|
RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) are nucleic acids. The nucleic acids constitute one of the four major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the nucleobase, nitrogenous bases of guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine, denoted by the letters G, U, A, and C) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome. Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is Protein biosynthesis, protein synthesis, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ribosomal RNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribosomal DNA (rDNA) and then bound to ribosomal proteins to form SSU rRNA, small and LSU rRNA, large ribosome subunits. rRNA is the physical and mechanical factor of the ribosome that forces transfer RNA (tRNA) and messenger RNA (mRNA) to process and Translation (biology), translate the latter into proteins. Ribosomal RNA is the predominant form of RNA found in most cells; it makes up about 80% of cellular RNA despite never being translated into proteins itself. Ribosomes are composed of approximately 60% rRNA and 40% ribosomal proteins, though this ratio differs between Prokaryote, prokaryotes and Eukaryote, eukaryotes. Structure Although the primary structure of rRNA sequences can vary across organisms, Base pair, base-pairing within these sequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Non-coding RNA
A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is a functional RNA molecule that is not Translation (genetics), translated into a protein. The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene. Abundant and functionally important list of RNAs, types of non-coding RNAs include transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as small RNAs such as microRNAs, siRNAs, piRNAs, snoRNAs, snRNAs, Extracellular RNA, exRNAs, scaRNAs and the long noncoding RNA, long ncRNAs such as Xist and HOTAIR. The number of non-coding RNAs within the human genome is unknown; however, recent Transcriptomics, transcriptomic and Bioinformatics, bioinformatic studies suggest that there are thousands of non-coding transcripts. Many of the newly identified ncRNAs have unknown functions, if any. There is no consensus on how much of non-coding transcription is functional: some believe most ncRNAs to be non-functional "junk RNA", spurious transcriptions, while others expect that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Transfer RNA
Transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA), formerly referred to as soluble ribonucleic acid (sRNA), is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length (in eukaryotes). In a cell, it provides the physical link between the genetic code in messenger RNA (mRNA) and the amino acid sequence of proteins, carrying the correct sequence of amino acids to be combined by the protein-synthesizing machinery, the ribosome. Each three-nucleotide codon in mRNA is complemented by a three-nucleotide anticodon in tRNA. As such, tRNAs are a necessary component of translation, the biological synthesis of new proteins in accordance with the genetic code. Overview The process of translation starts with the information stored in the nucleotide sequence of DNA. This is first transformed into mRNA, then tRNA specifies which three-nucleotide codon from the genetic code corresponds to which amino acid. Each mRNA codon is recognized by a particular type of tRNA, which docks to it along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
RNA World
The RNA world is a hypothetical stage in the evolutionary history of life on Earth in which self-replicating RNA molecules proliferated before the evolution of DNA and proteins. The term also refers to the hypothesis that posits the existence of this stage. Alexander Rich first proposed the concept of the RNA world in 1962, and Walter Gilbert coined the term in 1986. Among the characteristics of RNA that suggest its original prominence are that: * Like DNA, RNA can store and replicate genetic information. Although RNA is considerably more fragile than DNA, some ancient RNAs may have evolved the ability to methylate other RNAs to protect them. The concurrent formation of all four RNA building blocks further strengthens the hypothesis. * Enzymes made of RNA ( ribozymes) can catalyze (start or accelerate) chemical reactions that are critical for life, so it is conceivable that in an RNA world, ribozymes might have preceded enzymes made of protein. * Many coenzymes that have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gene Expression
Gene expression is the process (including its Regulation of gene expression, regulation) by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, proteins or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein-coding genes such as Transfer RNA, transfer RNA (tRNA) and Small nuclear RNA, small nuclear RNA (snRNA), the product is a functional List of RNAs, non-coding RNA. The process of gene expression is used by all known life—eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and viruses—to generate the macromolecule, macromolecular machinery for life. In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, ''i.e.'' observable trait. The genetic information stored in DNA represents the genotype, whereas the phenotype results from the "interpretation" of that informati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Messenger RNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein. mRNA is created during the process of transcription, where an enzyme (RNA polymerase) converts the gene into primary transcript mRNA (also known as pre-mRNA). This pre-mRNA usually still contains introns, regions that will not go on to code for the final amino acid sequence. These are removed in the process of RNA splicing, leaving only exons, regions that will encode the protein. This exon sequence constitutes mature mRNA. Mature mRNA is then read by the ribosome, and the ribosome creates the protein utilizing amino acids carried by transfer RNA (tRNA). This process is known as translation. All of these processes form part of the central dogma of molecular biology, which describes the flow of genetic information in a biological system. As in DNA, genetic inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ribozyme
Ribozymes (ribonucleic acid enzymes) are RNA molecules that have the ability to Catalysis, catalyze specific biochemical reactions, including RNA splicing in gene expression, similar to the action of protein enzymes. The 1982 discovery of ribozymes demonstrated that RNA can be both genetic material (like DNA) and a biological catalyst (like protein enzymes), and contributed to the RNA world hypothesis, which suggests that RNA may have been important in the evolution of prebiotic self-replicating systems. The most common activities of natural or Directed evolution, ''in vitro'' evolved ribozymes are the cleavage (or Ligation (molecular biology), ligation) of RNA and DNA and peptide bond formation. For example, the smallest ribozyme known (GUGGC-3') can aminoacylate a GCCU-3' sequence in the presence of PheAMP. Within the ribosome, ribozymes function as part of the large subunit ribosomal RNA to link amino acids during Translation (biology), protein synthesis. They also participate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
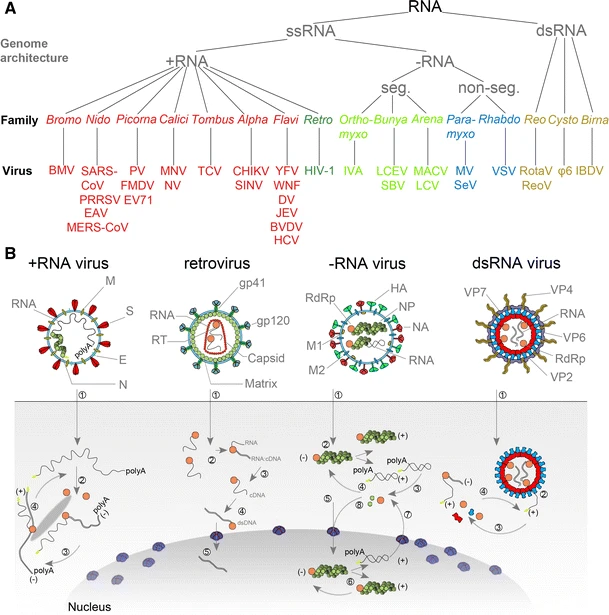
RNA Virus
An RNA virus is a virus characterized by a ribonucleic acid (RNA) based genome. The genome can be single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) or double-stranded (Double-stranded RNA, dsRNA). Notable human diseases caused by RNA viruses include influenza, SARS, MERS, COVID-19, Dengue virus, hepatitis C, hepatitis E, West Nile fever, Ebola virus disease, rabies, polio, mumps, and measles. All known RNA viruses, that is viruses that use a homologous RNA-dependent polymerase for replication, are categorized by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) into the realm ''Riboviria''. This includes RNA viruses belonging to ''Group III'', ''Group IV'' or ''Group V'' of the Virus classification#Baltimore classification, Baltimore classification system as well as ''Group VI. Group VI'' viruses are retroviruses, viruses with RNA genetic material that use DNA intermediates in their Viral life cycle, life cycle including HIV-1 and HIV-2 which cause AIDS. The majority of such RNA viruses fall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ribosome
Ribosomes () are molecular machine, macromolecular machines, found within all cell (biology), cells, that perform Translation (biology), biological protein synthesis (messenger RNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA molecules to form polypeptide chains. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small and large ribosomal subunits. Each subunit consists of one or more ribosomal RNA molecules and many ribosomal proteins (). The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the ''translational apparatus''. Overview The sequence of DNA that encodes the sequence of the amino acids in a protein is transcribed into a messenger RNA (mRNA) chain. Ribosomes bind to the messenger RNA molecules and use the RNA's sequence of nucleotides to determine the sequence of amino acids needed to generate a protein. Amino acids are selected and carried to the ribosome by transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules, which enter the riboso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Protein Biosynthesis
Protein biosynthesis, or protein synthesis, is a core biological process, occurring inside Cell (biology), cells, homeostasis, balancing the loss of cellular proteins (via Proteolysis, degradation or Protein targeting, export) through the production of new proteins. Proteins perform a number of critical functions as enzymes, structural proteins or hormones. Protein synthesis is a very similar process for both prokaryotes and eukaryotes but there are some distinct differences. Protein synthesis can be divided broadly into two phases: Transcription (biology), transcription and Translation (biology), translation. During transcription, a section of DNA encoding a protein, known as a gene, is converted into a molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA). This conversion is carried out by enzymes, known as RNA polymerases, in the cell nucleus, nucleus of the cell. In eukaryotes, this mRNA is initially produced in a premature form (Primary transcript, pre-mRNA) which undergoes post-transcriptio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898, more than 16,000 of the millions of List of virus species, virus species have been described in detail. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent viral particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) genetic material, i.e., long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of all known organisms and many viruses. DNA and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are nucleic acids. Alongside proteins, lipids and complex carbohydrates (polysaccharides), nucleic acids are one of the four major types of macromolecules that are essential for all known forms of life. The two DNA strands are known as polynucleotides as they are composed of simpler monomeric units called nucleotides. Each nucleotide is composed of one of four nitrogen-containing nucleobases (cytosine guanine adenine or thymine , a sugar called deoxyribose, and a phosphate group. The nucleotides are joined to one another in a chain by covalent bonds (known as the phosphodiester linkage) between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of the next, res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |