Lupus, formally called systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an
autoimmune disease
An autoimmune disease is a condition that results from an anomalous response of the adaptive immune system, wherein it mistakenly targets and attacks healthy, functioning parts of the body as if they were foreign organisms. It is estimated tha ...
in which the body's
immune system
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic ...
mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body.
Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe.
[ Common symptoms include painful and swollen joints, ]fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, s ...
, chest pain
Chest pain is pain or discomfort in the chest, typically the front of the chest. It may be described as sharp, dull, pressure, heaviness or squeezing. Associated symptoms may include pain in the shoulder, arm, upper abdomen, or jaw, along with n ...
, hair loss
Hair loss, also known as alopecia or baldness, refers to a loss of hair from part of the head or body. Typically at least the head is involved. The severity of hair loss can vary from a small area to the entire body. Inflammation or scarring ...
, mouth ulcer
A mouth ulcer (aphtha), or sometimes called a canker sore or salt blister, is an ulcer that occurs on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. Mouth ulcers are very common, occurring in association with many diseases and by many different mechanis ...
s, swollen lymph nodes
Edema (American English), also spelled oedema (British English), and also known as fluid retention, swelling, dropsy and hydropsy, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may inclu ...
, feeling tired, and a red rash
A rash is a change of the skin that affects its color, appearance, or texture.
A rash may be localized in one part of the body, or affect all the skin. Rashes may cause the skin to change color, itch, become warm, bumpy, chapped, dry, cracke ...
which is most commonly on the face.[ Often there are periods of illness, called ]flares
A flare, also sometimes called a fusée, fusee, or bengala, bengalo in several European countries, is a type of pyrotechnic that produces a bright light or intense heat without an explosion. Flares are used for distress signaling, illuminatio ...
, and periods of remission during which there are few symptoms.[ Children up to 18 years old develop a more severe form of SLE termed ]childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus
Childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus (i.e., cSLE), also termed juvenile-onset systemic lupus erythematosus, juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus, and pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus, is a form of the chronic inflammatory and autoi ...
.[ It is thought to involve a combination of ]genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinians, Augustinian ...
and environmental factor
An environmental factor, ecological factor or eco factor is any factor, abiotic or biotic, that influences living organisms. Abiotic factors include ambient temperature, amount of sunlight, air, soil, water and pH of the water soil in which an ...
s.[ Among ]identical twins
Twins are two offspring produced by the same pregnancy.MedicineNet > Definition of Twin Last Editorial Review: 19 June 2000 Twins can be either ''monozygotic'' ('identical'), meaning that they develop from one zygote, which splits and forms two e ...
, if one is affected there is a 24% chance the other one will also develop the disease.[ ]Female
An organism's sex is female ( symbol: ♀) if it produces the ovum (egg cell), the type of gamete (sex cell) that fuses with the male gamete (sperm cell) during sexual reproduction.
A female has larger gametes than a male. Females and ...
sex hormone
Sex hormones, also known as sex steroids, gonadocorticoids and gonadal steroids, are steroid hormones that interact with vertebrate steroid hormone receptors. The sex hormones include the androgens, estrogens, and progestogens. Their effects a ...
s, sunlight, smoking, vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency or hypovitaminosis D is a vitamin D level that is below normal. It most commonly occurs in people when they have inadequate exposure to sunlight, particularly sunlight with adequate ultraviolet B rays (UVB). Vitamin D def ...
, and certain infections are also believed to increase a person's risk.[ The mechanism involves an immune response by ]autoantibodies
An autoantibody is an antibody (a type of protein) produced by the immune system that is directed against one or more of the individual's own proteins. Many autoimmune diseases (notably lupus erythematosus) are associated with such antibodies.
Pr ...
against a person's own tissues.[ These are most commonly ]anti-nuclear antibodies
Antinuclear antibodies (ANAs, also known as antinuclear factor or ANF) are autoantibodies that bind to contents of the cell nucleus. In normal individuals, the immune system produces antibodies to foreign proteins (antigens) but not to human pro ...
and they result in inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
.[ Diagnosis can be difficult and is based on a combination of symptoms and laboratory tests.][ There are a number of other kinds of ]lupus erythematosus
is a collection of autoimmune diseases in which the human immune system becomes hyperactive and attacks healthy tissues. Symptoms of these diseases can affect many different body systems, including joints, skin, kidneys, blood cells, heart, ...
including discoid lupus erythematosus
Discoid lupus erythematosus is the most common type of chronic cutaneous lupus (CCLE), an autoimmune skin condition on the lupus erythematosus spectrum of illnesses. It presents with red, painful, inflamed and coin-shaped patches of skin with a sc ...
, neonatal lupus
Neonatal lupus erythematosus is an autoimmune disease in an infant born to a mother with anti-Ro/SSA and with or without anti-La/SSB antibodies. The disease most commonly presents with a diffuse/periorbital rash resembling subacute cutaneous lupu ...
, and subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus.[
There is no cure for SLE,][ but there are experimental and symptomatic treatments. Treatments may include ]NSAID
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of ...
s, corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
s, immunosuppressants
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent the activity of the immune system.
Classification
Immunosuppressive drugs can be classified ...
, hydroxychloroquine
Hydroxychloroquine, sold under the brand name Plaquenil among others, is a medication used to prevent and treat malaria in areas where malaria remains sensitive to chloroquine. Other uses include treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, an ...
, and methotrexate
Methotrexate, formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immunosuppressive drug, immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancy, ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is u ...
.[ Although corticosteroids are rapidly effective, long-term use results in side effects. ]Alternative medicine
Alternative medicine refers to practices that aim to achieve the healing effects of conventional medicine, but that typically lack biological plausibility, testability, repeatability, or supporting evidence of effectiveness. Such practices are ...
has not been shown to affect the disease.[ Men have higher mortality.]cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina, heart attack), heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumati ...
, with this being the most common cause of death.[ While women with lupus have higher-risk pregnancies, most are successful.][
Rate of SLE varies between countries from 20 to 70 per 100,000.][ Women of childbearing age are affected about nine times more often than men.]Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America ...
, and Chinese descent are at higher risk than those of European descent
White is a Race (human categorization), racial classification of people generally used for those of predominantly Ethnic groups in Europe, European ancestry. It is also a Human skin color, skin color specifier, although the definition can var ...
.[ Rates of disease in the developing world are unclear.]
Signs and symptoms
 SLE is one of several diseases known as "
SLE is one of several diseases known as "the great imitator
The Great Imitator (also the Great Masquerader) is a phrase used for medical conditions that feature nonspecific symptoms and may be confused with a number of other diseases.J.C. Segen. The Dictionary of Modern Medicine'. CRC Press; 1992. . p. 265 ...
" because it often mimics or is mistaken for other illnesses. SLE is a classical item in differential diagnosis
In healthcare, a differential diagnosis (DDx) is a method of analysis that distinguishes a particular disease or condition from others that present with similar clinical features. Differential diagnostic procedures are used by clinicians to di ...
,fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, s ...
, malaise
In medicine, malaise is a feeling of general discomfort, uneasiness or lack of wellbeing and often the first sign of an infection or other disease. It is considered a vague termdescribing the state of simply not feeling well. The word has exist ...
, joint pains, muscle pains
Myalgia or muscle pain is a painful sensation evolving from muscle tissue. It is a symptom of many diseases. The most common cause of acute myalgia is the overuse of a muscle or group of muscles; another likely cause is viral infection, espec ...
, and fatigue
Fatigue is a state of tiredness (which is not sleepiness), exhaustion or loss of energy. It is a signs and symptoms, symptom of any of various diseases; it is not a disease in itself.
Fatigue (in the medical sense) is sometimes associated wit ...
. Because these symptoms are so often seen in association with other diseases, these signs and symptoms are not part of the diagnostic criteria for SLE. When occurring in conjunction with other signs and symptoms, however, they are considered suggestive.relapse
In internal medicine, relapse or recidivism is a recurrence of a past (typically medical) condition. For example, multiple sclerosis and malaria often exhibit peaks of activity and sometimes very long periods of dormancy, followed by relapse or r ...
s, a low white blood cell count, more arthritis
Arthritis is a general medical term used to describe a disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, Joint effusion, swelling, and decreased range of motion of ...
, Raynaud syndrome
Raynaud syndrome, also known as Raynaud's phenomenon, is a medical condition in which the spasm of small arteries causes episodes of reduced blood flow to end arterioles. Typically the fingers, and, less commonly, the toes, are involved. Rare ...
, and psychiatric symptoms. Males tend to have more seizure
A seizure is a sudden, brief disruption of brain activity caused by abnormal, excessive, or synchronous neuronal firing. Depending on the regions of the brain involved, seizures can lead to changes in movement, sensation, behavior, awareness, o ...
s, kidney disease
Kidney disease, or renal disease, technically referred to as nephropathy, is damage to or disease of a kidney. Nephritis is an Inflammation, inflammatory kidney disease and has several types according to the location of the inflammation. Infla ...
, serositis
Serositis refers to inflammation of the serous tissues of the body, the tissues lining the lungs (pleura), heart (pericardium), and the inner lining of the abdomen (peritoneum) and organs within. It is commonly found with fat wrapping or creepin ...
(inflammation of tissues lining the lungs and heart), skin problems, and peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, refers to damage or disease affecting the nerves. Damage to nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland function, and/or organ function depending on which nerve fibers are affected. Neuropa ...
.
Skin

 As many as 70% of people with lupus have some skin symptoms. The three main categories of lesions are chronic cutaneous (discoid) lupus, subacute cutaneous lupus, and acute cutaneous lupus. People with discoid lupus may exhibit thick, red scaly patches on the skin. Similarly, subacute cutaneous lupus manifests as red, scaly patches of skin but with distinct edges. Acute cutaneous lupus manifests as a rash. Some have the classic
As many as 70% of people with lupus have some skin symptoms. The three main categories of lesions are chronic cutaneous (discoid) lupus, subacute cutaneous lupus, and acute cutaneous lupus. People with discoid lupus may exhibit thick, red scaly patches on the skin. Similarly, subacute cutaneous lupus manifests as red, scaly patches of skin but with distinct edges. Acute cutaneous lupus manifests as a rash. Some have the classic malar rash
A malar rash (), also called butterfly rash, is a medical sign consisting of a characteristic form of facial rash. It is often seen in lupus erythematosus. More rarely, it is also seen in other diseases, such as pellagra, dermatomyositis, and ...
(commonly known as the ''butterfly rash'') associated with the disease. This rash occurs in 30–60% of people with SLE.
Hair loss
Hair loss, also known as alopecia or baldness, refers to a loss of hair from part of the head or body. Typically at least the head is involved. The severity of hair loss can vary from a small area to the entire body. Inflammation or scarring ...
, mouth
A mouth also referred to as the oral is the body orifice through which many animals ingest food and animal communication#Auditory, vocalize. The body cavity immediately behind the mouth opening, known as the oral cavity (or in Latin), is also t ...
and nasal ulcers, and lesions on the skin are other possible manifestations.
Muscles and bones
The most commonly sought medical attention is for joint pain
Arthralgia () literally means 'joint pain'. Specifically, arthralgia is a symptom of injury, infection, illness (in particular arthritis), or an allergic reaction to medication
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutic ...
, with the small joints of the hand and wrist usually affected, although all joints are at risk. More than 90 percent of those affected will experience joint or muscle pain at some time during the course of their illness.[Joint and Muscle Pain](_blank)
Lupus Foundation of America Unlike rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and h ...
, lupus arthritis is less disabling and usually does not cause severe destruction of the joints. Fewer than ten percent of people with lupus arthritis will develop deformities of the hands and feet.tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
.rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and h ...
and SLE has been suggested,bone fracture
A bone fracture (abbreviated FRX or Fx, Fx, or #) is a medical condition in which there is a partial or complete break in the continuity of any bone in the body. In more severe cases, the bone may be broken into several fragments, known as a ''c ...
s in relatively young women.
Blood
Anemia
Anemia (also spelt anaemia in British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen. This can be due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin availabl ...
is common in children with SLEthrombocytopenia
In hematology, thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by abnormally low levels of platelets (also known as thrombocytes) in the blood. Low levels of platelets in turn may lead to prolonged or excessive bleeding. It is the most common coag ...
) and low white blood cell count (leukopenia
Leukopenia () is a decrease in the number of white blood cells (leukocytes). It places individuals at increased risk of infection as white blood cells are the body's primary defense against infections.
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms may include:
* s ...
) may be due to the disease or a side effect of pharmacological treatment. People with SLE may have an association with antiphospholipid antibody syndromepartial thromboplastin time
The partial thromboplastin time (PTT), also known as the activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT or APTT), is a blood test that characterizes coagulation of the blood. A historical name for this measure is the Kaolin-cephalin clotting time ...
(which usually occurs in hemorrhagic disorders) and a positive test for antiphospholipid antibodies; the combination of such findings have earned the term "lupus anticoagulant
Lupus anticoagulant is an immunoglobulin that binds to phospholipids and proteins associated with the cell membrane. Its name is a partial misnomer, as it is actually a prothrombotic antibody ''in vivo''. The name derives from their properties ''i ...
-positive". Another autoantibody finding in SLE is the anti-cardiolipin antibody, which can cause a false positive test for syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms depend on the stage it presents: primary, secondary, latent syphilis, latent or tertiary. The prim ...
.
Heart
SLE may cause pericarditis
Pericarditis () is inflammation of the pericardium, the fibrous sac surrounding the heart. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp chest pain, which may also be felt in the shoulders, neck, or back. The pain is typically less severe whe ...
(inflammation of the outer lining surrounding the heart), myocarditis
Myocarditis is inflammation of the cardiac muscle. Myocarditis can progress to inflammatory cardiomyopathy when there is associated ventricular remodeling and cardiac dysfunction due to chronic inflammation. Symptoms can include shortness of bre ...
(inflammation of the heart muscle), or endocarditis
Endocarditis is an inflammation of the inner layer of the heart, the endocardium. It usually involves the heart valves. Other structures that may be involved include the interventricular septum, the chordae tendineae, the mural endocardium, o ...
(inflammation of the inner lining of the heart). The endocarditis of SLE is non-infectious, and is also called Libman–Sacks endocarditis
Libman–Sacks endocarditis is a form of non-bacterial endocarditis that is seen in association with systemic lupus erythematosus, antiphospholipid syndrome, and malignancies. It is one of the most common cardiac manifestations of lupus (the mos ...
. It involves either the mitral valve
The mitral valve ( ), also known as the bicuspid valve or left atrioventricular valve, is one of the four heart valves. It has two Cusps of heart valves, cusps or flaps and lies between the atrium (heart), left atrium and the ventricle (heart), ...
or the tricuspid valve
The tricuspid valve, or right atrioventricular valve, is on the right dorsal side of the mammalian heart, at the superior portion of the right ventricle. The function of the valve is to allow blood to flow from the right atrium to the right vent ...
. Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis, characterized by development of abnormalities called lesions in walls of arteries. This is a chronic inflammatory disease involving many different cell types and is driven by eleva ...
also occurs more often and advances more rapidly than in the general population.
Steroids are sometimes prescribed as an anti-inflammatory treatment for lupus; however, they can increase one's risk for heart disease, high cholesterol, and atherosclerosis.
Lungs
SLE can cause pleuritic pain as well as inflammation of the pleurae
The pleurae (: pleura) are the two flattened closed sacs filled with pleural fluid, each ensheathing each lung and lining their surrounding tissues, locally appearing as two opposing layers of serous membrane separating the lungs from the media ...
known as pleurisy
Pleurisy, also known as pleuritis, is inflammation of the membranes that surround the lungs and line the chest cavity (Pulmonary pleurae, pleurae). This can result in a sharp chest pain while breathing. Occasionally the pain may be a constant d ...
, which can rarely give rise to shrinking lung syndrome involving a reduced lung volume.pneumonitis
Pneumonitis describes general inflammation of lung tissue. Possible causative agents include radiation therapy of the chest, exposure to medications used during chemo-therapy, the inhalation of debris (e.g., animal dander), aspiration, herbicide ...
, chronic diffuse interstitial lung disease
Interstitial lung disease (ILD), or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD), is a group of respiratory diseases affecting the interstitium (the tissue) and space around the alveoli (air sacs) of the lungs. It concerns alveolar epithelium, pulm ...
, pulmonary hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension (PH or PHTN) is a condition of increased blood pressure in the pulmonary artery, arteries of the lungs. Symptoms include dypsnea, shortness of breath, Syncope (medicine), fainting, tiredness, chest pain, pedal edema, swell ...
, pulmonary emboli
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include shortness of breath, chest pain particularly upon breathin ...
, and pulmonary hemorrhage
Pulmonary hemorrhage (or pulmonary haemorrhage) is an acute bleeding from the lung, from the upper respiratory tract and the trachea, and the pulmonary alveoli. When evident clinically, the condition is usually massive.[blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells.
Blood is com ...]
or protein in the urine may often be the only presenting sign of kidney involvement. Acute or chronic renal impairment may develop with lupus nephritis
Lupus nephritis is an inflammation of the kidneys caused by systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus which is a more severe form of SLE that develops in children up to 18 years old; both are autoimmune d ...
, leading to acute or end-stage kidney failure
Kidney failure, also known as renal failure or end-stage renal disease (ESRD), is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney fa ...
. Because of early recognition and management of SLE with immunosuppressive drugs or corticosteroids, end-stage renal failure occurs in less than 5%glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis (GN) is a term used to refer to several kidney diseases (usually affecting both kidneys). Many of the diseases are characterised by inflammation either of the glomeruli or of the small blood vessels in the kidneys, hence the ...
with "wire loop" abnormalities. This finding is due to immune complex deposition along the glomerular basement membrane
The glomerular basement membrane of the kidney is the basal lamina layer of the glomerulus. The glomerular endothelial cells, the glomerular basement membrane, and the filtration slits between the podocytes perform the filtration function of th ...
, leading to a typical granular appearance in immunofluorescence
Immunofluorescence (IF) is a light microscopy-based technique that allows detection and localization of a wide variety of target biomolecules within a cell or tissue at a quantitative level. The technique utilizes the binding specificity of anti ...
testing.
Neuropsychiatric
Neuropsychiatric
Neuropsychiatry is a branch of medicine that deals with psychiatry as it relates to neurology, in an effort to understand and attribute behavior to the interaction of neurobiology and social psychology factors. Within neuropsychiatry, the mind i ...
syndromes can result when SLE affects the central or peripheral nervous system
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of Bilateria, bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside t ...
. The American College of Rheumatology
The American College of Rheumatology (ACR; until 1985 called American Rheumatism Association) is an organization of and for physicians, health professionals, and scientists that advances rheumatology through programs of education, research, advocac ...
defines 19 neuropsychiatric syndromes in systemic lupus erythematosus.neurological disorder
Neurological disorders represent a complex array of medical conditions that fundamentally disrupt the functioning of the nervous system. These disorders affect the brain, spinal cord, and nerve networks, presenting unique diagnosis, treatment, and ...
people with SLE have is headache
A headache, also known as cephalalgia, is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of Depression (mood), depression in those with severe ...
,cognitive disorder
Neurocognitive disorders (NCDs), also known as cognitive disorders (CDs), are a category of mental health disorders that primarily affect cognitive abilities including learning, memory, perception, and problem-solving. Neurocognitive disorders in ...
, mood disorder
A mood disorder, also known as an affective disorder, is any of a group of conditions of mental and behavioral disorder where the main underlying characteristic is a disturbance in the person's mood. The classification is in the ''Diagnostic ...
, cerebrovascular disease
Cerebrovascular disease includes a variety of medical conditions that affect the blood vessels of the brain and the cerebral circulation. Arteries supplying oxygen and nutrients to the brain are often damaged or deformed in these disorders. Th ...
,seizures
A seizure is a sudden, brief disruption of brain activity caused by abnormal, excessive, or synchronous neuronal firing. Depending on the regions of the brain involved, seizures can lead to changes in movement, sensation, behavior, awareness, o ...
, polyneuropathy
Polyneuropathy () is damage or disease affecting peripheral nerves (peripheral neuropathy) in roughly the same areas on both sides of the body, featuring weakness, numbness, and burning pain. It usually begins in the hands and feet and may prog ...
,anxiety disorder
Anxiety disorders are a group of mental disorders characterized by significant and uncontrollable feelings of anxiety and fear such that a person's social, occupational, and personal functions are significantly impaired. Anxiety may cause phys ...
, psychosis
In psychopathology, psychosis is a condition in which a person is unable to distinguish, in their experience of life, between what is and is not real. Examples of psychotic symptoms are delusions, hallucinations, and disorganized or inco ...
, depression, and in some extreme cases, personality disorders. Steroid psychosis can also occur as a result of treating the disease.intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the pressure exerted by fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside the skull and on the brain tissue. ICP is measured in millimeters of mercury ( mmHg) and at rest, is normally 7–15 mmHg for a supine adu ...
, papilledema
Papilledema or papilloedema is optic disc swelling that is caused by increased intracranial pressure due to any cause. The swelling is usually bilateral and can occur over a period of hours to weeks. Unilateral presentation is extremely rare.
In ...
, and headache
A headache, also known as cephalalgia, is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of Depression (mood), depression in those with severe ...
with occasional abducens nerve
The abducens nerve or abducent nerve, also known as the sixth cranial nerve, cranial nerve VI, or simply CN VI, is a cranial nerve in humans and various other animals that controls the movement of the lateral rectus muscle, one of the extraocula ...
paresis
In medicine, paresis (), compound word from Greek , (πᾰρᾰ- “beside” + ἵημι “let go, release”), is a condition typified by a weakness of voluntary movement, or by partial loss of voluntary movement or by impaired movement. Whe ...
, absence of a space-occupying lesion or ventricular enlargement, and normal cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless Extracellular fluid#Transcellular fluid, transcellular body fluid found within the meninges, meningeal tissue that surrounds the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, and in the ventricular system, ven ...
chemical
A chemical substance is a unique form of matter with constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Chemical substances may take the form of a single element or chemical compounds. If two or more chemical substances can be combin ...
and hematological constituents.Guillain–Barré syndrome
Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS) is a rapid-onset Paralysis, muscle weakness caused by the immune system damaging the peripheral nervous system. Typically, both sides of the body are involved, and the initial symptoms are changes in sensation ...
, aseptic meningitis
Aseptic meningitis is the inflammation of the meninges, a membrane covering the brain and spinal cord, in patients whose cerebral spinal fluid test result is negative with routine bacterial cultures. Aseptic meningitis is caused by viruses, mycob ...
, autonomic disorder, demyelinating syndrome, mononeuropathy (which might manifest as mononeuritis multiplex), movement disorder
Movement disorders are clinical syndromes with either an excess of movement or a paucity of voluntary and involuntary movements, unrelated to weakness or spasticity. Movement disorders present with extrapyramidal symptoms and are caused by basa ...
(more specifically, chorea
Chorea, or (rarely) choreia, () is an abnormal involuntary movement disorder, characterized by quick movements of the hands or feet. It is one of a group of neurological disorders called dyskinesias. The term ''chorea'' is derived , as the move ...
), myasthenia gravis
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is a long-term neuromuscular junction disease that leads to varying degrees of skeletal muscle weakness. The most commonly affected muscles are those of the eyes, face, and swallowing. It can result in double vision, ...
, myelopathy
Myelopathy describes any neurologic deficit related to the spinal cord.
When due to trauma, myelopathy is known as (acute) spinal cord injury. When inflammatory, it is known as myelitis. Disease that is vascular in nature is known as vascular ...
, cranial
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek language, Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. Thi ...
neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, refers to damage or disease affecting the nerves. Damage to nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland function, and/or organ function depending on which nerve fibers are affected. Neuropa ...
and plexopathy
Plexopathy is a disorder of the network of nerves in the brachial or lumbosacral plexus. Symptoms include pain, muscle weakness, and sensory deficits (numbness).
Types
There are two main types of plexopathy, based on the location of the sympto ...
.
Neurological disorders contribute to a significant percentage of morbidity and mortality in people with lupus.blood–brain barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable membrane, semipermeable border of endothelium, endothelial cells that regulates the transfer of solutes and chemicals between the circulatory system and the central nervous system ...
. In certain regions, depression affects up to 60% of women with SLE.
Eyes
Up to one-third of patients report that their eyes are affected. The most common diseases are dry eye syndrome
Dry eye syndrome, also known as keratoconjunctivitis sicca, is the condition of having dry eyes. Symptoms include dryness in the eye, irritation, redness, discharge, blurred vision, and easily fatigued eyes. Symptoms range from mild and occas ...
and secondary Sjögren's syndrome, but episcleritis, scleritis
Scleritis is a serious inflammatory disease that affects the white outer coating of the eye, known as the sclera. The disease is often contracted through association with other diseases of the body, such as granulomatosis with polyangiitis or rheu ...
, retinopathy
Retinopathy is any damage to the retina of the eyes, which may cause vision impairment. Retinopathy often refers to retinal vascular disease, or damage to the retina caused by abnormal blood flow. Age-related macular degeneration is technically in ...
(more often affecting both eyes than one), ischemic optic neuropathy
Ischemic optic neuropathy (ION) is the loss of structure and function of a portion of the optic nerve due to obstruction of blood flow to the nerve (i.e. ischemia). Ischemic forms of optic neuropathy are typically classified as either anterior is ...
, retinal detachment
Retinal detachment is a condition where the retina pulls away from the tissue underneath it. It may start in a small area, but without quick treatment, it can spread across the entire retina, leading to serious vision loss and possibly blindness. ...
, and secondary angle-closure glaucoma may occur. In addition, the medications used to treat SLE can cause eye disease: long-term glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebra ...
use can cause cataract
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens (anatomy), lens of the eye that leads to a visual impairment, decrease in vision of the eye. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colours, blurry or ...
s and secondary open-angle glaucoma, and long-term hydroxychloroquine
Hydroxychloroquine, sold under the brand name Plaquenil among others, is a medication used to prevent and treat malaria in areas where malaria remains sensitive to chloroquine. Other uses include treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, an ...
treatment can cause vortex keratopathy and maculopathy
A maculopathy is any pathological condition of the macula, an area at the centre of the retina that is associated with highly sensitive, accurate vision.
Forms of maculopathies
* Age-Related Macular Degeneration is a degenerative maculopathy ass ...
.
Reproductive
While most pregnancies have positive outcomes, there is a greater risk of adverse events occurring during pregnancy. SLE causes an increased rate of fetal death ''in utero'' and spontaneous abortion
Miscarriage, also known in medical terms as a spontaneous abortion, is an end to pregnancy resulting in the loss and expulsion of an embryo or fetus from the womb before it can survive independently. Miscarriage before 6 weeks of gestation is ...
(miscarriage). The overall live-birth rate in people with SLE has been estimated to be 72%. Pregnancy outcome appears to be worse in people with SLE whose disease flares up during pregnancy.
Neonatal lupus
Neonatal lupus erythematosus is an autoimmune disease in an infant born to a mother with anti-Ro/SSA and with or without anti-La/SSB antibodies. The disease most commonly presents with a diffuse/periorbital rash resembling subacute cutaneous lupu ...
is the occurrence of SLE symptoms in an infant
In common terminology, a baby is the very young offspring of adult human beings, while infant (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'baby' or 'child') is a formal or specialised synonym. The terms may also be used to refer to juveniles of ...
born from a mother with SLE, most commonly presenting with a rash resembling discoid lupus erythematosus
Discoid lupus erythematosus is the most common type of chronic cutaneous lupus (CCLE), an autoimmune skin condition on the lupus erythematosus spectrum of illnesses. It presents with red, painful, inflamed and coin-shaped patches of skin with a sc ...
, and sometimes with systemic abnormalities such as heart block
Heart block (HB) is a disorder in the heart's rhythm due to a fault in the natural pacemaker. This is caused by an obstruction – a block – in the electrical conduction system of the heart. Sometimes a disorder can be inherited. Despite the ...
or enlargement of the liver and spleen.[thefreedictionary.com > neonatal lupus]
Citing: Dorland's Medical Dictionary for Health Consumers. Copyright 2007 Neonatal lupus is usually benign and self-limited.[
Medications for treatment of SLE can carry severe risks for female and male reproduction. ]Cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian cancer, breast cancer ...
(also known as Cytoxan), can lead to infertility by causing premature ovarian insufficiency (POI), the loss of normal function of one's ovaries prior to age forty. Methotrexate
Methotrexate, formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immunosuppressive drug, immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancy, ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is u ...
can cause termination or deformity in fetuses and is a common abortifacient
An abortifacient ("that which will cause a miscarriage" from Latin: '' abortus'' "miscarriage" and '' faciens'' "making") is a substance that induces abortion. This is a nonspecific term which may refer to any number of substances or medications, ...
, and for men taking a high dose and planning to father, a discontinuation period of 6 months is recommended before insemination.
Systemic
Fatigue
Fatigue is a state of tiredness (which is not sleepiness), exhaustion or loss of energy. It is a signs and symptoms, symptom of any of various diseases; it is not a disease in itself.
Fatigue (in the medical sense) is sometimes associated wit ...
in SLE is probably multifactorial and has been related to not only disease activity or complications such as anemia
Anemia (also spelt anaemia in British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen. This can be due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin availabl ...
or hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is an endocrine disease in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as cold intolerance, poor ability to tolerate cold, fatigue, extreme fatigue, muscle aches, co ...
, but also to pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging Stimulus (physiology), stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sense, sensory and emotional experience associated with, or res ...
, depression, poor sleep
Sleep is a state of reduced mental and physical activity in which consciousness is altered and certain Sensory nervous system, sensory activity is inhibited. During sleep, there is a marked decrease in muscle activity and interactions with th ...
quality, poor physical fitness
Physical fitness is a state of health and well-being and, more specifically, the ability to perform aspects of Outline of sports, sports, occupations, and daily activities. Physical fitness is generally achieved through proper nutrition, modera ...
and lack of social support
Social support is the perception and actuality that one is cared for, has assistance available from other people, and, most popularly, that one is part of a supportive social network. These supportive resources can be emotional (e.g., nurturance), ...
.
Causes
Vitamin D deficiency
Some studies have found that vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency or hypovitaminosis D is a vitamin D level that is below normal. It most commonly occurs in people when they have inadequate exposure to sunlight, particularly sunlight with adequate ultraviolet B rays (UVB). Vitamin D def ...
(i.e., a low serum level of vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of structurally related, fat-soluble compounds responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, along with numerous other biological functions. In humans, the most important compo ...
) often occurs in patients with SLE and that its level is particularly low in patients with more active SLE.
Genetics
Studies of identical twins (i.e., twins
Twins are two offspring produced by the same pregnancy.MedicineNet > Definition of Twin Last Editorial Review: 19 June 2000 Twins can be either ''monozygotic'' ('identical'), meaning that they develop from one zygote, which splits and forms two e ...
that develop from the same fertilized egg
An egg is an organic vessel grown by an animal to carry a possibly fertilized egg cell (a zygote) and to incubate from it an embryo within the egg until the embryo has become an animal fetus that can survive on its own, at which point the ...
) and genome-wide association studies
In genomics, a genome-wide association study (GWA study, or GWAS), is an observational study of a genome-wide set of genetic variants in different individuals to see if any variant is associated with a trait. GWA studies typically focus on assoc ...
have identified numerous genes that by themselves promote the development of SLE, particularly childhood-onset SLE, i.e., cSLE, in rare cases of SLE/cSLE.macrophage activation syndrome
Macrophage activation syndrome is a severe, potentially life-threatening, complication of several chronic rheumatic diseases of childhood. It occurs most commonly with systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis (SoJIA). In addition, MAS has be ...
.Mutations
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosi ...
in about 40 genes have been reported to cause cSLE and/or a cSLE-like disease.DNASE1L3
Deoxyribonuclease gamma (also termed DNase γ, deoxyribonuclease 1L3, DNASE1L3, of deoxyribonuclease I like 3) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''DNASE1L3'' (also termed the ''deoxyribonuclease 1L3'' or ''deoxyribonuclease 1 like 3'' ...
, TREX1, IFIH1
MDA5 (melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5) is a RIG-I-like receptor dsRNA helicase enzyme that is encoded by the ''IFIH1'' gene in humans. MDA5 is part of the RIG-I-like receptor (RLR) family, which also includes RIG-I and LGP2, and f ...
, Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase
Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP or TRAPase), also called acid phosphatase 5, tartrate resistant (ACP5) or TRAP5b, is a glycosylated monomeric metalloprotein enzyme expressed in mammals. It has a molecular weight of approximately 35kDa, ...
'' and ''PRKCD
Protein kinase C delta type (or PKC-δ) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PRKCD'' gene.
Function
Protein kinase C (PKC) is a family of serine- and threonine-specific protein kinases that can be activated by the second messeng ...
''SOS1
Son of sevenless homolog 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SOS1'' gene.
Function
SOS1 is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) which interacts with Ras protein, Ras proteins to phosphorylate GDP into GTP, or from an inacti ...
, FASLG, FAS receptor gene, RAG1, RAG2
Recombination activating gene 2 protein (also known as RAG-2) is a lymphocyte-specific protein encoded by the RAG2 gene on human chromosome 11. Together with the RAG1 protein, RAG2 forms a V(D)J recombinase, a protein complex required for the proc ...
, DNASE1, SHOC2, KRAS
''KRAS'' ( Kirsten rat sarcoma virus) is a gene that provides instructions for making a protein called K-Ras, a part of the RAS/MAPK pathway. The protein relays signals from outside the cell to the cell's nucleus. These signals instruct the ce ...
, PTPN11
Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 11 (PTPN11) also known as protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1D (PTP-1D), Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase-2 (SHP-2), or protein-tyrosine phosphatase 2C (PTP-2C) is an enzyme that in hu ...
, PTEN, BLK, RNASEH2A, RNASEH2B, RNASEH2C, Complement component 1qA, Complement component 1qB, Complement component 1r
Complement C1r subcomponent (, ''activated complement C1r'', ''C overbar 1r esterase'', ''C1r'') is a protein involved in the complement system of the innate immune system. In humans, C1r is encoded by the ''C1R'' gene.
C1r along with C1q and C1 ...
, Complement component 1s, Complement component 2
Complement C2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''C2'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is part of the classical pathway of the complement system, acting as a multi-domain serine protease. Deficiency of C2 has been associated wi ...
, Complement component 3
Complement may refer to:
The arts
* Complement (music), an interval that, when added to another, spans an octave
** Aggregate complementation, the separation of pitch-class collections into complementary sets
* Complementary color, in the vi ...
, UNC93B1'', and the two complement component 4
Complement component 4 (C4), in humans, is a protein involved in the intricate complement system, originating from the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system. It serves a number of critical functions in immunity, tolerance, and autoimmunity with ...
genes ,'' C4A'' and '' C4B''.code
In communications and information processing, code is a system of rules to convert information—such as a letter, word, sound, image, or gesture—into another form, sometimes shortened or secret, for communication through a communicati ...
respectively for complement component A and complement component B proteins. These two proteins combine to form the complement component 4
Complement component 4 (C4), in humans, is a protein involved in the intricate complement system, originating from the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system. It serves a number of critical functions in immunity, tolerance, and autoimmunity with ...
protein which plays various roles in regulating immune function. Individuals normally have multiple copies of the ''C4A'' and ''C4B'' gene but if they have reduced levels of one and/or both of these genes make low levels of complement component 4 protein and thereby are at risk for developing cSLE or a cSLE-like disorders.polygenic inheritance
A quantitative trait locus (QTL) is a locus (section of DNA) that correlates with variation of a quantitative trait in the phenotype of a population of organisms. QTLs are mapped by identifying which molecular markers (such as SNPs or AFLPs) co ...
.DNA damage
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. A weakened capacity for DNA repair is a risk factor for the development of cancer. DNA is constantly modified ...
than normal subjects, and several proteins involved in the preservation of genomic
Genomics is an interdisciplinary field of molecular biology focusing on the structure, function, evolution, mapping, and editing of genomes. A genome is an organism's complete set of DNA, including all of its genes as well as its hierarchical, ...
stability show polymorphisms, some of which increase the risk for SLE development. Defective DNA repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell (biology), cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. A weakened capacity for DNA repair is a risk factor for the development of cancer. DNA is cons ...
is a likely mechanism underlying lupus development.
Drug-induced SLE
Drug-induced lupus erythematosus
Drug-induced lupus erythematosus is an autoimmune disorder caused by chronic use of certain drugs. These drugs cause an autoimmune response (the body attacks its own cells) producing symptoms similar to those of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). ...
is a (generally) reversible condition that usually occurs in people being treated for a long-term illness. Drug-induced lupus mimics SLE. However, symptoms of drug-induced lupus generally disappear once the medication that triggered the episode is stopped.antiarrhythmic agents
Antiarrhythmic agents, also known as cardiac dysrhythmia medications, are a class of drugs that are used to suppress abnormally fast rhythms (tachycardias), such as atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia and ventricular tachycardia.
...
such as procainamide
Procainamide (PCA) is a medication of the antiarrhythmic class used for the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias. It is a sodium channel blocker of cardiomyocytes; thus it is classified by the Vaughan Williams classification system as class Ia. ...
or quinidine
Quinidine is a class I antiarrhythmic agent, class IA antiarrhythmic agent used to treat heart rhythm disturbances. It is a diastereomer of Antimalarial medication, antimalarial agent quinine, originally derived from the bark of the cinchona tre ...
; antihypertensive
Antihypertensives are a class of drugs that are used to treat hypertension (high blood pressure). Antihypertensive therapy seeks to prevent the complications of high blood pressure, such as stroke, heart failure, kidney failure and myocardial infa ...
agents such as hydralazine
Hydralazine, sold under the brand name Apresoline among others, is a medication used to treat high blood pressure and heart failure. This includes high blood pressure in pregnancy and very high blood pressure resulting in symptoms. It has bee ...
, captopril
Captopril, sold under the brand name Capoten among others, is an ACE inhibitor, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor used for the treatment of hypertension and some types of congestive heart failure. Captopril was the first oral ACE inh ...
, or acebutolol; antimicrobial
An antimicrobial is an agent that kills microorganisms (microbicide) or stops their growth (bacteriostatic agent). Antimicrobial medicines can be grouped according to the microorganisms they are used to treat. For example, antibiotics are used aga ...
agents such as minocycline
Minocycline, sold under the brand name Minocin among others, is a tetracycline antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections such as some occurring in certain forms of pneumonia. It is generally (but not always) less pre ...
, isoniazid
Isoniazid, also known as isonicotinic acid hydrazide (INH), is an antibiotic used for the treatment of tuberculosis. For active tuberculosis, it is often used together with rifampicin, pyrazinamide, and either streptomycin or ethambutol. F ...
, carbamazepine
Carbamazepine, sold under the brand name Tegretol among others, is an anticonvulsant medication used in the treatment of epilepsy and neuropathic pain. It is used as an adjunctive treatment in schizophrenia along with other medications and as ...
, or phenytoin
Phenytoin (PHT), sold under the brand name Dilantin among others, is an anticonvulsant, anti-seizure medication. It is useful for the prevention of tonic-clonic seizures (also known as grand mal seizures) and focal seizures, but not absence se ...
; and agents that inhibit the inflammation-inducing actions of interferon
Interferons (IFNs, ) are a group of signaling proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of several viruses. In a typical scenario, a virus-infected cell will release interferons causing nearby cells to heighten ...
or tumor necrosis factor
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF), formerly known as TNF-α, is a chemical messenger produced by the immune system that induces inflammation. TNF is produced primarily by activated macrophages, and induces inflammation by binding to its receptors o ...
.
Non-systemic forms of lupus
Discoid (cutaneous) lupus is limited to skin symptoms and is diagnosed by biopsy of rash on the face, neck, scalp or arms. Approximately 5% of people with DLE progress to SLE.
Pathophysiology
SLE is triggered by environmental factors that are unknown. In SLE, the body's immune system produces antibodies against self-protein Self-protein refers to all proteins endogenously produced by DNA-level transcription and translation within an organism of interest. This does not include proteins synthesized due to viral infection, but may include those synthesized by commensal ...
, particularly against proteins in the cell nucleus. These antibody attacks are the immediate cause of SLE.type III hypersensitivity
Type III hypersensitivity, in the Gell and Coombs classification of allergic reactions, occurs when there is accumulation of immune complexes (antigen-antibody complexes) that have not been adequately cleared by innate immune cells, giving ris ...
response with potential type II involvement. Reticulate and stellate acral pigmentation should be considered a possible manifestation of SLE and high titer
Titer (American English) or titre (British English) is a way of expressing concentration. Titer testing employs serial dilution to obtain approximate quantitative information from an analytical procedure that inherently only evaluates as positi ...
s of anti-cardiolipin antibodies
Anti-cardiolipin antibodies (ACA) are antibodies often directed against cardiolipin and found in several diseases, including syphilis, antiphospholipid syndrome, livedoid vasculitis, vertebrobasilar insufficiency, Behçet's syndrome, idiopathi ...
, or a consequence of therapy.
People with SLE have intense polyclonal B-cell activation, with a population shift towards immature B cells. Memory B cells with increased CD27
CD27 is a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily. It is currently of interest to immunologists as a co-stimulatory immune checkpoint molecule, and is the target of an anti-cancer drug in clinical trials.
Expression
During mo ...
+/ IgD—are less susceptible to immunosuppression. CD27-/IgD- memory B cells are associated with increased disease activity and renal lupus. T cells, which regulate B-cell responses and infiltrate target tissues, have defects in signaling, adhesion, co-stimulation, gene transcription, and alternative splicing. The cytokines B-lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS), also known as B-cell activating factor
B-cell activating factor (BAFF) also known as tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 13B and CD257 among other names, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TNFSF13B'' gene. BAFF is also known as B Lymphocyte Stimulator (BLyS) a ...
(BAFF), interleukin 6, interleukin 17, interleukin 18, type I interferons, and tumor necrosis factor α
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF), formerly known as TNF-α, is a chemical messenger produced by the immune system that induces inflammation. TNF is produced primarily by activated macrophages, and induces inflammation by binding to its receptors o ...
(TNFα) are involved in the inflammatory process and are potential therapeutic targets.complement system
The complement system, also known as complement cascade, is a part of the humoral, innate immune system and enhances (complements) the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes and damaged cells from an organism, promote inf ...
.
Cell death signaling
*Apoptosis is increased in monocyte
Monocytes are a type of leukocyte or white blood cell. They are the largest type of leukocyte in blood and can differentiate into macrophages and monocyte-derived dendritic cells. As a part of the vertebrate innate immune system monocytes also ...
s and keratinocyte
Keratinocytes are the primary type of cell found in the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. In humans, they constitute 90% of epidermal skin cells. Basal cells in the basal layer (''stratum basale'') of the skin are sometimes referre ...
s
* Expression of Fas by B cell
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasm ...
s and T cell
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell ...
s is increased
*There are correlations between the apoptotic rates of lymphocytes and disease activity.
*Necrosis is increased in T lymphocytes.
Tingible body macrophages (TBMs) – large phagocytic cells
Phagocytes are cells that protect the body by ingesting harmful foreign particles, bacteria, and dead or dying cells. Their name comes from the Greek ', "to eat" or "devour", and "-cyte", the suffix in biology denoting "cell", from the Greek ...
in the germinal center
Germinal centers or germinal centres (GCs) are transiently formed structures within B cell zone (follicles) in secondary lymphoid organs – lymph nodes, ileal Peyer's patches, and the spleen – where mature B cells are activated, prolifera ...
s of secondary lymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that includ ...
s – express CD68
CD68 ( Cluster of Differentiation 68) is a protein highly expressed by cells in the monocyte lineage (e.g., monocytic phagocytes, osteoclasts), by circulating macrophages, and by tissue macrophages (e.g., Kupffer cells, microglia).
Structure and ...
protein. These cells normally engulf B cells that have undergone apoptosis after somatic hypermutation
Somatic hypermutation (or SHM) is a cellular mechanism by which the immune system adapts to the new foreign elements that confront it (e.g. microbes). A major component of the process of affinity maturation, SHM diversifies B cell receptors used t ...
. In some people with SLE, significantly fewer TBMs can be found, and these cells rarely contain material from apoptotic B cells. Also, uningested apoptotic nuclei can be found outside of TBMs. This material may present a threat to the tolerization of B cells and T cells. Dendritic cell
A dendritic cell (DC) is an antigen-presenting cell (also known as an ''accessory cell'') of the mammalian immune system. A DC's main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system ...
s in the germinal center may endocytose such antigenic material and present it to T cells, activating them. Also, apoptotic chromatin and nuclei may attach to the surfaces of follicular dendritic cell
Follicular dendritic cells (FDC) are cells of the immune system found in primary and secondary lymph follicles (lymph nodes) of the B cell areas of the lymphoid tissue. Unlike dendritic cells (DC), FDCs are not derived from the bone-marrow hem ...
s and make this material available for activating other B cells that may have randomly acquired self-protein Self-protein refers to all proteins endogenously produced by DNA-level transcription and translation within an organism of interest. This does not include proteins synthesized due to viral infection, but may include those synthesized by commensal ...
specificity through somatic hypermutation. Necrosis, a pro-inflammatory form of cell death, is increased in T lymphocytes, due to mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and depletion of ATP.
Clearance deficiency
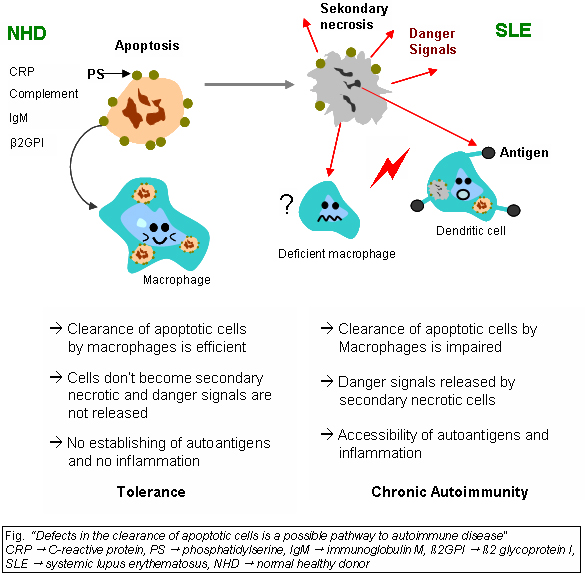 Impaired clearance of dying cells is a potential pathway for the development of this systemic
Impaired clearance of dying cells is a potential pathway for the development of this systemic autoimmune disease
An autoimmune disease is a condition that results from an anomalous response of the adaptive immune system, wherein it mistakenly targets and attacks healthy, functioning parts of the body as if they were foreign organisms. It is estimated tha ...
. This includes deficient phagocytic activity, impaired lysosomal degradation, and scant serum components in addition to increased apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biol ...
.[
]Monocytes
Monocytes are a type of leukocyte or white blood cell. They are the largest type of leukocyte in blood and can differentiate into macrophages and monocyte-derived dendritic cells. As a part of the vertebrate innate immune system monocytes also i ...
isolated from whole blood
Whole blood (WB) is human blood from a standard blood donation. It is used in the treatment of massive bleeding, in exchange transfusion, and when people donate blood to themselves (autologous transfusion). One unit of whole blood (approxima ...
of people with SLE show reduced expression of CD44
The CD44 antigen is a cell-surface glycoprotein involved in cell–cell interactions, cell adhesion and migration. In humans, the CD44 antigen is encoded by the ''CD44'' gene on chromosome 11. CD44 has been referred to as HCAM (homing cell adhes ...
surface molecules involved in the uptake of apoptotic cells. Most of the monocytes and tingible body macrophages (TBMs), which are found in the germinal centre
Germinal centers or germinal centres (GCs) are transiently formed structures within B cell zone (follicles) in secondary lymphoid organs – lymph nodes, ileal Peyer's patches, and the spleen – where mature B cells are activated, prolifera ...
s of lymph nodes
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped Organ (anatomy), organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphoc ...
, even show a definitely different morphology; they are smaller or scarce and die earlier. Serum components like complement
Complement may refer to:
The arts
* Complement (music), an interval that, when added to another, spans an octave
** Aggregate complementation, the separation of pitch-class collections into complementary sets
* Complementary color, in the visu ...
factors, CRP, and some glycoproteins
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide (sugar) chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known a ...
are, furthermore, decisively important for an efficiently operating phagocytosis. With SLE, these components are often missing, diminished, or inefficient.lysosome
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle that is found in all mammalian cells, with the exception of red blood cells (erythrocytes). There are normally hundreds of lysosomes in the cytosol, where they function as the cell’s degradation cent ...
s and as a result have impaired degradation of internalized apoptotic debris, which results in chronic activation of Toll-like receptor
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are a class of proteins that play a key role in the innate immune system. They are single-pass membrane protein, single-spanning receptor (biochemistry), receptors usually expressed on sentinel cells such as macrophages ...
s and permeabilization of the phagolysosomal membrane, allowing activation of cytosolic sensors. In addition, intact apoptotic debris recycles back to the cell membrane and accumulate on the surface of the cell.
Recent research has found an association between certain people with lupus (especially those with lupus nephritis
Lupus nephritis is an inflammation of the kidneys caused by systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus which is a more severe form of SLE that develops in children up to 18 years old; both are autoimmune d ...
) and an impairment in degrading neutrophil extracellular traps
Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) are networks of extracellular fibers, primarily composed of DNA from neutrophils, which bind pathogens. Neutrophils are the immune system's first line of defense against infection and have conventionally bee ...
(NETs). These were due to DNAse1 inhibiting factors, or NET protecting factors in people's serum, rather than abnormalities in the DNAse1 itself. DNAse1 mutations in lupus have so far only been found in some Japanese cohorts.
The clearance of early apoptotic cells is an important function in multicellular organisms. It leads to a progression of the apoptosis process and finally to secondary necrosis
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. The term "necrosis" came about in the mid-19th century and is commonly attributed to German pathologist Rudolf Virchow, who i ...
of the cells if this ability is disturbed. Necrotic cells release nuclear fragments as potential autoantigens
In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an "autoimmune disease". ...
, as well as internal danger signals, inducing maturation of dendritic cells
A dendritic cell (DC) is an antigen-presenting cell (also known as an ''accessory cell'') of the mammalian immune system. A DC's main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system ...
(DCs) since they have lost their membranes' integrity. Increased appearance of apoptotic cells also stimulates inefficient clearance. That leads to the maturation of DCs and also to the presentation of intracellular antigens of late apoptotic or secondary necrotic cells, via MHC molecules.Autoimmunity
In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an " autoimmune disease ...
possibly results from the extended exposure to nuclear and intracellular autoantigens derived from late apoptotic and secondary necrotic cells. B and T cell
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell ...
tolerance for apoptotic cells is abrogated, and the lymphocytes
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include T cells (for cell-mediated and cytotoxic adaptive immunity), B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity), and ...
get activated by these autoantigens; inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
and the production of autoantibodies by plasma cell
Plasma cells, also called plasma B cells or effector B cells, are white blood cells that originate in the lymphoid organs as B cells and secrete large quantities of proteins called antibodies in response to being presented specific substances ca ...
s is initiated. A clearance deficiency in the skin for apoptotic cells has also been observed in people with cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE).
Germinal centers
 In healthy conditions, apoptotic lymphocytes are removed in
In healthy conditions, apoptotic lymphocytes are removed in germinal center
Germinal centers or germinal centres (GCs) are transiently formed structures within B cell zone (follicles) in secondary lymphoid organs – lymph nodes, ileal Peyer's patches, and the spleen – where mature B cells are activated, prolifera ...
s (GC) by specialized phagocytes, the tingible body macrophages (TBM), which is why no free apoptotic and potential autoantigenic material can be seen. In some people with SLE, a buildup of apoptotic debris
Debris (, ) is rubble, wreckage, ruins, litter and discarded waste, garbage/refuse/trash, scattered remains of something destroyed, or, as in geology, large rock fragments left by a melting glacier, etc. Depending on context, ''debris'' can ref ...
can be observed in GC because of an ineffective clearance of apoptotic cells. Close to TBM, follicular dendritic cells (FDC) are localised in GC, which attach antigen material to their surface and, in contrast to bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It i ...
-derived DC, neither take it up nor present it via MHC molecules.B cell
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasm ...
s can accidentally emerge during somatic hypermutation
Somatic hypermutation (or SHM) is a cellular mechanism by which the immune system adapts to the new foreign elements that confront it (e.g. microbes). A major component of the process of affinity maturation, SHM diversifies B cell receptors used t ...
and migrate into the germinal center light zone. Autoreactive B cells, maturated coincidentally, normally do not receive survival signals by antigen planted on follicular dendritic cells and perish by apoptosis. In the case of clearance deficiency, apoptotic nuclear debris accumulates in the light zone of GC and gets attached to FDC.mantle zone
The mantle zone (or just mantle) of a lymphatic nodule (or lymphatic follicle) is an outer ring of small lymphocytes surrounding a germinal center.
It is also known as the "corona".
It contains transient lymphocytes.
It is the location of th ...
, autoreactive B cells require further survival signals from autoreactive helper T cells, which promote the maturation of autoantibody-producing plasma cells and B memory cells. In the presence of autoreactive T cell
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell ...
s, a chronic autoimmune disease
An autoimmune disease is a condition that results from an anomalous response of the adaptive immune system, wherein it mistakenly targets and attacks healthy, functioning parts of the body as if they were foreign organisms. It is estimated tha ...
may be the consequence.
Anti-nRNP autoimmunity
Anti-nRNP
Anti-nRNP is a type of antibody.
They are autoantibodies against some ribonucleoproteins.
Anti-nRNP antibodies can be elevated in mixed connective tissue disease.
See also
* snRNP70
snRNP70 also known as U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein 70 ...
autoantibodies
An autoantibody is an antibody (a type of protein) produced by the immune system that is directed against one or more of the individual's own proteins. Many autoimmune diseases (notably lupus erythematosus) are associated with such antibodies.
Pr ...
to nRNP A and nRNP C initially targeted restricted, proline
Proline (symbol Pro or P) is an organic acid classed as a proteinogenic amino acid (used in the biosynthesis of proteins), although it does not contain the amino group but is rather a secondary amine. The secondary amine nitrogen is in the p ...
-rich motifs. Antibody binding subsequently spread to other epitope
An epitope, also known as antigenic determinant, is the part of an antigen that is recognized by the immune system, specifically by antibodies, B cells, or T cells. The part of an antibody that binds to the epitope is called a paratope. Although e ...
s. The similarity and cross-reactivity
Cross-reactivity, in a general sense, is the reactivity of an observed agent which initiates reactions outside the main reaction expected. This has implications for any kind of test or assay, including diagnostic tests in medicine, and can be a c ...
between the initial targets of nRNP and Sm autoantibodies identifies a likely commonality in cause and a focal point for intermolecular epitope spreading.
Others
Elevated expression of HMGB1
High mobility group box 1 protein, also known as high-mobility group protein 1 (HMG-1) and amphoterin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HMGB1'' gene.
HMG-1 belongs to the high mobility group and contains a HMG-box domain.
Funct ...
was found in the sera of people and mice with systemic lupus erythematosus, high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1
High mobility group box 1 protein, also known as high-mobility group protein 1 (HMG-1) and amphoterin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HMGB1'' gene.
HMG-1 belongs to the high mobility group and contains a HMG-box domain.
Funct ...
) is a nuclear
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
*Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
* Nuclear space
*Nuclear ...
protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
participating in chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important r ...
architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and construction, constructi ...
and transcriptional regulation
In molecular biology and genetics, transcriptional regulation is the means by which a cell regulates the conversion of DNA to RNA ( transcription), thereby orchestrating gene activity. A single gene can be regulated in a range of ways, from al ...
. Recently, there is increasing evidence HMGB1 contributes to the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases
An autoimmune disease is a condition that results from an anomalous response of the adaptive immune system, wherein it mistakenly targets and attacks healthy, functioning parts of the body as if they were foreign organisms. It is estimated that ...
due to its inflammatory and immune stimulating properties.
Diagnosis

Laboratory tests
Antinuclear antibody
Antinuclear antibodies (ANAs, also known as antinuclear factor or ANF) are autoantibodies that bind to contents of the cell nucleus. In normal individuals, the immune system produces antibodies to foreign proteins (antigens) but not to human pro ...
(ANA) testing and anti-extractable nuclear antigen (anti-ENA Extractable nuclear antigens (ENAs) are over 100 different soluble cytoplasmic and nuclear antigens. They are known as "extractable" because they can be removed from cell nuclei using saline and represent six main proteins: Ro, La, Sm, RNP, Scl-70, ...
) form the mainstay of serologic testing for SLE. ANA testing for lupus is highly sensitive, with the vast majority of individuals with Lupus testing positive; but the test is not specific, as a positive result may or may not be indicative of Lupus.
Several techniques are used to detect ANAs. The most widely used is indirect immunofluorescence
Immunofluorescence (IF) is a light microscopy-based technique that allows detection and localization of a wide variety of target biomolecules within a cell or tissue at a quantitative level. The technique utilizes the binding specificity of anti ...
(IF). The pattern of fluorescence suggests the type of antibody present in the people's serum. Direct immunofluorescence can detect deposits of immunoglobulins and complement proteins in people's skin. When skin not exposed to the sun is tested, a positive direct IF (the so-called lupus band test) is evidence of systemic lupus erythematosus.
ANA screening yields positive results in many connective tissue disorders and other autoimmune diseases, and may occur in normal individuals. Subtypes of antinuclear antibodies include anti-Smith and anti-double stranded DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
(anti-dsDNA
Anti-double stranded DNA (Anti-dsDNA) antibodies are a group of anti-nuclear antibodies (ANA) the target antigen of which is double stranded DNA. Blood tests such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and immunofluorescence are routinely p ...
) antibodies (which are linked to SLE) and anti-histone antibodies (which are linked to drug-induced lupus). Anti-dsDNA antibodies are highly specific for SLE; they are present in 70% of cases, whereas they appear in only 0.5% of people without SLE.titer
Titer (American English) or titre (British English) is a way of expressing concentration. Titer testing employs serial dilution to obtain approximate quantitative information from an analytical procedure that inherently only evaluates as positi ...
s also tend to reflect disease activity, although not in all cases.systemic sclerosis
Systemic scleroderma, or systemic sclerosis, is an autoimmune rheumatic disease characterised by excessive production and accumulation of collagen, called fibrosis, in the skin and internal organs and by injuries to small arteries. There are tw ...
and mixed connective tissue disease
Mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD) is a systemic autoimmune disease that shares characteristics with at least two other systemic autoimmune diseases, including Systemic scleroderma, systemic sclerosis (Ssc), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE),� ...
), SS-A
Anti-SSA autoantibodies (anti–Sjögren's-syndrome-related antigen A autoantibodies, also called anti-Ro, or similar names including anti-SSA/Ro, anti-Ro/SSA, anti–SS-A/Ro, and anti-Ro/SS-A) are a type of anti-nuclear autoantibodies that are ...
(or anti-Ro
Anti-SSA autoantibodies (anti–Sjögren's-syndrome-related antigen A autoantibodies, also called anti-Ro, or similar names including anti-SSA/Ro, anti-Ro/SSA, anti–SS-A/Ro, and anti-Ro/SS-A) are a type of anti-nuclear autoantibodies that are ...
) and SS-B
Antinuclear antibodies (ANAs, also known as antinuclear factor or ANF) are autoantibodies that bind to contents of the cell nucleus. In normal individuals, the immune system produces antibodies to foreign proteins (antigens) but not to human pro ...
(or anti-La; both of which are more common in Sjögren's syndrome). SS-A and SS-B confer a specific risk for heart conduction block in neonatal lupus.complement system
The complement system, also known as complement cascade, is a part of the humoral, innate immune system and enhances (complements) the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes and damaged cells from an organism, promote inf ...
levels (low levels suggest consumption by the immune system), electrolyte
An electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity through the movement of ions, but not through the movement of electrons. This includes most soluble Salt (chemistry), salts, acids, and Base (chemistry), bases, dissolved in a polar solven ...
s and kidney function
Assessment of kidney function occurs in different ways, using the presence of symptoms and medical sign, signs, as well as measurements using urine tests, blood tests, and medical imaging.
Renal physiology, Functions of a healthy kidney include ...
(disturbed if the kidney is involved), liver enzyme
Liver function tests (LFTs or LFs), also referred to as a hepatic panel or liver panel, are groups of blood tests that provide information about the state of a patient's liver. These tests include prothrombin time (PT/INR), activated partial t ...
s, and complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC), also known as a full blood count (FBC) or full haemogram (FHG), is a set of medical laboratory tests that provide cytometry, information about the cells in a person's blood. The CBC indicates the counts of white blo ...
.
The lupus erythematosus
is a collection of autoimmune diseases in which the human immune system becomes hyperactive and attacks healthy tissues. Symptoms of these diseases can affect many different body systems, including joints, skin, kidneys, blood cells, heart, ...
(LE) cell test was commonly used for diagnosis, but it is no longer used because the LE cell
A lupus erythematosus cell (LE cell), also known as Hargraves cell, is a neutrophil or macrophage that has phagocytized (engulfed) the denatured nuclear material of another cell. The denatured material is an absorbed hematoxylin body (also called ...
s are only found in 50–75% of SLE cases and they are also found in some people with rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma, and drug sensitivities. Because of this, the LE cell test is now performed only rarely and is mostly of historical significance.
Diagnostic criteria
Some physicians make a diagnosis based on the American College of Rheumatology
The American College of Rheumatology (ACR; until 1985 called American Rheumatism Association) is an organization of and for physicians, health professionals, and scientists that advances rheumatology through programs of education, research, advocac ...
(ACR) classification criteria. However, these criteria were primarily established for use in scientific research, including selection for randomized controlled trial
A randomized controlled trial (or randomized control trial; RCT) is a form of scientific experiment used to control factors not under direct experimental control. Examples of RCTs are clinical trials that compare the effects of drugs, surgical ...
s, which require higher confidence levels. As a result, many people with SLE may not meet the full ACR criteria.
Criteria
The American College of Rheumatology (ACR) established eleven criteria in 1982, which were revised in 1997 as a classificatory instrument to operationalise the definition of SLE in clinical trials. They were not intended to be used to diagnose individuals and do not do well in that capacity. For the purpose of identifying people for clinical studies, a person has SLE if any 4 out of 11 symptoms are present simultaneously or serially on two separate occasions.
# Malar rash
A malar rash (), also called butterfly rash, is a medical sign consisting of a characteristic form of facial rash. It is often seen in lupus erythematosus. More rarely, it is also seen in other diseases, such as pellagra, dermatomyositis, and ...
(rash on cheeks); sensitivity = 57%; specificity = 96%.Pleurisy
Pleurisy, also known as pleuritis, is inflammation of the membranes that surround the lungs and line the chest cavity (Pulmonary pleurae, pleurae). This can result in a sharp chest pain while breathing. Occasionally the pain may be a constant d ...
(inflammation of the membrane around the lungs) or pericarditis
Pericarditis () is inflammation of the pericardium, the fibrous sac surrounding the heart. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp chest pain, which may also be felt in the shoulders, neck, or back. The pain is typically less severe whe ...
(inflammation of the membrane around the heart); sensitivity = 56%; specificity = 86% (pleural is more sensitive; cardiac is more specific).Arthritis
Arthritis is a general medical term used to describe a disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, Joint effusion, swelling, and decreased range of motion of ...
: nonerosive arthritis of two or more peripheral joints, with tenderness, swelling, or effusion; sensitivity = 86%; specificity = 37%.Photosensitivity Photosensitivity is the amount to which an object reacts upon receiving photons, especially visible light. In medicine, the term is principally used for abnormal reactions of the skin, and two types are distinguished, photoallergy and phototoxicit ...
(exposure to ultraviolet light causes rash, or other symptoms of SLE flareups); sensitivity = 43%; specificity = 96%.hemolytic anemia
Hemolytic anemia or haemolytic anaemia is a form of anemia due to hemolysis, the abnormal breakdown of red blood cells (RBCs), either in the blood vessels (intravascular hemolysis) or elsewhere in the human body (extravascular). This most commonl ...
(low red blood cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), referred to as erythrocytes (, with -''cyte'' translated as 'cell' in modern usage) in academia and medical publishing, also known as red cells, erythroid cells, and rarely haematids, are the most common type of blood cel ...
count), leukopenia
Leukopenia () is a decrease in the number of white blood cells (leukocytes). It places individuals at increased risk of infection as white blood cells are the body's primary defense against infections.
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms may include:
* s ...
(white blood cell count<4000/μL), lymphopenia
Lymphocytopenia is the condition of having an abnormally low level of lymphocytes in the blood. Lymphocytes are a white blood cell with important functions in the immune system. It is also called lymphopenia. The opposite is lymphocytosis, which r ...
(<1500/μL), or low platelet count (<100000/μL) in the absence of offending drug; sensitivity = 59%; specificity = 89%.Antinuclear antibody
Antinuclear antibodies (ANAs, also known as antinuclear factor or ANF) are autoantibodies that bind to contents of the cell nucleus. In normal individuals, the immune system produces antibodies to foreign proteins (antigens) but not to human pro ...
test positive; sensitivity = 99%; specificity = 49%.serological
Serology is the scientific study of serum and other body fluids. In practice, the term usually refers to the diagnostic identification of antibodies in the serum. Such antibodies are typically formed in response to an infection (against a given mi ...
test for syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms depend on the stage it presents: primary, secondary, latent syphilis, latent or tertiary. The prim ...
; sensitivity = 85%; specificity = 93%.Seizure
A seizure is a sudden, brief disruption of brain activity caused by abnormal, excessive, or synchronous neuronal firing. Depending on the regions of the brain involved, seizures can lead to changes in movement, sensation, behavior, awareness, o ...
s or psychosis
In psychopathology, psychosis is a condition in which a person is unable to distinguish, in their experience of life, between what is and is not real. Examples of psychotic symptoms are delusions, hallucinations, and disorganized or inco ...
; sensitivity = 20%; specificity = 98%.Raynaud syndrome
Raynaud syndrome, also known as Raynaud's phenomenon, is a medical condition in which the spasm of small arteries causes episodes of reduced blood flow to end arterioles. Typically the fingers, and, less commonly, the toes, are involved. Rare ...
)
Criteria for individual diagnosis
Some people, especially those with antiphospholipid syndrome
Antiphospholipid syndrome, or antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS or APLS), is an autoimmune, hypercoagulable state caused by antiphospholipid antibodies. APS can lead to blood clots (thrombosis) in both arteries and veins, pregnancy-relate ...
, may have SLE without four of the above criteria, and also SLE may present with features other than those listed in the criteria.Recursive partitioning
Recursive partitioning is a statistics, statistical method for multivariable analysis. Recursive partitioning creates a Decision tree learning, decision tree that strives to correctly classify members of the population by splitting it into sub-popu ...
has been used to identify more parsimonious criteria.malar rash
A malar rash (), also called butterfly rash, is a medical sign consisting of a characteristic form of facial rash. It is often seen in lupus erythematosus. More rarely, it is also seen in other diseases, such as pellagra, dermatomyositis, and ...
. It has sensitivity = 92% and specificity = 92%.
# Full classification tree: Uses six criteria. It has sensitivity = 97% and specificity = 95%.
Other alternative criteria have been suggested, e.g. the St. Thomas' Hospital "alternative" criteria in 1998.
Treatment
There is no cure for Lupus. The treatment of SLE involves preventing flares and reducing their severity and duration when they occur.
Hydroxychloroquine
Hydroxychloroquine, sold under the brand name Plaquenil among others, is a medication used to prevent and treat malaria in areas where malaria remains sensitive to chloroquine. Other uses include treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, an ...
was approved by the FDA
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
for lupus in 1955.[ Hydroxychloroquine is a first line agent for SLE and is associated with reduced mortality, complications and disease activity. Hydroxychloroquiine is associated with a 54% reduction in mortality due to SLE.]corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
s and anti-malarial drugs. Certain types of lupus nephritis such as diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis require intermittent cytotoxic drugs. These drugs include cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian cancer, breast cancer ...
and mycophenolate
Mycophenolic acid is an immunosuppressant medication used to prevent rejection following organ transplantation and to treat autoimmune conditions such as Crohn's disease and lupus. Specifically it is used following kidney, heart, and liver t ...
. Cyclophosphamide increases the risk of developing infections, pancreas problems, high blood sugar, and high blood pressure.
Some drugs approved for other diseases are used for SLE 'off-label'. In November 2010, an FDA advisory panel recommended approving belimumab
Belimumab, sold under the brand name Benlysta, is a human monoclonal antibody that inhibits B-cell activating factor (BAFF), also known as B-lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS). It is approved in the United States and Canada, and the European Union to ...
(Benlysta) as a treatment for the pain and flare-ups common in lupus. The drug was approved by the FDA in March 2011.
Medications
Due to the variety of symptoms and organ system involvement with SLE, its severity in an individual must be assessed to successfully treat SLE. Mild or remittent disease may, sometimes, be safely left untreated. If required, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a Indication (medicine), therapeutic drug class which Analgesic, reduces pain, Anti-inflammatory, decreases inflammation, Antipyretic, decreases fever, and Antithrombotic, prevents bl ...
s and antimalarials may be used. Medications such as prednisone
Prednisone is a glucocorticoid medication mostly used to immunosuppressive drug, suppress the immune system and decrease inflammation in conditions such as asthma, COPD, and rheumatologic diseases. It is also used to treat high blood calcium ...
, mycophenolic acid
Mycophenolic acid is an immunosuppressant medication used to prevent rejection following organ transplantation and to treat autoimmune conditions such as Crohn's disease and lupus. Specifically it is used following kidney, heart, and live ...
and tacrolimus
Tacrolimus, sold under the brand name Prograf among others, is an immunosuppressive drug. After Allotransplantation, allogenic organ transplant, the risk of organ Transplant rejection, rejection is moderate. To lower the risk of organ rejectio ...
have been used in the past.
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drug
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) comprise a category of otherwise unrelated disease-modifying drugs defined by their use in rheumatoid arthritis to slow down disease progression. The term is often used in contrast to nonsteroida ...
s (DMARDs) are used preventively to reduce the incidence of flares, the progress of the disease, and the need for steroid use; when flares occur, they are treated with corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invol ...
. DMARDs commonly in use are antimalarials such as hydroxychloroquine
Hydroxychloroquine, sold under the brand name Plaquenil among others, is a medication used to prevent and treat malaria in areas where malaria remains sensitive to chloroquine. Other uses include treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, an ...
and immunosuppressants
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent the activity of the immune system.
Classification
Immunosuppressive drugs can be classified ...
(e.g. methotrexate
Methotrexate, formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immunosuppressive drug, immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancy, ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is u ...
and azathioprine
Azathioprine, sold under the brand name Imuran, among others, is an immunosuppressive medication. It is used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, and systemic lupus er ...
). Hydroxychloroquine is an FDA-approved antimalarial used for constitutional, cutaneous, and articular manifestations. Hydroxychloroquine has relatively few side effects, and there is evidence that it improves survival among people who have SLE.Cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian cancer, breast cancer ...
is used for severe glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis (GN) is a term used to refer to several kidney diseases (usually affecting both kidneys). Many of the diseases are characterised by inflammation either of the glomeruli or of the small blood vessels in the kidneys, hence the ...
or other organ-damaging complications. Mycophenolic acid
Mycophenolic acid is an immunosuppressant medication used to prevent rejection following organ transplantation and to treat autoimmune conditions such as Crohn's disease and lupus. Specifically it is used following kidney, heart, and live ...
is also used for the treatment of lupus nephritis, but it is not FDA-approved for this indication, and FDA is investigating reports that it may be associated with birth defects when used by pregnant women. A study involving more than 1,000 people with lupus found that people have a similar risk of serious infection with azathioprine and mycophenolic acid as with newer biological therapies (rituximab
Rituximab, sold under the brand name Rituxan among others, is a monoclonal antibody medication used to treat certain autoimmune diseases and types of cancer. It is used for non-Hodgkin lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (in children and ad ...
and belimumab
Belimumab, sold under the brand name Benlysta, is a human monoclonal antibody that inhibits B-cell activating factor (BAFF), also known as B-lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS). It is approved in the United States and Canada, and the European Union to ...
).
Immunosuppressive drugs
In more severe cases, medications that modulate the immune system (primarily corticosteroids and immunosuppressants
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent the activity of the immune system.
Classification
Immunosuppressive drugs can be classified ...
) are used to control the disease and prevent recurrence of symptoms (known as flares). Depending on the dosage, people who require steroids may develop Cushing's syndrome
Cushing's syndrome is a collection of signs and symptoms due to prolonged exposure to glucocorticoids such as cortisol. Signs and symptoms may include high blood pressure, abdominal obesity but with thin arms and legs, reddish stretch marks, ...
, symptoms of which may include obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi ...
, puffy round face, diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained hyperglycemia, high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or th ...
, increased appetite, difficulty sleeping, and osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to more porous bone, and consequent increase in Bone fracture, fracture risk.
It is the most common reason f ...
. These may subside if and when the large initial dosage is reduced, but long-term use of even low doses can cause elevated blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of Circulatory system, circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term ...
and cataracts
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens of the eye that leads to a decrease in vision of the eye. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colours, blurry or double vision, halos around ligh ...
.
Numerous new immunosuppressive drugs are being actively tested for SLE. Rather than broadly suppressing the immune system, as corticosteroids do, they target the responses of specific types of immune cells. Some of these drugs are already FDA-approved for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and h ...
, however due to high-toxicity, their use remains limited.[
]
Analgesia
Since a large percentage of people with SLE have varying amounts of chronic pain
Chronic pain is pain that persists or recurs for longer than 3 months.https://icd.who.int/browse/2025-01/mms/en#1581976053 It is also known as gradual burning pain, electrical pain, throbbing pain, and nauseating pain. This type of pain is in cont ...
, stronger prescription analgesics
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic, antalgic, pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used for pain management. Analgesics are conceptually distinct from anesthetics, which temporarily reduce, and in s ...
(painkillers) may be used if over-the-counter drugs (mainly nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a Indication (medicine), therapeutic drug class which Analgesic, reduces pain, Anti-inflammatory, decreases inflammation, Antipyretic, decreases fever, and Antithrombotic, prevents bl ...
s) do not provide effective relief. Potent NSAIDs such as indomethacin
Indometacin, also known as indomethacin, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) commonly used as a prescription medication to reduce fever, pain, stiffness, and swelling from inflammation. It works by inhibiting the production of pr ...
and diclofenac
Diclofenac, sold under the brand name Voltaren among others, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat pain and inflammatory diseases such as gout. It can be taken orally (swallowed by mouth), inserted rectally as a ...
are relatively contraindicated for people with SLE because they increase the risk of kidney failure and heart failure.[
Pain is typically treated with ]opioids
Opioids are a class of Drug, drugs that derive from, or mimic, natural substances found in the Papaver somniferum, opium poppy plant. Opioids work on opioid receptors in the brain and other organs to produce a variety of morphine-like effects, ...
, varying in potency based on the severity of symptoms. When opioids are used for prolonged periods, drug tolerance, chemical dependency, and addiction may occur. Opiate addiction is not typically a concern since the condition is not likely to ever completely disappear. Thus, lifelong treatment with opioids is fairly common for chronic pain symptoms, accompanied by periodic titration that is typical of any long-term opioid regimen.
Intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIGs)
Intravenous immunoglobulin
Immunoglobulin therapy is the use of a mixture of antibodies (normal human immunoglobulin) to treat several health conditions. These conditions include primary immunodeficiency, immune thrombocytopenic purpura, chronic inflammatory demyelinat ...
s may be used to control SLE with organ involvement, or vasculitis
Vasculitis is a group of disorders that destroy blood vessels by inflammation. Both artery, arteries and veins are affected. Lymphangitis (inflammation of lymphatic vessels) is sometimes considered a type of vasculitis. Vasculitis is primarily c ...
. It is believed that they reduce antibody
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as pathogenic bacteria, bacteria and viruses, includin ...
production or promote the clearance of immune complex
An immune complex, sometimes called an antigen-antibody complex or antigen-bound antibody, is a molecule formed from the binding of multiple antigens to antibodies. The bound antigen and antibody act as a unitary object, effectively an antigen of ...
es from the body, even though their mechanism of action
In pharmacology, the term mechanism of action (MOA) refers to the specific biochemical Drug interaction, interaction through which a Medication, drug substance produces its pharmacological effect. A mechanism of action usually includes mention o ...
is not well understood. Unlike immunosuppressive
Immunosuppression is a reduction of the activation or efficacy of the immune system. Some portions of the immune system itself have immunosuppressive effects on other parts of the immune system, and immunosuppression may occur as an adverse react ...
s and corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invol ...
, IVIG
Immunoglobulin therapy is the use of a mixture of antibodies (normal human immunoglobulin) to treat several health conditions. These conditions include primary immunodeficiency, immune thrombocytopenic purpura, chronic inflammatory demyelin ...
s do not suppress the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic ...
, so there is less risk of serious infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
s with these drugs.
Lifestyle changes
Avoiding sunlight in SLE is critical since ultraviolet radiation is known to exacerbate skin manifestations of the disease.silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , commonly found in nature as quartz. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and abundant f ...
, pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for approximately 50% of all p ...
s, and mercury can also worsen the disease.
Kidney transplantation
Kidney transplants are the treatment of choice for end-stage kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a type of long-term kidney disease, defined by the sustained presence of abnormal kidney function and/or abnormal kidney structure. To meet criteria for CKD, the abnormalities must be present for at least three m ...
, which is one of the complications of lupus nephritis
Lupus nephritis is an inflammation of the kidneys caused by systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus which is a more severe form of SLE that develops in children up to 18 years old; both are autoimmune d ...
, but the recurrence of the full disease is common in up to 30% of people.
Antiphospholipid syndrome
Approximately 20% of people with SLE have clinically significant levels of antiphospholipid antibodies, which are associated with antiphospholipid syndrome
Antiphospholipid syndrome, or antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS or APLS), is an autoimmune, hypercoagulable state caused by antiphospholipid antibodies. APS can lead to blood clots (thrombosis) in both arteries and veins, pregnancy-relate ...
. Antiphospholipid syndrome is also related to the onset of neural lupus symptoms in the brain. In this form of the disease, the cause is very different from lupus: thromboses (blood clots or "sticky blood") form in blood vessels, which prove to be fatal if they move within the bloodstream.stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemor ...
by blocking the blood supply to the brain.
If this disorder is suspected in people, brain scans are usually required for early detection. These scans can show localized areas of the brain where blood supply has not been adequate. The treatment plan for these people requires anticoagulation. Often, low-dose aspirin
Aspirin () is the genericized trademark for acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions that aspirin is ...
is prescribed for this purpose, although for cases involving thrombosis anticoagulants such as warfarin
Warfarin, sold under the brand name Coumadin among others. It is used as an anticoagulant, anticoagulant medication. It is commonly used to prevent deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism, and to protect against stroke in people who ha ...
are used.
Management of pregnancy
While most infants born to mothers who have SLE are healthy, pregnant mothers with SLE should remain under medical care until delivery. However, SLE in the pregnant mother poses a higher risk of neonatal lupus
Neonatal lupus erythematosus is an autoimmune disease in an infant born to a mother with anti-Ro/SSA and with or without anti-La/SSB antibodies. The disease most commonly presents with a diffuse/periorbital rash resembling subacute cutaneous lupu ...
, intrauterine growth restriction
Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), or fetal growth restriction, is the poor growth of a fetus while in the womb during pregnancy. IUGR is defined by clinical features of malnutrition and evidence of reduced growth regardless of an infant's ...
, preterm membrane rupture, preterm birth
Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the Childbirth, birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks Gestational age (obstetrics), gestational age, as opposed to full-term delivery at approximately 40 weeks. Extreme preterm is less than 28 ...
, and miscarriage
Miscarriage, also known in medical terms as a spontaneous abortion, is an end to pregnancy resulting in the loss and expulsion of an embryo or fetus from the womb before it can fetal viability, survive independently. Miscarriage before 6 weeks ...
.Neonatal lupus
Neonatal lupus erythematosus is an autoimmune disease in an infant born to a mother with anti-Ro/SSA and with or without anti-La/SSB antibodies. The disease most commonly presents with a diffuse/periorbital rash resembling subacute cutaneous lupu ...
is rare, but identification of mothers at the highest risk for complications allows for prompt treatment before or after birth. In addition, SLE can flare up during pregnancy, and proper treatment can maintain the health of the mother longer. Women pregnant and known to have anti-Ro
Anti-SSA autoantibodies (anti–Sjögren's-syndrome-related antigen A autoantibodies, also called anti-Ro, or similar names including anti-SSA/Ro, anti-Ro/SSA, anti–SS-A/Ro, and anti-Ro/SS-A) are a type of anti-nuclear autoantibodies that are ...
(SSA) or anti-La antibodies (SSB) often have echocardiograms during the 16th and 30th weeks of pregnancy to monitor the health of the heart and surrounding vasculature.Contraception
Birth control, also known as contraception, anticonception, and fertility control, is the use of methods or devices to prevent pregnancy. Birth control has been used since ancient times, but effective and safe methods of birth control only be ...
and other reliable forms of pregnancy prevention are routinely advised for women with SLE since getting pregnant during active disease was found to be harmful. Lupus nephritis
Lupus nephritis is an inflammation of the kidneys caused by systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus which is a more severe form of SLE that develops in children up to 18 years old; both are autoimmune d ...
, gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a condition in which a woman without diabetes develops hyperglycemia, high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes generally results in few symptoms. Obesity increases the rate of pre-eclampsia, cesarea ...
, and pre-eclampsia
Pre-eclampsia is a multi-system disorder specific to pregnancy, characterized by the new onset of hypertension, high blood pressure and often a significant amount of proteinuria, protein in the urine or by the new onset of high blood pressure a ...
are common manifestations.
Prognosis
No cure is available for SLE but there are many treatments for the disease.[
In the 1950s, most people diagnosed with SLE lived fewer than five years. Today, over 90% now survive for more than ten years, and many live relatively symptom-free. 80–90% can expect to live a normal lifespan.][ To reduce the potential for cardiovascular issues, high blood pressure and high cholesterol should be prevented or treated aggressively. Steroids should be used at the lowest dose for the shortest possible period, and other drugs that can reduce symptoms should be used whenever possible.][
]
Epidemiology
The global rates of SLE are approximately 20–70 per 100,000 people. In females, the rate is highest between 45 and 64 years of age. The lowest overall rate exists in Iceland and Japan. The highest rates exist in the US and France. However, there is not sufficient evidence to conclude why SLE is less common in some countries compared to others; it could be the environmental variability in these countries. For example, different countries receive different levels of sunlight, and exposure to UV rays affects dermatological symptoms of SLE.[
Certain studies hypothesize that a genetic connection exists between race and lupus which affects disease prevalence. If this is true, the racial composition of countries affects disease and will cause the incidence in a country to change as the racial makeup changes. To understand if this is true, countries with largely homogenous and racially stable populations should be studied to better understand incidence.][ Rates of disease in the developing world are unclear.][
The rate of SLE varies between countries, ethnicity, and sex, and changes over time.][ another estimate places the total affected population at 322,000 to over 1 million (98 to over 305 per 100,000).][ In Northern Europe the rate is about 40 per 100,000 people.][ Childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus generally presents between the ages of 3 and 15 and is four times more common in girls.
While the onset and persistence of SLE can show disparities between genders, socioeconomic status also plays a major role. Women with SLE and of lower socioeconomic status have been shown to have higher depression scores, higher body mass index, and more restricted access to medical care than women of higher socioeconomic statuses with the illness. People with SLE had more self-reported anxiety and depression scores if they were from a lower socioeconomic status.
]
Race
There are assertions that race affects the rate of SLE. However, a 2010 review of studies that correlate race and SLE identified several sources of systematic and methodological error, indicating that the connection between race and SLE may be spurious.[ Studies have not been conducted to determine whether people of different racial backgrounds receive differing levels of social support.][
If there is a difference, this could act as a confounding variable in studies correlating race and SLE.
Another caveat to note when examining studies about SLE is that symptoms are often self-reported. This process introduces additional sources of methodological error. Studies have shown that self-reported data is affected by more than just the patient's experience with the disease- social support, the level of helplessness, and abnormal illness-related behaviors also factor into a self-assessment. Additionally, other factors like the degree of social support that a person receives, socioeconomic status, health insurance, and access to care can contribute to an individual's disease progression.][
Racial differences in lupus progression have not been found in studies that control for the socioeconomic status ESof participants.][ The people who receive medical care have often accrued less disease-related damage and are less likely to be below the poverty line.][
]
Sex
SLE, like many autoimmune diseases, affects females more frequently than males, at a rate of about 9 to 1.[
Hormonal mechanisms could explain the increased incidence of SLE in females. The onset of SLE could be attributed to the elevated ]hydroxylation
In chemistry, hydroxylation refers to the installation of a hydroxyl group () into an organic compound. Hydroxylations generate alcohols and phenols, which are very common functional groups. Hydroxylation confers some degree of water-solubility ...
of estrogen
Estrogen (also spelled oestrogen in British English; see spelling differences) is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three ...
and the abnormally decreased levels of androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning ) is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This includes ...
s in females. In addition, differences in GnRH
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) is a releasing hormone responsible for the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary. GnRH is a tropic peptide hormone synthesized and released ...
signalling have also been shown to contribute to the onset of SLE. While females are more likely to relapse than males, the intensity of these relapses is the same for both sexes.CD40L
CD154, also called CD40 ligand or CD40L, is a protein that is primarily expressed on activated T cells and is a member of the TNF superfamily of molecules. It binds to CD40 (protein), CD40 on antigen-presenting cells (APC), which leads to many e ...
'', which can mutate or simply escape silencing by X-chromosome inactivation and contribute to the onset of SLE.Klinefelter syndrome
Klinefelter syndrome (KS), also known as 47,XXY, is a chromosome anomaly where a male has an extra X chromosome. These complications commonly include infertility and small, poorly functioning testicles (if present). These symptoms are often n ...
and SLE. XXY males with SLE have an abnormal X–Y translocation resulting in the partial triplication of the PAR1 gene region. Research has also implicated '' XIST'', which encodes a long non-coding RNA
Long non-coding RNAs (long ncRNAs, lncRNA) are a type of RNA, generally defined as transcripts more than 200 nucleotides that are not translated into protein. This arbitrary limit distinguishes long ncRNAs from small non-coding RNAs, such as mic ...
that coats the inactive member of the pair of X chromosomes in females as part of a ribonucleoprotein
Nucleoproteins are proteins conjugated with nucleic acids (either DNA or RNA). Typical nucleoproteins include ribosomes, nucleosomes and viral nucleocapsid proteins.
Structures
Nucleoproteins tend to be positively charged, facilitating inter ...
complex, as a source of autoimmunity.
Changing rate of disease
The rate of SLE in the United States increased from 1.0 in 1955 to 7.6 in 1974. Whether the increase is due to better diagnosis or an increased frequency of the disease is unknown.[
]
History
The history of SLE can be divided into three periods: classical, neoclassical, and modern. In each period, research and documentation advanced the understanding and diagnosis of SLE, leading to its classification as an autoimmune
In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an " autoimmune disease" ...
disease in 1851, and to the various diagnostic options and treatments now available to people with SLE. The advances made by medical science in the diagnosis and treatment of SLE have dramatically improved the life expectancy of a person diagnosed with SLE.
Etymology
There are several explanations ventured for the term lupus erythematosus. ' is Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
for "wolf",[ and in ]Medieval Latin
Medieval Latin was the form of Literary Latin used in Roman Catholic Church, Roman Catholic Western Europe during the Middle Ages. It was also the administrative language in the former Western Roman Empire, Roman Provinces of Mauretania, Numidi ...
was also used to refer to a disease of the skin, and "erythematosus" is derived from , Ancient Greek for "redness of the skin". All explanations originate with the reddish, butterfly-shaped malar rash that the disease classically exhibits across the nose and cheeks. The reason the term lupus was used to describe this disease comes from the mid-19th century. Many diseases that caused ulceration or necrosis were given the term "lupus" due to the wound being reminiscent of a wolf's bite. This is similar to the naming of lupus vulgaris or chronic facial tuberculosis, where the lesions are ragged and punched out and are said to resemble the bite of a wolf.
Classical period
The classical period began when the disease was first recognized in the Middle Ages. The term lupus is attributed to 12th-century Italian physician Rogerius Frugard, who used it to describe ulcerating sores on the legs of people.
Neoclassical period
The neoclassical period began in 1851 when the skin disease which is now known as discoid lupus was documented by the French physician, Pierre Cazenave. Cazenave termed the illness lupus and added the word erythematosus to distinguish this disease from other illnesses that affected the skin except they were infectious.Moritz Kaposi
Moritz Kaposi (, ; 23 October 1837 – 6 March 1902) was a physician and dermatologist from the Austro-Hungarian Empire who discovered the skin tumor that received his name (Kaposi's sarcoma).
Biography
Early life and name
Born in Kaposvár, ...
. They documented the physical effects of lupus as well as some insights into the possibility that the disease caused internal trauma. Von Hebra observed that lupus symptoms could last many years and that the disease could go "dormant" after years of aggressive activity and then re-appear with symptoms following the same general pattern. These observations led Hebra to term lupus a chronic disease in 1872.
Kaposi observed that lupus assumed two forms: the skin lesions (now known as discoid lupus) and a more aggravated form that affected not only the skin but also caused fever, arthritis, and other systemic disorders in people. The latter also presented a rash confined to the face, appearing on the cheeks and across the bridge of the nose; he called this the " butterfly rash". Kaposi also observed those patients who developed the butterfly rash were often afflicted with another disease such as tuberculosis, anemia, or chlorisis which often caused death.
Modern period
The modern period, beginning in 1920, saw major developments in research into the cause and treatment of discoid and systemic lupus. Research conducted in the 1920s and 1930s led to the first detailed pathologic descriptions of lupus and demonstrated how the disease affected the kidney, heart, and lung tissue.Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic () is a Nonprofit organization, private American Academic health science centre, academic Medical centers in the United States, medical center focused on integrated health care, healthcare, Mayo Clinic College of Medicine and Science ...
, they discovered that the white blood cells contained the nucleus of another cell that was pushing against the white cell's proper nucleus.anti-nuclear antibody
Antinuclear antibodies (ANAs, also known as antinuclear factor or ANF) are autoantibodies that bind to contents of the cell nucleus. In normal individuals, the immune system produces antibodies to foreign proteins (antigens) but not to human pro ...
(ANA) reaction; the body produces antibodies against its own tissue. This discovery led to one of the first definitive tests for lupus since LE cells are found in approximately 60% of all people diagnosed with lupus. The LE cell test is rarely performed as a definitive lupus test today as LE cells do not always occur in people with SLE and can occur in individuals with other autoimmune diseases. Their presence can help establish a diagnosis but no longer indicates a definitive SLE diagnosis.
The discovery of the LE cell led to further research and this resulted in more definitive tests for lupus. Building on the knowledge that those with SLE had auto-antibodies that would attach themselves to the nuclei of normal cells, causing the immune system to send white blood cells to fight off these "invaders", a test was developed to look for the anti-nuclear antibody (ANA) rather than the LE cell specifically. This ANA test was easier to perform and led not only to a definitive diagnosis of lupus but also many other related diseases. This discovery led to the understanding of what is now known as autoimmune diseases.
To ensure that the person has lupus and not another autoimmune disease, the American College of Rheumatology
The American College of Rheumatology (ACR; until 1985 called American Rheumatism Association) is an organization of and for physicians, health professionals, and scientists that advances rheumatology through programs of education, research, advocac ...
(ACR) established a list of clinical and immunologic criteria that, in any combination, point to SLE. The criteria include symptoms that the person can identify (e.g. pain) and things that a physician can detect in a physical examination and through laboratory test results. The list was originally compiled in 1971, initially revised in 1982, and further revised and improved in 2009.
Medical historians have theorized that people with porphyria
Porphyria ( or ) is a group of disorders in which substances called porphyrins build up in the body, adversely affecting the skin or nervous system. The types that affect the nervous system are also known as Porphyria#Acute porphyrias, acute p ...
(a disease that shares many symptoms with SLE) generated folklore stories of vampires and werewolves, due to the photosensitivity, scarring, hair growth, and porphyrin brownish-red stained teeth in severe recessive forms of porphyria (or combinations of the disorder, known as dual, homozygous, or compound heterozygous porphyrias).quinine
Quinine is a medication used to treat malaria and babesiosis. This includes the treatment of malaria due to ''Plasmodium falciparum'' that is resistant to chloroquine when artesunate is not available. While sometimes used for nocturnal leg ...
was first reported as an effective therapy. Four years later, the use of salicylate
Salicylic acid is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H4COOH. A colorless (or white), bitter-tasting solid, it is a precursor to and a metabolite of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin). It is a plant hormone, and has been listed by the EPA To ...
s in conjunction with quinine was noted to be of still greater benefit. This was the best available treatment until the middle of the twentieth century when Hench discovered the efficacy of corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
s in the treatment of SLE.
Research
A study called BLISS-76 tested the drug belimumab
Belimumab, sold under the brand name Benlysta, is a human monoclonal antibody that inhibits B-cell activating factor (BAFF), also known as B-lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS). It is approved in the United States and Canada, and the European Union to ...
, a fully human monoclonal anti- BAFF (or anti-BLyS) antibody.self-protein Self-protein refers to all proteins endogenously produced by DNA-level transcription and translation within an organism of interest. This does not include proteins synthesized due to viral infection, but may include those synthesized by commensal ...
. It was approved by the FDA in March 2011.[ Genetically engineered immune cells are also being studied in animal models of the disease as of 2019.
In September 2022, researchers at the ]University of Erlangen-Nuremberg
A university () is an institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Univ ...
published promising results using genetically altered immune cells to treat severely ill patients. Four women and one man received transfusions of CAR T cells modified to attack their B cell
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasm ...
s, eliminating the aberrant ones. The therapy drove the disease into remission in all five patients, who have been off lupus medication for several months after the treatment ended.
Famous cases
* Shannon Boxx
Shannon Leigh Boxx Spearman (; born June 29, 1977) is an American retired soccer player and former member of the United States women's national soccer team, playing the defensive midfielder position. She last played club soccer for the Chicago Re ...
, U.S. Olympic team soccer player
* Nick Cannon
Nicholas Scott Cannon (born October 8, 1980) is an American comedian, television presenter, actor, and rapper. In television, he began his career as a teenager on Nickelodeon's '' All That'' before going on to host '' The Nick Cannon Show'', '' ...
, American television host, actor, rapper, and comedian
* Pumpuang Duangjan, Thai Luk Thung
Luk thung (, , ) is a genre of Thai music that emerged after World War II in the Central Thailand, central region of Thailand. The genre was derived from phleng Thai sakon, and developed in the early-20th century. Suphan Buri in particular beca ...
singer many Thai people know this disease as "Phumpuang disease" because she died from the disease.
* Selena Gomez
Selena Marie Gomez ( ; born July 22, 1992) is an American actress, singer, songwriter, producer, and businesswoman. Gomez began her career as a child actress, appearing on the children's television series ''Barney & Friends'' (2002–2004), a ...
, singer, actress, producer, and businesswoman
* Sally Hawkins
Sally Cecilia Hawkins (born 27 April 1976) is an English actress of stage and screen. She began her career on stage and then moved into film, for which she has received several accolades including a Golden Globe Award, in addition to nominatio ...
, actress
* Flannery O'Connor
Mary Flannery O'Connor (March 25, 1925August 3, 1964) was an American novelist, short story writer, and essayist. She wrote two novels and 31 short stories, as well as a number of reviews and commentaries.
O'Connor was a Southern writer who of ...
, Southern Gothic
Southern Gothic is an artistic subgenre of Gothic fiction, fiction, Popular music, music, Gothic film, film, theatre, and television that are heavily influenced by Gothic fiction, Gothic elements and the Southern United States, American South. ...
novelist and short-story author
* Michael Jackson
Michael Joseph Jackson (August 29, 1958 – June 25, 2009) was an American singer, songwriter, dancer, and philanthropist. Dubbed the "King of Pop", he is regarded as Cultural impact of Michael Jackson, one of the most culturally significan ...
, American singer, songwriter, dancer and philanthropist
* Seal
Seal may refer to any of the following:
Common uses
* Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly:
** Earless seal, also called "true seal"
** Fur seal
** Eared seal
* Seal ( ...
, British singerToni Braxton
Toni Michele Braxton (born October 7, 1966) is an American singer, songwriter, actress and television personality. She has sold over 70 million records worldwide and is one of the best-selling female artists in history. Braxton has won seven ...
, American singer, songwriter, actress and television personality
See also
*Childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus
Childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus (i.e., cSLE), also termed juvenile-onset systemic lupus erythematosus, juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus, and pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus, is a form of the chronic inflammatory and autoi ...
* Canine discoid lupus erythematosus in dogs
* List of people with lupus
This is a categorised, alphabetical list of notable people who have been diagnosed with lupus.
Lupus is a collection of autoimmune diseases in which the human immune system becomes hyperactive and attacks healthy tissues. Symptoms of these dis ...
References
External links
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
at the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases
{{Autoimmune diseases
Autoimmune diseases
Cutaneous lupus erythematosus
Disorders causing seizures
Disorders of fascia
Epstein–Barr virus–associated diseases
Steroid-responsive inflammatory conditions
Systemic connective tissue disorders
Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate
William Osler
 SLE is one of several diseases known as "
SLE is one of several diseases known as "
 As many as 70% of people with lupus have some skin symptoms. The three main categories of lesions are chronic cutaneous (discoid) lupus, subacute cutaneous lupus, and acute cutaneous lupus. People with discoid lupus may exhibit thick, red scaly patches on the skin. Similarly, subacute cutaneous lupus manifests as red, scaly patches of skin but with distinct edges. Acute cutaneous lupus manifests as a rash. Some have the classic
As many as 70% of people with lupus have some skin symptoms. The three main categories of lesions are chronic cutaneous (discoid) lupus, subacute cutaneous lupus, and acute cutaneous lupus. People with discoid lupus may exhibit thick, red scaly patches on the skin. Similarly, subacute cutaneous lupus manifests as red, scaly patches of skin but with distinct edges. Acute cutaneous lupus manifests as a rash. Some have the classic  Impaired clearance of dying cells is a potential pathway for the development of this systemic
Impaired clearance of dying cells is a potential pathway for the development of this systemic  In healthy conditions, apoptotic lymphocytes are removed in
In healthy conditions, apoptotic lymphocytes are removed in 