Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of
tetrapod
A tetrapod (; from Ancient Greek :wiktionary:τετρα-#Ancient Greek, τετρα- ''(tetra-)'' 'four' and :wiktionary:πούς#Ancient Greek, πούς ''(poús)'' 'foot') is any four-Limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animal of the clade Tetr ...
s with an
ectotherm
An ectotherm (), more commonly referred to as a "cold-blooded animal", is an animal in which internal physiological sources of heat, such as blood, are of relatively small or of quite negligible importance in controlling body temperature.Dav ...
ic metabolism and
amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four
orders
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* A socio-political or established or existing order, e.g. World order, Ancien Regime, Pax Britannica
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* H ...
:
Testudines
Turtles are reptiles of the order (biology), order Testudines, characterized by a special turtle shell, shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Crypt ...
,
Crocodilia
Crocodilia () is an order of semiaquatic, predatory reptiles that are known as crocodilians. They first appeared during the Late Cretaceous and are the closest living relatives of birds. Crocodilians are a type of crocodylomorph pseudosuchia ...
,
Squamata
Squamata (, Latin ''squamatus'', 'scaly, having scales') is the largest Order (biology), order of reptiles; most members of which are commonly known as Lizard, lizards, with the group also including Snake, snakes. With over 11,991 species, it i ...
, and
Rhynchocephalia
Rhynchocephalia (; ) is an order of lizard-like reptiles that includes only one living species, the tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus'') of New Zealand. Despite its current lack of diversity, during the Mesozoic rhynchocephalians were a speciose g ...
. About 12,000 living species of reptiles are listed in the
Reptile Database
The Reptile Database is a scientific database that collects taxonomic information on all living reptile species (i.e. no fossil species such as dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared ...
. The study of the traditional reptile orders, customarily in combination with the study of modern
amphibian
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excl ...
s, is called
herpetology
Herpetology (from Ancient Greek ἑρπετόν ''herpetón'', meaning "reptile" or "creeping animal") is a branch of zoology concerned with the study of amphibians (including frogs, salamanders, and caecilians (Gymnophiona)) and reptiles (in ...
.
Reptiles have been subject to several conflicting
taxonomic definitions.
In
Linnaean taxonomy
Linnaean taxonomy can mean either of two related concepts:
# The particular form of biological classification (taxonomy) set up by Carl Linnaeus, as set forth in his ''Systema Naturae'' (1735) and subsequent works. In the taxonomy of Linnaeus th ...
, reptiles are gathered together under the
class
Class, Classes, or The Class may refer to:
Common uses not otherwise categorized
* Class (biology), a taxonomic rank
* Class (knowledge representation), a collection of individuals or objects
* Class (philosophy), an analytical concept used d ...
Reptilia ( ), which corresponds to common usage. Modern
cladistic taxonomy regards that group as
paraphyletic
Paraphyly is a taxonomic term describing a grouping that consists of the grouping's last common ancestor and some but not all of its descendant lineages. The grouping is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In co ...
, since
genetic and
paleontological
Paleontology, also spelled as palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of the life of the past, mainly but not exclusively through the study of fossils. Paleontologists use fossils as a means to classify organisms, measure geolo ...
evidence has determined that
bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
s (class Aves), as members of
Dinosauria, are more closely related to living
crocodilian
Crocodilia () is an Order (biology), order of semiaquatic, predatory reptiles that are known as crocodilians. They first appeared during the Late Cretaceous and are the closest living relatives of birds. Crocodilians are a type of crocodylomorp ...
s than to other reptiles, and are thus nested among reptiles from an evolutionary perspective. Many cladistic systems therefore redefine Reptilia as a
clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach t ...
(
monophyletic
In biological cladistics for the classification of organisms, monophyly is the condition of a taxonomic grouping being a clade – that is, a grouping of organisms which meets these criteria:
# the grouping contains its own most recent co ...
group) including birds, though the precise definition of this clade varies between authors.
Others prioritize the clade
Sauropsida
Sauropsida (Greek language, Greek for "lizard faces") is a clade of amniotes, broadly equivalent to the Class (biology), class Reptile, Reptilia, though typically used in a broader sense to also include extinct stem-group relatives of modern repti ...
, which typically refers to all
amniote
Amniotes are tetrapod vertebrate animals belonging to the clade Amniota, a large group that comprises the vast majority of living terrestrial animal, terrestrial and semiaquatic vertebrates. Amniotes evolution, evolved from amphibious Stem tet ...
s more closely related to modern reptiles than to
mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s.
The earliest known proto-reptiles originated from the
Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a Geologic time scale, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era that spans 60 million years, from the end of the Devonian Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the ...
period, having evolved from advanced
reptiliomorph
Reptiliomorpha (meaning reptile-shaped; in PhyloCode known as ''Pan-Amniota'') is a clade containing the amniotes and those tetrapods that share a more recent common ancestor with amniotes than with living amphibians (lissamphibians). It was defi ...
tetrapods which became increasingly adapted to life on dry land. The earliest known
eureptile
Sauropsida (Greek for "lizard faces") is a clade of amniotes, broadly equivalent to the class Reptilia, though typically used in a broader sense to also include extinct stem-group relatives of modern reptiles and birds (which, as theropod dinosaur ...
("true reptile") was ''
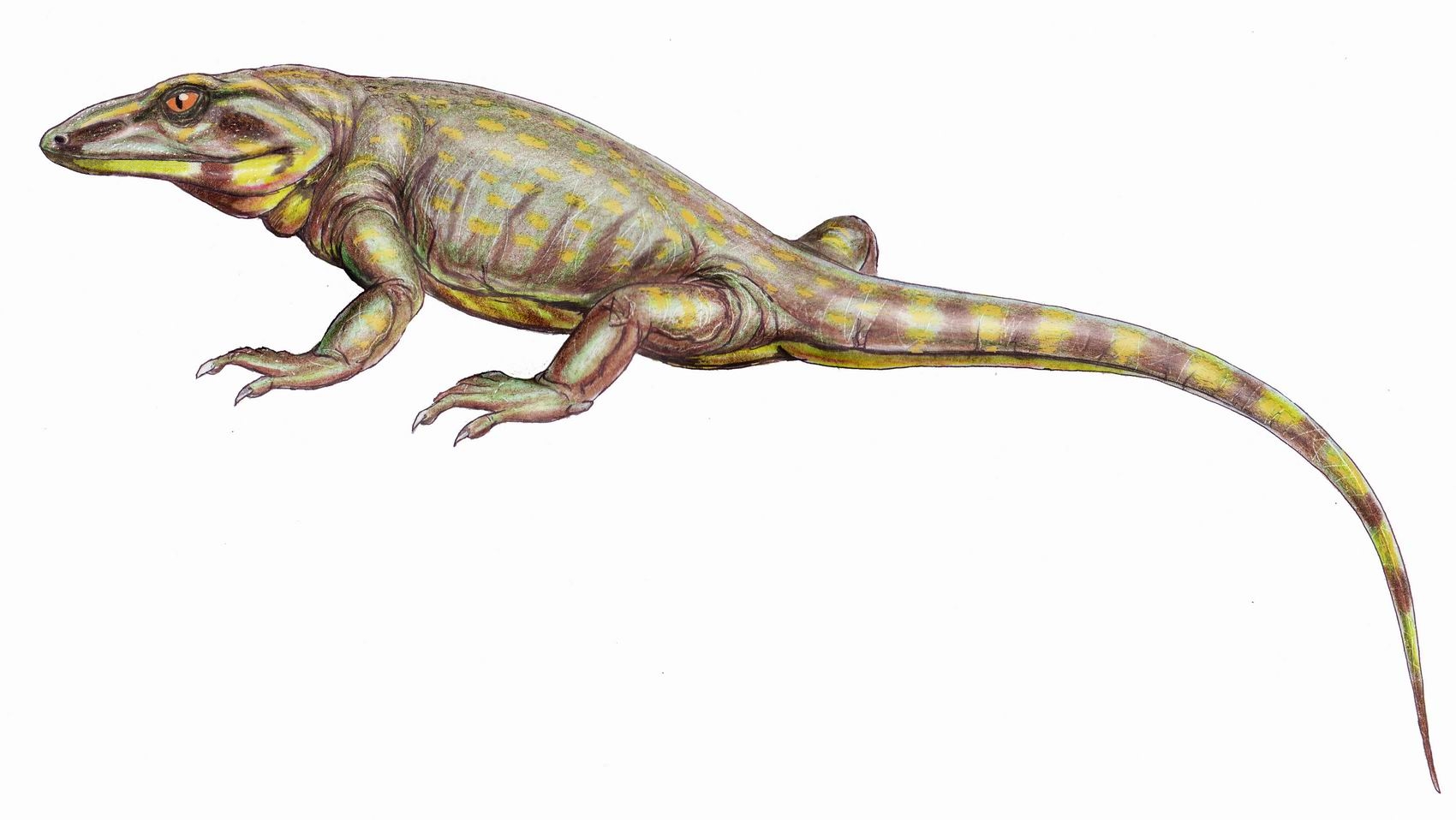
Hylonomus
''Hylonomus'' (; ''hylo-'' "forest" + ''nomos'' "dweller") is an extinct genus of reptile that lived during the Bashkirian stage of the Late Carboniferous. It is the earliest known crown group amniote and the oldest known unquestionable reptile, ...
'', a small and superficially lizard-like animal which lived in
Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, located on its east coast. It is one of the three Maritime Canada, Maritime provinces and Population of Canada by province and territory, most populous province in Atlan ...
during the
Bashkirian
The Bashkirian is in the International Commission on Stratigraphy geologic timescale the lowest stage (stratigraphy), stage or oldest age (geology), age of the Pennsylvanian (geology), Pennsylvanian. The Bashkirian age lasted from to Mega annu ...
age of the
Late Carboniferous
Late or LATE may refer to:
Everyday usage
* Tardy, or late, not being on time
* Late (or the late) may refer to a person who is dead
Music
* Late (The 77s album), ''Late'' (The 77s album), 2000
* Late (Alvin Batiste album), 1993
* Late!, a pseudo ...
, around .
[ Genetic and fossil data argues that the two largest lineages of reptiles, ]Archosauromorpha
Archosauromorpha ( Greek for "ruling lizard forms") is a clade of diapsid reptiles containing all reptiles more closely related to archosaurs (such as crocodilians and dinosaurs, including birds) than to lepidosaurs (such as tuataras, lizards, ...
(crocodilians, birds, and kin) and Lepidosauromorpha (lizards, and kin), diverged during the Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years, from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.902 Mya. It is the s ...
period. In addition to the living reptiles, there are many diverse groups that are now extinct
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
, in some cases due to mass extinction events. In particular, the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event
The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) extinction event, also known as the K–T extinction, was the extinction event, mass extinction of three-quarters of the plant and animal species on Earth approximately 66 million years ago. The event cau ...
wiped out the pterosaur
Pterosaurs are an extinct clade of flying reptiles in the order Pterosauria. They existed during most of the Mesozoic: from the Late Triassic to the end of the Cretaceous (228 million to 66 million years ago). Pterosaurs are the earli ...
s, plesiosaurs
The Plesiosauria or plesiosaurs are an Order (biology), order or clade of extinct Mesozoic marine reptiles, belonging to the Sauropterygia.
Plesiosaurs first appeared in the latest Triassic Period (geology), Period, possibly in the Rhaetian st ...
, and all non-avian dinosaurs
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic Geological period, period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the #Evolutio ...
alongside many species of crocodyliforms and squamates (e.g., mosasaur
Mosasaurs (from Latin ''Mosa'' meaning the 'Meuse', and Ancient Greek, Greek ' meaning 'lizard') are an extinct group of large aquatic reptiles within the family Mosasauridae that lived during the Late Cretaceous. Their first fossil remains wer ...
s). Modern non-bird reptiles inhabit all the continents except Antarctica.
Reptiles are tetrapod vertebrates
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
, creatures that either have four limbs or, like snakes, are descended from four-limbed ancestors. Unlike amphibian
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excl ...
s, reptiles do not have an aquatic larval stage. Most reptiles are oviparous
Oviparous animals are animals that reproduce by depositing fertilized zygotes outside the body (i.e., by laying or spawning) in metabolically independent incubation organs known as eggs, which nurture the embryo into moving offsprings kno ...
, although several species of squamates are viviparous
In animals, viviparity is development of the embryo inside the body of the mother, with the maternal circulation providing for the metabolic needs of the embryo's development, until the mother gives birth to a fully or partially developed juve ...
, as were some extinct aquatic cladeseggshell
An eggshell is the outer covering of a hard-shelled egg (biology), egg and of some forms of eggs with soft outer coats.
Worm eggs
Nematode eggs present a two layered structure: an external vitellin layer made of chitin that confers mechanical ...
. As amniotes, reptile eggs are surrounded by membranes for protection and transport, which adapt them to reproduction on dry land. Many of the viviparous species feed their fetus
A fetus or foetus (; : fetuses, foetuses, rarely feti or foeti) is the unborn offspring of a viviparous animal that develops from an embryo. Following the embryonic development, embryonic stage, the fetal stage of development takes place. Pren ...
es through various forms of placenta analogous to those of mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s, with some providing initial care for their hatchlings. Extant
Extant or Least-concern species, least concern is the opposite of the word extinct. It may refer to:
* Extant hereditary titles
* Extant literature, surviving literature, such as ''Beowulf'', the oldest extant manuscript written in English
* Exta ...
reptiles range in size from a tiny gecko, ''Sphaerodactylus ariasae
''Sphaerodactylus ariasae'', commonly called the Jaragua sphaero or the Jaragua dwarf gecko, is the smallest species of lizard in the family Sphaerodactylidae.
Description
''Sphaerodactylus ariasae'' is the world's smallest known reptile. The ...
'', which can grow up to to the saltwater crocodile
The saltwater crocodile (''Crocodylus porosus'') is a crocodilian native to saltwater habitats, brackish wetlands and freshwater rivers from India's east coast across Southeast Asia and the Sundaland to northern Australia and Micronesia. It ha ...
, ''Crocodylus porosus'', which can reach over in length and weigh over .
Classification
Research history
 In the 13th century, the category of ''reptile'' was recognized in Europe as consisting of a miscellany of egg-laying creatures, including "snakes, various fantastic monsters, lizards, assorted amphibians, and worms", as recorded by
In the 13th century, the category of ''reptile'' was recognized in Europe as consisting of a miscellany of egg-laying creatures, including "snakes, various fantastic monsters, lizards, assorted amphibians, and worms", as recorded by Beauvais
Beauvais ( , ; ) is a town and Communes of France, commune in northern France, and prefecture of the Oise Departments of France, département, in the Hauts-de-France Regions of France, region, north of Paris.
The Communes of France, commune o ...
in his ''Mirror of Nature''.
In the 18th century, the reptiles were, from the outset of classification, grouped with the amphibian
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excl ...
s. Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming o ...
, working from species-poor Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
, where the common adder and grass snake
The grass snake (''Natrix natrix''), sometimes called the ringed snake or water snake, is a Eurasian semi-aquatic non- venomous colubrid snake. It is often found near water and feeds almost exclusively on amphibians.
Subspecies
Many subspecie ...
are often found hunting in water, included all reptiles and amphibians in class
Class, Classes, or The Class may refer to:
Common uses not otherwise categorized
* Class (biology), a taxonomic rank
* Class (knowledge representation), a collection of individuals or objects
* Class (philosophy), an analytical concept used d ...
in his '' Systema Naturæ''.herpetology
Herpetology (from Ancient Greek ἑρπετόν ''herpetón'', meaning "reptile" or "creeping animal") is a branch of zoology concerned with the study of amphibians (including frogs, salamanders, and caecilians (Gymnophiona)) and reptiles (in ...
.
 It was not until the beginning of the 19th century that it became clear that reptiles and amphibians are, in fact, quite different animals, and P.A. Latreille erected the class ''Batracia'' (1825) for the latter, dividing the
It was not until the beginning of the 19th century that it became clear that reptiles and amphibians are, in fact, quite different animals, and P.A. Latreille erected the class ''Batracia'' (1825) for the latter, dividing the tetrapod
A tetrapod (; from Ancient Greek :wiktionary:τετρα-#Ancient Greek, τετρα- ''(tetra-)'' 'four' and :wiktionary:πούς#Ancient Greek, πούς ''(poús)'' 'foot') is any four-Limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animal of the clade Tetr ...
s into the four familiar classes of reptiles, amphibians, birds, and mammals. The British anatomist T.H. Huxley made Latreille's definition popular and, together with Richard Owen
Sir Richard Owen (20 July 1804 – 18 December 1892) was an English biologist, comparative anatomy, comparative anatomist and paleontology, palaeontologist. Owen is generally considered to have been an outstanding naturalist with a remarkabl ...
, expanded Reptilia to include the various fossil "antediluvian
The antediluvian (alternatively pre-diluvian or pre-flood) period is the time period chronicled in the Bible between the fall of man and the Genesis flood narrative in biblical cosmology. The term was coined by Thomas Browne (1605–1682). The n ...
monsters", including dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic Geological period, period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the #Evolutio ...
s and the mammal-like (synapsid
Synapsida is a diverse group of tetrapod vertebrates that includes all mammals and their extinct relatives. It is one of the two major clades of the group Amniota, the other being the more diverse group Sauropsida (which includes all extant rept ...
) '' Dicynodon'' he helped describe. This was not the only possible classification scheme: In the Hunterian lectures delivered at the Royal College of Surgeons
The Royal College of Surgeons is an ancient college (a form of corporation) established in England to regulate the activity of surgeons. Derivative organisations survive in many present and former members of the Commonwealth. These organisations ...
in 1863, Huxley grouped the vertebrates into mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s, sauroids, and ichthyoids (the latter containing the fishes and amphibians). He subsequently proposed the names of Sauropsida
Sauropsida (Greek language, Greek for "lizard faces") is a clade of amniotes, broadly equivalent to the Class (biology), class Reptile, Reptilia, though typically used in a broader sense to also include extinct stem-group relatives of modern repti ...
and Ichthyopsida for the latter two groups. In 1866, Haeckel demonstrated that vertebrates could be divided based on their reproductive strategies, and that reptiles, birds, and mammals were united by the amniotic egg
Amniotes are tetrapod vertebrate animals belonging to the clade Amniota, a large group that comprises the vast majority of living terrestrial and semiaquatic vertebrates. Amniotes evolved from amphibious stem tetrapod ancestors during the C ...
.
The terms ''Sauropsida'' ("lizard faces") and '' Theropsida'' ("beast faces") were used again in 1916 by E.S. Goodrich to distinguish between lizards, birds, and their relatives on the one hand (Sauropsida) and mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s and their extinct relatives (Theropsida) on the other. Goodrich supported this division by the nature of the hearts and blood vessels in each group, and other features, such as the structure of the forebrain. According to Goodrich, both lineages evolved from an earlier stem group, Protosauria ("first lizards") in which he included some animals today considered reptile-like amphibians, as well as early reptiles.Procolophonia
Procolophonia is an extinct suborder (clade) of herbivorous reptiles that lived from the Middle Permian till the end of the Triassic period. They were originally included as a suborder of the Cotylosauria (later renamed Captorhinida Carroll ...
, Eosuchia, Millerosauria, Chelonia (turtles), Squamata
Squamata (, Latin ''squamatus'', 'scaly, having scales') is the largest Order (biology), order of reptiles; most members of which are commonly known as Lizard, lizards, with the group also including Snake, snakes. With over 11,991 species, it i ...
(lizards and snakes), Rhynchocephalia
Rhynchocephalia (; ) is an order of lizard-like reptiles that includes only one living species, the tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus'') of New Zealand. Despite its current lack of diversity, during the Mesozoic rhynchocephalians were a speciose g ...
, Crocodilia
Crocodilia () is an order of semiaquatic, predatory reptiles that are known as crocodilians. They first appeared during the Late Cretaceous and are the closest living relatives of birds. Crocodilians are a type of crocodylomorph pseudosuchia ...
, " thecodonts" (paraphyletic
Paraphyly is a taxonomic term describing a grouping that consists of the grouping's last common ancestor and some but not all of its descendant lineages. The grouping is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In co ...
basal Archosaur
Archosauria () or archosaurs () is a clade of diapsid sauropsid tetrapods, with birds and crocodilians being the only extant taxon, extant representatives. Although broadly classified as reptiles, which traditionally exclude birds, the cladistics ...
ia), non- avian dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic Geological period, period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the #Evolutio ...
s, pterosaur
Pterosaurs are an extinct clade of flying reptiles in the order Pterosauria. They existed during most of the Mesozoic: from the Late Triassic to the end of the Cretaceous (228 million to 66 million years ago). Pterosaurs are the earli ...
s, ichthyosaur
Ichthyosauria is an order of large extinct marine reptiles sometimes referred to as "ichthyosaurs", although the term is also used for wider clades in which the order resides.
Ichthyosaurians thrived during much of the Mesozoic era; based on fo ...
s, and sauropterygia
Sauropterygia ("lizard flippers") is an extinct taxon of diverse, aquatic diapsid reptiles that developed from terrestrial ancestors soon after the end-Permian extinction and flourished during the Triassic before all except for the Plesiosau ...
ns.occipital condyle
The occipital condyles are undersurface protuberances of the occipital bone in vertebrates, which function in articulation with the superior facets of the Atlas (anatomy), atlas vertebra.
The condyles are oval or reniform (kidney-shaped) in shape ...
, a jaw joint formed by the quadrate and articular
The articular bone is part of the lower jaw of most vertebrates, including most jawed fish, amphibians, birds and various kinds of reptiles, as well as ancestral mammals.
Anatomy
In most vertebrates, the articular bone is connected to two o ...
bones, and certain characteristics of the vertebrae
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal ...
. The animals singled out by these formulations, the amniote
Amniotes are tetrapod vertebrate animals belonging to the clade Amniota, a large group that comprises the vast majority of living terrestrial animal, terrestrial and semiaquatic vertebrates. Amniotes evolution, evolved from amphibious Stem tet ...
s other than the mammals and the birds, are still those considered reptiles today. The synapsid/sauropsid division supplemented another approach, one that split the reptiles into four subclasses based on the number and position of
The synapsid/sauropsid division supplemented another approach, one that split the reptiles into four subclasses based on the number and position of temporal fenestra
Temporal fenestrae are openings in the temporal region of the skull of some amniotes, behind the orbit (eye socket). These openings have historically been used to track the evolution and affinities of reptiles. Temporal fenestrae are commonly (al ...
e, openings in the sides of the skull behind the eyes. This classification was initiated by Henry Fairfield Osborn
Henry Fairfield Osborn, Sr. (August 8, 1857 – November 6, 1935) was an American paleontologist, geologist and eugenics advocate. He was professor of anatomy at Columbia University, president of the American Museum of Natural History for 25 y ...
and elaborated and made popular by Romer's classic ''Vertebrate Paleontology
Vertebrate paleontology is the subfield of paleontology that seeks to discover, through the study of fossilized remains, the behavior, reproduction and appearance of extinct vertebrates (animals with vertebrae and their descendants). It also t ...
''.Anapsid
An anapsid is an amniote whose skull lacks one or more skull openings (fenestra, or fossae) near the temples. Traditionally, the Anapsida are considered the most primitive subclass of amniotes, the ancestral stock from which Synapsida and Dia ...
a – no fenestrae – cotylosaurs and chelonia (turtle
Turtles are reptiles of the order (biology), order Testudines, characterized by a special turtle shell, shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Crypt ...
s and relatives)
* Synapsida
Synapsida is a diverse group of tetrapod vertebrates that includes all mammals and their extinct relatives. It is one of the two major clades of the group Amniota, the other being the more diverse group Sauropsida (which includes all extant rep ...
– one low fenestra – pelycosaur
Pelycosaur ( ) is an older term for basal or primitive Late Paleozoic synapsids, excluding the therapsids and their descendants. Previously, the term mammal-like reptile was used, and Pelycosauria was considered an order, but this is now thoug ...
s and therapsids (the 'mammal-like reptiles
Synapsida is a diverse group of tetrapod vertebrates that includes all mammals and their extinct relatives. It is one of the two major clades of the group Amniota, the other being the more diverse group Sauropsida (which includes all extant rept ...
')
* Euryapsida __NOTOC__
Euryapsida is a polyphyletic (unnatural, as the various members are not closely related) group of sauropsids that are distinguished by a single temporal fenestra, an opening behind the orbit, under which the post-orbital and squamosal bo ...
– one high fenestra (above the postorbital and squamosal) – protorosaurs (small, early lizard-like reptiles) and the marine sauropterygia
Sauropterygia ("lizard flippers") is an extinct taxon of diverse, aquatic diapsid reptiles that developed from terrestrial ancestors soon after the end-Permian extinction and flourished during the Triassic before all except for the Plesiosau ...
ns and ichthyosaurs
Ichthyosauria is an taxonomy (biology), order of large extinction, extinct marine reptiles sometimes referred to as "ichthyosaurs", although the term is also used for wider clades in which the order resides.
Ichthyosaurians thrived during much of ...
, the latter called Parapsida in Osborn's work.
* Diapsid
Diapsids ("two arches") are a clade of sauropsids, distinguished from more primitive eureptiles by the presence of two holes, known as temporal fenestrae, in each side of their skulls. The earliest traditionally identified diapsids, the araeosc ...
a – two fenestrae – most reptiles, including lizard
Lizard is the common name used for all Squamata, squamate reptiles other than snakes (and to a lesser extent amphisbaenians), encompassing over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most Island#Oceanic isla ...
s, snake
Snakes are elongated limbless reptiles of the suborder Serpentes (). Cladistically squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales much like other members of the group. Many species of snakes have s ...
s, crocodilian
Crocodilia () is an Order (biology), order of semiaquatic, predatory reptiles that are known as crocodilians. They first appeared during the Late Cretaceous and are the closest living relatives of birds. Crocodilians are a type of crocodylomorp ...
s, dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic Geological period, period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the #Evolutio ...
s and pterosaur
Pterosaurs are an extinct clade of flying reptiles in the order Pterosauria. They existed during most of the Mesozoic: from the Late Triassic to the end of the Cretaceous (228 million to 66 million years ago). Pterosaurs are the earli ...
s.
 The composition of Euryapsida was uncertain.
The composition of Euryapsida was uncertain. Ichthyosaurs
Ichthyosauria is an taxonomy (biology), order of large extinction, extinct marine reptiles sometimes referred to as "ichthyosaurs", although the term is also used for wider clades in which the order resides.
Ichthyosaurians thrived during much of ...
were, at times, considered to have arisen independently of the other euryapsids, and given the older name Parapsida. Parapsida was later discarded as a group for the most part (ichthyosaurs being classified as ''incertae sedis
or is a term used for a taxonomy (biology), taxonomic group where its broader relationships are unknown or undefined. Alternatively, such groups are frequently referred to as "enigmatic taxa". In the system of open nomenclature, uncertainty ...
'' or with Euryapsida). However, four (or three if Euryapsida is merged into Diapsida) subclasses remained more or less universal for non-specialist work throughout the 20th century. It has largely been abandoned by recent researchers: In particular, the anapsid condition has been found to occur so variably among unrelated groups that it is not now considered a useful distinction.
Phylogenetics and modern definition
By the early 21st century, vertebrate paleontologists were beginning to adopt phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical dat ...
taxonomy, in which all groups are defined in such a way as to be monophyletic
In biological cladistics for the classification of organisms, monophyly is the condition of a taxonomic grouping being a clade – that is, a grouping of organisms which meets these criteria:
# the grouping contains its own most recent co ...
; that is, groups which include all descendants of a particular ancestor. The reptiles as historically defined are paraphyletic
Paraphyly is a taxonomic term describing a grouping that consists of the grouping's last common ancestor and some but not all of its descendant lineages. The grouping is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In co ...
, since they exclude both birds and mammals. These respectively evolved from dinosaurs and from early therapsids, both of which were traditionally called "reptiles".crocodilian
Crocodilia () is an Order (biology), order of semiaquatic, predatory reptiles that are known as crocodilians. They first appeared during the Late Cretaceous and are the closest living relatives of birds. Crocodilians are a type of crocodylomorp ...
s than the latter are to the rest of extant reptiles. Colin Tudge wrote:
Mammals are a clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach t ...
, and therefore the cladists are happy to acknowledge the traditional taxon Mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
ia; and birds, too, are a clade, universally ascribed to the formal taxon Aves
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight ...
. Mammalia and Aves are, in fact, subclades within the grand clade of the Amniota. But the traditional class Reptilia is not a clade. It is just a section of the clade Amniota
Amniotes are tetrapod vertebrate animals belonging to the clade Amniota, a large group that comprises the vast majority of living terrestrial and semiaquatic vertebrates. Amniotes evolved from amphibious stem tetrapod ancestors during the C ...
: The section that is left after the Mammalia and Aves have been hived off. It cannot be defined by synapomorphies
In phylogenetics, an apomorphy (or derived trait) is a novel character or character state that has evolved from its ancestral form (or plesiomorphy). A synapomorphy is an apomorphy shared by two or more taxa and is therefore hypothesized to ...
, as is the proper way. Instead, it is defined by a combination of the features it has and the features it lacks: reptiles are the amniotes that lack fur or feathers. At best, the cladists suggest, we could say that the traditional Reptilia are 'non-avian, non-mammalian amniotes'.
Despite the early proposals for replacing the paraphyletic Reptilia with a monophyletic Sauropsida
Sauropsida (Greek language, Greek for "lizard faces") is a clade of amniotes, broadly equivalent to the Class (biology), class Reptile, Reptilia, though typically used in a broader sense to also include extinct stem-group relatives of modern repti ...
, which includes birds, that term was never adopted widely or, when it was, was not applied consistently. When Sauropsida was used, it often had the same content or even the same definition as Reptilia. In 1988, Jacques Gauthier proposed a
When Sauropsida was used, it often had the same content or even the same definition as Reptilia. In 1988, Jacques Gauthier proposed a cladistic
Cladistics ( ; from Ancient Greek 'branch') is an approach to biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups ("clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesized relationships is ...
definition of Reptilia as a monophyletic node-based crown group
In phylogenetics, the crown group or crown assemblage is a collection of species composed of the living representatives of the collection, the most recent common ancestor of the collection, and all descendants of the most recent common ancestor ...
containing turtles, lizards and snakes, crocodilians, and birds, their common ancestor and all its descendants. While Gauthier's definition was close to the modern consensus, nonetheless, it became considered inadequate because the actual relationship of turtles to other reptiles was not yet well understood at this time.[ Major revisions since have included the reassignment of synapsids as non-reptiles, and classification of turtles as diapsids.][ Gauthier 1994 and Laurin and Reisz 1995's definition of Sauropsida defined the scope of the group as distinct and broader than that of Reptilia, encompassing Mesosauridae as well as Reptilia ''sensu stricto''.]PhyloCode
The ''International Code of Phylogenetic Nomenclature'', known as the ''PhyloCode'' for short, is a formal set of rules governing phylogenetic nomenclature. Its current version is specifically designed to regulate the naming of clades, leaving the ...
, was published by Modesto and Anderson in 2004.[ Modesto and Anderson reviewed the many previous definitions and proposed a modified definition, which they intended to retain most traditional content of the group while keeping it stable and monophyletic. They defined Reptilia as all amniotes closer to '']Lacerta agilis #REDIRECT Sand lizard #REDIRECT Sand lizard
{{redirect category shell, {{R from alternative capitalisation{{R from move ...
{{redirect category shell, {{R from alternative capitalisation{{R from move ...
''. This stem-based definition is equivalent to the more common definition of Sauropsida, which Modesto and Anderson synonymized with Reptilia, since the latter is better known and more frequently used. Unlike most previous definitions of Reptilia, however, Modesto and Anderson's definition includes birds, as they are within the clade that includes both lizards and crocodiles.
 In the 13th century, the category of ''reptile'' was recognized in Europe as consisting of a miscellany of egg-laying creatures, including "snakes, various fantastic monsters, lizards, assorted amphibians, and worms", as recorded by
In the 13th century, the category of ''reptile'' was recognized in Europe as consisting of a miscellany of egg-laying creatures, including "snakes, various fantastic monsters, lizards, assorted amphibians, and worms", as recorded by  It was not until the beginning of the 19th century that it became clear that reptiles and amphibians are, in fact, quite different animals, and P.A. Latreille erected the class ''Batracia'' (1825) for the latter, dividing the
It was not until the beginning of the 19th century that it became clear that reptiles and amphibians are, in fact, quite different animals, and P.A. Latreille erected the class ''Batracia'' (1825) for the latter, dividing the  The synapsid/sauropsid division supplemented another approach, one that split the reptiles into four subclasses based on the number and position of
The synapsid/sauropsid division supplemented another approach, one that split the reptiles into four subclasses based on the number and position of  The composition of Euryapsida was uncertain.
The composition of Euryapsida was uncertain.  When Sauropsida was used, it often had the same content or even the same definition as Reptilia. In 1988, Jacques Gauthier proposed a
When Sauropsida was used, it often had the same content or even the same definition as Reptilia. In 1988, Jacques Gauthier proposed a 
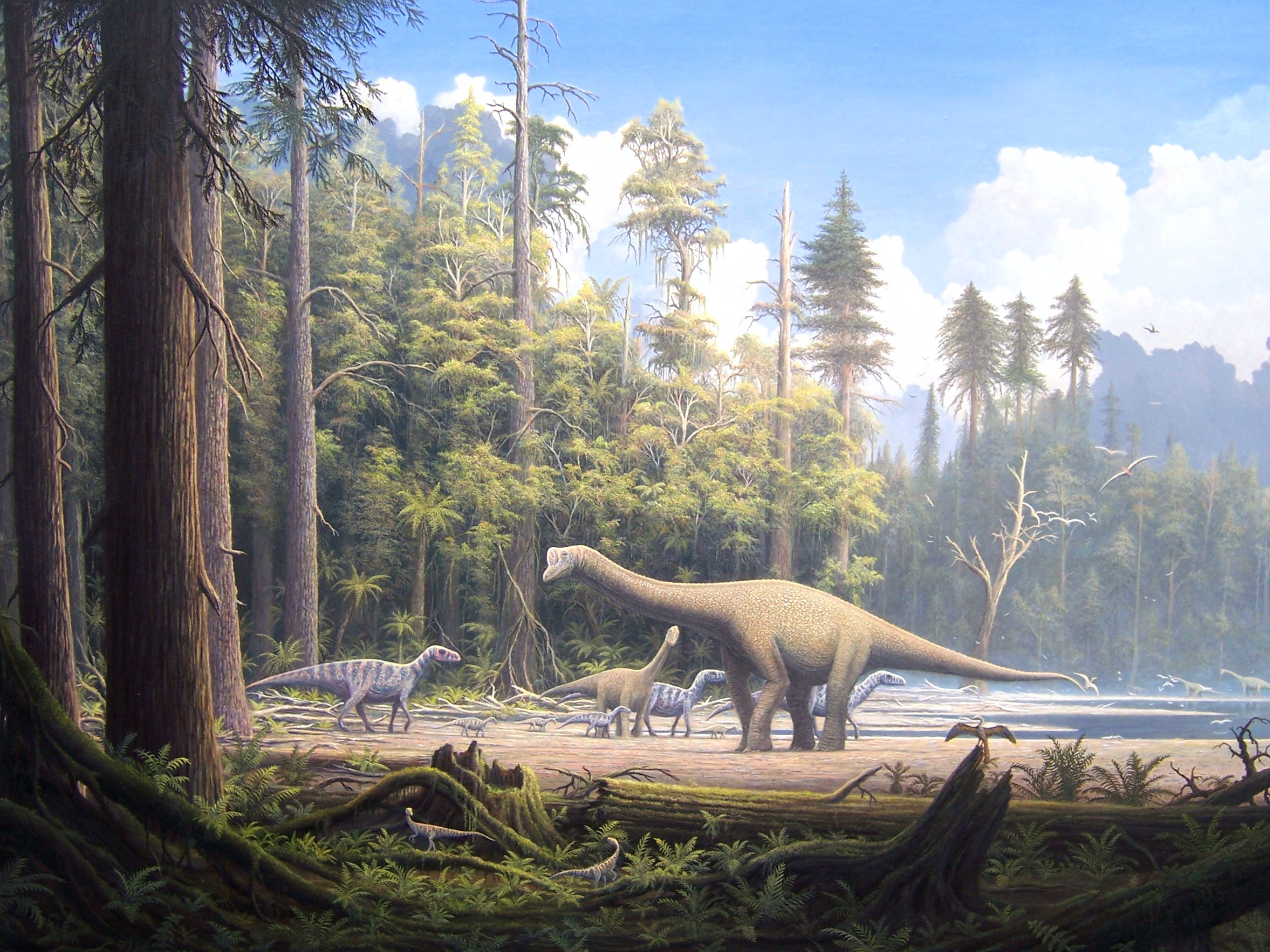 The origin of the reptiles lies about 310–320 million years ago, in the steaming swamps of the late
The origin of the reptiles lies about 310–320 million years ago, in the steaming swamps of the late  It was traditionally assumed that the first reptiles retained an
It was traditionally assumed that the first reptiles retained an 
 The close of the
The close of the  For example,
For example,  Modern non-avian reptiles exhibit some form of cold-bloodedness (i.e. some mix of
Modern non-avian reptiles exhibit some form of cold-bloodedness (i.e. some mix of  How
How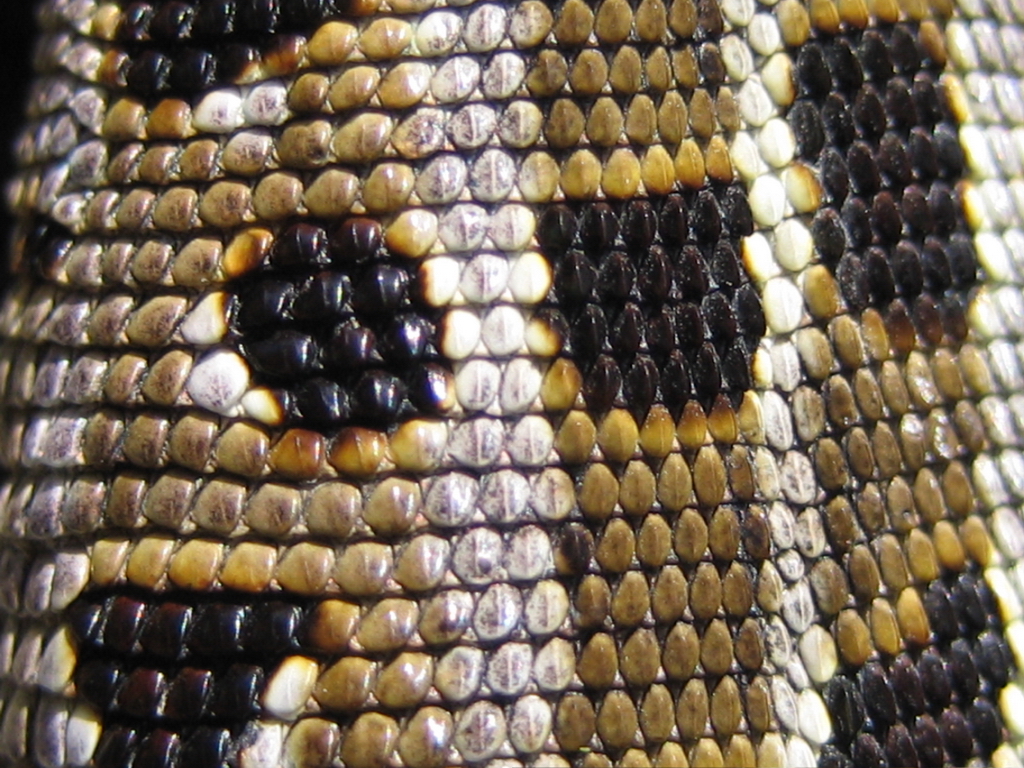  Reptilian skin is covered in a horny
Reptilian skin is covered in a horny 
 Most reptiles are insectivorous or carnivorous and have simple and comparatively short digestive tracts due to meat being fairly simple to break down and digest.
Most reptiles are insectivorous or carnivorous and have simple and comparatively short digestive tracts due to meat being fairly simple to break down and digest. 
 Reptiles generally
Reptiles generally  Reptiles tend to avoid confrontation through
Reptiles tend to avoid confrontation through  Some species try to bite immediately. Some will use their heads as
Some species try to bite immediately. Some will use their heads as  Dinosaurs have been widely depicted in culture since the English palaeontologist
Dinosaurs have been widely depicted in culture since the English palaeontologist