|
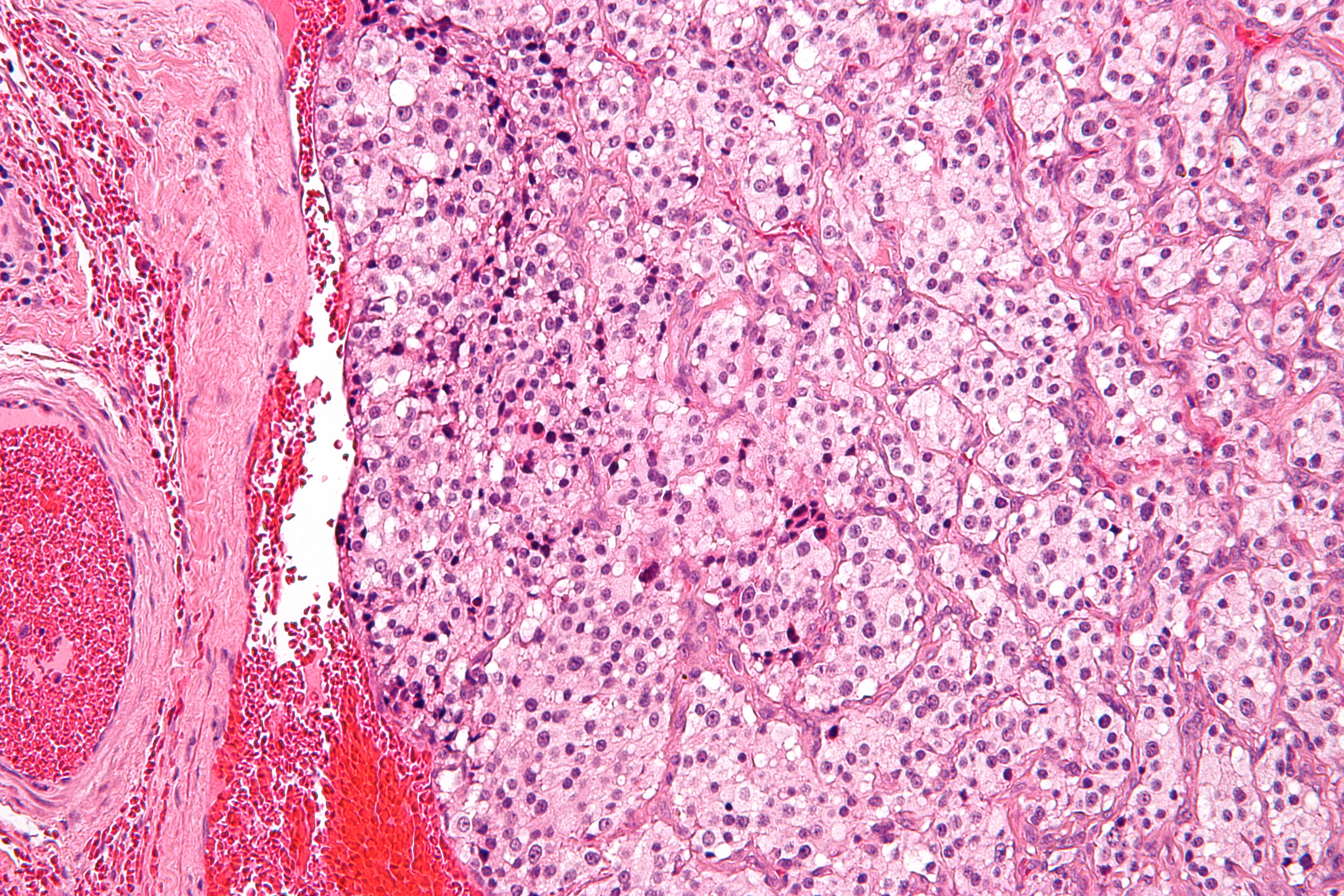
Carotid Body
The carotid body is a small cluster of peripheral chemoreceptor cells and supporting sustentacular cells situated at the bifurcation of each common carotid artery in its tunica externa. The carotid body detects changes in the composition of arterial blood flowing through it, mainly the partial pressure of arterial oxygen, but also of carbon dioxide. It is also sensitive to changes in blood pH, and temperature. Structure The carotid body is situated on the posterior aspect of the bifurcation of the common carotid artery. The carotid body is made up of two types of cells, called glomus cells: glomus type I cells are peripheral chemoreceptors, and glomus type II cells are sustentacular supportive cells. * Glomus type I cells are derived from the neural crest. They release a variety of neurotransmitters, including acetylcholine, ATP, and dopamine that trigger EPSPs in synapsed neurons leading to the respiratory center. They are innervated by axons of the glossopharyngeal n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Branch Of Glossopharyngeal Nerve To Carotid Sinus
The carotid branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve (carotid sinus nerve or Hering's nerve) is a small branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve, glossopharyngeal nerve (cranial nerve IX) that innervates the carotid sinus, and carotid body. Anatomy Course and relations It runs downward anterior to the internal carotid artery. It communicates with the vagus nerve and sympathetic trunk before dividing in the angle of the bifurcation of the common carotid artery to innervate the carotid body, and carotid sinus. Function It conveys information from the baroreceptors of the carotid sinus to the vasomotor center in the brainstem (in order to mediate blood pressure homeostasis), and from chemoreceptors of the carotid body (mainly conveying information about Partial pressure, partial pressures of blood oxygen, and carbon dioxide). References External links * () * {{Authority control Glossopharyngeal nerve Blood pressure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Respiratory Center
The respiratory center is located in the medulla oblongata and pons, in the brainstem. The respiratory center is made up of three major respiratory groups of neurons, two in the medulla and one in the pons. In the medulla they are the dorsal respiratory group, and the ventral respiratory group. In the pons, the pontine respiratory group includes two areas known as the pneumotaxic center and the apneustic center. The respiratory center is responsible for generating and maintaining the rhythm of respiration, and also of adjusting this in homeostatic response to physiological changes. The respiratory center receives input from chemoreceptors, mechanoreceptors, the cerebral cortex, and the hypothalamus in order to regulate the rate and depth of breathing. Input is stimulated by altered levels of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and blood pH, by hormonal changes relating to stress and anxiety from the hypothalamus, and also by signals from the cerebral cortex to give a conscious con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystathionine Gamma-lyase
The enzyme cystathionine γ-lyase (EC 4.4.1.1, CTH or CSE; also cystathionase; systematic name L-cystathionine cysteine-lyase (deaminating; 2-oxobutanoate-forming)) breaks down cystathionine into cysteine, 2-oxobutanoate ( α-ketobutyrate), and ammonia: :L-cystathionine + H2O = L-cysteine + 2-oxobutanoate + NH3 (overall reaction) ::(1a) L-cystathionine = L-cysteine + 2-aminobut-2-enoate ::(1b) 2-aminobut-2-enoate = 2-iminobutanoate (spontaneous) ::(1c) 2-iminobutanoate + H2O = 2-oxobutanoate + NH3 (spontaneous) Pyridoxal phosphate is a prosthetic group of this enzyme. Cystathionine γ-lyase also catalyses the following elimination reactions: * L- homoserine to form H2O, NH3 and 2-oxobutanoate * L-cystine, producing thiocysteine, pyruvate and NH3 * L-cysteine producing pyruvate, NH3 and H2S In some bacteria and mammals, including humans, this enzyme takes part in generating hydrogen sulfide. Hydrogen sulfide is one of a few gases that was recently discovered to have a role ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is toxic, corrosive, and flammable. Trace amounts in ambient atmosphere have a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele is credited with having discovered the chemical composition of purified hydrogen sulfide in 1777. Hydrogen sulfide is toxic to humans and most other animals by inhibiting cellular respiration in a manner similar to hydrogen cyanide. When it is inhaled or its salts are ingested in high amounts, damage to organs occurs rapidly with symptoms ranging from breathing difficulties to convulsions and death. Despite this, the human body produces small amounts of this sulfide and its mineral salts, and uses it as a signalling molecule. Hydrogen sulfide is often produced from the microbial breakdown of organic matter in the absence of oxygen, such as in swamps and sewers; this process is commonly known as anaerobic digestio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoxia (medical)
Hypoxia is a condition in which the body or a region of the body is deprived of an adequate oxygen supply at the tissue (biology), tissue level. Hypoxia may be classified as either ''Generalized hypoxia, generalized'', affecting the whole body, or ''local'', affecting a region of the body. Although hypoxia is often a pathological condition, variations in arterial oxygen concentrations can be part of the normal physiology, for example, during strenuous physical exercise. Hypoxia differs from hypoxemia and anoxemia, in that hypoxia refers to a state in which oxygen present in a tissue or the whole body is insufficient, whereas hypoxemia and anoxemia refer specifically to states that have low or no Oxygen saturation (medicine), oxygen in the blood. Hypoxia in which there is complete absence of oxygen supply is referred to as anoxia. Hypoxia can be due to external causes, when the breathing gas is hypoxic, or internal causes, such as reduced effectiveness of gas transfer in the lung ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pascal (unit)
The pascal (symbol: Pa) is the unit of pressure in the International System of Units (SI). It is also used to quantify internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus, and ultimate tensile strength. The unit, named after Blaise Pascal, is an SI coherent derived unit defined as one newton per square metre (N/m2). It is also equivalent to 10 barye (10 Ba) in the CGS system. Common multiple units of the pascal are the hectopascal (1 hPa = 100 Pa), which is equal to one millibar, and the kilopascal (1 kPa = 1000 Pa), which is equal to one centibar. The unit of measurement called '' standard atmosphere (atm)'' is defined as . Meteorological observations typically report atmospheric pressure in hectopascals per the recommendation of the World Meteorological Organization, thus a standard atmosphere (atm) or typical sea-level air pressure is about 1013 hPa. Reports in the United States typically use inches of mercury or millibars (hectopascals). In Cana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partial Pressure
In a mixture of gases, each constituent gas has a partial pressure which is the notional pressure of that constituent gas as if it alone occupied the entire volume of the original mixture at the same temperature. The total pressure of an ideal gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of the gases in the mixture (Dalton's Law). In respiratory physiology, the partial pressure of a dissolved gas in liquid (such as oxygen in arterial blood) is also defined as the partial pressure of that gas as it would be undissolved in gas phase yet in equilibrium with the liquid. This concept is also known as blood gas tension. In this sense, the diffusion of a gas liquid is said to be driven by differences in partial pressure (not concentration). In chemistry and thermodynamics, this concept is generalized to non-ideal gases and instead called fugacity. The partial pressure of a gas is a measure of its Thermodynamic activity, thermodynamic activity. Gases dissolve, diffuse, and react accor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medulla Oblongata
The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involuntary) functions, ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla contains the cardiovascular center, the respiratory center, vomiting and vasomotor centers, responsible for the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep–wake cycle. "Medulla" is from Latin, ‘pith or marrow’. And "oblongata" is from Latin, ‘lengthened or longish or elongated'. During embryonic development, the medulla oblongata develops from the myelencephalon. The myelencephalon is a secondary brain vesicle which forms during the maturation of the rhombencephalon, also referred to as the hindbrain. The bulb is an archaic term for the medulla oblongata. In modern clinical usage, the word bulbar (as in bulbar palsy) is r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Chemoreceptors
A central chemoreceptor is a chemoreceptor sensitive to the pH of its environment. Central chemoreceptors are located on the ventrolateral medulla oblongata, medullary surface in vicinity of the exit of CN IX and CN X in the central nervous system. These act to detect the changes in pH of nearby cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that are indicative of altered oxygen or carbon dioxide concentrations available to brain tissues. An increase in carbon dioxide causes tension of the arteries, often resulting from increased CO2 output (hypercapnia), indirectly causes the blood to become more acidic; the cerebrospinal fluid pH is closely comparable to blood plasma, plasma, as carbon dioxide easily diffuses across the blood–brain barrier. However, a change in plasma pH alone will not stimulate central chemoreceptors as are not able to diffuse across the blood–brain barrier into the CSF. Only CO2 levels affect this as it can diffuse across, reacting with H2O to form carbonic acid and thus dec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peripheral Chemoreceptors
Peripheral chemoreceptors (of the carotid body, carotid and aortic bodies) are so named because they are sensory neuron, sensory extensions of the peripheral nervous system into blood vessels where they detect changes in chemical concentrations. As transducers of patterns of variability in the surrounding environment, carotid and aortic bodies count as chemosensors in a similar way as taste buds and photoreceptor cell, photoreceptors. However, because carotid and aortic bodies detect variation within the body's internal organs, they are considered interoceptors. Taste buds, olfactory bulbs, photoreceptors, and other receptors associated with the five traditional sensory modalities, by contrast, are exteroceptors in that they respond to stimuli outside the body. The body also contains proprioceptors, which respond to the amount of stretch within the organ (anatomy), organ, usually muscle, that they occupy. As for their particular function, peripheral chemoreceptors help maintain home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossopharyngeal Nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve (), also known as the ninth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IX, or simply CN IX, is a cranial nerve that exits the brainstem from the sides of the upper Medulla oblongata, medulla, just anterior (closer to the nose) to the vagus nerve. Being a mixed nerve (sensorimotor), it carries afferent sensory and efferent motor information. The motor division of the glossopharyngeal nerve is derived from the Basal plate (neural tube), basal plate of the embryonic medulla oblongata, whereas the sensory division originates from the cranial neural crest. Structure From the anterior portion of the medulla oblongata, the glossopharyngeal nerve passes laterally across or below the Flocculus (cerebellar), flocculus, and leaves the skull through the central part of the jugular foramen. From the superior and inferior ganglia in jugular foramen, it has its own sheath of dura mater. The inferior ganglion on the inferior surface of petrous part of temporal is related with a tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afferent Nerve Fiber
Afferent nerve fibers are axons (nerve fibers) of sensory neurons that carry sensory information from sensory receptors to the central nervous system. Many afferent projections ''arrive'' at a particular brain region. In the peripheral nervous system, afferent nerve fibers are part of the sensory nervous system and arise from outside of the central nervous system. Sensory and mixed nerves contain afferent fibers. Structure Afferent neurons are pseudounipolar neurons that have a single process leaving the cell body dividing into two branches: the long one towards the sensory organ, and the short one toward the central nervous system (e.g. spinal cord). These cells do have sensory afferent dendrites, similar to those typically inherent in neurons. They have a smooth and rounded cell body located in the ganglia of the peripheral nervous system. Just outside the spinal cord, thousands of afferent neuronal cell bodies are aggregated in a swelling in the dorsal root known a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |