|
Phylum (biology)
In biology, a phylum (; : phyla) is a level of classification, or taxonomic rank, that is below kingdom and above class. Traditionally, in botany the term division has been used instead of phylum, although the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants accepts the terms as equivalent. Depending on definitions, the animal kingdom Animalia contains about 31 phyla, the plant kingdom Plantae contains about 14 phyla, and the fungus kingdom Fungi contains about eight phyla. Current research in phylogenetics is uncovering the relationships among phyla within larger clades like Ecdysozoa and Embryophyta. General description The term phylum was coined in 1866 by Ernst Haeckel from the Greek (, "race, stock"), related to (, "tribe, clan"). Haeckel noted that species constantly evolved into new species that seemed to retain few consistent features among themselves and therefore few features that distinguished them as a group ("a self-contained unity"): "perhap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biology
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, History of life, origin, evolution, and distribution of life. Central to biology are five fundamental themes: the cell (biology), cell as the basic unit of life, genes and heredity as the basis of inheritance, evolution as the driver of biological diversity, energy transformation for sustaining life processes, and the maintenance of internal stability (homeostasis). Biology examines life across multiple biological organisation, levels of organization, from molecules and cells to organisms, populations, and ecosystems. Subdisciplines include molecular biology, physiology, ecology, evolutionary biology, developmental biology, and systematics, among others. Each of these fields applies a range of methods to investigate biological phenomena, including scientific method, observation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eichler System
A system of plant taxonomy, the Eichler system was the first phylogenetic (phyletic) or evolutionary system. It was developed by August W. Eichler (1839–1887), initially in his ''Blüthendiagramme'' (1875–1878) and then in successive editions of his ''Syllabus'' (1876–1890). After his death his colleague Adolf Engler (1844–1930) continued its development, and it became widely accepted. The system was based on dividing the plant kingdom into those plants with concealed reproductive organs (non-floral), the ( Cryptogamae, = hidden reproduction) and those with visible reproductive organs (floral), the ( Phanerogamae, = visible reproduction). Moreover, Eichler was the first taxonomist to separate the Phanerogamae into Angiosperms and Gymnosperms and the former into Monocotyledonae and Dicotyledonae. His primary ranks were Divisions (''Abtheilung''), followed by orders (''Reihe''). ''Blüthendiagramme'' (1875–1878) Volume I (1875) Contents pp. VI–VIII Syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protostome
Protostomia () is the clade of animals once thought to be characterized by the formation of the organism's mouth before its anus during embryonic development. This nature has since been discovered to be extremely variable among Protostomia's members, although the reverse is typically true of its sister clade, Deuterostomia. Well-known examples of protostomes are arthropods, molluscs, annelids, flatworms and nematodes. They are also called schizocoelomates since schizocoely typically occurs in them. Together with the Deuterostomia and Xenacoelomorpha, these form the clade Bilateria, animals with bilateral symmetry, anteroposterior axis and three germ layers. Protostomy In animals at least as complex as earthworms, the first phase in gut development involves the embryo forming a dent on one side (the blastopore) which deepens to become its digestive tube (the archenteron). In the sister-clade, the deuterostomes (), the original dent becomes the anus while the gut eventua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deuterostome
Deuterostomes (from Greek: ) are bilaterian animals of the superphylum Deuterostomia (), typically characterized by their anus forming before the mouth during embryonic development. Deuterostomia comprises three phyla: Chordata, Echinodermata, Hemichordata, and the extinct clade Cambroernida. In deuterostomes, the developing embryo's first opening (the blastopore) becomes the anus and cloaca, while the mouth is formed at a different site later on. This was initially the group's distinguishing characteristic, but deuterostomy has since been discovered among protostomes as well. The deuterostomes are also known as enterocoelomates, because their coelom develops through pouching of the gut, enterocoely. Deuterostomia's sister clade is Protostomia, animals that develop mouth first and whose digestive tract development is more varied. Protostomia includes the ecdysozoans and spiralians, as well as the extinct '' Kimberella''. Together with the Xenacoelomorpha, these constit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhombozoa
Dicyemida, also known as Rhombozoa, is a phylum of tiny parasites that live in the renal appendages of cephalopods. Taxonomy Classification is controversial. Traditionally, dicyemids have been grouped with the Orthonectida in the phylum Mesozoa and, from 2017, molecular evidence appears to confirm this. However, other molecular phylogenies have placed the dicyemids more closely related to the roundworms. Additional molecular evidence suggests that this phylum is derived from the Lophotrochozoa. The phylum (or class if retained within Mesozoa) contains three families, Conocyemidae, Dicyemidae and Kantharellidae, which have sometimes been further grouped into orders. Authors who treat Dicyemida as an order and separate the family Conocyemidae into a different order ( Heterocyemida) prefer 'Rhombozoa' as a more inclusive and unambiguous name to cover all three families. Anatomy Adult dicyemids range in length from , and they can be easily viewed through a light microsco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthonectida
Orthonectida () is a small phylum (biology), phylum of poorly known parasites of marine invertebrates that are among the simplest of multi-cellular organisms. Members of this phylum are known as orthonectids. Biology The adults, which are the sexual stage, are microscopic wormlike animals, consisting of a single layer of ciliated outer cells surrounding a mass of sex cells. They swim freely within the bodies of their hosts, which include flatworms, polychaete worms, Bivalvia, bivalve molluscs, and echinoderms. Most are gonochorism, gonochoristic, with separate male and female individuals, but a few species are hermaphroditic. When they are ready to reproduce, adults leave the host, and sperm from the males penetrate the bodies of the females to achieve internal fertilisation. The resulting zygote develops into a ciliated larva that escapes from the mother to seek out new hosts. Once it finds a host, the larva loses its cilia and develops into a syncytium, syncytial Plasmodium (li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesozoa
The Mesozoa are minuscule, worm-like parasites of marine invertebrates. Generally, these tiny, elusive creatures consist of a somatoderm (outer layer) of ciliated cells surrounding one or more reproductive cells. A 2017 study recovered Mesozoa as a monophyletic group that emerged in the Lophotrochozoa as sister of the Rouphozoa. Some workers previously classified Mesozoa as the sole phylum of the lonely subkingdom Agnotozoa. Cavalier-Smith argued that at least some of the mesozoans are in fact protistans, not animals. In the 19th century, the Mesozoa were a wastebasket taxon for multicellular organisms which lacked the invaginating gastrula which was thought to define the Metazoa. Evolution Mesozoa were once thought to be evolutionary intermediate forms between Protozoans and Metazoans, but now they are thought to be degenerate or simplified metazoa. Their ciliated larvae are similar to the miracidium of trematodes, and their internal multiplication is similar to what h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family (, : ) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". The delineation of what constitutes a family—or whether a described family should be acknowledged—is established and decided upon by active taxonomists. There are not strict regulations for outlining or acknowledging a family, yet in the realm of plants, these classifications often rely on both the vegetative and reproductive characteristics of plant species. Taxonomists frequently hold varying perspectives on these descriptions, leading to a lack of widespread consensus within the scientific community ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annelid
The annelids (), also known as the segmented worms, are animals that comprise the phylum Annelida (; ). The phylum contains over 22,000 extant species, including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to various ecologies – some in marine environments as distinct as tidal zones and hydrothermal vents, others in fresh water, and yet others in moist terrestrial environments. The annelids are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, coelomate, invertebrate organisms. They also have parapodia for locomotion. Most textbooks still use the traditional division into polychaetes (almost all marine), oligochaetes (which include earthworms) and leech-like species. Cladistic research since 1997 has radically changed this scheme, viewing leeches as a sub-group of oligochaetes and oligochaetes as a sub-group of polychaetes. In addition, the Pogonophora, Echiura and Sipuncula, previously regarded as separate phyla, are now regarded as sub-grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
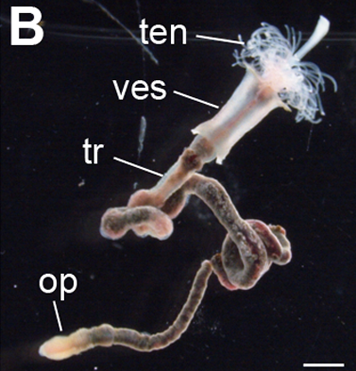
Siboglinidae
Siboglinidae is a family (biology), family of polychaete Annelida, annelid worms whose members made up the former phylum, phyla Pogonophora and Vestimentifera (the giant tube worms). The family is composed of around 100 species of vermiform creatures which live in thin tubes buried in sediment (Pogonophora) or in tubes attached to hard substratum (Vestimentifera) at ocean depths ranging from . They can also be found in association with hydrothermal vents, methane seeps, sunken plant material, and Whale fall, whale carcasses. The first specimen was dredged from the waters of Indonesia in 1900. These specimens were given to French zoologist Maurice Caullery, who studied them for nearly 50 years. Anatomy Most siboglinids are less than in diameter, but in length. They inhabit tubular structures composed of chitin which are fixed to rocks or substrates. The tubes are often clustered together in large colonies. Their bodies are divided into four regions. The anterior end is called th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical data and observed heritable traits of DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, and morphology. The results are a phylogenetic tree—a diagram depicting the hypothetical relationships among the organisms, reflecting their inferred evolutionary history. The tips of a phylogenetic tree represent the observed entities, which can be living taxa or fossils. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the taxa represented on the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about directionality of character state transformation, and does not show the origin or "root" of the taxa in question. In addition to their use for inferring phylogenetic pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenetic
In biology, phenetics (; ), also known as taximetrics, is an attempt to classify organisms based on overall similarity, usually with respect to Morphology (biology), morphology or other observable traits, regardless of their phylogeny or evolutionary relation. It is related closely to numerical taxonomy which is concerned with the use of numerical methods for taxonomic classification. Many people contributed to the development of phenetics, but the most influential were Peter Sneath and Robert R. Sokal. Their books are still primary references for this sub-discipline, although now out of print. Phenetics has been largely superseded by cladistics for research into evolutionary relationships among species. However, certain phenetic methods, such as neighbor-joining, are used for phylogenetics, as a reasonable approximation of phylogeny when more advanced methods (such as Bayesian inference) are too expensive computationally. Phenetic techniques include various forms of Cluster ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |