|
Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is a rare and aggressive skin cancer occurring in about three people per million members of the population. It is also known as cutaneous APUDoma, Primary tumor, primary neuroendocrine tumor, neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin, primary small cell carcinoma of the skin, and trabecular carcinoma of the skin. Factors involved in the development of MCC include the Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCPyV or MCV), a weakened immune system, and exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Merkel cell carcinoma usually arises on the head, neck, and extremities, as well as in the perianal region and on the eyelid. It is more common in people over sixty years old, Caucasian people, and males. MCC is less common in children. Signs and symptoms Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) usually presents as a firm Nodule (medicine), nodule (up to 2 cm diameter) or mass (>2 cm diameter). These flesh-colored, red, or blue tumors typically vary in size from 0.5 cm (less than one-qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrograph
A micrograph is an image, captured photographically or digitally, taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnify, magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A photographic micrograph is a photomicrograph, and one taken with an electron microscope is an electron micrograph. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphoma
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). The name typically refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, drenching sweats, unintended weight loss, itching, and constantly feeling tired. The enlarged lymph nodes are usually painless. The sweats are most common at night. Many subtypes of lymphomas are known. The two main categories of lymphomas are the non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) (90% of cases) and Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) (10%). Lymphomas, leukemias and myelomas are a part of the broader group of tumors of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Risk factors for Hodgkin lymphoma include infection with Epstein–Barr virus and a history of the disease in the family. Risk factors for common types of non-Hodgkin lymphomas include autoimmune diseases, HIV/AIDS, infection with human T-lymphotropic virus, immunosuppressant medicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATOH1
Protein atonal homolog 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ATOH1'' gene. Function This protein belongs to the basic helix-loop-helix (BHLH) family of transcription factors. It activates E-box dependent transcription along with TCF3 (E47). ATOH1 is required for the formation of both neural and non-neural cell types. Using genetic deletion in mice, Atoh1 has been shown to be essential for formation of cerebellar granule neurons, inner ear hair cells, spinal cord interneurons, Merkel cells of the skin, and intestinal secretory cells (goblet, enteroendocrine, and Paneth cells). ATOH1 is a mammalian homolog of the ''Drosophila melanogaster'' gene ''atonal''. ATOH1 is considered part of the Notch signaling pathway. In 2009, ATOH1 was identified as a tumor suppressor gene A tumor suppressor gene (TSG), or anti-oncogene, is a gene that regulates a cell (biology), cell during cell division and replication. If the cell grows uncontrollably, it will result in cancer. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PIEZO2
Piezo-type mechanosensitive ion channel component 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PIEZO2'' gene. It has a homotrimeric structure, with three blades curving into a nano-dome, with a diameter of 28 nanometers. Function Piezos are large transmembrane proteins conserved among various species, all having between 24 and 36 predicted transmembrane domains. 'Piezo' comes from the Greek 'piesi,' meaning 'pressure.' The PIEZO2 protein has a role in rapidly adapting mechanically activated (MA) currents in somatosensory neurons. Its structure is resolved via a mouse version in 2019, showing the predicted homotrimeric propeller. PIEZO2 is typically found in cell types that respond to physical touch, such as Merkel cells, and is thought to regulate light touch response. Pathology * Gain-of-function mutations in the mechanically activated ion channel PIEZO2 cause a subtype of Distal Arthrogryposis. * Mice without PIEZO2 in their proprioceptive neurons show uncoordinated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromogranin A
Chromogranin-A (CgA) or parathyroid secretory protein 1 is encoded in the human by the gene ''CHGA''. Cga is a member of the granin family of neuroendocrine secretory proteins. As such, it is located in secretory vesicles of neurons and endocrine cells such as islet beta cell secretory granules in the pancreas. Tissue distribution Examples of cells producing chromogranin-A (CgA) are chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla, paraganglia, enterochromaffin-like cells and beta cells of the pancreas. It is present in islet beta cell secretory granules. chromogranin-A (CgA)+ Pulmonary neuroendocrine cells account for 0.41% of all epithelial cells in the conducting airway, but are absent from the alveoli. Function Chromogranin-A is the precursor to several functional peptides including vasostatin-1, vasostatin-2, pancreastatin, catestatin and . These peptides negatively modulate the neuroendocrine function of the releasing cell (autocrine) or nearby cells (paracrine). Chromogra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synaptophysin
Synaptophysin, also known as the major synaptic vesicle protein p38, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SYP'' gene. Gene The gene is located on the short arm of X chromosome (Xp11.23-p11.22). It is 12,406 bases in length and lies on the minus strand. Tissue distribution It is expressed in neuroendocrine cells and in virtually all neurons in the brain and spinal cord that participate in synaptic transmission. Structure The protein is a synaptic vesicle glycoprotein with four transmembrane domains weighing 38 kDa. Function The exact function of the protein is unknown: it interacts with the essential synaptic vesicle protein synaptobrevin, but when the synaptophysin gene is experimentally inactivated in animals, they still develop and function normally. Recent research has shown, however, that elimination of synaptophysin in mice creates behavioral changes such as increased exploratory behavior, impaired object novelty recognition, and reduced spatia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratin 20
Keratin 20, often abbreviated CK20, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KRT20'' gene. Keratin 20 is a type I cytokeratin. It is a major cellular protein of mature enterocytes and goblet cells and is specifically found in the gastric and intestinal mucosa. In immunohistochemistry, antibodies to CK20 can be used to identify a range of adenocarcinoma arising from epithelia that normally contain the CK20 protein. For example, the protein is commonly found in colorectal cancer, transitional cell carcinomas and in Merkel cell carcinoma, but is absent in lung cancer, prostate cancer Prostate cancer is the neoplasm, uncontrolled growth of cells in the prostate, a gland in the male reproductive system below the bladder. Abnormal growth of the prostate tissue is usually detected through Screening (medicine), screening tests, ..., and non-mucinous ovarian cancer. It is often used in combination with antibodies to CK7 to distinguish different types of glandular tumour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
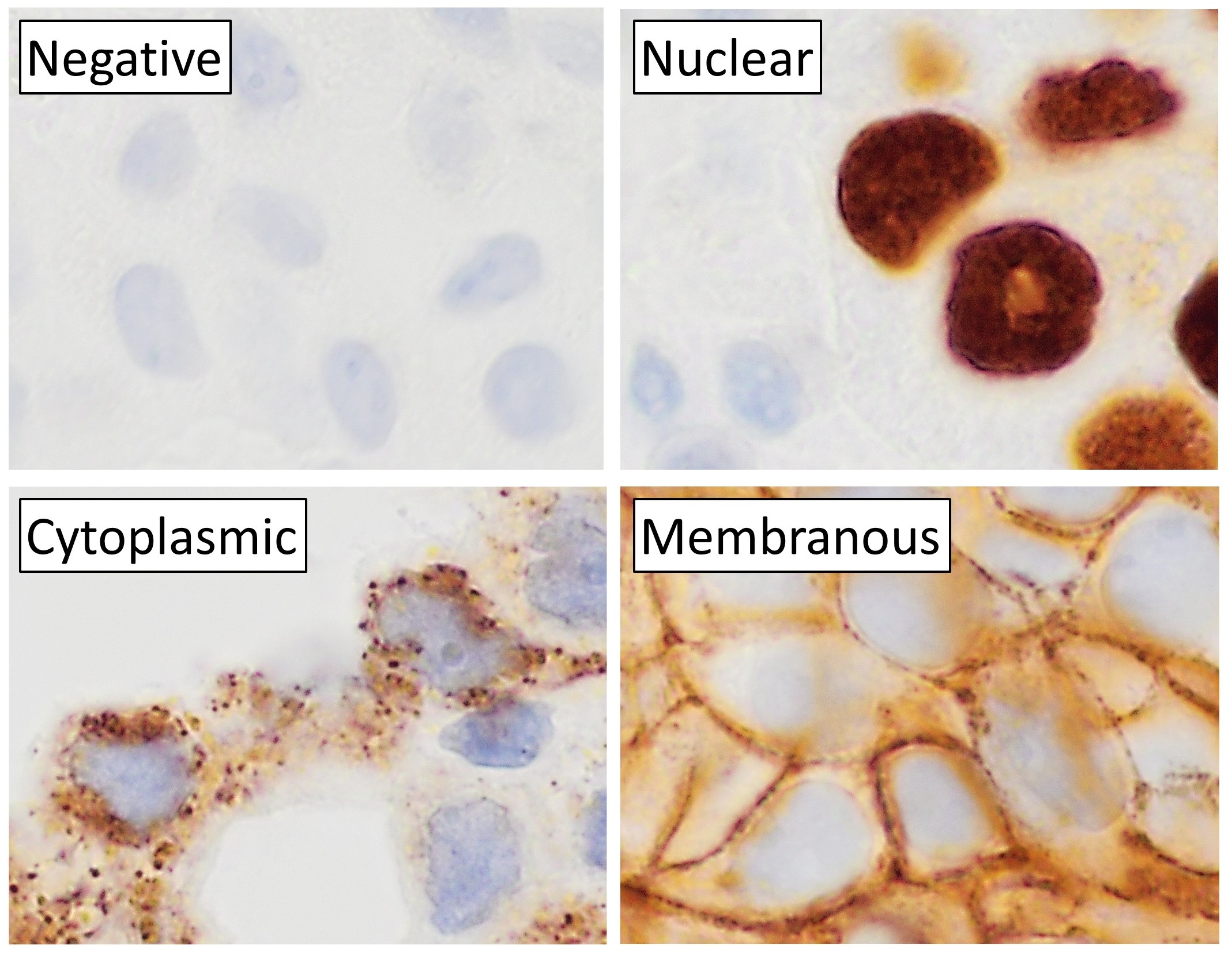
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry is a form of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens in cells and tissue, by exploiting the principle of Antibody, antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. Albert Coons, Albert Hewett Coons, Ernst Berliner, Ernest Berliner, Norman Jones and Hugh J Creech was the first to develop immunofluorescence in 1941. This led to the later development of immunohistochemistry. Immunohistochemical staining is widely used in the diagnosis of abnormal cells such as those found in cancerous tumors. In some cancer cells certain tumor antigens are expressed which make it possible to detect. Immunohistochemistry is also widely used in basic research, to understand the distribution and localization of biomarkers and differentially expressed proteins in different parts of a biological tissue. Sample preparation Immunohistochemistry can be performed on tissue that has been fixed and embedded in Paraffin wax, paraffin, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merkel Cell
Merkel cells, also known as Merkel–Ranvier cells or tactile epithelial cells, are oval-shaped mechanoreceptors essential for light touch sensation and found in the skin of vertebrates. They are abundant in highly sensitive skin like that of the fingertips in humans, and make synaptic contacts with somatosensory afferent nerve fibers. It has been reported that Merkel cells are derived from neural crest cells, though more recent experiments in mammals have indicated that they are epithelial in origin. Merkel cells functionally resemble the enterochromaffin cell, the mechanosensory cell of the gastrointestinal epithelium.Chang W, Kanda H, Ikeda R, Ling J, DeBerry JJ, Gu JG. Merkel disc is a serotonergic synapse in the epidermis for transmitting tactile signals in mammals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Sep 13;113(37): E5491-500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1610176113. Structure Merkel cells are found in the skin and some parts of the mucosa of all vertebrates. In mammalian skin, they ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metastasize
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spreading from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, are metastases (mets). It is generally distinguished from cancer invasion, which is the direct extension and penetration by cancer cells into neighboring tissues. Cancer occurs after cells are genetically altered to proliferate rapidly and indefinitely. This uncontrolled proliferation by mitosis produces a primary tumor, primary tumour heterogeneity, heterogeneic tumour. The cells which constitute the tumor eventually undergo metaplasia, followed by dysplasia then anaplasia, resulting in a Malignancy, malignant phenotype. This malignancy allows for invasion into the circulation, followed by invasion to a second site for tumorigenesis. Some cancer cells, known as circulating tumor cells (CTCs), are able to penetrate the walls of lymp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fascia
A fascia (; : fasciae or fascias; adjective fascial; ) is a generic term for macroscopic membranous bodily structures. Fasciae are classified as superficial, visceral or deep, and further designated according to their anatomical location. The knowledge of fascial structures is essential in surgery, as they create borders for infectious processes (for example Psoas abscess) and haematoma. An increase in pressure may result in a compartment syndrome, where a prompt fasciotomy may be necessary. For this reason, profound descriptions of fascial structures are available in anatomical literature from the 19th century. Function Fasciae were traditionally thought of as passive structures that transmit mechanical tension generated by muscular activities or external forces throughout the body. An important function of muscle fasciae is to reduce friction of muscular force. In doing so, fasciae provide a supportive and movable wrapping for nerves and blood vessels as they pass thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |