|
Channelopathies
Channelopathies are a group of diseases caused by the dysfunction of ion channel subunits or their interacting proteins. These diseases can be inherited or acquired by other disorders, drugs, or toxins. Mutations in genes encoding ion channels, which impair channel function, are the most common cause of channelopathies. There are more than 400 genes that encode ion channels, found in all human cell types and are involved in almost all physiological processes. Each type of channel is a multimeric complex of subunits encoded by a number of genes. Depending where the mutation occurs it may affect the gating, conductance, ion selectivity, or signal transduction of the channel. Channelopathies can be categorized based on the organ system which they are associated with. In the cardiovascular system, the electrical impulse needed for each heartbeat is made possible by the electrochemical gradient of each heart cell. Because the heartbeat is dependent on the proper movement of ions across ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paramyotonia Congenita
''Paramyotonia congenita'' (PC) is a rare congenital autosomal dominant neuromuscular disorder characterized by "paradoxical" myotonia. This type of myotonia has been termed paradoxical because it becomes worse with exercise whereas classical myotonia, as seen in myotonia congenita, is alleviated by exercise. PC is also distinguished as it can be induced by cold temperatures. Although more typical of the periodic paralytic disorders, patients with PC may also have potassium-provoked paralysis. PC typically presents within the first decade of life and has 100% penetrance. Patients with this disorder commonly present with myotonia in the face or upper extremities. The lower extremities are generally less affected. While some other related disorders result in muscle atrophy, this is not normally the case with PC. This disease can also present as hyperkalemic periodic paralysis and there is debate as to whether the two disorders are actually distinct. Symptoms and signs Patients ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT) is an inherited genetic disorder that predisposes those affected to potentially life-threatening abnormal heart rhythms or arrhythmias. The arrhythmias seen in CPVT typically occur during exercise or at times of emotional stress, and classically take the form of bidirectional ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation. Those affected may be asymptomatic, but they may also experience blackouts or even sudden cardiac death. CPVT is caused by genetic mutations affecting proteins that regulate the concentrations of calcium within cardiac muscle cells. The most commonly identified gene is RYR2, which encodes a protein included in an ion channel known as the ryanodine receptor; this channel releases calcium from a cell's internal calcium store, the sarcoplasmic reticulum, during every heartbeat. CPVT is often diagnosed from an ECG recorded during an exercise tolerance test, but it may also be diagnosed with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synaptopathy
A synaptopathy is a disease of the brain, spinal cord or peripheral nervous system relating to the dysfunction of synapses. This can arise as a result of a mutation in a gene encoding a synaptic protein such as an ion channel, neurotransmitter receptor, or a protein involved in neurotransmitter release. It can also arise as a result of an autoantibody targeting a synaptic protein. Synaptopathies caused by ion channel mutations are also known as synaptic channelopathies. An example is episodic ataxia. Myasthenia gravis is an example of an autoimmune synaptopathy. Some toxins also affect synaptic function. Tetanus toxin and botulinum toxin affect neurotransmitter release. Tetanus toxin can enter the body via a wound, and botulinum toxin can be ingested or administered therapeutically to alleviate dystonia or as cosmetic treatment. Another example of synaptopathy occurs in the auditory system. This cochlear synaptopathy has been seen after prolonged noise exposure in both primate a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Channel
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by Gating (electrophysiology), gating the flow of ions across the cell membrane, controlling the flow of ions across secretion, secretory and epithelial cells, and regulating cell (biology), cell volume. Ion channels are present in the membranes of all cells. Ion channels are one of the two classes of ionophore, ionophoric proteins, the other being ion transporters. The study of ion channels often involves biophysics, electrophysiology, and pharmacology, while using techniques including voltage clamp, patch clamp, immunohistochemistry, X-ray crystallography, fluoroscopy, and RT-PCR. Their classification as molecules is referred to as channelomics. Basic features There are two distinctive features of ion channels that differentiate them from other types of ion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Arrest
Cardiac arrest (also known as sudden cardiac arrest [SCA]) is when the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating. When the heart stops beating, blood cannot properly Circulatory system, circulate around the body and the blood flow to the brain and other organs is decreased. When the brain does not receive enough blood, this can cause a person to lose consciousness and brain cells can start to die due to lack of oxygen. Coma and persistent vegetative state may result from cardiac arrest. Cardiac arrest is also identified by a lack of Pulse, central pulses and respiratory arrest, abnormal or absent breathing. Cardiac arrest and resultant hemodynamic collapse often occur due to arrhythmias (irregular heart rhythms). Ventricular fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia are most commonly recorded. However, as many incidents of cardiac arrest occur out-of-hospital or when a person is not having their cardiac activity monitored, it is difficult to identify the specific mechanism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myotonia Congenita
''Myotonia congenita'' is a congenital neuromuscular channelopathy that affects skeletal muscles (muscles used for movement). It is a genetic disorder. The hallmark of the disease is the failure of initiated contraction to terminate, often referred to as delayed relaxation of the muscles (myotonia) and rigidity. Symptoms include delayed relaxation of the muscles after voluntary contraction (myotonia), and may also include stiffness, hypertrophy (enlargement), transient weakness in some forms of the disorder (from certain genetic mutations), severe masseter spasm, and cramping. The condition is sometimes referred to as fainting goat syndrome, as it is responsible for the eponymous 'fainting' seen in fainting goats when presented with a sudden stimulus. Of note, ''myotonia congenita'' has no association with malignant hyperthermia (MH). Symptoms and signs The prolonged muscle contractions, which occur most commonly in the leg muscles in recessive mutations, and more commonly in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synapse
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that allows a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or a target effector cell. Synapses can be classified as either chemical or electrical, depending on the mechanism of signal transmission between neurons. In the case of electrical synapses, neurons are coupled bidirectionally with each other through gap junctions and have a connected cytoplasmic milieu. These types of synapses are known to produce synchronous network activity in the brain, but can also result in complicated, chaotic network level dynamics. Therefore, signal directionality cannot always be defined across electrical synapses. Chemical synapses, on the other hand, communicate through neurotransmitters released from the presynaptic neuron into the synaptic cleft. Upon release, these neurotransmitters bind to specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, inducing an electrical or chemical response in the target neuron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease resulting in damage to myelinthe insulating covers of nerve cellsin the brain and spinal cord. As a demyelinating disease, MS disrupts the nervous system's ability to Action potential, transmit signals, resulting in a range of signs and symptoms, including physical, cognitive disability, mental, and sometimes psychiatric problems. Symptoms include double vision, vision loss, eye pain, muscle weakness, and loss of Sensation (psychology), sensation or coordination. MS takes several forms, with new symptoms either occurring in isolated attacks (relapsing forms) or building up over time (progressive forms). In relapsing forms of MS, symptoms may disappear completely between attacks, although some permanent neurological problems often remain, especially as the disease advances. In progressive forms of MS, bodily function slowly deteriorates once symptoms manifest and will steadily worsen if left untreated. While its cause is unclear, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
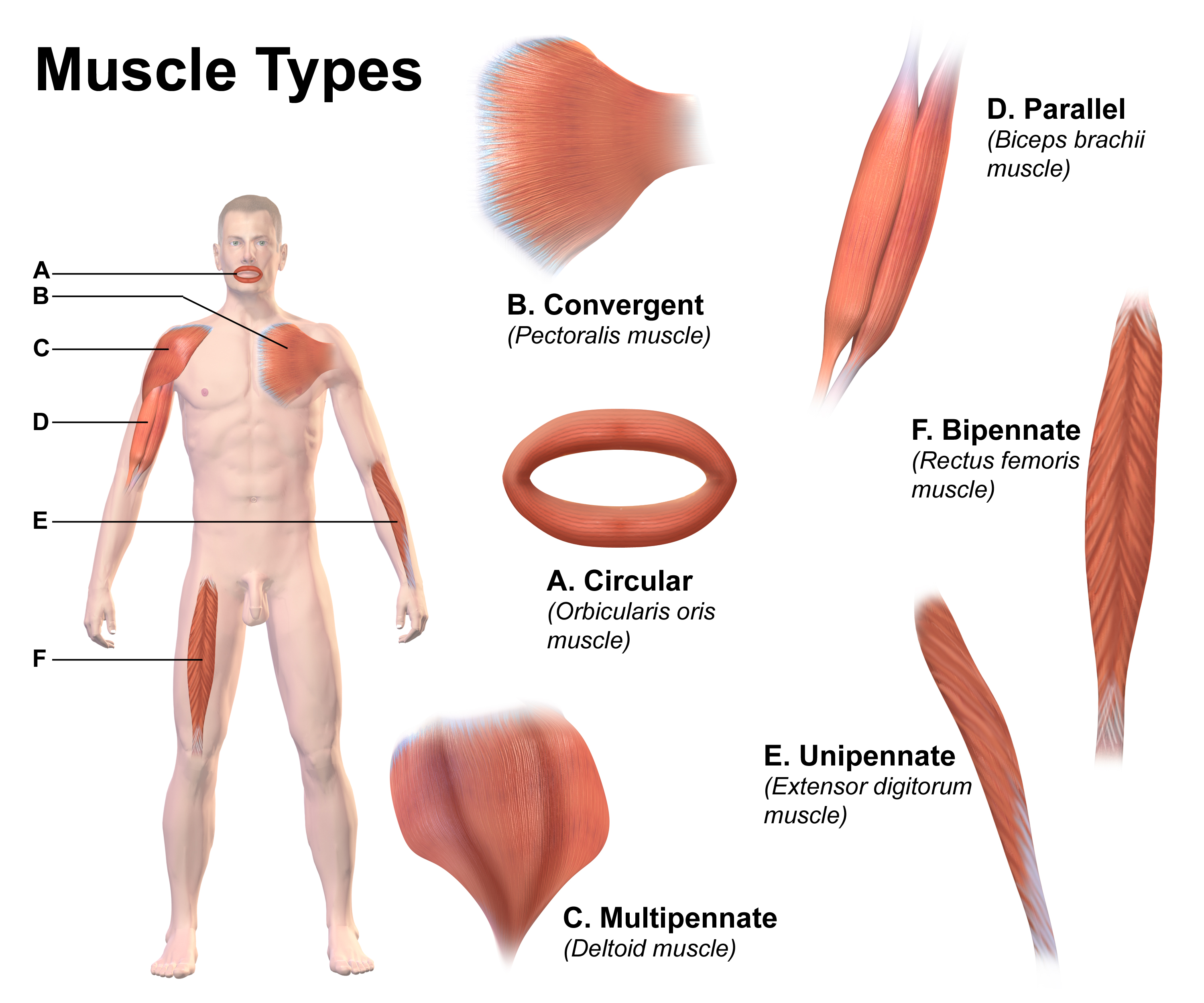
Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal muscle (commonly referred to as muscle) is one of the three types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. They are part of the somatic nervous system, voluntary muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The skeletal muscle cells are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are also known as ''muscle fibers''. The tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated muscle tissue, striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. A skeletal muscle contains multiple muscle fascicle, fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the cell fusion, fusion of developmental myoblasts in a process known as myogenesis resulting in long multinucleated cells. In these cells, the cell nucleus, nuclei, termed ''myonuclei'', are located along the inside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |