|
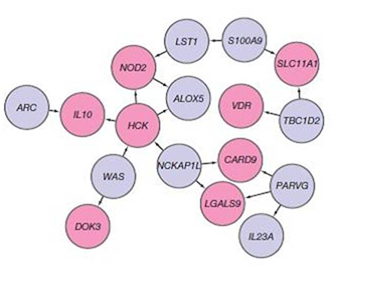
DNASE1L3
Deoxyribonuclease gamma (also termed DNase γ, deoxyribonuclease 1L3, DNASE1L3, of deoxyribonuclease I like 3) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''DNASE1L3'' (also termed the ''deoxyribonuclease 1L3'' or ''deoxyribonuclease 1 like 3'') gene. This gene's is located on chromosome 3's " p arm", i.e., short arm, between region 1, band 4, sub-band 3 and region 2, band 1, sub-band 1 (this location's is abbreviation as 3p14.3-p21.1) Function DNASE1L3 belongs to the family of deoxyribonuclease enzymes that are responsible for degrading DNA. Specifically, DNASE1L3 plays a key role in the breakdown of extracellular DNA, particularly DNA released from dying cells due to apoptosis or necrosis. This function is important for maintaining cellular homeostasis and preventing the accumulation of DNA debris, which could otherwise trigger widespread inflammatory autoimmune responses. Clinical significance Role in autoimmune response Humans with inactivating mutations in both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deoxyribonuclease
Deoxyribonuclease (DNase, for short) refers to a group of glycoprotein endonucleases which are enzymes that catalyze the hydrolytic cleavage of phosphodiester linkages in the DNA backbone, thus degrading DNA. The role of the DNase enzyme in cells includes breaking down extracellular DNA (ecDNA) excreted by apoptosis, necrosis, and neutrophil extracellular traps (NET) of cells to help reduce inflammatory responses that otherwise are elicited. A wide variety of deoxyribonucleases are known and fall into one of two families ( DNase I or DNase II), which differ in their substrate specificities, chemical mechanisms, and biological functions. Laboratory applications of DNase include purifying proteins when extracted from prokaryotic organisms. Additionally, DNase has been applied as a treatment for diseases that are caused by ecDNA in the blood plasma. Assays of DNase are emerging in the research field as well. Types The two main types of DNase found in animals are known as deoxy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigens
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule, moiety, foreign particulate matter, or an allergen, such as pollen, that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. Antigens can be proteins, peptides (amino acid chains), polysaccharides (chains of simple sugars), lipids, or nucleic acids. Antigens exist on normal cells, cancer cells, parasites, viruses, fungi, and bacteria. Antigens are recognized by antigen receptors, including antibodies and T-cell receptors. Diverse antigen receptors are made by cells of the immune system so that each cell has a specificity for a single antigen. Upon exposure to an antigen, only the lymphocytes that recognize that antigen are activated and expanded, a process known as clonal selection. In most cases, antibodies are ''antigen-specific'', meaning that an antibody can only react to and bind one specific antigen; in some instances, however, antibodies may cross-react ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
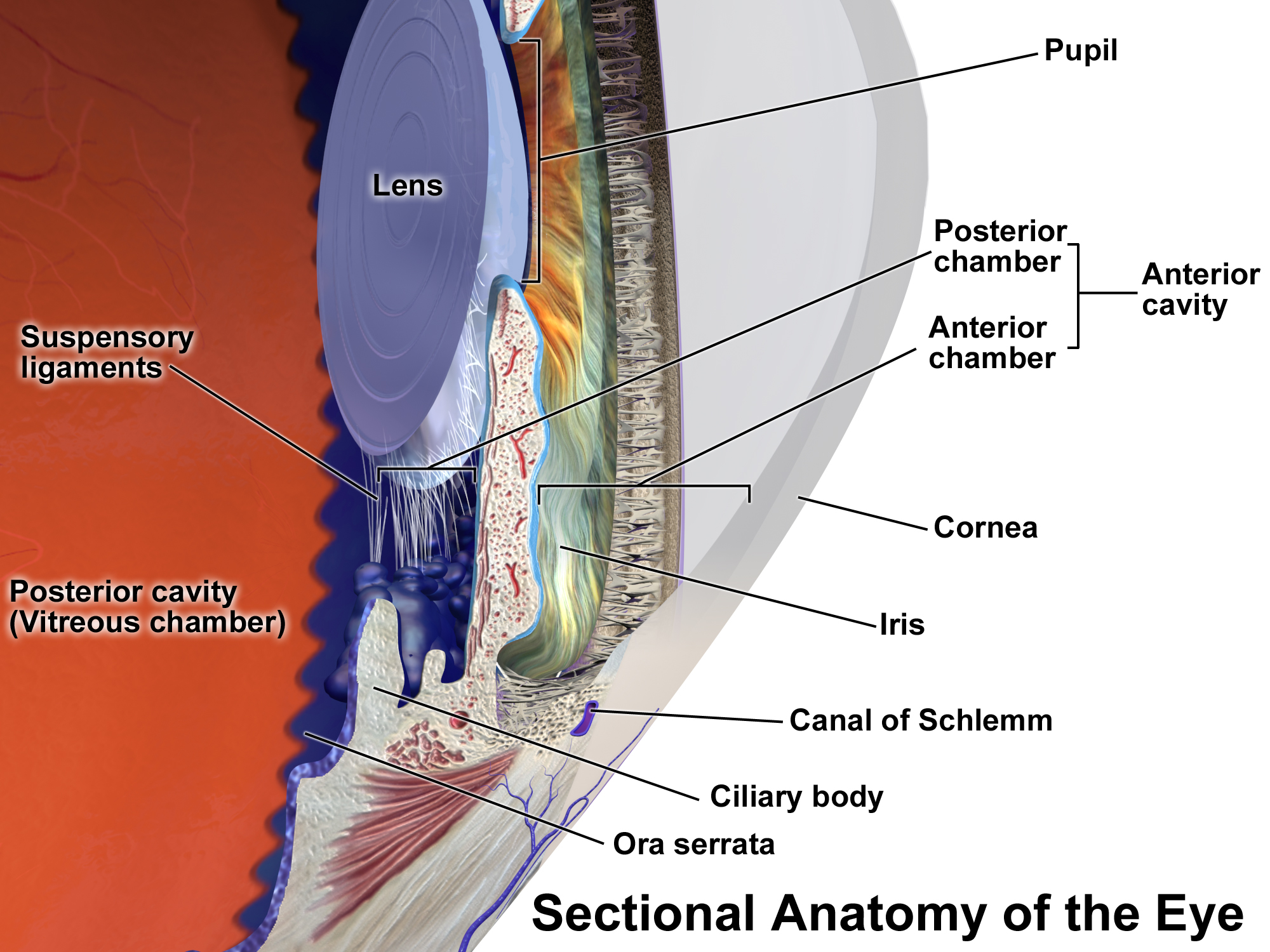
Scleritis
Scleritis is a serious inflammatory disease that affects the white outer coating of the eye, known as the sclera. The disease is often contracted through association with other diseases of the body, such as granulomatosis with polyangiitis or rheumatoid arthritis. There are three types of scleritis: diffuse scleritis (the most common), nodular scleritis, and necrotizing scleritis (the most severe). Scleritis may be the first symptom of onset of connective tissue disease. Episcleritis is inflammation of the episclera, a less serious condition that seldom develops into scleritis. Signs and symptoms Symptoms of scleritis include: *Redness of the sclera and conjunctiva, sometimes changing to a purple hue *Severe ocular pain, which may radiate to the temple or jaw. The pain is often described as deep or boring. *Photophobia and tearing *Decrease in visual acuity, possibly leading to blindness The pain of episcleritis is less severe than in scleritis. In hyperemia, there is a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uveitis
Uveitis () is inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented layer of the eye between the inner retina and the outer fibrous layer composed of the sclera and cornea. The uvea consists of the middle layer of pigmented vascular structures of the eye and includes the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. Uveitis is described anatomically, by the part of the eye affected, as anterior, intermediate or posterior, or panuveitic if all parts are involved. Anterior uveitis ( iridocyclitis) is the most common, with the incidence of uveitis overall affecting approximately 1:4500, most commonly those between the ages of 20–60. Symptoms include eye pain, eye redness, floaters and blurred vision, and ophthalmic examination may show dilated ciliary blood vessels and the presence of cells in the anterior chamber. Uveitis may arise spontaneously, have a genetic component, or be associated with an autoimmune disease or infection. While the eye is a relatively protected environment, its immune mecha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of inflammatory conditions of the colon and small intestine, with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis (UC) being the principal types. Crohn's disease affects the small intestine and large intestine, as well as the mouth, esophagus, stomach and the anus, whereas UC primarily affects the colon and the rectum. Signs and symptoms In spite of Crohn's and UC being very different diseases, both may present with any of the following symptoms: abdominal pain, diarrhea, rectal bleeding, severe internal cramps/muscle spasms in the region of the pelvis and weight loss. Anemia is the most prevalent extraintestinal complication of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Associated complaints or diseases include arthritis, pyoderma gangrenosum, primary sclerosing cholangitis, and non-thyroidal illness syndrome (NTIS). Associations with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP) have also been reported. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are involved, with the same joints typically involved on both sides of the body. The disease may also affect other parts of the body, including skin, eyes, lungs, heart, nerves, and blood. This may result in a anemia, low red blood cell count, pleurisy, inflammation around the lungs, and pericarditis, inflammation around the heart. Fever and low energy may also be present. Often, symptoms come on gradually over weeks to months. While the cause of rheumatoid arthritis is not clear, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The underlying mechanism involves the body's immune system attacking the joints. This results in inflammation and thickening of the synovium, joint capsule. It also affects the und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inborn Error Of Immunity
Inborn errors of immunity (IEI) are a heterogenous group of disorders in which a mutation in any one of various genes that regulate the immune system causes increases in the susceptibility of individuals to develop a dysfunction in their immune system. (As used here, mutations include deletions or other changes in any part of a gene that causes it to be dysfunctional.) Depending on the gene involved, this dysfunction may induce the development of an: a) autoinflammatory disease by causing a malfunction in the innate immune system; b) autoimmune disease by causing a malfunction in the adaptive immune system; c) viral, bacterial, fungal, or mycobacterial infection by causing a malfunction in one of the various components of the immune system that combat these pathogens; d) allergic disease by causing a hypersensitive immune system that overreacts to otherwise harmless substances; e) lose of one or more types of circulating blood cells by causing a failure of the bone marrow to pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilateria, bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and Coelenterata, diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the Anatomical_terms_of_location#Rostral,_cranial,_and_caudal, rostral (nose end) to caudal (tail end) axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain, though precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets. The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals. Overview In vertebrates, the brain and spinal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney Failure
Kidney failure, also known as renal failure or end-stage renal disease (ESRD), is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as either acute kidney failure, which develops rapidly and may resolve; and chronic kidney failure, which develops slowly and can often be irreversible. Symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vomiting, loss of appetite, and confusion. Complications of acute and chronic failure include uremia, hyperkalemia, and volume overload. Complications of chronic failure also include heart disease, high blood pressure, and anaemia. Causes of acute kidney failure include low blood pressure, blockage of the urinary tract, certain medications, muscle breakdown, and hemolytic uremic syndrome. Causes of chronic kidney failure include diabetes, high blood pressure, nephrotic syndrome, and polycystic kidney diseas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lupus Nephritis
Lupus nephritis is an inflammation of the kidneys caused by systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus which is a more severe form of SLE that develops in children up to 18 years old; both are autoimmune diseases. It is a type of glomerulonephritis in which the glomerulus (kidney), glomeruli become inflamed. Since it is a result of SLE, this type of glomerulonephritis is said to be ''secondary'', and has a different pattern and outcome from conditions with a ''primary'' cause originating in the kidney. The diagnosis of lupus nephritis depends on blood tests, urinalysis, X-rays, ultrasound scans of the kidneys, and a kidney biopsy. On urinalysis, a nephritic picture is found and urinary cast#Red blood cell casts, red blood cell casts, red blood cells and proteinuria is found. Signs and symptoms In lupus nephritis, common symptoms of lupus such as fever, arthralgia, joint pain, myalgia, muscle pain, and a malar rash, butterfly-shaped rash on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |