|
Archosaur
Archosauria () or archosaurs () is a clade of diapsid sauropsid tetrapods, with birds and crocodilians being the only extant taxon, extant representatives. Although broadly classified as reptiles, which traditionally exclude birds, the cladistics, cladistic sense of the term includes all living and extinct relatives of birds and crocodilians such as non-avian dinosaurs, pterosaurs, phytosaurs, aetosaurs and rauisuchians as well as many marine reptile#Extinct groups, Mesozoic marine reptiles. Modern paleontologists define Archosauria as a crown group that includes the most recent common ancestor of living birds and crocodilians, and all of its descendants. The base of Archosauria splits into two clades: Pseudosuchia, which includes crocodilians and their extinct relatives; and Avemetatarsalia, which includes birds and their extinct relatives (such as non-avian dinosaurs and pterosaurs). Older definitions of the group Archosauria rely on shared morphology (biology), morphological ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudosuchia
Pseudosuchia, from Ancient Greek ψεύδος (''pseúdos)'', meaning "false", and σούχος (''soúkhos''), meaning "crocodile" is one of two major divisions of Archosauria, including living crocodilians and all archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds. Pseudosuchians are also informally known as "crocodilian-line archosaurs", in contrast to the "bird-line archosaurs" or Avemetatarsalia. Despite Pseudosuchia meaning "false crocodiles", the name is a misnomer as true crocodilians are now defined as a subset of the group. The clade Pseudosuchia is potentially equivalent to another term, Crurotarsi, even though the latter has a different, Node-based taxon, node-based definition: "all taxa the least inclusive clade containing ''Rutiodon carolinensis'' (Emmons, 1856), and ''Crocodylus niloticus'' (Laurenti, 1768)." Many paleontologists of the late 20th century took this proposal for granted, using Crurotarsi as the term for crocodilian ancestors. In 2011, a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytosauria
Phytosaurs (Φυτόσαυροι in greek language, Greek, meaning 'plant lizard') are an extinct group of large, mostly semiaquatic Late Triassic archosauriform or Basal (phylogenetics), basal archosaurian reptiles. Phytosaurs belong to the order (biology), order Phytosauria and are sometimes referred to as parasuchians. Phytosauria, Parasuchia, Parasuchidae, and Phytosauridae have often been considered equivalent groupings containing the same species. Some recent studies have offered a more nuanced approach, defining Parasuchidae and Phytosauridae as nested clades within Phytosauria as a whole. The clade Phytosauria was defined by Paul Sereno in 2005 as ''Rutiodon, Rutiodon carolinensis'' and all taxa more closely related to it than to ''Aetosaurus ferratus'', ''Rauisuchus, Rauisuchus tiradentes'', ''Prestosuchus chiniquensis'', ''Ornithosuchus, Ornithosuchus woodwardi'', or ''Crocodylus niloticus'' (the Nile crocodile). Phytosaurs were long-snouted and heavily armoured, bearin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smok (archosaur)
''Smok'' (meaning "dragon" in Polish language, Polish) is an extinct genus of large carnivorous archosaur. It lived during the Late Triassic, latest Triassic period (geology), period (latest Norian to early Rhaetian stage, between 208.5–205 mya (unit), Ma). Its remains have been found in Lisowice, Silesian Voivodeship, Lisowice, southern Poland. The Monotypic taxon, only species is ''Smok wawelski'' (after the Wawel Dragon, a dragon from Polish folklore) and was named in 2012 in paleontology, 2012. It is larger than any other known predatory archosaur from the Late Triassic or Early Jurassic of central Europe. The relation of ''Smok'' to other archosaurs has not yet been thoroughly studied; it may be a rauisuchidae, rauisuchid, prestosuchidae, prestosuchid, an ornithosuchid pseudosuchian (part of the crocodilian lineage of archosaurs) or a theropod dinosaur. Description At an estimated in length, ''Smok'' was the largest carnivorous archosaur in central Europe in the time it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avemetatarsalia
Avemetatarsalia (meaning "bird metatarsals") is a clade of diapsid Reptile, reptiles containing all archosaurs more closely related to birds than to crocodilians. The two most successful groups of avemetatarsalians were the dinosaurs and pterosaurs. Dinosaur, Dinosaurs were the largest terrestrial animals for much of the Mesozoic era, Mesozoic Era, and one group of small feathered dinosaurs (Aves, i.e. birds) has survived up to the present day. Pterosaur, Pterosaurs were the first flying vertebrates and persisted through the Mesozoic before dying out at the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) extinction event. Both dinosaurs and pterosaurs appeared in the Triassic period, Triassic Period, shortly after avemetatarsalians as a whole. The name Avemetatarsalia was first established by British palaeontologist Michael J. Benton, Michael Benton in 1999. An alternate name is Pan-Aves, or "all birds", in reference to its definition containing all animals, li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
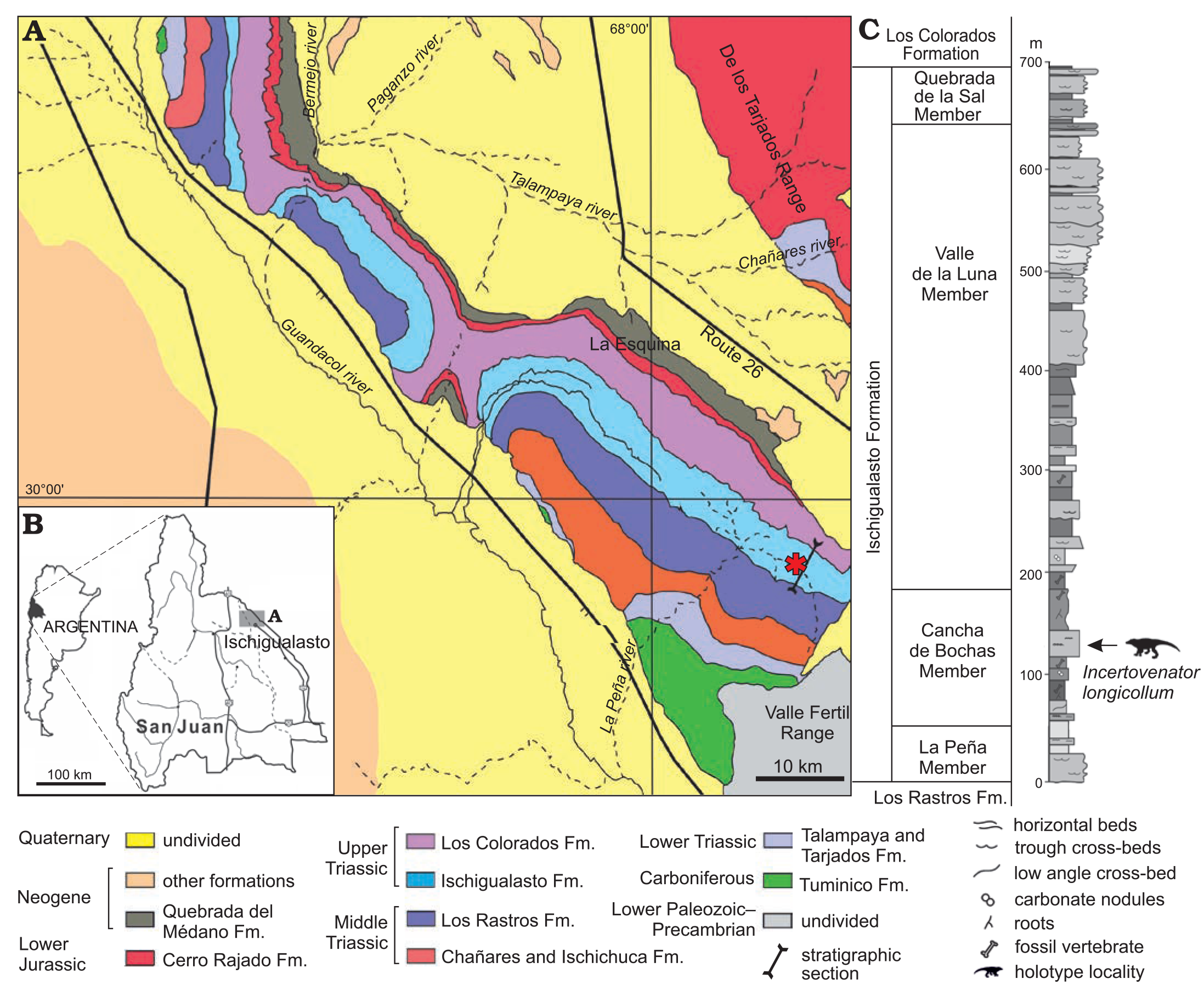
Incertovenator
''Incertovenator'' (meaning "uncertain hunter") is an extinct genus of archosauriform reptile, likely an archosaur, of uncertain affinities. Its unstable position is a result of possessing a number features found in both the bird-line avemetatarsalian archosaurs and the crocodylian-line pseudosuchians. The Type species, type and only known species is ''I. longicollum'', which is known from single specimen discovered in the Late Triassic (Carnian aged) Ischigualasto Formation of Argentina. ''Incertovenator'' is known almost entirely by its vertebral column. This indicates that it had a relatively long neck, leading to its uncertain classification due to the convergent evolution of elongated neck vertebrae in both avemetatarsalian and pseudosuchian archosaurs. Discovery and naming The Type specimen, type and only known specimen of ''Incertovenator'', PVSJ 397, was discovered in the Cancha de Bochas Stratigraphic unit#Member, member of the Ischigualasto Formation. The specimen was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocephalia. About 12,000 living species of reptiles are listed in the Reptile Database. The study of the traditional reptile orders, customarily in combination with the study of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. Reptiles have been subject to several conflicting Taxonomy, taxonomic definitions. In Linnaean taxonomy, reptiles are gathered together under the Class (biology), class Reptilia ( ), which corresponds to common usage. Modern Cladistics, cladistic taxonomy regards that group as Paraphyly, paraphyletic, since Genetics, genetic and Paleontology, paleontological evidence has determined that birds (class Aves), as members of Dinosauria, are more closely related to living crocodilians than to other reptiles, and are thus nested among re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeosaurus
''Palaeosaurus'' (or ''Paleosaurus'') is a genus of indeterminate archosaur known from two teeth found in the Bromsgrove Sandstone Formation and also either the Magnesian Conglomerate or the Avon Fissure Fill of Clifton, Bristol, England (originally Avon). It has had a convoluted taxonomic history. Richard Owen's mistake of associating prosauropod skeletal remains with the carnivorous teeth which Riley and Stutchbury called ''Palaeosaurus'', combined with Friedrich von Huene's '' Teratosaurus minor'', which was also a combination of carnivore and prosauropod remains, led paleontologists to view prosauropods as carnivorous animals for quite a long time. This error was included in several textbooks and other dinosaur reference works. History and classification Nineteenth century In the autumn of 1834, surgeon Henry Riley (1797–1848) and the curator of the Bristol Institution, Samuel Stutchbury (15 January 1798 – 12 February 1859), began to excavate " saurian remains" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picrodon
''Picrodon'' is the name given to a genus of archosaur, possibly a sauropodomorph dinosaur, from the Rhaetian of England which was possibly synonymous with the dubious archosaur '' Avalonianus''. The type, and only species, ''P. herveyi'', was named in 1898.H. G. Seeley. 1898. On large terrestrial saurians from the Rhaetic Beds of Wedmore Hill, described as '' Avalonia sanfordi'' and ''Picrodon herveyi''. Geological Magazine, decade 4 5:1-6 Discovery and naming In 1894, W. A. Sanford described the fossil remains of what he considered to be two large reptiles discovered near Westbury-on-Severn, Glastonbury (Westbury Formation) by Eev. Sydenham H. A. Hervey and Sanford himself.''Proceedings of the Somerset Archaeological Society'' - vol. xl, 1894, p. 234 Harry Govier Seeley described the fossils and named two genera: ''Avalonia'' (preoccupied; now '' Avalonianus'') and ''Picrodon''; both are based solely on teeth. Only a single tooth, holotype BMNH R2875, belonging to ''P. herv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crocodilia
Crocodilia () is an order of semiaquatic, predatory reptiles that are known as crocodilians. They first appeared during the Late Cretaceous and are the closest living relatives of birds. Crocodilians are a type of crocodylomorph pseudosuchian, a subset of archosaurs that appeared about 235 million years ago and were the only survivors of the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event. While other crocodylomorph groups further survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, notably sebecosuchians, only the crocodilians have survived into the Quaternary. The order includes the true crocodiles (family Crocodylidae), the alligators and caimans (family Alligatoridae), and the gharial and false gharial (family Gavialidae). Although the term "crocodiles" is sometimes used to refer to all of these families, the term "crocodilians" is less ambiguous. Extant crocodilians have flat heads with long snouts and tails that are compressed on the sides, with their eyes, ears, and n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crocodilian
Crocodilia () is an Order (biology), order of semiaquatic, predatory reptiles that are known as crocodilians. They first appeared during the Late Cretaceous and are the closest living relatives of birds. Crocodilians are a type of crocodylomorph pseudosuchian, a subset of archosaurs that appeared about 235 million years ago and were the only survivors of the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event. While other crocodylomorph groups further survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, notably sebecosuchians, only the crocodilians have survived into the Quaternary. The order includes the crocodile, true crocodiles (Family (biology), family Crocodylidae), the alligators and caimans (family Alligatoridae), and the gharial and false gharial (family Gavialidae). Although the term "crocodiles" is sometimes used to refer to all of these families, the term "crocodilians" is less ambiguous. Extant crocodilians have flat heads with long snouts and tails that are compressed on the si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zanclodon
''Zanclodon'' ("scythe tooth") is an extinct genus of archosauriform from the Erfurt Formation in southern Germany. It was once a wastebasket taxon until a taxonomic revision by Schoch (2011) left only the paratype (SMNS 6045) within ''Zanclodon laevis'' proper.Schoch, R.R. (2011). New archosauriform remains from the German Lower Keuper. ''Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie, Abhandlungen'' 260: 87–100. . The type species is ''Z. laevis''. Discovery and naming The paratype, SMNS 56045, a maxilla with teeth, was discovered in the Gaildorf Alumn Mine in southern Germany. ''Zanclodon'' was originally named ''Smilodon'' by Plieninger (1846), but this name had previously been used for the saber-toothed cat (a preoccupied name), prompting Plieninger to erect the replacement name ''Zanclodon'' in 1847. A paralectotype was also assigned to ''Z. laevis'': SMNS 6045a, a loose germ tooth. ''Z. plieningeri'' was named by Fraas in 1896, but it became a junior synonym of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jushatyria
''Jushatyria'' is an extinct genus of archosaur. Fossils have been found in the Koltaevo III Locality, district of Kumertau near the Ural Mountains in European Russia from the Bukobay Gorizont. The locality dates back to the Ladinian stage of the Middle Triassic. Additional material has been described from a locality on the banks of the Berdyanka River that was previously assigned to a rauisuchid-like archosaur. However, this material differed from the original specimens because it lacked slit-like antorbital openings accompanying the antorbital fossa. Nesbitt (2009) and Gower and Sennikov (2000) suggested that all material currently referred to ''Jushatyria'' most likely does not represent a single taxon.Gower, D. J. and Sennikov, A. G. (2000). Early Archosaurs from Russia ''In:'' Benton, M. J., Kurochkin, E. N., Shishkin, M. A. and Unwin, D. M., eds., ''The Age of Dinosaurs in Russia and Mongolia''. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press; pp. 140–159. Thus, ''Jushatyria'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |