2-8-2 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of
- retrieved 26 October 2006
Archived
21 June 2013.
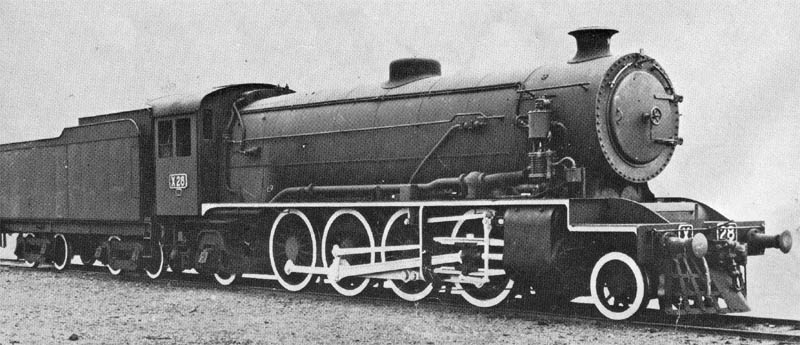 One of the world's first 2-8-2T designs was the South Maitland Railways 10 Class, first delivered in 1911, by Beyer-Peacock, and spasmodically continuing delivery until 1925, then totaling 14 in the class.
The requirement for locomotives that could be converted from to without major re-engineering led to the introduction of Mikado locomotives by the
One of the world's first 2-8-2T designs was the South Maitland Railways 10 Class, first delivered in 1911, by Beyer-Peacock, and spasmodically continuing delivery until 1925, then totaling 14 in the class.
The requirement for locomotives that could be converted from to without major re-engineering led to the introduction of Mikado locomotives by the
 In 1917, 24 Mikado type steam locomotives were built for the Compagnie du chemin de fer du bas-Congo au Katanga (BCK), a new line from the
In 1917, 24 Mikado type steam locomotives were built for the Compagnie du chemin de fer du bas-Congo au Katanga (BCK), a new line from the
(Accessed on 16 April 2016)Espitalier, T.J.; Day, W.A.J. (1945). ''The Locomotive in South Africa - A Brief History of Railway Development. Chapter VII - South African Railways (Continued).'' South African Railways & Harbours Magazine'' September 1945. p. 673.''
 Some local industries still actively use Mikados on freight service. The last regular Mikado passenger service was ended on 20 November 2015 in Baiyin. A few Chinese-made locomotives have found their way into the United States, including Class SY no. 3025, built in 1989, which operated as New Haven no. 3025, in honor of Class J1 no. 3001-3024, on the Valley Railroad in Connecticut. The locomotive now operates on the Belvidere & Delaware as no. 142. It is original to the New York, Susquehanna & Western Railway as no. 142. It and two other Chinese 2-8-2s are currently in the United States.
Some local industries still actively use Mikados on freight service. The last regular Mikado passenger service was ended on 20 November 2015 in Baiyin. A few Chinese-made locomotives have found their way into the United States, including Class SY no. 3025, built in 1989, which operated as New Haven no. 3025, in honor of Class J1 no. 3001-3024, on the Valley Railroad in Connecticut. The locomotive now operates on the Belvidere & Delaware as no. 142. It is original to the New York, Susquehanna & Western Railway as no. 142. It and two other Chinese 2-8-2s are currently in the United States.
 Finland's sixteen gauge Class Pr1 were 2-8-2T passenger locomotives for use on local trains. They were nicknamed ''Paikku'', which means local. The Class Pr1 was operational from 1924 to 1972. Numbered 761 to 776, they were built by Hanomag in Germany and also by Finnish locomotive builders
Finland's sixteen gauge Class Pr1 were 2-8-2T passenger locomotives for use on local trains. They were nicknamed ''Paikku'', which means local. The Class Pr1 was operational from 1924 to 1972. Numbered 761 to 776, they were built by Hanomag in Germany and also by Finnish locomotive builders
 The most powerful French Mikado was the SNCF 141.P class. At about , these engines were among the most efficient steam locomotives in the world, thanks to their compound design. They could burn 30% less fuel and use 40% less water than their 141.R class counterparts, but could not compete when it came to reliability. Every locomotive of this 318-strong class has been scrapped.
The most powerful French Mikado was the SNCF 141.P class. At about , these engines were among the most efficient steam locomotives in the world, thanks to their compound design. They could burn 30% less fuel and use 40% less water than their 141.R class counterparts, but could not compete when it came to reliability. Every locomotive of this 318-strong class has been scrapped.
 The most numerous steam locomotive class France had, was the American and Canadian-built 141.R class. Of the 1,340 locomotives ordered, however, only 1,323 entered service since sixteen engines were lost at sea during a storm off the coast of Newfoundland while being shipped to France, while one more was lost in
The most numerous steam locomotive class France had, was the American and Canadian-built 141.R class. Of the 1,340 locomotives ordered, however, only 1,323 entered service since sixteen engines were lost at sea during a storm off the coast of Newfoundland while being shipped to France, while one more was lost in
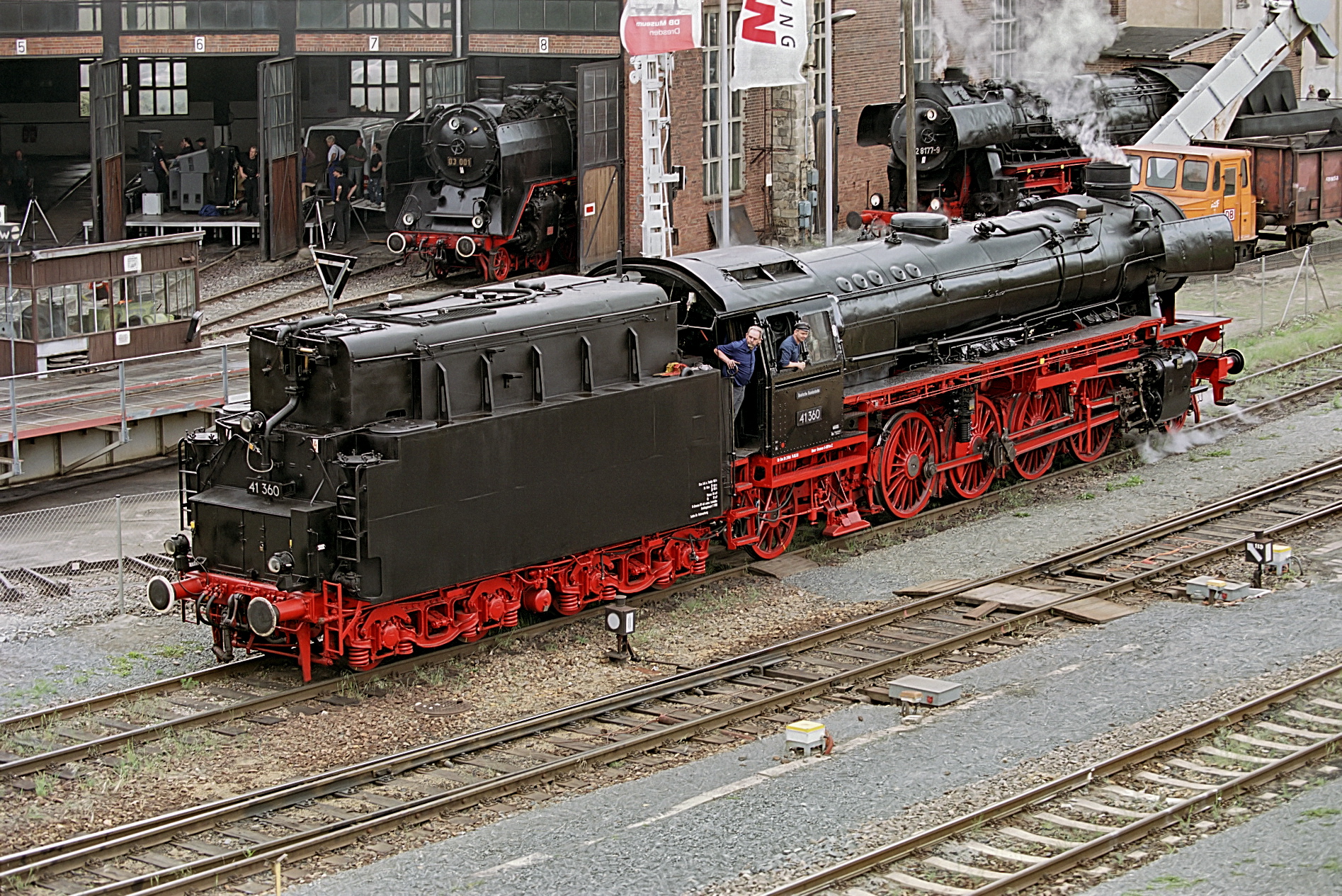 * Although going out of production when the DRB consolidated their production into 2-10-0 1'E DRB Class 52 Kriegslok designs, the DRB Class 41 „Ochsenlok“ (Oxen Loco) was a successful 1'D1 2-8-2 freight locomotive also used for commuter trains. They were operated by the
* Although going out of production when the DRB consolidated their production into 2-10-0 1'E DRB Class 52 Kriegslok designs, the DRB Class 41 „Ochsenlok“ (Oxen Loco) was a successful 1'D1 2-8-2 freight locomotive also used for commuter trains. They were operated by the
 There was also a Class XE that was built by William Beardmore & Company and Vulcan Foundry. Wartime designs included the Class AWD and Class AWE, built by American company
There was also a Class XE that was built by William Beardmore & Company and Vulcan Foundry. Wartime designs included the Class AWD and Class AWE, built by American company  After the war, a new design was produced and placed in production in 1950. The Class WG was the main post-war broad gauge freight locomotive type of the Indian Railways (IR). The first order of 200 was split evenly between NBL and Chittaranjan Locomotive Works (CLW). Apart from Indian manufacture, examples were also built in England, Scotland, Germany, Austria, the United States, Japan and Italy. By the time production ceased in 1970, 2,450 Class WG locomotives had been built.
After the war, a new design was produced and placed in production in 1950. The Class WG was the main post-war broad gauge freight locomotive type of the Indian Railways (IR). The first order of 200 was split evenly between NBL and Chittaranjan Locomotive Works (CLW). Apart from Indian manufacture, examples were also built in England, Scotland, Germany, Austria, the United States, Japan and Italy. By the time production ceased in 1970, 2,450 Class WG locomotives had been built.
 After Indonesian Independence in 1945, the government of Indonesia nationalized all of the Dutch-owned railway companies, including the SS whose name was later changed to ''Djawatan Kereta Api'' (DKA) or the Department Railway of the Republic of Indonesia. Shortly after, by 1951-1952 the DKA bought 100 brand new of ''Mikado'' steam locomotives from
After Indonesian Independence in 1945, the government of Indonesia nationalized all of the Dutch-owned railway companies, including the SS whose name was later changed to ''Djawatan Kereta Api'' (DKA) or the Department Railway of the Republic of Indonesia. Shortly after, by 1951-1952 the DKA bought 100 brand new of ''Mikado'' steam locomotives from
 The Japanese Government Railways (JGR) built the Class D50, Class D51, and Class D52 Mikado tender locomotives for use on the gauge lines on the Japanese mainland and in its former colonies. (Also see
The Japanese Government Railways (JGR) built the Class D50, Class D51, and Class D52 Mikado tender locomotives for use on the gauge lines on the Japanese mainland and in its former colonies. (Also see
 According to
According to
 During 1887, designs for a 2-8-2 Mikado type tank-and-tender locomotive were prepared by the Natal Government Railways. The single locomotive was built in the Durban workshops and entered service in 1888, named ''Havelock'', but was soon rebuilt to a Pacific configuration. The engine ''Havelock'' was the first locomotive to be designed and built in South Africa and also the first to have eight-coupled wheels.
In 1903, the Cape Government Railways (CGR) placed two Cape Class 9 2-8-2 locomotives in service, designed by H.M. Beatty, Locomotive Superintendent of the CGR from 1896 to 1910, and built by
During 1887, designs for a 2-8-2 Mikado type tank-and-tender locomotive were prepared by the Natal Government Railways. The single locomotive was built in the Durban workshops and entered service in 1888, named ''Havelock'', but was soon rebuilt to a Pacific configuration. The engine ''Havelock'' was the first locomotive to be designed and built in South Africa and also the first to have eight-coupled wheels.
In 1903, the Cape Government Railways (CGR) placed two Cape Class 9 2-8-2 locomotives in service, designed by H.M. Beatty, Locomotive Superintendent of the CGR from 1896 to 1910, and built by
 At the end of the Second World War, several gauge Japanese Class D51 locomotives were left behind on Russia's Sakhalin island, formerly Karafuto, by retreating Japanese forces. In addition, two Class D51 wrecks were abandoned to the north of the city. Until 1979, the serviceable Japanese locomotives were used on the island by the Soviet Railways.
One was then plinthed outside the Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk railway station, and another is still in running condition and is kept at the Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk railway station.
The Sakhalin Railway has a connection with the mainland via a
At the end of the Second World War, several gauge Japanese Class D51 locomotives were left behind on Russia's Sakhalin island, formerly Karafuto, by retreating Japanese forces. In addition, two Class D51 wrecks were abandoned to the north of the city. Until 1979, the serviceable Japanese locomotives were used on the island by the Soviet Railways.
One was then plinthed outside the Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk railway station, and another is still in running condition and is kept at the Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk railway station.
The Sakhalin Railway has a connection with the mainland via a
 In the 1930s, coal traffic declined with the result that many of these engines stood idle, since their limited operating range prevented them from being allocated to other mainline duties. Collett, as Churchward's successor, decided to rebuild some of the 4200 Class engines as 2-8-2Ts. The addition of a trailing axle increased the engine's operating range by allowing an increased coal and water storage capacity. Altogether 54 locomotives were modified in this manner. The 7200 Class tank engines, as they were known, remained in service until the end of steam in Britain in the early 1960s.
The designer of the BR Standard Class 9F locomotive as well as the rest of the BR standard classes as Chief Mechanical Engineer of
In the 1930s, coal traffic declined with the result that many of these engines stood idle, since their limited operating range prevented them from being allocated to other mainline duties. Collett, as Churchward's successor, decided to rebuild some of the 4200 Class engines as 2-8-2Ts. The addition of a trailing axle increased the engine's operating range by allowing an increased coal and water storage capacity. Altogether 54 locomotives were modified in this manner. The 7200 Class tank engines, as they were known, remained in service until the end of steam in Britain in the early 1960s.
The designer of the BR Standard Class 9F locomotive as well as the rest of the BR standard classes as Chief Mechanical Engineer of
 The locomotive originally was built as a 2-10-0 "Decapod" type locomotive. The engines were troublesome and curves and were prone to instability. So the locomotives rearmost driver was removed and replaced with a pair of small wheels connected to a trailing truck slightly hanging behind the cab.
The locomotive originally was built as a 2-10-0 "Decapod" type locomotive. The engines were troublesome and curves and were prone to instability. So the locomotives rearmost driver was removed and replaced with a pair of small wheels connected to a trailing truck slightly hanging behind the cab.
 The 2-8-2 saw great success in the
The 2-8-2 saw great success in the  The Mikado type was, in turn, ousted from the top-flight trains by larger freight locomotive wheel arrangements such as the 2-8-4, 2-10-2, 2-10-4 and articulated locomotives, but no successor type became ubiquitous and the Mike remained the most common road freight locomotive with most railroads until the end of steam. More than 14,000 were built in the United States, about 9,500 of these for North American service, constituting about one-fifth of all locomotives in service there at the time. The heaviest Mikados were the Great Northern's class O-8, with an axle load of .
Almost all North American railroads rostered the type, notable exceptions being the Richmond, Fredericksburg & Potomac, the Boston & Maine, the Delaware & Hudson, the Western Maryland, the Cotton Belt and the Norfolk & Western. The largest users included the New York Central with 715 locomotives, the Baltimore & Ohio with 610, the
The Mikado type was, in turn, ousted from the top-flight trains by larger freight locomotive wheel arrangements such as the 2-8-4, 2-10-2, 2-10-4 and articulated locomotives, but no successor type became ubiquitous and the Mike remained the most common road freight locomotive with most railroads until the end of steam. More than 14,000 were built in the United States, about 9,500 of these for North American service, constituting about one-fifth of all locomotives in service there at the time. The heaviest Mikados were the Great Northern's class O-8, with an axle load of .
Almost all North American railroads rostered the type, notable exceptions being the Richmond, Fredericksburg & Potomac, the Boston & Maine, the Delaware & Hudson, the Western Maryland, the Cotton Belt and the Norfolk & Western. The largest users included the New York Central with 715 locomotives, the Baltimore & Ohio with 610, the
steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, Fuel oil, oil or, rarely, Wood fuel, wood) to heat ...
s, represents the wheel arrangement
In rail transport, a wheel arrangement or wheel configuration is a system of classifying the way in which wheels are distributed under a locomotive. Several notations exist to describe the wheel assemblies of a locomotive by type, position, and c ...
of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheel
On a steam locomotive, a driving wheel is a powered wheel which is driven by the locomotive's pistons (or turbine, in the case of a steam turbine locomotive). On a conventional, non-articulated locomotive, the driving wheels are all coupled t ...
s on four axles and two trailing wheels on one axle, usually in a trailing truck. This configuration of steam locomotive is most often referred to as a Mikado, frequently shortened to Mike.
It was also at times referred to on some railroads in the United States as the McAdoo Mikado and, during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, the MacArthur.
The notation 2-8-2T indicates a tank locomotive
A tank locomotive is a steam locomotive which carries its water in one or more on-board water tanks, instead of a more traditional tender (rail), tender. Most tank engines also have Fuel bunker, bunkers (or fuel tanks) to hold fuel; in a #Tender ...
of this wheel arrangement, the "T" suffix indicating a locomotive on which the water is carried in tanks mounted on the engine rather than in an attached tender.
Overview
The 2-8-2 wheel arrangement allowed the locomotive's firebox to be placed behind instead of above the driving wheels, thereby allowing a larger firebox that could be both wide and deep. This supported a greater rate of combustion and thus a greater capacity for steam generation, allowing for more power at higher speeds. Allied with the largerdriving wheel
On a steam locomotive, a driving wheel is a powered wheel which is driven by the locomotive's pistons (or turbine, in the case of a steam turbine locomotive). On a conventional, non-articulated locomotive, the driving wheels are all coupled t ...
diameter which was possible when they did not impinge on the firebox, it meant that the 2-8-2 was capable of higher speeds than a with a heavy train. These locomotives did not suffer from the imbalance of reciprocating parts as much as did the 2-6-2 or the , because the center of gravity
In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space (sometimes referred to as the barycenter or balance point) is the unique point at any given time where the weighted relative position of the distributed mass sums to zero. For ...
was between the second and third drivers instead of above the centre driver.
The first 2-8-2 locomotive was built in 1884. It was originally named ''Calumet'' by Angus Sinclair, in reference to the engines built for the Chicago & Calumet Terminal Railway (C&CT). However, this name did not take hold.LeMassena, Robert. (1993). ''America's Workhorse Locomotive: the 2-8-2''. Quadrant Press, Inc., p. 6.
The wheel arrangement name "Mikado" originated from a group of Japanese type 9700 2-8-2 locomotives that were built by Baldwin Locomotive Works
The Baldwin Locomotive Works (BLW) was an American manufacturer of railway locomotives from 1825 to 1951. Originally located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, it moved to nearby Eddystone, Pennsylvania, Eddystone in the early 20th century. The com ...
for the gauge Nippon Railway of Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
in 1897. In the 19th century, the Emperor of Japan was often referred to as "the Mikado" in English. The Gilbert and Sullivan
Gilbert and Sullivan refers to the Victorian-era theatrical partnership of the dramatist W. S. Gilbert (1836–1911) and the composer Arthur Sullivan (1842–1900) and to the works they jointly created. The two men collaborated on fourteen com ...
opera, ''The Mikado
''The Mikado; or, The Town of Titipu'' is a comic opera in two acts, with music by Arthur Sullivan and libretto by W. S. Gilbert, their ninth of fourteen Gilbert and Sullivan, operatic collaborations. It opened on 14 March 1885, in London, whe ...
'', set in Japan, had premiered in 1885 and achieved great popularity in both Britain and America.
The 2-8-2 was one of the more common configurations in the first half of the 20th century, before dieselisation
Dieselisation (US: dieselization) is the process of equipping vehicles with a diesel engine or diesel engines.
It can involve replacing an internal combustion engine powered by petrol (US: gasoline) fuel with an engine powered by diesel fuel, ...
. Between 1917 and 1944, nearly 2,200 of this type were constructed by Baldwin, the American Locomotive Company
The American Locomotive Company (often shortened to ALCO, ALCo or Alco) was an American manufacturer that operated from 1901 to 1969, initially specializing in the production of locomotives but later diversifying and fabricating at various time ...
(ALCO) and the Lima Locomotive Works
Lima Locomotive Works (LLW) was an American firm that manufactured railroad locomotives from the 1870s through the 1950s. The company's name is derived from the location of its main manufacturing plant in Lima, Ohio ( ). The shops were located be ...
, based on designs by the United States Railroad Administration (USRA). It was also known as the "McAdoo Mikado" in the United States, after William Gibbs McAdoo who was appointed as Director General of Railroads when the United States commenced hostilities during the latter part of the First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
and the USRA was established. Of all of the USRA designs, the Mikado proved to be the most popular. The total American production was about 14,000, of which 9,500 were for local customers and the rest exported.Bruce, Alfred. (1952). ''The Steam Locomotive in America: Its Development in the Twentieth Century''. W.W. Norton, pp. 296–298.
"Mikado" remained the type name until the attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Empire of Japan on the United States Pacific Fleet at Naval Station Pearl Harbor, its naval base at Pearl Harbor on Oahu, Territory of ...
in 1941. Seeking a more American name, "MacArthur", after General Douglas MacArthur
Douglas MacArthur (26 January 18805 April 1964) was an American general who served as a top commander during World War II and the Korean War, achieving the rank of General of the Army (United States), General of the Army. He served with dis ...
, came into use to describe the locomotive type in the United States. After the war, the type name "Mikado" again became the most common for that locomotive type.Steam Locomotive dot com: 2-8-2 "Mikado" Type Locomotives- retrieved 26 October 2006
Archived
21 June 2013.
Usage
Locomotives of this wheel arrangement saw service on all six populated continents. The 2-8-2 type was particularly popular in North America, but was also used extensively in Continental Europe and elsewhere.Argentina
broad gauge
The Buenos Aires and Pacific Railway bought eighteen 2-8-2T locomotives in three batches of six as their class 701 class. The first two batches came fromNorth British Locomotive Company
The North British Locomotive Company (NBL, NB Loco or North British) was created in 1903 through the merger of three Glasgow locomotive manufacturing companies; Sharp, Stewart and Company (Atlas Works), Neilson, Reid and Company (Hyde Park W ...
in 1908 and 1912, the third from Henschel & Son
Henschel & Son () was a German company, located in Kassel, best known during the 20th century as a maker of transportation equipment, including locomotives, trucks, buses and trolleybuses, and armoured fighting vehicles and weapons.
Georg Ch ...
in 1913.
The BA&P also bought eight 2-8-2 tender locomotives from Beyer, Peacock & Company in 1928 as their 3001 class.
The Central Argentine Railway (FCCA) bought fifteen 2-8-2T locomotives as their class C7 in 1912; they were built by Robert Stephenson & Company with works numbers 3506 to 3520.
The FCCA also bought sixty 2-8-2 locomotives: twenty class CS8A from Beyer, Peacock & Company in 1926, and another twenty in 1928 from Robert Stephenson & Company. The final twenty to class CS9A were supplied by Vulcan Foundry in 1930. Both classes were cross-compound locomotives with one high-pressure cylinder with a bore of and one low-pressure cylinder with a bore of , with a stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemor ...
of . The earlier class had coupled wheels with a diameter of , whereas on the later class they were .
Standard gauge
The East Argentine Railway bought four 2-8-2 locomotives fromBaldwin Locomotive Works
The Baldwin Locomotive Works (BLW) was an American manufacturer of railway locomotives from 1825 to 1951. Originally located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, it moved to nearby Eddystone, Pennsylvania, Eddystone in the early 20th century. The com ...
in 1924. As class X they were numbered 70 to 74; they became General Urquiza Railway 701 to 704 in the 1948 nationalisation. Baldwin had classified them as 12-30--E.
gauge
The Province of Buenos Aires Railway bought a single 2-8-2 locomotive from Hanomag of Germany in 1910. Numbered 251 and classified as class E, it was the only 2-8-2 on that railway's system. The Central Northern Railway (FCCN) bought seven classes of 2-8-2 locomotives totalling 134 locomotives. The first 100 were all bought in 1911: Fifteen from Borsig (class C7, numbered 700–714), 25 from Henschel & Sohn (class C8, 715–739), 10 from Hanomag (class C9, 740–749) and 50 from North British Locomotive (class C10, 750–799). The next 25 came from Baldwin Locomotive Works in 1920; they were Baldwin class 12-30--E, 55 to 79, FCCN class C11, numbered 7000–7024. The last nine new locomotives were built by Henschel between 1928 and 1930 (class C13, numbers 7025–7033, and class C13A, number 7034). In addition the FCCN rebuilt 20 4-8-0 locomotives of classes C6 and C7 into 2-8-2s between 1938 and 1940. The Córdoba Central Railway (FCCC) bought 31 locomotives in four classes. The first was a solitary locomotive, numbered 800, class C6A built by Alco's Brooks Works in 1910. It was nearly a decade before they bought any more with a dozen class C9A locomotives, numbered 1451 to 1462, coming from Montreal Locomotive Works, half in 1919 and half in 1920. MLW delivered another 15 Mikados later that same year; as class C10A they were numbered 1463 to 1477. FCCC's final three came from Baldwin Locomotive Works in 1925, they were Baldwin class 12-26--E; FCCC numbered them 1501 to 1503, class C11A. When the FCCC was taken over by the FCCN in 1939, their new owner changed the classification by adding 20 to the FCCC's old classification; the locomotives kept their old numbers, except for FCCC 800 which became FCCN 1400.gauge
On the Ferrocarriles Patagónicos, 75 locomotives were bought in 1922. Fifty were built by Henschel & Sohn, numbered 101 to 150 and class 75H; 25 were built by Baldwin, numbered 1 to 25, class 75B with Baldwin classifying then as 12-18--E.Australia
 One of the world's first 2-8-2T designs was the South Maitland Railways 10 Class, first delivered in 1911, by Beyer-Peacock, and spasmodically continuing delivery until 1925, then totaling 14 in the class.
The requirement for locomotives that could be converted from to without major re-engineering led to the introduction of Mikado locomotives by the
One of the world's first 2-8-2T designs was the South Maitland Railways 10 Class, first delivered in 1911, by Beyer-Peacock, and spasmodically continuing delivery until 1925, then totaling 14 in the class.
The requirement for locomotives that could be converted from to without major re-engineering led to the introduction of Mikado locomotives by the Victorian Railways
The Victorian Railways (VR), trading from 1974 as VicRail, was the state-owned operator of most rail transport in the Australian state of Victoria from 1859 to 1983. The first railways in Victoria were private companies, but when these companie ...
(VR) in the 1920s. Whereas previous 2-8-0 Consolidation type locomotives featured long, narrow fireboxes between the frames that made gauge conversion impractical, the N class light lines and X class heavy goods locomotives both featured wide fireboxes positioned behind the coupled wheels and above the frames.Pearce et al. (1980). '' Newport Railway Museum''. Melbourne: ARHS, p. 14.
The South Australian Railways
South Australian Railways (SAR) was the organisation through which the Government of South Australia built and operated railways in South Australia from 1854 until March 1978, when its non-urban railways were incorporated into Australian Natio ...
(SAR) employed four distinct classes of 2-8-2 locomotive, the locally designed 700 and 710 class, the 740 class that was originally built for China by Clyde Engineering and purchased by the SAR after the order was cancelled in the wake of the Chinese Communist Revolution
The Chinese Communist Revolution was a social revolution, social and political revolution in China that began in 1927 and culminated with the proclamation of the People's Republic of China (PRC) in 1949. The revolution was led by the Chinese C ...
, and the 750 class, a group of ten surplus VR N class locomotives.
To assist with the postwar rebuilding of Australian railways, American-designed Mikado locomotives were also introduced after the Second World War, such as the Baldwin-built New South Wales Government Railways (NSWGR) D59 class and the Queensland Rail
Queensland Rail (QR) is a railway operator in Queensland, Australia. Queensland Rail is owned by the Queensland Government, and operates both Commuter rail, suburban and Regional rail, interurban rail services in South East Queensland, as well ...
(QR) AC16 class.
A Mikado was also the last new class of mainline steam locomotive to be introduced in Australia, the V class heavy freight locomotive of the Western Australian Government Railways (WAGR) of 1955.
Austria
The 4-cylinder compound class 470, developed in 1914 by Karl Gölsdorf, was built for express trains on mountain lines. From 1927, some of these locomotives were rebuilt to two-cylinder superheated steam locomotives and designated class 670. They were reclassified to class 39 from 1938 and remained in service until 1957.Belgian Congo
 In 1917, 24 Mikado type steam locomotives were built for the Compagnie du chemin de fer du bas-Congo au Katanga (BCK), a new line from the
In 1917, 24 Mikado type steam locomotives were built for the Compagnie du chemin de fer du bas-Congo au Katanga (BCK), a new line from the Northern Rhodesia
Northern Rhodesia was a British protectorate in Southern Africa, now the independent country of Zambia. It was formed in 1911 by Amalgamation (politics), amalgamating the two earlier protectorates of Barotziland-North-Western Rhodesia and North ...
n border to Port Francqui in the Belgian Congo
The Belgian Congo (, ; ) was a Belgian colonial empire, Belgian colony in Central Africa from 1908 until independence in 1960 and became the Republic of the Congo (Léopoldville). The former colony adopted its present name, the Democratic Repu ...
. Since the line was just being completed at the time, the full complement of locomotives were not required immediately and four, possibly six, of them were temporarily leased to the South African Railways to alleviate a wartime shortage of locomotives. In South Africa, they were known as the Katanga Mikado. Six more of these engines were leased to the Beira and Mashonaland and Rhodesia Railways (BMR), which operated between Umtali in Southern Rhodesia
Southern Rhodesia was a self-governing British Crown colony in Southern Africa, established in 1923 and consisting of British South Africa Company (BSAC) territories lying south of the Zambezi River. The region was informally known as South ...
and Beira in Mozambique
Mozambique, officially the Republic of Mozambique, is a country located in Southeast Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi and Zambia to the northwest, Zimbabwe to the west, and Eswatini and South Afr ...
. The locomotives were all forwarded to the Belgian Congo after the war, where they were numbered in the BCK range from 201 to 224.C.F. du Bas Congo a Katanga 2-8-2 Locomotives of Congo - Class Details by Steve Llanso of Sweat House Media - Class 201 (Locobase 15020)(Accessed on 16 April 2016)Espitalier, T.J.; Day, W.A.J. (1945). ''The Locomotive in South Africa - A Brief History of Railway Development. Chapter VII - South African Railways (Continued).'' South African Railways & Harbours Magazine'' September 1945. p. 673.''
Canada
Canadian National (CN) operated a few Mikado locomotives: * One locomotive in the R-1 class, number 3000. * Thirty locomotives in the R-2 class, numbered 300 to 329. * Several locomotives in the S-1 and S-4 classes, numbered in the range between 3200-3524 and 3198-3199 and 3525-3599 and 3700-3757 and 3800-3805 .Canadian Pacific
The Canadian Pacific Railway () , also known simply as CPR or Canadian Pacific and formerly as CP Rail (1968–1996), is a Canadian Class I railway incorporated in 1881. The railway is owned by Canadian Pacific Kansas City, Canadian Pacific Ka ...
(CP) used Mikado locomotives for passenger and freight trains throughout Canada. Most worked in the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in great-circle distance, straight-line distance from the northernmost part of Western Can ...
, where the standard 4-6-2 Pacifics and 4-6-4 Hudsons could not provide enough traction to handle the steep mountain grades.
The Temiskaming & Northern Ontario (renamed Ontario Northland Railway
The Ontario Northland Railway is a Canadian railway operated by the Ontario Northland Transportation Commission, a Crown agency (Ontario), provincial Crown agency of the government of Ontario.
Originally built to develop the Lake Timiskaming ...
in 1946) operated seventeen Mikados, all ordered from Canadian Locomotive Company in three batches, the first six in 1916, second batch of four in 1921, and the final seven in 1923 to 1925. They were scrapped between 1955 and 1957 when the Ontario Northland was completely dieselized, except for three wrecked and scrapped in the 1940s. The Temiskaming & Northern Ontario operated its Mikados on both freight and passenger service, and were fitted with smoke deflectors. In 1946 65 out of 199 Canadian Pacific N2 2-8-0's were rebuilt and converted to Class P1n 2-8-2's . However all were scrapped around 1955 and 1958 . No P1n 2-8-2's were preserved however CP no . 5468 is preserved
CP's no. 5468, on display in Revelstoke, British Columbia. And CP's 5361 a Class P2e is preserved Depew New York.
China
 Some local industries still actively use Mikados on freight service. The last regular Mikado passenger service was ended on 20 November 2015 in Baiyin. A few Chinese-made locomotives have found their way into the United States, including Class SY no. 3025, built in 1989, which operated as New Haven no. 3025, in honor of Class J1 no. 3001-3024, on the Valley Railroad in Connecticut. The locomotive now operates on the Belvidere & Delaware as no. 142. It is original to the New York, Susquehanna & Western Railway as no. 142. It and two other Chinese 2-8-2s are currently in the United States.
Some local industries still actively use Mikados on freight service. The last regular Mikado passenger service was ended on 20 November 2015 in Baiyin. A few Chinese-made locomotives have found their way into the United States, including Class SY no. 3025, built in 1989, which operated as New Haven no. 3025, in honor of Class J1 no. 3001-3024, on the Valley Railroad in Connecticut. The locomotive now operates on the Belvidere & Delaware as no. 142. It is original to the New York, Susquehanna & Western Railway as no. 142. It and two other Chinese 2-8-2s are currently in the United States.
Finland
 Finland's sixteen gauge Class Pr1 were 2-8-2T passenger locomotives for use on local trains. They were nicknamed ''Paikku'', which means local. The Class Pr1 was operational from 1924 to 1972. Numbered 761 to 776, they were built by Hanomag in Germany and also by Finnish locomotive builders
Finland's sixteen gauge Class Pr1 were 2-8-2T passenger locomotives for use on local trains. They were nicknamed ''Paikku'', which means local. The Class Pr1 was operational from 1924 to 1972. Numbered 761 to 776, they were built by Hanomag in Germany and also by Finnish locomotive builders Tampella
Oy Tampella Ab was a Finland, Finnish heavy industry manufacturer, a maker of paper machines, locomotives, military weaponry, as well as wood-based products such as packaging. The company was based mainly in the Naistenlahti, Naistenlahti di ...
and Lokomo. The last one, no. 776, is preserved at the Finnish Railway Museum.
The Finnish Class Tr1 (or R1) tender locomotive was built by Tampella, Lokomo and German locomotive builders Arnold Jung from 1940 and remained in service until 1975. They were numbered from 1030 to 1096 and were nicknamed ''Risto'', after Finnish President Risto Ryti. 1030, 1033, 1037, 1047, 1051, 1055, 1057, 1060, 1067, 1071, 1074, 1077, 1082, 1087, 1088, 1092, 1093, 1094, 1095 and 1096 are preserved
France
France used a fairly large number of 2-8-2s in both tender and tank configurations, designated 141 class from the French classification system of wheel arrangements.Tender locomotives
Of the pre-nationalisation railway companies that existed before the formation of theSNCF
The Société nationale des chemins de fer français (, , SNCF ) is France's national State-owned enterprise, state-owned railway company. Founded in 1938, it operates the Rail transport in France, country's national rail traffic along with th ...
, the Chemins de fer de Paris à Lyon et à la Méditerranée (PLM) had the most Mikados. Their first twelve were initially numbered from 1001 to 1012 and later renumbered to 141.A.1 to 141.A.12. The PLM's second series, numbered from 1013 to 1129 and later renumbered 141.B.1 to 141.B.117, were built by Baldwin Locomotive Works
The Baldwin Locomotive Works (BLW) was an American manufacturer of railway locomotives from 1825 to 1951. Originally located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, it moved to nearby Eddystone, Pennsylvania, Eddystone in the early 20th century. The com ...
in the United States. Their third and largest class was numbered from 141.C.1 to 141.C.680. Of these latter locomotives, those fitted with feedwater heater
A feedwater heater is a power plant component used to pre-heat water delivered to a steam generating boiler. Preheating the feedwater reduces the irreversibilities involved in steam generation and therefore improves the thermodynamic efficiency o ...
s bore the class letter D. The PLM also rebuilt forty-four 141.C and 141.D class locomotives to 141.E class. The SNCF modified the PLM numbers by adding the regional prefix digit "5".
The PLM's 141.A class Mikados were copied by the Chemins de fer du Nord, who had fifty, numbered from 4.1101 to 4.1150, which became 2-141.A.1 to 2-141.A.50 on the SNCF.
The Chemins de fer de l'État also had a class of 250 Mikados, numbered from 141-001 to 141-250. These later became the 141.B class on the SNCF and were renumbered 3-141.B.1 to 3-141.B.250. After modifications, the 141.B class locomotives became the 141.C class, as well as one 141.D class (no. 141.D.136) and one 141.E class (no. 141.E.113). No. has been preserved and designated a Monument historique.
 The most powerful French Mikado was the SNCF 141.P class. At about , these engines were among the most efficient steam locomotives in the world, thanks to their compound design. They could burn 30% less fuel and use 40% less water than their 141.R class counterparts, but could not compete when it came to reliability. Every locomotive of this 318-strong class has been scrapped.
The most powerful French Mikado was the SNCF 141.P class. At about , these engines were among the most efficient steam locomotives in the world, thanks to their compound design. They could burn 30% less fuel and use 40% less water than their 141.R class counterparts, but could not compete when it came to reliability. Every locomotive of this 318-strong class has been scrapped.
 The most numerous steam locomotive class France had, was the American and Canadian-built 141.R class. Of the 1,340 locomotives ordered, however, only 1,323 entered service since sixteen engines were lost at sea during a storm off the coast of Newfoundland while being shipped to France, while one more was lost in
The most numerous steam locomotive class France had, was the American and Canadian-built 141.R class. Of the 1,340 locomotives ordered, however, only 1,323 entered service since sixteen engines were lost at sea during a storm off the coast of Newfoundland while being shipped to France, while one more was lost in Marseille
Marseille (; ; see #Name, below) is a city in southern France, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Departments of France, department of Bouches-du-Rhône and of the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur Regions of France, region. Situated in the ...
harbour. They were praised for being easy to maintain and proved to be very reliable, which may account for the fact that they remained in service until the very end of the steam era in 1975. Twelve of these locomotives have been preserved.
Tank locomotives
The Chemins de fer d'Alsace et de Lorraine had a class of forty 2-8-2T locomotives, the T 14 class, later numbered SNCF to . They were identical to Germany's Prussian T 14 class locomotive and were built between 1914 and 1918. (Also seeGermany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
)
The Chemins de fer de l'Est
The Compagnie des chemins de fer de l'Est (, , CF de l'Est), often referred to simply as the Est company, was an early France, French railway, railway company. The company was formed in 1853 by the merger of ''Compagnie du chemin de fer de Pari ...
had two Mikado classes. The first was numbered from 4401 to 4512, later renumbered 141.401 to 141.512 and finally SNCF 1-141.TB.401 to 1-141.TB.512. The other was numbered from 141.701 to 141.742 and later SNCF 1-141.TC.701 to 1-141.TC.742.
The Chemin de Fer du Nord also had two 2-8-2T classes. The first, consisting of only two locomotives, was numbered 4.1201 and 4.1202, later renumbered 4.1701 and 4.1702 and finally SNCF 2-141.TB.1 and 2-141.TB.2. The second, with 72 locomotives, was numbered from 4.1201 to 4.1272 and later SNCF 2-141.TC.1 to 2-141.TC.72.
The Chemins de Fer de l'État also had two Mikado classes. The first, numbered from to , later became the SNCF 141.TC class and were renumbered 3-141.TC.1 to 3-141.TC.20. The second, numbered from to , later became the SNCF 141TD class and were renumbered to . They were copies of the series of the ''Chemins de fer de l'Est''.
The Compagnie du chemin de fer de Paris à Orléans
The ''Compagnie du chemin de fer de Paris à Orléans'' (, PO) was an early French railway company.
It merged with the '' Chemins de fer du Midi'' to form the '' Chemins de fer de Paris à Orléans et du Midi'' (PO-Midi) in 1934. In 1938 the PO ...
(PO) also had two classes. The first was numbered from 5301 to 5490 and later SNCF to . The second was numbered from 5616 to 5740 and later 4-SNCF to .
Germany
German 2-8-2 tender locomotives were built in both passenger and freight versions. * An Express-service locomotive was the DRG Class 19 „Sachsenstolz“ (Pride of Saxony), developed by the Royal Saxon State Railways as type XX (Roman Numeral
Roman numerals are a numeral system that originated in ancient Rome and remained the usual way of writing numbers throughout Europe well into the Late Middle Ages. Numbers are written with combinations of letters from the Latin alphabet, ea ...
20; superheated steam (H); compound (V)) to provide express service in the Saxonian Bohemian Massif
The Bohemian Massif ( or ''Český masiv'', or ''Böhmisches Massiv'') is a geomorphological province in Central Europe. It is a large massif stretching over most of the Czech Republic, eastern Germany, southern Poland and northern Austria.
Th ...
.
* The passenger locomotive was the DRG Class 39, initially the Class P 10 of the Prussian state railways
The term Prussian state railways (German: ''Preußische Staatseisenbahnen'') encompasses those railway organisations that were owned or managed by the state of Prussia. The words "state railways" are not capitalized because Prussia did not have a ...
, which was built for hauling heavy express trains in the hilly and mountainous terrain of the ''Mittelgebirge''. When they were assimilated into the Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft (DRG), they were designated as DRG Class 39.
 * Although going out of production when the DRB consolidated their production into 2-10-0 1'E DRB Class 52 Kriegslok designs, the DRB Class 41 „Ochsenlok“ (Oxen Loco) was a successful 1'D1 2-8-2 freight locomotive also used for commuter trains. They were operated by the
* Although going out of production when the DRB consolidated their production into 2-10-0 1'E DRB Class 52 Kriegslok designs, the DRB Class 41 „Ochsenlok“ (Oxen Loco) was a successful 1'D1 2-8-2 freight locomotive also used for commuter trains. They were operated by the Deutsche Reichsbahn
The ''Deutsche Reichsbahn'' (), also known as the German National Railway, the German State Railway, German Reich Railway, and the German Imperial Railway, was the Weimar Republic, German national Rail transport, railway system created after th ...
(DRB) and were built from 1937 to 1941, gaining notoriety as the German steam locomotive with the highest efficiency
Efficiency is the often measurable ability to avoid making mistakes or wasting materials, energy, efforts, money, and time while performing a task. In a more general sense, it is the ability to do things well, successfully, and without waste.
...
η of 10%.
Both standard gauge and narrow gauge 1D1 2-8-2 tank locomotive classes were used in Germany.
* The DRG Class 93.0-4 was a German 2-8-2T goods train tank locomotive that was used by the Prussian state railways as well as the French Chemins de fer d'Alsace et de Lorraine, designated as Class T14 by both railways. The Prussian locomotives were later incorporated by the Deutsche Reichsbahn
The ''Deutsche Reichsbahn'' (), also known as the German National Railway, the German State Railway, German Reich Railway, and the German Imperial Railway, was the Weimar Republic, German national Rail transport, railway system created after th ...
and designated Class 93.0-4 under the DRG renumbering plan. Altogether 457 locomotives of this class were built for the Prussian state railways between 1914 and 1918. (Also see France - Tank locomotives)
* The DRG Class 86 was a standard goods train tank locomotive of the DRG. It was intended for duties on branch lines and was manufactured by almost all the locomotive building firms producing for the DRG. From 1942, a simplified wartime version was built, on which the most obvious changes were the omission of the second side windows in the cab and the solid disc carrying wheels.
* The Molli railway (''Mollibahn''), a narrow-gauge steam-powered railway in Mecklenburg
Mecklenburg (; ) is a historical region in northern Germany comprising the western and larger part of the federal-state Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. The largest cities of the region are Rostock, Schwerin, Neubrandenburg, Wismar and Güstrow. ...
running on gauge track, operates three 2-8-2T locomotives built by Orenstein & Koppel in 1932.
India
Broad gauge
On the gauge, the Class XD was the first 2-8-2 in India to be built in quantity. Introduced in 1927, 78 were built before the Second World War by Vulcan Foundry,North British Locomotive Company
The North British Locomotive Company (NBL, NB Loco or North British) was created in 1903 through the merger of three Glasgow locomotive manufacturing companies; Sharp, Stewart and Company (Atlas Works), Neilson, Reid and Company (Hyde Park W ...
(NBL), Armstrong Whitworth
Sir W G Armstrong Whitworth & Co Ltd was a major British manufacturing company of the early years of the 20th century. With headquarters in Elswick, Tyne and Wear, Elswick, Newcastle upon Tyne, Armstrong Whitworth built armaments, ships, locomot ...
and Škoda Works
The Škoda Works (, ) was one of the largest European industrial conglomerates of the 20th century. In 1859, Czech engineer Emil Škoda bought a foundry and machine factory in Plzeň, Bohemia, Austria-Hungary that had been established ten ye ...
. Production resumed after the war, and 110 were built by NBL in 1945 and 1946, while Vulcan Foundry built the last six in 1948.
 There was also a Class XE that was built by William Beardmore & Company and Vulcan Foundry. Wartime designs included the Class AWD and Class AWE, built by American company
There was also a Class XE that was built by William Beardmore & Company and Vulcan Foundry. Wartime designs included the Class AWD and Class AWE, built by American company Baldwin Locomotive Works
The Baldwin Locomotive Works (BLW) was an American manufacturer of railway locomotives from 1825 to 1951. Originally located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, it moved to nearby Eddystone, Pennsylvania, Eddystone in the early 20th century. The com ...
, and the Class X-Dominion (later Class CWD) built as part of Canada's Mutual Aid program by two Canadian companies, the Canadian Locomotive Company and Montreal Locomotive Works
Montreal Locomotive Works (MLW) was a Canadian railway locomotive manufacturer that existed under several names from 1883 to 1985, producing both Steam locomotive, steam and diesel locomotives. For many years it was a subsidiary of the American ...
.Hughes, Hugh. (1996). ''Indian Locomotives, Part 4 – 1941-1990''. Harrow, Middlesex: Continental Railway Circle, pp. 19-20, 24.
 After the war, a new design was produced and placed in production in 1950. The Class WG was the main post-war broad gauge freight locomotive type of the Indian Railways (IR). The first order of 200 was split evenly between NBL and Chittaranjan Locomotive Works (CLW). Apart from Indian manufacture, examples were also built in England, Scotland, Germany, Austria, the United States, Japan and Italy. By the time production ceased in 1970, 2,450 Class WG locomotives had been built.
After the war, a new design was produced and placed in production in 1950. The Class WG was the main post-war broad gauge freight locomotive type of the Indian Railways (IR). The first order of 200 was split evenly between NBL and Chittaranjan Locomotive Works (CLW). Apart from Indian manufacture, examples were also built in England, Scotland, Germany, Austria, the United States, Japan and Italy. By the time production ceased in 1970, 2,450 Class WG locomotives had been built.
Metre gauge
AfterWorld War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, an Indian Railway Standards (IRS) 2-8-2 class became the main heavy freight locomotive on the . While two versions were designed, the Class YD with a 10-ton axle load and the Class YE with a 12-ton axle load, none was built of the latter class.Hughes, Hugh. (1992). ''Indian Locomotives, Part 2 – Metre Gauge 1872-1940''. Harrow, Middlesex: Continental Railway Circle, p. 19.
During World War II, many of the war-time United States Army Transportation Corps class S118 locomotives were sent to India and 33 more were ordered after the war.
The post World War II Mikado design was the Class YG, of which 1,074 were built between 1949 and 1972, with nearly half of them being manufactured in India.
Narrow gauges
Two narrow track gauges were in use in India. The gauge was the more widely used while the gauge was used by theDarjeeling Himalayan Railway
The Darjeeling Himalayan Railway, also known as the DHR or the Toy Train, is a narrow-gauge, gauge railway that runs between New Jalpaiguri and Darjeeling in the Indian state of West Bengal. Built between 1879 and 1881, it is about long. It c ...
and the Scindia State Railway. Mikado type locomotives were used by the following:
* The Bengal Nagpur Railway used a saturated steam B class, a superheated BS class, and a BC class comprising B class locomotives that had been converted from saturated to superheated.
* The Barsi Light Railway used an F class of thirteen locomotives, ten built by Nasmyth, Wilson & Company between 1926 and 1929, and three built by Hunslet Engine Company
The Hunslet Engine Company is a locomotive building company, founded in 1864 in Hunslet, England. It manufactured steam locomotives for over 100 years and currently manufactures Diesel engine, diesel Switcher, shunting locomotives. The company ...
in 1949.
* The Great Indian Peninsula Railway used a B/1 class of seven locomotives, four built by NBL in 1917, one more by NBL in 1922, and two by Nasmyth, Wilson & Company in 1926.
* The Scindia State Railway used sixteen locomotives of five classes, the Classes NH/1 through NH/5, built between 1914 and 1959.Hughes, Hugh & Jux, Frank. (1980). ''Steam Locomotives in India, Part 1 – Narrow Gauge''. Harrow, Middlesex: Continental Railway Circle, p. 29.
The standard narrow gauge 2-8-2 locomotive was the ZE class, with 65 engines built by five companies between 1928 and 1954. Nasmyth, Wilson built ten in 1928, Hanomag built sixteen in 1931, Corpet-Louvet built twelve in 1950, KraussMaffei built fifteen in 1952 and another ten in 1954, and Kawasaki Heavy Industries
is a Japanese Public company, public multinational corporation manufacturer of motorcycles, engines, Heavy equipment (construction), heavy equipment, aerospace and Military, defense equipment, rolling stock and ships, headquartered in Minato, To ...
built ten in 1954. In 1957 and 1958, six ZD class locomotives were also built by Nippon Sharyo
, formed in 1896, is a major rolling stock, Heavy equipment, heavy equipment, Diesel generator, generator, Special-purpose entity, special purpose vehicle and bridge manufacturer based in Nagoya, Japan. In 1996, it abbreviated its ...
in Japan.
Indonesia
Before 1945, the Dutch East Indies Railway Administration, '' Staatspoorwegen'' (SS), received two types of locomotives with a 2-8-2 wheel arrangement. First, they received 10 units of 1,050 mm gauge of SS Class 1500 tender engine of 1920 from Hartmann that was previously intended for the Hejaz Railway, but later diverted to Java prior to theFirst World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
and the drive wheels were adjusted to 1,067 mm gauge. After delivered, they present a difficulty. Their axle weigh 13 tons which way much heavier than weight permitted on bridges and mountainous lines (11 tons). Hence for safety reason, the SS 1500s were only allowed to haul light freight trains on flat lines. Second, they received 24 units of 2-8-2 T from Hanomag and Werkspoor later classified as SS Class 1400 in 1921-22 which were the tank version of the 2-8-0 SS Class 900 (DKA D50). The SS Class 1400 initially was intended to be heavyweight shunter
A switcher locomotive (American English), shunter locomotive (British English), station pilot (British English), or shifter locomotive ( Pennsylvania Railroad terminology) is a locomotive used for maneuvering railway vehicles over short distan ...
, but due to Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
, the SS had to preserve some of their large locomotives. So, the SS 1400s were used to haul express trains on the Bogor
Bogor City (), or Bogor (, ), is a landlocked city in the West Java, Indonesia. Located around south of the national capital of Jakarta, Bogor is the 6th largest city in the Jakarta metropolitan area and the 14th overall nationwide.
–Sukabumi
Sukabumi () is a landlocked city surrounded by the Sukabumi Regency, regency of the same name (within which it is an enclave and exclave, enclave) in the southern foothills of Mount Gede, in West Java, Indonesia, about south of the national ca ...
line.
This decision was made by the top brass of SS that the SS 1400s were also tough, have power output to 1171 hp. In addition, SS Class 1400 also has compact characteristic, so it was suitable to work on mountainous line. After Japanese occupation and Indonesian Independence both locomotives renumbered to D51 (SS 1500) and D14 (SS 1400) based on Japanese numberings. During the 1970s report, one of D51 (D5101) was sighted at Klakah depot at Lumajang, East Java
East Java (, , ) is a Provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia located in the easternmost third of Java island. It has a land border only with the province of Central Java to the west; the Java Sea and the Indian Ocean border its northern ...
while most of her sisters were found normally worked on Surabaya
Surabaya is the capital city of East Java Provinces of Indonesia, province and the List of Indonesian cities by population, second-largest city in Indonesia, after Jakarta. Located on the northeastern corner of Java island, on the Madura Strai ...
– Kroya southern line. Out of 10 units, only D51 06 preserved at Ambarawa Railway Museum. In 1970, the population of D14 locomotives continued to dwindle as they were replaced by the presence of diesel locomotives, and from 24 units only D14 10 of Hanomag is preserved. Previously, D14 10 was a static display at Taman Mini Indonesia Indah
Taman Mini Indonesia Indah (; formerly Taman Mini "Indonesia Indah" with apostrophes—abbreviated as TMII) is a culture-based recreational area located in East Jakarta, Indonesia. Since July 2021, it is operated by InJourney Destination Managem ...
before it was brought to Pengok Workshop to conserved it and converted from oil to wood burner. Finally successfully restored in November 2019 and used today to haul excursion train in Surakarta
Surakarta (Javanese script, Javanese: , Pegon script, Pegon: ), known colloquially as Solo (Javanese script, Javanese: ; ), is a major List of regencies and cities of Indonesia, city in Central Java, Indonesia. The city adjoins Karanganyar Reg ...
, Central Java
Central Java (, ) is a Provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia, located in the middle of the island of Java. Its administrative capital is Semarang. It is bordered by West Java in the west, the Indian Ocean and the Special Region of Yogya ...
beside Rob's C12 18 named ''Sepur Kluthuk Jaladara''.
 After Indonesian Independence in 1945, the government of Indonesia nationalized all of the Dutch-owned railway companies, including the SS whose name was later changed to ''Djawatan Kereta Api'' (DKA) or the Department Railway of the Republic of Indonesia. Shortly after, by 1951-1952 the DKA bought 100 brand new of ''Mikado'' steam locomotives from
After Indonesian Independence in 1945, the government of Indonesia nationalized all of the Dutch-owned railway companies, including the SS whose name was later changed to ''Djawatan Kereta Api'' (DKA) or the Department Railway of the Republic of Indonesia. Shortly after, by 1951-1952 the DKA bought 100 brand new of ''Mikado'' steam locomotives from Krupp
Friedrich Krupp AG Hoesch-Krupp (formerly Fried. Krupp AG and Friedrich Krupp GmbH), trade name, trading as Krupp, was the largest company in Europe at the beginning of the 20th century as well as Germany's premier weapons manufacturer dur ...
, Germany. These locomotives, designated the D52 type, were the most modern steam locomotive in Indonesia at that time, with a large physical appearance and equipped with electric lighting. It was similar to the Class 41 locomotive of the Deutsche Reichsbahn
The ''Deutsche Reichsbahn'' (), also known as the German National Railway, the German State Railway, German Reich Railway, and the German Imperial Railway, was the Weimar Republic, German national Rail transport, railway system created after th ...
.
In Java
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. With a population of 156.9 million people (including Madura) in mid 2024, proje ...
, the D52 locomotives were placed in passenger service, but was occasionally also used as freight locomotives. Some people even idolized the D52 because of its loyalty in taking passengers anywhere, as happened on the Rapih Dhoho Train from Madiun to Kertosono. The D52 was a mainstay for this train until the end of steam operation in Indonesia.
In contrast to the Java-based units, Sumatra
Sumatra () is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the list of islands by area, sixth-largest island in the world at 482,286.55 km2 (182,812 mi. ...
-based D52 locomotives were used for hauling freight trains, mainly coal trains from the Tanjung Enim coal mine, now owned by the PT Bukit Asam mining company, to the coal dumping sites at Kertapati and Tarahan.
The D52 locomotives were initially coal-fired but, from mid-1956, 28 locomotives, numbers D52002 to D52029, were converted to oil burners. The work was done in stages over five years by the locomotive repair shop at Madiun.
One locomotive from this class was written off from service near Linggapura station after a boiler explosion that killed its driver, as a result of steam pipe failure. The only one of the original 100 locomotives that survived into the 21st century is D52 number D52099, which is on display at the Transport Museum in Taman Mini Indonesia Indah. Later on, the D52099 was moved to Purwosari station along with D14 10 which was successfully restored to action, but the D52099 still remained at the station and awaiting for another restoration.
Italy
Italian railways relied primarily on 2-6-2s for fast passenger services, while heavy passenger service was assigned to 2-8-0s of the classes 744 and745
__NOTOC__
Year 745 ( DCCXLV) was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 745 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe ...
. Although Mikado types had little opportunity for development in Italy, Ferrovie dello Stato Italiane (FS) commissioned the class 746 for heavy passenger service on the Adriatic route. To serve local branches and mountain lines where tank locomotives were more suitable, FS derived the new class 940 from the 2-8-0 class 740, with the same dimensions but adding a rear Bissel truck to support the coal bunker behind the cab to make it a 2-8-2.
Japan
 The Japanese Government Railways (JGR) built the Class D50, Class D51, and Class D52 Mikado tender locomotives for use on the gauge lines on the Japanese mainland and in its former colonies. (Also see
The Japanese Government Railways (JGR) built the Class D50, Class D51, and Class D52 Mikado tender locomotives for use on the gauge lines on the Japanese mainland and in its former colonies. (Also see Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
.) Among those, the D51 was the most popular with a total of 1,115 units produced, the most of any single class of locomotive in Japan. A few of the D51s remain in operation for excursion services, with many preserved nationwide.
New Zealand
Only one 2-8-2 locomotive ever operated onNew Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
's national rail network, and it was not even ordered by the New Zealand Railways Department, who ran almost the entire network. The locomotive was ordered in 1901 from Baldwin Locomotive Works
The Baldwin Locomotive Works (BLW) was an American manufacturer of railway locomotives from 1825 to 1951. Originally located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, it moved to nearby Eddystone, Pennsylvania, Eddystone in the early 20th century. The com ...
by the Wellington & Manawatu Railway Company (WMR) for use on their main line's steep section between Wellington
Wellington is the capital city of New Zealand. It is located at the south-western tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Remutaka Range. Wellington is the third-largest city in New Zealand (second largest in the North Island ...
and Paekakariki. It entered service on 10 June 1902 as the WMR's no. 17. At the time, it was the most powerful locomotive in New Zealand and successfully performed its intended tasks.
When the WMR was incorporated into the national network in 1908, the Railways Department reclassified no. 17 as the solitary member of the BC class, no. BC 463, and the locomotive continued to operate on the Wellington-Paekakariki line until it was withdrawn on 31 March 1927.
Philippines
 According to
According to Iowa State University
Iowa State University of Science and Technology (Iowa State University, Iowa State, or ISU) is a Public university, public land-grant university, land-grant research university in Ames, Iowa, United States. Founded in 1858 as the Iowa Agricult ...
professor Jonathan Smith, the Mikado was the most popular wheel arrangement of freight-purpose tender locomotives on the Manila Railroad. 67 units of the wheel class were delivered between 1927 and 1951, distributed into 4 classes.
The first 2-8-2 steam locomotive was the Baldwin-built Manila Railroad 250 class introduced in 1928. It was the freight version of the 4-6-2 ''Pacific''-type 140 class built for passenger rail services in Luzon
Luzon ( , ) is the largest and most populous List of islands in the Philippines, island in the Philippines. Located in the northern portion of the List of islands of the Philippines, Philippine archipelago, it is the economic and political ce ...
. More classes were ordered after the war. The United States Army Transportation Corps class S118, locally referred to as the Manila Railroad 800 class ''USA'' in which 45 units were ordered in 1944. These were numbered 851 to 895, with three named locomotives have been named: No. 865 Huckleberry Finn, No. 866 Tom Sawyer and No. 867 ''Hanibella''. Two more locomotives were ordered in 1948 from the War Assets Administration
The War Assets Administration (WAA) was created to dispose of United States government-owned surplus material and property from World War II. The WAA was established in the Office for Emergency Management, effective March 25, 1946, by Executive Or ...
and were numbered the 630 class. These were locally assembled at the MRR workshop in Caloocan
Caloocan, officially the City of Caloocan (; ), is a highly urbanized city in Metro Manila, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 1,661,584 people making it the fourth-most populous city in the Philippines.
Caloo ...
. Lastly, 10 JNR Class D51 locomotives were ordered from Nippon Sharyo
, formed in 1896, is a major rolling stock, Heavy equipment, heavy equipment, Diesel generator, generator, Special-purpose entity, special purpose vehicle and bridge manufacturer based in Nagoya, Japan. In 1996, it abbreviated its ...
in 1951 and were numbered the 300 class according to the Brotherhood of Locomotive Engineers and Trainmen.
All of these locomotives were decommissioned in 1956 and were scrapped afterwards.
Poland
Between 1932 and 1939, Polish industry supplied PKP with 98 Mikados of class Pt31 of own design (further 12 were built under German occupation). After World War II additional 180 of improved class Pt47 were built until 1951. Both classes were used to run heavy (600 ton) long-distance passenger trains on main lines. They were the most powerful passenger locomotives in Poland. Their wheel diameter was 1.85 m, power output 2000 hp and speed 110 km/h. 191 TKt48 2-8-2 tank locomotives were delivered to PKP between 1950 and 1957, with additional two built for the industry and six exported toAlbania
Albania ( ; or ), officially the Republic of Albania (), is a country in Southeast Europe. It is located in the Balkans, on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea, and shares land borders with Montenegro to ...
. They were used on suburban passenger trains and on goods trains in lower mountain areas.
South Africa
Only six Mikado locomotive classes saw service in South Africa, five on Cape gauge and one on narrow gauge. The type was rare, with only two of these classes built in quantity.Cape gauge
 During 1887, designs for a 2-8-2 Mikado type tank-and-tender locomotive were prepared by the Natal Government Railways. The single locomotive was built in the Durban workshops and entered service in 1888, named ''Havelock'', but was soon rebuilt to a Pacific configuration. The engine ''Havelock'' was the first locomotive to be designed and built in South Africa and also the first to have eight-coupled wheels.
In 1903, the Cape Government Railways (CGR) placed two Cape Class 9 2-8-2 locomotives in service, designed by H.M. Beatty, Locomotive Superintendent of the CGR from 1896 to 1910, and built by
During 1887, designs for a 2-8-2 Mikado type tank-and-tender locomotive were prepared by the Natal Government Railways. The single locomotive was built in the Durban workshops and entered service in 1888, named ''Havelock'', but was soon rebuilt to a Pacific configuration. The engine ''Havelock'' was the first locomotive to be designed and built in South Africa and also the first to have eight-coupled wheels.
In 1903, the Cape Government Railways (CGR) placed two Cape Class 9 2-8-2 locomotives in service, designed by H.M. Beatty, Locomotive Superintendent of the CGR from 1896 to 1910, and built by Kitson & Company
Kitson and Company was a locomotive manufacturer based in Hunslet, Leeds, West Yorkshire, England.
Early history
The company was started in 1835 by James Kitson (businessman), James Kitson at the Airedale Foundry, off Pearson Street, Hunslet, ...
. They had bar frames, Stephenson's link motion valve gear and used saturated steam. In comparison with the Cape Class 8 2-8-0 locomotive of 1901, however, it was found that their maintenance costs were much higher without any advantage in terms of efficiency. As a result, no more of the type were ordered. In 1912, when these locomotives were assimilated into the South African Railways (SAR), they were classified as Class Experimental 4.Classification of S.A.R. Engines with Renumbering Lists, issued by the Chief Mechanical Engineer's Office, Pretoria, January 1912, pp. 9, 12, 15, 36-37 (Reprinted in April 1987 by SATS Museum, R.3125-6/9/11-1000)
In 1904, the Central South African Railways (CSAR) placed 36 Class 11 Mikados in service. Built by the North British Locomotive Company
The North British Locomotive Company (NBL, NB Loco or North British) was created in 1903 through the merger of three Glasgow locomotive manufacturing companies; Sharp, Stewart and Company (Atlas Works), Neilson, Reid and Company (Hyde Park W ...
(NBL), it was designed by P.A. Hyde, Chief Locomotive Superintendent of the CSAR from 1902 to 1904, for goods train service on the Witwatersrand
The Witwatersrand (, ; ; locally the Rand or, less commonly, the Reef) is a , north-facing scarp in South Africa. It consists of a hard, erosion-resistant quartzite metamorphic rock, over which several north-flowing rivers form waterfalls, w ...
. It was superheated, with a Belpaire firebox, Walschaerts valve gear and plate frame. The Class 11 designation was retained when the CSAR was amalgamated into the SAR in 1912.
In 1906, the CGR placed a single experimental 2-8-2 in service, designed by H.M. Beatty and built by Kitson. It was a larger version of the Cape Class 9 in all respects, also with a bar frame, Stephenson's link motion valve gear and using saturated steam. The locomotive was not classified and was simply referred to as "the Mikado". On the CGR it was exceeded in size only by the Kitson-Meyer 0-6-0+0-6-0 of 1904. At the time, it was considered as a big advance in motive power, but the design was never repeated and the Cape Mikado remained unique. In 1912, it was classified as Class Experimental 5 on the SAR.
In 1917, the South African Railways placed at least four, possibly six, Mikado type steam locomotives in service. They had been built for the ''Chemins de Fer du Bas Congo á Katanga'' in the Belgian Congo
The Belgian Congo (, ; ) was a Belgian colonial empire, Belgian colony in Central Africa from 1908 until independence in 1960 and became the Republic of the Congo (Léopoldville). The former colony adopted its present name, the Democratic Repu ...
and were obtained on temporary lease, to alleviate the critical shortage of locomotives as a result of the First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
's disruption of locomotive production in Europe and the United Kingdom. The Katanga Mikados, as the locomotives were known on the SAR, were all forwarded to the Belgian Congo
The Belgian Congo (, ; ) was a Belgian colonial empire, Belgian colony in Central Africa from 1908 until independence in 1960 and became the Republic of the Congo (Léopoldville). The former colony adopted its present name, the Democratic Repu ...
after the war.
Narrow gauge
Between 1931 and 1958, 21narrow gauge
A narrow-gauge railway (narrow-gauge railroad in the US) is a railway with a track gauge (distance between the rails) narrower than . Most narrow-gauge railways are between and .
Since narrow-gauge railways are usually built with Minimum railw ...
Class NG15 Mikados, developed from the Class Hd and Class NG5 of South West Africa
South West Africa was a territory under Union of South Africa, South African administration from 1915 to 1990. Renamed ''Namibia'' by the United Nations in 1968, Independence of Namibia, it became independent under this name on 21 March 1990. ...
(SWA), were acquired for the Otavi Railway in SWA. Designed by the SAR, it was built by Henschel & Son
Henschel & Son () was a German company, located in Kassel, best known during the 20th century as a maker of transportation equipment, including locomotives, trucks, buses and trolleybuses, and armoured fighting vehicles and weapons.
Georg Ch ...
and Société Franco-Belge
The Société Franco-Belge was a Franco-Belgian engineering firm that specialised in the construction of railway vehicles and their components and accessories. The company originated in 1859 as the Belgian firm Compagnie Belge pour la Constructio ...
. A major improvement on the earlier locomotives was the use of a Krauss-Helmholtz bogie, with the leading pair of driving wheels linked to the leading pony truck. The leading driving wheels had a limited amount of side play while the axle still remained parallel to the other three driving axles at all times, thus allowing the locomotive to negotiate sharper curves than its two predecessors. When the SWA narrow gauge line was regauged to Cape gauge in 1960, all these locomotives were transferred to the Eastern Cape
The Eastern Cape ( ; ) is one of the nine provinces of South Africa. Its capital is Bhisho, and its largest city is Gqeberha (Port Elizabeth). Due to its climate and nineteenth-century towns, it is a common location for tourists. It is also kno ...
for further service on the Langkloof narrow gauge line from Port Elizabeth
Gqeberha ( , ), formerly named Port Elizabeth, and colloquially referred to as P.E., is a major seaport and the most populous city in the Eastern Cape province of South Africa. It is the seat of the Nelson Mandela Bay Metropolitan Municipal ...
to Avontuur. Here they were nicknamed the ''Kalahari''. Victorias Milling Co. 2H is a Henschel built 0-8-0T dated 1927.
South West Africa (Namibia)
Two very similar Mikado classes saw service on the narrow gauge Otavi Railway in South West Africa (SWA). In 1912, the German administration inDeutsch-Südwest-Afrika
German South West Africa () was a colony of the German Empire from 1884 until 1915, though Germany did not officially recognise its loss of this territory until the 1919 Treaty of Versailles.
German rule over this territory was punctuated by ...
acquired three locomotives for use on the line from Swakopmund to Karibib. They were built by Henschel & Son
Henschel & Son () was a German company, located in Kassel, best known during the 20th century as a maker of transportation equipment, including locomotives, trucks, buses and trolleybuses, and armoured fighting vehicles and weapons.
Georg Ch ...
and were designated Class Hd. The locomotives were superheated, with Heusinger valve gear, piston valves and outside plate frames. Since they did not have separate bogie trucks, the leading and trailing carrying wheels were arranged as radial axles to allow for sideways motion of the wheels with respect to the locomotive frame. After the First World War, they were taken onto the roster of the South African Railways (SAR) and later reclassified as Class NG5 along with the similar locomotives of 1922.South African Railways and Harbours Narrow Gauge Locomotive Diagram Book, 2’0" Gauge, S.A.R. Mechanical Dept. Drawing Office, Pretoria, 28 November 1932
In 1922, the SAR placed six Class NG5 locomotives in service on the Otavi branch in SWA, also built by Henschel. They were built to the same design as the Class Hd, but had a different coupled wheel suspension arrangement, different boilers and slide valves. In service, they were operated in a common pool with the Class Hd locomotives until they were all withdrawn from service when the SWA system was regauged to Cape gauge in 1960.South African Railways and Harbours Locomotive Diagram Book, 2’0" & 3’6" Gauge Steam Locomotives, 15 August 1941, as amended
Soviet Union
 At the end of the Second World War, several gauge Japanese Class D51 locomotives were left behind on Russia's Sakhalin island, formerly Karafuto, by retreating Japanese forces. In addition, two Class D51 wrecks were abandoned to the north of the city. Until 1979, the serviceable Japanese locomotives were used on the island by the Soviet Railways.
One was then plinthed outside the Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk railway station, and another is still in running condition and is kept at the Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk railway station.
The Sakhalin Railway has a connection with the mainland via a
At the end of the Second World War, several gauge Japanese Class D51 locomotives were left behind on Russia's Sakhalin island, formerly Karafuto, by retreating Japanese forces. In addition, two Class D51 wrecks were abandoned to the north of the city. Until 1979, the serviceable Japanese locomotives were used on the island by the Soviet Railways.
One was then plinthed outside the Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk railway station, and another is still in running condition and is kept at the Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk railway station.
The Sakhalin Railway has a connection with the mainland via a train ferry
A train ferry is a ship (ferry) designed to carry Railroad car, railway vehicles, as well as their cargoes and passengers. Typically, one level of the ship is fitted with Track (rail transport), railway tracks, and the vessel has a door at the f ...
operating between Kholmsk on the island and Vanino on the mainland. The Japanese gauge still remains in use on the island, although in 2004 conversion began to the Russian gauge. (Also see Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
)
Spain
The network of Spain used one Mikado tank locomotive and two versions of tender locomotives. The Spanish manufacturer MTM delivered six 2-8-2T locomotives to the Madrid-Caceres-Portugal line in 1925. A project at MTM in 1942 to build a big 2-8-2 never realised. The first tender version was built by two American companies in 1917, fifteen by Brooks Locomotive Works and forty by Schenectady Locomotive Works. They were numbered from 4501 to 4555 and were a slightly smaller version of the USRA Light Mikado. The locomotives served well in the Norte system, where they were nicknamed ''Chalecos''. In 1953, RENFE (acronym of '' Red Nacional de los Ferrocarriles Españoles''), the nationalised railway company, acquired twenty-five locomotives of the second tender version fromNorth British Locomotive Company
The North British Locomotive Company (NBL, NB Loco or North British) was created in 1903 through the merger of three Glasgow locomotive manufacturing companies; Sharp, Stewart and Company (Atlas Works), Neilson, Reid and Company (Hyde Park W ...
(NBL) of Glasgow. Spanish builders MTM, MACOSA and Euskalduna
Euskalduna de Construcción y Reparación de Buques de Bilbao (shortened to Euskalduna) was a Basques, Basque engineering company specialising in ship construction, firearms, locomotives, and automobiles. The company was based in Bilbao, Spain and ...
and the American Babcock & Wilcox
Babcock & Wilcox Enterprises, Inc. is an American energy technology and service provider that is active and has operations in many international markets with its headquarters in Akron, Ohio. Historically, the company is best known for their stea ...
built 213 more between 1953 and 1960, with only minor detail differences such as double chimneys, Llubera sanders, ACFI feedwater heaters and oil-burning. Their empty weight was and they had diameter coupled wheels. They performed well in both freight and passenger service and lasted until the official end of steam in common service in 1975.
One Norte and eighteen RENFE locomotives are preserved, three of them in good working condition.
Thailand (Siam)
The first Mikado locomotives of the Royal State Railways of Siam (RSR), the predecessor of theState Railway of Thailand
The State Railway of Thailand (SRT) (, abbrev. รฟท., ) is the state-owned rail operator under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Transport (Thailand), Ministry of Transport in Thailand.
History
The SRT was founded as the Royal State Rail ...
(SRT), were acquired from 1923 as standard locomotives for express and mixed trains, to supersede the E-Class locomotives which had been commissioned between 1915 and 1921. The first Siamese Mikado class was built by Baldwin Locomotive Works
The Baldwin Locomotive Works (BLW) was an American manufacturer of railway locomotives from 1825 to 1951. Originally located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, it moved to nearby Eddystone, Pennsylvania, Eddystone in the early 20th century. The com ...
in 1923, Nasmyth, Wilson & Company in 1924 and Batignolles-Châtillon, France in 1925.
However, it was not until the first batch of eight of Thailand's second class of 2-8-2 locomotives, numbers 351 to 358, was imported from Japan in 1936 that Mikado locomotives really became successful in Thailand. The RSR imported more Mikado standard locomotives to meet railways as well as military demands between 1938 and 1945.
After the Second World War, in 1946, the RSR imported fifty used United States Army Transportation Corps class S118 locomotives, the so-called MacArthur Locomotives. Another eighteen new engines of the same Class were purchased around 1948-1949 to meet the post-war demand.
The last type of Mikado steam locomotives for Thailand were seventy engines imported by SRT from Japan between 1949 and 1951, numbered 901 to 970. Of these, only Mikado no. 953 is still serviceable, and runs passenger trains on special occasions.
United Kingdom
The 2-8-2 wheel arrangement was rarely, but successfully, used on British rails.Nigel Gresley
Sir Herbert Nigel Gresley (19 June 1876 – 5 April 1941) was a British railway engineer. He was one of Britain's most famous steam locomotive engineers, who rose to become Chief Mechanical Engineer (CME) of the London and North Eastern Rail ...
of the London & North Eastern Railway (LNER) designed two Mikado types of note:
* The Class P1 was a freight derivative of his famed Class A1 4-6-2, inspired by the Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad ( reporting mark PRR), legal name as the Pennsylvania Railroad Company, also known as the "Pennsy," was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. At its ...
's twin K4s 4-6-2 and L1s 2-8-2 locomotives. Two were built, but there was never really much call for their ability and they remained under-utilised throughout their short existence.
* Gresley's other class of Mikados was his Class P2. These were express passenger locomotives, rather more inspired by European influences than American. They were built to haul heavy express trains in hilly terrain north of Edinburgh
Edinburgh is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. The city is located in southeast Scotland and is bounded to the north by the Firth of Forth and to the south by the Pentland Hills. Edinburgh ...
, where Gresley thought the additional adhesion possible with a 2-8-2 might serve well. Unfortunately, poor self-centering on the leading truck meant that the leading driving wheels wore against the rails on tighter curves, being hard on both track and wheels. Gresley's successor Edward Thompson converted the Class P2s into 4-6-2 Pacifics. In June 2014, a new Class P2 Mikado locomotive, 2007 ''The Prince of Wales'', intended to work both on mainline and preserved railways, was under construction by the P2 Steam Locomotive Company.
The Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a History of rail transport in Great Britain, British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands (region), West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, ...
(GWR) operated a class of 54 2-8-2T engines that had been rebuilt from 2-8-0T locomotives by Charles Collett, chief mechanical engineer of the GWR. As early as 1906, the chief mechanical engineer at the time, George Churchward, planned a class of Mikado tank engines to handle heavy coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal i ...
trains in South Wales
South Wales ( ) is a Regions of Wales, loosely defined region of Wales bordered by England to the east and mid Wales to the north. Generally considered to include the Historic counties of Wales, historic counties of Glamorgan and Monmouthshire ( ...
. The plan was abandoned, however, as it was feared they would be unable to handle the sharp curves present on Welsh mineral branches. Instead, Churchward designed the 4200 Class of 2-8-0 tank engines, of which nearly 200 were built.
 In the 1930s, coal traffic declined with the result that many of these engines stood idle, since their limited operating range prevented them from being allocated to other mainline duties. Collett, as Churchward's successor, decided to rebuild some of the 4200 Class engines as 2-8-2Ts. The addition of a trailing axle increased the engine's operating range by allowing an increased coal and water storage capacity. Altogether 54 locomotives were modified in this manner. The 7200 Class tank engines, as they were known, remained in service until the end of steam in Britain in the early 1960s.
The designer of the BR Standard Class 9F locomotive as well as the rest of the BR standard classes as Chief Mechanical Engineer of
In the 1930s, coal traffic declined with the result that many of these engines stood idle, since their limited operating range prevented them from being allocated to other mainline duties. Collett, as Churchward's successor, decided to rebuild some of the 4200 Class engines as 2-8-2Ts. The addition of a trailing axle increased the engine's operating range by allowing an increased coal and water storage capacity. Altogether 54 locomotives were modified in this manner. The 7200 Class tank engines, as they were known, remained in service until the end of steam in Britain in the early 1960s.
The designer of the BR Standard Class 9F locomotive as well as the rest of the BR standard classes as Chief Mechanical Engineer of British Rail
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. Originally a trading brand of the Railway Executive of the British Transport Comm ...
ways, Robert Riddles, originally designed the aforementioned locomotive to be a 2-8-2 using the boiler from one of the 4-6-2 passenger locomotive standard classes. However, he later decided to use a 2-10-0 wheel arrangement with a new boiler design, as it offered more tractive effort and better weight distribution.
United States
The first 2-8-2 type ever built wasLehigh Valley
The Lehigh Valley () is a geography, geographic and urban area, metropolitan region formed by the Lehigh River in Lehigh County, Pennsylvania, Lehigh and Northampton County, Pennsylvania, Northampton counties in eastern Pennsylvania. It is a co ...
No. 82 "Bee" designed by Alexander Mitchell and built by the Norris Locomotive Works in 1867.
 The locomotive originally was built as a 2-10-0 "Decapod" type locomotive. The engines were troublesome and curves and were prone to instability. So the locomotives rearmost driver was removed and replaced with a pair of small wheels connected to a trailing truck slightly hanging behind the cab.
The locomotive originally was built as a 2-10-0 "Decapod" type locomotive. The engines were troublesome and curves and were prone to instability. So the locomotives rearmost driver was removed and replaced with a pair of small wheels connected to a trailing truck slightly hanging behind the cab.
 The 2-8-2 saw great success in the
The 2-8-2 saw great success in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, mostly as a freight locomotive. In the 1910s it largely replaced the 2-8-0 Consolidation as the main heavy freight locomotive type. Its tractive effort
In railway engineering, the term tractive effort describes the pulling or pushing capability of a locomotive. The published tractive force value for any vehicle may be theoretical—that is, calculated from known or implied mechanical proper ...
was similar to that of the best 2-8-0s, but a developing requirement for higher speed freight trains drove the shift to the 2-8-2 wheel arrangement.
 The Mikado type was, in turn, ousted from the top-flight trains by larger freight locomotive wheel arrangements such as the 2-8-4, 2-10-2, 2-10-4 and articulated locomotives, but no successor type became ubiquitous and the Mike remained the most common road freight locomotive with most railroads until the end of steam. More than 14,000 were built in the United States, about 9,500 of these for North American service, constituting about one-fifth of all locomotives in service there at the time. The heaviest Mikados were the Great Northern's class O-8, with an axle load of .
Almost all North American railroads rostered the type, notable exceptions being the Richmond, Fredericksburg & Potomac, the Boston & Maine, the Delaware & Hudson, the Western Maryland, the Cotton Belt and the Norfolk & Western. The largest users included the New York Central with 715 locomotives, the Baltimore & Ohio with 610, the
The Mikado type was, in turn, ousted from the top-flight trains by larger freight locomotive wheel arrangements such as the 2-8-4, 2-10-2, 2-10-4 and articulated locomotives, but no successor type became ubiquitous and the Mike remained the most common road freight locomotive with most railroads until the end of steam. More than 14,000 were built in the United States, about 9,500 of these for North American service, constituting about one-fifth of all locomotives in service there at the time. The heaviest Mikados were the Great Northern's class O-8, with an axle load of .
Almost all North American railroads rostered the type, notable exceptions being the Richmond, Fredericksburg & Potomac, the Boston & Maine, the Delaware & Hudson, the Western Maryland, the Cotton Belt and the Norfolk & Western. The largest users included the New York Central with 715 locomotives, the Baltimore & Ohio with 610, the Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad ( reporting mark PRR), legal name as the Pennsylvania Railroad Company, also known as the "Pennsy," was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. At its ...
with 579, the Illinois Central with 565, the Milwaukee Road
The Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad (CMStP&P), better known as the Milwaukee Road , was a Class I railroad that operated in the Midwestern United States, Midwest and Pacific Northwest, Northwest of the United States from 1847 ...
with 500, the Southern with 435, and the Chicago, Burlington & Quincy with 388.
A number of North American 2-8-2s have been preserved as either static display pieces, or steam excursion stars. These include Baltimore and Ohio 4500, Nickel Plate Road 587, Grand Trunk Western 4070, Southern Railway 4501
Southern Railway 4501 is a preserved 2-8-2 "Mikado"-type steam locomotive. Built in October 1911 by the Baldwin Locomotive Works in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, No. 4501 was the first of its wheel arrangement type for the Southern Railway (U.S.), ...
, Grand Canyon Railway 4960, Spokane, Portland and Seattle 539, Southern Pacific 745, Tremont and Gulf 30, Duluth and Northern Minnesota 14, Soo Line 1003, McCloud Railway 18, McCloud Railway 19, Denver and Rio Grande Western 463, Pennsylvania Railroad 520, and California Western 45.
Yugoslavia
Borsig built 2-8-2s were delivered to the railway of theKingdom of Yugoslavia
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia was a country in Southeast Europe, Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 1918 to 1929, it was officially called the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes, but the term "Yugoslavia" () h ...
in 1930. These became the JDZ class 06, of which a few remain in the former Yugoslav nations.
References
*External links
{{Authority control