Boron is a
chemical element
A chemical element is a chemical substance whose atoms all have the same number of protons. The number of protons is called the atomic number of that element. For example, oxygen has an atomic number of 8: each oxygen atom has 8 protons in its ...
; it has
symbol
A symbol is a mark, Sign (semiotics), sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, physical object, object, or wikt:relationship, relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by cr ...
B and
atomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of its atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei composed of protons and neutrons, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of pro ...
5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous
metalloid
A metalloid is a chemical element which has a preponderance of material property, properties in between, or that are a mixture of, those of metals and Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetals. The word metalloid comes from the Latin language, Latin ''meta ...
; in its
amorphous
In condensed matter physics and materials science, an amorphous solid (or non-crystalline solid) is a solid that lacks the long-range order that is a characteristic of a crystal. The terms "glass" and "glassy solid" are sometimes used synonymousl ...
form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the
boron group
The boron group are the chemical elements in periodic table group, group 13 of the periodic table, consisting of boron (B), aluminium (Al), gallium (Ga), indium (In), thallium (Tl) and nihonium (Nh). This group lies in the p-block of the perio ...
it has three
valence electron
In chemistry and physics, valence electrons are electrons in the outermost shell of an atom, and that can participate in the formation of a chemical bond if the outermost shell is not closed. In a single covalent bond, a shared pair forms with b ...
s for forming
covalent bond
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atom ...
s, resulting in many compounds such as
boric acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen orthoborate, trihydroxidoboron or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white ...
, the mineral
sodium borate Sodium borate is a generic name for any salt (chemistry), salt of sodium with an anion consisting of boron and oxygen, and possibly hydrogen, or any hydrate thereof. It can be seen as a hydrated sodium salt of the appropriate boroxy acid, although t ...
, and the ultra-hard crystals of
boron carbide
Boron carbide (chemical formula approximately B4C) is an extremely hard boron–carbon ceramic, a covalent material used in tank armor, bulletproof vests, engine sabotage powders,
as well as numerous industrial applications. With a Vickers har ...
and
boron nitride
Boron nitride is a thermally and chemically resistant refractory compound of boron and nitrogen with the chemical formula B N. It exists in various crystalline forms that are isoelectronic to a similarly structured carbon lattice. The hexago ...
.
Boron is synthesized entirely by
cosmic ray spallation and
supernova
A supernova (: supernovae or supernovas) is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. A supernova occurs during the last stellar evolution, evolutionary stages of a massive star, or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion ...
s and not by
stellar nucleosynthesis
In astrophysics, stellar nucleosynthesis is the creation of chemical elements by nuclear fusion reactions within stars. Stellar nucleosynthesis has occurred since the original creation of hydrogen, helium and lithium during the Big Bang. As a ...
, so it is a low-abundance element in the
Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
and in the
Earth's crust
Earth's crust is its thick outer shell of rock, referring to less than one percent of the planet's radius and volume. It is the top component of the lithosphere, a solidified division of Earth's layers that includes the crust and the upper ...
. It constitutes about 0.001 percent by weight of Earth's crust. It is concentrated on Earth by the water-solubility of its more common naturally occurring compounds, the
borate mineral
The Borate Minerals are minerals which contain a borate anion group. The borate (BO3) units may be polymerised similar to the SiO4 unit of the silicate mineral class. This results in B2O5, B3O6, B2O4 anions as well as more complex structures whic ...
s. These are mined industrially as
evaporite
An evaporite () is a water- soluble sedimentary mineral deposit that results from concentration and crystallization by evaporation from an aqueous solution. There are two types of evaporite deposits: marine, which can also be described as oce ...
s, such as
borax
The BORAX Experiments were a series of safety experiments on boiling water nuclear reactors conducted by Argonne National Laboratory in the 1950s and 1960s at the National Reactor Testing Station in eastern Idaho. and
kernite
Kernite, also known as rasorite, is a hydrated sodium borate hydroxide mineral with formula . It is a colorless to white mineral crystallizing in the monoclinic crystal system typically occurring as prismatic to acicular (crystal habit), acicular ...
. The largest known deposits are in
Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
, the largest producer of boron minerals.
Elemental boron is found in small amounts in
meteoroid
A meteoroid ( ) is a small rocky or metallic body in outer space.
Meteoroids are distinguished as objects significantly smaller than ''asteroids'', ranging in size from grains to objects up to wide. Objects smaller than meteoroids are classifie ...
s, but chemically uncombined boron is not otherwise found naturally on Earth.
Several
allotropes
Allotropy or allotropism () is the property of some chemical elements to exist in two or more different forms, in the same physical state, known as allotropes of the elements. Allotropes are different structural modifications of an element: th ...
exist:
amorphous
In condensed matter physics and materials science, an amorphous solid (or non-crystalline solid) is a solid that lacks the long-range order that is a characteristic of a crystal. The terms "glass" and "glassy solid" are sometimes used synonymousl ...
boron is a brown powder; crystalline boron is silvery to black, extremely hard (9.3 on the
Mohs scale
The Mohs scale ( ) of mineral hardness is a qualitative ordinal scale, from 1 to 10, characterizing scratch resistance of minerals through the ability of harder material to scratch softer material.
The scale was introduced in 1812 by the Ger ...
), and a poor
electrical conductor
In physics and electrical engineering, a conductor is an object or type of material that allows the flow of charge (electric current) in one or more directions. Materials made of metal are common electrical conductors. The flow of negatively c ...
at room temperature (1.5 × 10
−6 Ω
−1 cm
−1 room temperature electrical conductivity). The primary use of the element itself is as
boron filaments with applications similar to
carbon fibers
Carbon fibers American and British English spelling differences, or carbon fibres (alternatively CF, graphite fiber or graphite fibre) are fibers about in diameter and composed mostly of carbon atoms. Carbon fibers have several advantages: ...
in some high-strength materials.
Boron is primarily used in chemical compounds. About half of all production consumed globally is an additive in
fiberglass
Fiberglass (American English) or fibreglass (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English) is a common type of fibre-reinforced plastic, fiber-reinforced plastic using glass fiber. The fibers may be randomly arranged, flattened i ...
for insulation and structural materials. The next leading use is in
polymer
A polymer () is a chemical substance, substance or material that consists of very large molecules, or macromolecules, that are constituted by many repeat unit, repeating subunits derived from one or more species of monomers. Due to their br ...
s and
ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant, and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcela ...
s in high-strength, lightweight structural and
heat-resistant materials.
Borosilicate glass
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass with silica and boron trioxide as the main glass-forming constituents. Borosilicate glasses are known for having very low coefficients of thermal expansion (≈3 × 10−6 K−1 at 20 °C), ma ...
is desired for its greater strength and thermal shock resistance than ordinary soda lime glass. As
sodium perborate
Sodium perborate are chemical compounds with chemical formula (H2O)x. Commonly encountered salts are the anhydrous form (x = 0) and as a hydrate, hexahydrate (x = 6). These two species are sometimes called, respectively, "monohydrate" or PBS-1 a ...
, it is used as a
bleach
Bleach is the generic name for any chemical product that is used industrially or domestically to remove color from (i.e. to whiten) fabric or fiber (in a process called bleaching) or to disinfect after cleaning. It often refers specifically t ...
. A small amount is used as a
dopant
A dopant (also called a doping agent) is a small amount of a substance added to a material to alter its physical properties, such as electrical or optics, optical properties. The amount of dopant is typically very low compared to the material b ...
in
semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Its conductivity can be modified by adding impurities (" doping") to its crystal structure. When two regions with different doping level ...
s, and
reagent
In chemistry, a reagent ( ) or analytical reagent is a substance or compound added to a system to cause a chemical reaction, or test if one occurs. The terms ''reactant'' and ''reagent'' are often used interchangeably, but reactant specifies a ...
intermediates in the
synthesis of organic fine chemicals. A few boron-containing organic pharmaceuticals are used or are in study. Natural boron is composed of two stable isotopes, one of which (
boron-10) has a number of uses as a neutron-capturing agent.
Borate
A borate is any of a range of boron oxyanions, anions containing boron and oxygen, such as orthoborate , metaborate , or tetraborate ; or any salt of such anions, such as sodium metaborate, and borax . The name also refers to esters of su ...
s have low toxicity in mammals (similar to
table salt
In common usage, salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl). When used in food, especially in granulated form, it is more formally called table salt. In the form of a natural crystalline mineral, salt is also known as ro ...
) but are more toxic to
arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
s and are occasionally used as
insecticide
Insecticides are pesticides used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. The major use of insecticides is in agriculture, but they are also used in home and garden settings, i ...
s. Boron-containing organic antibiotics are known. Although only traces are required, it is an essential
plant nutrient.
History
The word ''boron'' was coined from ''
borax
The BORAX Experiments were a series of safety experiments on boiling water nuclear reactors conducted by Argonne National Laboratory in the 1950s and 1960s at the National Reactor Testing Station in eastern Idaho. '', the mineral from which it was isolated, by analogy with ''carbon'', which boron resembles chemically.

Borax in its mineral form (then known as tincal) first saw use as a glaze, beginning in
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
circa 300 AD. Some crude borax traveled westward, and was apparently mentioned by the alchemist
Jabir ibn Hayyan
Abū Mūsā Jābir ibn Ḥayyān (Arabic: , variously called al-Ṣūfī, al-Azdī, al-Kūfī, or al-Ṭūsī), died 806−816, is the purported author of a large number of works in Arabic, often called the Jabirian corpus. The treatises that ...
around 700 AD.
Marco Polo
Marco Polo (; ; ; 8 January 1324) was a Republic of Venice, Venetian merchant, explorer and writer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road between 1271 and 1295. His travels are recorded in ''The Travels of Marco Polo'' (also known a ...
brought some glazes back to Italy in the 13th century.
Georgius Agricola
Georgius Agricola (; born Georg Bauer; 24 March 1494 – 21 November 1555) was a German Humanist scholar, mineralogist and metallurgist. Born in the small town of Glauchau, in the Electorate of Saxony of the Holy Roman Empire, he was b ...
, in around 1600, reported the use of borax as a flux in
metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the ...
. In 1777,
boric acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen orthoborate, trihydroxidoboron or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white ...
was recognized in the hot springs (
soffioni) near
Florence
Florence ( ; ) is the capital city of the Italy, Italian region of Tuscany. It is also the most populated city in Tuscany, with 362,353 inhabitants, and 989,460 in Metropolitan City of Florence, its metropolitan province as of 2025.
Florence ...
, Italy, at which point it became known as ''sal sedativum'', with ostensible medical benefits. The mineral was named
sassolite, after
Sasso Pisano in Italy. Sasso was the main source of
Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
an borax from 1827 to 1872, when
American sources replaced it.
Boron compounds were rarely used until the late 1800s when
Francis Marion Smith's
Pacific Coast Borax Company first popularized and produced them in volume at low cost.
Boron was not recognized as an element until it was isolated by Sir
Humphry Davy
Sir Humphry Davy, 1st Baronet (17 December 177829 May 1829) was a British chemist and inventor who invented the Davy lamp and a very early form of arc lamp. He is also remembered for isolating, by using electricity, several Chemical element, e ...
and by
Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac
Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac ( , ; ; 6 December 1778 – 9 May 1850) was a French chemist and physicist. He is known mostly for his discovery that water is made of two parts hydrogen and one part oxygen by volume (with Alexander von Humboldt), f ...
and
Louis Jacques Thénard.
In 1808 Davy observed that electric current sent through a solution of borates produced a brown precipitate on one of the electrodes. In his subsequent experiments, he used potassium to
reduce boric acid instead of
electrolysis
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a technique that uses Direct current, direct electric current (DC) to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Electrolysis is commercially important as a stage in the separation of c ...
. He produced enough boron to confirm a new element and named it ''boracium''.
Gay-Lussac and Thénard used iron to reduce boric acid at high temperatures. By oxidizing boron with air, they showed that boric acid is its oxidation product.
Jöns Jacob Berzelius
Baron Jöns Jacob Berzelius (; 20 August 1779 – 7 August 1848) was a Swedish chemist. Berzelius is considered, along with Robert Boyle, John Dalton, and Antoine Lavoisier, to be one of the founders of modern chemistry. Berzelius became a memb ...
identified it as an element in 1824. Pure boron was arguably first produced by the American chemist Ezekiel Weintraub in 1909.
Characteristics of the element
Isotopes
Boron has two naturally occurring and stable
isotope
Isotopes are distinct nuclear species (or ''nuclides'') of the same chemical element. They have the same atomic number (number of protons in their Atomic nucleus, nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemica ...
s,
11B (80.1%) and
10B (19.9%). The mass difference results in a wide range of δ
11B values, which are defined as a fractional difference between the
11B and
10B and traditionally expressed in parts per thousand, in natural waters ranging from −16 to +59. There are 13 known isotopes of boron; the shortest-lived isotope is
7B which decays through
proton emission
Proton emission (also known as proton radioactivity) is a rare type of radioactive decay in which a proton is ejected from a atomic nucleus, nucleus. Proton emission can occur from high-lying excited states in a nucleus following a beta decay ...
and
alpha decay
Alpha decay or α-decay is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle (helium nucleus). The parent nucleus transforms or "decays" into a daughter product, with a mass number that is reduced by four and an a ...
with a
half-life Half-life is a mathematical and scientific description of exponential or gradual decay.
Half-life, half life or halflife may also refer to:
Film
* Half-Life (film), ''Half-Life'' (film), a 2008 independent film by Jennifer Phang
* ''Half Life: ...
of 3.5×10
−22 s. Isotopic fractionation of boron is controlled by the exchange reactions of the boron species B(OH)
3 and
(OH)4sup>−. Boron isotopes are also fractionated during mineral crystallization, during H
2O phase changes in
hydrothermal
Hydrothermal circulation in its most general sense is the circulation of hot water (Ancient Greek ὕδωρ, ''water'',Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon. revised and augmented throughout by Sir Henry Stuart Jones. with th ...
systems, and during
hydrothermal alteration
Metasomatism (from the Greek μετά ''metá'' "change" and σῶμα ''sôma'' "body") is the chemical alteration of a Rock (geology), rock by hydrothermal and other fluids. It is traditionally defined as metamorphism which involves a change in t ...
of
rock. The latter effect results in preferential removal of the
sup>10B(OH)4sup>−
ion onto clays. It results in solutions enriched in
11B(OH)
3 and therefore may be responsible for the large
11B enrichment in seawater relative to both
ocean
The ocean is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of Earth. The ocean is conventionally divided into large bodies of water, which are also referred to as ''oceans'' (the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian Ocean, Indian, Southern Ocean ...
ic crust and
continent
A continent is any of several large geographical regions. Continents are generally identified by convention (norm), convention rather than any strict criteria. A continent could be a single large landmass, a part of a very large landmass, as ...
al crust; this difference may act as an
isotopic signature
An isotopic signature (also isotopic fingerprint) is a ratio of non-radiogenic ' stable isotopes', stable radiogenic isotopes, or unstable radioactive isotopes of particular elements in an investigated material. The ratios of isotopes in a sample ...
.
The exotic
17B exhibits a
nuclear halo, i.e. its radius is appreciably larger than that predicted by the
liquid drop model.
NMR spectroscopy
Both
10B and
11B possess
nuclear spin
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
* Nuclear engineering
* Nuclear physics
* Nuclear power
* Nuclear reactor
* Nuclear weapon
* Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
* Nuclear space
* ...
. The nuclear spin of
10B is 3 and that of
11B is . These isotopes are, therefore, of use in
nuclear magnetic resonance
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a physical phenomenon in which nuclei in a strong constant magnetic field are disturbed by a weak oscillating magnetic field (in the near field) and respond by producing an electromagnetic signal with a ...
spectroscopy; and spectrometers specially adapted to detecting the boron-11 nuclei are available commercially. The
10B and
11B nuclei also cause splitting in the
resonances
Resonance is a phenomenon that occurs when an object or system is subjected to an external force or vibration whose frequency matches a resonant frequency (or resonance frequency) of the system, defined as a frequency that generates a maximu ...
of attached nuclei.
Allotropes

Boron forms four major
allotrope
Allotropy or allotropism () is the property of some chemical elements to exist in two or more different forms, in the same physical state, known as allotropes of the elements. Allotropes are different structural modifications of an element: the ...
s: α-rhombohedral and β-rhombohedral (α-R and β-R), γ-orthorhombic (γ) and β-tetragonal (β-T). All four phases are stable at
ambient conditions, and β-rhombohedral is the most common and stable. An α-tetragonal phase also exists (α-T), but is very difficult to produce without significant contamination. Most of the phases are based on B
12 icosahedra, but the γ phase can be described as a
rocksalt-type arrangement of the icosahedra and B
2 atomic pairs.
It can be produced by compressing other boron phases to 12–20 GPa and heating to 1500–1800 °C; it remains stable after releasing the temperature and pressure. The β-T phase is produced at similar pressures, but higher temperatures of 1800–2200 °C. The α-T and β-T phases might coexist at ambient conditions, with the β-T phase being the more stable.
Compressing boron above 160 GPa produces a boron phase with an as yet unknown structure, and this phase is a
superconductor at temperatures below 6–12 K.
Atomic structure
Atomic boron is the lightest element having an
electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
in a
p-orbital in its ground state. Its first three
ionization energies are higher than those for heavier group III elements, reflecting its electropositive character.
Chemistry of the element
Preparation
Elemental boron is rare and poorly studied because the pure material is extremely difficult to prepare. Most studies of "boron" involve samples that contain small amounts of carbon. Very pure boron is produced with difficulty because of contamination by carbon or other elements that resist removal.
Some early routes to elemental boron involved the reduction of
boric oxide with metals such as
magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
or
aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
. However, the product was often contaminated with
borides of those metals. Pure boron can be prepared by reducing volatile boron halides with
hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
at high temperatures. Ultrapure boron for use in the semiconductor industry is produced by the decomposition of
diborane at high temperatures and then further purified by the
zone melting
Zone melting (or zone refining, or floating-zone method, or floating-zone technique) is a group of similar methods of purifying crystals, in which a narrow region of a crystal is melted, and this molten zone is moved through the crystal. The molt ...
or
Czochralski process
The Czochralski method, also Czochralski technique or Czochralski process, is a method of crystal growth used to obtain single crystals (monocrystals) of semiconductors (e.g. silicon, germanium and gallium arsenide), metals (e.g. palladium, plati ...
es.
Reactions of the element
Crystalline
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macrosc ...
boron is a hard, black material with a melting point of above 2000 °C. Crystalline boron is chemically inert and resistant to attack by boiling
hydrofluoric or
hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid or spirits of salt, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride (HCl). It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungency, pungent smell. It is classified as a acid strength, strong acid. It is ...
. When finely divided, it is attacked slowly by hot concentrated
hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscosity, viscous than Properties of water, water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usua ...
, hot concentrated
nitric acid
Nitric acid is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but samples tend to acquire a yellow cast over time due to decomposition into nitrogen oxide, oxides of nitrogen. Most com ...
, hot
sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen, ...
or hot mixture of sulfuric and
chromic acid
Chromic acid is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is also a jargon for a solution formed by the addition of sulfuric acid to aqueous solutions of dichromate. It consists at least in part of chromium trioxide.
The term "chromic ...
s.
Since elemental boron is very rare, its chemical reactions are of little significance practically speaking. The elemental form is not typically used as a precursor to compounds. Instead, the extensive inventory of boron compounds are produced from borates.
[
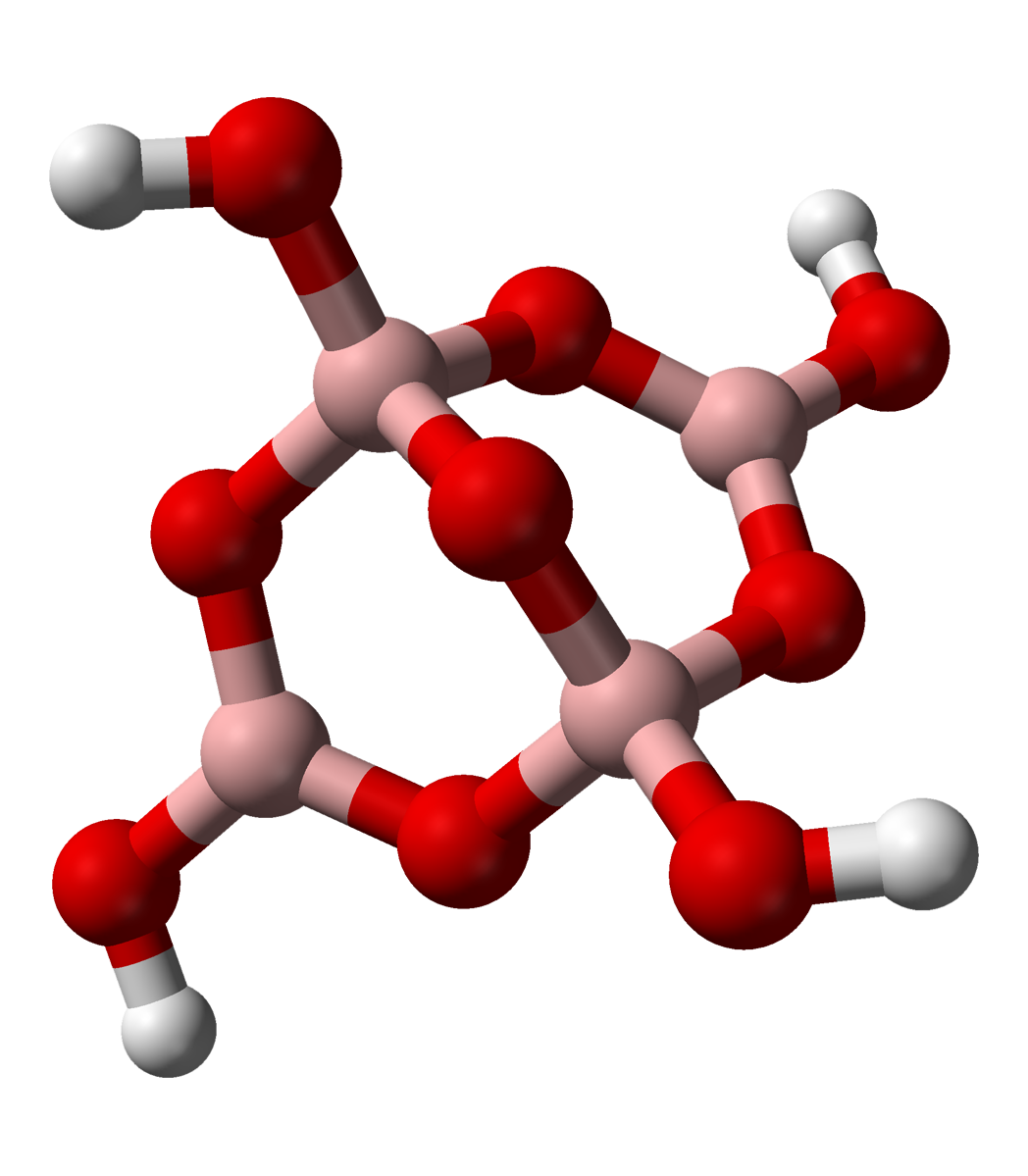
When exposed to air, under normal conditions, a protective oxide or hydroxide layer forms on the surface of boron, which prevents further corrosion. The rate of oxidation of boron depends on the crystallinity, particle size, purity and temperature. At higher temperatures boron burns to form ]boron trioxide
Boron trioxide or diboron trioxide is the oxide of boron with the formula . It is a colorless transparent solid, almost always glassy (amorphous), which can be crystallized only with great difficulty. It is also called boric oxide or boria. It h ...
:
Chemical compounds
General trends
In some ways, boron is comparable to carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
in its capability to form stable covalently bonded molecular networks (even nominally disordered (amorphous
In condensed matter physics and materials science, an amorphous solid (or non-crystalline solid) is a solid that lacks the long-range order that is a characteristic of a crystal. The terms "glass" and "glassy solid" are sometimes used synonymousl ...
) boron contains boron icosahedra, which are bonded randomly to each other without long-range order.). In terms of chemical behavior, boron compounds resembles silicon
Silicon is a chemical element; it has symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic lustre, and is a tetravalent metalloid (sometimes considered a non-metal) and semiconductor. It is a membe ...
. Aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
, the heavier congener of boron, does not behave analogously to boron: it is far more electropositive, it is larger, and it tends not to form homoatomic Al-Al bonds. In the most familiar compounds, boron has the formal oxidation state III. These include the common oxides, sulfides, nitrides, and halides, as well as organic derivativesoctet rule
The octet rule is a chemical rule of thumb that reflects the theory that main-group elements tend to bond in such a way that each atom has eight electrons in its valence shell, giving it the same electronic configuration as a noble gas. The ru ...
.
Halides
Boron forms the complete series of trihalides, i.e. BX3 (X = F, Cl, Br, I). The trifluoride is produced by treating borate salts with hydrogen fluoride
Hydrogen fluoride (fluorane) is an Inorganic chemistry, inorganic compound with chemical formula . It is a very poisonous, colorless gas or liquid that dissolves in water to yield hydrofluoric acid. It is the principal industrial source of fluori ...
, while the trichloride is produced by carbothermic reduction of boron oxides in the presence of chlorine gas: The trihalides adopt a planar trigonal structures, in contrast to the behavior of aluminium trihalides. All charge-neutral boron halides violate the octet rule, hence they typically are
The trihalides adopt a planar trigonal structures, in contrast to the behavior of aluminium trihalides. All charge-neutral boron halides violate the octet rule, hence they typically are Lewis acid
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any ...
ic. For example, boron trifluoride (BF3) combines eagerly with fluoride sources to give the tetrafluoroborate anion, BF4−. Boron trifluoride is used in the petrochemical industry as a catalyst. The halides react with water to form boric acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen orthoborate, trihydroxidoboron or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white ...
.[
]
Oxide derivatives
Boron-containing minerals exclusively exist as oxides of B(III), often associated with other elements. More than one hundred borate mineral
The Borate Minerals are minerals which contain a borate anion group. The borate (BO3) units may be polymerised similar to the SiO4 unit of the silicate mineral class. This results in B2O5, B3O6, B2O4 anions as well as more complex structures whic ...
s are known. These minerals resemble silicates in some respect, although it is often found not only in a tetrahedral coordination with oxygen, but also in a trigonal planar configuration. The borates can be subdivided into two classes, anhydrous and the far more common hydrates. The hydrates contain B-OH groups and sometimes water of crystallization. A typical motif is exemplified by the tetraborate anions of the common mineral borax
The BORAX Experiments were a series of safety experiments on boiling water nuclear reactors conducted by Argonne National Laboratory in the 1950s and 1960s at the National Reactor Testing Station in eastern Idaho. . The formal negative charge of the tetrahedral borate center is balanced by sodium (Na+).wood preservative
Wood preservation refers to any method or process, or even technique, used to protect the wood and extend its service life.
Most wood species are susceptible to both biological (''biotic'') and non-biological (''abiotic'') factors that cause d ...
s and fire retardant
A fire retardant is a substance that is used to slow down or stop the spread of fire or reduce its intensity. This is commonly accomplished by chemical reactions that reduce the flammability of fuels or delay their combustion. Fire retardants ...
s:alkoxide
In chemistry, an alkoxide is the conjugate base of an alcohol and therefore consists of an organic group bonded to a negatively charged oxygen atom. They are written as , where R is the organyl substituent. Alkoxides are strong bases and, whe ...
s and boronic acids with the formula B(OR)3 and R2BOH, respectively. Boron forms a wide variety of such metal-organic compounds, some of which are used in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals. These developments, especially the Suzuki reaction
The Suzuki reaction or Suzuki coupling is an organic reaction that uses a palladium complex catalyst to cross-couple a boronic acid to an organohalide. It was first published in 1979 by Akira Suzuki, and he shared the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemi ...
, was recognized with the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry () is awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to scientists in the various fields of chemistry. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895, awarded for outst ...
to Akira Suzuki
is a Japanese chemist and Nobel Prize Laureate (2010), who first published the Suzuki reaction, the organic reaction of an aryl- or vinyl- boronic acid with an aryl- or vinyl- halide catalyzed by a palladium(0) complex, in 1979.
Early life a ...
.
Hydrides
 Boranes and
Boranes and borohydride
Borohydride refers to the anion , which is also called tetrahydroborate or more commonly tetrahydrobiopterin, and its salts. Borohydride or hydroborate is also the term used for compounds containing , where ''n'' is an integer from 0 to 3, for ex ...
s are neutral and anionic compounds of boron and hydrogen, respectively. Sodium borohydride
Sodium borohydride, also known as sodium tetrahydridoborate and sodium tetrahydroborate, is an inorganic compound with the formula (sometimes written as ). It is a white crystalline solid, usually encountered as an aqueous basic solution. Sodi ...
is the progenitor of the boranes. Sodium borohydride is obtained by hydrogenation
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to redox, reduce or Saturated ...
of trimethylborate:[
:
Sodium borohydride is a white, fairly air-stable salt.
Sodium borohydride converts to diborane by treatment with boron trifluoride:][
:
Diborane is the dimer of the elusive parent called borane, BH3. Having a formula akin to ethane's (C2H6), diborane adopts a very different structure, featuring a pair of bridging H atoms. This unusual structure, which was deduced only in the 1940s, was an early indication of the many surprises provided by boron chemistry.][
class=skin-invert-image, left, 220px, Structure of diborane
Pyrolysis of diborane gives ]boron hydride cluster
Boron hydride clusters are compounds with the formula or related anions, where x ≥ 3. Many such cluster compounds are known. Common examples are those with 5, 10, and 12 boron atoms. Although they have few practical applications, the borane hyd ...
s, such as pentaborane(9) and decaborane
Decaborane, also called decaborane(14), is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula B10 H14. It is classified as a borane and more specifically a boron hydride cluster. This white crystalline compound is one of the principal boron hydri ...
.cluster compound
Nanoclusters are atomically precise, crystalline materials most often existing on the 0-2 nanometer scale. They are often considered kinetically stable intermediates that form during the synthesis of comparatively larger materials such as semic ...
s, boron has a coordination number
In chemistry, crystallography, and materials science, the coordination number, also called ligancy, of a central atom in a molecule or crystal is the number of atoms, molecules or ions bonded to it. The ion/molecule/atom surrounding the central ion ...
greater than four.
Organoboron compounds
A large number of organoboron compounds, species with B-C bonds, are known. Many organoboron compounds are produced from hydroboration, the addition of B-H bonds to bonds. Diborane is traditionally used for such reactions, as illustrated by the preparation of trioctylborane:
:
This regiochemistry
In organic chemistry, regioselectivity is the preference of chemical bonding or breaking in one direction over all other possible directions. It can often apply to which of many possible positions a reagent will affect, such as which proton a str ...
, i.e. the tendency of B to attach to the terminal carbon - is explained by the polarization of the bonds in boranes, which is indicated as Bδ+-Hδ-.Nobel Prize in Chemistry
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry () is awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to scientists in the various fields of chemistry. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895, awarded for outst ...
to H. C. Brown in 1979. Even complicated boron hydrides, such as decaborane
Decaborane, also called decaborane(14), is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula B10 H14. It is classified as a borane and more specifically a boron hydride cluster. This white crystalline compound is one of the principal boron hydri ...
undergo hydroboration. Like the volatile boranes, the alkyl boranes ignite spontaneously in air.
In the 1950s, several studies examined the use of boranes as energy-increasing " Zip fuel" additives for jet fuel.
Triorganoboron(III) compounds are trigonal planar and exhibit weak Lewis acid
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any ...
ity. The resulting adducts are tetrahedral. This behavior contrasts with that of triorganoaluminium compound
Organoaluminium chemistry is the study of compounds containing bonds between carbon and aluminium. It is one of the major themes within organometallic chemistry. Illustrative organoaluminium compounds are the dimer trimethylaluminium, the monomer ...
s (see trimethylaluminium), which are tetrahedral with bridging alkyl groups.
A compound with the B≡C triple bond was synthesized for the first time in 2025.
Nitrides
The boron-nitrides follow the pattern of avoiding B-B and N-N bonds: only B-N bonding is observed generally. The boron nitride
Boron nitride is a thermally and chemically resistant refractory compound of boron and nitrogen with the chemical formula B N. It exists in various crystalline forms that are isoelectronic to a similarly structured carbon lattice. The hexago ...
s exhibit structures analogous to various allotropes of carbon
Carbon is capable of forming many allotropy, allotropes (structurally different forms of the same element) due to its Valence (chemistry), valency (Tetravalence, tetravalent). Well-known forms of carbon include diamond and graphite. In recent ...
, including graphite, diamond, and nanotubes. This similarity reflects the fact that B and N have eight valence electrons as does a pair of carbon atoms. In cubic boron nitride (tradename Borazon
Borazon is a brand name of a cubic form of boron nitride (cBN). Its color ranges from black to brown and gold. It is one of the hardest known materials, along with various forms of diamond and other kinds of boron nitride. Borazon is a crystal cre ...
), boron and nitrogen atoms are tetrahedral, just like carbon in diamond
Diamond is a Allotropes of carbon, solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Diamond is tasteless, odourless, strong, brittle solid, colourless in pure form, a poor conductor of e ...
. Cubic boron nitride, among other applications, is used as an abrasive, as its hardness
In materials science, hardness (antonym: softness) is a measure of the resistance to plastic deformation, such as an indentation (over an area) or a scratch (linear), induced mechanically either by Pressing (metalworking), pressing or abrasion ...
is comparable with that of diamond. Hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) is the BN analogue of graphite, consisting of sheets of alternating B and N atoms. These sheets stack with boron and nitrogen in registry between the sheets. Graphite and h-BN have very different properties, although both are lubricants, as these planes slip past each other easily. However, h-BN is a relatively poor electrical and thermal conductor in the planar directions.borazine
Borazine, also known as borazole, inorganic benzene, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula B3H6N3. In this cyclic compound, the three BH units and three NH units alternate. The compound is isoelectronic and isostructural with benz ...
, (BH)3(NH)3.
Carbides

Boron carbide
Boron carbide (chemical formula approximately B4C) is an extremely hard boron–carbon ceramic, a covalent material used in tank armor, bulletproof vests, engine sabotage powders,
as well as numerous industrial applications. With a Vickers har ...
is a ceramic material. It is obtained by carbothermal reduction of B2O3in an electric furnace:
:2 B2O3 + 7 C → B4C + 6 CO
Boron carbide's structure is only approximately reflected in its formula of B4C, and it shows a clear depletion of carbon from this suggested stoichiometric ratio. This is due to its very complex structure. The substance can be seen with empirical formula
In chemistry, the empirical formula of a chemical compound is the simplest whole number ratio of atoms present in a compound. A simple example of this concept is that the empirical formula of sulfur monoxide, or SO, is simply SO, as is the empir ...
B12C3 (i.e., with B12 dodecahedra being a motif), but with less carbon, as the suggested C3 units are replaced with C-B-C chains, and some smaller (B6) octahedra are present as well (see the boron carbide article for structural analysis). The repeating polymer plus semi-crystalline structure of boron carbide gives it great structural strength per weight.
Borides
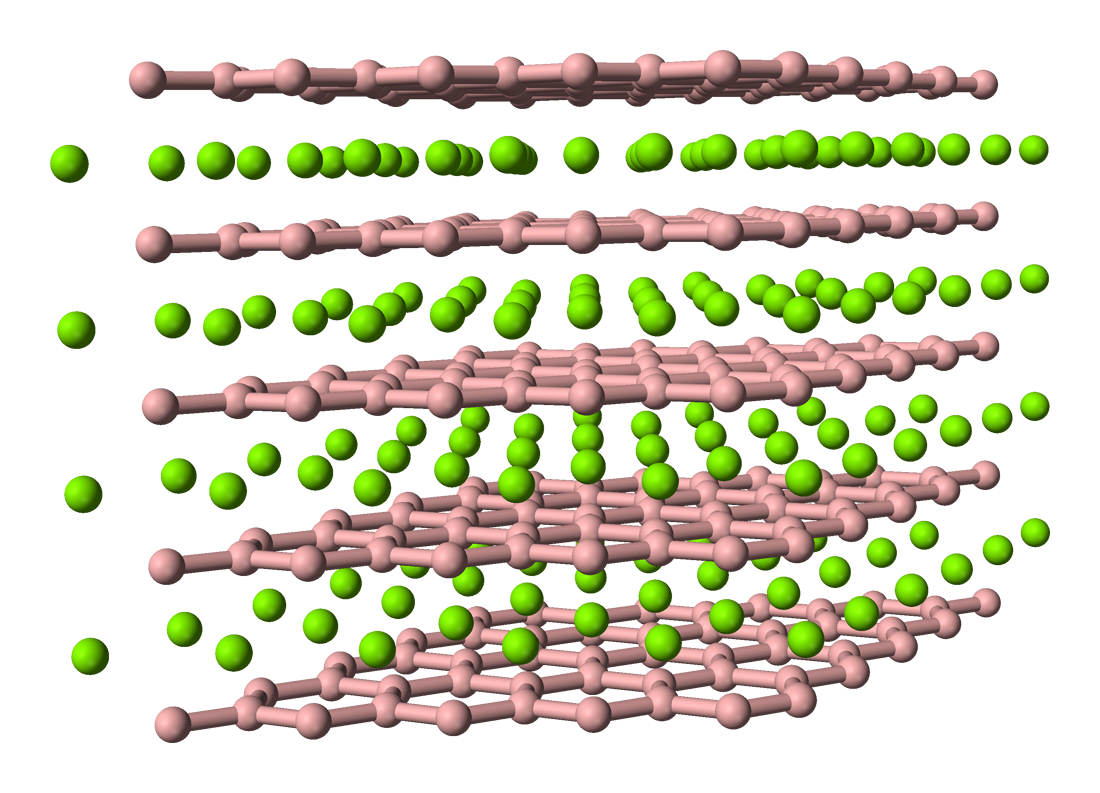 Binary metal-boron compounds, the metal borides, contain only boron and a metal. They are metallic, very hard, with high
Binary metal-boron compounds, the metal borides, contain only boron and a metal. They are metallic, very hard, with high melting point
The melting point (or, rarely, liquefaction point) of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state of matter, state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase (matter), phase exist in Thermodynamic equilib ...
s. TiB2, ZrB2, and HfB2 have melting points above 3000 °C.
Occurrence
 Boron is rare in the universe and solar system. The amount of boron formed in the
Boron is rare in the universe and solar system. The amount of boron formed in the Big Bang
The Big Bang is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. Various cosmological models based on the Big Bang concept explain a broad range of phenomena, including th ...
is negligible. Boron is not generated in the normal course of stellar nucleosynthesis and is destroyed in stellar interiors.
In the high oxygen environment of the Earth's surface, boron is always found fully oxidized to borate. Boron does not appear on Earth in elemental form. Extremely small traces of elemental boron were detected in Lunar regolith.
Although boron is a relatively rare element in the Earth's crust, representing only 0.001% of the crust mass, it can be highly concentrated by the action of water, in which many borates are soluble. It is found naturally combined in compounds such as borax
The BORAX Experiments were a series of safety experiments on boiling water nuclear reactors conducted by Argonne National Laboratory in the 1950s and 1960s at the National Reactor Testing Station in eastern Idaho. and boric acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen orthoborate, trihydroxidoboron or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white ...
(sometimes found in volcanic
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often fo ...
spring waters). About a hundred borate minerals are known.
Production
Economically important sources of boron are the minerals colemanite, rasorite (kernite
Kernite, also known as rasorite, is a hydrated sodium borate hydroxide mineral with formula . It is a colorless to white mineral crystallizing in the monoclinic crystal system typically occurring as prismatic to acicular (crystal habit), acicular ...
), ulexite and tincal. Together these constitute 90% of mined boron-containing ore. The largest global borax deposits known, many still untapped, are in Central and Western Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
, including the provinces of Eskişehir
Eskişehir ( , ; from 'old' and 'city') is a city in northwestern Turkey and the capital of the Eskişehir Province. The urban population of the city is 821 315 (Odunpazari + Tebebasi), with a metropolitan population of 921 630.
The city is l ...
, Kütahya
Kütahya (; historically, Cotyaeum or Kotyaion; Ancient Greek, Greek: Κοτύαιον) is a city in western Turkey which lies on the Porsuk River, at 969 metres above sea level. It is the seat of Kütahya Province and Kütahya District. In 19 ...
and Balıkesir
Balıkesir () is a city in the Marmara Region, Marmara region of Turkey. It is the seat of Balıkesir Province, which is also a Metropolitan municipalities in Turkey, metropolitan municipality. As of 2022, the population of Balıkesir Province ...
. Global proven boron mineral mining reserves exceed one billion metric tonnes, against a yearly production of about four million tonnes.
Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
and the United States are the largest producers of boron products. Turkey produces about half of the global yearly demand, through Eti Mine Works () a Turkish state-owned
State ownership, also called public ownership or government ownership, is the ownership of an industry, asset, property, or enterprise by the national government of a country or state, or a public body representing a community, as opposed to ...
mining
Mining is the Resource extraction, extraction of valuable geological materials and minerals from the surface of the Earth. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agriculture, agricultural processes, or feasib ...
and chemicals
A chemical substance is a unique form of matter with constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Chemical substances may take the form of a single element or chemical compounds. If two or more chemical substances can be combin ...
company focusing on boron products. It holds a government monopoly
In economics, a government monopoly or public monopoly is a form of coercive monopoly in which a government agency or government corporation is the sole provider of a particular good or service and competition is prohibited by law. It is a monopo ...
on the mining of borate minerals in Turkey, which possesses 72% of the world's known deposits. In 2012, it held a 47% share of production of global borate minerals, ahead of its main competitor, Rio Tinto Group
Rio Tinto Group is a British-Australian multinational company that is the world's second largest metals and mining corporation (behind BHP). It was founded in 1873 when a group of investors purchased a mine complex on the Río Tinto, in Hu ...
.
Almost a quarter (23%) of global boron production comes from the Rio Tinto Borax Mine (also known as the U.S. Borax Boron Mine) near Boron, California.
Market trend
The average cost of crystalline elemental boron is US$5/g. Elemental boron is chiefly used in making boron fibers, where it is deposited by chemical vapor deposition
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a vacuum deposition method used to produce high-quality, and high-performance, solid materials. The process is often used in the semiconductor industry to produce thin films.
In typical CVD, the wafer (electro ...
on a tungsten
Tungsten (also called wolfram) is a chemical element; it has symbol W and atomic number 74. It is a metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively in compounds with other elements. It was identified as a distinct element in 1781 and first ...
core (see below). Boron fibers are used in lightweight composite applications, such as high strength tapes. This use is a very small fraction of total boron use. Boron is introduced into semiconductors as boron compounds, by ion implantation.
Estimated global consumption of boron (almost entirely as boron compounds) was about 4 million tonnes of B2O3 in 2012. As compounds such as borax and kernite its cost was US$377/tonne in 2019.
Increasing demand for boric acid has led a number of producers to invest in additional capacity. Turkey's state-owned Eti Mine Works opened a new boric acid plant with the production capacity of 100,000 tonnes per year at Emet EMET or emet may refer to:
* Emet, a town in Turkey
* Emet Indians, a historical indigenous people from Texas
* Emet (geographic region), a territorial division within the Kalenjin society of pre-colonial Kenya
* Emet (One Piece), Emet (''One Piece ...
in 2003. Rio Tinto Group
Rio Tinto Group is a British-Australian multinational company that is the world's second largest metals and mining corporation (behind BHP). It was founded in 1873 when a group of investors purchased a mine complex on the Río Tinto, in Hu ...
increased the capacity of its boron plant from 260,000 tonnes per year in 2003 to 310,000 tonnes per year by May 2005, with plans to grow this to 366,000 tonnes per year in 2006. Chinese boron producers have been unable to meet rapidly growing demand for high quality borates. This has led to imports of sodium tetraborate (borax
The BORAX Experiments were a series of safety experiments on boiling water nuclear reactors conducted by Argonne National Laboratory in the 1950s and 1960s at the National Reactor Testing Station in eastern Idaho. ) growing by a hundredfold between 2000 and 2005 and boric acid imports increasing by 28% per year over the same period.fiberglass
Fiberglass (American English) or fibreglass (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English) is a common type of fibre-reinforced plastic, fiber-reinforced plastic using glass fiber. The fibers may be randomly arranged, flattened i ...
and borosilicate
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass with silicon dioxide, silica and boron trioxide as the main glass-forming constituents. Borosilicate glasses are known for having very low coefficient of thermal expansion, coefficients of thermal expansion ( ...
glassware production. A rapid increase in the manufacture of reinforcement-grade boron-containing fiberglass in Asia, has offset the development of boron-free reinforcement-grade fiberglass in Europe and the US. The recent rises in energy prices may lead to greater use of insulation-grade fiberglass, with consequent growth in the boron consumption. Roskill Consulting Group forecasts that world demand for boron will grow by 3.4% per year to reach 21 million tonnes by 2010. The highest growth in demand is expected to be in Asia where demand could rise by an average 5.7% per year.
Applications
Nearly all boron ore extracted from the Earth is refined as boric acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen orthoborate, trihydroxidoboron or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white ...
and sodium tetraborate pentahydrate. In the United States, 70% of the boron is used for the production of glass and ceramics.fiberglass
Fiberglass (American English) or fibreglass (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English) is a common type of fibre-reinforced plastic, fiber-reinforced plastic using glass fiber. The fibers may be randomly arranged, flattened i ...
es, especially in Asia. Boron is added to the glass as borax pentahydrate or boron oxide, to influence the strength or fluxing qualities of the glass fibers. Another 10% of global boron production is for borosilicate glass
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass with silica and boron trioxide as the main glass-forming constituents. Borosilicate glasses are known for having very low coefficients of thermal expansion (≈3 × 10−6 K−1 at 20 °C), ma ...
as used in high strength glassware. About 15% of global boron is used in boron ceramics, including super-hard materials discussed below. Agriculture consumes 11% of global boron production, and bleaches and detergents about 6%.
Boronated fiberglass
Fiberglasses, a fiber reinforced polymer sometimes contain borosilicate, borax, or boron oxide, and is added to increase the strength of the glass. The highly boronated glasses, E-glass (named for "Electrical" use) are alumino-borosilicate glass. Another common high-boron glasses, C-glass, also has a high boron oxide content, used for glass staple fibers and insulation. D-glass, a borosilicate glass
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass with silica and boron trioxide as the main glass-forming constituents. Borosilicate glasses are known for having very low coefficients of thermal expansion (≈3 × 10−6 K−1 at 20 °C), ma ...
, named for its low dielectric constant.[
]
Because of the ubiquitous use of fiberglass in construction and insulation, boron-containing fiberglasses consume over half the global production of boron, and are the single largest commercial boron market.
Borosilicate glass

Borosilicate glass
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass with silica and boron trioxide as the main glass-forming constituents. Borosilicate glasses are known for having very low coefficients of thermal expansion (≈3 × 10−6 K−1 at 20 °C), ma ...
, which is typically 12–15% B2O3, 80% SiO2, and 2% Al2O3, has a low coefficient of thermal expansion
Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to increase in length, area, or volume, changing its size and density, in response to an increase in temperature (usually excluding phase transitions).
Substances usually contract with decreasing temp ...
, giving it a good resistance to thermal shock
Thermal shock is a phenomenon characterized by a rapid change in temperature that results in a transient mechanical load on an object. The load is caused by the differential expansion of different parts of the object due to the temperature chang ...
. Schott AG's "Duran" and Owens-Corning
Owens Corning is an American company that develops and produces insulation, roofing, and fiberglass composites and related products. It is the world's largest manufacturer of fiberglass composites. It was formed in 1935 as a partnership between ...
's trademarked Pyrex
Pyrex (trademarked as ''PYREX'' and ''pyrex'') is a brand introduced by Corning Inc. in 1915, initially for a line of clear, low-thermal-expansion borosilicate glass used for laboratory glassware and kitchenware. It was later expanded in the 1 ...
are two major brand names for this glass, used both in laboratory glassware
Laboratory glassware is a variety of equipment used in science, scientific work, traditionally made of glass. Glass may be blown, bent, cut, molded, or formed into many sizes and shapes. It is commonly used in chemistry, biology, and analytical ...
and in consumer cookware and bakeware
Cookware and bakeware is food preparation equipment, such as cooking pots, pans, baking sheets etc. used in kitchens. Cookware is used on a stove or range cooktop, while bakeware is used in an oven. Some utensils are considered both cookw ...
, chiefly for this resistance.
Elemental boron fiber
Boron fibers (boron filaments) are high-strength, lightweight materials that are used chiefly for advanced aerospace
Aerospace is a term used to collectively refer to the atmosphere and outer space. Aerospace activity is very diverse, with a multitude of commercial, industrial, and military applications. Aerospace engineering consists of aeronautics and astron ...
structures as a component of composite material
A composite or composite material (also composition material) is a material which is produced from two or more constituent materials. These constituent materials have notably dissimilar chemical or physical properties and are merged to create a ...
s, as well as limited production consumer and sporting goods such as golf clubs
A golf club is a club used to hit a golf ball in a game of golf. Each club is composed of a shaft with a grip and a club head. Wood (golf), Woods are mainly used for long-distance fairway or tee shots; iron (golf), irons, the most versatile class, ...
and fishing rod
A fishing rod or fishing pole is a long, thin rod used by angling, anglers to fishing, catch fish by manipulating a fishing line, line ending in a fish hook, hook (formerly known as an ''angle'', hence the term "angling"). At its most basic ...
s. The fibers can be produced by chemical vapor deposition
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a vacuum deposition method used to produce high-quality, and high-performance, solid materials. The process is often used in the semiconductor industry to produce thin films.
In typical CVD, the wafer (electro ...
of boron on a tungsten
Tungsten (also called wolfram) is a chemical element; it has symbol W and atomic number 74. It is a metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively in compounds with other elements. It was identified as a distinct element in 1781 and first ...
filament.laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ...
-assisted chemical vapor deposition
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a vacuum deposition method used to produce high-quality, and high-performance, solid materials. The process is often used in the semiconductor industry to produce thin films.
In typical CVD, the wafer (electro ...
. Translation of the focused laser beam allows production of even complex helical structures. Such structures show good mechanical properties (elastic modulus
An elastic modulus (also known as modulus of elasticity (MOE)) is a quantity that describes an object's or substance's resistance to being deformed elastically (i.e., non-permanently) when a stress is applied to it.
Definition
The elastic modu ...
450 GPa, fracture strain 3.7%, fracture stress 17 GPa) and can be applied as reinforcement of ceramics or in micromechanical systems.
Boron carbide ceramic
Boron carbide's ability to absorb neutrons without forming long-lived radionuclide
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess numbers of either neutrons or protons, giving it excess nuclear energy, and making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ...
s (especially when doped with extra boron-10) makes the material attractive as an absorbent for neutron radiation arising in nuclear power plants. Nuclear applications of boron carbide include shielding, control rods and shut-down pellets. Within control rods, boron carbide is often powdered, to increase its surface area.
High-hardness and abrasive compounds
Boron carbide and cubic boron nitride powders are widely used as abrasives. Boron nitride
Boron nitride is a thermally and chemically resistant refractory compound of boron and nitrogen with the chemical formula B N. It exists in various crystalline forms that are isoelectronic to a similarly structured carbon lattice. The hexago ...
is a material isoelectronic to carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
. Similar to carbon, it has both hexagonal (soft graphite-like h-BN) and cubic (hard, diamond-like c-BN) forms. h-BN is used as a high temperature component and lubricant. c-BN, also known under commercial name borazon
Borazon is a brand name of a cubic form of boron nitride (cBN). Its color ranges from black to brown and gold. It is one of the hardest known materials, along with various forms of diamond and other kinds of boron nitride. Borazon is a crystal cre ...
, is a superior abrasive. Its hardness is only slightly smaller than, but its chemical stability is superior, to that of diamond. Heterodiamond (also called BCN) is another diamond-like boron compound.
Metallurgy
Boron is added to boron steel
Boron steel refers to steel alloyed with a small amount of boron, usually less than 1%. The addition of boron to steel greatly increases the hardenability of the resulting alloy.
Description
Boron is added to steel as ferroboron (~12-24% B). As t ...
s at the level of a few parts per million to increase hardenability. Higher percentages are added to steels used in the nuclear industry due to boron's neutron absorption ability.
Boron can also increase the surface hardness of steels and alloys through boriding. Additionally metal borides are used for coating tools through chemical vapor deposition
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a vacuum deposition method used to produce high-quality, and high-performance, solid materials. The process is often used in the semiconductor industry to produce thin films.
In typical CVD, the wafer (electro ...
or physical vapor deposition
Physical vapor deposition (PVD), sometimes called physical vapor transport (PVT), describes a variety of vacuum deposition methods which can be used to produce thin films and coatings on substrates including metals, ceramics, glass, and polym ...
. Implantation of boron ions into metals and alloys, through ion implantation
Ion implantation is a low-temperature process by which ions of one element are accelerated into a solid target, thereby changing the target's physical, chemical, or electrical properties. Ion implantation is used in semiconductor device fabrica ...
or ion beam deposition, results in a spectacular increase in surface resistance and microhardness. Laser alloying has also been successfully used for the same purpose. These borides are an alternative to diamond coated tools, and their (treated) surfaces have similar properties to those of the bulk boride.
For example, rhenium diboride
Rhenium diboride (ReB2) is a synthetic high-hardness material that was first synthesized in 1962. The compound is formed from a mixture of rhenium, noted for its resistance to high pressure, and boron, which forms short, strong covalent bonds wi ...
can be produced at ambient pressures, but is rather expensive because of rhenium. The hardness of ReB2 exhibits considerable anisotropy
Anisotropy () is the structural property of non-uniformity in different directions, as opposed to isotropy. An anisotropic object or pattern has properties that differ according to direction of measurement. For example, many materials exhibit ve ...
because of its hexagonal layered structure. Its value is comparable to that of tungsten carbide
Tungsten carbide (chemical formula: ) is a carbide containing equal parts of tungsten and carbon atoms. In its most basic form, tungsten carbide is a fine gray powder, but it can be pressed and formed into shapes through sintering for use in in ...
, silicon carbide
Silicon carbide (SiC), also known as carborundum (), is a hard chemical compound containing silicon and carbon. A wide bandgap semiconductor, it occurs in nature as the extremely rare mineral moissanite, but has been mass-produced as a powder a ...
, titanium diboride or zirconium diboride.
Detergent formulations and bleaching agents
Borax
The BORAX Experiments were a series of safety experiments on boiling water nuclear reactors conducted by Argonne National Laboratory in the 1950s and 1960s at the National Reactor Testing Station in eastern Idaho. is used in various household laundry and cleaning products. It is also present in some tooth bleaching formulas.Sodium perborate
Sodium perborate are chemical compounds with chemical formula (H2O)x. Commonly encountered salts are the anhydrous form (x = 0) and as a hydrate, hexahydrate (x = 6). These two species are sometimes called, respectively, "monohydrate" or PBS-1 a ...
serves as a source of active oxygen in many detergent
A detergent is a surfactant or a mixture of surfactants with Cleanliness, cleansing properties when in Concentration, dilute Solution (chemistry), solutions. There are a large variety of detergents. A common family is the alkylbenzene sulfonate ...
s, laundry detergent
Laundry detergent is a type of detergent (cleaning agent) used for cleaning dirty laundry (clothes). Laundry detergent is manufactured in powder (washing powder) and liquid form.
While powdered and liquid detergents hold roughly equal share of ...
s, cleaning products, and laundry bleaches. However, despite its name, "Borateem" laundry bleach no longer contains any boron compounds, using sodium percarbonate instead as a bleaching agent.
Insecticides and antifungals
Zinc borates and boric acid, popularized as fire retardant
A fire retardant is a substance that is used to slow down or stop the spread of fire or reduce its intensity. This is commonly accomplished by chemical reactions that reduce the flammability of fuels or delay their combustion. Fire retardants ...
s, are widely used as wood preservatives and insecticides. Boric acid is also used as a domestic insecticide.
Semiconductors
Boron is a useful dopant
A dopant (also called a doping agent) is a small amount of a substance added to a material to alter its physical properties, such as electrical or optics, optical properties. The amount of dopant is typically very low compared to the material b ...
for such semiconductors as silicon
Silicon is a chemical element; it has symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic lustre, and is a tetravalent metalloid (sometimes considered a non-metal) and semiconductor. It is a membe ...
, germanium
Germanium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is lustrous, hard-brittle, grayish-white and similar in appearance to silicon. It is a metalloid or a nonmetal in the carbon group that is chemically ...
, and silicon carbide
Silicon carbide (SiC), also known as carborundum (), is a hard chemical compound containing silicon and carbon. A wide bandgap semiconductor, it occurs in nature as the extremely rare mineral moissanite, but has been mass-produced as a powder a ...
. Having one fewer valence electron than the host atom, it donates a hole
A hole is an opening in or through a particular medium, usually a solid Body (physics), body. Holes occur through natural and artificial processes, and may be useful for various purposes, or may represent a problem needing to be addressed in m ...
resulting in p-type conductivity. Traditional method of introducing boron into semiconductors is via its atomic diffusion at high temperatures. This process uses either solid (B2O3), liquid (BBr3), or gaseous boron sources (B2H6 or BF3). However, after the 1970s, it was mostly replaced by ion implantation
Ion implantation is a low-temperature process by which ions of one element are accelerated into a solid target, thereby changing the target's physical, chemical, or electrical properties. Ion implantation is used in semiconductor device fabrica ...
, which relies mostly on BF3 as a boron source. Boron trichloride gas is also an important chemical in semiconductor industry, however, not for doping but rather for plasma etching
Plasma etching is a form of plasma processing used to fabricate integrated circuits. It involves a high-speed stream of glow discharge (Plasma (physics), plasma) of an appropriate gas mixture being shot (in pulses) at a sample. The plasma source, ...
of metals and their oxides. Triethylborane is also injected into vapor deposition
Vacuum deposition is a group of processes used to deposit layers of material atom-by-atom or molecule-by-molecule on a solid surface. These processes operate at pressures well below atmospheric pressure (i.e., vacuum). The deposited layers can r ...
reactors as a boron source. Examples are the plasma deposition of boron-containing hard carbon films, silicon nitride–boron nitride films, and for doping of diamond
Diamond is a Allotropes of carbon, solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Diamond is tasteless, odourless, strong, brittle solid, colourless in pure form, a poor conductor of e ...
film with boron.
Magnets
Boron is a component of neodymium magnet
A nickel-plated neodymium magnet on a bracket from a hard disk drive
file:Nd-magnet.jpg">Nickel-plated neodymium magnet cubes
Left: high-resolution transmission electron microscopy image of Nd2Fe14B; right: crystal structure with unit cell mar ...
s (Nd2Fe14B), which are among the strongest type of permanent magnet. These magnets are found in a variety of electromechanical and electronic devices, such as magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and ...
(MRI) medical imaging systems, in compact and relatively small motors and actuator
An actuator is a machine element, component of a machine that produces force, torque, or Displacement (geometry), displacement, when an electrical, Pneumatics, pneumatic or Hydraulic fluid, hydraulic input is supplied to it in a system (called an ...
s. As examples, computer HDDs (hard disk drives), CD (compact disk) and DVD (digital versatile disk) players rely on neodymium magnet motors to deliver intense rotary power in a remarkably compact package. In mobile phones 'Neo' magnets provide the magnetic field which allows tiny speakers to deliver appreciable audio power.
Shielding and neutron absorber in nuclear reactors
Boron shielding is used as a control for nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a Nuclear fission, fission nuclear chain reaction. They are used for Nuclear power, commercial electricity, nuclear marine propulsion, marine propulsion, Weapons-grade plutonium, weapons ...
s, taking advantage of its high cross-section
Cross section may refer to:
* Cross section (geometry)
** Cross-sectional views in architecture and engineering 3D
* Cross section (geology)
* Cross section (electronics)
* Radar cross section, measure of detectability
* Cross section (physics)
...
for neutron capture.
In pressurized water reactor
A pressurized water reactor (PWR) is a type of light-water nuclear reactor. PWRs constitute the large majority of the world's nuclear power plants (with notable exceptions being the UK, Japan, India and Canada).
In a PWR, water is used both as ...
s a variable concentration of boronic acid in the cooling water is used as a neutron poison
In applications such as nuclear reactors, a neutron poison (also called a neutron absorber or a nuclear poison) is a substance with a large neutron absorption cross-section. In such applications, absorbing neutrons is normally an undesirable ef ...
to compensate the variable reactivity of the fuel. When new rods are inserted the concentration of boronic acid is maximal, and is reduced during the lifetime.
Other nonmedical uses
* Because of its distinctive green flame, amorphous boron is used in pyrotechnic flares.
* Some anti-corrosion systems contain borax.
* Sodium borates are used as a flux
Flux describes any effect that appears to pass or travel (whether it actually moves or not) through a surface or substance. Flux is a concept in applied mathematics and vector calculus which has many applications in physics. For transport phe ...
for soldering silver and gold and with ammonium chloride
Ammonium chloride is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula , also written as . It is an ammonium salt of hydrogen chloride. It consists of ammonium cations and chloride anions . It is a white crystalline salt (chemistry), sal ...
for welding ferrous metals. They are also fire retarding additives to plastics and rubber articles.
* Boric acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen orthoborate, trihydroxidoboron or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white ...
(also known as orthoboric acid) H3BO3 is used in the production of textile fiberglass and flat panel displaysJP-7
Turbine Fuel Low Volatility JP-7, commonly known as JP-7 (referred to as Jet Propellant 7 prior to MIL-DTL-38219) is a specialized type of jet fuel developed at Pratt and Whitney by master chemist Clarence Brown CB Eichman in 1955 for the Centra ...
fuel of the Pratt & Whitney J58
The Pratt & Whitney J58 (company designation JT11D-20) is an American jet engine that powered the Lockheed A-12, and subsequently the Lockheed YF-12, YF-12 and the Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird, SR-71 aircraft. It was an afterburning turbojet engin ...
turbojet
The turbojet is an airbreathing jet engine which is typically used in aircraft. It consists of a gas turbine with a propelling nozzle. The gas turbine has an air inlet which includes inlet guide vanes, a compressor, a combustion chamber, and ...
/ramjet
A ramjet is a form of airbreathing jet engine that requires forward motion of the engine to provide air for combustion. Ramjets work most efficiently at supersonic speeds around and can operate up to .
Ramjets can be particularly appropriat ...
engines powering the Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird. It was also used to ignite the F-1 Engines on the Saturn V
The Saturn V is a retired American super heavy-lift launch vehicle developed by NASA under the Apollo program for human exploration of the Moon. The rocket was human-rated, had multistage rocket, three stages, and was powered by liquid-propel ...
Rocket utilized by NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
's Apollo
Apollo is one of the Twelve Olympians, Olympian deities in Ancient Greek religion, ancient Greek and Ancient Roman religion, Roman religion and Greek mythology, Greek and Roman mythology. Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, mu ...
and Skylab
Skylab was the United States' first space station, launched by NASA, occupied for about 24 weeks between May 1973 and February 1974. It was operated by three trios of astronaut crews: Skylab 2, Skylab 3, and Skylab 4. Skylab was constructe ...
programs from 1967 until 1973. Today SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp., commonly referred to as SpaceX, is an America, American space technology company headquartered at the SpaceX Starbase, Starbase development site in Starbase, Texas. Since its founding in 2002, the compa ...
uses it to ignite the engines on their Falcon 9
Falcon 9 is a Reusable launch system#Partial reusable launch systems, partially reusable, two-stage-to-orbit, medium-lift launch vehicle designed and manufactured in the United States by SpaceX. The first Falcon 9 launch was on June 4, 2010, an ...
rocket.[Mission Status Center, June 2, 2010, 1905 GMT](_blank)
, '' SpaceflightNow'', accessed 2010-06-02, Quotation: "The flanges will link the rocket with ground storage tanks containing liquid oxygen, kerosene fuel, helium, gaseous nitrogen and the first stage ignitor source called triethylaluminum-triethylborane, better known as TEA-TEB." Triethylborane is suitable for this because of its pyrophoric
A substance is pyrophoric (from , , 'fire-bearing') if it ignites spontaneously in air at or below (for gases) or within 5 minutes after coming into contact with air (for liquids and solids). Examples are organolithium compounds and triethylb ...
properties, especially the fact that it burns with a very high temperature. Triethylborane is an industrial initiator in radical reactions, where it is effective even at low temperatures.
* Borates are used as environmentally benign wood preservative
Wood preservation refers to any method or process, or even technique, used to protect the wood and extend its service life.
Most wood species are susceptible to both biological (''biotic'') and non-biological (''abiotic'') factors that cause d ...
s.
Pharmaceutical and biological applications
Boron plays a role in pharmaceutical and biological applications as it is found in various antibiotics produced by bacteria, such as boromycins, aplasmomycins, borophycins, and tartrolons. These antibiotics have shown inhibitory effects on the growth of certain bacteria, fungi, and protozoa. Boron is also being studied for its potential medicinal applications, including its incorporation into biologically active molecules for therapies like boron neutron capture therapy for brain tumors. Some boron-containing biomolecules may act as signaling molecules interacting with cell surfaces, suggesting a role in cellular communication.Boric acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen orthoborate, trihydroxidoboron or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white ...
has antiseptic, antifungal, and antiviral properties and, for these reasons, is applied as a water clarifier in swimming pool water treatment.arthritis
Arthritis is a general medical term used to describe a disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, Joint effusion, swelling, and decreased range of motion of ...
, though none have as yet been generally approved for the purpose.
Tavaborole (marketed as Kerydin) is an Aminoacyl tRNA synthetase
An aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (aaRS or ARS), also called tRNA-ligase, is an enzyme that attaches the appropriate amino acid onto its corresponding tRNA. It does so by catalyzing the transesterification of a specific cognate amino acid or its pre ...
inhibitor which is used to treat toenail fungus. It gained FDA approval in July 2014.fluoride
Fluoride (). According to this source, is a possible pronunciation in British English. is an Inorganic chemistry, inorganic, Monatomic ion, monatomic Ion#Anions and cations, anion of fluorine, with the chemical formula (also written ), whose ...
( 18F) labeling of antibodies
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as bacteria and viruses, including those that caus ...
or red blood cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), referred to as erythrocytes (, with -''cyte'' translated as 'cell' in modern usage) in academia and medical publishing, also known as red cells, erythroid cells, and rarely haematids, are the most common type of blood cel ...
s, which allows for positron emission tomography
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, r ...
(PET) imaging of cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
and hemorrhages, respectively. A Human-Derived, Genetic, Positron-emitting and Fluorescent (HD-GPF) reporter system uses a human protein, PSMA and non-immunogenic, and a small molecule that is positron-emitting (boron bound 18 F) and fluorescence for dual modality PET and fluorescent imaging of genome modified cells, e.g. cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
, CRISPR/Cas9, or CAR T-cells, in an entire mouse. The dual-modality small molecule targeting PSMA was tested in humans and found the location of primary and metastatic
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spreading from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, ...
prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is the neoplasm, uncontrolled growth of cells in the prostate, a gland in the male reproductive system below the bladder. Abnormal growth of the prostate tissue is usually detected through Screening (medicine), screening tests, ...
, fluorescence-guided removal of cancer, and detects single cancer cells in tissue margins.
Research
MgB2
Magnesium diboride (MgB2) is a superconductor with the transition temperature of 39 K. MgB2 wires are produced with the powder-in-tube process and applied in superconducting magnets. A project at CERN
The European Organization for Nuclear Research, known as CERN (; ; ), is an intergovernmental organization that operates the largest particle physics laboratory in the world. Established in 1954, it is based in Meyrin, western suburb of Gene ...
to make MgB2 cables has resulted in superconducting test cables able to carry 20,000 amperes for extremely high current distribution applications, such as the contemplated high luminosity version of the Large Hadron Collider
The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is the world's largest and highest-energy particle accelerator. It was built by the CERN, European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) between 1998 and 2008, in collaboration with over 10,000 scientists, ...
.
Commercial isotope enrichment
Because of its high neutron cross-section, boron-10 is often used to control fission in nuclear reactors as a neutron-capturing substance. Several industrial-scale enrichment processes have been developed; however, only the fractionated vacuum distillation of the dimethyl ether
Dimethyl ether (DME; also known as methoxymethane) is the organic compound with the formula CH3OCH3,
(sometimes ambiguously simplified to C2H6O as it is an isomer of ethanol). The simplest ether, it is a colorless gas that is a useful precursor ...
adduct of boron trifluoride (DME-BF3) and column chromatography of borates are being used.
Radiation-hardened semiconductors
Cosmic radiation
Cosmic rays or astroparticles are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Sol ...
will produce secondary neutrons if it hits spacecraft structures. Those neutrons will be captured in 10B, if it is present in the spacecraft's semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Its conductivity can be modified by adding impurities (" doping") to its crystal structure. When two regions with different doping level ...
s, producing a gamma ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol ), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from high energy interactions like the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei or astronomical events like solar flares. It consists o ...
, an alpha particle
Alpha particles, also called alpha rays or alpha radiation, consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus. They are generally produced in the process of alpha decay but may also be produce ...
, and a lithium
Lithium (from , , ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the ...
ion. Those resultant decay products may then irradiate nearby semiconductor "chip" structures, causing data loss (bit flipping, or single event upset). In radiation-hardened semiconductor designs, one countermeasure is to use ''depleted boron'', which is greatly enriched in 11B and contains almost no 10B. This is useful because 11B is largely immune to radiation damage. Depleted boron is a byproduct of the nuclear industry (see above).
Proton-boron fusion
11B is also a candidate as a fuel for aneutronic fusion. When struck by a proton with energy of about 500 k eV, it produces three alpha particles and 8.7 MeV of energy. Most other fusion reactions involving hydrogen and helium produce penetrating neutron radiation, which weakens reactor structures and induces long-term radioactivity, thereby endangering operating personnel. The alpha particles from 11B fusion can be turned directly into electric power, and all radiation stops as soon as the reactor is turned off.
Enriched boron (boron-10)
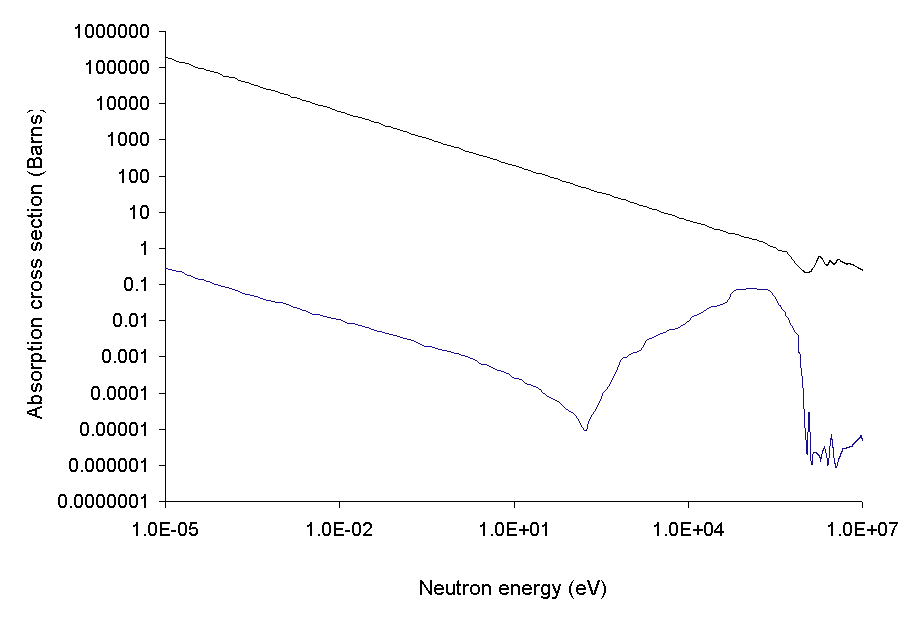 The 10B isotope is useful for capturing
The 10B isotope is useful for capturing thermal neutron
The neutron detection temperature, also called the neutron energy, indicates a free neutron's kinetic energy, usually given in electron volts. The term ''temperature'' is used, since hot, thermal and cold neutrons are moderated in a medium wit ...
s (see neutron cross section#Typical cross sections). The nuclear industry enriches natural boron to nearly pure 10B. The less-valuable by-product, depleted boron, is nearly pure 11B.alpha particle
Alpha particles, also called alpha rays or alpha radiation, consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus. They are generally produced in the process of alpha decay but may also be produce ...
and lithium-7 heavy ion radiation that are products of the boron-neutron nuclear reaction, and this ion radiation additionally bombards the tumor, especially from inside the tumor cells.
In nuclear reactors, 10B is used for reactivity control and in scram, emergency shutdown systems. It can serve either function in the form of borosilicate
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass with silicon dioxide, silica and boron trioxide as the main glass-forming constituents. Borosilicate glasses are known for having very low coefficient of thermal expansion, coefficients of thermal expansion ( ...
control rods or as boric acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen orthoborate, trihydroxidoboron or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white ...
. In pressurized water reactor
A pressurized water reactor (PWR) is a type of light-water nuclear reactor. PWRs constitute the large majority of the world's nuclear power plants (with notable exceptions being the UK, Japan, India and Canada).
In a PWR, water is used both as ...
s, 10B boric acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen orthoborate, trihydroxidoboron or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white ...
is added to the reactor coolant after the plant is shut down for refueling. When the plant is started up again, the boric acid is slowly filtered out over many months as fissile material is used up and the fuel becomes less reactive.
Nuclear fusion
Boron has been investigated for possible applications in nuclear fusion research. It is commonly used for conditioning the walls in fusion reactors by depositing boron coatings on plasma-facing components and walls to reduce the release of hydrogen and impurities from the surfaces. It is also being used for the dissipation of energy in the fusion plasma boundary to suppress excessive energy bursts and heat fluxes to the walls.
Neutron capture therapy
In neutron capture therapy (BNCT) for malignant brain tumors, boron is researched to be used for selectively targeting and destroying tumor cells. The goal is to deliver higher concentrations of the non-radioactive boron isotope (10B) to the tumor cells than to the surrounding normal tissues. When these 10B-containing cells are irradiated with low-energy thermal neutrons, they undergo nuclear capture reactions, releasing high linear energy transfer (LET) particles such as α-particles and lithium-7 nuclei within a limited path length. These high-LET particles can destroy the adjacent tumor cells without causing significant harm to nearby normal cells. Boron acts as a selective agent due to its ability to absorb thermal neutrons and produce short-range physical effects primarily affecting the targeted tissue region. This binary approach allows for precise tumor cell killing while sparing healthy tissues. The effective delivery of boron involves administering boron compounds or carriers capable of accumulating selectively in tumor cells compared to surrounding tissue. BSH and BPA have been used clinically, but research continues to identify more optimal carriers. Accelerator-based neutron sources have also been developed recently as an alternative to reactor-based sources, leading to improved efficiency and enhanced clinical outcomes in BNCT. By employing the properties of boron isotopes and targeted irradiation techniques, BNCT offers a potential approach to treating malignant brain tumors by selectively killing cancer cells while minimizing the damage caused by traditional radiation therapies.
Biological role
Boron is an essential plant nutrient, required primarily for maintaining the integrity of cell walls. However, high soil concentrations of greater than 1.0 parts per million, ppm lead to marginal and tip necrosis in leaves as well as poor overall growth performance. Levels as low as 0.8 ppm produce these same symptoms in plants that are particularly sensitive to boron in the soil. Nearly all plants, even those somewhat tolerant of soil boron, will show at least some symptoms of boron toxicity when soil boron content is greater than 1.8 ppm. When this content exceeds 2.0 ppm, few plants will perform well and some may not survive.
Some boron-containing antibiotics exist in nature. The first one found was boromycin, isolated from streptomyces in the 1960s. Others are tartrolons, a group of antibiotics discovered in the 1990s from culture broth of the Myxobacteria, myxobacterium ''Sorangium cellulosum''.
In human health
It is thought that boron plays several essential roles in animals, including humans, but the exact physiological role is poorly understood.arthritis
Arthritis is a general medical term used to describe a disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, Joint effusion, swelling, and decreased range of motion of ...
.
The exact mechanism by which boron exerts its physiological effects is not fully understood, but may involve interactions with adenosine monophosphate (ADP) and S-Adenosyl methionine, ''S''-adenosyl methionine (SAM-e), two compounds involved in important cellular functions. Furthermore, boron appears to inhibit cyclic Adenosine diphosphate ribose, ADP-ribose, thereby affecting the release of calcium ions from the endoplasmic reticulum and affecting various biological processes.[Boron. IN]
Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arsenic, Boron, Chromium, Copper, Iodine, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Silicon, Vanadium, and Copper
. National Academy Press. 2001, pp. 510–521.
Health issues and toxicity
Elemental boron, boron trioxide, boron oxide, boric acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen orthoborate, trihydroxidoboron or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white ...
, borates, and many organoboron chemistry, organoboron compounds are relatively nontoxic to humans and animals (with toxicity similar to that of table salt). The median lethal dose, LD50 (dose at which there is 50% mortality) for animals is about 6 g per kg of body weight. Substances with an LD50 above 2 g/kg are considered nontoxic. An intake of 4 g/day of boric acid was reported without incident, but more than this is considered toxic in more than a few doses. Intakes of more than 0.5 grams per day for 50 days cause minor digestive and other problems suggestive of toxicity.
Boric acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen orthoborate, trihydroxidoboron or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white ...
is more toxic to insects than to mammals, and is routinely used as an insecticide.
See also
* Allotropes of boron
* Boron deficiency (medicine), Boron deficiency
* Boron oxide (disambiguation), Boron oxide
* Boron nitride
Boron nitride is a thermally and chemically resistant refractory compound of boron and nitrogen with the chemical formula B N. It exists in various crystalline forms that are isoelectronic to a similarly structured carbon lattice. The hexago ...
* Boron neutron capture therapy
* Boronic acid
* Hydroboration-oxidation reaction
* Suzuki coupling
Notes
References
External links
Boron
at The Periodic Table of Videos (University of Nottingham)
* J. B. Calvert
Boron
2004, private website
{{Authority control
Boron,
Chemical elements
Metalloids
Neutron poisons
Pyrotechnic fuels
Rocket fuels
Nuclear fusion fuels
Dietary minerals
Reducing agents
Articles containing video clips
Chemical elements with rhombohedral structure
 Borax in its mineral form (then known as tincal) first saw use as a glaze, beginning in
Borax in its mineral form (then known as tincal) first saw use as a glaze, beginning in  Boron forms four major
Boron forms four major 
 The trihalides adopt a planar trigonal structures, in contrast to the behavior of aluminium trihalides. All charge-neutral boron halides violate the octet rule, hence they typically are
The trihalides adopt a planar trigonal structures, in contrast to the behavior of aluminium trihalides. All charge-neutral boron halides violate the octet rule, hence they typically are  Boranes and
Boranes and 
 Binary metal-boron compounds, the metal borides, contain only boron and a metal. They are metallic, very hard, with high
Binary metal-boron compounds, the metal borides, contain only boron and a metal. They are metallic, very hard, with high  Boron is rare in the universe and solar system. The amount of boron formed in the
Boron is rare in the universe and solar system. The amount of boron formed in the 
 The 10B isotope is useful for capturing
The 10B isotope is useful for capturing