac catheterization is coronary catheterization tha ...
can also play a role.
Examination
The cardiac examination includes inspection, feeling the chest with the hands (palpation
Palpation is the process of using one's hands to check the body, especially while perceiving/diagnosing a disease or illness. Usually performed by a health care practitioner, it is the process of feeling an object in or on the body to determine ...
) and listening with a stethoscope (auscultation
Auscultation (based on the Latin verb ''auscultare'' "to listen") is listening to the internal sounds of the body, usually using a stethoscope. Auscultation is performed for the purposes of examining the circulatory system, circulatory and resp ...
).splinter haemorrhage
Splinter hemorrhages (or haemorrhages) are tiny blood clots that tend to run vertically under the nails. Splinter hemorrhages are not specific to any particular condition, and can be associated with subacute infective endocarditis, scleroderma, tri ...
s), joints and other areas. A person's pulse is taken, usually at the radial artery
In human anatomy, the radial artery is the main artery of the lateral aspect of the forearm.
Structure
The radial artery arises from the bifurcation of the brachial artery in the antecubital fossa. It runs distally on the anterior part of the ...
near the wrist, in order to assess for the rhythm and strength of the pulse. The blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of Circulatory system, circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term ...
is taken, using either a manual or automatic sphygmomanometer
A sphygmomanometer ( ), also known as a blood pressure monitor, blood pressure machine, or blood pressure gauge, is a device used to measure blood pressure, composed of an inflatable cuff to collapse and then release the artery under the cuff i ...
or using a more invasive measurement from within the artery. Any elevation of the jugular venous pulse
The jugular veins () are veins that take blood from the head back to the heart via the superior vena cava. The internal jugular vein descends next to the internal carotid artery and continues posteriorly to the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
Struc ...
is noted. A person's chest
The thorax (: thoraces or thoraxes) or chest is a part of the anatomy of mammals and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen.
In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main di ...
is felt for any transmitted vibrations from the heart, and then listened to with a stethoscope.
Heart sounds
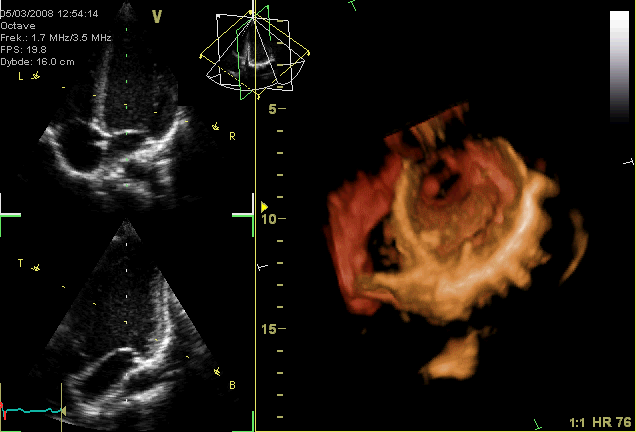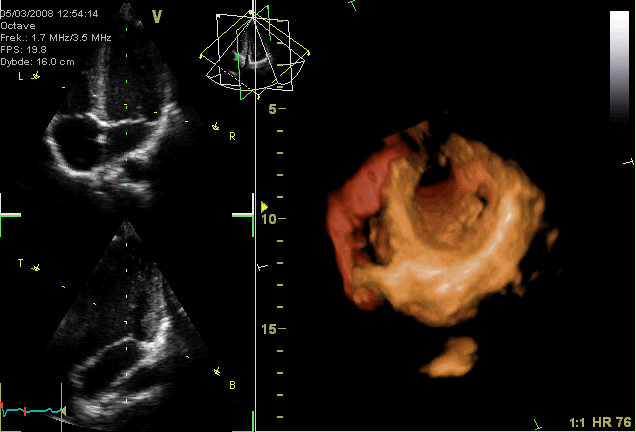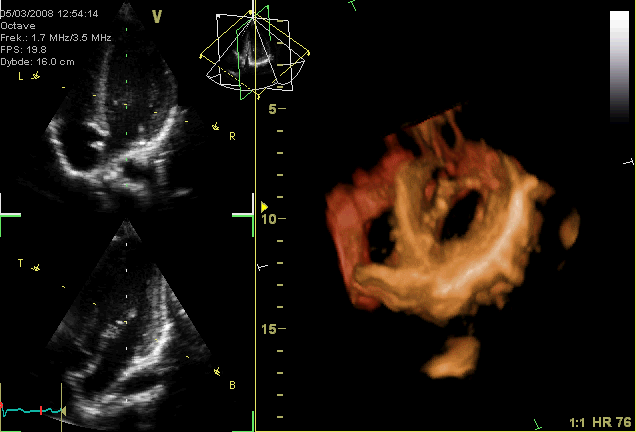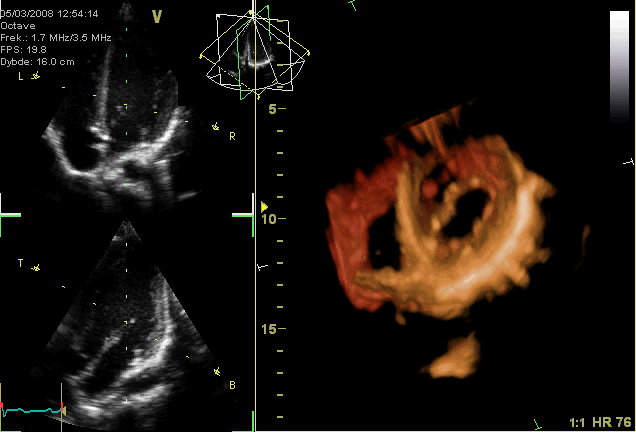 Typically, healthy hearts have only two audible
Typically, healthy hearts have only two audible heart sounds
Heart sounds are the noises generated by the beating heart and the resultant flow of blood through it. Specifically, the sounds reflect the turbulence created when the heart valves snap shut. In cardiac auscultation, an examiner may use a stetho ...
, called S1 and S2. The first heart sound
Heart sounds are the noises generated by the beating heart and the resultant flow of blood through it. Specifically, the sounds reflect the turbulence created when the heart valves snap shut. In cardiac auscultation, an examiner may use a stetho ...
S1, is the sound created by the closing of the atrioventricular valves during ventricular contraction and is normally described as "lub". The second heart sound
Heart sounds are the noises generated by the beating heart and the resultant flow of blood through it. Specifically, the sounds reflect the turbulence created when the heart valves snap shut. In cardiac auscultation, an examiner may use a steth ...
, S2, is the sound of the semilunar valves closing during ventricular diastole and is described as "dub".split
Split(s) or The Split may refer to:
Places
* Split, Croatia, the largest coastal city in Croatia
* Split Island, Canada, an island in the Hudson Bay
* Split Island, Falkland Islands
* Split Island, Fiji, better known as Hạfliua
Arts, enter ...
into two distinct sounds, either as a result of inspiration or different valvular or cardiac problems.[ Additional heart sounds may also be present and these give rise to ]gallop rhythm
A gallop rhythm refers to a (usually abnormal) rhythm of the heart on auscultation. It includes three or four sounds, thus resembling the sounds of a gallop.
The normal heart rhythm contains two audible heart sounds called S1 and S2 that give ...
s. A third heart sound
The third heart sound or S3 is a rare extra heart sound that occurs soon after the normal two "lub-dub" heart sounds (S1 and S2). S3 is associated with heart failure.
Physiology
It occurs at the beginning of the middle third of diastole, approxima ...
, S3 usually indicates an increase in ventricular blood volume. A fourth heart sound
The fourth heart sound or S4 is an extra heart sound that occurs during late diastole, immediately before the normal two "lub-dub" heart sounds (S1 and S2). It occurs just after atrial contraction and immediately before the systolic S1 and is cau ...
S4 is referred to as an atrial gallop and is produced by the sound of blood being forced into a stiff ventricle. The combined presence of S3 and S4 give a quadruple gallop.Heart murmur
Heart murmurs are unique heart sounds produced when blood flows across a heart valve or blood vessel. This occurs when turbulent blood flow creates a sound loud enough to hear with a stethoscope. The sound differs from normal heart sounds by th ...
s are abnormal heart sounds which can be either related to disease or benign, and there are several kinds. There are normally two heart sounds, and abnormal heart sounds can either be extra sounds, or "murmurs" related to the flow of blood between the sounds. Murmurs are graded by volume, from 1 (the quietest), to 6 (the loudest), and evaluated by their relationship to the heart sounds, position in the cardiac cycle, and additional features such as their radiation to other sites, changes with a person's position, the frequency of the sound as determined by the side of the stethoscope
The stethoscope is a medicine, medical device for auscultation, or listening to internal sounds of an animal or human body. It typically has a small disc-shaped resonator that is placed against the skin, with either one or two tubes connected t ...
by which they are heard, and site at which they are heard loudest. Murmurs may be caused by damaged heart valves or congenital heart disease such as ventricular septal defect
A ventricular septal defect (VSD) is a defect in the ventricular septum, the wall dividing the left and right ventricles of the heart. It's a common heart problem present at birth ( congenital heart defect). The extent of the opening may vary ...
s, or may be heard in normal hearts. A different type of sound, a pericardial friction rub
A pericardial friction rub, also pericardial rub, is an audible medical sign used in the diagnosis of pericarditis. Upon auscultation, this sign is an extra heart sound of to-and-fro character, typically with three components, two systolic and one ...
can be heard in cases of pericarditis where the inflamed membranes can rub together.
Blood tests
Blood tests play an important role in the diagnosis and treatment of many cardiovascular conditions.
Troponin
Troponin, or the troponin complex, is a complex of three regulatory proteins (troponin C, troponin I, and troponin T) that are integral to muscle contraction in skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle, but not smooth muscle. Measurements of cardiac-spe ...
is a sensitive biomarker
In biomedical contexts, a biomarker, or biological marker, is a measurable indicator of some biological state or condition. Biomarkers are often measured and evaluated using blood, urine, or soft tissues to examine normal biological processes, ...
for a heart with insufficient blood supply. It is released 4–6 hours after injury and usually peaks at about 12–24 hours.brain natriuretic peptide
Brain natriuretic peptide (BNP), also known as B-type natriuretic peptide, is a hormone secreted by cardiomyocytes in the heart ventricles in response to stretching caused by increased ventricular blood volume. BNP is one of the three natriuret ...
(BNP) can be used to evaluate for the presence of heart failure, and rises when there is increased demand on the left ventricle. These tests are considered biomarker
In biomedical contexts, a biomarker, or biological marker, is a measurable indicator of some biological state or condition. Biomarkers are often measured and evaluated using blood, urine, or soft tissues to examine normal biological processes, ...
s because they are highly specific for cardiac disease. Testing for the MB form of creatine kinase provides information about the heart's blood supply, but is used less frequently because it is less specific and sensitive.
Other blood tests are often taken to help understand a person's general health and risk factors that may contribute to heart disease. These often include a full blood count
A complete blood count (CBC), also known as a full blood count (FBC) or full haemogram (FHG), is a set of medical laboratory tests that provide cytometry, information about the cells in a person's blood. The CBC indicates the counts of white blo ...
investigating for anaemia
Anemia (also spelt anaemia in British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen. This can be due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin availab ...
, and basic metabolic panel
A basic metabolic panel (BMP) is a blood test consisting of a set of seven or eight biochemical tests and is one of the most common lab tests ordered by health care providers. Outside the United States, blood tests made up of the majority of the ...
that may reveal any disturbances in electrolytes. A coagulation screen
A coagulation screen is a combination of screening laboratory tests, designed to provide rapid non-specific information, which allows an initial broad categorization of haemostatic problems.
__TOC__
Process
The basic screen consists of:
* plat ...
is often required to ensure that the right level of anticoagulation is given. Fasting lipids and fasting blood glucose (or an HbA1c
Glycated hemoglobin, also called glycohemoglobin, is a form of hemoglobin (Hb) that is chemically linked to a sugar. Most monosaccharides, including glucose, galactose, and fructose, spontaneously (that is, non-enzymatically) bond with hemoglob ...
level) are often ordered to evaluate a person's cholesterol
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body Tissue (biology), tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in Animal fat, animal fats and oils.
Cholesterol is biosynthesis, biosynthesized by all anima ...
and diabetes status, respectively.
Electrocardiogram
 Using surface electrodes on the body, it is possible to record the electrical activity of the heart. This tracing of the electrical signal is the electrocardiogram (ECG) or (EKG). An ECG is a bedside test and involves the placement of ten leads on the body. This produces a "12 lead" ECG (three extra leads are calculated mathematically, and one lead is electrically ground, or earthed).
There are five prominent features on the ECG: the
Using surface electrodes on the body, it is possible to record the electrical activity of the heart. This tracing of the electrical signal is the electrocardiogram (ECG) or (EKG). An ECG is a bedside test and involves the placement of ten leads on the body. This produces a "12 lead" ECG (three extra leads are calculated mathematically, and one lead is electrically ground, or earthed).
There are five prominent features on the ECG: the P wave
A P wave (primary wave or pressure wave) is one of the two main types of elastic body waves, called seismic waves in seismology. P waves travel faster than other seismic waves and hence are the first signal from an earthquake to arrive at any ...
(atrial depolarisation), the QRS complex
The QRS complex is the combination of three of the graphical deflections seen on a typical electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). It is usually the central and most visually obvious part of the tracing. It corresponds to the depolarization of the ri ...
(ventricular depolarisation) and the T wave
In electrocardiography, the T wave represents the repolarization of the ventricles. The interval from the beginning of the QRS complex to the apex of the T wave is referred to as the ''absolute refractory period''. The last half of the T wav ...
(ventricular repolarisation).Holter monitor
In medicine, a Holter monitor (often simply Holter) is a type of ambulatory electrocardiography device, a portable device for cardiac monitoring (the monitoring of the electrical activity of the cardiovascular system) for at least 24 hours.
...
if a suspected rhythm abnormality is not present at the time of assessment.
Imaging
Several imaging
Imaging is the representation or reproduction of an object's form; especially a visual representation (i.e., the formation of an image).
Imaging technology is the application of materials and methods to create, preserve, or duplicate images.
...
methods can be used to assess the anatomy and function of the heart, including ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply ...
(echocardiography
Echocardiography, also known as cardiac ultrasound, is the use of ultrasound to examine the heart. It is a type of medical imaging, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound. The visual image formed using this technique is called an ec ...
), angiography
Angiography or arteriography is a medical imaging technique used to visualize the inside, or lumen, of blood vessels and organs of the body, with particular interest in the arteries, veins, and the heart chambers. Modern angiography is perfo ...
, CT, MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and rad ...
, and PET, scans. An echocardiogram is an ultrasound of the heart used to measure the heart's function, assess for valve disease, and look for any abnormalities. Echocardiography can be conducted by a probe on the chest ( transthoracic), or by a probe in the esophagus
The esophagus (American English), oesophagus (British English), or œsophagus (Œ, archaic spelling) (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, see spelling difference) all ; : ((o)e)(œ)sophagi or ((o)e)(œ)sophaguses), c ...
( transesophageal). A typical echocardiography report will include information about the width of the valves noting any stenosis
Stenosis () is the abnormal narrowing of a blood vessel or other tubular organ or structure such as foramina and canals. It is also sometimes called a stricture (as in urethral stricture).
''Stricture'' as a term is usually used when narrowing ...
, whether there is any backflow of blood ( regurgitation) and information about the blood volumes at the end of systole and diastole, including an ejection fraction
An ejection fraction (EF) is the volumetric fraction (or portion of the total) of fluid (usually blood) ejected from a chamber (usually the heart) with each contraction (or heartbeat). It can refer to the cardiac atrium, cardiac ventricle, gall ...
, which describes how much blood is ejected from the left and right ventricles after systole. Ejection fraction can then be obtained by dividing the volume ejected by the heart (stroke volume) by the volume of the filled heart (end-diastolic volume). Echocardiograms can also be conducted under circumstances when the body is more stressed, in order to examine for signs of lack of blood supply. This cardiac stress test
A cardiac stress test is a cardiological examination that evaluates the cardiovascular system's response to external stress within a controlled clinical setting. This stress response can be induced through physical exercise (usually a treadmill) o ...
involves either direct exercise, or where this is not possible, injection of a drug such as dobutamine
Dobutamine is a medication used in the treatment of cardiogenic shock (as a result of inadequate tissue perfusion) and severe heart failure. It may also be used in certain types of cardiac stress tests. It is given by IV only, as an injection ...
.
CT scans, chest X-rays
A chest radiograph, chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film is a Projectional radiography, projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common fi ...
and other forms of imaging can help evaluate the heart's size, evaluate for signs of pulmonary oedema
Pulmonary edema (British English: oedema), also known as pulmonary congestion, is excessive fluid accumulation in the tissue or air spaces (usually alveoli) of the lungs. This leads to impaired gas exchange, most often leading to shortness ...
, and indicate whether there is fluid around the heart. They are also useful for evaluating the aorta, the major blood vessel which leaves the heart.
Treatment
Diseases affecting the heart can be treated by a variety of methods including lifestyle modification, drug treatment, and surgery.
Ischemic heart disease
Narrowings of the coronary arteries (ischemic heart disease) are treated to relieve symptoms of chest pain caused by a partially narrowed artery (angina pectoris), to minimise heart muscle damage when an artery is completely occluded (myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when Ischemia, blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom ...
), or to prevent a myocardial infarction from occurring. Medications to improve angina symptoms include nitroglycerin
Nitroglycerin (NG) (alternative spelling nitroglycerine), also known as trinitroglycerol (TNG), nitro, glyceryl trinitrate (GTN), or 1,2,3-trinitroxypropane, is a dense, colorless or pale yellow, oily, explosive liquid most commonly produced by ...
, beta blocker
Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage abnormal heart rhythms ( arrhythmia), and to protect the heart from a second heart attack after a first heart attack ( secondary prevention ...
s, and calcium channel blockers, while preventative treatments include antiplatelets such as aspirin
Aspirin () is the genericized trademark for acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions that aspirin is ...
and statin
Statins (or HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors) are a class of medications that lower cholesterol. They are prescribed typically to people who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease.
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) carriers of cholesterol play ...
s, lifestyle measures such as stopping smoking and weight loss, and treatment of risk factors such as high blood pressure and diabetes.
In addition to using medications, narrowed heart arteries can be treated by expanding the narrowings or redirecting the flow of blood to bypass an obstruction. This may be performed using a percutaneous coronary intervention
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is a minimally invasive non-surgical procedure used to treat stenosis, narrowing of the coronary artery, coronary arteries of the heart found in coronary artery disease. The procedure is used to place and ...
, during which narrowings can be expanded by passing small balloon-tipped wires into the coronary arteries, inflating the balloon to expand the narrowing, and sometimes leaving behind a metal scaffold known as a stent to keep the artery open.coronary artery bypass graft
Coronary artery bypass surgery, also known as coronary artery bypass graft (CABG, pronounced "cabbage"), is a surgical procedure to treat coronary artery disease (CAD), the buildup of plaques in the arteries of the heart. It can relieve chest p ...
can be performed, whereby a blood vessel from another part of the body (the saphenous vein, radial artery
In human anatomy, the radial artery is the main artery of the lateral aspect of the forearm.
Structure
The radial artery arises from the bifurcation of the brachial artery in the antecubital fossa. It runs distally on the anterior part of the ...
, or internal mammary artery
The internal thoracic artery (ITA), also known as the internal mammary artery, is an artery that supplies the anterior chest wall and the breasts. It is a paired artery, with one running along each side of the sternum, to continue after its bifurc ...
) is used to redirect blood from a point before the narrowing (typically the aorta
The aorta ( ; : aortas or aortae) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the Ventricle (heart), left ventricle of the heart, branching upwards immediately after, and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits at ...
) to a point beyond the obstruction.
Valvular heart disease
Diseased heart valves that have become abnormally narrow or abnormally leaky may require surgery. This is traditionally performed as an open surgical procedure to replace the damaged heart valve with a tissue or metallic prosthetic valve. In some circumstances, the tricuspid
The tricuspid valve, or right atrioventricular valve, is on the right dorsal side of the mammalian heart, at the superior portion of the right ventricle. The function of the valve is to allow blood to flow from the right atrium to the right vent ...
or mitral
The mitral valve ( ), also known as the bicuspid valve or left atrioventricular valve, is one of the four heart valves. It has two Cusps of heart valves, cusps or flaps and lies between the atrium (heart), left atrium and the ventricle (heart), ...
valves can be repaired surgically
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery s ...
, avoiding the need for a valve replacement. Heart valves can also be treated percutaneously, using techniques that share many similarities with percutaneous coronary intervention. Transcatheter aortic valve replacement
Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) is the implantation of the aortic valve of the heart through the blood vessels without actual removal of the native valve (as opposed to the aortic valve replacement by open heart surgery, surgical ...
is increasingly used for patients consider very high risk for open valve replacement.
Cardiac arrhythmias
Abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. Essentially, this is anything but normal sinus rhythm. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats ...
) can be treated using antiarrhythmic drugs. These may work by manipulating the flow of electrolytes across the cell membrane (such as calcium channel blocker
Calcium channel blockers (CCB), calcium channel antagonists or calcium antagonists are a group of medications that disrupt the movement of calcium () through calcium channels. Calcium channel blockers are used as antihypertensive drugs, i.e., as ...
s, sodium channel blocker
Sodium channel blockers are drugs which impair the conduction of sodium ions (Na+) through sodium channels.
Extracellular
The following naturally-produced substances block sodium channels by binding to and occluding the extracellular pore opening ...
s, amiodarone
Amiodarone is an antiarrhythmic medication used to treat and prevent a number of types of cardiac dysrhythmias. This includes ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, and wide complex tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, and paroxys ...
, or digoxin
Digoxin (better known as digitalis), sold under the brand name Lanoxin among others, is a medication used to treat various heart disease, heart conditions. Most frequently it is used for atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and heart failure. ...
), or modify the autonomic nervous system's effect on the heart (beta blocker
Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage abnormal heart rhythms ( arrhythmia), and to protect the heart from a second heart attack after a first heart attack ( secondary prevention ...
s and atropine
Atropine is a tropane alkaloid and anticholinergic medication used to treat certain types of nerve agent and pesticide poisonings as well as some types of slow heart rate, and to decrease saliva production during surgery. It is typically give ...
). In some arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation which increase the risk of stroke, this risk can be reduced using anticoagulants such as warfarin
Warfarin, sold under the brand name Coumadin among others. It is used as an anticoagulant, anticoagulant medication. It is commonly used to prevent deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism, and to protect against stroke in people who ha ...
or novel oral anticoagulants.catheter ablation
Catheter ablation is a procedure that uses radio-frequency energy or other sources to terminate or modify a faulty electrical pathway from sections of the heart of those who are prone to developing cardiac arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation ...
. In these procedures, wires are passed from a vein
Veins () are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and feta ...
or artery
An artery () is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in ...
in the leg to the heart to find the abnormal area of tissue that is causing the arrhythmia. The abnormal tissue can be intentionally damaged, or ablated, by heating
In thermodynamics, heat is energy in transfer between a thermodynamic system and its surroundings by such mechanisms as thermal conduction, electromagnetic radiation, and friction, which are microscopic in nature, involving sub-atomic, atom ...
or freezing
Freezing is a phase transition in which a liquid turns into a solid when its temperature is lowered below its freezing point.
For most substances, the melting and freezing points are the same temperature; however, certain substances possess dif ...
to prevent further heart rhythm disturbances. Whilst the majority of arrhythmias can be treated using minimally invasive catheter techniques, some arrhythmias (particularly atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (AF, AFib or A-fib) is an Heart arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia) characterized by fibrillation, rapid and irregular beating of the Atrium (heart), atrial chambers of the heart. It often begins as short periods ...
) can also be treated using open or thoracoscopic surgery, either at the time of other cardiac surgery or as a standalone procedure. A cardioversion
Cardioversion is a medical procedure by which an abnormally fast heart rate (tachycardia) or other cardiac arrhythmia is converted to a normal rhythm using electricity or drugs.
Synchronized electrical cardioversion uses a therapeutic dose of ...
, whereby an electric shock is used to stun the heart out of an abnormal rhythm, may also be used.
Cardiac devices in the form of pacemakers
A pacemaker, also known as an artificial cardiac pacemaker, is an implanted medical device that generates electrical pulses delivered by electrodes to one or more of the chambers of the heart. Each pulse causes the targeted chamber(s) to co ...
or implantable defibrillators may also be required to treat arrhythmias. Pacemakers, comprising a small battery powered generator implanted under the skin and one or more leads that extend to the heart, are most commonly used to treat abnormally slow heart rhythms.cardiomyopathies
Cardiomyopathy is a group of primary diseases of the heart muscle. Early on there may be few or no symptoms. As the disease worsens, shortness of breath, feeling tired, and swelling of the legs may occur, due to the onset of heart failure. An ...
, or inherited arrhythmia syndromes.
Heart failure
As well as addressing the underlying cause for a patient's heart failure (most commonly ischemic heart disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), or ischemic heart disease (IHD), is a type of heart disease involving the reduction of blood flow to the cardiac muscle due to a build-up of atheromatous plaque in the ...
or hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms i ...
), the mainstay of heart failure treatment is with medication. These include drugs to prevent fluid from accumulating in the lungs by increasing the amount of urine a patient produces (diuretic
A diuretic () is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics ...
s), and drugs that attempt to preserve the pumping function of the heart (beta blocker
Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage abnormal heart rhythms ( arrhythmia), and to protect the heart from a second heart attack after a first heart attack ( secondary prevention ...
s, ACE inhibitor
Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors) are a class of medication used primarily for the treatment of high blood pressure and heart failure. This class of medicine works by causing relaxation of blood vessels as well as a decr ...
s and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists).ventricular assist device
A ventricular assist device (VAD) is an electromechanics, electromechanical device that provides support for cardiac pump function, which is used either to partially or to completely replace the function of a failing heart. VADs can be used in p ...
may be implanted which supplements the heart's own pumping ability. In the most severe cases, a cardiac transplant
A heart transplant, or a cardiac transplant, is a surgical transplant procedure performed on patients with end-stage heart failure when other medical or surgical treatments have failed. , the most common procedure is to take a functioning heart ...
may be considered.
History
Ancient
Humans have known about the heart since ancient times, although its precise function and anatomy were not clearly understood.ancient Greeks
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically re ...
are considered to have been the primary seat of scientific understanding of the heart in the ancient world.Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
considered the heart to be the organ responsible for creating blood; Plato
Plato ( ; Greek language, Greek: , ; born BC, died 348/347 BC) was an ancient Greek philosopher of the Classical Greece, Classical period who is considered a foundational thinker in Western philosophy and an innovator of the writte ...
considered the heart as the source of circulating blood and Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; ; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician and philosopher of the Classical Greece, classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of medicine. He is traditionally referr ...
noted blood circulating cyclically from the body through the heart to the lungs.Erasistratos
Erasistratus (; ; c. 304 – c. 250 BC) was a Greek anatomist and royal physician under Seleucus I Nicator of Syria. Along with fellow physician Herophilus, he founded a school of anatomy in Alexandria, where they carried out anatomical research. ...
(304–250 BCE) noted the heart as a pump, causing dilation of blood vessels, and noted that arteries and veins both radiate from the heart, becoming progressively smaller with distance, although he believed they were filled with air and not blood. He also discovered the heart valves.Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus (; September 129 – AD), often Anglicization, anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Ancient Rome, Roman and Greeks, Greek physician, surgeon, and Philosophy, philosopher. Considered to be one o ...
(2nd century CE) knew blood vessels carried blood and identified venous (dark red) and arterial (brighter and thinner) blood, each with distinct and separate functions.[
These ideas went unchallenged for almost a thousand years.][
]
Pre-modern
The earliest descriptions of the coronary Coronary () may, as shorthand in English, be used to mean:
* Coronary circulation, the system of arteries and veins in mammals
** Coronary artery disease
** Coronary occlusion
** A myocardial infarction, a heart attack
As adjective
* Referring to ...
and pulmonary circulation systems can be found in the ''Commentary on Anatomy in Avicenna's Canon
The ''Commentary on Anatomy in Avicenna's Canon'' is a work written in the 13th century by the Arab physician Ibn al-Nafis. A manuscript of the work was discovered in 1924 in the archives of the Prussian State Library in Berlin, Germany. It contai ...
'', published in 1242 by Ibn al-Nafis
ʿAlāʾ al-Dīn Abū al-Ḥasan ʿAlī ibn Abī Ḥazm al-Qarashī (Arabic: علاء الدين أبو الحسن عليّ بن أبي حزم القرشي ), known as Ibn al-Nafīs (Arabic: ابن النفيس), was an Arab polymath whose area ...
.Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
by Andrea Alpago.
In Europe, the teachings of Galen continued to dominate the academic community and his doctrines were adopted as the official canon of the Church. Andreas Vesalius
Andries van Wezel (31 December 1514 – 15 October 1564), latinized as Andreas Vesalius (), was an anatomist and physician who wrote '' De Humani Corporis Fabrica Libri Septem'' (''On the fabric of the human body'' ''in seven books''), which is ...
questioned some of Galen's beliefs of the heart in ''De humani corporis fabrica
''De Humani Corporis Fabrica Libri Septem'' (Latin, "On the Fabric of the Human Body in Seven Books") is a set of books on human anatomy written by Andreas Vesalius (1514–1564) and published in 1543. It was a major advance in the history of a ...
'' (1543), but his magnum opus
A masterpiece, , or ; ; ) is a creation that has been given much critical praise, especially one that is considered the greatest work of a person's career or a work of outstanding creativity, skill, profundity, or workmanship.
Historically, ...
was interpreted as a challenge to the authorities and he was subjected to a number of attacks.Michael Servetus
Michael Servetus (; ; ; also known as ''Michel Servetus'', ''Miguel de Villanueva'', ''Revés'', or ''Michel de Villeneuve''; 29 September 1509 or 1511 – 27 October 1553) was a Spanish theologian, physician, cartographer, and Renaissance ...
wrote in ''Christianismi Restitutio
''Christianismi Restitutio'' (''The Restoration of Christianity'') was a book published anonymously in a clandestine workshop in 1553 by Michael Servetus, after it had been rejected by a publisher in Basel. It rejected the Christian doctrine of t ...
'' (1553) that blood flows from one side of the heart to the other via the lungs.
Modern
 A breakthrough in understanding the flow of blood through the heart and body came with the publication of ''
A breakthrough in understanding the flow of blood through the heart and body came with the publication of ''De Motu Cordis
''Exercitatio Anatomica de Motu Cordis et Sanguinis in Animalibus'' (Latin, 'An Anatomical Exercise on the Motion of the Heart and Blood in Living Beings'), commonly called ''De Motu Cordis'', is the best-known work of the physician William Harv ...
'' (1628) by the English physician William Harvey
William Harvey (1 April 1578 – 3 June 1657) was an English physician who made influential contributions to anatomy and physiology. He was the first known physician to describe completely, and in detail, pulmonary and systemic circulation ...
. Harvey's book completely describes the systemic circulation and the mechanical force of the heart, leading to an overhaul of the Galenic doctrines.Otto Frank
Otto Heinrich Frank (12 May 1889 – 19 August 1980) was a German businessman, and the father of Anne Frank. He edited and published the first edition of her diary in 1947 (subsequently known in English as ''The Diary of a Young Girl'') and adv ...
(1865–1944) was a German physiologist; among his many published works are detailed studies of this important heart relationship. Ernest Starling
Ernest Henry Starling (17 April 1866 – 2 May 1927) was a British physiologist who contributed many fundamental ideas to this subject. These ideas were important parts of the British contribution to physiology, which at that time led the world. ...
(1866–1927) was an important English physiologist who also studied the heart. Although they worked largely independently, their combined efforts and similar conclusions have been recognized in the name " Frank–Starling mechanism".Purkinje fibers
The Purkinje fibers, named for Jan Evangelista Purkyně, ( ; ; Purkinje tissue or subendocardial branches) are located in the inner ventricular walls of the heart, just beneath the endocardium in a space called the subendocardium. The Purki ...
and the bundle of His
The bundle of His (BH) or His bundle (HB) ( "hiss"Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spiral bound Version'. Cengage Learning; 2016. . pp. 129–.) is a collection of heart muscle cells specialized for electrical conduction. As part of ...
were discovered as early as the 19th century, their specific role in the electrical conduction system of the heart
The cardiac conduction system (CCS, also called the electrical conduction system of the heart) transmits the Cardiac action potential, signals generated by the sinoatrial node – the heart's Cardiac pacemaker, pacemaker, to cause the heart musc ...
remained unknown until Sunao Tawara
was a Japanese pathologist known for the discovery of the atrioventricular node.
Tawara was born in Ōita Prefecture and studied at the Medical School, Imperial University of Tokyo in Tokyo, graduating in 1901 and receiving his Medical Doctor, ...
published his monograph, titled ''Das Reizleitungssystem des Säugetierherzens
''Das Reizleitungssystem des Säugetierherzens'' (English: "''The Conduction System of the Mammalian Heart''") is a scientific monograph published in 1906 by Sunao Tawara. It has been recognized by cardiologists as a monumental discovery, and a mi ...
'', in 1906. Tawara's discovery of the atrioventricular node
The atrioventricular node (AV node, or Aschoff-Tawara node) electrically connects the heart's atria and ventricles to coordinate beating in the top of the heart; it is part of the electrical conduction system of the heart. The AV node lies at the ...
prompted Arthur Keith
Sir Arthur Keith FRS FRAI (5 February 1866 – 7 January 1955) was a British anatomist and anthropologist, and a proponent of scientific racism. He was a fellow and later the Hunterian Professor and conservator of the Hunterian Museum of the ...
and Martin Flack
Martin William Flack (20 March 1882 – 16 August 1931) was a British physiologist who co-discovered the sinoatrial node with Sir Arthur Keith in 1907.
Flack later became demonstrator of physiology at the London Hospital and later a lecturer. ...
to look for similar structures in the heart, leading to their discovery of the sinoatrial node
The sinoatrial node (also known as the sinuatrial node, SA node, sinus node or Keith–Flack node) is an ellipse, oval shaped region of special cardiac muscle in the upper back wall of the right atrium made up of Cell (biology), cells known as pa ...
several months later. These structures form the anatomical basis of the electrocardiogram, whose inventor, Willem Einthoven
Willem Einthoven (21 May 1860 – 29 September 1927) was a Dutch medical doctor and physiologist. He invented the first practical electrocardiograph (ECG or EKG) in 1895 and received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1924 for it ("fo ...
, was awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine or Physiology in 1924.
The first heart transplant
A heart transplant, or a cardiac transplant, is a surgical transplant procedure performed on patients with end-stage heart failure when other medical or surgical treatments have failed. , the most common procedure is to take a functioning heart ...
in a human ever performed was by James Hardy in 1964, using a chimpanzee heart, but the patient died within 2 hours. The first human to human heart transplantation was performed in 1967 by the South African surgeon Christiaan Barnard
Christiaan Neethling Barnard (8November 19222September 2001) was a South African cardiac surgeon who performed the world's first human-to-human heart transplant operation. On 3 December 1967, Barnard transplanted the heart of accident victim ...
at Groote Schuur Hospital
Groote Schuur Hospital is a large government-funded teaching hospital situated on the slopes of Devil's Peak (Cape Town), Devil's Peak in the city of Cape Town, South Africa. It was founded in 1938 and is famous for being the institution where ...
in Cape Town
Cape Town is the legislature, legislative capital city, capital of South Africa. It is the country's oldest city and the seat of the Parliament of South Africa. Cape Town is the country's List of municipalities in South Africa, second-largest ...
. This marked an important milestone in cardiac surgery, capturing the attention of both the medical profession and the world at large. However, long-term survival rates of patients were initially very low. Louis Washkansky
Louis Joshua Washkansky (12 April 1912 – 21 December 1967) was a South African man who was the recipient of the world's first human-to-human heart transplant, and the first patient to regain consciousness following the operation. Washkansky l ...
, the first recipient of a donated heart, died 18 days after the operation while other patients did not survive for more than a few weeks. The American surgeon Norman Shumway
Norman Edward Shumway (February 9, 1923 – February 10, 2006) was a pioneer of heart surgery at Stanford University. He was the 67th president of the American Association for Thoracic Surgery and the first to perform an adult human to huma ...
has been credited for his efforts to improve transplantation techniques, along with pioneers Richard Lower, Vladimir Demikhov
Vladimir Petrovich Demikhov (; 31 July 1916 – 22 November 1998) was a Soviet Russian scientist and organ transplantation pioneer, who performed several transplants in the 1940s and 1950s, including the transplantation of a heart into an anim ...
and Adrian Kantrowitz
Adrian Kantrowitz (October 4, 1918 – November 14, 2008) was an American cardiac surgeon whose team performed the world's second heart transplant attempt (after Christiaan Barnard) at Maimonides Medical Center in Brooklyn, New York on December ...
. As of March 2000, more than 55,000 heart transplantations have been performed worldwide. The first successful transplant of a heart from a genetically modified
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification or genetic manipulation, is the modification and manipulation of an organism's genes using technology. It is a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including th ...
pig to a human in which the patient lived for a longer time, was performed January 7, 2022 in Baltimore
Baltimore is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland. With a population of 585,708 at the 2020 census and estimated at 568,271 in 2024, it is the 30th-most populous U.S. city. The Baltimore metropolitan area is the 20th-large ...
by heart surgeon Bartley P. Griffith
Bartley P. Griffith (born 1949) is an American heart surgeon.
Griffith joined Muhammad Mohiuddin's MD Xenoheart laboratory in 2018. Together, they were able to demonstrate that the heart of a genetically altered pig could support life when tra ...
, recipient was David Bennett (57) this successfully extended his life until 8 March 2022 (1 month and 30 days).
By the middle of the 20th century, Cardiovascular disease, heart disease had surpassed infectious disease as the leading cause of death in the United States, and it is currently the leading cause of deaths worldwide. Since 1948, the ongoing Framingham Heart Study has shed light on the effects of various influences on the heart, including diet, exercise, and common medications such as aspirin. Although the introduction of ACE inhibitor
Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors) are a class of medication used primarily for the treatment of high blood pressure and heart failure. This class of medicine works by causing relaxation of blood vessels as well as a decr ...
s and beta blocker
Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage abnormal heart rhythms ( arrhythmia), and to protect the heart from a second heart attack after a first heart attack ( secondary prevention ...
s has improved the management of chronic heart failure, the disease continues to be an enormous medical and societal burden, with 30 to 40% of patients dying within a year of receiving the diagnosis.
Society and culture
Symbolism
 As one of the vital organs, the heart was long identified as the center of the entire body, the seat of life, or emotion, or reason, will, intellect, purpose or the mind.
As one of the vital organs, the heart was long identified as the center of the entire body, the seat of life, or emotion, or reason, will, intellect, purpose or the mind.Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
, considered the heart the seat of thought, reason, or emotion, often disregarding the brain as contributing to those functions. The identification of the heart as the seat of emotions in particular is due to the Roman Empire, Roman physician Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus (; September 129 – AD), often Anglicization, anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Ancient Rome, Roman and Greeks, Greek physician, surgeon, and Philosophy, philosopher. Considered to be one o ...
, who also located the seat of the passions in the liver, and the seat of reason in the brain.
The heart also played a role in the Aztec system of belief. The most common form of human sacrifice practiced by the Aztecs was heart-extraction. The Aztec believed that the heart (''tona'') was both the seat of the individual and a fragment of the Sun's heat (''istli''). To this day, the Nahua consider the Sun to be a heart-soul (''tona-tiuh''): "round, hot, pulsating".
Indigenous leaders from Alaska to Australia came together in 2020 to deliver a message to the world that humanity needs to shift from the mind to the heart, and let our heart be in charge of what we do.
Food
Animal hearts are widely consumed as a type of offal. As they are almost entirely muscle, they are high in protein. They are often included in dishes with other internal organs, for example in the Ottoman cuisine, pan-Ottoman kokoretsi.
Chicken (food), Chicken hearts are considered to be giblets, and are often grilled on skewers; examples of this are Japanese cuisine, Japanese yakitori, ''hāto yakitori'', Brazilian cuisine, Brazilian churrasco, ''churrasco de coração'', and Indonesian cuisine, Indonesian satay, chicken heart satay. They can also be pan-fried, as in Jerusalem mixed grill. In Egyptian cuisine, they can be used, finely chopped, as part of stuffing for chicken. Many recipes combined them with other giblets, such as the Mexican cuisine, Mexican ''pollo en menudencias'' and the Russian cuisine, Russian ''ragu iz kurinyikh potrokhov''.
The hearts of beef, pork, and mutton can generally be interchanged in recipes. As heart is a hard-working muscle, it makes for "firm and rather dry" meat, so is generally slow-cooked. Another way of dealing with toughness is to Julienning, julienne the meat, as in Chinese cuisine, Chinese stir-fried heart.
Beef heart is valued for its high meat quality and low price, being commonly disregarded in conventional meat pricing. It can be cut into steaks, comparable in quality to the more expensive cuts of meat from the same animal, though it is distinguished by a lack of a discernible grain. It was historically eaten in the United States as a cost-saving measure, but is today also eaten as an independently desirable ingredient. Beef heart may be grilled or braised.[Irma S. Rombauer, Rombauer, Irma S. and Rombauer Becker, Marion (1975) ''The Joy of Cooking'', p. 508] In the Peruvian cuisine, Peruvian anticuchos, ''anticuchos de corazón'', barbecued beef hearts are grilled after being tenderized through long marination in a spice and vinegar mixture. An Australian cuisine, Australian recipe for "mock goose" is actually braised stuffed beef heart.
Pork heart can be stewed, poached, braised, or made into sausage. The Balinese cuisine, Balinese ''oret'' is a sort of blood sausage made with pig heart and blood. A French cuisine, French recipe for ''cœur de porc à l'orange'' is made of braised heart with an orange sauce.
Other animals
Vertebrates
The size of the heart varies among the different animal phylum, groups, with hearts in vertebrates ranging from those of the smallest mice (12 mg) to the blue whale (600 kg). In vertebrates, the heart lies in the middle of the ventral part of the body, surrounded by a pericardium
The pericardium (: pericardia), also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong inelastic connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), ...
.
Double circulatory systems
 Adult amphibians and most reptiles have a double circulatory system, meaning a circulatory system divided into arterial and venous parts. However, the heart itself is not completely separated into two sides. Instead, it is separated into three chambers—two atria and one ventricle. Blood returning from both the systemic circulation and the lungs is returned, and blood is pumped simultaneously into the systemic circulation and the lungs. The double system allows blood to circulate to and from the lungs which deliver oxygenated blood directly to the heart.
Adult amphibians and most reptiles have a double circulatory system, meaning a circulatory system divided into arterial and venous parts. However, the heart itself is not completely separated into two sides. Instead, it is separated into three chambers—two atria and one ventricle. Blood returning from both the systemic circulation and the lungs is returned, and blood is pumped simultaneously into the systemic circulation and the lungs. The double system allows blood to circulate to and from the lungs which deliver oxygenated blood directly to the heart.blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of Circulatory system, circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term ...
due to gravitational change.
Full division
Archosaurs (crocodilians and birds) and mammals show complete separation of the heart into two pumps for a total of four heart chambers; it is thought that the four-chambered heart of archosaurs evolved independently from that of mammals. In crocodilians, there is a small opening, the foramen of Panizza, at the base of the arterial trunks and there is some degree of mixing between the blood in each side of the heart, during a dive underwater;
Fish
 The heart evolved no less than 380 million years ago in fish.
The heart evolved no less than 380 million years ago in fish.
Invertebrates
 Arthropods and most mollusks have an open circulatory system. In this system, deoxygenated blood collects around the heart in cavities (:wikt:sinus, sinuses). This blood slowly permeates the heart through many small one-way channels. The heart then pumps the blood into the hemocoel, a cavity between the organs. The heart in arthropods is typically a muscular tube that runs the length of the body, under the back and from the base of the head. Instead of blood the circulatory fluid is haemolymph which carries the most commonly used respiratory pigment, copper-based haemocyanin as the oxygen transporter. Haemoglobin is only used by a few arthropods.
Arthropods and most mollusks have an open circulatory system. In this system, deoxygenated blood collects around the heart in cavities (:wikt:sinus, sinuses). This blood slowly permeates the heart through many small one-way channels. The heart then pumps the blood into the hemocoel, a cavity between the organs. The heart in arthropods is typically a muscular tube that runs the length of the body, under the back and from the base of the head. Instead of blood the circulatory fluid is haemolymph which carries the most commonly used respiratory pigment, copper-based haemocyanin as the oxygen transporter. Haemoglobin is only used by a few arthropods. In some other invertebrates such as earthworms, the circulatory system is not used to transport oxygen and so is much reduced, having no veins or arteries and consisting of two connected tubes. Oxygen travels by diffusion and there are five small muscular vessels that connect these vessels that contract at the front of the animals that can be thought of as "hearts".
In some other invertebrates such as earthworms, the circulatory system is not used to transport oxygen and so is much reduced, having no veins or arteries and consisting of two connected tubes. Oxygen travels by diffusion and there are five small muscular vessels that connect these vessels that contract at the front of the animals that can be thought of as "hearts".[
Cephalopod, Squids and other cephalopods have two "gill hearts" also known as branchial hearts, and one "systemic heart". The branchial hearts have two atria and one ventricle each, and pump to the gills, whereas the systemic heart pumps to the body.]aorta
The aorta ( ; : aortas or aortae) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the Ventricle (heart), left ventricle of the heart, branching upwards immediately after, and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits at ...
and contracts to pump blood. This suggests a presence of it in the last deuterostome, common ancestor of these groups (may have been lost in the echinoderms).
Additional images
File:Blausen 0451 Heart Anterior.png, The human heart viewed from the front
File:Blausen 0456 Heart Posterior.png, The human heart viewed from behind
File:Blausen 0260 CoronaryVessels Anterior.png, The coronary circulation
File:2008 Internal Anatomy of the HeartN.jpg, Frontal section of the human heart
File:Slide2aaaaaa.JPG, An anatomical specimen of the heart
File:Human Heart and Circulatory System.png, Heart illustration with circulatory system
File:Animated Heart.gif, Animated heart 3D model rendered in computer
Notes
References
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
External links
Transplantation of pig heart to human. BBC, 11 Jan 2022.
Heart surgeon Bartley P Griffith talks about the unique transplant of pig heart to human.
– NIH
Atlas of Human Cardiac Anatomy
Dissection review of the anatomy of the Human Heart including vessels, internal and external features
The Heart
BBC Radio 4 interdisciplinary discussion with David Wootton, Fay Bound Alberti & Jonathan Sawday (''In Our Time'', 1 June 2006)
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Human Heart
Heart,
Cardiac anatomy
Articles containing video clips
Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate
Organs (anatomy)


 The human heart is situated in the
The human heart is situated in the  The heart has four chambers, two upper
The heart has four chambers, two upper  The heart has four valves, which separate its chambers. One valve lies between each atrium and ventricle, and one valve rests at the exit of each ventricle.
The valves between the atria and ventricles are called the atrioventricular valves. Between the right atrium and the right ventricle is the
The heart has four valves, which separate its chambers. One valve lies between each atrium and ventricle, and one valve rests at the exit of each ventricle.
The valves between the atria and ventricles are called the atrioventricular valves. Between the right atrium and the right ventricle is the  The heart wall is made up of three layers: the inner
The heart wall is made up of three layers: the inner  The middle layer of the heart wall is the myocardium, which is the
The middle layer of the heart wall is the myocardium, which is the  The heart receives nerve signals from the
The heart receives nerve signals from the  The heart is the first functional organ to develop and starts to beat and pump blood at about three weeks into
The heart is the first functional organ to develop and starts to beat and pump blood at about three weeks into  The heart functions as a pump in the
The heart functions as a pump in the  The cardiac cycle is the sequence of events in which the heart contracts and relaxes with every heartbeat. The period of time during which the ventricles contract, forcing blood out into the aorta and main pulmonary artery, is known as
The cardiac cycle is the sequence of events in which the heart contracts and relaxes with every heartbeat. The period of time during which the ventricles contract, forcing blood out into the aorta and main pulmonary artery, is known as  Cardiac output (CO) is a measurement of the amount of blood pumped by each ventricle (stroke volume) in one minute. This is calculated by multiplying the stroke volume (SV) by the beats per minute of the heart rate (HR). So that: CO = SV x HR.
The cardiac output is normalized to body size through
Cardiac output (CO) is a measurement of the amount of blood pumped by each ventricle (stroke volume) in one minute. This is calculated by multiplying the stroke volume (SV) by the beats per minute of the heart rate (HR). So that: CO = SV x HR.
The cardiac output is normalized to body size through  The normal rhythmical heart beat, called
The normal rhythmical heart beat, called  The normal
The normal  Typically, healthy hearts have only two audible
Typically, healthy hearts have only two audible  Using surface electrodes on the body, it is possible to record the electrical activity of the heart. This tracing of the electrical signal is the electrocardiogram (ECG) or (EKG). An ECG is a bedside test and involves the placement of ten leads on the body. This produces a "12 lead" ECG (three extra leads are calculated mathematically, and one lead is electrically ground, or earthed).
There are five prominent features on the ECG: the
Using surface electrodes on the body, it is possible to record the electrical activity of the heart. This tracing of the electrical signal is the electrocardiogram (ECG) or (EKG). An ECG is a bedside test and involves the placement of ten leads on the body. This produces a "12 lead" ECG (three extra leads are calculated mathematically, and one lead is electrically ground, or earthed).
There are five prominent features on the ECG: the  A breakthrough in understanding the flow of blood through the heart and body came with the publication of ''
A breakthrough in understanding the flow of blood through the heart and body came with the publication of '' As one of the vital organs, the heart was long identified as the center of the entire body, the seat of life, or emotion, or reason, will, intellect, purpose or the mind. The heart is an emblematic symbol in many religions, signifying "truth, conscience or moral courage in many religions—the temple or throne of God in Islamic and Judeo-Christian thought; the divine centre, or Ātman (Hinduism), atman, and the third eye of transcendent wisdom in Hinduism; the diamond of purity and essence of the Buddha; the Taoism, Taoist centre of understanding."
In the Hebrew Bible, the word for heart, ''lev'', is used in these meanings, as the seat of emotion, the mind, and referring to the anatomical organ. It is also connected in function and symbolism to the stomach.
An important part of the concept of the Egyptian soul, soul in Ancient Egyptian religion was thought to be the heart, or ''ib''. The ''ib'' or metaphysical heart was believed to be formed from one drop of blood from the child's mother's heart, taken at conception. To ancient Egyptians, the heart was the seat of emotion, thought, will, and intention. This is evidenced by Egyptian language, Egyptian expressions which incorporate the word ''ib'', such as ''Awi-ib'' for "happy" (literally, "long of heart"), ''Xak-ib'' for "estranged" (literally, "truncated of heart"). In Egyptian religion, the heart was the key to the afterlife. It was conceived as surviving death in the nether world, where it gave evidence for, or against, its possessor. The heart was therefore not removed from the body during mummification, and was believed to be the center of intelligence and feeling, and needed in the afterlife. It was thought that the heart was examined by Anubis and a variety of ancient Egyptian deities, deities during the ''Weighing of the Heart'' ceremony. If the heart weighed more than the feather of Maat, which symbolized the ideal standard of behavior. If the scales balanced, it meant the heart's possessor had lived a just life and could enter the afterlife; if the heart was heavier, it would be devoured by the monster Ammit.
The Chinese language, Chinese character for "heart", 心, derives from a comparatively realistic depiction of a heart (indicating the heart chambers) in seal script. The Chinese word :wikt:心#Mandarin, ''xīn'' also takes the metaphorical meanings of "mind", "intention", or "core", and is often translated as "heart-mind" as the ancient Chinese believed the heart was the center of human cognition. Heart (Chinese medicine), In Chinese medicine, the heart is seen as the center of Shen (Chinese religion), 神 ''shén'' "spirit, consciousness". The heart is associated with the small intestine, tongue, governs the Zang-fu, six organs and five viscera, and belongs to fire in the five elements.
The Sanskrit word for heart is ''hṛd'' or ''hṛdaya'', found in the oldest surviving Sanskrit text, the Rigveda. In Sanskrit, it may mean both the anatomical object and "mind" or "soul", representing the seat of emotion. ''Hrd'' may be a cognate of the word for heart in Greek, Latin, and English.
Many classical antiquity, classical philosophers and scientists, including
As one of the vital organs, the heart was long identified as the center of the entire body, the seat of life, or emotion, or reason, will, intellect, purpose or the mind. The heart is an emblematic symbol in many religions, signifying "truth, conscience or moral courage in many religions—the temple or throne of God in Islamic and Judeo-Christian thought; the divine centre, or Ātman (Hinduism), atman, and the third eye of transcendent wisdom in Hinduism; the diamond of purity and essence of the Buddha; the Taoism, Taoist centre of understanding."
In the Hebrew Bible, the word for heart, ''lev'', is used in these meanings, as the seat of emotion, the mind, and referring to the anatomical organ. It is also connected in function and symbolism to the stomach.
An important part of the concept of the Egyptian soul, soul in Ancient Egyptian religion was thought to be the heart, or ''ib''. The ''ib'' or metaphysical heart was believed to be formed from one drop of blood from the child's mother's heart, taken at conception. To ancient Egyptians, the heart was the seat of emotion, thought, will, and intention. This is evidenced by Egyptian language, Egyptian expressions which incorporate the word ''ib'', such as ''Awi-ib'' for "happy" (literally, "long of heart"), ''Xak-ib'' for "estranged" (literally, "truncated of heart"). In Egyptian religion, the heart was the key to the afterlife. It was conceived as surviving death in the nether world, where it gave evidence for, or against, its possessor. The heart was therefore not removed from the body during mummification, and was believed to be the center of intelligence and feeling, and needed in the afterlife. It was thought that the heart was examined by Anubis and a variety of ancient Egyptian deities, deities during the ''Weighing of the Heart'' ceremony. If the heart weighed more than the feather of Maat, which symbolized the ideal standard of behavior. If the scales balanced, it meant the heart's possessor had lived a just life and could enter the afterlife; if the heart was heavier, it would be devoured by the monster Ammit.
The Chinese language, Chinese character for "heart", 心, derives from a comparatively realistic depiction of a heart (indicating the heart chambers) in seal script. The Chinese word :wikt:心#Mandarin, ''xīn'' also takes the metaphorical meanings of "mind", "intention", or "core", and is often translated as "heart-mind" as the ancient Chinese believed the heart was the center of human cognition. Heart (Chinese medicine), In Chinese medicine, the heart is seen as the center of Shen (Chinese religion), 神 ''shén'' "spirit, consciousness". The heart is associated with the small intestine, tongue, governs the Zang-fu, six organs and five viscera, and belongs to fire in the five elements.
The Sanskrit word for heart is ''hṛd'' or ''hṛdaya'', found in the oldest surviving Sanskrit text, the Rigveda. In Sanskrit, it may mean both the anatomical object and "mind" or "soul", representing the seat of emotion. ''Hrd'' may be a cognate of the word for heart in Greek, Latin, and English.
Many classical antiquity, classical philosophers and scientists, including  Arthropods and most mollusks have an open circulatory system. In this system, deoxygenated blood collects around the heart in cavities (:wikt:sinus, sinuses). This blood slowly permeates the heart through many small one-way channels. The heart then pumps the blood into the hemocoel, a cavity between the organs. The heart in arthropods is typically a muscular tube that runs the length of the body, under the back and from the base of the head. Instead of blood the circulatory fluid is haemolymph which carries the most commonly used respiratory pigment, copper-based haemocyanin as the oxygen transporter. Haemoglobin is only used by a few arthropods.
Arthropods and most mollusks have an open circulatory system. In this system, deoxygenated blood collects around the heart in cavities (:wikt:sinus, sinuses). This blood slowly permeates the heart through many small one-way channels. The heart then pumps the blood into the hemocoel, a cavity between the organs. The heart in arthropods is typically a muscular tube that runs the length of the body, under the back and from the base of the head. Instead of blood the circulatory fluid is haemolymph which carries the most commonly used respiratory pigment, copper-based haemocyanin as the oxygen transporter. Haemoglobin is only used by a few arthropods.