|
Hydrogen Azide
Hydrazoic acid, also known as hydrogen azide, azic acid or azoimide, This also contains a detailed description of the contemporaneous production process. is a compound with the chemical formula . It is a colorless, volatile, and explosive liquid at room temperature and pressure. It is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen, and is therefore a pnictogen hydride. It was first isolated in 1890 by Theodor Curtius. The acid has few applications, but its conjugate base, the azide ion, is useful in specialized processes. Hydrazoic acid, like its fellow mineral acids, is soluble in water. Undiluted hydrazoic acid is dangerously explosive with a standard enthalpy of formation ΔfHo (l, 298K) = +264 kJ/mol. When dilute, the gas and aqueous solutions (<10%) can be safely prepared but should be used immediately; because of its low boiling point, hydrazoic acid is enriched upon evaporation and condensation such that dilute solutions incapable of explosion can form droplets in the headspace of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkali
In chemistry, an alkali (; from the Arabic word , ) is a basic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7.0. The adjective alkaline, and less often, alkalescent, is commonly used in English as a synonym for basic, especially for bases soluble in water. This broad use of the term is likely to have come about because alkalis were the first bases known to obey the Arrhenius definition of a base, and they are still among the most common bases. Etymology The word ''alkali'' is derived from Arabic ''al qalīy'' (or ''alkali''), meaning (see calcination), referring to the original source of alkaline substances. A water-extract of burned plant ashes, called potash and composed mostly of potassium carbonate, was mildly basic. After heating this substance with calcium hydroxide (''slaked lime''), a far more strongly basic substance known as ''caustic potash ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Enthalpy Of Formation
In chemistry and thermodynamics, the standard enthalpy of formation or standard heat of formation of a compound is the change of enthalpy during the formation of 1 mole of the substance from its constituent elements in their reference state, with all substances in their standard states. The standard pressure value is recommended by IUPAC, although prior to 1982 the value 1.00 atm (101.325 kPa) was used. There is no standard temperature. Its symbol is Δf''H''⦵. The superscript Plimsoll on this symbol indicates that the process has occurred under standard conditions at the specified temperature (usually 25 °C or 298.15 K). Standard states are defined for various types of substances. For a gas, it is the hypothetical state the gas would assume if it obeyed the ideal gas equation at a pressure of 1 bar. For a gaseous or solid solute present in a diluted ideal solution, the standard state is the hypothetical state of concentration of the solute of exactly one m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkali Metal
The alkali metals consist of the chemical elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K),The symbols Na and K for sodium and potassium are derived from their Latin names, ''natrium'' and ''kalium''; these are still the origins of the names for the elements in some languages, such as German and Russian. rubidium (Rb), caesium (Cs), and francium (Fr). Together with hydrogen they constitute Group (periodic table)#Group names, group 1, which lies in the s-block of the periodic table. All alkali metals have their outermost electron in an s-orbital: this shared electron configuration results in their having very similar characteristic properties. Indeed, the alkali metals provide the best example of periodic trends, group trends in properties in the periodic table, with elements exhibiting well-characterised Homologous series, homologous behaviour. This family of elements is also known as the lithium family after its leading element. The alkali metals are all shiny, hardness, sof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkyl Iodide
Organoiodine chemistry is the study of the synthesis and properties of organoiodine compounds, or organoiodides, organic compounds that contain one or more carbon–iodine bonds. They occur widely in organic chemistry, but are relatively rare in nature. The thyroxine hormones are organoiodine compounds that are required for health and the reason for government-mandated iodization of salt. Structure, bonding, general properties Almost all organoiodine compounds feature iodide connected to one carbon center. These are usually classified as derivatives of I−. Some organoiodine compounds feature iodine in higher oxidation states. The C–I bond is the weakest of the carbon–halogen bonds. These bond strengths correlate with the electronegativity of the halogen, decreasing in the order F > Cl > Br > I. This periodic order also follows the atomic radius of halogens and the length of the carbon-halogen bond. For example, in the molecules represented by CH3X, where X ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitric Acid
Nitric acid is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but samples tend to acquire a yellow cast over time due to decomposition into nitrogen oxide, oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available nitric acid has a concentration of 68% in water. When the solution contains more than 86% , it is referred to as ''fuming nitric acid''. Depending on the amount of nitrogen dioxide present, fuming nitric acid is further characterized as red fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 86%, or white fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 95%. Nitric acid is the primary reagent used for nitration – the addition of a nitro group, typically to an organic molecule. While some resulting nitro compounds are shock- and thermally-sensitive explosives, a few are stable enough to be used in munitions and demolition, while others are still more stable and used as synthetic dyes and medicines (e.g. metronidazole). Nitric acid is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichloramine
Nitrogen trichloride, also known as trichloramine, is the chemical compound with the formula . This yellow, oily, and explosive liquid is most commonly encountered as a product of chemical reactions between ammonia-derivatives and chlorine (for example, in swimming pools). Alongside monochloramine and dichloramine, trichloramine is responsible for the distinctive 'chlorine smell' associated with swimming pools, where the compound is readily formed as a product from hypochlorous acid reacting with ammonia and other nitrogenous substances in the water, such as urea from urine. Preparation and occurrence The compound is generated by treatment of ammonium chloride with calcium hypochlorite. When prepared in an aqueous-dichloromethane mixture, the trichloramine is extracted into the nonaqueous phase. Intermediates in this conversion include monochloramine and dichloramine, and , respectively. Nitrogen trichloride, trademarked as Agene, was at one time used to bleach flour, but th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
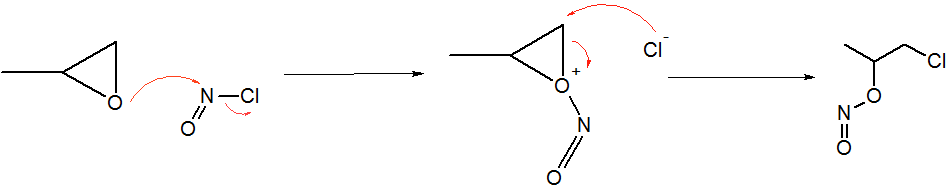
Nitrosyl Chloride
Nitrosyl chloride is the chemical compound with the formula NOCl. It is a yellow gas that is commonly encountered as a component of aqua regia, a mixture of 3 parts concentrated hydrochloric acid and 1 part of concentrated nitric acid. It is a strong electrophile and oxidizing agent. It is sometimes called Tilden's reagent, after William A. Tilden, who was the first to produce it as a pure compound. Structure and synthesis The molecule is bent. A double bond exists between N and O (distance = 1.16 Å) and a single bond between N and Cl (distance = 1.96 Å). The O=N–Cl angle is 113°. Production Nitrosyl chloride can be produced in many ways. * Combining nitrosylsulfuric acid and HCl affords the compound. This method is used industrially. :HCl + NOHSO4 → H2SO4 + NOCl * A more convenient laboratory method involves the (reversible) dehydration of nitrous acid by HCl : HNO2 + HCl → H2O + NOCl * By the direct combination of chlorine and nitric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscosity, viscous than Properties of water, water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3%–6% by weight) in water for consumer use and in higher concentrations for industrial use. Concentrated hydrogen peroxide, or "high-test peroxide", decomposes explosively when heated and has been used as both a monopropellant and an oxidizer in rocketry. Hydrogen peroxide is a reactive oxygen species and the simplest peroxide, a compound having an oxygen–oxygen single bond. It decomposes slowly into water and elemental oxygen when exposed to light, and rapidly in the presence of organic or reactive compounds. It is typically stored with a Stabilizer (chemistry), stabilizer in a weakly acidic solution in an opaque bottle. Hydrogen peroxide is found in biological systems including the human body. Enzymes that u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrous Acid
Nitrous acid (molecular formula ) is a weak and monoprotic acid known only in solution, in the gas phase, and in the form of nitrite () salts. It was discovered by Carl Wilhelm Scheele, who called it " phlogisticated acid of niter". Nitrous acid is used to make diazonium salts from amines. The resulting diazonium salts are reagents in azo coupling reactions to give azo dyes. Structure In the gas phase, the planar nitrous acid molecule can adopt both a ''syn'' and an ''anti'' form. The ''anti'' form predominates at room temperature, and IR measurements indicate it is more stable by around 2.3 kJ/mol. p. 462. Image:Trans-nitrous-acid-2D-dimensions.png , Dimensions of the ''anti'' form(from the microwave spectrum) Image:Trans-nitrous-acid-3D-balls.png , Model of the ''anti'' form Image:Cis-nitrous-acid-3D-balls.png , ''syn'' form Preparation and decomposition Free, gaseous nitrous acid is unstable, rapidly disproportionating to nitric oxides: :2 HNO2 → NO2 + ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrazine
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a simple pnictogen hydride, and is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odour. Hydrazine is highly hazardous unless handled in solution as, for example, hydrazine hydrate (). Hydrazine is mainly used as a foaming agent in preparing Polymeric foam, polymer foams, but applications also include its uses as a precursor (chemistry), precursor to pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals, as well as a long-term storable propellant for in-outer space, space spacecraft propulsion. Additionally, hydrazine is used in various rocket propellant, rocket fuels and to prepare the gas precursors used in airbags. Hydrazine is used within both nuclear and conventional electrical power plant steam cycles as an oxygen scavenger to control concentrations of dissolved oxygen in an effort to reduce corrosion. , approximately 120,000 tons of hydrazine hydrate (corresponding to a 64% solution of hydrazine in water by weight) we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barium Sulfate
Barium sulfate (or sulphate) is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ba SO4. It is a white crystalline solid that is odorless and insoluble in water. It occurs in nature as the mineral barite, which is the main commercial source of barium and materials prepared from it. Its opaque white appearance and its high density are exploited in its main applications.Holleman, A. F. and Wiberg, E. (2001) ''Inorganic Chemistry'', San Diego, CA. Academic Press, . Uses Drilling fluids About 80% of the world's barium sulfate production, mostly purified mineral, is consumed as a component of oil well drilling fluid. It increases the density of the fluid, increasing the hydrostatic pressure in the well and reducing the chance of a blowout. Radiocontrast agent Barium sulfate in suspension is often used medically as a radiocontrast agent for X-ray imaging and other diagnostic procedures. It is most often used in imaging of the GI tract during what is colloquially known as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfuric Acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen, and hydrogen, with the molecular formula . It is a colorless, odorless, and Viscosity, viscous liquid that is Miscibility, miscible with water. Pure sulfuric acid does not occur naturally due to its Dehydration reaction, strong affinity to water vapor; it is Hygroscopy, hygroscopic and readily absorbs water vapor from the Atmosphere of Earth, air. Concentrated sulfuric acid is a strong oxidant with powerful dehydrating properties, making it highly corrosive towards other materials, from rocks to metals. Phosphorus pentoxide is a notable exception in that it is not dehydrated by sulfuric acid but, to the contrary, dehydrates sulfuric acid to sulfur trioxide. Upon addition of sulfuric acid to water, a considerable amount of heat is releas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |