A virus is a submicroscopic
infectious agent
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ.
The term ...
that replicates only inside the living
cells of an
organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have be ...
.
Viruses infect all
life forms
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to life forms:
A life form (also spelled life-form or lifeform) is an entity that is living, such as plants (flora), animals (fauna), and fungi ( funga). It is estimated tha ...
, from animals and plants to
microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic scale, microscopic size, which may exist in its unicellular organism, single-celled form or as a Colony (biology)#Microbial colonies, colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen ...
s, including
bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
and
archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even thou ...
.
Viruses are found in almost every
ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity.
Since
Dmitri Ivanovsky
Dmitri Iosifovich Ivanovsky (alternative spelling ''Dmitrii'' or ''Dmitry Iwanowski''; ; 28 October 1864 – 20 June 1920) was a Russian botanist, the co-discoverer of :viruses (1892), and one of the founders of virology.
Life
Ivanovsky was bo ...
's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial
pathogen
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a Germ theory of d ...
infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the
tobacco mosaic virus
Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus species in the genus '' Tobamovirus'' that infects a wide range of plants, especially tobacco and other members of the family Solanaceae. The infection causes characteris ...
by
Martinus Beijerinck
Martinus Willem Beijerinck (, 16 March 1851 – 1 January 1931) was a Dutch microbiologist and botanist who was one of the founders of virology and environmental microbiology. He is credited with the co-discovery of viruses
A virus i ...
in 1898,
more than 16,000 of the millions of
virus species have been described in detail.
The study of viruses is known as
virology
Virology is the Scientific method, scientific study of biological viruses. It is a subfield of microbiology that focuses on their detection, structure, classification and evolution, their methods of infection and exploitation of host (biology), ...
, a subspeciality of
microbiology
Microbiology () is the branches of science, scientific study of microorganisms, those being of unicellular organism, unicellular (single-celled), multicellular organism, multicellular (consisting of complex cells), or non-cellular life, acellula ...
.
When infected, a
host cell
In biology and medicine, a host is a larger organism that harbours a smaller organism; whether a parasitic, a mutualistic, or a commensalist ''guest'' (symbiont). The guest is typically provided with nourishment and shelter. Examples include ...
is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent viral particles, or ''
virion
A virion (plural, ''viria'' or ''virions'') is an inert virus particle capable of invading a Cell (biology), cell. Upon entering the cell, the virion disassembles and the genetic material from the virus takes control of the cell infrastructure, t ...
s'', consisting of (i)
genetic material
Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that are crucial in all cells and viruses. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomer components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nucleic aci ...
, i.e., long
molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemi ...
s of
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
or
RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyrib ...
that encode the structure of the proteins by which the virus acts; (ii) a
protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
coat, the ''
capsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or m ...
'', which surrounds and protects the genetic material; and in some cases (iii) an outside
envelope
An envelope is a common packaging item, usually made of thin, flat material. It is designed to contain a flat object, such as a letter (message), letter or Greeting card, card.
Traditional envelopes are made from sheets of paper cut to one o ...
of
lipid
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing ...
s. The shapes of these virus particles range from simple
helical and
icosahedral forms to more complex structures. Most virus species have virions too small to be seen with an
optical microscope
The optical microscope, also referred to as a light microscope, is a type of microscope that commonly uses visible light and a system of lenses to generate magnified images of small objects. Optical microscopes are the oldest design of micros ...
and are one-hundredth the size of most bacteria.
The origins of viruses in the
evolutionary history of life
The history of life on Earth traces the processes by which living and extinct organisms evolved, from the earliest emergence of life to the present day. Earth formed about 4.5 billion years ago (abbreviated as ''Ga'', for '' gigaannum'') and ...
are still unclear. Some viruses may have evolved from
plasmid
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria and ...
s, which are pieces of DNA that can move between cells. Other viruses may have evolved from bacteria. In evolution, viruses are an important means of
horizontal gene transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). HGT is an important factor in the e ...
, which increases
genetic diversity
Genetic diversity is the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species. It ranges widely, from the number of species to differences within species, and can be correlated to the span of survival for a species. It is d ...
in a way analogous to
sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete ( haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote tha ...
.
Viruses are considered by some
biologist
A biologist is a scientist who conducts research in biology. Biologists are interested in studying life on Earth, whether it is an individual Cell (biology), cell, a multicellular organism, or a Community (ecology), community of Biological inter ...
s to be a life form, because they carry genetic material, reproduce, and evolve through
natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the Heredity, heritable traits characteristic of a population over generation ...
, although they lack some key characteristics, such as cell structure, that are generally considered necessary criteria for defining life. Because they possess some but not all such qualities, viruses have been described as "organisms at the edge of life"
and as
replicators.
in many ways. One transmission pathway is through disease-bearing organisms known as
vectors: for example, viruses are often transmitted from plant to plant by insects that feed on
plant sap
Sap is a fluid transported in the xylem cells (vessel elements or tracheids) or phloem sieve tube elements of a plant. These cells transport water and nutrients throughout the plant.
Sap is distinct from latex, resin, or cell sap; it is a sep ...
, such as
aphid
Aphids are small sap-sucking insects in the Taxonomic rank, family Aphididae. Common names include greenfly and blackfly, although individuals within a species can vary widely in color. The group includes the fluffy white Eriosomatinae, woolly ...
s; and viruses in animals can be carried by
blood-sucking insects. Many viruses spread
in the air
IN, In or in may refer to:
Dans
* India (country code IN)
* Indiana, United States (postal code IN)
* Ingolstadt, Germany (license plate code IN)
* In, Russia, a town in the Jewish Autonomous Oblast
Businesses and organizations
* Independen ...
by coughing and sneezing, including
influenza viruses
''Orthomyxoviridae'' () is a family of negative-sense RNA viruses. It includes nine genera: '' Alphainfluenzavirus'', '' Betainfluenzavirus'', '' Gammainfluenzavirus'', '' Deltainfluenzavirus'', '' Isavirus'', '' Mykissvirus'', '' Quaranjavir ...
,
SARS-CoV-2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19, the respiratory illness responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had the Novel coronavirus, provisional nam ...
,
chickenpox
Chickenpox, also known as varicella ( ), is a highly contagious disease caused by varicella zoster virus (VZV), a member of the herpesvirus family. The disease results in a characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which ...
,
smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by Variola virus (often called Smallpox virus), which belongs to the genus '' Orthopoxvirus''. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (W ...
, and
measles
Measles (probably from Middle Dutch or Middle High German ''masel(e)'', meaning "blemish, blood blister") is a highly contagious, Vaccine-preventable diseases, vaccine-preventable infectious disease caused by Measles morbillivirus, measles v ...
.
Norovirus
Norovirus, also known as Norwalk virus and sometimes referred to as the winter vomiting disease, is the most common cause of gastroenteritis. Infection is characterized by non-bloody diarrhea, vomiting, and stomach pain. Fever or headaches may ...
and
rotavirus
Rotaviruses are the most common cause of diarrhea, diarrhoeal disease among infants and young children. Nearly every child in the world is infected with a rotavirus at least once by the age of five. Immunity (medical), Immunity develops with ...
, common causes of viral
gastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis, also known as infectious diarrhea, is an inflammation of the Human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract including the stomach and intestine. Symptoms may include diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Fever, lack of ...
, are transmitted by the
faecal–oral route, passed by hand-to-mouth contact or in food or water. The
infectious dose The concept of a minimal infective dose (MID), also known as the infectious dose, has traditionally been used for infectious microorganisms that contaminate foods. MID was defined as the number of microorganisms ingested (the dose) from which a pat ...
of norovirus required to produce infection in humans is fewer than 100 particles.
HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of '' Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the im ...
is one of several viruses
transmitted through sexual contact and by
exposure to infected blood. The variety of host cells that a virus can infect is called its
''host range'': this is ''narrow'' for viruses specialized to infect only a few species, or ''broad'' for viruses capable of infecting many.
Viral infections in animals provoke an
immune response
An immune response is a physiological reaction which occurs within an organism in the context of inflammation for the purpose of defending against exogenous factors. These include a wide variety of different toxins, viruses, intra- and extracellula ...
that usually eliminates the infecting virus. Immune responses can also be produced by
vaccine
A vaccine is a biological Dosage form, preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease, infectious or cancer, malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verifi ...
s, which confer an
artificially acquired immunity to the specific viral infection. Some viruses, including those that cause
HIV/AIDS
The HIV, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. Without treatment, it can lead to a spectrum of conditions including acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It is a Preventive healthcare, pr ...
,
HPV infection, and
viral hepatitis, evade these immune responses and result in
chronic infections. Several classes of
antiviral drug
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Antiviral drugs are a class of antimicrobials ...
s have been developed.
Etymology
The English word "virus" comes from the
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
word , which refers to
poison
A poison is any chemical substance that is harmful or lethal to living organisms. The term is used in a wide range of scientific fields and industries, where it is often specifically defined. It may also be applied colloquially or figurati ...
and other noxious liquids. comes from the same
Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e. ...
root as
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
,
Avestan
Avestan ( ) is the liturgical language of Zoroastrianism. It belongs to the Iranian languages, Iranian branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family and was First language, originally spoken during the Avestan period, Old ...
, and
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
(), which all mean "poison". The first attested use of "virus" in English appeared in 1398 in
John Trevisa
350px,
John Trevisa (or John of Trevisa; ; fl. 1342–1402 AD) was a Cornish writer and professional translator.
Trevisa was born at Trevessa in the parish of St Enoder in mid-Cornwall, in Britain and was a native Cornish speaker. He was edu ...
's translation of
Bartholomeus Anglicus
Bartholomaeus Anglicus (before 1203–1272), also known as Bartholomew the Englishman and Berthelet, was an early 13th-century scholasticism, Scholastic of Paris, a member of the Franciscan order. He was the author of the compendium ''De propri ...
's ''De Proprietatibus Rerum''.
''Virulent'', from Latin ''virulentus'' ('poisonous'), dates to . A meaning of 'agent that causes infectious disease' is first recorded in 1728,
long before the discovery of viruses by
Dmitri Ivanovsky
Dmitri Iosifovich Ivanovsky (alternative spelling ''Dmitrii'' or ''Dmitry Iwanowski''; ; 28 October 1864 – 20 June 1920) was a Russian botanist, the co-discoverer of :viruses (1892), and one of the founders of virology.
Life
Ivanovsky was bo ...
in 1892. The English
plural
In many languages, a plural (sometimes list of glossing abbreviations, abbreviated as pl., pl, , or ), is one of the values of the grammatical number, grammatical category of number. The plural of a noun typically denotes a quantity greater than ...
is ''viruses'' (sometimes also ''vira''), whereas the Latin word is a
mass noun
In linguistics, a mass noun, uncountable noun, non-count noun, uncount noun, or just uncountable, is a noun with the syntactic property that any quantity of it is treated as an undifferentiated unit, rather than as something with discrete eleme ...
, which has no
classically attested plural (''vīra'' is used in
Neo-Latin
Neo-LatinSidwell, Keith ''Classical Latin-Medieval Latin-Neo Latin'' in ; others, throughout. (also known as New Latin and Modern Latin) is the style of written Latin used in original literary, scholarly, and scientific works, first in Italy d ...
). The adjective ''viral'' dates to 1948. The term ''virion'' (plural ''virions''), which dates from 1959,
is also used to refer to a single viral particle that is released from the cell and is capable of infecting other cells of the same type.
Origins
Viruses are found wherever there is life and have probably existed since living cells
first evolved.
The origin of viruses is unclear because they do not form fossils, so
molecular techniques are used to infer how they arose.
In addition, viral genetic material occasionally integrates into the
germline
In biology and genetics, the germline is the population of a multicellular organism's cells that develop into germ cells. In other words, they are the cells that form gametes ( eggs and sperm), which can come together to form a zygote. They dif ...
of the host organisms, by which they can be passed on
vertically to the offspring of the host for many generations. This provides an invaluable source of information for
paleovirologists to trace back ancient viruses that existed as far back as millions of years ago.
There are three main hypotheses that aim to explain the origins of viruses:
; Regressive hypothesis: Viruses may have once been small cells that
parasitised larger cells. Over time, genes not required by their parasitism were lost. The bacteria
rickettsia
''Rickettsia'' is a genus of nonmotile, gram-negative, nonspore-forming, highly pleomorphic bacteria that may occur in the forms of cocci (0.1 μm in diameter), bacilli (1–4 μm long), or threads (up to about 10 μm long). The genus was n ...
and
chlamydia
Chlamydia, or more specifically a chlamydia infection, is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Chlamydia trachomatis''. Most people who are infected have no symptoms. When symptoms do appear, they may occur only several w ...
are living cells that, like viruses, can reproduce only inside host cells. They lend support to this hypothesis, as their dependence on parasitism is likely to have caused the loss of genes that enabled them to survive outside a cell. This is also called the "degeneracy hypothesis",
or "reduction hypothesis".
; Cellular origin hypothesis: Some viruses may have evolved from bits of DNA or RNA that "escaped" from the genes of a larger organism. The escaped DNA could have come from
plasmid
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria and ...
s (pieces of naked DNA that can move between cells) or
transposons
A transposable element (TE), also transposon, or jumping gene, is a type of mobile genetic element, a nucleic acid sequence in DNA that can change its position within a genome.
The discovery of mobile genetic elements earned Barbara McClinto ...
(molecules of DNA that replicate and move around to different positions within the genes of the cell).
Once called "jumping genes", transposons are examples of
mobile genetic elements
Mobile genetic elements (MGEs), sometimes called selfish genetic elements, are a type of genetic material that can move around within a genome, or that can be transferred from one species or replicon to another. MGEs are found in all organisms. In ...
and could be the origin of some viruses. They were discovered in maize by
Barbara McClintock
Barbara McClintock (June 16, 1902 – September 2, 1992) was an American scientist and cytogenetics, cytogeneticist who was awarded the 1983 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. McClintock received her PhD in botany from Cornell University ...
in 1950. This is sometimes called the "vagrancy hypothesis",
or the "escape hypothesis".
; Co-evolution hypothesis: This is also called the "virus-first hypothesis"
and proposes that viruses may have evolved from complex molecules of protein and
nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that are crucial in all cells and viruses. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomer components: a pentose, 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nuclei ...
at the same time that cells first appeared on Earth and would have been dependent on cellular life for billions of years.
Viroids
Viroids are small single-stranded, circular RNAs that are infectious pathogens. Unlike viruses, they have no protein coating. All known viroids are inhabitants of angiosperms (flowering plants), and most cause diseases, whose respective econo ...
are molecules of RNA that are not classified as viruses because they lack a protein coat. They have characteristics that are common to several viruses and are often called
subviral agents.
Viroids are important pathogens of plants.
They do not code for proteins but interact with the host cell and use the host machinery for their replication.
The
hepatitis delta virus
Hepatitis D is a type of viral hepatitis caused by the hepatitis delta virus (HDV). HDV is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E. HDV is considered to be a satellite (a type of subviral agent) because it can propagate only in ...
of humans has an RNA
genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
similar to viroids but has a protein coat derived from hepatitis B virus and cannot produce one of its own. It is, therefore, a defective virus. Although hepatitis delta virus genome may replicate independently once inside a host cell, it requires the help of hepatitis B virus to provide a protein coat so that it can be transmitted to new cells.
In similar manner, the
sputnik virophage
Sputnik virophage (from Russian "satellite") is a subviral agent that reproduces in amoeba cells that are already infected by a certain helper virus; Sputnik uses the helper virus's machinery for reproduction and inhibits replication of the ...
is dependent on
mimivirus
''Mimivirus'' is a genus of giant viruses, in the family ''Mimiviridae''. It is believed that Amoeba serve as their natural hosts. It also refers to a group of phylogenetically related large viruses.
In colloquial speech, APMV is more commonly ...
, which infects the protozoan ''
Acanthamoeba
''Acanthamoeba'' is a genus of amoeboid, amoebae that are commonly recovered from soil, fresh water, and other habitat (ecology), habitats.
The genus ''Acanthamoeba'' has two stages in its life cycle, the metabolically active trophozoite stage a ...
castellanii''.
These viruses, which are dependent on the presence of other virus species in the host cell, are called "
satellites
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scientif ...
" and may represent evolutionary intermediates of viroids and viruses.
In the past, there were problems with all of these hypotheses: the regressive hypothesis did not explain why even the smallest of cellular parasites do not resemble viruses in any way. The escape hypothesis did not explain the complex capsids and other structures on virus particles. The virus-first hypothesis contravened the definition of viruses in that they require host cells.
Viruses are now recognised as ancient and as having origins that pre-date the divergence of life into the
three domains.
This discovery has led modern virologists to reconsider and re-evaluate these three classical hypotheses.
The evidence for an
ancestral world of RNA cells
and computer analysis of viral and host DNA sequences give a better understanding of the evolutionary relationships between different viruses and may help identify the ancestors of modern viruses. To date, such analyses have not proved which of these hypotheses is correct.
It seems unlikely that all currently known viruses have a common ancestor, and viruses have probably arisen numerous times in the past by one or more mechanisms.
Microbiology
Discovery
The first evidence of the existence of viruses came from experiments with filters that had pores small enough to retain bacteria. In 1892,
Dmitri Ivanovsky
Dmitri Iosifovich Ivanovsky (alternative spelling ''Dmitrii'' or ''Dmitry Iwanowski''; ; 28 October 1864 – 20 June 1920) was a Russian botanist, the co-discoverer of :viruses (1892), and one of the founders of virology.
Life
Ivanovsky was bo ...
used one of these filters to show that sap from a diseased tobacco plant remained infectious to healthy tobacco plants despite having been filtered. Martinus Beijerinck called the filtered, infectious substance a "virus" and this discovery is considered to be the beginning of virology.
The subsequent discovery and partial characterization of
bacteriophage
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a phage (), is a virus that infects and replicates within bacteria. The term is derived . Bacteriophages are composed of proteins that Capsid, encapsulate a DNA or RNA genome, and may have structu ...
s by
Frederick Twort
Frederick William Twort FRS (22 October 1877 – 20 March 1950) was an English bacteriologist and was the original discoverer in 1915 of bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria). He studied medicine at St Thomas's Hospital, London, was sup ...
and
Félix d'Herelle further catalyzed the field, and by the early 20th century many viruses had been discovered. In 1926,
Thomas Milton Rivers
Thomas Milton Rivers (September 3, 1888 – May 12, 1962) was an American bacteriologist and virologist. He has been described as the "father of modern virology."
Life
Born in Jonesboro, Georgia, he graduated from Emory College in 1909 with ...
defined viruses as obligate parasites. Viruses were demonstrated to be particles, rather than a fluid, by
Wendell Meredith Stanley, and the invention of the
electron microscope
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of electrons as a source of illumination. It uses electron optics that are analogous to the glass lenses of an optical light microscope to control the electron beam, for instance focusing it ...
in 1931 allowed their complex structures to be visualised.
Life properties
Scientific opinions differ on whether viruses are a form of life or organic structures that interact with living organisms.
They have been described as "organisms at the edge of life",
since they resemble organisms in that they possess
genes
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
, evolve by
natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the Heredity, heritable traits characteristic of a population over generation ...
,
and reproduce by creating multiple copies of themselves through self-assembly. Although they have genes, they do not have a cellular structure, which is often seen as the basic unit of life. Viruses do not have their own
metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the co ...
and require a host cell to make new products. They therefore cannot naturally reproduce outside a host cell
—although some bacteria such as
rickettsia
''Rickettsia'' is a genus of nonmotile, gram-negative, nonspore-forming, highly pleomorphic bacteria that may occur in the forms of cocci (0.1 μm in diameter), bacilli (1–4 μm long), or threads (up to about 10 μm long). The genus was n ...
and
chlamydia
Chlamydia, or more specifically a chlamydia infection, is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Chlamydia trachomatis''. Most people who are infected have no symptoms. When symptoms do appear, they may occur only several w ...
are considered living organisms despite the same limitation.
Accepted forms of life use
cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell (biology), cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukar ...
to reproduce, whereas viruses spontaneously assemble within cells. They differ from
autonomous growth of
crystals
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macrosc ...
as they inherit genetic mutations while being subject to natural selection. Virus self-assembly within host cells has implications for the study of the
origin of life
Abiogenesis is the natural process by which life arises from abiotic component, non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The prevailing scientific hypothesis is that the transition from non-living to organism, living entities on ...
, as it lends further credence to the hypothesis that life could have started as
self-assembling organic molecules.
The
virocell model first proposed by
Patrick Forterre considers the infected cell to be the "living form" of viruses and that virus particles (virions) are analogous to
spore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual reproduction, sexual (in fungi) or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for biological dispersal, dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores fo ...
s. Although the living versus non-living debate continues, the virocell model has gained some acceptance.
Structure
Viruses display a wide diversity of sizes and shapes, called '
morphologies'. In general, viruses are much smaller than bacteria and more than a thousand bacteriophage viruses would fit inside an ''
Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' ( )Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Escherichia'' that is commonly fo ...
'' bacterium's cell.
Many viruses that have been studied are spherical and have a diameter between 20 and 300
nanometres
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the Molecule">molecular scale.
The nanometre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: nm), or nanometer (American spelling), is a unit of length ...
. Some
filovirus
''Filoviridae'' () is a family of single-stranded negative-sense RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Two members of the family that are commonly known are Ebola virus and Marburg virus. Both viruses, and some of their lesser known rela ...
es, which are filaments, have a total length of up to 1400 nm; their diameters are only about 80 nm.
Most viruses cannot be seen with an
optical microscope
The optical microscope, also referred to as a light microscope, is a type of microscope that commonly uses visible light and a system of lenses to generate magnified images of small objects. Optical microscopes are the oldest design of micros ...
, so scanning and transmission
electron microscope
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of electrons as a source of illumination. It uses electron optics that are analogous to the glass lenses of an optical light microscope to control the electron beam, for instance focusing it ...
s are used to visualise them.
To increase the contrast between viruses and the background, electron-dense "stains" are used. These are solutions of
salts
In chemistry, a salt or ionic compound is a chemical compound consisting of an assembly of positively charged ions ( cations) and negatively charged ions (anions), which results in a compound with no net electric charge (electrically neutral). ...
of heavy metals, such as
tungsten
Tungsten (also called wolfram) is a chemical element; it has symbol W and atomic number 74. It is a metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively in compounds with other elements. It was identified as a distinct element in 1781 and first ...
, that scatter the electrons from regions covered with the stain. When virions are coated with stain (positive staining), fine detail is obscured.
Negative staining In microscopy, negative staining is an established method, often used in diagnostic microscopy, for contrasting a thin biological specimen, specimen with an optics, optically opacity (optics), opaque fluid. In this technique, the background is stain ...
overcomes this problem by staining the background only.
A complete virus particle, known as a ''virion'', consists of nucleic acid surrounded by a protective coat of protein called a
capsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or m ...
. These are formed from protein subunits called
capsomere
The capsomere is a subunit of the capsid, an outer covering of protein that protects the genetic material of a virus. Capsomeres self-assemble to form the capsid.
Subunits called protomers aggregate to form capsomeres. Various arrangements of c ...
s.
Viruses can have a
lipid
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing ...
"envelope" derived from the host
cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extr ...
. The capsid is made from proteins encoded by the viral
genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
and its shape serves as the basis for morphological distinction.
Virally-coded protein subunits will self-assemble to form a capsid, in general requiring the presence of the virus genome. Complex viruses code for proteins that assist in the construction of their capsid. Proteins associated with nucleic acid are known as
nucleoprotein
Nucleoproteins are proteins conjugated with nucleic acids (either DNA or RNA). Typical nucleoproteins include ribosomes, nucleosomes and viral nucleocapsid proteins.
Structures
Nucleoproteins tend to be positively charged, facilitating inte ...
s, and the association of viral capsid proteins with viral nucleic acid is called a nucleocapsid. The capsid and entire virus structure can be mechanically (physically) probed through
atomic force microscopy
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) or scanning force microscopy (SFM) is a very-high-resolution type of scanning probe microscopy (SPM), with demonstrated resolution on the order of fractions of a nanometer, more than 1000 times better than the opti ...
.
In general, there are five main morphological virus types:
; Helical: These viruses are composed of a single type of capsomere stacked around a central axis to form a
helical structure, which may have a central cavity, or tube. This arrangement results in virions which can be short and highly rigid rods, or long and very flexible filaments. The genetic material (typically single-stranded RNA, but single-stranded DNA in some cases) is bound into the protein helix by interactions between the negatively charged nucleic acid and positive charges on the protein. Overall, the length of a helical capsid is related to the length of the nucleic acid contained within it, and the diameter is dependent on the size and arrangement of capsomeres. The well-studied tobacco mosaic virus
and inovirus are examples of helical viruses.
; Icosahedral: Most animal viruses are icosahedral or near-spherical with chiral
icosahedral symmetry
In mathematics, and especially in geometry, an object has icosahedral symmetry if it has the same symmetries as a regular icosahedron. Examples of other polyhedra with icosahedral symmetry include the regular dodecahedron (the dual polyhedr ...
. A
regular icosahedron
The regular icosahedron (or simply ''icosahedron'') is a convex polyhedron that can be constructed from pentagonal antiprism by attaching two pentagonal pyramids with Regular polygon, regular faces to each of its pentagonal faces, or by putting ...
is the optimum way of forming a closed shell from identical subunits. The minimum number of capsomeres required for each triangular face is 3, which gives 60 for the icosahedron. Many viruses, such as rotavirus, have more than 60 capsomers and appear spherical but they retain this symmetry. To achieve this, the capsomeres at the apices are surrounded by five other capsomeres and are called pentons. Capsomeres on the triangular faces are surrounded by six others and are called
hexons.
Hexons are in essence flat and pentons, which form the 12 vertices, are curved. The same protein may act as the subunit of both the pentamers and hexamers or they may be composed of different proteins.
; Prolate: This is an icosahedron elongated along the fivefold axis and is a common arrangement of the heads of bacteriophages. This structure is composed of a cylinder with a cap at either end.
; Enveloped:Some species of virus
envelop themselves in a modified form of one of the
cell membranes
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extra ...
, either the outer membrane surrounding an infected host cell or internal membranes such as a nuclear membrane or
endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a part of a transportation system of the eukaryote, eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. The word endoplasmic means "within the cytoplasm", and reticulum is Latin for ...
, thus gaining an outer lipid bilayer known as a
viral envelope
A viral envelope is the outermost layer of many types of viruses. It protects the genetic material in their life cycle when traveling between host cells. Not all viruses have envelopes. A viral envelope protein or E protein is a protein in the en ...
. This membrane is studded with proteins coded for by the viral genome and host genome; the lipid membrane itself and any carbohydrates present originate entirely from the host.
Influenza virus
''Orthomyxoviridae'' () is a family of negative-sense RNA viruses. It includes nine genera: '' Alphainfluenzavirus'', '' Betainfluenzavirus'', '' Gammainfluenzavirus'', '' Deltainfluenzavirus'', '' Isavirus'', '' Mykissvirus'', '' Quaranjavir ...
,
HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of '' Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the im ...
(which causes
AIDS
The HIV, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. Without treatment, it can lead to a spectrum of conditions including acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It is a Preventive healthcare, pr ...
), and
severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19, the respiratory illness responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had the Novel coronavirus, provisional nam ...
(which causes
COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. In January 2020, the disease spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic.
The symptoms of COVID‑19 can vary but often include fever ...
)
use this strategy. Most enveloped viruses are dependent on the envelope for their infectivity.
; Complex: These viruses possess a capsid that is neither purely helical nor purely icosahedral, and that may possess extra structures such as protein tails or a complex outer wall. Some bacteriophages, such as
Enterobacteria phage T4
Escherichia virus T4 is a species of bacteriophages that infect ''Escherichia coli'' bacteria. It is a double-stranded DNA virus in the subfamily '' Tevenvirinae'' of the family '' Straboviridae''. T4 is capable of undergoing only a lytic li ...
, have a complex structure consisting of an icosahedral head bound to a helical tail, which may have a
hexagon
In geometry, a hexagon (from Greek , , meaning "six", and , , meaning "corner, angle") is a six-sided polygon. The total of the internal angles of any simple (non-self-intersecting) hexagon is 720°.
Regular hexagon
A regular hexagon is de ...
al base plate with protruding protein tail fibres. This tail structure acts like a molecular syringe, attaching to the bacterial host and then injecting the viral genome into the cell.
The
poxviruses
''Poxviridae'' is a family of double-stranded DNA viruses. Vertebrates and arthropods serve as natural hosts. The family contains 22 genera that are assigned to two subfamilies: ''Chordopoxvirinae'' and ''Entomopoxvirinae''. ''Entomopoxvirinae'' ...
are large, complex viruses that have an unusual morphology. The viral genome is associated with proteins within a central disc structure known as a
nucleoid
The nucleoid (meaning '' nucleus-like'') is an irregularly shaped region within the prokaryotic cell that contains all or most of the genetic material. The chromosome of a typical prokaryote is circular, and its length is very large compared to ...
. The nucleoid is surrounded by a membrane and two lateral bodies of unknown function. The virus has an outer envelope with a thick layer of protein studded over its surface. The whole virion is slightly
pleomorphic, ranging from ovoid to brick-shaped.
Giant viruses
Mimivirus
''Mimivirus'' is a genus of giant viruses, in the family ''Mimiviridae''. It is believed that Amoeba serve as their natural hosts. It also refers to a group of phylogenetically related large viruses.
In colloquial speech, APMV is more commonly ...
is one of the largest characterised viruses, with a capsid diameter of 400 nm. Protein filaments measuring 100 nm project from the surface. The capsid appears hexagonal under an electron microscope, therefore the capsid is probably icosahedral.
In 2011, researchers discovered the largest then known virus in samples of water collected from the ocean floor off the coast of Las Cruces, Chile. Provisionally named ''
Megavirus
''Megavirus'' is a viral genus, phylogenetically related to '' Acanthamoeba polyphaga mimivirus'' (APMV). In colloquial speech, ''Megavirus chilense'' is more commonly referred to as just "Megavirus". Until the discovery of pandoraviruses in 2 ...
chilensis'', it can be seen with a basic optical microscope.
In 2013, the
Pandoravirus
''Pandoravirus'' is a proposed genus of giant virus, first discovered in 2013. It is the third largest in physical size of any known viral genus, behind Pithovirus and Megaklothovirus. Pandoraviruses have double stranded DNA genomes, with t ...
genus was discovered in Chile and Australia, and has genomes about twice as large as Megavirus and Mimivirus.
All giant viruses have dsDNA genomes and they are classified into several families: ''
Mimiviridae
''Mimiviridae'' is a family of viruses. Amoeba and other protists serve as natural hosts. The family contains three subfamilies that contain nine genera., UCPMS ID: 1889607PDF/ref> Fig. 4 and §Discussion: "Considering that tupanviruses c ...
, Pithoviridae,
Pandoraviridae
''Pandoraviridae'' is a proposed family of double-stranded DNA viruses that infect amoebae. There is only one genus in this family: ''Pandoravirus''. Several species in this genus have been described, including '' Pandoravirus dulcis'', '' Pand ...
,
Phycodnaviridae
''Phycodnaviridae'' is a family of large (100–560 kb) double-stranded DNA viruses that infect marine or freshwater eukaryotic algae. Viruses within this family have a similar morphology, with an icosahedral capsid (polyhedron with 20 f ...
,'' and the
Mollivirus genus.
Some viruses that infect
Archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even thou ...
have complex structures unrelated to any other form of virus, with a wide variety of unusual shapes, ranging from spindle-shaped structures to viruses that resemble hooked rods, teardrops or even bottles. Other archaeal viruses resemble the tailed bacteriophages, and can have multiple tail structures.
Genome
An enormous variety of genomic structures can be seen among
viral species
Virus classification is the process of naming viruses and placing them into a taxonomic system similar to the classification systems used for cellular organisms.
Viruses are classified by phenotypic characteristics, such as morphology, nucleic ...
; as a group, they contain more structural genomic diversity than plants, animals, archaea, or bacteria. There are millions of different types of viruses,
although fewer than 7,000 types have been described in detail.
As of January 2021, the
NCBI
The National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) is part of the National Library of Medicine (NLM), a branch of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). It is approved and funded by the government of the United States. The NCBI is loca ...
Virus genome database has more than 193,000 complete genome sequences,
but there are doubtlessly many more to be discovered.
A virus has either a
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
or an
RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyrib ...
genome and is called a
DNA virus
A DNA virus is a virus that has a genome made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that is replicated by a DNA polymerase. They can be divided between those that have two strands of DNA in their genome, called double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses, and t ...
or an
RNA virus
An RNA virus is a virus characterized by a ribonucleic acid (RNA) based genome. The genome can be single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) or double-stranded (Double-stranded RNA, dsRNA). Notable human diseases caused by RNA viruses include influenza, SARS, ...
, respectively. Some RNA viruses, for example retroviruses, have a stage in their replication cycle where the genome is encoded in DNA.
Most viruses have RNA genomes. Plant viruses tend to have single-stranded RNA genomes and bacteriophages tend to have double-stranded DNA genomes.
Viral genomes are circular, as in the
polyomavirus
''Polyomaviridae'' is a family of DNA viruses whose natural hosts are mammals and birds. As of 2024, there are eight recognized genera. Fourteen species are known to infect humans, while others, such as Simian Virus 40, have been identified i ...
es, or linear, as in the
adenoviruses
Adenoviruses (members of the family ''Adenoviridae'') are medium-sized (90–100 nm), nonenveloped (without an outer lipid bilayer) viruses with an icosahedral nucleocapsid containing a double-stranded DNA genome. Their name derives from the ...
. The type of nucleic acid is irrelevant to the shape of the genome. Among RNA viruses and certain DNA viruses, the genome is often divided into separate parts, in which case it is called segmented. For RNA viruses, each segment often codes for only one protein and they are usually found together in one capsid. All segments are not required to be in the same virion for the virus to be infectious, as demonstrated by
brome mosaic virus
Brome mosaic virus (BMV) is a small (28 nanometer, nm, 86Svedberg, S), positive-stranded, icosahedral RNA plant virus belonging to the genus ''Bromovirus'', family ''Bromoviridae'', in the ''Alphavirus''-like superfamily.
Brome mosaic virus was ...
and several other plant viruses.
A viral genome, irrespective of nucleic acid type, is almost always either single-stranded (ss) or double-stranded (ds). Single-stranded genomes consist of an unpaired nucleic acid, analogous to one-half of a ladder split down the middle. Double-stranded genomes consist of two complementary paired nucleic acids, analogous to a ladder. The virus particles of some virus families, such as those belonging to the ''
Hepadnaviridae
''Hepadnaviridae'' is a family of viruses. Humans, apes, and birds serve as natural hosts. The family contains five genera. Its best-known member is hepatitis B virus. Diseases associated with this family include: liver infections, such as hep ...
'', contain a genome that is partially double-stranded and partially single-stranded.
For most viruses with RNA genomes and some with single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) genomes, the single strands are said to be either
positive-sense (called the 'plus-strand') or
negative-sense
In molecular biology and genetics, the sense of a nucleic acid molecule, particularly of a strand of DNA or RNA, refers to the nature of the roles of the strand and its complement in specifying a sequence of amino acids. Depending on the context, ...
(called the 'minus-strand'), depending on if they are complementary to the viral
messenger RNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is created during the ...
(mRNA). Positive-sense viral RNA is in the same sense as viral mRNA and thus at least a part of it can be immediately
translated by the host cell. Negative-sense viral RNA is complementary to mRNA and thus must be converted to positive-sense RNA by an
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) or RNA replicase is an enzyme that catalyzes the self-replication, replication of RNA from an RNA template. Specifically, it catalyzes synthesis of the RNA strand Complementarity (molecular biology), compleme ...
before translation. DNA nomenclature for viruses with genomic ssDNA is similar to RNA nomenclature, in that positive-strand viral ssDNA is identical in sequence to the viral mRNA and is thus a coding strand, while negative-sense viral ssDNA is complementary to the viral mRNA and is thus a template strand.
Several types of ssDNA and ssRNA viruses have genomes that are
ambisense
In molecular biology and genetics, the sense of a nucleic acid molecule, particularly of a strand of DNA or RNA, refers to the nature of the roles of the strand and its complement in specifying a sequence of amino acids. Depending on the context, ...
in that transcription can occur off both strands in a double-stranded replicative intermediate. Examples include
geminiviruses, which are ssDNA plant viruses and
arenavirus
An arenavirus is a bi- or trisegmented ambisense RNA virus that is a member of the family ''Arenaviridae''. These viruses infect rodents and occasionally humans. A class of novel, highly divergent arenaviruses, properly known as reptarenavirus ...
es, which are ssRNA viruses of animals.
Genome size
Genome size varies greatly between species. The smallest—the ssDNA circoviruses, family ''
Circoviridae
''Circoviridae'' is a family of DNA viruses. Birds and mammals serve as natural hosts. The family has two genera. Diseases associated with this family include: PCV-2: postweaning multisystemic wasting syndrome; CAV: chicken infectious anemia.
...
''—code for only two proteins and have a genome size of only two kilobases; the largest—the
pandoravirus
''Pandoravirus'' is a proposed genus of giant virus, first discovered in 2013. It is the third largest in physical size of any known viral genus, behind Pithovirus and Megaklothovirus. Pandoraviruses have double stranded DNA genomes, with t ...
es—have genome sizes of around two megabases which code for about 2500 proteins.
Virus genes rarely have
intron
An intron is any nucleotide sequence within a gene that is not expressed or operative in the final RNA product. The word ''intron'' is derived from the term ''intragenic region'', i.e., a region inside a gene."The notion of the cistron .e., gen ...
s and often are arranged in the genome so that they
overlap
Overlap may refer to:
* In set theory, an overlap of elements shared between sets is called an intersection, as in a Venn diagram.
* In music theory, overlap is a synonym for reinterpretation of a chord at the boundary of two musical phrases
* Ove ...
.
In general, RNA viruses have smaller genome sizes than DNA viruses because of a higher error-rate when replicating, and have a maximum upper size limit.
Beyond this, errors when replicating render the virus useless or uncompetitive. To compensate, RNA viruses often have segmented genomes—the genome is split into smaller molecules—thus reducing the chance that an error in a single-component genome will incapacitate the entire genome. In contrast, DNA viruses generally have larger genomes because of the high fidelity of their replication enzymes. Single-strand DNA viruses are an exception to this rule, as mutation rates for these genomes can approach the extreme of the ssRNA virus case.
Genetic mutation and recombination

Viruses undergo genetic change by several mechanisms. These include a process called
antigenic drift
Antigenic drift is a kind of genetic variation in viruses, arising from the accumulation of mutations in the virus genes that code for virus-surface proteins that host antibodies recognize. This results in a new strain of virus particles that is ...
where individual bases in the DNA or RNA
mutate
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis ...
to other bases. Most of these
point mutations
A point mutation is a genetic mutation where a single nucleotide base is changed, inserted or deleted from a DNA or RNA sequence of an organism's genome. Point mutations have a variety of effects on the downstream protein product—consequences ...
are "silent"—they do not change the protein that the gene encodes—but others can confer evolutionary advantages such as resistance to
antiviral drugs
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Antiviral drugs are a class of antimicrobials ...
.
Antigenic shift
Antigenic shift is the process by which two or more different strains of a virus, or strains of two or more different viruses, combine to form a new subtype having a mixture of the surface antigens of the two or more original strains. The term is ...
occurs when there is a major change in the genome of the virus. This can be a result of
recombination or
reassortment
Reassortment is the mixing of the genetic material of a species into new combinations in different individuals. The product of reassortment is called a reassortant. It is particularly used when two similar viruses that are infecting the same cell ...
. The
Influenza A virus
''Influenza A virus'' (''Alphainfluenzavirus influenzae'') or IAV is the only species of the genus ''Alphainfluenzavirus'' of the virus family '' Orthomyxoviridae''. It is a pathogen with strains that infect birds and some mammals, as well as c ...
is highly prone to reassortment; occasionally this has resulted in novel
strains which have caused
pandemics
A pandemic ( ) is an epidemic of an infectious disease that has a sudden increase in cases and spreads across a large region, for instance multiple continents or worldwide, affecting a substantial number of individuals. Widespread endemic dis ...
.
RNA viruses often exist as
quasispecies
The quasispecies model is a description of the process of the Darwinian evolution of certain self-replicating entities within the framework of physical chemistry. A quasispecies is a large group or "cloud" of related genotypes that exist in an env ...
or swarms of viruses of the same species but with slightly different genome nucleoside sequences. Such quasispecies are a prime target for natural selection.
Segmented genomes confer evolutionary advantages; different strains of a virus with a segmented genome can shuffle and combine genes and produce progeny viruses (or offspring) that have unique characteristics. This is called reassortment or 'viral sex'.
Genetic recombination
Genetic recombination (also known as genetic reshuffling) is the exchange of genetic material between different organisms which leads to production of offspring with combinations of traits that differ from those found in either parent. In eukaryot ...
is a process by which a strand of DNA (or RNA) is broken and then joined to the end of a different DNA (or RNA) molecule. This can occur when viruses infect cells simultaneously and studies of
viral evolution
Viral evolution is a subfield of evolutionary biology and virology concerned with the evolution of viruses. Viruses have short generation times, and many—in particular RNA viruses—have relatively high mutation rates (on the order of one poin ...
have shown that recombination has been rampant in the species studied.
Recombination is common to both RNA and DNA viruses.
Coronavirus
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the comm ...
es have a single-strand positive-sense
RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyrib ...
genome. Replication of the
genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
is catalyzed by an
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) or RNA replicase is an enzyme that catalyzes the self-replication, replication of RNA from an RNA template. Specifically, it catalyzes synthesis of the RNA strand Complementarity (molecular biology), compleme ...
. The mechanism of
recombination used by coronaviruses likely involves template switching by the polymerase during genome replication.
This process appears to be an adaptation for coping with genome damage.
Replication cycle


Viral populations do not grow through cell division, because they are acellular. Instead, they use the machinery and metabolism of a host cell to produce multiple copies of themselves, and they assemble in the cell.
When infected, the host cell is forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus.
Their life cycle differs greatly between species, but there are six basic stages in their life cycle:
''Attachment'' is a specific binding between viral capsid proteins and specific receptors on the host cellular surface. This specificity determines the host range and type of host cell of a virus. For example, HIV infects a limited range of human
leucocytes
White blood cells (scientific name leukocytes), also called immune cells or immunocytes, are cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign entities. White blood cells are genera ...
. This is because its surface protein,
gp120
Envelope glycoprotein GP120 (or gp120) is a glycoprotein exposed on the surface of the HIV envelope. It was discovered by Professors Tun-Hou Lee and Myron "Max" Essex of the Harvard School of Public Health in 1984. The 120 in its name comes f ...
, specifically interacts with the
CD4
In molecular biology, CD4 (cluster of differentiation 4) is a glycoprotein that serves as a co-receptor for the T-cell receptor (TCR). CD4 is found on the surface of immune cells such as helper T cells, monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic c ...
molecule—a
chemokine receptor
Chemokine receptors are cytokine receptors found on the surface of certain cells that interact with a type of cytokine called a chemokine. There have been 20 distinct chemokine receptors discovered in humans. Each has a rhodopsin-like 7-tran ...
—which is most commonly found on the surface of
CD4+ T-Cells
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell ...
. This mechanism has evolved to favour those viruses that infect only cells in which they are capable of replication. Attachment to the receptor can induce the viral envelope protein to undergo changes that result in the
fusion of viral and cellular membranes, or changes of non-enveloped virus surface proteins that allow the virus to enter.
''Penetration'' or ''
viral entry
Viral entry is the earliest stage of infection in the viral life cycle, as the virus comes into contact with the host cell (biology), cell and introduces viral material into the cell. The major steps involved in viral entry are shown below. Desp ...
'' follows attachment: Virions enter the host cell through receptor-mediated
endocytosis
Endocytosis is a cellular process in which Chemical substance, substances are brought into the cell. The material to be internalized is surrounded by an area of cell membrane, which then buds off inside the cell to form a Vesicle (biology and chem ...
or
membrane fusion
In membrane biology, fusion is the process by which two initially distinct lipid bilayers merge their hydrophobic cores, resulting in one interconnected structure. If this fusion proceeds completely through both leaflets of both bilayers, an aqueou ...
. The infection of plant and fungal cells is different from that of animal cells. Plants have a rigid cell wall made of
cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of glycosidic bond, β(1→4) linked glucose, D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important s ...
, and fungi one of chitin, so most viruses can get inside these cells only after trauma to the cell wall.
Nearly all plant viruses (such as tobacco mosaic virus) can also move directly from cell to cell, in the form of single-stranded nucleoprotein complexes, through pores called
plasmodesma
Plasmodesmata (singular: plasmodesma) are microscopic channels which traverse the cell walls of plant cells and some algal cells, enabling transport and communication between them. Plasmodesmata evolved independently in several lineages, and spec ...
ta. Bacteria, like plants, have strong cell walls that a virus must breach to infect the cell. Given that bacterial cell walls are much thinner than plant cell walls due to their much smaller size, some viruses have evolved mechanisms that inject their genome into the bacterial cell across the cell wall, while the viral capsid remains outside.
''Uncoating'' is a process in which the viral capsid is removed: This may be by degradation by viral enzymes or host enzymes or by simple dissociation; the end-result is the releasing of the viral genomic nucleic acid.
''
Replication'' of viruses involves primarily multiplication of the genome. Replication involves the synthesis of viral messenger RNA (mRNA) from "early" genes (with exceptions for positive-sense RNA viruses), viral
protein synthesis
Protein biosynthesis, or protein synthesis, is a core biological process, occurring inside cells, balancing the loss of cellular proteins (via degradation or export) through the production of new proteins. Proteins perform a number of critica ...
, possible assembly of viral proteins, then viral genome replication mediated by early or regulatory protein expression. This may be followed, for complex viruses with larger genomes, by one or more further rounds of mRNA synthesis: "late" gene expression is, in general, of structural or virion proteins.
''Assembly'' – Following the structure-mediated self-assembly of the virus particles, some modification of the proteins often occurs. In viruses such as HIV, this modification (sometimes called maturation) occurs after the virus has been released from the host cell.
''Release'' – Viruses can be
released from the host cell by
lysis
Lysis ( ; from Greek 'loosening') is the breaking down of the membrane of a cell, often by viral, enzymic, or osmotic (that is, "lytic" ) mechanisms that compromise its integrity. A fluid containing the contents of lysed cells is called a ...
, a process that kills the cell by bursting its membrane and cell wall if present: this is a feature of many bacterial and some animal viruses. Some viruses undergo a
lysogenic cycle
Lysogeny, or the lysogenic cycle, is one of two cycles of Virus, viral reproduction (the lytic cycle being the other). Lysogeny is characterized by integration of the bacteriophage nucleic acid into the host Bacteria, bacterium's genome or form ...
where the viral genome is incorporated by
genetic recombination
Genetic recombination (also known as genetic reshuffling) is the exchange of genetic material between different organisms which leads to production of offspring with combinations of traits that differ from those found in either parent. In eukaryot ...
into a specific place in the host's chromosome. The viral genome is then known as a "
provirus
A provirus is a virus genome that is integrated into the DNA of a host cell. In the case of bacterial viruses (bacteriophages), proviruses are often referred to as prophages. However, proviruses are distinctly different from prophages and these te ...
" or, in the case of bacteriophages a "
prophage
A prophage is a bacteriophage (often shortened to "phage") genome that is integrated into the circular bacterial chromosome or exists as an extrachromosomal plasmid within the bacterial cell (biology), cell. Integration of prophages into the bacte ...
".
Whenever the host divides, the viral genome is also replicated. The viral genome is mostly silent within the host. At some point, the provirus or prophage may give rise to the active virus, which may lyse the host cells.
Enveloped viruses (e.g., HIV) typically are released from the host cell by
budding
Budding or blastogenesis is a type of asexual reproduction in which a new organism develops from an outgrowth or bud due to cell division at one particular site. For example, the small bulb-like projection coming out from the yeast cell is kno ...
. During this process, the virus acquires its envelope, which is a modified piece of the host's plasma or other, internal membrane.
Genome replication
The genetic material within virus particles, and the method by which the material is replicated, varies considerably between different types of viruses.
; DNA viruses: The genome replication of most
DNA virus
A DNA virus is a virus that has a genome made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that is replicated by a DNA polymerase. They can be divided between those that have two strands of DNA in their genome, called double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses, and t ...
es takes place in the cell's
nucleus
Nucleus (: nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucleu ...
. If the cell has the appropriate receptor on its surface, these viruses enter the cell either by direct fusion with the cell membrane (e.g., herpesviruses) or—more usually—by receptor-mediated endocytosis. Most DNA viruses are entirely dependent on the host cell's DNA and RNA synthesising machinery and RNA processing machinery. Viruses with larger genomes may encode much of this machinery themselves. In eukaryotes, the viral genome must cross the cell's nuclear membrane to access this machinery, while in bacteria it need only enter the cell.
; RNA viruses: Replication of
RNA virus
An RNA virus is a virus characterized by a ribonucleic acid (RNA) based genome. The genome can be single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) or double-stranded (Double-stranded RNA, dsRNA). Notable human diseases caused by RNA viruses include influenza, SARS, ...
es usually takes place in the
cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell a ...
. RNA viruses can be placed into four different groups depending on their modes of replication. The
polarity (whether or not it can be used directly by ribosomes to make proteins) of single-stranded RNA viruses largely determines the replicative mechanism; the other major criterion is whether the genetic material is single-stranded or double-stranded. All RNA viruses use their own
RNA replicase
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) or RNA replicase is an enzyme that catalyzes the replication of RNA from an RNA template. Specifically, it catalyzes synthesis of the RNA strand complementary to a given RNA template. This is in contrast to ...
enzymes to create copies of their genomes.
; Reverse transcribing viruses:
Reverse transcribing viruses
''Revtraviricetes'' is a class of viruses that contains all viruses that encode a reverse transcriptase. The group includes all ssRNA-RT viruses (including the retroviruses) and dsDNA-RT viruses. It is the sole class in the phylum ''Artverviric ...
have ssRNA (''
Retroviridae
A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell. After invading a host cell's cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptase ...
'', ''
Metaviridae
''Metaviridae'' is a family of viruses which exist as Ty3-gypsy LTR retrotransposons in a eukaryotic host's genome. They are closely related to retroviruses: members of the family ''Metaviridae'' share many genomic elements with retroviruses, i ...
'', ''
Pseudoviridae
''Pseudoviridae'' is a family of viruses, which includes three genera.
Viruses of the family are actually LTR retrotransposons of the Ty1-copia family. They replicate via structures called virus-like particles (VLPs). VLPs are not infectious li ...
'') or dsDNA (''
Caulimoviridae
''Caulimoviridae'' is a family of viruses infecting plants. The family contains 11 genera. Viruses belonging to the family ''Caulimoviridae'' are termed double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) reverse-transcribing viruses (or pararetroviruses) i.e. viruses ...
'', and ''
Hepadnaviridae
''Hepadnaviridae'' is a family of viruses. Humans, apes, and birds serve as natural hosts. The family contains five genera. Its best-known member is hepatitis B virus. Diseases associated with this family include: liver infections, such as hep ...
'') in their particles. Reverse transcribing viruses with RNA genomes (
retrovirus
A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell. After invading a host cell's cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptase e ...
es) use a DNA intermediate to replicate, whereas those with DNA genomes (
pararetroviruses) use an RNA intermediate during genome replication. Both types use a
reverse transcriptase
A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to convert RNA genome to DNA, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B to replicate their genomes, by retrotransposon mobi ...
, or RNA-dependent DNA polymerase enzyme, to carry out the nucleic acid conversion. Retroviruses integrate the DNA produced by
reverse transcription
A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to convert RNA genome to DNA, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B virus, hepatitis B to replicate their genomes, by retrot ...
into the host genome as a provirus as a part of the replication process; pararetroviruses do not, although integrated genome copies of especially plant pararetroviruses can give rise to infectious virus.
They are susceptible to
antiviral drug
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Antiviral drugs are a class of antimicrobials ...
s that inhibit the reverse transcriptase enzyme, e.g.
zidovudine
Zidovudine (ZDV), also known as azidothymidine (AZT), was the first antiretroviral medication used to prevent and treat HIV/AIDS. It is generally recommended for use in combination with other antiretrovirals. It may be used to prevent mothe ...
and
lamivudine
Lamivudine, commonly called 3TC, is an antiretroviral medication used to prevent and treat HIV/AIDS. It is also used to treat chronic hepatitis B when other options are not possible. It is effective against both HIV-1 and HIV-2. It is typi ...
. An example of the first type is HIV, which is a retrovirus. Examples of the second type are the ''
Hepadnaviridae
''Hepadnaviridae'' is a family of viruses. Humans, apes, and birds serve as natural hosts. The family contains five genera. Its best-known member is hepatitis B virus. Diseases associated with this family include: liver infections, such as hep ...
'', which includes Hepatitis B virus.
Cytopathic effects on the host cell
The range of structural and biochemical effects that viruses have on the host cell is extensive.
These are called '
cytopathic effect
Cytopathic effect (abbreviated CPE) refers to structural changes in host cells that are caused by viral invasion. The infecting virus causes lysis of the host cell or when the cell dies without lysis due to an inability to replicate. If a virus c ...
s'.
Most virus infections eventually result in the death of the host cell. The causes of death include cell lysis, alterations to the cell's surface membrane and
apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biol ...
.
Often cell death is caused by cessation of its normal activities because of suppression by virus-specific proteins, not all of which are components of the virus particle.
The distinction between cytopathic and harmless is gradual. Some viruses, such as
Epstein–Barr virus
The Epstein–Barr virus (EBV), also known as human herpesvirus 4 (HHV-4), is one of the nine known Herpesviridae#Human herpesvirus types, human herpesvirus types in the Herpesviridae, herpes family, and is one of the most common viruses in ...
, can cause cells to proliferate without causing malignancy,
while others, such as
papillomavirus
''Papillomaviridae'' is a family of non- enveloped double-stranded DNA viruses whose members are known as papillomaviruses. Several hundred species of papillomaviruses, traditionally referred to as "types", have been identified infecting all car ...
es, are established causes of cancer.
Dormant and latent infections
Some viruses cause no apparent changes to the infected cell. Cells in which the virus is
latent and inactive show few signs of infection and often function normally.
This causes persistent infections and the virus is often dormant for many months or years. This is often the case with
herpes viruses.
Host range
Viruses are by far the most abundant biological entities on Earth and they outnumber all the others put together.
They infect all types of cellular life including animals, plants,
bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
and
fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
.
Different types of viruses can infect only a limited range of hosts and many are species-specific. Some, such as
smallpox virus
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by Variola virus (often called Smallpox virus), which belongs to the genus ''Orthopoxvirus''. The Ali Maow Maalin#Maalin's case, last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the ...
for example, can infect only one species—in this case humans,
and are said to have a narrow
host range
In biology and medicine, a host is a larger organism that harbours a smaller organism; whether a parasite, parasitic, a mutualism (biology), mutualistic, or a commensalism, commensalist ''guest'' (symbiont). The guest is typically provided with ...
. Other viruses, such as rabies virus, can infect different species of mammals and are said to have a broad range.
The viruses that infect plants are harmless to animals, and most viruses that infect other animals are harmless to humans.
The host range of some bacteriophages is limited to a single
strain of bacteria and they can be used to trace the source of outbreaks of infections by a method called
phage typing
Phage typing is a phenotypic method that uses bacteriophages ("phages" for short) for detecting and identifying single strains of bacteria. Phages are viruses that infect bacteria and may lead to bacterial cell lysis. The bacterial strain is assi ...
.
The complete set of viruses in an organism or habitat is called the
virome
Virome refers to the assemblage of viruses that is often investigated and described by metagenomic sequencing of viral nucleic acids that are found associated with a particular ecosystem, organism or holobiont. The word is frequently used to d ...
; for example, all human viruses constitute the
human virome
The human virome is the total collection of viruses in and on the human body. Viruses in the human body may infect both human cells and other microbes such as bacteria (as with bacteriophages). Some viruses cause disease, while others may be asy ...
.
Novel viruses
A novel virus is one that has not previously been recorded. It can be a virus that is isolated from its
natural reservoir
In Infection, infectious disease ecology and epidemiology, a natural reservoir, also known as a disease reservoir or a reservoir of infection, is the population of organisms or the specific environment in which an infectious pathogen naturally li ...
or isolated as the result of
spread to an animal or human host where the virus had not been identified before. It can be an
emergent virus
An emergent virus (or emerging virus) is a virus that is either newly appeared, notably increasing in incidence/ geographic range or has the potential to increase in the near future. Emergent viruses are a leading cause of emerging infectious di ...
, one that represents a new virus, but it can also be an extant virus that has not been
previously identified.
The
SARS-CoV-2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19, the respiratory illness responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had the Novel coronavirus, provisional nam ...
coronavirus that caused the COVID-19 pandemic is an example of a novel virus.
Classification
Classification seeks to describe the diversity of viruses by naming and grouping them on the basis of similarities. In 1962,
André Lwoff
André — sometimes transliterated as Andre — is the French and Portuguese form of the name Andrew and is now also used in the English-speaking world. It used in France, Quebec, Canada and other French-speaking countries, as well in Portugal ...
,
Robert Horne, and Paul Tournier were the first to develop a means of virus classification, based on the
Linnaean hierarchical system.
This system based classification on
phylum
In biology, a phylum (; : phyla) is a level of classification, or taxonomic rank, that is below Kingdom (biology), kingdom and above Class (biology), class. Traditionally, in botany the term division (taxonomy), division has been used instead ...
,
class
Class, Classes, or The Class may refer to:
Common uses not otherwise categorized
* Class (biology), a taxonomic rank
* Class (knowledge representation), a collection of individuals or objects
* Class (philosophy), an analytical concept used d ...
,
order
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* A socio-political or established or existing order, e.g. World order, Ancien Regime, Pax Britannica
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
...
,
family
Family (from ) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictabili ...
,
genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
, and
species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
. Viruses were grouped according to their shared properties (not those of their hosts) and the type of nucleic acid forming their genomes.
In 1966, the
International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses
The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) authorizes and organizes the taxonomic classification of and the nomenclature for viruses. The ICTV develops a universal taxonomic scheme for viruses, and thus has the means to appropri ...
(ICTV) was formed. The system proposed by Lwoff, Horne and Tournier was initially not accepted by the ICTV because the small genome size of viruses and their high rate of mutation made it difficult to determine their ancestry beyond order. As such, the
Baltimore classification
Baltimore classification is a system used to classify viruses based on their manner of messenger RNA (mRNA) synthesis. By organizing viruses based on their manner of mRNA production, it is possible to study viruses that behave similarly as a disti ...
system has come to be used to supplement the more traditional hierarchy.
Starting in 2018, the ICTV began to acknowledge deeper evolutionary relationships between viruses that have been discovered over time and adopted a 15-rank classification system ranging from realm to species. Additionally, some species within the same genus are grouped into a genogroup.
ICTV classification
The ICTV developed the current classification system and wrote guidelines that put a greater weight on certain virus properties to maintain family uniformity. A unified taxonomy (a universal system for classifying viruses) has been established. Only a small part of the total diversity of viruses has been studied. As of 2024, 7 realms, 11 kingdoms, 22 phyla, 4 subphyla, 49 classes, 93 orders, 12 suborders,
368 families, 213 subfamilies,
3,769 genera, 86 subgenera, and
16,215 species of viruses have been defined by the ICTV.
The general taxonomic structure of taxon ranges and the suffixes used in taxonomic names are shown hereafter. As of 2022, the ranks of subrealm, subkingdom, and subclass are unused, whereas all other ranks are in use.
[
:]Realm
A realm is a community or territory over which a sovereign rules. The term is commonly used to describe a monarchical or dynastic state. A realm may also be a subdivision within an empire, if it has its own monarch, e.g. the German Empire.
Etymo ...
(''-viria'')
::Subrealm (''-vira'')
::: Kingdom (''-virae'')
::::Subkingdom (''-virites'')
:::::Phylum
In biology, a phylum (; : phyla) is a level of classification, or taxonomic rank, that is below Kingdom (biology), kingdom and above Class (biology), class. Traditionally, in botany the term division (taxonomy), division has been used instead ...
(''-viricota'')
::::::Subphylum (''-viricotina'')
:::::::Class
Class, Classes, or The Class may refer to:
Common uses not otherwise categorized
* Class (biology), a taxonomic rank
* Class (knowledge representation), a collection of individuals or objects
* Class (philosophy), an analytical concept used d ...
(''-viricetes'')
::::::::Subclass (''-viricetidae'')
:::::::::Order
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* A socio-political or established or existing order, e.g. World order, Ancien Regime, Pax Britannica
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
...
(''-virales'')
::::::::::Suborder (''-virineae'')
:::::::::::Family
Family (from ) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictabili ...
(''-viridae'')
::::::::::::Subfamily (''-virinae'')
:::::::::::::Genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
(''-virus'')
::::::::::::::Subgenus (''-virus'')
:::::::::::::::Species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
Baltimore classification
 The Nobel Prize-winning biologist
The Nobel Prize-winning biologist David Baltimore
David Baltimore (born March 7, 1938) is an American biologist, university administrator, and 1975 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, Nobel laureate in Physiology or Medicine. He is a professor of biology at the California Institute of Tech ...
devised the Baltimore classification
Baltimore classification is a system used to classify viruses based on their manner of messenger RNA (mRNA) synthesis. By organizing viruses based on their manner of mRNA production, it is possible to study viruses that behave similarly as a disti ...
system.mRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of Protein biosynthesis, synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is ...
production. Viruses must generate mRNAs from their genomes to produce proteins and replicate themselves, but different mechanisms are used to achieve this in each virus family. Viral genomes may be single-stranded (ss) or double-stranded (ds), RNA or DNA, and may or may not use reverse transcriptase
A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to convert RNA genome to DNA, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B to replicate their genomes, by retrotransposon mobi ...
(RT). In addition, ssRNA viruses may be either sense
A sense is a biological system used by an organism for sensation, the process of gathering information about the surroundings through the detection of Stimulus (physiology), stimuli. Although, in some cultures, five human senses were traditio ...
(+) or antisense (−). This classification places viruses into seven groups:
Role in human disease
 Examples of common human diseases caused by viruses include the
Examples of common human diseases caused by viruses include the common cold
The common cold, or the cold, is a virus, viral infectious disease of the upper respiratory tract that primarily affects the Respiratory epithelium, respiratory mucosa of the human nose, nose, throat, Paranasal sinuses, sinuses, and larynx. ...
, influenza
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These sympto ...
, chickenpox
Chickenpox, also known as varicella ( ), is a highly contagious disease caused by varicella zoster virus (VZV), a member of the herpesvirus family. The disease results in a characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which ...
, and cold sores
A cold sore is a type of herpes infection caused by the herpes simplex virus that affects primarily the lip. Symptoms typically include a burning pain followed by small blisters or sores. The first attack may also be accompanied by fever, so ...
. Many serious diseases such as rabies
Rabies is a viral disease that causes encephalitis in humans and other mammals. It was historically referred to as hydrophobia ("fear of water") because its victims panic when offered liquids to drink. Early symptoms can include fever and abn ...
, Ebola virus disease
Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and other primates, caused by ebolaviruses. Symptoms typically start anywhere between two days and three weeks after infe ...
, AIDS (HIV), avian influenza
Avian influenza, also known as avian flu or bird flu, is a disease caused by the influenza A virus, which primarily affects birds but can sometimes affect mammals including humans. Wild aquatic birds are the primary host of the influenza A viru ...
, and SARS
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is a viral respiratory disease of zoonotic origin caused by the virus SARS-CoV-1, the first identified strain of the SARS-related coronavirus. The first known cases occurred in November 2002, and the ...
are caused by viruses. The relative ability of viruses to cause disease is described in terms of virulence
Virulence is a pathogen's or microorganism's ability to cause damage to a host.
In most cases, especially in animal systems, virulence refers to the degree of damage caused by a microbe to its host. The pathogenicity of an organism—its abili ...
. Other diseases are under investigation to discover if they have a virus as the causative agent, such as the possible connection between human herpesvirus 6
Human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) is the common collective name for human herpesvirus 6A (HHV-6A) and human herpesvirus 6B (HHV-6B). These closely related viruses are two of the nine known herpesviruses that have humans as their primary host.
HHV-6 ...
(HHV6) and neurological diseases such as multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease resulting in damage to myelinthe insulating covers of nerve cellsin the brain and spinal cord. As a demyelinating disease, MS disrupts the nervous system's ability to Action potential, transmit ...
and chronic fatigue syndrome
Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) is a disabling Chronic condition, chronic illness. People with ME/CFS experience profound fatigue that does not go away with rest, as well as sleep issues and problems with memory ...
.bornavirus
''Bornaviridae'' is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Horses, sheep, cattle, rodents, birds, reptiles, and humans serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with bornaviruses include Borna disease, a fata ...
, previously thought to cause neurological
Neurology (from , "string, nerve" and the suffix -logia, "study of") is the branch of medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the nervous system, which comprises the brain, the s ...
diseases in horses, could be responsible for psychiatric
Psychiatry is the medical specialty devoted to the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of deleterious mental conditions. These include matters related to cognition, perceptions, mood, emotion, and behavior.
Initial psychiatric assessment of ...
illnesses in humans.multicellular organism
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell (biology), cell, unlike unicellular organisms. All species of animals, Embryophyte, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organism ...
s, if enough cells die, the whole organism will start to suffer the effects. Although viruses cause disruption of healthy homeostasis
In biology, homeostasis (British English, British also homoeostasis; ) is the state of steady internal physics, physical and chemistry, chemical conditions maintained by organism, living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning fo ...
, resulting in disease, they may exist relatively harmlessly within an organism. An example would include the ability of the herpes simplex virus
Herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2) are two members of the Herpesviridae#Human herpesvirus types, human ''Herpesviridae'' family, a set of viruses that produce Viral disease, viral infections in the majority of humans. Both HSV-1 a ...
, which causes cold sores, to remain in a dormant state within the human body. This is called latencyvaricella zoster virus
Varicella zoster virus (VZV), also known as human herpesvirus 3 (HHV-3, HHV3), is one of nine known herpes viruses that can infect humans. It causes chickenpox (varicella) commonly affecting children and young adults, and shingles (herpes zos ...
, which causes chickenpox and shingles
Shingles, also known as herpes zoster or zona, is a viral disease characterized by a painful skin rash with blisters in a localized area. Typically the rash occurs in a single, wide mark either on the left or right side of the body or face. T ...
. Most people have been infected with at least one of these types of herpes virus. These latent viruses might sometimes be beneficial, as the presence of the virus can increase immunity against bacterial pathogens, such as ''Yersinia pestis
''Yersinia pestis'' (''Y. pestis''; formerly ''Pasteurella pestis'') is a Gram-negative bacteria, gram-negative, non-motile bacteria, non-motile, coccobacillus Bacteria, bacterium without Endospore, spores. It is related to pathogens ''Yer ...
''.
Some viruses can cause lifelong or chronic infections, where the viruses continue to replicate in the body despite the host's defence mechanisms.endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
.
Epidemiology
Viral epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and Risk factor (epidemiology), determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population, and application of this knowledge to prevent dise ...
is the branch of medical science that deals with the transmission and control of virus infections in humans. Transmission of viruses can be vertical, which means from mother to child, or horizontal, which means from person to person. Examples of vertical transmission
Vertical transmission of symbionts is the transfer of a microbial symbiont from the parent directly to the offspring. Many metazoan species carry symbiotic bacteria which play a mutualistic, commensal, or parasitic role. A symbiont is acq ...
include hepatitis B virus and HIV, where the baby is born already infected with the virus.varicella zoster virus
Varicella zoster virus (VZV), also known as human herpesvirus 3 (HHV-3, HHV3), is one of nine known herpes viruses that can infect humans. It causes chickenpox (varicella) commonly affecting children and young adults, and shingles (herpes zos ...
, which, although causing relatively mild infections in children and adults, can be fatal to the foetus and newborn baby.Horizontal transmission
Horizontal transmission is the transmission of organisms between biotic and/or abiotic members of an ecosystem that are not in a parent-progeny relationship. Because the evolutionary fate of the agent is not tied to reproductive success of the host ...
is the most common mechanism of spread of viruses in populations.aerosol
An aerosol is a suspension (chemistry), suspension of fine solid particles or liquid Drop (liquid), droplets in air or another gas. Aerosols can be generated from natural or Human impact on the environment, human causes. The term ''aerosol'' co ...
s containing viruses are inhaled or by insect vectors such as when infected mosquitoes penetrate the skin of a host.viral disease
A viral disease (or viral infection) occurs when an organism's body is invaded by pathogenic viruses, and infectious virus particles (virions) attach to and enter susceptible cells.
Examples include the common cold, gastroenteritis, COVID-19, ...
s.quarantine
A quarantine is a restriction on the movement of people, animals, and goods which is intended to prevent the spread of disease or pests. It is often used in connection to disease and illness, preventing the movement of those who may have bee ...
.outbreak
In epidemiology, an outbreak is a sudden increase in occurrences of a disease when cases are in excess of normal expectancy for the location or season. It may affect a small and localized group or impact upon thousands of people across an entire ...
of foot-and-mouth disease
Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) or hoof-and-mouth disease (HMD) is an infectious disease, infectious and sometimes fatal virus (biology), viral disease that primarily affects even-toed ungulates, including domestic and wild Bovidae, bovids. The vir ...
in cattle in Britain in 2001, thousands of cattle were slaughtered.incubation period
Incubation period (also known as the latent period or latency period) is the time elapsed between exposure to a pathogenic organism, a chemical, or ionizing radiation, radiation, and when symptoms and signs are first apparent. In a typical infect ...
s during which the infection causes no signs or symptoms.pandemic
A pandemic ( ) is an epidemic of an infectious disease that has a sudden increase in cases and spreads across a large region, for instance multiple continents or worldwide, affecting a substantial number of individuals. Widespread endemic (epi ...
s.
Epidemics and pandemics
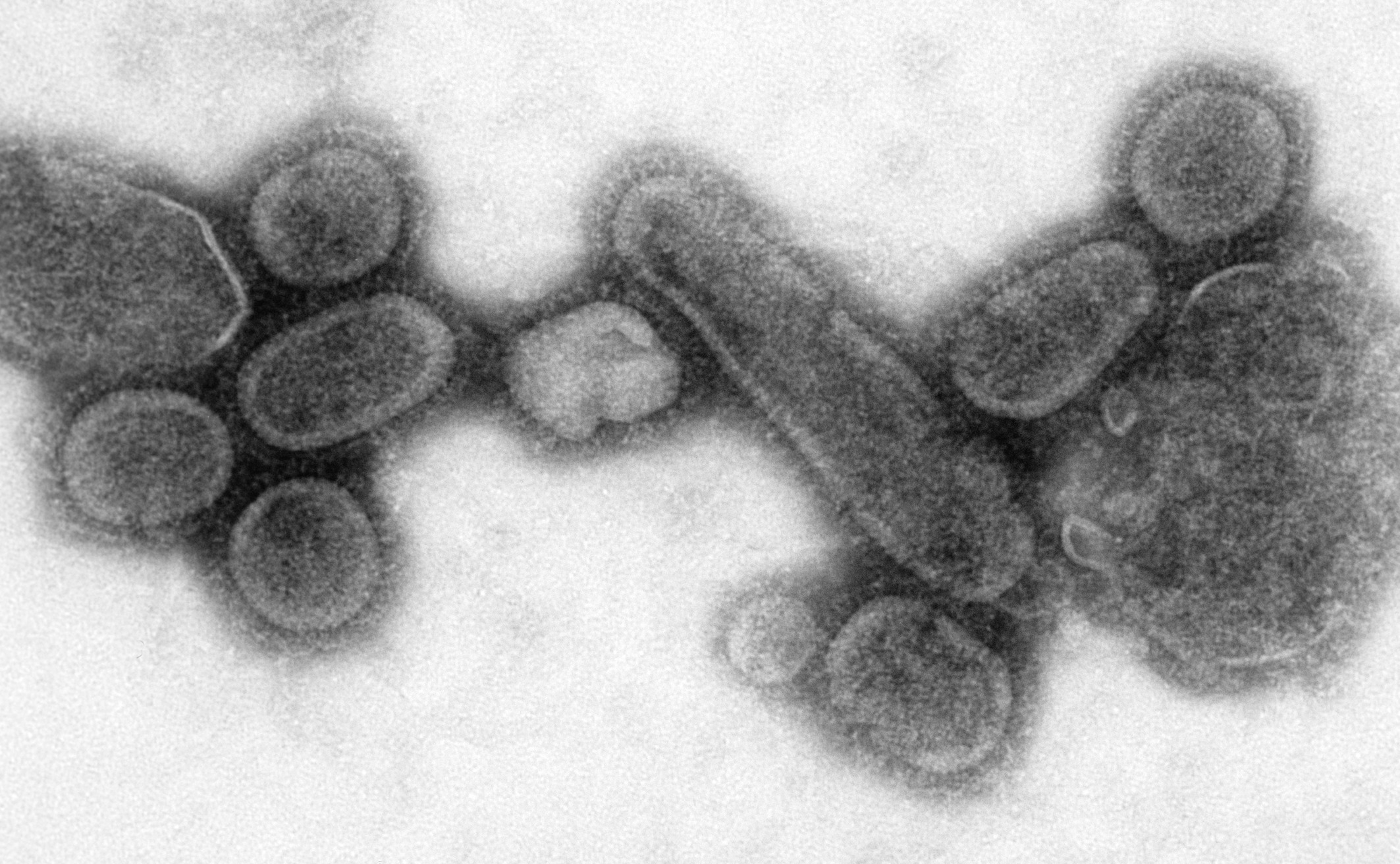 A
A pandemic
A pandemic ( ) is an epidemic of an infectious disease that has a sudden increase in cases and spreads across a large region, for instance multiple continents or worldwide, affecting a substantial number of individuals. Widespread endemic (epi ...
is a worldwide epidemic
An epidemic (from Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of hosts in a given population within a short period of time. For example, in meningococcal infection ...
. The 1918 flu pandemic
The 1918–1920 flu pandemic, also known as the Great Influenza epidemic or by the common misnomer Spanish flu, was an exceptionally deadly global influenza pandemic caused by the Influenza A virus subtype H1N1, H1N1 subtype of the influenz ...
, which lasted until 1919, was a category 5 influenza pandemic caused by an unusually severe and deadly influenza A virus. The victims were often healthy young adults, in contrast to most influenza outbreaks, which predominantly affect juvenile, elderly, or otherwise-weakened patients.sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lie south of the Sahara. These include Central Africa, East Africa, Southern Africa, and West Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the list of sovereign states and ...
during the 20th century;Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV and AIDS (UNAIDS; , ONUSIDA) is the main advocate for accelerated, comprehensive and coordinated global action on the HIV/AIDS
The HIV, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus t ...
(UNAIDS) and the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
(WHO) estimate that AIDS has killed more than 25 million people since it was first recognised on 5 June 1981, making it one of the most destructive epidemics in recorded history.Filoviridae
''Filoviridae'' () is a International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses, family of RNA virus#Group_V_–_negative-sense_ssRNA_viruses, single-stranded negative-sense RNA viruses in the order (biology), order ''Mononegavirales''. Two members of the ...
''. Filoviruses are filament-like viruses that cause viral hemorrhagic fever
Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) are a diverse group of diseases. "Viral" means a health problem caused by infection from a virus, " hemorrhagic" means to bleed, and "fever" means an unusually high body temperature. Bleeding and fever are comm ...
, and include ebolavirus
The genus ''Ebolavirus'' (- or ; - or ) is a International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses, virological taxon included in the family ''Filoviridae'' (filament-shaped viruses), order ''Mononegavirales''. The members of this genus are called ebo ...
es and marburgvirus
The genus ''Marburgvirus'' is the taxonomic home of ''Marburg marburgvirus'', whose members are the two known marburgviruses, Marburg virus (MARV) and Ravn virus (RAVV). Both viruses cause Marburg virus disease in humans and nonhuman primat ...
es. Marburg virus
Marburg virus (MARV) is a hemorrhagic fever virus of the '' Filoviridae'' family of viruses and a member of the species '' Marburg marburgvirus'', genus '' Marburgvirus''. It causes Marburg virus disease in primates, a form of viral hemorrhag ...
, first discovered in 1967, attracted widespread press attention in April 2005 for an outbreak in Angola
Angola, officially the Republic of Angola, is a country on the west-Central Africa, central coast of Southern Africa. It is the second-largest Portuguese-speaking world, Portuguese-speaking (Lusophone) country in both total area and List of c ...
.Ebola virus disease
Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and other primates, caused by ebolaviruses. Symptoms typically start anywhere between two days and three weeks after infe ...
has also caused intermittent outbreaks with high mortality rates since 1976 when it was first identified. The worst and most recent one is the 2013–2016 West Africa epidemic.
Except for smallpox, most pandemics are caused by newly evolved viruses. These "emergent" viruses are usually mutants of less harmful viruses that have circulated previously either in humans or other animals.
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is a viral respiratory disease of zoonotic origin caused by the virus SARS-CoV-1, the first identified strain of the SARS-related coronavirus. The first known cases occurred in November 2002, and the ...
) and Middle East respiratory syndrome
Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) is a viral respiratory infection caused by '' Middle East respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus'' (MERS-CoV). Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe depending on age and risk level. Typi ...
(MERS) are caused by new types of coronavirus
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the comm ...
es. Other coronaviruses are known to cause mild infections in humans,Wuhan
Wuhan; is the capital of Hubei, China. With a population of over eleven million, it is the most populous city in Hubei and the List of cities in China by population, eighth-most-populous city in China. It is also one of the nine National cent ...
, China in November 2019 and spread rapidly around the world. Infections with the virus caused the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
that started in 2020.curfews
A curfew is an order that imposes certain regulations during specified hours. Typically, curfews order all people affected by them to remain indoors during the evening and nighttime hours. Such an order is most often issued by public authorit ...
were imposed in several major cities worldwide in response to the pandemic.
Cancer
Viruses are an established cause of cancer in humans and other species. Viral cancers occur only in a minority of infected persons (or animals). Cancer viruses come from a range of virus families, including both RNA and DNA viruses, and so there is no single type of "oncovirus
An oncovirus or oncogenic virus is a virus that can cause cancer. This term originated from studies of acutely transforming retroviruses in the 1950–60s, when the term ''oncornaviruses'' was used to denote their RNA virus origin. With the let ...
" (an obsolete term originally used for acutely transforming retroviruses). The development of cancer is determined by a variety of factors such as host immunityhuman papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the ''Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and r ...
, hepatitis B virus
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, a species of the genus '' Orthohepadnavirus'' and a member of the '' Hepadnaviridae'' family of viruses. This virus causes the disease hepatitis B.
Classification
Hepatitis B ...
, hepatitis C virus
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a small (55–65 nm in size), enveloped, positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus of the family ''Flaviviridae''. The hepatitis C virus is the cause of hepatitis C and some cancers such as liver cancer ( hepatoc ...
, Epstein–Barr virus
The Epstein–Barr virus (EBV), also known as human herpesvirus 4 (HHV-4), is one of the nine known Herpesviridae#Human herpesvirus types, human herpesvirus types in the Herpesviridae, herpes family, and is one of the most common viruses in ...
, Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is the ninth known human herpesvirus. It is also called Human herpesvirus 8, or HHV-8 in short. This virus causes Kaposi's sarcoma, a cancer commonly occurring in AIDS patients, as well as primary ...
and human T-lymphotropic virus
The primate T-lymphotropic viruses (PTLVs) are a group of retroviruses that infect primates, using their lymphocytes to reproduce. The ones that infect humans are known as human T-lymphotropic virus (HTLV), and the ones that infect Old World monk ...
. The most recently discovered human cancer virus is a polyomavirus (Merkel cell polyomavirus
Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCV or MCPyV) was first described in January 2008 in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. It was the first example of a human viral pathogen discovered using unbiased metagenomic next-generation sequencing with a technique called ...
) that causes most cases of a rare form of skin cancer called Merkel cell carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is a rare and aggressive skin cancer occurring in about three people per million members of the population. It is also known as cutaneous APUDoma, Primary tumor, primary neuroendocrine tumor, neuroendocrine carcinoma ...
.liver cancer
Liver cancer, also known as hepatic cancer, primary hepatic cancer, or primary hepatic malignancy, is cancer that starts in the liver. Liver cancer can be primary in which the cancer starts in the liver, or it can be liver metastasis, or secondar ...
. Infection by human T-lymphotropic virus can lead to tropical spastic paraparesis
Tropical spastic paraparesis (TSP), is a medical condition that causes weakness, muscle spasms, and sensory disturbance by human T-lymphotropic virus resulting in paraparesis, weakness of the legs. As the name suggests, it is most common in Tropics ...
and adult T-cell leukaemia. Human papillomaviruses are an established cause of cancers of cervix
The cervix (: cervices) or cervix uteri is a dynamic fibromuscular sexual organ of the female reproductive system that connects the vagina with the uterine cavity. The human female cervix has been documented anatomically since at least the time ...
, skin, anus
In mammals, invertebrates and most fish, the anus (: anuses or ani; from Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is the external body orifice at the ''exit'' end of the digestive tract (bowel), i.e. the opposite end from the mouth. Its function is to facil ...
, and penis
A penis (; : penises or penes) is a sex organ through which male and hermaphrodite animals expel semen during copulation (zoology), copulation, and through which male placental mammals and marsupials also Urination, urinate.
The term ''pen ...
. Within the ''Herpesviridae
''Orthoherpesviridae'', previously named and more widely known as ''Herpesviridae'', is a large family of DNA viruses that cause infections and certain diseases in animals, including humans. The members of this family are commonly known as herp ...
'', Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is the ninth known human herpesvirus. It is also called Human herpesvirus 8, or HHV-8 in short. This virus causes Kaposi's sarcoma, a cancer commonly occurring in AIDS patients, as well as primary ...
causes Kaposi's sarcoma
Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) is a type of cancer that can form masses on the skin, in lymph nodes, in the mouth, or in other organs. The skin lesions are usually painless, purple and may be flat or raised. Lesions can occur singly, multiply in a limite ...
and body-cavity lymphoma, and Epstein–Barr virus causes Burkitt's lymphoma
Burkitt's lymphoma is a cancer of the lymphatic system, particularly B lymphocytes found in the germinal center. It is named after Denis Parsons Burkitt, the Irish surgeon who first described the disease in 1958 while working in equatorial Africa ...
, Hodgkin's lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a type of lymphoma in which cancer originates from a specific type of white blood cell called lymphocytes, where multinucleated Reed–Sternberg cells (RS cells) are present in the lymph nodes. The condition was named a ...
, B lymphoproliferative disorder, and nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), or nasopharynx cancer, is the most common cancer originating in the nasopharynx, most commonly in the postero-lateral nasopharynx or pharyngeal recess (fossa of Rosenmüller), accounting for 50% of cases. NPC occurs ...
. Merkel cell polyomavirus closely related to SV40
SV40 is an abbreviation for simian vacuolating virus 40 or simian virus 40, a polyomavirus that is found in both monkeys and humans. Like other polyomaviruses, SV40 is a DNA virus that is found to cause tumors in humans and animals, but most ofte ...
and mouse polyomaviruses that have been used as animal models for cancer viruses for over 50 years.
Host defence mechanisms
The body's first line of defence against viruses is the innate immune system
The innate immune system or nonspecific immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies in vertebrates (the other being the adaptive immune system). The innate immune system is an alternate defense strategy and is the dominant immune s ...
. This comprises cells and other mechanisms that defend the host from infection in a non-specific manner. This means that the cells of the innate system recognise, and respond to, pathogens in a generic way, but, unlike the adaptive immune system
The adaptive immune system (AIS), also known as the acquired immune system, or specific immune system is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized cells, organs, and processes that eliminate pathogens specifically. The ac ...
, it does not confer long-lasting or protective immunity to the host.RNA interference
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules are involved in sequence-specific suppression of gene expression by double-stranded RNA, through translational or transcriptional repression. Historically, RNAi was known by ...
is an important innate defence against viruses.dicer
Dicer, also known as endoribonuclease Dicer or helicase with RNase motif, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the gene. Being part of the RNase III family, Dicer cleaves double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) and pre-microRNA (pre-miRNA) into shor ...
that cuts the RNA into smaller pieces. A biochemical pathway—the RISC complex—is activated, which ensures cell survival by degrading the viral mRNA. Rotaviruses have evolved to avoid this defence mechanism by not uncoating fully inside the cell, and releasing newly produced mRNA through pores in the particle's inner capsid. Their genomic dsRNA remains protected inside the core of the virion.adaptive immune system
The adaptive immune system (AIS), also known as the acquired immune system, or specific immune system is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized cells, organs, and processes that eliminate pathogens specifically. The ac ...
of a vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
encounters a virus, it produces specific antibodies
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as bacteria and viruses, including those that caus ...
that bind to the virus and often render it non-infectious. This is called humoral immunity
Humoral immunity is the aspect of immunity (medical), immunity that is mediated by macromolecules – including secreted antibodies, complement proteins, and certain antimicrobial peptides – located in extracellular fluids. Humoral immunity is ...
. Two types of antibodies are important. The first, called IgM
Immunoglobulin M (IgM) is the largest of several isotypes of antibodies (also known as immunoglobulin) that are produced by vertebrates. IgM is the first antibody to appear in the response to initial exposure to an antigen;
causing it to also ...
, is highly effective at neutralising viruses but is produced by the cells of the immune system only for a few weeks. The second, called IgG, is produced indefinitely. The presence of IgM in the blood of the host is used to test for acute infection, whereas IgG indicates an infection sometime in the past.immunity
Immunity may refer to:
Medicine
* Immunity (medical), resistance of an organism to infection or disease
* ''Immunity'' (journal), a scientific journal published by Cell Press
Biology
* Immune system
Engineering
* Radiofrequence immunity ...
are carried out.TRIM21
Tripartite motif-containing protein 21, also known as E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM21, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TRIM21'' gene. Alternatively spliced transcript variants for this gene have been described but the full-lengt ...
, can attach to the antibodies on the surface of the virus particle. This primes the subsequent destruction of the virus by the enzymes of the cell's proteosome
Proteasomes are essential protein complexes responsible for the degradation of proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds. Enzymes that help such reactions are called proteases. Proteasomes are found inside all e ...
system. A second defence of vertebrates against viruses is called cell-mediated immunity and involves immune cells known as
A second defence of vertebrates against viruses is called cell-mediated immunity and involves immune cells known as T cells
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their ce ...
. The body's cells constantly display short fragments of their proteins on the cell's surface, and, if a T cell recognises a suspicious viral fragment there, the host cell is destroyed by 'killer T' cells and the virus-specific T-cells proliferate. Cells such as the macrophage
Macrophages (; abbreviated MPhi, φ, MΦ or MP) are a type of white blood cell of the innate immune system that engulf and digest pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that ...
are specialists at this antigen presentation
Antigen presentation is a vital immune process that is essential for T cell immune response triggering. Because T cells recognize only fragmented antigens displayed on cell surfaces, antigen processing must occur before the antigen fragment can ...
.interferon
Interferons (IFNs, ) are a group of signaling proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of several viruses. In a typical scenario, a virus-infected cell will release interferons causing nearby cells to heighten ...
is an important host defence mechanism. This is a hormone produced by the body when viruses are present. Its role in immunity is complex; it eventually stops the viruses from reproducing by killing the infected cell and its close neighbours.antigen presentation
Antigen presentation is a vital immune process that is essential for T cell immune response triggering. Because T cells recognize only fragmented antigens displayed on cell surfaces, antigen processing must occur before the antigen fragment can ...
, cytokine
Cytokines () are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling.
Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B cell, B lymphocytes, T cell, T lymphocytes ...
resistance, evasion of natural killer cell
Natural killer cells, also known as NK cells, are a type of cytotoxic lymphocyte critical to the innate immune system. They are a kind of large granular lymphocytes (LGL), and belong to the rapidly expanding family of known innate lymphoid cells ...
activities, escape from apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biol ...
, and antigenic shift
Antigenic shift is the process by which two or more different strains of a virus, or strains of two or more different viruses, combine to form a new subtype having a mixture of the surface antigens of the two or more original strains. The term is ...
.neurotropic virus
A neurotropic virus is a virus that is capable of infecting nerve tissue.
Terminology
A neurotropic virus is said to be neuroinvasive if it is capable of accessing or entering the nervous system and neurovirulent if it is capable of causing dis ...
es', are disseminated by neural spread where the immune system may be unable to reach them due to immune privilege
Certain sites of the mammalian body have immune privilege (no immune response), meaning they are able to tolerate the introduction of antigens without eliciting an inflammatory immune response. Tissue grafts are normally recognised as foreign an ...
.
Prevention and treatment
Because viruses use vital metabolic pathways within host cells to replicate, they are difficult to eliminate without using drugs that cause toxic effects to host cells in general. The most effective medical approaches to viral diseases are vaccination
Vaccination is the administration of a vaccine to help the immune system develop immunity from a disease. Vaccines contain a microorganism or virus in a weakened, live or killed state, or proteins or toxins from the organism. In stimulating ...
s to provide immunity to infection, and antiviral drugs
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Antiviral drugs are a class of antimicrobials ...
that selectively interfere with viral replication.
Vaccines
Vaccination is a cheap and effective way of preventing infections by viruses. Vaccines were used to prevent viral infections long before the discovery of the actual viruses. Their use has resulted in a dramatic decline in morbidity (illness) and mortality (death) associated with viral infections such as polio
Poliomyelitis ( ), commonly shortened to polio, is an infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. Approximately 75% of cases are asymptomatic; mild symptoms which can occur include sore throat and fever; in a proportion of cases more severe ...
, measles
Measles (probably from Middle Dutch or Middle High German ''masel(e)'', meaning "blemish, blood blister") is a highly contagious, Vaccine-preventable diseases, vaccine-preventable infectious disease caused by Measles morbillivirus, measles v ...
, mumps
MUMPS ("Massachusetts General Hospital Utility Multi-Programming System"), or M, is an imperative, high-level programming language with an integrated transaction processing key–value database. It was originally developed at Massachusetts Gen ...
and rubella
Rubella, also known as German measles or three-day measles, is an infection caused by the rubella virus. This disease is often mild, with half of people not realizing that they are infected. A rash may start around two weeks after exposure and ...
.Smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by Variola virus (often called Smallpox virus), which belongs to the genus '' Orthopoxvirus''. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (W ...
infections have been eradicated.antigens
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule, moiety, foreign particulate matter, or an allergen, such as pollen, that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response.
An ...
), or RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyrib ...
.immunocompromised
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromise, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that affe ...
), because in these people, the weakened virus can cause the original disease.immunocompromised
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromise, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that affe ...
patients because they cannot cause the disease.
Antiviral drugs
 Antiviral drugs are often
Antiviral drugs are often nucleoside analogues
Nucleoside analogues are structural analogues of a nucleoside, which normally contain a nucleobase and a sugar. Nucleotide analogues are analogues of a nucleotide, which normally has one to three phosphates linked to a nucleoside. Both types ...
(fake DNA building-blocks), which viruses mistakenly incorporate into their genomes during replication.hydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy ...
groups, which, along with phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol P and atomic number 15. All elemental forms of phosphorus are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive and are therefore never found in nature. They can nevertheless be prepared ar ...
atoms, link together to form the strong "backbone" of the DNA molecule. This is called DNA chain termination
In polymer chemistry, chain termination is any chemical reaction that ceases the formation of reactive intermediates in a chain propagation step in the course of a polymerization, effectively bringing it to a halt.
Mechanisms of termination ...
.aciclovir
Aciclovir, also known as acyclovir, is an antiviral medication. It is primarily used for the treatment of herpes simplex virus infections, chickenpox, and shingles. Other uses include the prevention of cytomegalovirus infections following tran ...
for Herpes simplex virus infections and lamivudine
Lamivudine, commonly called 3TC, is an antiretroviral medication used to prevent and treat HIV/AIDS. It is also used to treat chronic hepatitis B when other options are not possible. It is effective against both HIV-1 and HIV-2. It is typi ...
for HIV and hepatitis B virus infections. Aciclovir is one of the oldest and most frequently prescribed antiviral drugs.HIV-1 protease
HIV-1 protease or PR is a retroviral aspartyl protease (retropepsin), an enzyme involved with peptide bond hydrolysis in retroviruses, that is essential for the life-cycle of HIV, the retrovirus that causes AIDS. HIV-1 PR cleaves newly synthesized ...
for it to become fully infectious. There is a large class of drugs called protease inhibitors
Protease inhibitors (PIs) are medications that act by interfering with protease, enzymes that cleave proteins. Some of the most well known are antiviral drugs widely used to treat HIV/AIDS, hepatitis C and COVID-19. These protease inhibitors pre ...
that inactivate this enzyme.direct-acting antivirals
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Antiviral drugs are a class of antimicrobials ...
.
Infection in other species
Viruses infect all cellular life and, although viruses occur universally, each cellular species has its own specific range that often infects only that species.satellites
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scientif ...
, can replicate only within cells that have already been infected by another virus.
Animal viruses
Viruses are important pathogens of livestock. Diseases such as foot-and-mouth disease and bluetongue are caused by viruses.Canine parvovirus
Canine parvovirus (also referred to as CPV, CPV2, or parvo) is a contagious virus mainly affecting dogs and wolves. CPV is highly contagious and is spread from dog to dog by direct or indirect contact with their feces. Vaccines can prevent thi ...
is caused by a small DNA virus and infections are often fatal in pups. Like all invertebrates
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordate subphylum ...
, the honey bee is susceptible to many viral infections. Most viruses co-exist harmlessly in their host and cause no signs or symptoms of disease.
Plant viruses
 There are many types of plant viruses, but often they cause only a loss of yield, and it is not economically viable to try to control them. Plant viruses are often spread from plant to plant by organisms, known as vectors. These are usually insects, but some fungi, nematode worms,
There are many types of plant viruses, but often they cause only a loss of yield, and it is not economically viable to try to control them. Plant viruses are often spread from plant to plant by organisms, known as vectors. These are usually insects, but some fungi, nematode worms, single-celled organisms
A unicellular organism, also known as a single-celled organism, is an organism that consists of a single cell, unlike a multicellular organism that consists of multiple cells. Organisms fall into two general categories: prokaryotic organisms and ...
, and parasitic plants are vectors. When control of plant virus infections is considered economical, for perennial fruits, for example, efforts are concentrated on killing the vectors and removing alternate hosts such as weeds.potato virus Y
Potato virus Y (PVY) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family ''Potyviridae'', and one of the most important plant viruses affecting potato production.
PVY infection of potato plants results in a variety of symptoms depending on the viral str ...
causes disease in potatoes and related species including tomatoes and peppers. In the 1980s, this virus acquired economical importance when it proved difficult to control in seed potato crops. Transmitted by aphid
Aphids are small sap-sucking insects in the Taxonomic rank, family Aphididae. Common names include greenfly and blackfly, although individuals within a species can vary widely in color. The group includes the fluffy white Eriosomatinae, woolly ...
s, this virus can reduce crop yields by up to 80 per cent, causing significant losses to potato yields.salicylic acid
Salicylic acid is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H4COOH. A colorless (or white), bitter-tasting solid, it is a precursor to and a active metabolite, metabolite of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin). It is a plant hormone, and has been lis ...
, nitric oxide
Nitric oxide (nitrogen oxide, nitrogen monooxide, or nitrogen monoxide) is a colorless gas with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes den ...
, and reactive oxygen molecules.
Plant virus particles or virus-like particles (VLPs) have applications in both biotechnology
Biotechnology is a multidisciplinary field that involves the integration of natural sciences and Engineering Science, engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms and parts thereof for products and services. Specialists ...
and nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). At this scale, commonly known as the nanoscale, surface area and quantum mechanical effects become important in describing propertie ...
. The capsids of most plant viruses are simple and robust structures and can be produced in large quantities either by the infection of plants or by expression in a variety of heterologous systems. Plant virus particles can be modified genetically and chemically to encapsulate foreign material and can be incorporated into supramolecular structures for use in biotechnology.
Bacterial viruses
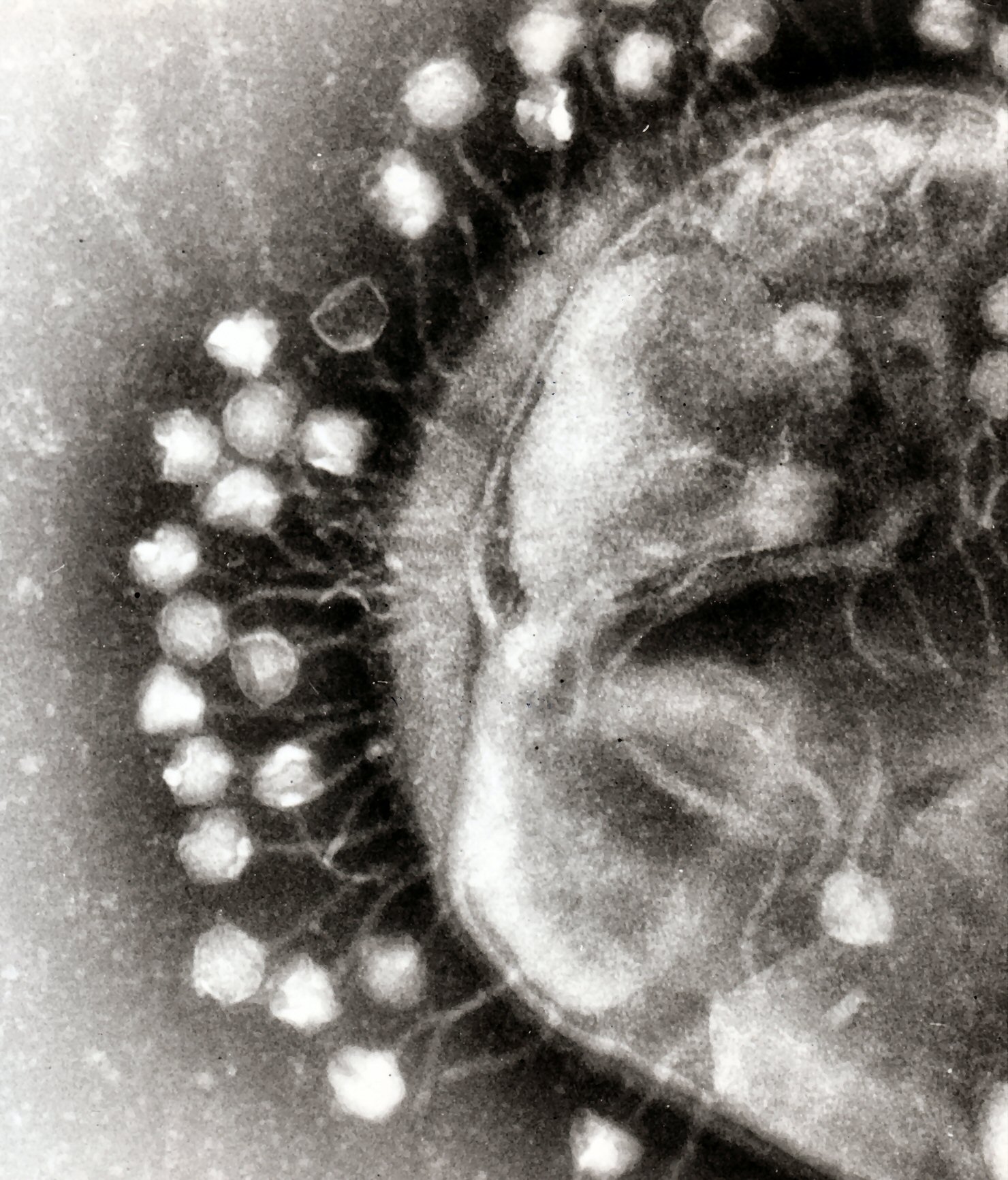 Bacteriophages are a common and diverse group of viruses and are the most abundant biological entity in aquatic environments—there are up to ten times more of these viruses in the oceans than there are bacteria, reaching levels of 250,000,000 bacteriophages per millilitre of seawater. These viruses infect specific bacteria by binding to surface receptor molecules and then entering the cell. Within a short amount of time, in some cases, just minutes, bacterial
Bacteriophages are a common and diverse group of viruses and are the most abundant biological entity in aquatic environments—there are up to ten times more of these viruses in the oceans than there are bacteria, reaching levels of 250,000,000 bacteriophages per millilitre of seawater. These viruses infect specific bacteria by binding to surface receptor molecules and then entering the cell. Within a short amount of time, in some cases, just minutes, bacterial polymerase
In biochemistry, a polymerase is an enzyme (Enzyme Commission number, EC 2.7.7.6/7/19/48/49) that synthesizes long chains of polymers or nucleic acids. DNA polymerase and RNA polymerase are used to assemble DNA and RNA molecules, respectively, by ...
starts translating viral mRNA into protein. These proteins go on to become either new virions within the cell, helper proteins, which help assembly of new virions, or proteins involved in cell lysis. Viral enzymes aid in the breakdown of the cell membrane, and, in the case of the T4 phage
Escherichia virus T4 is a species of bacteriophages that infect ''Escherichia coli'' bacteria. It is a double-stranded DNA virus in the subfamily '' Tevenvirinae'' of the family '' Straboviridae''. T4 is capable of undergoing only a lytic li ...
, in just over twenty minutes after injection over three hundred phages could be released.CRISPR
CRISPR (; acronym of clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) is a family of DNA sequences found in the genomes of prokaryotic organisms such as bacteria and archaea. Each sequence within an individual prokaryotic CRISPR is d ...
sequences to retain fragments of the genomes of viruses that the bacteria have come into contact with previously, which allows them to block the virus's replication through a form of RNA interference
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules are involved in sequence-specific suppression of gene expression by double-stranded RNA, through translational or transcriptional repression. Historically, RNAi was known by ...
. This genetic system provides bacteria with acquired immunity
The adaptive immune system (AIS), also known as the acquired immune system, or specific immune system is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized cells, organs, and processes that eliminate pathogens specifically. The ac ...
to infection.temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (approximately 23.5° to 66.5° N/S of the Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ran ...
" because they cause latent infections and do not immediately destroy their host cells. Instead, their DNA is incorporated with the host cell's as a prophage
A prophage is a bacteriophage (often shortened to "phage") genome that is integrated into the circular bacterial chromosome or exists as an extrachromosomal plasmid within the bacterial cell (biology), cell. Integration of prophages into the bacte ...
. These latent infections become productive when the prophage DNA is activated by stimuli such as changes in the environment.
Archaeal viruses
Some viruses replicate within archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even thou ...
: these are DNA viruses with unusual and sometimes unique shapes.thermophilic
A thermophile is a type of extremophile that thrives at relatively high temperatures, between . Many thermophiles are archaea, though some of them are bacteria and fungi. Thermophilic eubacteria are suggested to have been among the earliest bact ...
archaea, particularly the orders Sulfolobales
Sulfolobales is an order of archaeans in the class Thermoprotei.
Phylogeny
The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI)
...
and Thermoproteales
Thermoproteales are an order of archaeans in the class Thermoprotei. They are the only organisms known to lack the SSB proteins, instead possessing the protein ThermoDBP that has displaced them.
The rRNA genes of these organisms contain multi ...
. Defences against these viruses involve RNA interference from repetitive DNA
Repeated sequences (also known as repetitive elements, repeating units or repeats) are short or long patterns that occur in multiple copies throughout the genome. In many organisms, a significant fraction of the genomic DNA is repetitive, with ov ...
sequences within archaean genomes that are related to the genes of the viruses. Most archaea have CRISPR–Cas systems as an adaptive defence against viruses. These enable archaea to retain sections of viral DNA, which are then used to target and eliminate subsequent infections by the virus using a process similar to RNA interference.
Role in aquatic ecosystems
Viruses are the most abundant biological entity in aquatic environments.bacteriophages
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a phage (), is a virus that infects and replicates within bacteria. The term is derived . Bacteriophages are composed of proteins that encapsulate a DNA or RNA genome, and may have structures tha ...
infecting heterotrophic bacteria and cyanophages
Cyanophages are viruses that infect cyanobacteria, also known as Cyanophyta or blue-green algae. Cyanobacteria are a phylum of bacteria that obtain their energy through the process of photosynthesis. Although cyanobacteria metabolize photoauto ...
infecting cyanobacteria and they are essential to the regulation of saltwater and freshwater ecosystems.phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater Aquatic ecosystem, ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek language, Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), mea ...
, the base of the foodchain
A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web, often starting with an autotroph (such as grass or algae), also called a producer, and typically ending at an apex predator (such as grizzly bears or killer whales), detritivore (such a ...
in aquatic environments.nutrient cycling
A nutrient cycle (or ecological recycling) is the movement and exchange of inorganic and organic matter back into the production of matter. Energy flow is a unidirectional and noncyclic pathway, whereas the movement of mineral nutrients is cyc ...
in marine environments. The organic molecules released from the dead bacterial cells stimulate fresh bacterial and algal growth, in a process known as the viral shunt
The viral shunt is a mechanism that prevents marine microbial particulate organic matter (POM) from migrating up trophic levels by recycling them into dissolved organic matter (DOM), which can be readily taken up by microorganisms. The DOM recyc ...
. In particular, lysis of bacteria by viruses has been shown to enhance nitrogen cycling and stimulate phytoplankton growth. Viral activity may also affect the biological pump
The biological pump (or ocean carbon biological pump or marine biological carbon pump) is the ocean's biologically driven Carbon sequestration, sequestration of carbon from the atmosphere and land runoff to the ocean interior and seafloor sedim ...
, the process whereby carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
is sequestered in the deep ocean.phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater Aquatic ecosystem, ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek language, Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), mea ...
including harmful algal bloom
A harmful algal bloom (HAB), or excessive algae growth, sometimes called a red tide in marine environments, is an algal bloom that causes negative impacts to other organisms by production of natural algae-produced toxins, water deoxygenation, ...
s,
The number of viruses in the oceans decreases further offshore and deeper into the water, where there are fewer host organisms.Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
onto every square meter of the planet's surface, as the result of a global atmospheric stream of viruses, circulating above the weather system but below the altitude of usual airline travel, distributing viruses around the planet.marine mammal
Marine mammals are mammals that rely on marine ecosystems for their existence. They include animals such as cetaceans, pinnipeds, sirenians, sea otters and polar bears. They are an informal group, unified only by their reliance on marine enviro ...
s are susceptible to viral infections. In 1988 and 2002, thousands of harbour seals were killed in Europe by phocine distemper virus. Many other viruses, including calicivirus
The ''Caliciviridae'' are a family of "small round structured" viruses, members of Class IV of the Baltimore scheme. Caliciviridae bear resemblance to enlarged picornavirus and was formerly a separate genus within the picornaviridae. They are ...
es, herpesvirus
''Orthoherpesviridae'', previously named and more widely known as ''Herpesviridae'', is a large family of DNA viruses that cause infections and certain diseases in animals, including humans. The members of this family are commonly known as herp ...
es, adenovirus
Adenoviruses (members of the family ''Adenoviridae'') are medium-sized (90–100 nm), nonenveloped (without an outer lipid bilayer) viruses with an icosahedral nucleocapsid containing a double-stranded DNA genome. Their name derives from t ...
es and parvovirus
Parvoviruses are a family of animal viruses that constitute the family ''Parvoviridae''. They have linear, single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) genomes that typically contain two genes encoding for a replication initiator protein, called NS1, and the p ...
es, circulate in marine mammal populations.ciliate
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to flagellum, eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a ...
Halteria was observed to have increased in number due to the active consumption of chlorovirus as a food source instead of its typical bacterivore
A bacterivore is an organism which obtains energy and nutrients primarily or entirely from the consumption of bacteria. The term is most commonly used to describe free-living, heterotrophic, microscopic organisms such as nematodes as well as many s ...
diet.
Role in evolution
Viruses are an important natural means of transferring genes between different species, which increases genetic diversity
Genetic diversity is the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species. It ranges widely, from the number of species to differences within species, and can be correlated to the span of survival for a species. It is d ...
and drives evolution.last universal common ancestor
The last universal common ancestor (LUCA) is the hypothesized common ancestral cell from which the three domains of life, the Bacteria, the Archaea, and the Eukarya originated. The cell had a lipid bilayer; it possessed the genetic code a ...
into bacteria, archaea and eukaryotes.
Applications
Life sciences and medicine
 Viruses are important to the study of
Viruses are important to the study of molecular
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, ...
and cell biology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living an ...
as they provide simple systems that can be used to manipulate and investigate the functions of cells.genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinians, Augustinian ...
and helped our understanding of the basic mechanisms of molecular genetics
Molecular genetics is a branch of biology that addresses how differences in the structures or expression of DNA molecules manifests as variation among organisms. Molecular genetics often applies an "investigative approach" to determine the st ...
, such as DNA replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all life, living organisms, acting as the most essential part of heredity, biolog ...
, transcription, RNA processing
Transcriptional modification or co-transcriptional modification is a set of biological processes common to most eukaryotic cells by which an RNA primary transcript is chemically altered following transcription from a gene to produce a mature, fu ...
, translation
Translation is the communication of the semantics, meaning of a #Source and target languages, source-language text by means of an Dynamic and formal equivalence, equivalent #Source and target languages, target-language text. The English la ...
, protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
transport, and immunology
Immunology is a branch of biology and medicine that covers the study of Immune system, immune systems in all Organism, organisms.
Immunology charts, measures, and contextualizes the Physiology, physiological functioning of the immune system in ...
.
Geneticists often use viruses as vectors to introduce genes into cells that they are studying. This is useful for making the cell produce a foreign substance, or to study the effect of introducing a new gene into the genome. Similarly, virotherapy
Virotherapy is a treatment using biotechnology to convert viruses into therapeutic agents by reprogramming viruses to treat diseases. There are three main branches of virotherapy: anti-cancer oncolytic viruses, viral vectors for gene therapy and ...
uses viruses as vectors to treat various diseases, as they can specifically target cells and DNA. It shows promising use in the treatment of cancer and in gene therapy
Gene therapy is Health technology, medical technology that aims to produce a therapeutic effect through the manipulation of gene expression or through altering the biological properties of living cells.
The first attempt at modifying human DNA ...
. Eastern European scientists have used phage therapy
Phage therapy, viral phage therapy, or phagotherapy is the therapeutic use of bacteriophages for the treatment of pathogenic bacterial infections. This therapeutic approach emerged at the beginning of the 20th century but was progressively r ...
as an alternative to antibiotics for some time, and interest in this approach is increasing, because of the high level of antibiotic resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR or AR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from antimicrobials, which are drugs used to treat infections. This resistance affects all classes of microbes, including bacteria (antibiotic resis ...
now found in some pathogenic bacteria.antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule, moiety, foreign particulate matter, or an allergen, such as pollen, that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response.
...
s and antibodies. Industrial processes have been recently developed using viral vectors and several pharmaceutical proteins are currently in pre-clinical and clinical trials.
Virotherapy
Virotherapy involves the use of genetically modified viruses to treat diseases. Viruses have been modified by scientists to reproduce in cancer cells and destroy them but not infect healthy cells. Talimogene laherparepvec
Talimogene laherparepvec, sold under the brand name Imlygic among others, is a biopharmaceutical medication used to treat melanoma that cannot be operated on; it is injected directly into a subset of lesions which generates a systemic immune re ...
(T-VEC), for example, is a modified herpes simplex virus
Herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2) are two members of the Herpesviridae#Human herpesvirus types, human ''Herpesviridae'' family, a set of viruses that produce Viral disease, viral infections in the majority of humans. Both HSV-1 a ...
that has had a gene, which is required for viruses to replicate in healthy cells, deleted and replaced with a human gene ( GM-CSF) that stimulates immunity. When this virus infects cancer cells, it destroys them and in doing so the presence the GM-CSF gene attracts dendritic cells
A dendritic cell (DC) is an antigen-presenting cell (also known as an ''accessory cell'') of the mammalian immune system. A DC's main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system ...
from the surrounding tissues of the body. The dendritic cells process the dead cancer cells and present components of them to other cells of the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic ...
. Having completed successful clinical trials
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human subject research, human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel v ...
, the virus gained approval for the treatment of melanoma
Melanoma is the most dangerous type of skin cancer; it develops from the melanin-producing cells known as melanocytes. It typically occurs in the skin, but may rarely occur in the mouth, intestines, or eye (uveal melanoma). In very rare case ...
in late 2015. Viruses that have been reprogrammed to kill cancer cells are called oncolytic virus
An oncolytic virus is a virus that preferentially infects and kills cancer cells. As the infected cancer cells are destroyed by oncolysis, they release new infectious virus particles or virions to help destroy the remaining tumour. Oncolytic vi ...
es.
Materials science and nanotechnology
From the viewpoint of a materials scientist, viruses can be regarded as organic nanoparticle
A nanoparticle or ultrafine particle is a particle of matter 1 to 100 nanometres (nm) in diameter. The term is sometimes used for larger particles, up to 500 nm, or fibers and tubes that are less than 100 nm in only two directions. At ...
s. Their surface carries specific tools that enable them to cross the barriers of their host cells. The size and shape of viruses and the number and nature of the functional groups on their surface are precisely defined. As such, viruses are commonly used in materials science as scaffolds for covalently linked surface modifications. A particular quality of viruses is that they can be tailored by directed evolution. The powerful techniques developed by life sciences are becoming the basis of engineering approaches towards nanomaterials, opening a wide range of applications far beyond biology and medicine.Naval Research Laboratory
The United States Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) is the corporate research laboratory for the United States Navy and the United States Marine Corps. Located in Washington, DC, it was founded in 1923 and conducts basic scientific research, appl ...
in Washington, D.C., using Cowpea mosaic virus
Cowpea mosaic virus (CPMV) is a non-enveloped plant virus of the comovirus group. Infection of a susceptible cowpea leaf causes a "mosaic" pattern in the leaf, and results in high virus yields (1-2 g/kg). Its genome consists of 2 molecules of ...
(CPMV) particles to amplify signals in DNA microarray
A DNA microarray (also commonly known as a DNA chip or biochip) is a collection of microscopic DNA spots attached to a solid surface. Scientists use DNA microarrays to measure the expression levels of large numbers of genes simultaneously or t ...
based sensors. In this application, the virus particles separate the fluorescent
Fluorescence is one of two kinds of photoluminescence, the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. When exposed to ultraviolet radiation, many substances will glow (fluoresce) with color ...
dye
Juan de Guillebon, better known by his stage name DyE, is a French musician. He is known for the music video of the single "Fantasy
Fantasy is a genre of speculative fiction that involves supernatural or Magic (supernatural), magical ele ...
s used for signalling to prevent the formation of non-fluorescent dimers that act as quenchers. Another example is the use of CPMV as a nanoscale breadboard for molecular electronics.
Synthetic viruses
Many viruses can be synthesised de novo ("from scratch"). The first synthetic virus was created in 2002. Although somewhat of a misconception, it is not the actual virus that is synthesised, but rather its DNA genome (in case of a DNA virus), or a cDNA
In genetics, complementary DNA (cDNA) is DNA that was reverse transcribed (via reverse transcriptase) from an RNA (e.g., messenger RNA or microRNA). cDNA exists in both single-stranded and double-stranded forms and in both natural and engin ...
copy of its genome (in case of RNA viruses). For many virus families the naked synthetic DNA or RNA (once enzymatically converted back from the synthetic cDNA) is infectious when introduced into a cell. That is, they contain all the necessary information to produce new viruses. This technology is now being used to investigate novel vaccine strategies.permissive
Permissiveness may refer to:
* Permissiveness (endocrinology), between hormones and cells.
* Permissiveness (virology), between viruses and cells.
Permissive may refer to:
* Permissive society, a liberalization of social norms in a society.
* ...
cells are available. As of June 2021, the full-length genome sequences of 11,464 different viruses, including smallpox, are publicly available in an online database maintained by the National Institutes of Health
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in 1887 and is part of the United States Department of Health and Human Service ...
.
Weapons
The ability of viruses to cause devastating epidemics in human societies has led to the concern that viruses could be weaponised for biological warfare
Biological warfare, also known as germ warfare, is the use of biological toxins or Pathogen, infectious agents such as bacteria, viruses, insects, and Fungus, fungi with the intent to kill, harm or incapacitate humans, animals or plants as an ...
. Further concern was raised by the successful recreation of the infamous 1918 influenza virus in a laboratory.State Research Center of Virology and Biotechnology VECTOR
The State Research Center of Virology and Biotechnology VECTOR of Rospotrebnadzor (), also known as the Vector Institute, is a biological research center under Rospotrebnadzor in Koltsovo, Novosibirsk Oblast, Russia. It has research facilit ...
in Russia and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency under the United S ...
in the United States.
See also
* Cross-species transmission
Cross-species transmission (CST), also called interspecies transmission, host jump, or spillover, is the transmission of an infectious pathogen, such as a virus, between hosts belonging to different species. Once introduced into an individual o ...
* Glossary of virology
This glossary of virology is a list of definitions of terms and concepts used in virology, the study of viruses, particularly in the description of viruses and their actions. Related fields include microbiology, molecular biology, and genetics.
...
*
* Non-cellular life
Non-cellular life, also known as acellular life, is life that exists without a cellular structure for at least part of its life cycle. Historically, most definitions of life postulated that an organism must be composed of one or more cells, ...
* Gene transfer agent
* Retrozyme Retrozymes are a family of retrotransposons first discovered in the genomes of plants but now also known in genomes of animals. Retrozymes contain a hammerhead ribozyme (HHR) in their sequences (and so the name ''retrozyme'' is a combination of ''re ...
* Smallest organisms The smallest organisms found on Earth can be determined according to various aspects of organism size, including volume, mass, height, length, or genome size.
Given the incomplete nature of scientific knowledge, it is possible that the smallest or ...
*
* Viral metagenomics
Viral metagenomics uses metagenomic technologies to detect viral genomic material from diverse environmental and clinical samples. Viruses are the most abundant biological entity and are extremely diverse; however, only a small fraction of virus ...
* Viroplasm
A viroplasm, sometimes called "virus factory" or "virus inclusion", is an Inclusion bodies, inclusion body in a Cell (biology), cell where viral replication and assembly occurs. They may be thought of as viral factories in the cell. There are many ...
* Zoonosis
A zoonosis (; plural zoonoses) or zoonotic disease is an infectious disease of humans caused by a pathogen (an infectious agent, such as a virus, bacterium, parasite, fungi, or prion) that can jump from a non-human vertebrate to a human. When ...
References
External links
*
*
ViralZone
A Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics resource for all viral families, providing general molecular and epidemiological information
{{Authority control
*
1898 in biology
Medical tests
Epidemiology
Global health
Infectious diseases
Pandemics
Zoonoses
 Viruses undergo genetic change by several mechanisms. These include a process called
Viruses undergo genetic change by several mechanisms. These include a process called 
 A
A  A second defence of vertebrates against viruses is called cell-mediated immunity and involves immune cells known as
A second defence of vertebrates against viruses is called cell-mediated immunity and involves immune cells known as  There are many types of plant viruses, but often they cause only a loss of yield, and it is not economically viable to try to control them. Plant viruses are often spread from plant to plant by organisms, known as vectors. These are usually insects, but some fungi, nematode worms,
There are many types of plant viruses, but often they cause only a loss of yield, and it is not economically viable to try to control them. Plant viruses are often spread from plant to plant by organisms, known as vectors. These are usually insects, but some fungi, nematode worms,  Bacteriophages are a common and diverse group of viruses and are the most abundant biological entity in aquatic environments—there are up to ten times more of these viruses in the oceans than there are bacteria, reaching levels of 250,000,000 bacteriophages per millilitre of seawater. These viruses infect specific bacteria by binding to surface receptor molecules and then entering the cell. Within a short amount of time, in some cases, just minutes, bacterial
Bacteriophages are a common and diverse group of viruses and are the most abundant biological entity in aquatic environments—there are up to ten times more of these viruses in the oceans than there are bacteria, reaching levels of 250,000,000 bacteriophages per millilitre of seawater. These viruses infect specific bacteria by binding to surface receptor molecules and then entering the cell. Within a short amount of time, in some cases, just minutes, bacterial  Viruses are important to the study of
Viruses are important to the study of