dot operator on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]



 Multiplication (often denoted by the
Multiplication (often denoted by the
 Placing several stones into a rectangular pattern with rows and columns gives
:
stones.
Placing several stones into a rectangular pattern with rows and columns gives
:
stones.
 Geometric meaning of complex multiplication can be understood rewriting complex numbers in
Geometric meaning of complex multiplication can be understood rewriting complex numbers in
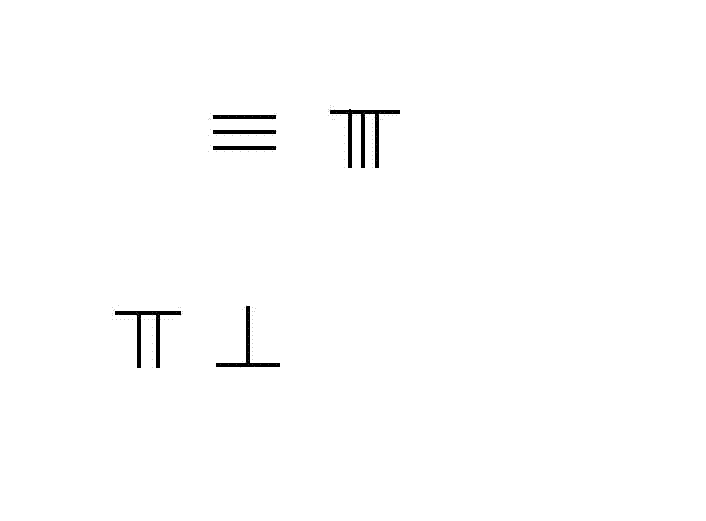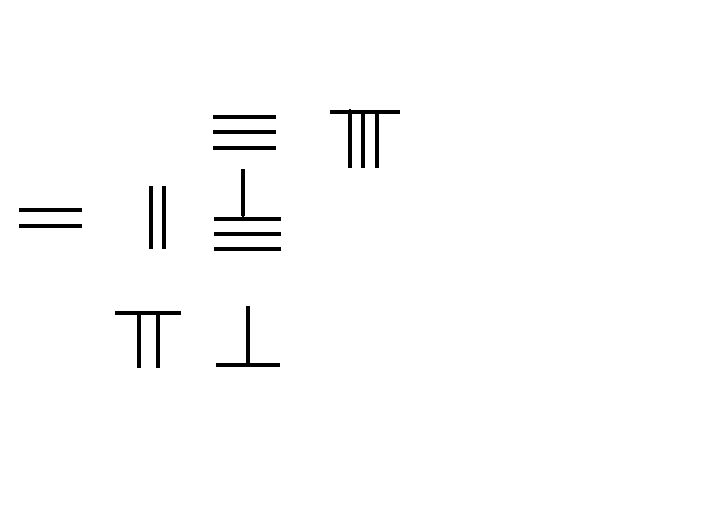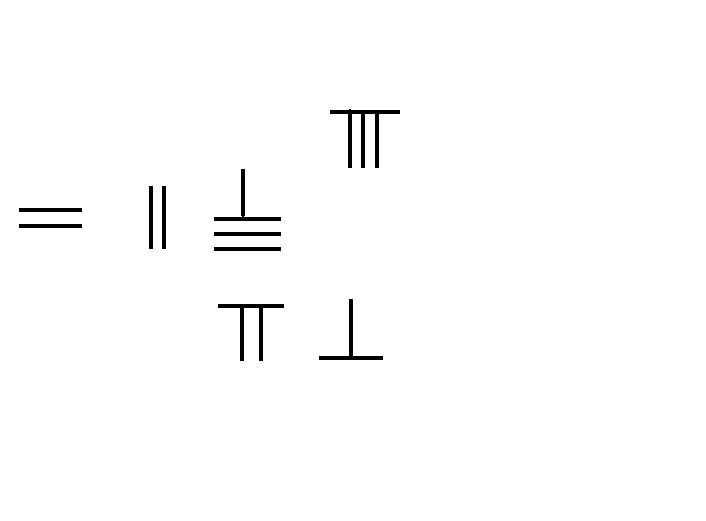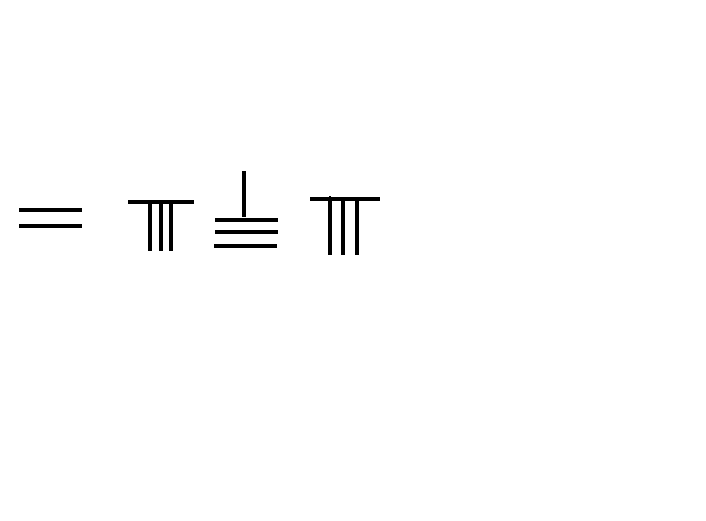 In the mathematical text '' Zhoubi Suanjing'', dated prior to 300 BC, and the '' Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art'', multiplication calculations were written out in words, although the early Chinese mathematicians employed Rod calculus involving place value addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. The Chinese were already using a decimal multiplication table by the end of the Warring States period.
In the mathematical text '' Zhoubi Suanjing'', dated prior to 300 BC, and the '' Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art'', multiplication calculations were written out in words, although the early Chinese mathematicians employed Rod calculus involving place value addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. The Chinese were already using a decimal multiplication table by the end of the Warring States period.
Multiplication
an
Arithmetic Operations In Various Number Systems
at
Modern Chinese Multiplication Techniques on an Abacus
{{Authority control Elementary arithmetic Mathematical notation Articles containing proofs


cross symbol
A cross is a geometrical figure consisting of two intersecting lines or bars, usually perpendicular to each other. The lines usually run vertically and horizontally. A cross of oblique lines, in the shape of the Latin letter X, is termed a s ...
, by the mid-line dot operator , by juxtaposition, or, on computers, by an asterisk
The asterisk ( ), from Late Latin , from Ancient Greek , ''asteriskos'', "little star", is a typographical symbol. It is so called because it resembles a conventional image of a heraldic star.
Computer scientists and mathematicians often v ...
) is one of the four elementary mathematical operations
In mathematics, an operation is a function which takes zero or more input values (also called "''operands''" or "arguments") to a well-defined output value. The number of operands is the arity of the operation.
The most commonly studied operati ...
of arithmetic
Arithmetic () is an elementary part of mathematics that consists of the study of the properties of the traditional operations on numbers—addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, exponentiation, and extraction of roots. In the 19th c ...
, with the other ones being addition
Addition (usually signified by the plus symbol ) is one of the four basic operations of arithmetic, the other three being subtraction, multiplication and division. The addition of two whole numbers results in the total amount or '' sum'' of ...
, subtraction, and division. The result of a multiplication operation is called a ''product
Product may refer to:
Business
* Product (business), an item that serves as a solution to a specific consumer problem.
* Product (project management), a deliverable or set of deliverables that contribute to a business solution
Mathematics
* Produ ...
''.
The multiplication of whole numbers may be thought of as repeated addition; that is, the multiplication of two numbers is equivalent to adding as many copies of one of them, the ''multiplicand'', as the quantity of the other one, the ''multiplier''. Both numbers can be referred to as ''factors''.
:
For example, 4 multiplied by 3, often written as and spoken as "3 times 4", can be calculated by adding 3 copies of 4 together:
:
Here, 3 (the ''multiplier'') and 4 (the ''multiplicand'') are the ''factors'', and 12 is the ''product''.
One of the main properties
Property is the ownership of land, resources, improvements or other tangible objects, or intellectual property.
Property may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Property (mathematics)
Philosophy and science
* Property (philosophy), in philosophy and ...
of multiplication is the commutative property
In mathematics, a binary operation is commutative if changing the order of the operands does not change the result. It is a fundamental property of many binary operations, and many mathematical proofs depend on it. Most familiar as the name of ...
, which states in this case that adding 3 copies of 4 gives the same result as adding 4 copies of 3:
:
Thus the designation of multiplier and multiplicand does not affect the result of the multiplication.
Systematic generalizations of this basic definition define the multiplication of integers (including negative numbers), rational numbers (fractions), and real numbers.
Multiplication can also be visualized as counting
Counting is the process of determining the number of elements of a finite set of objects, i.e., determining the size of a set. The traditional way of counting consists of continually increasing a (mental or spoken) counter by a unit for every elem ...
objects arranged in a rectangle (for whole numbers) or as finding the area
Area is the quantity that expresses the extent of a region on the plane or on a curved surface. The area of a plane region or ''plane area'' refers to the area of a shape or planar lamina, while ''surface area'' refers to the area of an open s ...
of a rectangle whose sides have some given lengths. The area of a rectangle does not depend on which side is measured first—a consequence of the commutative property.
The product of two measurements is a new type of measurement. For example, multiplying the lengths of the two sides of a rectangle gives its area. Such a product is the subject of dimensional analysis.
The inverse operation of multiplication is division. For example, since 4 multiplied by 3 equals 12, 12 divided by 3 equals 4. Indeed, multiplication by 3, followed by division by 3, yields the original number. The division of a number other than 0 by itself equals 1.
Multiplication is also defined for other types of numbers, such as complex numbers, and for more abstract constructs, like matrices. For some of these more abstract constructs, the order in which the operands are multiplied together matters. A listing of the many different kinds of products used in mathematics is given in Product (mathematics)
In mathematics, a product is the result of multiplication, or an expression that identifies objects (numbers or variables) to be multiplied, called ''factors''. For example, 30 is the product of 6 and 5 (the result of multiplication), and x\c ...
.
Notation and terminology
Inarithmetic
Arithmetic () is an elementary part of mathematics that consists of the study of the properties of the traditional operations on numbers—addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, exponentiation, and extraction of roots. In the 19th c ...
, multiplication is often written using the multiplication sign (either or ) between the terms (that is, in infix notation). For example,
: ("two times three equals six")
:
:
:
There are other mathematical notations for multiplication:
* To reduce confusion between the multiplication sign × and the common variable , multiplication is also denoted by dot signs, usually a middle-position dot (rarely period
Period may refer to:
Common uses
* Era, a length or span of time
* Full stop (or period), a punctuation mark
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Period (music), a concept in musical composition
* Periodic sentence (or rhetorical period), a concept ...
):
: or
:The middle dot notation, encoded in Unicode as , is now standard in the United States and other countries where the period is used as a decimal point. When the dot operator character is not accessible, the interpunct (·) is used. In other countries that use a comma
The comma is a punctuation mark that appears in several variants in different languages. It has the same shape as an apostrophe or single closing quotation mark () in many typefaces, but it differs from them in being placed on the baseline o ...
as a decimal mark, either the period or a middle dot is used for multiplication.
:Historically, in the United Kingdom and Ireland, the middle dot was sometimes used for the decimal to prevent it from disappearing in the ruled line, and the period/full stop was used for multiplication. However, since the Ministry of Technology
The Ministry of Technology was a department of the government of the United Kingdom, sometimes abbreviated as "MinTech". The Ministry of Technology was established by the incoming government of Harold Wilson in October 1964 as part of Wilson's am ...
ruled to use the period as the decimal point in 1968, and the SI standard has since been widely adopted, this usage is now found only in the more traditional journals such as '' The Lancet''.
* In algebra
Algebra () is one of the broad areas of mathematics. Roughly speaking, algebra is the study of mathematical symbols and the rules for manipulating these symbols in formulas; it is a unifying thread of almost all of mathematics.
Elementary a ...
, multiplication involving variables is often written as a juxtaposition (e.g., for times or for five times ), also called ''implied multiplication''. The notation can also be used for quantities that are surrounded by parentheses (e.g., , or for five times two). This implicit usage of multiplication can cause ambiguity when the concatenated variables happen to match the name of another variable, when a variable name in front of a parenthesis can be confused with a function name, or in the correct determination of the order of operations.
* In vector multiplication In mathematics, vector multiplication may refer to one of several operations between two (or more) vectors. It may concern any of the following articles:
* Dot product – also known as the "scalar product", a binary operation that takes two vector ...
, there is a distinction between the cross and the dot symbols. The cross symbol generally denotes the taking a cross product
In mathematics, the cross product or vector product (occasionally directed area product, to emphasize its geometric significance) is a binary operation on two vectors in a three-dimensional oriented Euclidean vector space (named here E), and is d ...
of two vectors, yielding a vector as its result, while the dot denotes taking the dot product
In mathematics, the dot product or scalar productThe term ''scalar product'' means literally "product with a scalar as a result". It is also used sometimes for other symmetric bilinear forms, for example in a pseudo-Euclidean space. is an algeb ...
of two vectors, resulting in a scalar
Scalar may refer to:
*Scalar (mathematics), an element of a field, which is used to define a vector space, usually the field of real numbers
*Scalar (physics), a physical quantity that can be described by a single element of a number field such a ...
.
In computer programming, the asterisk
The asterisk ( ), from Late Latin , from Ancient Greek , ''asteriskos'', "little star", is a typographical symbol. It is so called because it resembles a conventional image of a heraldic star.
Computer scientists and mathematicians often v ...
(as in 5*2) is still the most common notation. This is due to the fact that most computers historically were limited to small character set
Character encoding is the process of assigning numbers to graphical characters, especially the written characters of human language, allowing them to be stored, transmitted, and transformed using digital computers. The numerical values that ...
s (such as ASCII
ASCII ( ), abbreviated from American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for electronic communication. ASCII codes represent text in computers, telecommunications equipment, and other devices. Because of ...
and EBCDIC
Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code (EBCDIC; ) is an eight- bit character encoding used mainly on IBM mainframe and IBM midrange computer operating systems. It descended from the code used with punched cards and the corresponding ...
) that lacked a multiplication sign (such as ⋅ or ×), while the asterisk appeared on every keyboard. This usage originated in the FORTRAN programming language.
The numbers to be multiplied are generally called the " factors". The number to be multiplied is the "multiplicand", and the number by which it is multiplied is the "multiplier". Usually, the multiplier is placed first and the multiplicand is placed second; however sometimes the first factor is the multiplicand and the second the multiplier. Also, as the result of multiplication does not depend on the order of the factors, the distinction between "multiplicand" and "multiplier" is useful only at a very elementary level and in some multiplication algorithms, such as the long multiplication. Therefore, in some sources, the term "multiplicand" is regarded as a synonym for "factor". In algebra, a number that is the multiplier of a variable or expression (e.g., the 3 in ) is called a coefficient
In mathematics, a coefficient is a multiplicative factor in some term of a polynomial, a series, or an expression; it is usually a number, but may be any expression (including variables such as , and ). When the coefficients are themselves ...
.
The result of a multiplication is called a product
Product may refer to:
Business
* Product (business), an item that serves as a solution to a specific consumer problem.
* Product (project management), a deliverable or set of deliverables that contribute to a business solution
Mathematics
* Produ ...
. When one factor is an integer, the product is a multiple of the other or of the product of the others. Thus is a multiple of , as is . A product of integers is a multiple of each factor; for example, 15 is the product of 3 and 5 and is both a multiple of 3 and a multiple of 5.
Definitions
The product of two numbers or the multiplication between two numbers can be defined for common special cases: integers, natural numbers, fractions, real numbers, complex numbers, and quaternions.Product of two natural numbers
Product of two integers
Integers allow positive and negative numbers. Their product is determined by the product of their positive amounts, combined with the sign derived from the following rule: : (This rule is a necessary consequence of demanding distributivity of multiplication over addition, and is not an ''additional rule''.) In words, we have: * A negative number multiplied by a negative number is positive, * A negative number multiplied by a positive number is negative, * A positive number multiplied by a negative number is negative, * A positive number multiplied by a positive number is positive.Product of two fractions
Two fractions can be multiplied by multiplying their numerators and denominators: :Product of two real numbers
The rigorous definition of the product of two real numbers is a byproduct of theConstruction of the real numbers
In mathematics, there are several equivalent ways of defining the real numbers. One of them is that they form a complete ordered field that does not contain any smaller complete ordered field. Such a definition does not prove that such a complete ...
. This construction implies that, for every real number there is a set of rational number such that is the least upper bound of the elements of :
:
If is another real number that is the least upper bound of , the product
is defined as
:
This definition does not depend of a particular choice of and . That is, if they are changed without changing their least upper bound, then the least upper bound defining is not changed.
Product of two complex numbers
Two complex numbers can be multiplied by the distributive law and the fact that , as follows: :polar coordinates
In mathematics, the polar coordinate system is a two-dimensional coordinate system in which each point on a plane is determined by a distance from a reference point and an angle from a reference direction. The reference point (analogous to th ...
:
:
Furthermore,
:
from which one obtains
:
The geometric meaning is that the magnitudes are multiplied and the arguments are added.
Product of two quaternions
The product of two quaternions can be found in the article on quaternions. Note, in this case, that and are in general different.Computation
200px, The Educated Monkey – a For_example:_set_the_monkey's_feet_to_4_and_9,_and_get_the_product_–_36_–_in_its_hands..html" ;"title="tin toy dated 1918, used as a multiplication "calculator". For example: set the monkey's feet to 4 and 9, and get the product – 36 – in its hands.">tin toy dated 1918, used as a multiplication "calculator". For example: set the monkey's feet to 4 and 9, and get the product – 36 – in its hands. Many common methods for multiplying numbers using pencil and paper require a multiplication table of memorized or consulted products of small numbers (typically any two numbers from 0 to 9). However, one method, the peasant multiplication algorithm, does not. The example below illustrates "long multiplication" (the "standard algorithm", "grade-school multiplication"): 23958233 × 5830 ——————————————— 00000000 ( = 23,958,233 × 0) 71874699 ( = 23,958,233 × 30) 191665864 ( = 23,958,233 × 800) + 119791165 ( = 23,958,233 × 5,000) ——————————————— 139676498390 ( = 139,676,498,390 ) In some countries such as Germany, the above multiplication is depicted similarly but with the original product kept horizontal and computation starting with the first digit of the multiplier: 23958233 · 5830 ——————————————— 119791165 191665864 71874699 00000000 ——————————————— 139676498390 Multiplying numbers to more than a couple of decimal places by hand is tedious and error-prone.Common logarithm
In mathematics, the common logarithm is the logarithm with base 10. It is also known as the decadic logarithm and as the decimal logarithm, named after its base, or Briggsian logarithm, after Henry Briggs, an English mathematician who pioneered ...
s were invented to simplify such calculations, since adding logarithms is equivalent to multiplying. The slide rule allowed numbers to be quickly multiplied to about three places of accuracy. Beginning in the early 20th century, mechanical calculator
An electronic calculator is typically a portable electronic device used to perform calculations, ranging from basic arithmetic to complex mathematics.
The first solid-state electronic calculator was created in the early 1960s. Pocket-sized ...
s, such as the Marchant, automated multiplication of up to 10-digit numbers. Modern electronic computers and calculators have greatly reduced the need for multiplication by hand.
Historical algorithms
Methods of multiplication were documented in the writings of ancient Egyptian, andChinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of v ...
civilizations.
The Ishango bone, dated to about 18,000 to 20,000 BC, may hint at a knowledge of multiplication in the Upper Paleolithic
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories coi ...
era in Central Africa
Central Africa is a subregion of the African continent comprising various countries according to different definitions. Angola, Burundi, the Central African Republic, Chad, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of the Congo, ...
, but this is speculative.
Egyptians
The Egyptian method of multiplication of integers and fractions, which is documented in the Rhind Mathematical Papyrus, was by successive additions and doubling. For instance, to find the product of 13 and 21 one had to double 21 three times, obtaining , , . The full product could then be found by adding the appropriate terms found in the doubling sequence: :13 × 21 = (1 + 4 + 8) × 21 = (1 × 21) + (4 × 21) + (8 × 21) = 21 + 84 + 168 = 273.Babylonians
TheBabylonians
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. ...
used a sexagesimal
Sexagesimal, also known as base 60 or sexagenary, is a numeral system with sixty as its base. It originated with the ancient Sumerians in the 3rd millennium BC, was passed down to the ancient Babylonians, and is still used—in a modified form� ...
positional number system, analogous to the modern-day decimal system. Thus, Babylonian multiplication was very similar to modern decimal multiplication. Because of the relative difficulty of remembering different products, Babylonian mathematicians employed multiplication tables. These tables consisted of a list of the first twenty multiples of a certain ''principal number'' ''n'': ''n'', 2''n'', ..., 20''n''; followed by the multiples of 10''n'': 30''n'' 40''n'', and 50''n''. Then to compute any sexagesimal product, say 53''n'', one only needed to add 50''n'' and 3''n'' computed from the table.
Chinese
Modern methods
The modern method of multiplication based on the Hindu–Arabic numeral system was first described byBrahmagupta
Brahmagupta ( – ) was an Indian mathematician and astronomer. He is the author of two early works on mathematics and astronomy: the ''Brāhmasphuṭasiddhānta'' (BSS, "correctly established doctrine of Brahma", dated 628), a theoretical tr ...
. Brahmagupta gave rules for addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Henry Burchard Fine
Henry Burchard Fine (September 14, 1858 – December 22, 1928) was an American university dean and mathematician.
Life and career
Henry Burchard Fine (1858 – 1928) played a critical role in modernizing the American university and raising ...
, then a professor of mathematics at Princeton University, wrote the following:
:''The Indians are the inventors not only of the positional decimal system itself, but of most of the processes involved in elementary reckoning with the system. Addition and subtraction they performed quite as they are performed nowadays; multiplication they effected in many ways, ours among them, but division they did cumbrously.''
These place value decimal arithmetic algorithms were introduced to Arab countries by Al Khwarizmi
Muḥammad ibn Mūsā al-Khwārizmī ( ar, محمد بن موسى الخوارزمي, Muḥammad ibn Musā al-Khwārazmi; ), or al-Khwarizmi, was a Persian polymath from Khwarazm, who produced vastly influential works in mathematics, astronom ...
in the early 9th century and popularized in the Western world by Fibonacci in the 13th century.
Grid method
Grid method multiplication, or the box method, is used in primary schools in England and Wales and in some areas of the United States to help teach an understanding of how multiple digit multiplication works. An example of multiplying 34 by 13 would be to lay the numbers out in a grid as follows: : and then add the entries.Computer algorithms
The classical method of multiplying two -digit numbers requires digit multiplications. Multiplication algorithms have been designed that reduce the computation time considerably when multiplying large numbers. Methods based on thediscrete Fourier transform
In mathematics, the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) converts a finite sequence of equally-spaced samples of a function into a same-length sequence of equally-spaced samples of the discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT), which is a comp ...
reduce the computational complexity
In computer science, the computational complexity or simply complexity of an algorithm is the amount of resources required to run it. Particular focus is given to computation time (generally measured by the number of needed elementary operations ...
to . In 2016, the factor was replaced by a function that increases much slower, though still not constant. In March 2019, David Harvey and Joris van der Hoeven submitted a paper presenting an integer multiplication algorithm with a complexity of The algorithm, also based on the fast Fourier transform, is conjectured to be asymptotically optimal. The algorithm is not practically useful, as it only becomes faster for multiplying extremely large numbers (having more than bits).
Products of measurements
One can only meaningfully add or subtract quantities of the same type, but quantities of different types can be multiplied or divided without problems. For example, four bags with three marbles each can be thought of as: : bags× marbles per bag= 12 marbles. When two measurements are multiplied together, the product is of a type depending on the types of measurements. The general theory is given by dimensional analysis. This analysis is routinely applied in physics, but it also has applications in finance and other applied fields. A common example in physics is the fact that multiplying speed by time givesdistance
Distance is a numerical or occasionally qualitative measurement of how far apart objects or points are. In physics or everyday usage, distance may refer to a physical length or an estimation based on other criteria (e.g. "two counties over"). ...
. For example:
:50 kilometers per hour × 3 hours = 150 kilometers.
In this case, the hour units cancel out, leaving the product with only kilometer units.
Other examples of multiplication involving units include:
:2.5 meters × 4.5 meters = 11.25 square meters
:11 meters/seconds × 9 seconds = 99 meters
:4.5 residents per house × 20 houses = 90 residents
Product of a sequence
Capital pi notation
The product of a sequence of factors can be written with the product symbol , which derives from the capital letter Π (pi) in the Greek alphabet (much like the same way the summation symbol is derived from the Greek letter Σ (sigma). The meaning of this notation is given by : which results in : In such a notation, thevariable
Variable may refer to:
* Variable (computer science), a symbolic name associated with a value and whose associated value may be changed
* Variable (mathematics), a symbol that represents a quantity in a mathematical expression, as used in many ...
represents a varying integer, called the multiplication index, that runs from the lower value indicated in the subscript to the upper value given by the superscript. The product is obtained by multiplying together all factors obtained by substituting the multiplication index for an integer between the lower and the upper values (the bounds included) in the expression that follows the product operator.
More generally, the notation is defined as
:
where ''m'' and ''n'' are integers or expressions that evaluate to integers. In the case where , the value of the product is the same as that of the single factor ''x''''m''; if , the product is an empty product whose value is 1—regardless of the expression for the factors.
Properties of capital pi notation
By definition, : If all factors are identical, a product of factors is equivalent to exponentiation: :Associativity
In mathematics, the associative property is a property of some binary operations, which means that rearranging the parentheses in an expression will not change the result. In propositional logic, associativity is a valid rule of replacement ...
and commutativity
In mathematics, a binary operation is commutative if changing the order of the operands does not change the result. It is a fundamental property of many binary operations, and many mathematical proofs depend on it. Most familiar as the name ...
of multiplication imply
: and
:
if is a nonnegative integer, or if all are positive real numbers, and
:
if all are nonnegative integers, or if is a positive real number.
Infinite products
One may also consider products of infinitely many terms; these are called infinite products. Notationally, this consists in replacing ''n'' above by the Infinity symbol ∞. The product of such an infinite sequence is defined as thelimit
Limit or Limits may refer to:
Arts and media
* ''Limit'' (manga), a manga by Keiko Suenobu
* ''Limit'' (film), a South Korean film
* Limit (music), a way to characterize harmony
* "Limit" (song), a 2016 single by Luna Sea
* "Limits", a 2019 ...
of the product of the first ''n'' terms, as ''n'' grows without bound. That is,
:
One can similarly replace ''m'' with negative infinity, and define:
:
provided both limits exist.
Exponentiation
When multiplication is repeated, the resulting operation is known as '' exponentiation''. For instance, the product of three factors of two (2×2×2) is "two raised to the third power", and is denoted by 23, a two with asuperscript
A subscript or superscript is a character (such as a number or letter) that is set slightly below or above the normal line of type, respectively. It is usually smaller than the rest of the text. Subscripts appear at or below the baseline, whil ...
three. In this example, the number two is the ''base'', and three is the ''exponent''. In general, the exponent (or superscript) indicates how many times the base appears in the expression, so that the expression
:
indicates that ''n'' copies of the base ''a'' are to be multiplied together. This notation can be used whenever multiplication is known to be power associative.
Properties
Forreal
Real may refer to:
Currencies
* Brazilian real (R$)
* Central American Republic real
* Mexican real
* Portuguese real
* Spanish real
* Spanish colonial real
Music Albums
* ''Real'' (L'Arc-en-Ciel album) (2000)
* ''Real'' (Bright album) (2010) ...
and complex
Complex commonly refers to:
* Complexity, the behaviour of a system whose components interact in multiple ways so possible interactions are difficult to describe
** Complex system, a system composed of many components which may interact with each ...
numbers, which includes, for example, natural numbers, integers, and fractions, multiplication has certain properties:
;Commutative property
In mathematics, a binary operation is commutative if changing the order of the operands does not change the result. It is a fundamental property of many binary operations, and many mathematical proofs depend on it. Most familiar as the name of ...
:The order in which two numbers are multiplied does not matter:
::
;Associative property
In mathematics, the associative property is a property of some binary operations, which means that rearranging the parentheses in an expression will not change the result. In propositional logic, associativity is a valid rule of replacement ...
:Expressions solely involving multiplication or addition are invariant with respect to the order of operations:
::
;Distributive property
In mathematics, the distributive property of binary operations generalizes the distributive law, which asserts that the equality
x \cdot (y + z) = x \cdot y + x \cdot z
is always true in elementary algebra.
For example, in elementary arithmeti ...
:Holds with respect to multiplication over addition. This identity is of prime importance in simplifying algebraic expressions:
::
;Identity element
In mathematics, an identity element, or neutral element, of a binary operation operating on a set is an element of the set that leaves unchanged every element of the set when the operation is applied. This concept is used in algebraic structures ...
:The multiplicative identity is 1; anything multiplied by 1 is itself. This feature of 1 is known as the identity property:
::
; Property of 0
:Any number multiplied by 0 is 0. This is known as the zero property of multiplication:
::
; Negation
:−1 times any number is equal to the additive inverse
In mathematics, the additive inverse of a number is the number that, when added to , yields zero. This number is also known as the opposite (number), sign change, and negation. For a real number, it reverses its sign: the additive inverse (opp ...
of that number.
:: where
:–1 times –1 is 1.
::
;Inverse element
In mathematics, the concept of an inverse element generalises the concepts of opposite () and reciprocal () of numbers.
Given an operation denoted here , and an identity element denoted , if , one says that is a left inverse of , and that ...
:Every number ''x'', except 0, has a multiplicative inverse, , such that .
;Order
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of ...
preservation
:Multiplication by a positive number preserves the order
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of ...
:
::For , if then .
:Multiplication by a negative number reverses the order:
::For , if then .
:The complex numbers do not have an ordering that is compatible with both addition and multiplication.
Other mathematical systems that include a multiplication operation may not have all these properties. For example, multiplication is not, in general, commutative for matrices and quaternions.
Axioms
In the book ''Arithmetices principia, nova methodo exposita
The 1889 treatise ''Arithmetices principia, nova methodo exposita'' (''The principles of arithmetic, presented by a new method''; 1889) by Giuseppe Peano is a seminal document in mathematical logic and set theory, introducing what is now the s ...
'', Giuseppe Peano
Giuseppe Peano (; ; 27 August 1858 – 20 April 1932) was an Italian mathematician and glottologist. The author of over 200 books and papers, he was a founder of mathematical logic and set theory, to which he contributed much notation. The stan ...
proposed axioms for arithmetic based on his axioms for natural numbers. Peano arithmetic has two axioms for multiplication:
:
:
Here ''S''(''y'') represents the successor
Successor may refer to:
* An entity that comes after another (see Succession (disambiguation))
Film and TV
* ''The Successor'' (film), a 1996 film including Laura Girling
* ''The Successor'' (TV program), a 2007 Israeli television program Musi ...
of ''y''; i.e., the natural number that follows ''y''. The various properties like associativity can be proved from these and the other axioms of Peano arithmetic, including induction. For instance, ''S''(0), denoted by 1, is a multiplicative identity because
:
The axioms for integers typically define them as equivalence classes of ordered pairs of natural numbers. The model is based on treating (''x'',''y'') as equivalent to when ''x'' and ''y'' are treated as integers. Thus both (0,1) and (1,2) are equivalent to −1. The multiplication axiom for integers defined this way is
:
The rule that −1 × −1 = 1 can then be deduced from
:
Multiplication is extended in a similar way to rational numbers and then to real numbers.
Multiplication with set theory
The product of non-negative integers can be defined with set theory usingcardinal numbers
In mathematics, cardinal numbers, or cardinals for short, are a generalization of the natural numbers used to measure the cardinality (size) of sets. The cardinality of a finite set is a natural number: the number of elements in the set. Th ...
or the Peano axioms. See below
Below may refer to:
*Earth
* Ground (disambiguation)
*Soil
*Floor
* Bottom (disambiguation)
*Less than
*Temperatures below freezing
*Hell or underworld
People with the surname
*Ernst von Below (1863–1955), German World War I general
*Fred Below ...
how to extend this to multiplying arbitrary integers, and then arbitrary rational numbers. The product of real numbers is defined in terms of products of rational numbers; see construction of the real numbers
In mathematics, there are several equivalent ways of defining the real numbers. One of them is that they form a complete ordered field that does not contain any smaller complete ordered field. Such a definition does not prove that such a complete ...
.
Multiplication in group theory
There are many sets that, under the operation of multiplication, satisfy the axioms that definegroup
A group is a number of persons or things that are located, gathered, or classed together.
Groups of people
* Cultural group, a group whose members share the same cultural identity
* Ethnic group, a group whose members share the same ethnic ide ...
structure. These axioms are closure, associativity, and the inclusion of an identity element and inverses.
A simple example is the set of non-zero rational numbers
In mathematics, a rational number is a number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction of two integers, a numerator and a non-zero denominator . For example, is a rational number, as is every integer (e.g. ). The set of all rat ...
. Here we have identity 1, as opposed to groups under addition where the identity is typically 0. Note that with the rationals, we must exclude zero because, under multiplication, it does not have an inverse: there is no rational number that can be multiplied by zero to result in 1. In this example, we have an abelian group
In mathematics, an abelian group, also called a commutative group, is a group in which the result of applying the group operation to two group elements does not depend on the order in which they are written. That is, the group operation is comm ...
, but that is not always the case.
To see this, consider the set of invertible square matrices of a given dimension over a given field
Field may refer to:
Expanses of open ground
* Field (agriculture), an area of land used for agricultural purposes
* Airfield, an aerodrome that lacks the infrastructure of an airport
* Battlefield
* Lawn, an area of mowed grass
* Meadow, a grass ...
. Here, it is straightforward to verify closure, associativity, and inclusion of identity (the identity matrix) and inverses. However, matrix multiplication is not commutative, which shows that this group is non-abelian.
Another fact worth noticing is that the integers under multiplication do not form a group—even if we exclude zero. This is easily seen by the nonexistence of an inverse for all elements other than 1 and −1.
Multiplication in group theory is typically notated either by a dot or by juxtaposition (the omission of an operation symbol between elements). So multiplying element a by element b could be notated as a b or ab. When referring to a group via the indication of the set and operation, the dot is used. For example, our first example could be indicated by .
Multiplication of different kinds of numbers
Numbers can ''count'' (3 apples), ''order'' (the 3rd apple), or ''measure'' (3.5 feet high); as the history of mathematics has progressed from counting on our fingers to modelling quantum mechanics, multiplication has been generalized to more complicated and abstract types of numbers, and to things that are not numbers (such as matrices) or do not look much like numbers (such as quaternions). ;Integers : is the sum of ''N'' copies of ''M'' when ''N'' and ''M'' are positive whole numbers. This gives the number of things in an array ''N'' wide and ''M'' high. Generalization to negative numbers can be done by : and : :The same sign rules apply to rational and real numbers. ; Rational numbers :Generalization to fractions is by multiplying the numerators and denominators respectively: . This gives the area of a rectangle high and wide, and is the same as the number of things in an array when the rational numbers happen to be whole numbers. ; Real numbers :Real numbers and their products can be defined in terms of sequences of rational numbers. ; Complex numbers :Considering complex numbers and as ordered pairs of real numbers and , the product is . This is the same as for reals when the ''imaginary parts'' and are zero. :Equivalently, denoting as , we have :Alternatively, in trigonometric form, if , then ;Further generalizations :See Multiplication in group theory, above, and Multiplicative group, which for example includes matrix multiplication. A very general, and abstract, concept of multiplication is as the "multiplicatively denoted" (second) binary operation in aring
Ring may refer to:
* Ring (jewellery), a round band, usually made of metal, worn as ornamental jewelry
* To make a sound with a bell, and the sound made by a bell
:(hence) to initiate a telephone connection
Arts, entertainment and media Film and ...
. An example of a ring that is not any of the above number systems is a polynomial ring (you can add and multiply polynomials, but polynomials are not numbers in any usual sense.)
;Division
:Often division, , is the same as multiplication by an inverse, . Multiplication for some types of "numbers" may have corresponding division, without inverses; in an integral domain
In mathematics, specifically abstract algebra, an integral domain is a nonzero commutative ring in which the product of any two nonzero elements is nonzero. Integral domains are generalizations of the ring of integers and provide a natural se ...
''x'' may have no inverse "" but may be defined. In a division ring there are inverses, but may be ambiguous in non-commutative rings since need not be the same as .
See also
* Dimensional analysis * Multiplication algorithm ** Karatsuba algorithm, for large numbers **Toom–Cook multiplication Toom–Cook, sometimes known as Toom-3, named after Andrei Toom, who introduced the new algorithm with its low complexity, and Stephen Cook, who cleaned the description of it, is a multiplication algorithm for large integers.
Given two large intege ...
, for very large numbers
** Schönhage–Strassen algorithm, for huge numbers
* Multiplication table
* Binary multiplier
A binary multiplier is an electronic circuit used in digital electronics, such as a computer, to multiply two binary numbers.
A variety of computer arithmetic techniques can be used to implement a digital multiplier. Most techniques involve com ...
, how computers multiply
** Booth's multiplication algorithm
Booth's multiplication algorithm is a multiplication algorithm that multiplies two signed binary numbers in two's complement notation. The algorithm was invented by Andrew Donald Booth in 1950 while doing research on crystallography at Birkbeck ...
** Floating-point arithmetic
In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic that represents real numbers approximately, using an integer with a fixed precision, called the significand, scaled by an integer exponent of a fixed base. For example, 12.345 can be r ...
** Fused multiply–add
** Multiply–accumulate
** Wallace tree
* Multiplicative inverse, reciprocal
* Factorial
In mathematics, the factorial of a non-negative denoted is the product of all positive integers less than or equal The factorial also equals the product of n with the next smaller factorial:
\begin
n! &= n \times (n-1) \times (n-2) ...
* Genaille–Lucas rulers
* Lunar arithmetic
Lunar arithmetic, formerly called dismal arithmetic, is a version of arithmetic in which the addition and multiplication operations on digits are defined as the max and min operations. Thus, in lunar arithmetic,
:2+7=\max\=7 and 2\times 7 = \min\ ...
* Napier's bones
* Peasant multiplication
* Product (mathematics)
In mathematics, a product is the result of multiplication, or an expression that identifies objects (numbers or variables) to be multiplied, called ''factors''. For example, 30 is the product of 6 and 5 (the result of multiplication), and x\c ...
, for generalizations
* Slide rule
Notes
References
*External links
Multiplication
an
Arithmetic Operations In Various Number Systems
at
cut-the-knot
Alexander Bogomolny (January 4, 1948 July 7, 2018) was a Soviet-born Israeli-American mathematician. He was Professor Emeritus of Mathematics at the University of Iowa, and formerly research fellow at the Moscow Institute of Electronics and Math ...
Modern Chinese Multiplication Techniques on an Abacus
{{Authority control Elementary arithmetic Mathematical notation Articles containing proofs