|
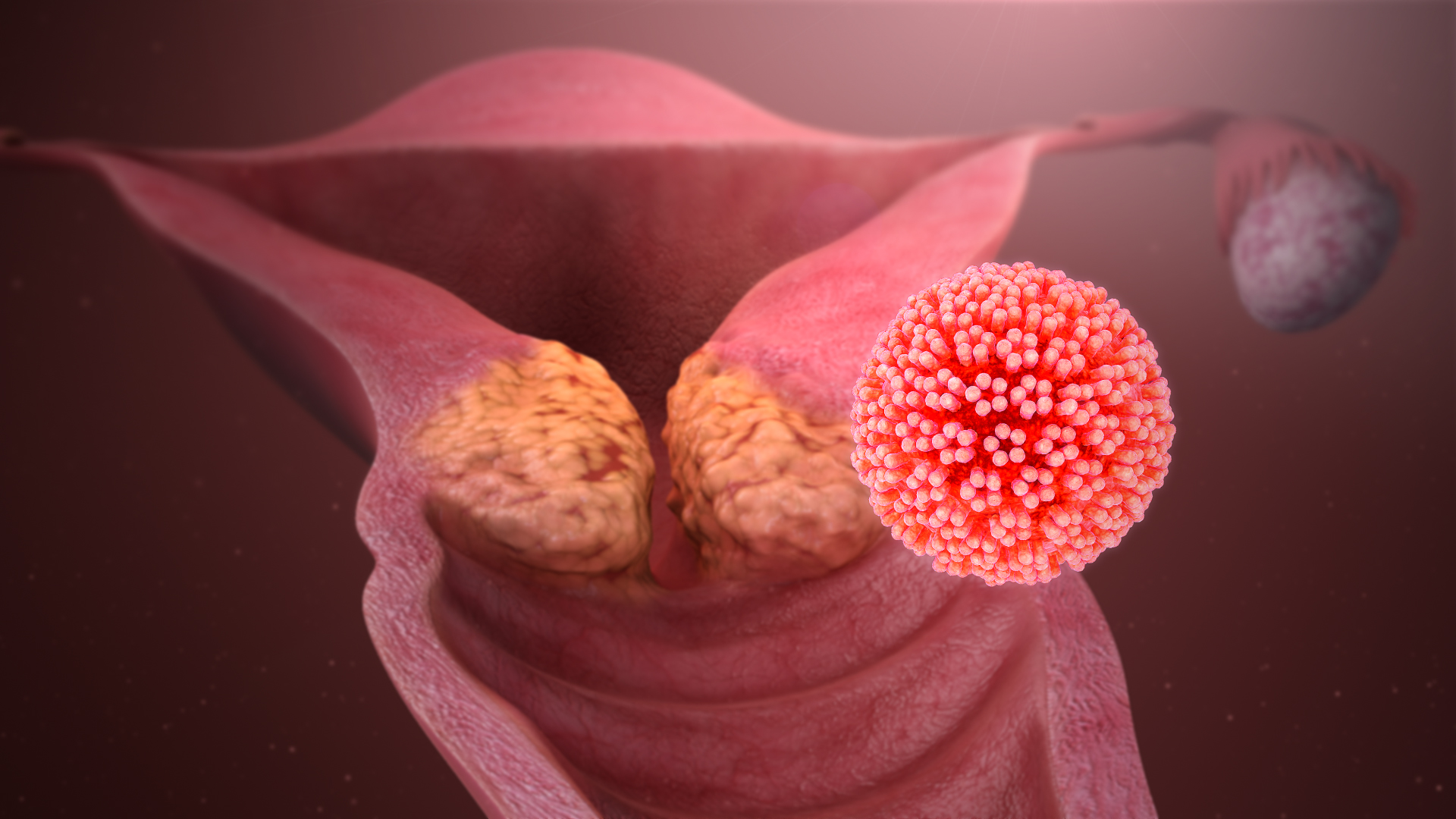
Papillomavirus
''Papillomaviridae'' is a family of non- enveloped double-stranded DNA viruses whose members are known as papillomaviruses. Several hundred species of papillomaviruses, traditionally referred to as "types", have been identified infecting all carefully inspected mammals, but also other vertebrates such as birds, snakes, turtles and fish. Infection by most papillomavirus types, depending on the type, is either asymptomatic (e.g. most Beta-PVs) or causes small benign tumors, known as papillomas or warts (e.g. human papillomavirus 1, HPV6 or HPV11). Papillomas caused by some types, however, such as human papillomaviruses 16 and 18, carry a risk of becoming cancerous. Papillomaviruses are usually considered as highly host- and tissue- tropic, and are thought to rarely be transmitted between species. Papillomaviruses replicate exclusively in the basal layer of the body surface tissues. All known papillomavirus types infect a particular body surface, typically the skin or mucosal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the ''Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and results in either warts or precancerous lesions. All warts are caused by HPV. These lesions, depending on the site affected, increase the risk of cancer of the cervical cancer, cervix, vulva cancer, vulva, vaginal cancer, vagina, penis cancer, penis, anal cancer, anus, oropharyngeal cancer, mouth, tonsils, or throat. Nearly all cervical cancer is due to HPV, and two strains – HPV16 and HPV18 – account for 70% of all cases. HPV16 is responsible for almost 90% of HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancers. Between 60% and 90% of the other cancers listed above are also linked to HPV. HPV6 and HPV11 are common causes of genital warts and laryngeal papillomatosis. An HPV infection is caused by the ''human papillomavirus'', a DNA virus from the papi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphapapillomavirus
''Alphapapillomavirus'' is a genus of viruses in the family ''Papillomaviridae''. Humans and monkeys serve as natural hosts. There are 14 species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include warts, papillomas, and malignant tumours. The genital-type species known to carry a high risk for malignancy are HPV-16 and 18 (cervical cancer), and those with a low risk of malignancy are HPV-6 and 11 (genital warts). Taxonomy The following species are assigned to the genus: * '' Alphapapillomavirus 1'' * '' Alphapapillomavirus 2'' * '' Alphapapillomavirus 3'' * '' Alphapapillomavirus 4'' * '' Alphapapillomavirus 5'' * '' Alphapapillomavirus 6'' * '' Alphapapillomavirus 7'' * '' Alphapapillomavirus 8'' * '' Alphapapillomavirus 9'' * '' Alphapapillomavirus 10'' * ''Alphapapillomavirus 11 ''Alphapapillomavirus'' is a genus of viruses in the family ''Papillomaviridae''. Humans and monkeys serve as natural hosts. There are 14 species in this genus. Diseases associated with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wart
Warts are non-cancerous viral growths usually occurring on the hands and feet but which can also affect other locations, such as the genitals or face. One or many warts may appear. They are distinguished from cancerous tumors as they are caused by a viral infection, such as a human papillomavirus, rather than a cancer growth. Factors that increase the risk include the use of public showers and pools, working with meat, eczema, and a weak immune system. The virus is believed to infect the host through the entrance of a skin wound. A number of types exist, including plantar warts, " filiform warts", and genital warts. Genital warts are often sexually transmitted. Without treatment, most types of warts resolve in months to years. A number of treatments may speed resolution, including salicylic acid applied to the skin and cryotherapy. In those who are otherwise healthy, they do not typically result in significant problems. Treatment of genital warts differs from that of o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papilloma
A papilloma (plural papillomas or papillomata) ('' papillo-'' + '' -oma'') is a benign epithelial tumor growing exophytically (outwardly projecting) in nipple-like and often finger-like fronds. In this context, papilla refers to the projection created by the tumor, not a tumor on an already existing papilla (such as the nipple). When used without context, it frequently refers to infections ( squamous cell papilloma) caused by human papillomavirus (HPV), such as warts. Human papillomavirus infection is a major cause of cervical cancer, vulvar cancer, vaginal cancer, penis cancer, anal cancer, and HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancers. Most viral warts are caused by human papillomavirus infection (HPV), of which there are nearly 200 distinct human papillomaviruses (HPVs), and many HPV types are carcinogenic. There are, however, a number of other conditions that cause papilloma, as well as many cases in which there is no known cause. Signs and symptoms A benign papillomatous tumor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyomaviridae
''Polyomaviridae'' is a family of DNA viruses whose natural hosts are mammals and birds. As of 2024, there are eight recognized genera. Fourteen species are known to infect humans, while others, such as Simian Virus 40, have been identified in humans to a lesser extent. Most of these viruses are very common and typically asymptomatic in most human populations studied. BK virus is associated with nephropathy in renal transplant and non-renal solid organ transplant patients, JC virus with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, and Merkel cell virus with Merkel cell cancer. Structure and genome Polyomaviruses are non-enveloped double-stranded DNA viruses with circular genomes of around 5000 base pairs. With such a small size, they are ranked among the smallest known double stranded DNA viruses. The genome is packaged in a viral capsid of about 40-50 nanometers in diameter, which is icosahedral in shape (T=7 symmetry). The capsid is composed of 72 pentameric capsom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Virus
A DNA virus is a virus that has a genome made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that is replicated by a DNA polymerase. They can be divided between those that have two strands of DNA in their genome, called double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses, and those that have one strand of DNA in their genome, called single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) viruses. dsDNA viruses primarily belong to two realms: ''Duplodnaviria'' and ''Varidnaviria'', and ssDNA viruses are almost exclusively assigned to the realm ''Monodnaviria'', which also includes some dsDNA viruses. Additionally, many DNA viruses are unassigned to higher taxa. Reverse transcribing viruses, which have a DNA genome that is replicated through an RNA intermediate by a reverse transcriptase, are classified into the kingdom '' Pararnavirae'' in the realm ''Riboviria''. DNA viruses are ubiquitous worldwide, especially in marine environments where they form an important part of marine ecosystems, and infect both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. They a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malignant Transformation
Malignant transformation is the process by which cells acquire the properties of cancer. This may occur as a primary process in normal tissue, or secondarily as ''malignant degeneration'' of a previously existing benign tumor. Causes There are many causes of primary malignant transformation, or tumorigenesis. Most human cancers in the United States are caused by external factors, and these factors are largely avoidable. These factors were summarized by Doll and Peto in 1981, and were still considered to be valid in 2015. These factors are listed in the table. a Reproductive and sexual behaviors include: number of partners; age at first menstruation; zero versus one or more live births Examples of diet-related malignant transformation Diet and colon cancer Colon cancer provides one example of the mechanisms by which diet, the top factor listed in the table, is an external factor in cancer. The Western diet of African Americans in the United States is associated with a ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetic Trees
A phylogenetic tree or phylogeny is a graphical representation which shows the evolutionary history between a set of species or taxa during a specific time.Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA. In other words, it is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological species or other entities based upon similarities and differences in their physical or genetic characteristics. In evolutionary biology, all life on Earth is theoretically part of a single phylogenetic tree, indicating common ancestry. Phylogenetics is the study of phylogenetic trees. The main challenge is to find a phylogenetic tree representing optimal evolutionary ancestry between a set of species or taxa. Computational phylogenetics (also phylogeny inference) focuses on the algorithms involved in finding optimal phylogenetic tree in the phylogenetic landscape. Phylogenetic trees may be rooted or unrooted. In a ''rooted'' ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaptive Radiation
In evolutionary biology, adaptive radiation is a process in which organisms diversify rapidly from an ancestral species into a multitude of new forms, particularly when a change in the environment makes new resources available, alters biotic interactions or opens new environmental niches. Starting with a single ancestor, this process results in the speciation and phenotypic adaptation of an array of species exhibiting different morphological and physiological traits. The prototypical example of adaptive radiation is finch speciation on the Galapagos ("Darwin's finches"), but examples are known from around the world. Characteristics Four features can be used to identify an adaptive radiation: #A common ancestry of component species: specifically a ''recent'' ancestry. Note that this is not the same as a monophyly in which ''all'' descendants of a common ancestor are included. #A phenotype-environment correlation: a ''significant'' association between environments and the mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoonosis
A zoonosis (; plural zoonoses) or zoonotic disease is an infectious disease of humans caused by a pathogen (an infectious agent, such as a virus, bacterium, parasite, fungi, or prion) that can jump from a non-human vertebrate to a human. When humans infect non-humans, it is called reverse zoonosis or anthroponosis. Major modern diseases such as Ebola and salmonellosis are zoonoses. HIV was a zoonotic disease transmitted to humans in the early part of the 20th century, though it has now evolved into a separate human-only disease. Human infection with animal influenza viruses is rare, as they do not transmit easily to or among humans. However, avian and swine influenza viruses in particular possess high zoonotic potential, and these occasionally recombine with human strains of the flu and can cause pandemics such as the 2009 swine flu. Zoonoses can be caused by a range of disease pathogens such as emergent viruses, bacteria, fungi and parasites; of 1,415 pathogens known t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Recombination
Genetic recombination (also known as genetic reshuffling) is the exchange of genetic material between different organisms which leads to production of offspring with combinations of traits that differ from those found in either parent. In eukaryotes, genetic recombination during meiosis can lead to a novel set of genetic information that can be further passed on from parents to offspring. Most recombination occurs naturally and can be classified into two types: (1) ''interchromosomal'' recombination, occurring through independent assortment of alleles whose loci are on different but homologous chromosomes (random orientation of pairs of homologous chromosomes in meiosis I); & (2) ''intrachromosomal'' recombination, occurring through crossing over. During meiosis in eukaryotes, genetic recombination involves the pairing of homologous chromosomes. This may be followed by information transfer between the chromosomes. The information transfer may occur without physical exchange (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. Phylogeneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |