|
Amiodarone
Amiodarone is an antiarrhythmic medication used to treat and prevent a number of types of cardiac dysrhythmias. This includes ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, and wide complex tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, and paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia. Evidence in cardiac arrest, however, is poor. It can be given by mouth, intravenously, or intraosseously. When used by mouth, it can take a few weeks for effects to begin. Common side effects include feeling tired, tremor, nausea, and constipation. As amiodarone can have serious side effects, it is mainly recommended only for significant ventricular arrhythmias. Serious side effects include lung toxicity such as interstitial pneumonitis, liver problems, heart arrhythmias, vision problems, thyroid problems, and death. If taken during pregnancy or breastfeeding it can cause problems in the fetus or the infant. It is a class III antiarrhythmic medication. It works partly by increasing the time before a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiarrhythmic Agent
Antiarrhythmic agents, also known as cardiac dysrhythmia medications, are a class of drugs that are used to suppress abnormally fast rhythms (tachycardias), such as atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia and ventricular tachycardia. Many attempts have been made to classify antiarrhythmic agents. Many of the antiarrhythmic agents have multiple modes of action, which makes any classification imprecise. Action potential The cardiac myocyte has two general types of action potentials: conduction system and working myocardium. The action potential is divided into 5 phases and shown in the diagram. The sharp rise in voltage ("0") corresponds to the influx of sodium ions, whereas the two decays ("1" and "3", respectively) correspond to the sodium-channel inactivation and the repolarizing efflux of potassium ions. The characteristic plateau ("2") results from the opening of voltage-sensitive calcium channels. Each phase utilizes different channels and it is useful to compar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiarrhythmic Medication
Antiarrhythmic agents, also known as cardiac dysrhythmia medications, are a class of drugs that are used to suppress abnormally fast rhythms (tachycardias), such as atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia and ventricular tachycardia. Many attempts have been made to classify antiarrhythmic agents. Many of the antiarrhythmic agents have multiple modes of action, which makes any classification imprecise. Action potential The cardiac myocyte has two general types of action potentials: conduction system and working myocardium. The action potential is divided into 5 phases and shown in the diagram. The sharp rise in voltage ("0") corresponds to the influx of sodium ions, whereas the two decays ("1" and "3", respectively) correspond to the sodium-channel inactivation and the repolarizing efflux of potassium ions. The characteristic plateau ("2") results from the opening of voltage-sensitive calcium channels. Each phase utilizes different channels and it is useful to com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
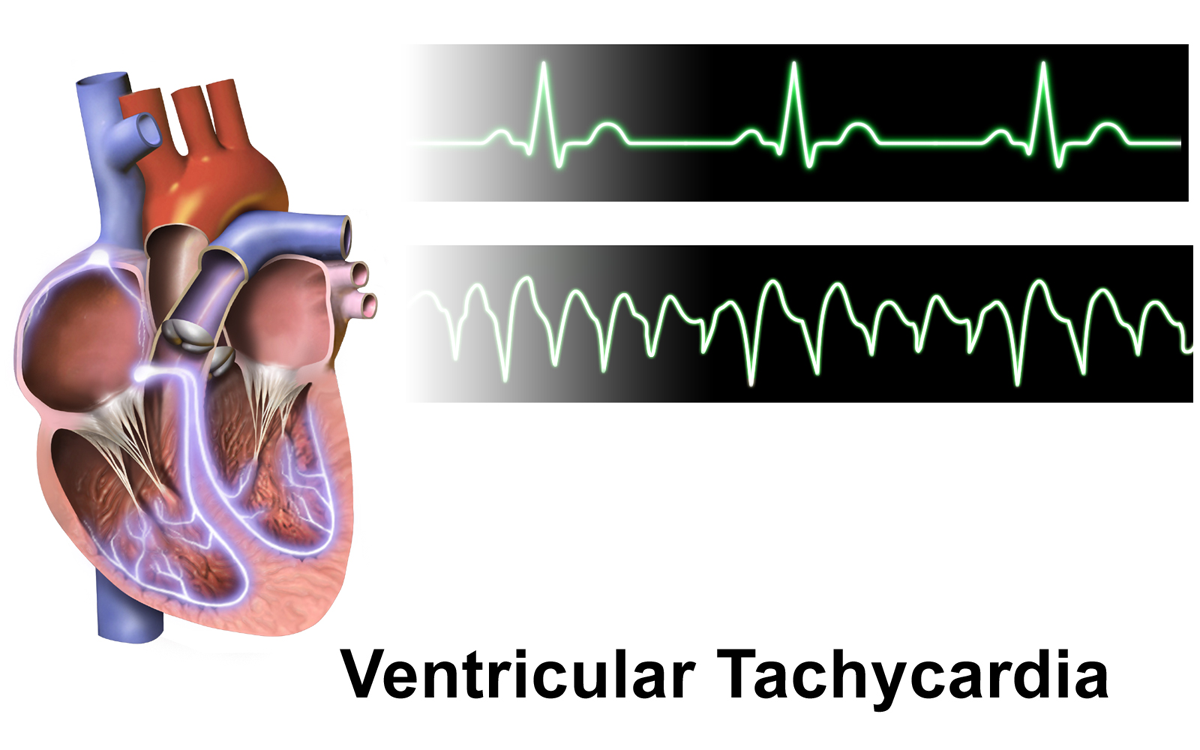
Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia (V-tach or VT) is a cardiovascular disorder in which fast heart rate occurs in the ventricles of the heart. Although a few seconds of VT may not result in permanent problems, longer periods are dangerous; and multiple episodes over a short period of time are referred to as an electrical storm. Short periods may occur without symptoms, or present with lightheadedness, palpitations, shortness of breath, chest pain, and decreased level of consciousness. Ventricular tachycardia may lead to coma and persistent vegetative state due to lack of blood and oxygen to the brain. Ventricular tachycardia may result in ventricular fibrillation (VF) and turn into cardiac arrest. This conversion of the VT into VF is called the degeneration of the VT. It is found initially in about 7% of people in cardiac arrest. Ventricular tachycardia can occur due to coronary heart disease, aortic stenosis, cardiomyopathy, electrolyte imbalance, or a heart attack. Diagnosis i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Arrest
Cardiac arrest (also known as sudden cardiac arrest [SCA]) is when the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating. When the heart stops beating, blood cannot properly Circulatory system, circulate around the body and the blood flow to the brain and other organs is decreased. When the brain does not receive enough blood, this can cause a person to lose consciousness and brain cells can start to die due to lack of oxygen. Coma and persistent vegetative state may result from cardiac arrest. Cardiac arrest is also identified by a lack of Pulse, central pulses and respiratory arrest, abnormal or absent breathing. Cardiac arrest and resultant hemodynamic collapse often occur due to arrhythmias (irregular heart rhythms). Ventricular fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia are most commonly recorded. However, as many incidents of cardiac arrest occur out-of-hospital or when a person is not having their cardiac activity monitored, it is difficult to identify the specific mechanism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardioversion
Cardioversion is a medical procedure by which an abnormally fast heart rate (tachycardia) or other cardiac arrhythmia is converted to a normal rhythm using electricity or drugs. Synchronized electrical cardioversion uses a therapeutic dose of electric current to the heart at a specific moment in the cardiac cycle, restoring the activity of the electrical conduction system of the heart. ( Defibrillation uses a therapeutic dose of electric current to the heart at a random moment in the cardiac cycle, and is the most effective resuscitation measure for cardiac arrest associated with ventricular fibrillation and pulseless ventricular tachycardia.) Pharmacologic cardioversion, also called chemical cardioversion, uses antiarrhythmia medication instead of an electrical shock. Electrical To perform synchronized electrical cardioversion, two electrode pads are used (or, alternatively, the traditional hand-held "paddles"), each comprising a metallic plate which is faced with a saline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
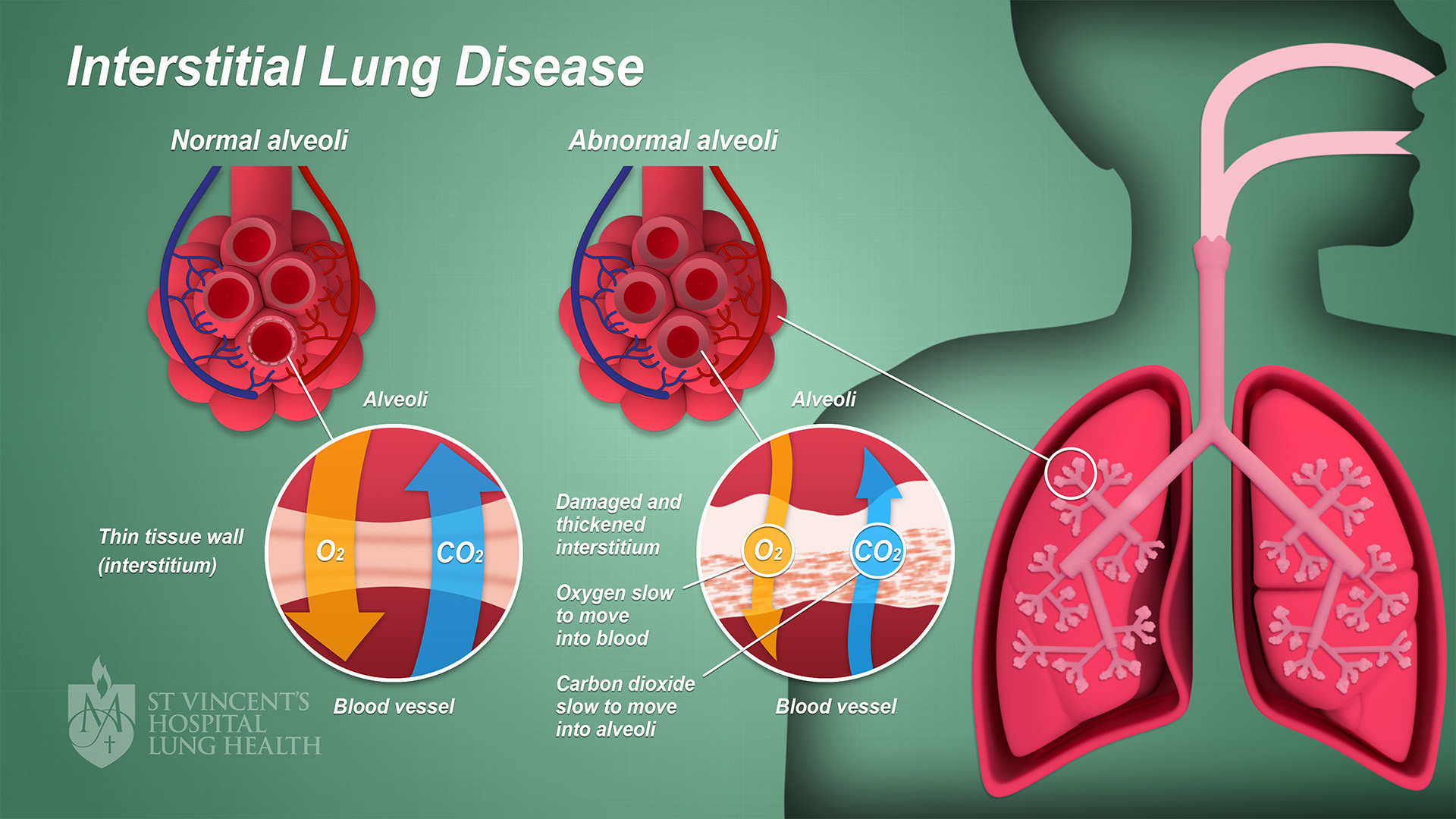
Interstitial Pneumonitis
Interstitial lung disease (ILD), or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD), is a group of respiratory diseases affecting the interstitium (the tissue) and space around the Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli (air sacs) of the lungs. It concerns Pulmonary alveolus, alveolar epithelium, pulmonary capillary endothelium, basement membrane, and Smooth muscle tissue, perivascular and perilymphatic tissues. It may occur when an injury to the lungs triggers an abnormal healing response. Ordinarily, the body generates just the right amount of tissue to repair damage, but in interstitial lung disease, the repair process is disrupted, and the tissue around the air sacs (alveoli) becomes scarred and thickened. This makes it more difficult for oxygen to pass into the bloodstream. The disease presents itself with the following symptoms: shortness of breath, nonproductive coughing, fatigue, and weight loss, which tend to develop slowly, over several months. The average rate of survival for someone with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (AF, AFib or A-fib) is an Heart arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia) characterized by fibrillation, rapid and irregular beating of the Atrium (heart), atrial chambers of the heart. It often begins as short periods of abnormal cardiac cycle, beating, which become longer or continuous over time. It may also start as other forms of arrhythmia such as atrial flutter that then transform into AF. Episodes can be asymptomatic. Symptomatic episodes may involve heart palpitations, syncope (medicine), fainting, Presyncope, lightheadedness, Unconsciousness, loss of consciousness, or shortness of breath. Atrial fibrillation is associated with an increased risk of heart failure, dementia, and stroke. It is a type of supraventricular tachycardia. Atrial fibrillation frequently results from bursts of tachycardia that originate in muscle bundles extending from the Atrium (heart), atrium to the pulmonary veins. Pulmonary vein isolation by catheter ablation, trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
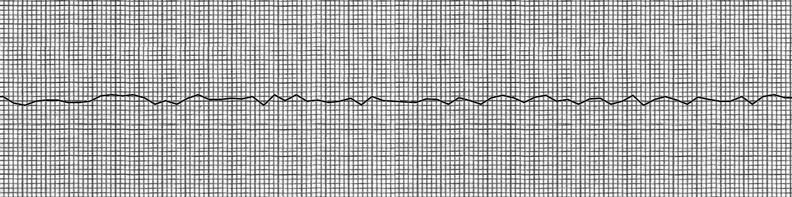
Ventricular Fibrillation
Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib or VF) is an abnormal heart rhythm in which the Ventricle (heart), ventricles of the heart Fibrillation, quiver. It is due to disorganized electrical conduction system of the heart, electrical activity. Ventricular fibrillation results in cardiac arrest with loss of consciousness and no pulse. This is followed by sudden cardiac death in the absence of treatment. Ventricular fibrillation is initially found in about 10% of people with cardiac arrest. Ventricular fibrillation can occur due to coronary heart disease, valvular heart disease, cardiomyopathy, Brugada syndrome, long QT syndrome, electric shock, or intracranial hemorrhage. Diagnosis is by an electrocardiogram (ECG) showing irregular unformed QRS complexes without any clear P wave (electrocardiography), P waves. An important differential diagnosis is torsades de pointes. Treatment is with cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and defibrillation. Defibrillation#Change to a biphasic waveform, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia
Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) is a type of supraventricular tachycardia, named for its intermittent episodes of abrupt onset and termination. Often people have no symptoms. Otherwise symptoms may include palpitations, feeling lightheaded, sweating, shortness of breath, and chest pain. The cause is not known. Risk factors include alcohol, psychostimulants such as caffeine, nicotine, and amphetamines, psychological stress, and Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, which often is heritability, inherited. The underlying mechanism typically involves an accessory pathway that results in re-entry tachycardia, re-entry. Diagnosis is typically by an electrocardiogram (ECG) which shows narrow QRS complexes and a fast heart rhythm typically between 150 and 240 pulse, beats per minute. Vagal maneuvers, such as the Valsalva maneuver, are often used as the initial treatment. If not effective and the person has a normal blood pressure the medication adenosine may be tried. If aden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QT Interval
The QT interval is a measurement made on an Electrocardiography, electrocardiogram used to assess some of the electrical properties of the heart. It is calculated as the time from the start of the QRS complex, Q wave to the end of the T wave, and approximates to the time taken from when the Ventricle (heart), cardiac ventricles start to contract to when they finish relaxing. An abnormally long or abnormally short QT interval is associated with an increased risk of developing Heart arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythms and Cardiac arrest, sudden cardiac death. Abnormalities in the QT interval can be caused by Genetics, genetic conditions such as long QT syndrome, by certain medications such as fluconazole, sotalol or pitolisant, by disturbances in the concentrations of certain Electrolyte, salts within the blood such as Hypokalemia, hypokalaemia, or by Endocrine disease, hormonal imbalances such as hypothyroidism. Measurement The QT interval is most commonly measured in Electrocardi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |