|
Hydrazine
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a simple pnictogen hydride, and is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odour. Hydrazine is highly toxic unless handled in solution as, for example, hydrazine hydrate (). Hydrazine is mainly used as a foaming agent in preparing polymer foams, but applications also include its uses as a precursor to polymerization catalysts, pharmaceuticals, and agrochemicals, as well as a long-term storable propellant for in- space spacecraft propulsion. Additionally, hydrazine is used in various rocket fuels and to prepare the gas precursors used in air bags. Hydrazine is used within both nuclear and conventional electrical power plant steam cycles as an oxygen scavenger to control concentrations of dissolved oxygen in an effort to reduce corrosion. the world hydrazine hydrate market amounted to $350 million. About two million tons of hydrazine hydrate were used in foam blowing agents in 2015. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrazines
Hydrazines (R2N−NR2) are a class of chemical compounds with two nitrogen atoms linked via a covalent bond and which carry from one up to four alkyl or aryl substituents. Hydrazines can be considered as derivatives of the inorganic hydrazine (H2N−NH2), in which one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by hydrocarbon groups. Production * 1,1-Dimethylhydrazine is produced by the reduction of ''N''-nitrosodimethylamine.Siegfried Hauptmann: ''Organische Chemie'', 2. durchgesehene Auflage, VEB Deutscher Verlag für Grundstoffindustrie, Leipzig, 1985, S. 522–523, . * The reduction of benzenediazonium chloride with tin(II) chloride and hydrochloric acid provides phenylhydrazine. * 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine is produced by the reaction of 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene with hydrazine. * Tetraphenylhydrazine is formed by the oxidation of diphenylamine with potassium permanganate in acetone. Classification Hydrazines can be divided into three groups according to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscous than water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3%–6% by weight) in water for consumer use, and in higher concentrations for industrial use. Concentrated hydrogen peroxide, or " high-test peroxide", decomposes explosively when heated and has been used as a propellant in rocketry. Hydrogen peroxide is a reactive oxygen species and the simplest peroxide, a compound having an oxygen–oxygen single bond. It decomposes slowly when exposed to light, and rapidly in the presence of organic or reactive compounds. It is typically stored with a stabilizer in a weakly acidic solution in a dark bottle to block light. Hydrogen peroxide is found in biological systems including the human body. Enzymes that use or decompose hydrogen peroxide are classified as peroxidases. Properties The boiling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
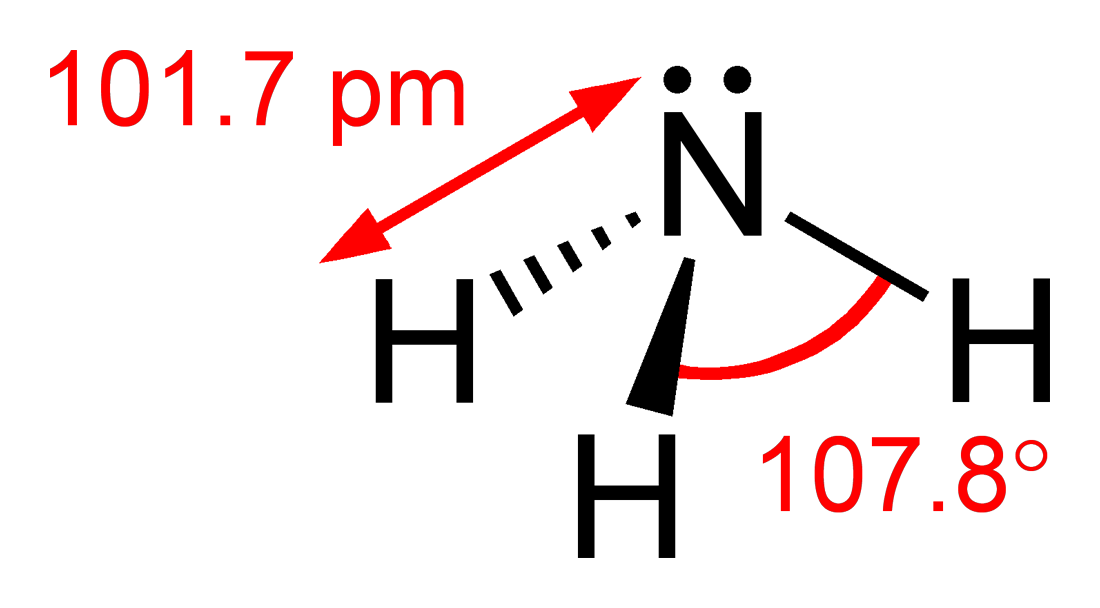
Ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous waste, particularly among aquatic organisms, and it contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to 45% of the world's food and fertilizers. Around 70% of ammonia is used to make fertilisers in various forms and composition, such as urea and Diammonium phosphate. Ammonia in pure form is also applied directly into the soil. Ammonia, either directly or indirectly, is also a building block for the synthesis of many pharmaceutical products and is used in many commercial cleaning products. It is mainly collected by downward displacement of both air and water. Although common in nature—both terrestrially and in the outer planets of the Solar System—and in wide use, ammonia i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrafluorohydrazine
Tetrafluorohydrazine or perfluorohydrazine, , is a colourless, reactive inorganic gas. It is a fluorinated analog of hydrazine. It is a highly hazardous chemical that explodes in the presence of organic materials. Tetrafluorohydrazine is manufactured from nitrogen trifluoride using an iron catalyst or iron(II) fluoride. It is used in some chemical syntheses, as a precursor or a catalyst. Tetrafluorohydrazine was considered for use as a high-energy liquid oxidizer in some never-flown rocket fuel formulas in 1959. Properties Tetrafluorohydrazine is in equilibrium with its radical monomer nitrogen difluoride. : N2F4 2 NF2• At room temperature N2F4 is mostly associated with only 0.7% in the form of NF2 at 5mm Hg pressure. When the temperature rises to 225 °C, it mostly dissociates with 99% in the form of NF2. molecule dimensions and angles The energy needed to break the N-N bond in N2F4 is 20.8 kcal/mol, with an entropy change of 38.6 eu. For comparison, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pnictogen Hydride
Pnictogen hydrides or hydrogen pnictides are binary compounds of hydrogen with pnictogen ( or ; from grc, πνῑ́γω "to choke" and -gen, "generator") atoms (elements of group 15: nitrogen, phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, and bismuth) covalently bonded to hydrogen. Pnictogen trihydrides The simplest series has the chemical formula XH3 (less commonly H3X), with X representing any of the pnictogens. They take on the pyramidal structure (as opposed to the trigonal planar arrangement of the group 13 hydrides), and therefore are polar. These pnictogen trihydrides are generally increasingly unstable and poisonous with heavier elements. Like the simple hydrogen halides and chalcogenides, the pnictogen hydrides are water- soluble. Unlike other hydrides such as hydrogen sulfide and hydrogen fluoride, which form acidic aqueous solutions, ammonia dissolves in water to make ammonium hydroxide which is basic (by forming a hydroxide ion as opposed to hydronium). Phosphine is also water- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrazinium
Hydrazinium is the cation with the formula . This cation has a methylamine-like structure (). It can be derived from hydrazine by protonation (treatment with a strong acid). Hydrazinium is a weak acid with p''K''a = 8.1. Salts of hydrazinium are common reagents in chemistry and are often used in certain industrial processes.Jean-Pierre Schirmann, Paul Bourdauducq "Hydrazine" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2002. . Notable examples are hydrazinium hydrogensulfate, or , and hydrazinium azide, or . In the common names of such salts, the cation is often called "hydrazine", as in " hydrazine sulfate" for hydrazinium hydrogensulfate. The terms "hydrazinium" and "hydrazine" may also be used for the doubly protonated cation , more properly called hydrazinediium or hydrazinium(2+). This cation has an ethane-like structure (). Salts of this cation include hydrazinediium sulfate and hydrazinediium bis(6-carboxypyridazine-3-carboxylate), .W. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triazane
Triazane is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula or . Triazane is the third simplest acyclic azane after ammonia and hydrazine. It can be synthesized from hydrazine but is unstable and cannot be isolated in the free base form, only as salt forms such as triazanium sulfate. Attempts to convert triazanium salts to the free base release only diazene and ammonia. Triazane was first synthesized as a ligand of the silver complex ion: tris(μ2-triazane-κ2''N''1,''N''3)disilver(2+). Triazane has also been synthesized in electron-irradiated ammonia ices and detected as a stable gas-phase product after sublimation.Forstel, Maksyutenko, Jones, Sun, Chen, Chang, & Kaiser. "Detection of the Elusive Triazane Molecule () in the Gas Phase", ''ChemPhysChem'', 2015, 16, 3139. Compounds containing the triazane skeleton Several compounds containing the triazane skeleton are known, including 1-methyl-1-nitrosohydrazine (), produced from the solventless reaction of methylhydrazine () and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrazene
Tetrazene is a chemical compound with the molecular formula H2NN=NNH2. It is a colorless explosive material. An analogue is the organosilicon derivative (tms)2NN=NN(tms)2 where tms is trimethylsilyl. Isomeric with tetrazine is ammonium azide. Tetrazene explosive, commonly known simply as tetrazene, is used for sensitization of priming compositions. Properties Tetrazene has eleven isomers. The most stable of these is the straight-chain 2-tetrazene (H2-NN=N-NH2), having a standard heat of formation at 301.3 kJ/mol. The eleven isomers can be arranged into three groups: straight-chain tetrazenes, four-membered cyclotetrazane, and three-membered cyclotriazanes. Each straight-chain tetrazene isomer possesses one N=N double bond and two N-N single bonds. Tautomerizations do occur between the isomers. The ionic compound ammonium azide is also a constitutional isomer of tetrazene. Organometallic derivatives A variety of coordination complex A coordination complex consists of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Storable Propellant
A propellant (or propellent) is a mass that is expelled or expanded in such a way as to create a thrust or other motive force in accordance with Newton's third law of motion, and "propel" a vehicle, projectile, or fluid payload. In vehicles, the engine that expels the propellant is called a reaction engine. Although technically a propellant is the reaction mass used to create thrust, the term "propellant" is often used to describe a substance which is contains both the reaction mass and the fuel that holds the energy used to accelerate the reaction mass. For example, the term "propellant" is often used in chemical rocket design to describe a combined fuel/propellant, although the propellants should not be confused with the fuel that is used by an engine to produce the energy that expels the propellant. Even though the byproducts of substances used as fuel are also often used as a reaction mass to create the thrust, such as with a chemical rocket engine, propellant and fuel are two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphosphane
Diphosphane, or diphosphine, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula P2H4. This colourless liquid is one of several binary phosphorus hydrides. It is the impurity that typically causes samples of phosphine to ignite in air. Properties, preparation, reactions Diphosphane adopts the gauche conformation (like hydrazine, less symmetrical than shown in the image) with a P−P distance of 2.219 angstroms. It is nonbasic, unstable at room temperature, and spontaneously flammable in air. It is only poorly soluble in water but dissolves in organic solvents. Its 1H NMR spectrum consists of 32 lines resulting from an A2XX'A'2 splitting system. Diphosphane is produced by the hydrolysis of calcium monophosphide Calcium monophosphide is the inorganic compound with the formula CaP. It is sometimes also known as "calcium phosphide", which also describes a different compound with composition Calcium phosphide, Ca3P2. Calcium monophosphide is a black solid. ..., which can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

-3D-balls.png)