|
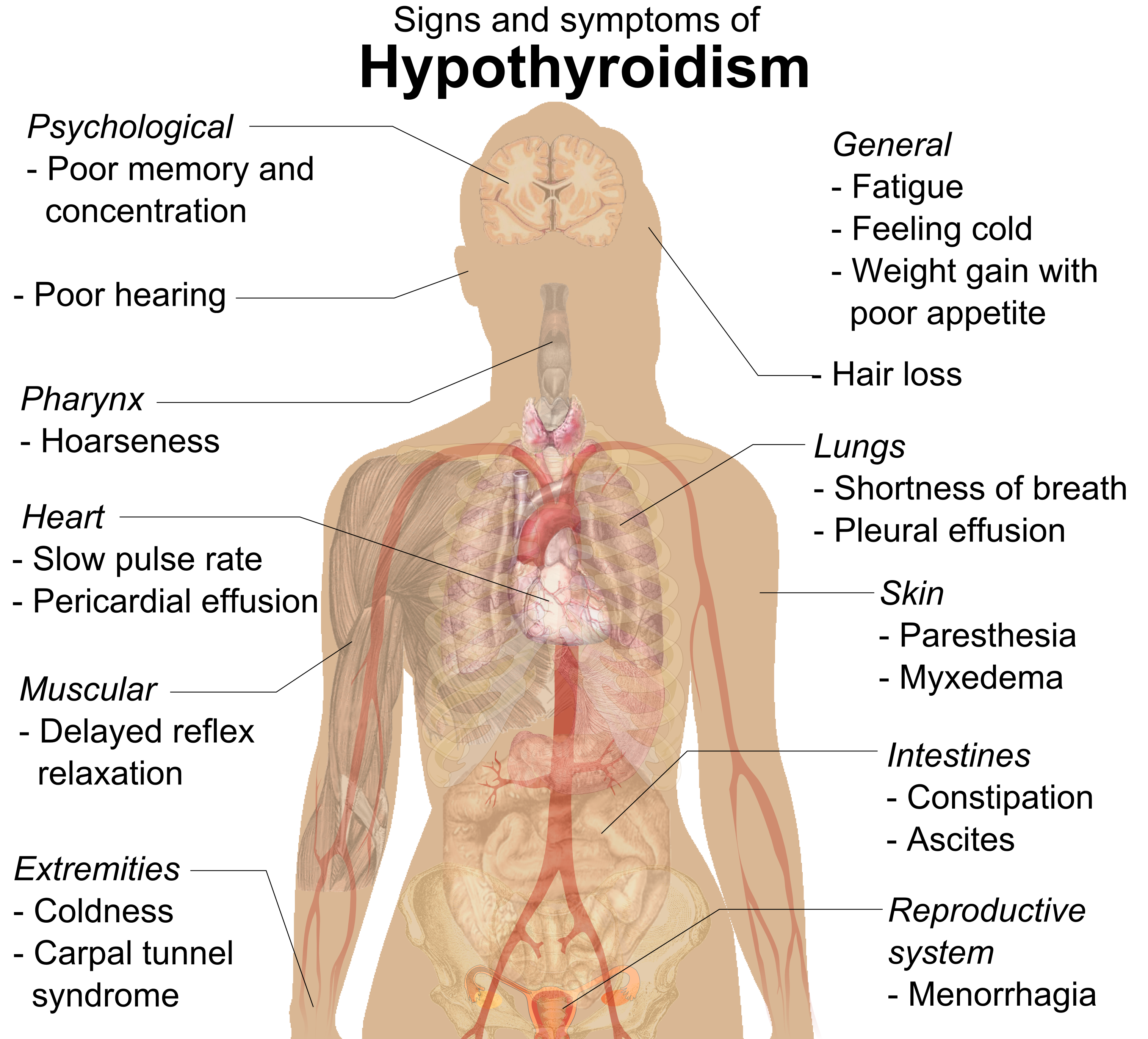
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism (also called ''underactive thyroid'', ''low thyroid'' or ''hypothyreosis'') is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as poor ability to tolerate cold, a feeling of tiredness, constipation, slow heart rate, depression, and weight gain. Occasionally there may be swelling of the front part of the neck due to goiter. Untreated cases of hypothyroidism during pregnancy can lead to delays in growth and intellectual development in the baby or congenital iodine deficiency syndrome. Worldwide, too little iodine in the diet is the most common cause of hypothyroidism. Hashimoto's thyroiditis is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in countries with sufficient dietary iodine. Less common causes include previous treatment with radioactive iodine, injury to the hypothalamus or the anterior pituitary gland, certain medications, a lack of a functioning t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
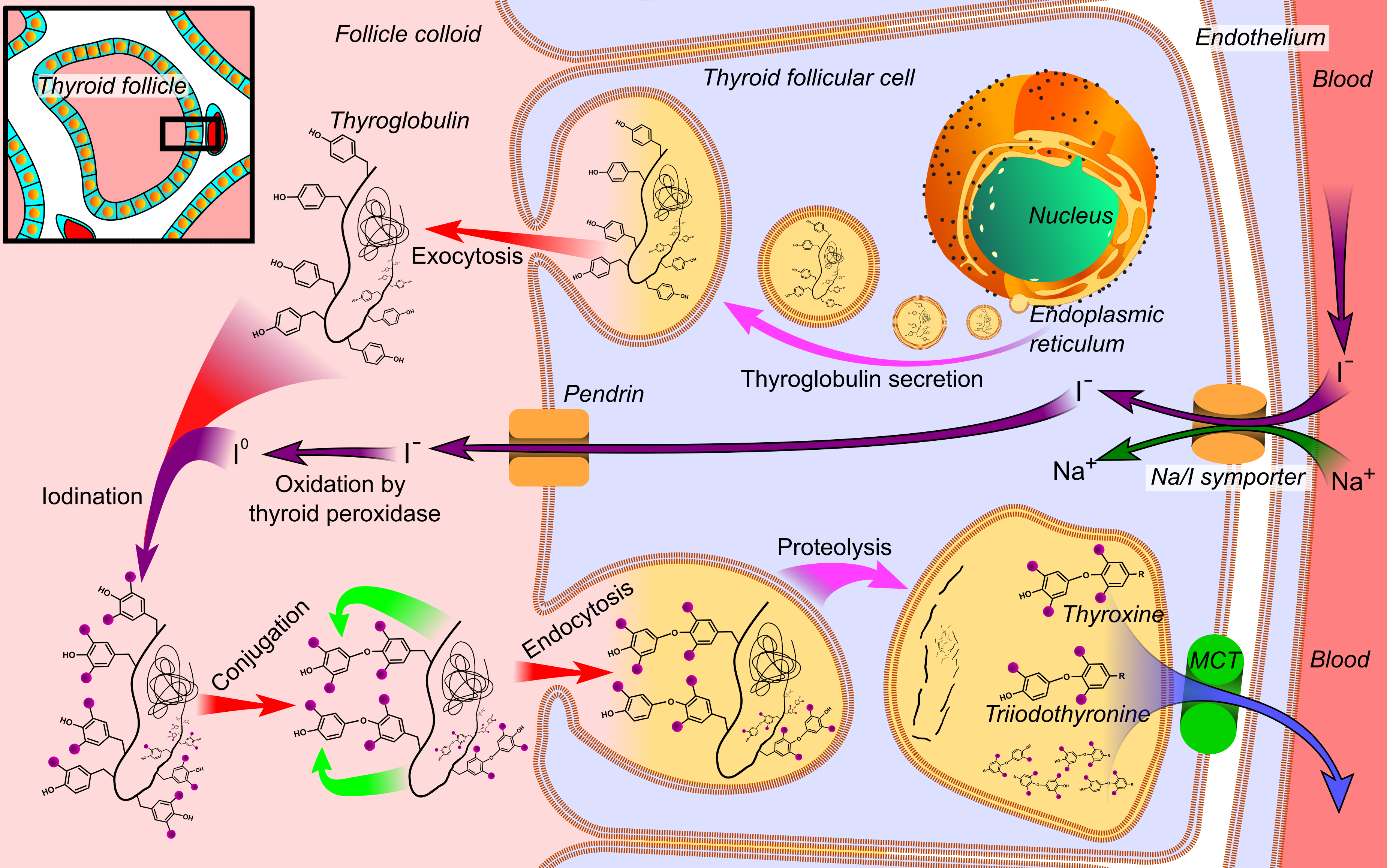
Thyroid Gland
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The thyroid is located at the front of the neck, below the Adam's apple. Microscopically, the functional unit of the thyroid gland is the spherical thyroid follicle, lined with follicular cells (thyrocytes), and occasional parafollicular cells that surround a lumen containing colloid. The thyroid gland secretes three hormones: the two thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)and a peptide hormone, calcitonin. The thyroid hormones influence the metabolic rate and protein synthesis, and in children, growth and development. Calcitonin plays a role in calcium homeostasis. Secretion of the two thyroid hormones is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland. TSH is regulated by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
Hashimoto's thyroiditis, also known as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis and Hashimoto's disease, is an autoimmune disease in which the thyroid gland is gradually destroyed. Early on, symptoms may not be noticed. Over time, the thyroid may enlarge, forming a painless goiter. Some people eventually develop hypothyroidism with accompanying weight gain, fatigue, constipation, depression, hair loss, and general pains. After many years the thyroid typically shrinks in size. Potential complications include thyroid lymphoma. Furthermore, because it is common for untreated patients of Hashimoto's to develop hypothyroidism, further complications can include, but are not limited to, high cholesterol, heart disease, heart failure, high blood pressure, myxedema, and potential pregnancy problems. Hashimoto's thyroiditis is thought to be due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Risk factors include a family history of the condition and having another autoimmune disease. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levothyroxine
Levothyroxine, also known as -thyroxine, is a manufactured form of the thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4). It is used to treat thyroid hormone deficiency (hypothyroidism), including a severe form known as myxedema coma. It may also be used to treat and prevent certain types of thyroid tumors. It is not indicated for weight loss. Levothyroxine is taken by mouth or given by intravenous injection. Maximum effect from a specific dose can take up to six weeks to occur. Side effects from excessive doses include weight loss, trouble tolerating heat, sweating, anxiety, trouble sleeping, tremor, and fast heart rate. Use is not recommended in people who have had a recent heart attack. Use during pregnancy has been found to be safe. Dosing should be based on regular measurements of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and T4 levels in the blood. Much of the effect of levothyroxine is following its conversion to triiodothyronine (T3). Levothyroxine was first made in 1927. It is on the World ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroxine
File:Thyroid_system.svg, upright=1.5, The thyroid system of the thyroid hormones T3 and T4 rect 376 268 820 433 Thyroid-stimulating hormone rect 411 200 849 266 Thyrotropin-releasing hormone rect 297 168 502 200 Hypothalamus rect 66 216 386 256 Anterior pituitary gland rect 66 332 342 374 Negative feedback rect 308 436 510 475 Thyroid gland rect 256 539 563 635 Thyroid hormones rect 357 827 569 856 Catecholamine rect 399 716 591 750 Metabolism desc bottom-left Thyroid hormones are any hormones produced and released by the thyroid gland, namely triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). They are tyrosine-based hormones that are primarily responsible for regulation of metabolism. T3 and T4 are partially composed of iodine. A deficiency of iodine leads to decreased production of T3 and T4, enlarges the thyroid tissue and will cause the disease known as simple goitre. The major form of thyroid hormone in the blood is thyroxine (T4), whose half-life of around one week ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid-stimulating Hormone
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (also known as thyrotropin, thyrotropic hormone, or abbreviated TSH) is a pituitary hormone that stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroxine (T4), and then triiodothyronine (T3) which stimulates the metabolism of almost every tissue in the body. It is a glycoprotein hormone produced by thyrotrope cells in the anterior pituitary gland, which regulates the endocrine function of the thyroid. Physiology Hormone levels TSH (with a half-life of about an hour) stimulates the thyroid gland to secrete the hormone thyroxine (T4), which has only a slight effect on metabolism. T4 is converted to triiodothyronine (T3), which is the active hormone that stimulates metabolism. About 80% of this conversion is in the liver and other organs, and 20% in the thyroid itself. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretinism
Congenital iodine deficiency syndrome is a medical condition present at birth marked by impaired physical and mental development, due to insufficient thyroid hormone (hypothyroidism) often caused by insufficient dietary iodine during pregnancy. It is one cause of underactive thyroid function at birth, called congenital hypothyroidism, historically referred to as cretinism (obsolete). If untreated, it results in impairment of both physical and mental development. Symptoms may include goiter, poor length growth in infants, reduced adult stature, thickened skin, hair loss, enlarged tongue, a protruding abdomen; delayed bone maturation and puberty in children; and mental deterioration, neurological impairment, impeded ovulation, and infertility in adults. In developed countries, thyroid function testing of newborns has assured that in those affected, treatment with the thyroid hormone thyroxine is begun promptly. This screening and treatment have virtually eliminated the consequences o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constipation
Constipation is a bowel dysfunction that makes bowel movements infrequent or hard to pass. The stool is often hard and dry. Other symptoms may include abdominal pain, bloating, and feeling as if one has not completely passed the bowel movement. Complications from constipation may include hemorrhoids, anal fissure or fecal impaction. The normal frequency of bowel movements in adults is between three per day and three per week. Babies often have three to four bowel movements per day while young children typically have two to three per day. Constipation has many causes. Common causes include slow movement of stool within the colon, irritable bowel syndrome, and pelvic floor disorders. Underlying associated diseases include hypothyroidism, diabetes, Parkinson's disease, celiac disease, non-celiac gluten sensitivity, colon cancer, diverticulitis, and inflammatory bowel disease. Medications associated with constipation include opioids, certain antacids, calcium channel b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goiter
A goitre, American and British English spelling differences#re er, or goiter, is a swelling in the neck resulting from an enlarged thyroid, thyroid gland. A goitre can be associated with a thyroid that is not functioning properly. Worldwide, over 90% of goitre cases are caused by iodine deficiency. The term is from the Latin ''gutturia'', meaning throat. Most goitres are not cancerous (Benign tumor, benign), though they may be potentially harmful. Signs and symptoms A goitre can present as a palpable or visible enlargement of the Thyroid, thyroid gland at the base of the neck. A goitre, if associated with hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, may be present with symptoms of the underlying disorder. For hyperthyroidism, the most common symptoms are associated with adrenergic stimulation: tachycardia (increased heart rate), palpitations, wikt:nervousness, nervousness, tremor, Hypertension, increased blood pressure and heat intolerance. Clinical manifestations are often related to hyperm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodine Deficiency
Iodine deficiency is a lack of the mineral (nutrient), trace element iodine, an essential nutrient in the diet (nutrition), diet. It may result in metabolic problems such as goiter, sometimes as an endemic goiter as well as congenital iodine deficiency syndrome due to untreated congenital hypothyroidism, which results in developmental delays and other health problems. Iodine deficiency is an important global health issue, especially for fertile and pregnant women. It is also a preventable cause of intellectual disability. Iodine is an essential mineral (nutrient), dietary mineral for neurodevelopment among children. The thyroid hormones thyroxine and triiodothyronine contain iodine. In areas where there is little iodine in the diet, typically remote inland areas where no marine foods are eaten, iodine deficiency is common. It is also common in mountainous regions of the world where food is grown in iodine-poor soil. Prevention includes adding small amounts of iodine to table sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |