|
Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk
Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk (, , ) is a city and the administrative center of Sakhalin Oblast, Russia. It is located on Sakhalin Island in the Russian Far East, north of Japan. Gas and oil extraction as well as processing are amongst the main industries on the island. It was called Vladimirovka () from 1882 to 1905, then during its period of Imperial Japanese control from 1905 to 1946. As of the 2010 Census, its population was 181,728. History Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk began as a small Russian settlement called Vladimirovka, founded by convicts in 1882. The Treaty of Portsmouth in 1905, which brought an end to the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–1905, awarded the southern half of the Sakhalin Island to Japan. Vladimirovka was renamed Toyohara (meaning "bountiful plain"), and was the prefect capital of the Japanese Karafuto Prefecture. During the Soviet–Japanese War within World War II, the city was recaptured by Soviet troops. Ownership of the city was transferred to the Soviet Union and it w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
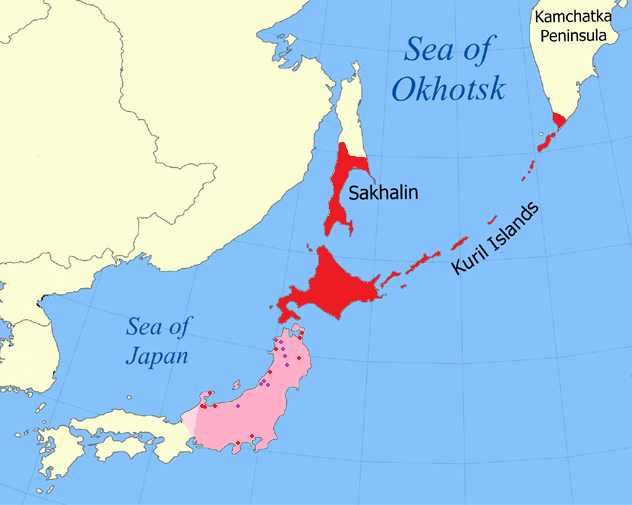
Sakhalin
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, p=səxɐˈlʲin) is an island in Northeast Asia. Its north coast lies off the southeastern coast of Khabarovsk Krai in Russia, while its southern tip lies north of the Japanese island of Hokkaido. An island of the West Pacific, Sakhalin divides the Sea of Okhotsk to its east from the Sea of Japan to its southwest. It is administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast and is the largest island of Russia, with an area of . The island has a population of roughly 500,000, the majority of whom are Russians. The indigenous peoples of the island are the Ainu, Oroks, and Nivkhs, who are now present in very small numbers. The island's name is derived from the Manchu word ''Sahaliyan'' (), which was the name of the Qing dynasty city of Aigun. The Ainu people of Sakhalin paid tribute to the Yuan, Ming, and Qing dynasties and accepted official appointments from them. Sometimes the relationship was forced but control from dynasties in China was loose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakhalin Oblast
Sakhalin Oblast ( rus, Сахали́нская о́бласть, r=Sakhalinskaya oblastʹ, p=səxɐˈlʲinskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast) comprising the island of Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands in the Russian Far East. The oblast has an area of . Its administrative center and largest city is Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk. As of the 2021 Census, the oblast has a population of 466,609. The vast majority of the oblast's residents are ethnic Russians, with a small minority of Sakhalin Koreans. Sakhalin Oblast is rich in natural gas and oil, and is Russia's second wealthiest federal subject after the Tyumen Oblast. It borders by sea Khabarovsk Krai to the west and Kamchatka Krai to the north, along with Hokkaido, Japan to the south. History The etymology of Sakhalin can be traced back to the Manchu hydronym ''Sahaliyan Ula'' (Manchu: ) for "Black River" (''i.e.'' the Amur River). Sakhalin shares this etymology with the Chinese province of Heilongjiang (C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk Airport
Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk International Airport (, ), also called Khomutovo International Airport (), is an international airport in Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk, on the Russian island of Sakhalin. The airport was established in 1945 as a military airfield. With currently one 3,400 m concrete runway, two passenger terminals, two cargo terminals and 16 aircraft stands, Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk International Airport is the largest airport in Sakhalin Oblast. The airport opened a new terminal in August 2023. The airport is also building a second concrete runway that should be finished by 2026 and a 4-star hotel. Facilities The airport resides at an elevation of above mean sea level. It has one runway designated 01/19 with a concrete surface measuring . Airlines and destinations Passenger References External links * New Airport Terminal Websites * * * Airport Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk (Homutovo) Aviateka.Handbook {{authority control Airports built in the Soviet Union Airports in Sakhalin Oblast Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
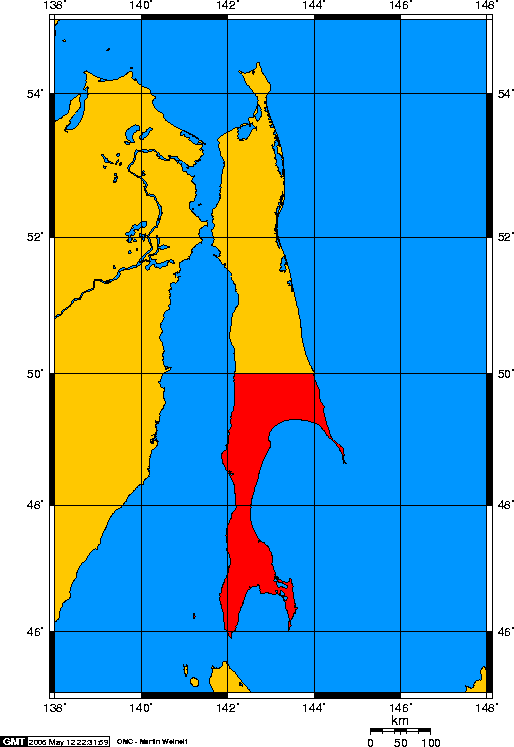
Karafuto Prefecture
, was established by the Empire of Japan in 1907 to govern the southern part of Sakhalin. This territory became part of the Empire of Japan in 1905 after the Russo-Japanese War, when the portion of Sakhalin south of 50°N was ceded by the Russian Empire under the Treaty of Portsmouth. Karafuto Prefecture was established in 1907 to govern Karafuto, which was part of Japan's External Land (''Gaichi''), until it was incorporated into an Inner Land (''Naichi'') of the Japanese metropole in 1943. Ōtomari (Korsakov) was the capital of Karafuto from 1905 to 1908 and Toyohara (Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk) from 1908 to 1945. In August 1945, the Japanese administration ceased to function following the invasion of South Sakhalin by the Soviet Union. Karafuto Prefecture was annexed to the Soviet Union, although it continued to exist under Japanese law until it was formally abolished by Japan in June 1949. Name The Japanese name ''Karafuto'' purportedly comes from Ainu (), which means ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakhalin Regional Museum Of Local Lore
The Sakhalin Regional Museum () is a museum in Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk on the Russian island of Sakhalin. It is the largest museum in the Sakhalin Oblast. The Museum collects, researches, and displays materials relating to the natural history, archaeology, history, and ethnography of the region. History The first museum on Sakhalin opened in what was then the military post of Alexandrovsk in North Sakhalin in 1896. A number of exhibits disappeared when the area was in Japanese hands, in 1905 and again between 1920 and 1925. The museum reopened in 1932. Meanwhile, in South Sakhalin, in the years when, as Karafuto Prefecture, it formed part of the Empire of Japan, the official residence of the garrison commander initially served for the , a situation that lasted until 1935, when the building was repurposed for the Toyohara Military Police. Construction work on a new, dedicated museum building began in July 1935 and continued for two years, until July 1937; related documentation from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
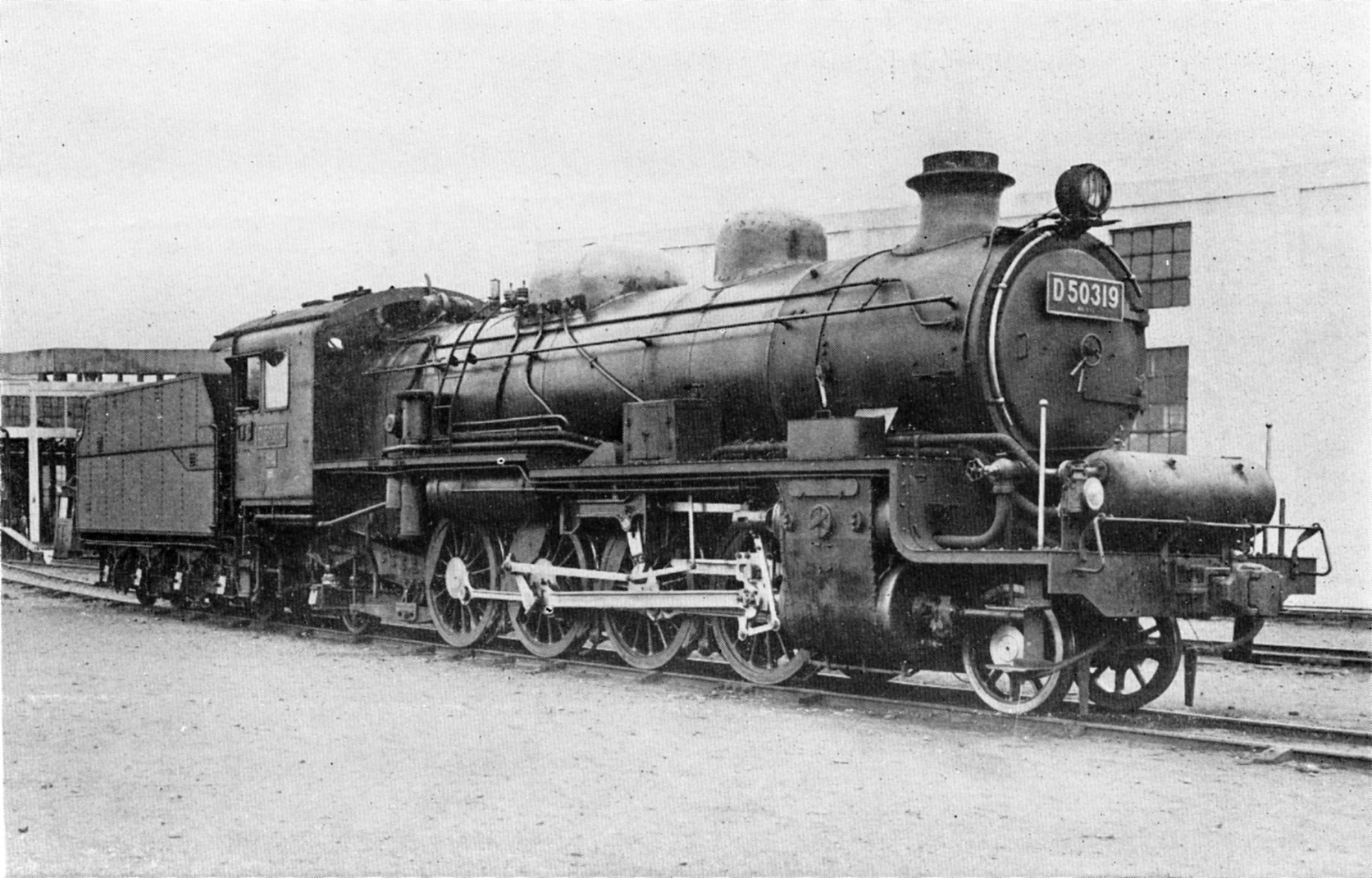
D51 Steam Locomotive
The is a type of 2-8-2 steam locomotive operated by the Japanese Government Railways (JGR) and later by the Japanese National Railways (JNR). Designed by JGR's chief mechanical engineer Hideo Shima, they were built by Kawasaki Heavy Industries Rolling Stock Company, Kisha Seizo, Hitachi, Nippon Sharyo, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries and JGR's factories from 1936 to 1945. Although surpassed in speed, power, and size by other locomotives, it is recognised as the most mass-manufactured locomotive in Japanese rail history. A total of 174 units are preserved in Japan, including five operational examples. An additional 13 are preserved in Russia and Taiwan, bringing the total number of preserved units to 187. Classification The classification consists of a "D" for the four sets of driving wheels and the class number 51 for tender locomotives that the numbers 50 through 99 were assigned to under the Japan Railways locomotive numbering and classification, 1928 locomotive classification r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurora (airline)
Aurora () is a Russian airline headquartered in Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk, Sakhalin Oblast. It operates domestic and international flights in the Russian Far East region. It is named after the Russian cruiser Aurora. It is currently banned from flying into the EU like all other Russian airlines. History Aurora was created by government order of Russian Prime Minister Dmitry Medvedev in September 2013. Originally called Taiga, it combined Vladivostok Air and SAT Airlines. SAT Airlines and Vladivostok Avia served 42 and 15 destinations respectively, and had a combined fleet of 24 fixed-wing aircraft, along with 11 helicopters. Aurora began operations on 8 December 2013 serving the Khabarovsk – Krasnoyarsk-Yemelyanovo route. The carrier's first aircraft was an Airbus A319, with a new aircraft livery. In December 2015, the airline received the first of three Bombardier Q400 aircraft it had on order. Aurora was 51%-owned by Aeroflot, with the regional government of Sakhalin Ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Administrative Divisions Of Sakhalin Oblast ...
Administrative and municipal divisions References {{Administrative divisions of the Russian federal subjects Sakhalin Oblast Sakhalin Oblast Sakhalin Oblast ( rus, Сахали́нская о́бласть, r=Sakhalinskaya oblastʹ, p=səxɐˈlʲinskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast) comprising the island of Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands in the Russian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Far East
The Russian Far East ( rus, Дальний Восток России, p=ˈdalʲnʲɪj vɐˈstok rɐˈsʲiɪ) is a region in North Asia. It is the easternmost part of Russia and the Asia, Asian continent, and is coextensive with the Far Eastern Federal District, which encompasses the area between Lake Baikal and the Pacific Ocean. The area's largest city is Khabarovsk, followed by Vladivostok. The region shares land borders with the countries of Mongolia, China, and North Korea to its south, as well as maritime boundary, maritime boundaries with Japan to its southeast, and with the United States along the Bering Strait to its northeast. Although the Russian Far East is often considered as a part of Siberia abroad, it has been historically categorized separately from Siberia in Russian regional schemes (and previously during the history of the Soviet Union, Soviet era when it was called the Soviet Far East). Terminology In Russia, the region is usually referred to as simply th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subdivisions Of Russia
Russia is divided into several types and levels of subdivisions. Federal districts The federal districts are groupings of the federal subjects of Russia. Federal districts are not mentioned in the nation's constitution, do not have competences of their own, and do not manage regional affairs. They exist solely to monitor consistency between the federal and regional bodies of law, and ensure governmental control over the civil service, judiciary, and federal agencies operating in the regions. The federal district system was established on 13 May 2000. There are total eight federal districts. Federal subjects Since 30 September 2022, the Russian Federation has consisted of eighty-nine federal subjects that are constituent members of the Federation.Constitution, Article 65 However, six of these federal subjects—the Republic of Crimea, the Donetsk People's Republic, the Kherson Oblast, the Lugansk People's Republic, the federal city of Sevastopol, and the Zaporoz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oblast
An oblast ( or ) is a type of administrative division in Bulgaria and several post-Soviet states, including Belarus, Russia and Ukraine. Historically, it was used in the Russian Empire and the Soviet Union. The term ''oblast'' is often translated into English language, English as 'region' or 'province'. In some countries, oblasts are also known by cognates of the Russian term. Etymology The term ''oblast'' is Loanword, borrowed from Russian language, Russian область (), where it is inherited from Old East Slavic, in turn borrowed from Church Slavonic область ''oblastĭ'' 'power, empire', formed from the prefix (cognate with Classical Latin ''ob'' 'towards, against' and Ancient Greek ἐπί/ἔπι ''epi'' 'in power, in charge') and the stem ''vlastǐ'' 'power, rule'. In Old East Slavic, it was used alongside ''obolostǐ''—the equivalent of 'against' and 'territory, state, power' (cognate with English 'wield'; see volost). History Russian Empire In the Russia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeroflot
PJSC AeroflotRussian Airlines (, ), commonly known as Aeroflot ( or ; , , ), is the flag carrier and the largest airline of Russia. Aeroflot is headquartered in the Central Administrative Okrug, Moscow, with its hub being Sheremetyevo International Airport. The Federal Agency for State Property Management, an agency of the Government of Russia, owns 73.77% of the company, with the rest of the shares being public float. During the time of the Soviet Union, Aeroflot was one of the largest airlines in the world. In 1992, following the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Aeroflot was divided into approximately 400 regional airlines informally known as Babyflots and was restructured into an open joint-stock company. It has a market share in Russia of approximately 42.3%. Including subsidiaries, the company carried 55.3 million passengers in 2024. Aeroflot also owns Rossiya Airlines and Pobeda, a low-cost carrier. The Aeroflot fleet, excluding subsidiaries, includes 171 airplanes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |