|
SOS1
Son of sevenless homolog 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SOS1'' gene. Function SOS1 is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) which interacts with Ras protein, Ras proteins to phosphorylate GDP into GTP, or from an inactive state to an active state to signal cell proliferation. RAS genes (e.g., MIM 190020) encode membrane-bound guanine nucleotide-binding proteins that function in the transduction of signals that control cell growth and differentiation. Binding of GTP activates RAS proteins, and subsequent hydrolysis of the bound GTP to GDP and phosphate inactivates signaling by these proteins. GTP binding can be catalyzed by guanine nucleotide exchange factors for RAS, and GTP hydrolysis can be accelerated by GTPase-activating protein, GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs). The first exchange factor to be identified for RAS was the ''S. cerevisiae'' Cdc25 gene product (not to be confused with the ''S. pombe'' Cdc25). Genetic analysis indicated that CDC25 is ess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Son Of Sevenless
In cell signalling, ''Son of Sevenless'' (''SOS'') refers to a set of genes encoding guanine nucleotide exchange factors that act on the Ras subfamily of small GTPases. History and name The gene was so named because the Sos protein that it encoded was found to operate downstream of the ''sevenless'' gene in ''Drosophila melanogaster'' in a MAPK/ERK pathway, Ras/MAP kinase pathway. When ''sevenless'' is mutated or otherwise dysfunctional during development of the fly's ultraviolet light-sensitive compound eye, the seventh, central photoreceptor (R7) of each ommatidium fails to form. Similarly, the mammalian orthologues of Sos, SOS1 and SOS2, function downstream of many growth factor and adhesion receptors. Function Ras-GTPases act as molecular switches that bind to downstream effectors, such as the protein kinase c-Raf, and localise them to the membrane, resulting in their activation. Ras-GTPases are considered inactive when bound to guanosine diphosphate (GDP), and active when b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
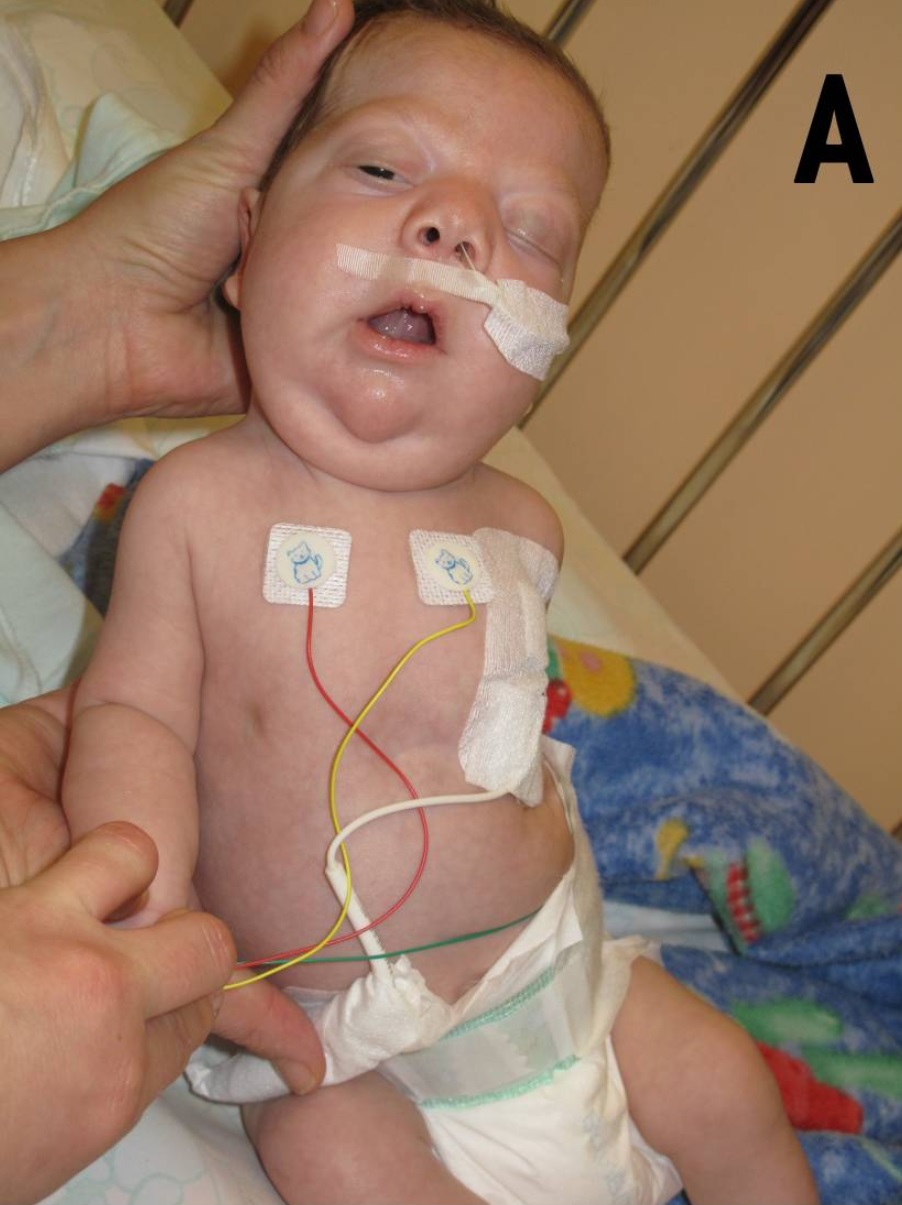
Noonan Syndrome
Noonan syndrome (NS) is a genetic disorder that may present with mildly unusual facial features, short height, congenital heart disease, bleeding problems, and skeletal malformations. Facial features include widely spaced eyes, light-colored eyes, low-set ears, a short neck, and a small lower jaw. Heart problems may include pulmonary valve stenosis. The breast bone may either protrude or be sunken, while the spine may be abnormally curved. Intelligence is often normal. Complications of NS can include leukemia. Some of NS' symptoms are shared with Watson syndrome, a related genetic condition. A number of genetic mutations can result in Noonan syndrome. The condition may be inherited as an autosomal dominant condition or occur as a new mutation. Noonan syndrome is a type of RASopathy, the underlying mechanism for which involves sustained activation of the RAS/MAPK cell signaling pathway. The diagnosis may be suspected based on symptoms, medical imaging, and blood test ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor
Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) are proteins or protein domains that activate monomeric GTPases by stimulating the release of guanosine diphosphate (GDP) to allow binding of guanosine triphosphate (GTP). A variety of unrelated structural domains have been shown to exhibit guanine nucleotide exchange activity. Some GEFs can activate multiple GTPases while others are specific to a single GTPase. Function Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) are proteins or protein domains involved in the activation of small GTPases. Small GTPases act as molecular switches in intracellular signaling pathways and have many downstream targets. The most well-known GTPases comprise the Ras superfamily and are involved in essential cell processes such as cell differentiation and proliferation, cytoskeletal organization, vesicle trafficking, and nuclear transport. GTPases are active when bound to GTP and inactive when bound to GDP, allowing their activity to be regulated by GEFs and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PTPN11
Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 11 (PTPN11) also known as protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1D (PTP-1D), Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase-2 (SHP-2), or protein-tyrosine phosphatase 2C (PTP-2C) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PTPN11'' gene. PTPN11 is a protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) Shp2. PTPN11 is a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family. PTPs are known to be signaling molecules that regulate a variety of cellular processes including cell growth, differentiation, mitotic cycle, and oncogenic transformation. This PTP contains two tandem Src homology-2 domains, which function as phospho-tyrosine binding domains and mediate the interaction of this PTP with its substrates. This PTP is widely expressed in most tissues and plays a regulatory role in various cell signaling events that are important for a diversity of cell functions, such as mitogenic activation, metabolic control, transcription regulation, and cell migra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ABI1
Abl interactor 1 also known as Abelson interactor 1 (Abi-1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ABI1'' gene. Function Abl interactor 1 has been found to form a complex with EPS8 and SOS1, and is thought to be involved in the transduction of signals from Ras to Rac. In addition, the encoded protein may play a role in the regulation of EGF-induced Erk pathway activation as well as cytoskeletal reorganization and EGFR signaling. Several transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been found for this gene. Abi1 is adaptor protein. It interacts with c-Abl and WAVE2 which is an actin polymerization regulator. It is known that Abi1 enhances the phosphorylation of WAVE2 by c-Abl. The phosphorylation of c-Abl promotes actin polymerization. Furthermore, Abi1 is a component of the WAVE complex. Some research has shown that knockdown of Abi1 by siRNA promoted degradation of WAVE complex proteins. Interactions ABI1 has been shown to interact with ENAH, NCKAP1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EPS8
Epidermal growth factor receptor kinase substrate 8 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''EPS8'' gene. Function This gene encodes a member of the EPS8 family. This protein contains one PH domain and one SH3 domain. It functions as part of the EGFR pathway, though its exact role has not been determined. Highly similar proteins in other organisms are involved in the transduction of signals from Ras to Rac and growth factor-mediated actin remodeling. Alternate transcriptional splice variants of this gene have been observed but have not been thoroughly characterized. Clinical significance Mutations in EPS8 cause congenital deafness. Interactions EPS8 has been shown to interact with: * ABI1, * BAIAP2, * DVL1, * SHB, * SHC1 * SOS1 Son of sevenless homolog 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SOS1'' gene. Function SOS1 is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) which interacts with Ras protein, Ras proteins to phosphorylate GDP into GTP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SH3KBP1
SH3 domain-containing kinase-binding protein 1 (synonyms - CIN85, in rodents - Ruk) is an adaptor protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SH3KBP1'' gene. Function CBL (MIM 165360) constitutively interacts with SH3 domain-containing proteins and, upon tyrosine phosphorylation, with SH2 domain-containing proteins. The SH3KBP1 gene encodes an 85-kD CBL-interacting protein that enhances tumor necrosis factor (MIM 191160)-mediated apoptotic cell death (Narita et al., 2001). upplied by OMIMref name="entrez"> Interactions SH3KBP1 has been shown to interact with B-cell linker, Grb2, SH3GLB2, SH3GL3, SH3GL2, BCAR1, Epidermal growth factor receptor, CBLB, Cbl gene, SOS1 Son of sevenless homolog 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SOS1'' gene. Function SOS1 is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) which interacts with Ras protein, Ras proteins to phosphorylate GDP into GTP, or from an inacti ..., CRK and PAK2. References Further reading ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NCK1
Cytoplasmic protein NCK1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NCK1'' gene. Gene The Nck (non-catalytic region of tyrosine kinase adaptor protein 1) belongs to the adaptor family of proteins. The nck gene was initially isolated from a human melanoma cDNA library using a monoclonal antibody produced against the human melanoma-associated antigen. The Nck family has two known members in human cells (Nck-1/Nckalpha and NcK2/NcKbeta), two in mouse cells (mNckalpha and mNckbeta/Grb4) and one in drosophila (Dock means dreadlocks-ortholog). The two murine gene products exhibit 68% amino acid identity to one another, with most of the sequence variation being located to the linker regions between the SH3 and SH2 domains, and are 96% identical to their human counterparts. While human nck-1 gene has been localised to the 3q21 locus of chromosome 3, the nck-2 gene can be found on chromosome 2 at the 2q12 locus. Function The protein encoded by this gene is one of the signal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MUC1
Mucin short variant S1, also called polymorphic epithelial mucin (PEM) or epithelial membrane antigen (EMA), is a mucin encoded by the ''MUC1'' gene in humans. Mucin short variant S1 is a glycoprotein with extensive O-linked glycosylation of its extracellular domain. Mucins line the apical surface of epithelial cells in the lungs, stomach, intestines, eyes and several other organs. Mucins protect the body from infection by pathogen binding to oligosaccharides in the extracellular domain, preventing the pathogen from reaching the cell surface. Overexpression of MUC1 is often associated with colon, breast, ovarian, lung and pancreatic cancers. Joyce Taylor-Papadimitriou identified and characterised the antigen during her work with breast and ovarian tumors. Structure MUC1 is a member of the mucin family and encodes a membrane bound, glycosylated phosphoprotein. MUC1 has a core protein mass of 120-225 kDa which increases to 250-500 kDa with glycosylation. It extends 200-500&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ITSN1
Intersectin-1 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''ITSN1'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a cytoplasmic membrane-associated protein that indirectly coordinates endocytic membrane traffic with the actin assembly machinery. In addition, the encoded protein may regulate the formation of clathrin-coated vesicles and could be involved in synaptic vesicle recycling. This protein has been shown to interact with dynamin, CDC42, SNAP23, SNAP25, SPIN90, EPS15, EPN1, EPN2, and STN2. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene, but the full-length nature of only two of them have been characterized so far. Interactions ITSN1 has been shown to Protein-protein interaction, interact with: * CDC42, * SCAMP1 * SNAP-25, and * SOS1. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{PDB Gallery, geneid=6453 EH-domain-containing proteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HRAS
GTPase HRas, from "Harvey Rat sarcoma virus", also known as transforming protein p21 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the gene. The ''HRAS'' gene is located on the short (p) arm of chromosome 11 (human), chromosome 11 at position 15.5, from base pair 522,241 to base pair 525,549. HRas is a small G protein in the Ras subfamily of the Ras superfamily of small GTPases. Once bound to Guanosine triphosphate, H-Ras will activate a Raf kinase like c-Raf, the next step in the MAPK/ERK pathway. Function GTPase HRas is involved in regulating cell division in response to growth factor stimulation. Growth factors act by binding cell surface Receptor (biochemistry), receptors that span the cell's plasma membrane. Once activated, receptors stimulate signal transduction events in the cytoplasm, a process by which proteins and second messengers relay signals from outside the cell to the cell nucleus and instructs the cell to grow or divide. The HRAS protein is a GTPase and is an earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grb2
Growth factor receptor-bound protein 2, also known as Grb2, is an adaptor protein involved in signal transduction/ cell communication. In humans, the GRB2 protein is encoded by the ''GRB2'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene binds receptors such as the epidermal growth factor receptor and contains one SH2 domain and two SH3 domains. Its two SH3 domains direct complex formation with proline-rich regions of other proteins, and its SH2 domain binds tyrosine phosphorylated sequences. This gene is similar to the ''sem-5'' gene of ''Caenorhabditis elegans'', which is involved in the signal transduction pathway. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Function and expression Grb2 is widely expressed and is essential for multiple cellular functions. Inhibition of Grb2 function impairs developmental processes in various organisms and blocks transformation and proliferation of various cell types. It is thus n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |