Uranium Ore Square on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Uranium is a
 Uranium is a silvery white, weakly radioactive
Uranium is a silvery white, weakly radioactive
 The major application of uranium in the military sector is in high-density penetrating projectiles. This ammunition consists of
The major application of uranium in the military sector is in high-density penetrating projectiles. This ammunition consists of
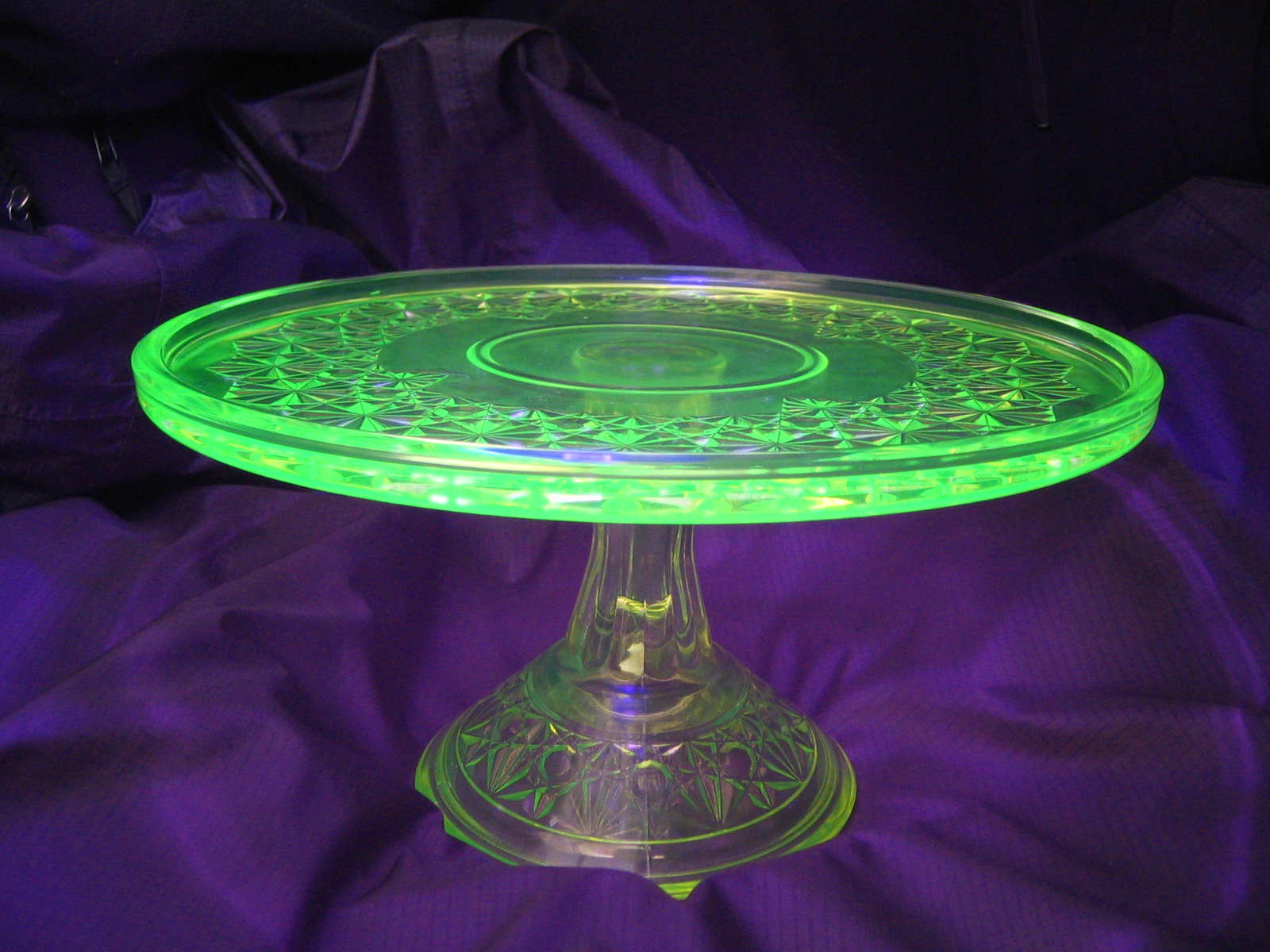 Before (and, occasionally, after) the discovery of radioactivity, uranium was primarily used in small amounts for yellow glass and pottery glazes, such as uranium glass and in Fiestaware.
The discovery and isolation of
Before (and, occasionally, after) the discovery of radioactivity, uranium was primarily used in small amounts for yellow glass and pottery glazes, such as uranium glass and in Fiestaware.
The discovery and isolation of
 The
The 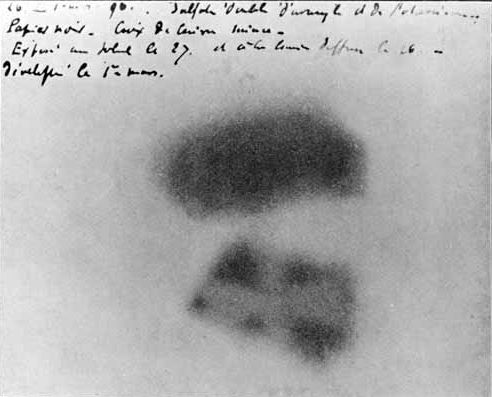
 A team led by Enrico Fermi in 1934 found that bombarding uranium with neutrons produces beta rays (
A team led by Enrico Fermi in 1934 found that bombarding uranium with neutrons produces beta rays (
 Two types of atomic bomb were developed by the United States during
Two types of atomic bomb were developed by the United States during
 The X-10 Graphite Reactor at
The X-10 Graphite Reactor at
 Above-ground nuclear tests by the Soviet Union and the United States in the 1950s and early 1960s and by
Above-ground nuclear tests by the Soviet Union and the United States in the 1950s and early 1960s and by
 Some bacteria, such as '' Shewanella putrefaciens'', '' Geobacter metallireducens'' and some strains of '' Burkholderia fungorum'', can use uranium for their growth and convert U(VI) to U(IV). Recent research suggests that this pathway includes reduction of the soluble U(VI) via an intermediate U(V) pentavalent state.
Other organisms, such as the
Some bacteria, such as '' Shewanella putrefaciens'', '' Geobacter metallireducens'' and some strains of '' Burkholderia fungorum'', can use uranium for their growth and convert U(VI) to U(IV). Recent research suggests that this pathway includes reduction of the soluble U(VI) via an intermediate U(V) pentavalent state.
Other organisms, such as the
U production-demand.png, World uranium production (mines) and demand
Yellowcake.jpg, alt=A yellow sand-like rhombic mass on black background., Yellowcake is a concentrated mixture of uranium oxides that is further refined to extract pure uranium.
Uranium production, OWID.svg, Uranium production 2015, in tonnes
 It is estimated that 6.1 million tonnes of uranium exists in ores that are economically viable at US$130 per kg of uranium, while 35 million tonnes are classed as mineral resources (reasonable prospects for eventual economic extraction).
Australia has 28% of the world's known uranium ore reserves and the world's largest single uranium deposit is located at the Olympic Dam Mine in
It is estimated that 6.1 million tonnes of uranium exists in ores that are economically viable at US$130 per kg of uranium, while 35 million tonnes are classed as mineral resources (reasonable prospects for eventual economic extraction).
Australia has 28% of the world's known uranium ore reserves and the world's largest single uranium deposit is located at the Olympic Dam Mine in
 In 2005, ten countries accounted for the majority of the world's concentrated uranium oxides:
In 2005, ten countries accounted for the majority of the world's concentrated uranium oxides:

 Salts of many
Salts of many
 All uranium fluorides are created using uranium tetrafluoride (); itself is prepared by hydrofluorination of uranium dioxide. Reduction of with hydrogen at 1000 °C produces uranium trifluoride (). Under the right conditions of temperature and pressure, the reaction of solid with gaseous uranium hexafluoride () can form the intermediate fluorides of , , and .
At room temperatures, has a high
All uranium fluorides are created using uranium tetrafluoride (); itself is prepared by hydrofluorination of uranium dioxide. Reduction of with hydrogen at 1000 °C produces uranium trifluoride (). Under the right conditions of temperature and pressure, the reaction of solid with gaseous uranium hexafluoride () can form the intermediate fluorides of , , and .
At room temperatures, has a high
 In nature, uranium is found as uranium-238 (99.2742%) and uranium-235 (0.7204%). Isotope separation concentrates (enriches) the fissile uranium-235 for nuclear weapons and most nuclear power plants, except for gas cooled reactors and pressurized heavy water reactors. Most neutrons released by a fissioning atom of uranium-235 must impact other uranium-235 atoms to sustain the nuclear chain reaction. The concentration and amount of uranium-235 needed to achieve this is called a ' critical mass'.
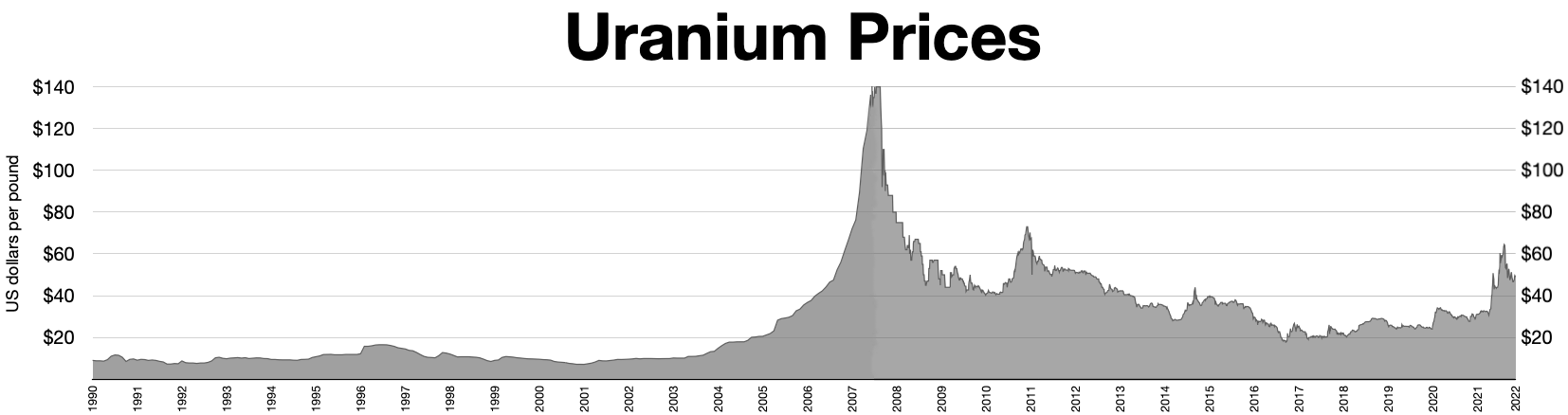
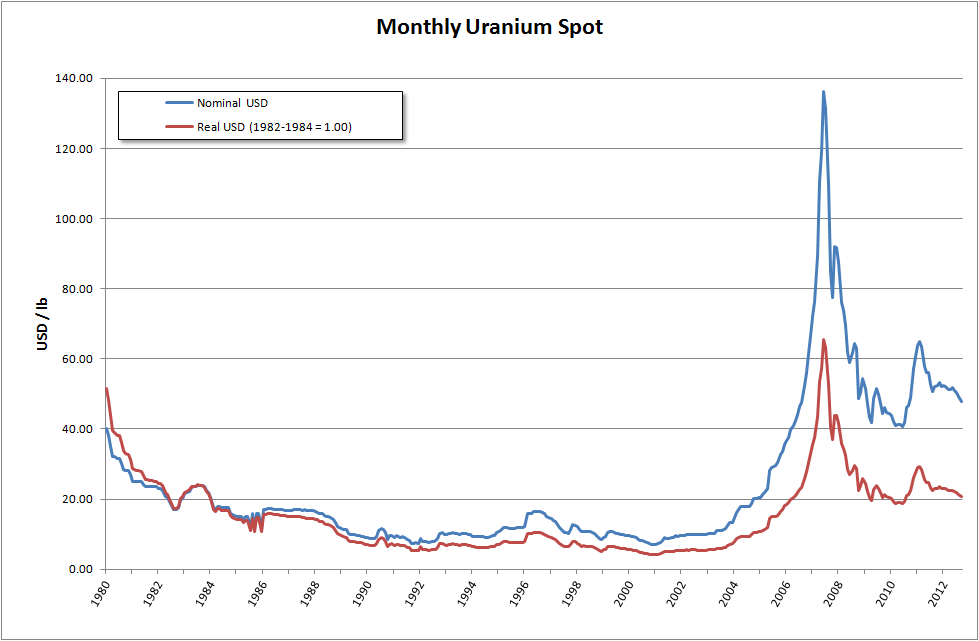
To be considered 'enriched', the uranium-235 fraction should be between 3% and 5%. This process produces huge quantities of uranium that is depleted of uranium-235 and with a correspondingly increased fraction of uranium-238, called depleted uranium or 'DU'. To be considered 'depleted', the U concentration should be no more than 0.3%. The price of uranium has risen since 2001, so enrichment tailings containing more than 0.35% uranium-235 are being considered for re-enrichment, driving the price of depleted uranium hexafluoride above $130 per kilogram in July 2007 from $5 in 2001.
The gas centrifuge process, where gaseous uranium hexafluoride () is separated by the difference in molecular weight between UF and UF using high-speed centrifuges, is the cheapest and leading enrichment process. The gaseous diffusion process had been the leading method for enrichment and was used in the
In nature, uranium is found as uranium-238 (99.2742%) and uranium-235 (0.7204%). Isotope separation concentrates (enriches) the fissile uranium-235 for nuclear weapons and most nuclear power plants, except for gas cooled reactors and pressurized heavy water reactors. Most neutrons released by a fissioning atom of uranium-235 must impact other uranium-235 atoms to sustain the nuclear chain reaction. The concentration and amount of uranium-235 needed to achieve this is called a ' critical mass'.
To be considered 'enriched', the uranium-235 fraction should be between 3% and 5%. This process produces huge quantities of uranium that is depleted of uranium-235 and with a correspondingly increased fraction of uranium-238, called depleted uranium or 'DU'. To be considered 'depleted', the U concentration should be no more than 0.3%. The price of uranium has risen since 2001, so enrichment tailings containing more than 0.35% uranium-235 are being considered for re-enrichment, driving the price of depleted uranium hexafluoride above $130 per kilogram in July 2007 from $5 in 2001.
The gas centrifuge process, where gaseous uranium hexafluoride () is separated by the difference in molecular weight between UF and UF using high-speed centrifuges, is the cheapest and leading enrichment process. The gaseous diffusion process had been the leading method for enrichment and was used in the
Nuclear fuel data and analysis
from the U.S. Energy Information Administration
World Uranium deposit maps
*
Annotated bibliography for uranium from the Alsos Digital Library
NLM Hazardous Substances Databank – Uranium, Radioactive
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
Uranium
at ''The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham) {{Authority control Uranium, Chemical elements Actinides Nuclear fuels Nuclear materials Suspected male-mediated teratogens Manhattan Project Pyrophoric materials
chemical element
A chemical element is a chemical substance whose atoms all have the same number of protons. The number of protons is called the atomic number of that element. For example, oxygen has an atomic number of 8: each oxygen atom has 8 protons in its ...
; it has symbol
A symbol is a mark, Sign (semiotics), sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, physical object, object, or wikt:relationship, relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by cr ...
U and atomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of its atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei composed of protons and neutrons, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of pro ...
92. It is a silvery-grey metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated wit ...
in the actinide
The actinide () or actinoid () series encompasses at least the 14 metallic chemical elements in the 5f series, with atomic numbers from 89 to 102, actinium through nobelium. Number 103, lawrencium, is also generally included despite being part ...
series of the periodic table
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the elements, is an ordered arrangement of the chemical elements into rows (" periods") and columns (" groups"). It is an icon of chemistry and is widely used in physics and other s ...
. A uranium atom has 92 proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , Hydron (chemistry), H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' (elementary charge). Its mass is slightly less than the mass of a neutron and approximately times the mass of an e ...
s and 92 electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
s, of which 6 are valence electron
In chemistry and physics, valence electrons are electrons in the outermost shell of an atom, and that can participate in the formation of a chemical bond if the outermost shell is not closed. In a single covalent bond, a shared pair forms with b ...
s. Uranium radioactively decays, usually by emitting an alpha particle
Alpha particles, also called alpha rays or alpha radiation, consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus. They are generally produced in the process of alpha decay but may also be produce ...
. The half-life Half-life is a mathematical and scientific description of exponential or gradual decay.
Half-life, half life or halflife may also refer to:
Film
* Half-Life (film), ''Half-Life'' (film), a 2008 independent film by Jennifer Phang
* ''Half Life: ...
of this decay varies between 159,200 and 4.5 billion years for different isotopes
Isotopes are distinct nuclear species (or ''nuclides'') of the same chemical element. They have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), but ...
, making them useful for dating the age of the Earth
The age of Earth is estimated to be 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years. This age may represent the age of Earth's accretion (astrophysics), accretion, or Internal structure of Earth, core formation, or of the material from which Earth formed. This dating ...
. The most common isotopes in natural uranium are uranium-238 (which has 146 neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , that has no electric charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. The Discovery of the neutron, neutron was discovered by James Chadwick in 1932, leading to the discovery of nucle ...
s and accounts for over 99% of uranium on Earth) and uranium-235
Uranium-235 ( or U-235) is an isotope of uranium making up about 0.72% of natural uranium. Unlike the predominant isotope uranium-238, it is fissile, i.e., it can sustain a nuclear chain reaction. It is the only fissile isotope that exists in nat ...
(which has 143 neutrons). Uranium has the highest atomic weight
Relative atomic mass (symbol: ''A''; sometimes abbreviated RAM or r.a.m.), also known by the deprecated synonym atomic weight, is a dimensionless physical quantity defined as the ratio of the average mass of atoms of a chemical element in a giv ...
of the primordially occurring elements. Its density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the ratio of a substance's mass to its volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' (or ''d'') can also be u ...
is about 70% higher than that of lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
and slightly lower than that of gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
or tungsten
Tungsten (also called wolfram) is a chemical element; it has symbol W and atomic number 74. It is a metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively in compounds with other elements. It was identified as a distinct element in 1781 and first ...
. It occurs naturally in low concentrations of a few parts per million
In science and engineering, the parts-per notation is a set of pseudo-units to describe the small values of miscellaneous dimensionless quantity, dimensionless quantities, e.g. mole fraction or mass fraction (chemistry), mass fraction.
Since t ...
in soil, rock and water, and is commercially extracted from uranium-bearing mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid substance with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Mi ...
s such as uraninite.
Many contemporary uses of uranium exploit its unique nuclear properties. Uranium is used in nuclear power plant
A nuclear power plant (NPP), also known as a nuclear power station (NPS), nuclear generating station (NGS) or atomic power station (APS) is a thermal power station in which the heat source is a nuclear reactor. As is typical of thermal power st ...
s and nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission or atomic bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear weapon), producing a nuclear exp ...
s because it is the only naturally occurring element with a fissile
In nuclear engineering, fissile material is material that can undergo nuclear fission when struck by a neutron of low energy. A self-sustaining thermal Nuclear chain reaction#Fission chain reaction, chain reaction can only be achieved with fissil ...
isotope – uranium-235 – present in non-trace amounts. However, because of the low abundance of uranium-235 in natural uranium (which is overwhelmingly uranium-238), uranium needs to undergo enrichment so that enough uranium-235 is present. Uranium-238 is fissionable by fast neutrons and is fertile, meaning it can be transmuted to fissile plutonium-239 in a nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a Nuclear fission, fission nuclear chain reaction. They are used for Nuclear power, commercial electricity, nuclear marine propulsion, marine propulsion, Weapons-grade plutonium, weapons ...
. Another fissile isotope, uranium-233
Uranium-233 ( or U-233) is a fissile isotope of uranium that is bred from thorium-232 as part of the thorium fuel cycle. Uranium-233 was investigated for use in nuclear weapons and as a Nuclear fuel, reactor fuel. It has been used successfully ...
, can be produced from natural thorium
Thorium is a chemical element; it has symbol Th and atomic number 90. Thorium is a weakly radioactive light silver metal which tarnishes olive grey when it is exposed to air, forming thorium dioxide; it is moderately soft, malleable, and ha ...
and is studied for future industrial use in nuclear technology. Uranium-238 has a small probability for spontaneous fission or even induced fission with fast neutrons; uranium-235, and to a lesser degree uranium-233, have a much higher fission cross-section for slow neutrons. In sufficient concentration, these isotopes maintain a sustained nuclear chain reaction. This generates the heat in nuclear power reactors and produces the fissile material for nuclear weapons. The primary civilian use for uranium harnesses the heat energy to produce electricity. Depleted uranium
Depleted uranium (DU), also referred to in the past as Q-metal, depletalloy, or D-38, is uranium with a lower content of the fissile isotope Uranium-235, 235U than natural uranium. The less radioactive and non-fissile Uranium-238, 238U is the m ...
(U) is used in kinetic energy penetrators and armor plating.
The 1789 discovery
Discovery may refer to:
* Discovery (observation), observing or finding something unknown
* Discovery (fiction), a character's learning something unknown
* Discovery (law), a process in courts of law relating to evidence
Discovery, The Discovery ...
of uranium in the mineral pitchblende
Uraninite, also known as pitchblende, is a radioactive, uranium-rich mineral and ore with a chemical composition that is largely UO2 but because of oxidation typically contains variable proportions of U3O8. Radioactive decay of the urani ...
is credited to Martin Heinrich Klaproth, who named the new element after the recently discovered planet Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It is a gaseous cyan-coloured ice giant. Most of the planet is made of water, ammonia, and methane in a Supercritical fluid, supercritical phase of matter, which astronomy calls "ice" or Volatile ( ...
. Eugène-Melchior Péligot
Eugène-Melchior Péligot (24 March 1811 – 15 April 1890), also known as Eugène Péligot, was a French chemist who isolated the first sample of uranium metal in 1841.
Péligot proved that the black powder of Martin Heinrich Klaproth was not ...
was the first person to isolate the metal, and its radioactive properties were discovered in 1896 by Henri Becquerel
Antoine Henri Becquerel ( ; ; 15 December 1852 – 25 August 1908) was a French nuclear physicist who shared the 1903 Nobel Prize in Physics with Marie and Pierre Curie for his discovery of radioactivity.
Biography
Family and education
Becq ...
. Research by Otto Hahn
Otto Hahn (; 8 March 1879 – 28 July 1968) was a German chemist who was a pioneer in the field of radiochemistry. He is referred to as the father of nuclear chemistry and discoverer of nuclear fission, the science behind nuclear reactors and ...
, Lise Meitner
Elise Lise Meitner ( ; ; 7 November 1878 – 27 October 1968) was an Austrian-Swedish nuclear physicist who was instrumental in the discovery of nuclear fission.
After completing her doctoral research in 1906, Meitner became the second woman ...
, Enrico Fermi and others, such as J. Robert Oppenheimer starting in 1934 led to its use as a fuel in the nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced by ...
industry and in Little Boy, the first nuclear weapon used in war. An ensuing arms race
An arms race occurs when two or more groups compete in military superiority. It consists of a competition between two or more State (polity), states to have superior armed forces, concerning production of weapons, the growth of a military, and ...
during the Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
between the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
and the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
produced tens of thousands of nuclear weapons that used uranium metal and uranium-derived plutonium-239. Dismantling of these weapons and related nuclear facilities is carried out within various nuclear disarmament
Nuclear disarmament is the act of reducing or eliminating nuclear weapons. Its end state can also be a nuclear-weapons-free world, in which nuclear weapons are completely eliminated. The term ''denuclearization'' is also used to describe the pro ...
programs and costs billions of dollars. Weapon-grade uranium obtained from nuclear weapons is diluted with uranium-238 and reused as fuel for nuclear reactors. Spent nuclear fuel
Spent nuclear fuel, occasionally called used nuclear fuel, is nuclear fuel that has been irradiated in a nuclear reactor (usually at a nuclear power plant). It is no longer useful in sustaining a nuclear reaction in an ordinary thermal reactor and ...
forms radioactive waste
Radioactive waste is a type of hazardous waste that contains radioactive material. It is a result of many activities, including nuclear medicine, nuclear research, nuclear power generation, nuclear decommissioning, rare-earth mining, and nuclear ...
, which mostly consists of uranium-238 and poses a significant health threat and environmental impact
Environmental issues are disruptions in the usual function of ecosystems. Further, these issues can be caused by humans ( human impact on the environment) or they can be natural. These issues are considered serious when the ecosystem cannot reco ...
.
Characteristics
metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated wit ...
. It has a Mohs hardness
The Mohs scale ( ) of mineral hardness is a qualitative ordinal scale, from 1 to 10, characterizing scratch resistance of mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid substance with a fair ...
of 6, sufficient to scratch glass and roughly equal to that of titanium
Titanium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in ...
, rhodium
Rhodium is a chemical element; it has symbol Rh and atomic number 45. It is a very rare, silvery-white, hard, corrosion-resistant transition metal. It is a noble metal and a member of the platinum group. It has only one naturally occurring isot ...
, manganese
Manganese is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese was first isolated in the 1770s. It is a transition m ...
and niobium
Niobium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Nb (formerly columbium, Cb) and atomic number 41. It is a light grey, crystalline, and Ductility, ductile transition metal. Pure niobium has a Mohs scale of mineral hardness, Mohs h ...
. It is malleable, ductile
Ductility refers to the ability of a material to sustain significant plastic deformation before fracture. Plastic deformation is the permanent distortion of a material under applied stress, as opposed to elastic deformation, which is reversi ...
, slightly paramagnetic, strongly electropositive and a poor electrical conductor
In physics and electrical engineering, a conductor is an object or type of material that allows the flow of charge (electric current) in one or more directions. Materials made of metal are common electrical conductors. The flow of negatively c ...
. Uranium metal has a very high density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the ratio of a substance's mass to its volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' (or ''d'') can also be u ...
of 19.1 g/cm, denser than lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
(11.3 g/cm), but slightly less dense than tungsten
Tungsten (also called wolfram) is a chemical element; it has symbol W and atomic number 74. It is a metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively in compounds with other elements. It was identified as a distinct element in 1781 and first ...
and gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
(19.3 g/cm).
Uranium metal reacts with almost all non-metallic elements (except noble gas
The noble gases (historically the inert gases, sometimes referred to as aerogens) are the members of Group (periodic table), group 18 of the periodic table: helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), radon (Rn) and, in some ...
es) and their compounds, with reactivity increasing with temperature. Hydrochloric and nitric acid
Nitric acid is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but samples tend to acquire a yellow cast over time due to decomposition into nitrogen oxide, oxides of nitrogen. Most com ...
s dissolve uranium, but non-oxidizing acids other than hydrochloric acid attack the element very slowly. When finely divided, it can react with cold water; in air, uranium metal becomes coated with a dark layer of uranium dioxide. Uranium in ores is extracted chemically and converted into uranium dioxide or other chemical forms usable in industry.
Uranium-235 was the first isotope that was found to be fissile
In nuclear engineering, fissile material is material that can undergo nuclear fission when struck by a neutron of low energy. A self-sustaining thermal Nuclear chain reaction#Fission chain reaction, chain reaction can only be achieved with fissil ...
. Other naturally occurring isotopes are fissionable, but not fissile. On bombardment with slow neutrons, uranium-235 most of the time splits into two smaller nuclei, releasing nuclear binding energy
In physics and chemistry, binding energy is the smallest amount of energy required to remove a particle from a system of particles or to disassemble a system of particles into individual parts. In the former meaning the term is predominantly use ...
and more neutrons. If too many of these neutrons are absorbed by other uranium-235 nuclei, a nuclear chain reaction occurs that results in a burst of heat or (in some circumstances) an explosion. In a nuclear reactor, such a chain reaction is slowed and controlled by a neutron poison, absorbing some of the free neutrons. Such neutron absorbent materials are often part of reactor control rods (see nuclear reactor physics for a description of this process of reactor control).
As little as of uranium-235 can be used to make an atomic bomb. The nuclear weapon detonated over Hiroshima
is the capital of Hiroshima Prefecture in Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 1,199,391. The gross domestic product (GDP) in Greater Hiroshima, Hiroshima Urban Employment Area, was US$61.3 billion as of 2010. Kazumi Matsui has b ...
, called Little Boy, relied on uranium fission. However, the first nuclear bomb (the ''Gadget'' used at Trinity
The Trinity (, from 'threefold') is the Christian doctrine concerning the nature of God, which defines one God existing in three, , consubstantial divine persons: God the Father, God the Son (Jesus Christ) and God the Holy Spirit, thr ...
) and the bomb that was detonated over Nagasaki ( Fat Man) were both plutonium bombs.
Uranium metal has three allotropic forms:
* α (orthorhombic
In crystallography, the orthorhombic crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Orthorhombic Lattice (group), lattices result from stretching a cubic crystal system, cubic lattice along two of its orthogonal pairs by two different factors, res ...
) stable up to . Orthorhombic, space group
In mathematics, physics and chemistry, a space group is the symmetry group of a repeating pattern in space, usually in three dimensions. The elements of a space group (its symmetry operations) are the rigid transformations of the pattern that ...
No. 63, ''Cmcm'', lattice parameters ''a'' = 285.4 pm, ''b'' = 587 pm, ''c'' = 495.5 pm.
* β (tetragonal
In crystallography, the tetragonal crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Tetragonal crystal lattices result from stretching a cubic lattice along one of its lattice vectors, so that the Cube (geometry), cube becomes a rectangular Pri ...
) stable from . Tetragonal, space group ''P''42/''mnm'', ''P''42''nm'', or ''P''4''n''2, lattice parameters ''a'' = 565.6 pm, ''b'' = ''c'' = 1075.9 pm.
* γ (body-centered cubic
In crystallography, the cubic (or isometric) crystal system is a crystal system where the Crystal structure#Unit cell, unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals.
There ...
) from to melting point—this is the most malleable and ductile state. Body-centered cubic, lattice parameter ''a'' = 352.4 pm.
Applications
Military
 The major application of uranium in the military sector is in high-density penetrating projectiles. This ammunition consists of
The major application of uranium in the military sector is in high-density penetrating projectiles. This ammunition consists of depleted uranium
Depleted uranium (DU), also referred to in the past as Q-metal, depletalloy, or D-38, is uranium with a lower content of the fissile isotope Uranium-235, 235U than natural uranium. The less radioactive and non-fissile Uranium-238, 238U is the m ...
(DU) alloyed with 1–2% other elements, such as titanium
Titanium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in ...
or molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mo (from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'') and atomic number 42. The name derived from Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ores. Molybdenum minerals hav ...
. At high impact speed, the density, hardness, and pyrophoricity of the projectile enable the destruction of heavily armored targets. Tank armor and other removable vehicle armor can also be hardened with depleted uranium plates. The use of depleted uranium became politically and environmentally contentious after the use of such munitions by the US, UK and other countries during wars in the Persian Gulf and the Balkans raised health questions concerning uranium compounds left in the soil (see Gulf War syndrome).
Depleted uranium is also used as a shielding material in some containers used to store and transport radioactive materials. While the metal itself is radioactive, its high density makes it more effective than lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
in halting radiation from strong sources such as radium
Radium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Ra and atomic number 88. It is the sixth element in alkaline earth metal, group 2 of the periodic table, also known as the alkaline earth metals. Pure radium is silvery-white, ...
. Other uses of depleted uranium include counterweights for aircraft control surfaces, as ballast for missile re-entry vehicles and as a shielding material. Due to its high density, this material is found in inertial guidance system
An inertial navigation system (INS; also inertial guidance system, inertial instrument) is a navigation device that uses motion sensors (accelerometers), rotation sensors ( gyroscopes) and a computer to continuously calculate by dead reckoning ...
s and in gyroscopic compass
A compass is a device that shows the cardinal directions used for navigation and geographic orientation. It commonly consists of a magnetized needle or other element, such as a compass card or compass rose, which can pivot to align itself with No ...
es. Depleted uranium is preferred over similarly dense metals due to its ability to be easily machined and cast as well as its relatively low cost. The main risk of exposure to depleted uranium is chemical poisoning by uranium oxide rather than radioactivity (uranium being only a weak alpha emitter).
During the later stages of World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, the entire Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
, and to a lesser extent afterwards, uranium-235 has been used as the fissile explosive material to produce nuclear weapons. Initially, two major types of fission bombs were built: a relatively simple device that uses uranium-235 and a more complicated mechanism that uses plutonium-239 derived from uranium-238. Later, a much more complicated and far more powerful type of fission/fusion bomb (thermonuclear weapon
A thermonuclear weapon, fusion weapon or hydrogen bomb (H-bomb) is a second-generation nuclear weapon design. Its greater sophistication affords it vastly greater destructive power than first-generation nuclear bombs, a more compact size, a lowe ...
) was built, that uses a plutonium-based device to cause a mixture of tritium
Tritium () or hydrogen-3 (symbol T or H) is a rare and radioactive isotope of hydrogen with a half-life of ~12.33 years. The tritium nucleus (t, sometimes called a ''triton'') contains one proton and two neutrons, whereas the nucleus of the ...
and deuterium
Deuterium (hydrogen-2, symbol H or D, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen; the other is protium, or hydrogen-1, H. The deuterium nucleus (deuteron) contains one proton and one neutron, whereas the far more c ...
to undergo nuclear fusion
Nuclear fusion is a nuclear reaction, reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei combine to form a larger nuclei, nuclei/neutrons, neutron by-products. The difference in mass between the reactants and products is manifested as either the rele ...
. Such bombs are jacketed in a non-fissile (unenriched) uranium case, and they derive more than half their power from the fission of this material by fast neutrons from the nuclear fusion process.
Civilian
The main use of uranium in the civilian sector is to fuelnuclear power plant
A nuclear power plant (NPP), also known as a nuclear power station (NPS), nuclear generating station (NGS) or atomic power station (APS) is a thermal power station in which the heat source is a nuclear reactor. As is typical of thermal power st ...
s. One kilogram of uranium-235 can theoretically produce about 20 terajoules of energy (2 joule
The joule ( , or ; symbol: J) is the unit of energy in the International System of Units (SI). In terms of SI base units, one joule corresponds to one kilogram- metre squared per second squared One joule is equal to the amount of work d ...
s), assuming complete fission; as much energy
Energy () is the physical quantity, quantitative physical property, property that is transferred to a physical body, body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of Work (thermodynamics), work and in the form of heat and l ...
as 1.5 million kilograms (1,500 tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1,000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton in the United States to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the s ...
s) of coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal i ...
.
Commercial nuclear power plants use fuel that is typically enriched to around 3% uranium-235. The CANDU and Magnox designs are the only commercial reactors capable of using unenriched uranium fuel. Fuel used for United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest Displacement (ship), displacement, at 4.5 millio ...
reactors is typically highly enriched in uranium-235
Uranium-235 ( or U-235) is an isotope of uranium making up about 0.72% of natural uranium. Unlike the predominant isotope uranium-238, it is fissile, i.e., it can sustain a nuclear chain reaction. It is the only fissile isotope that exists in nat ...
(the exact values are classified). In a breeder reactor, uranium-238 can also be converted into plutonium-239 through the following reaction:
: + n + γ
 Before (and, occasionally, after) the discovery of radioactivity, uranium was primarily used in small amounts for yellow glass and pottery glazes, such as uranium glass and in Fiestaware.
The discovery and isolation of
Before (and, occasionally, after) the discovery of radioactivity, uranium was primarily used in small amounts for yellow glass and pottery glazes, such as uranium glass and in Fiestaware.
The discovery and isolation of radium
Radium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Ra and atomic number 88. It is the sixth element in alkaline earth metal, group 2 of the periodic table, also known as the alkaline earth metals. Pure radium is silvery-white, ...
in uranium ore (pitchblende) by Marie Curie
Maria Salomea Skłodowska-Curie (; ; 7 November 1867 – 4 July 1934), known simply as Marie Curie ( ; ), was a Polish and naturalised-French physicist and chemist who conducted pioneering research on radioactivity.
She was List of female ...
sparked the development of uranium mining to extract the radium, which was used to make glow-in-the-dark paints for clock and aircraft dials. This left a prodigious quantity of uranium as a waste product, since it takes three tonnes of uranium to extract one gram of radium. This waste product was diverted to the glazing industry, making uranium glazes very inexpensive and abundant. Besides the pottery glazes, uranium tile glazes accounted for the bulk of the use, including common bathroom and kitchen tiles which can be produced in green, yellow, mauve, black, blue, red and other colors.
Uranium was also used in photographic chemicals (especially uranium nitrate as a toner), in lamp filaments for stage lighting
Stage lighting is the craft of lighting as it applies to the production of theater, dance, opera, and other performance arts.
bulbs, to improve the appearance of dentures
Dentures (also known as false teeth) are prosthetic devices constructed to replace missing teeth, supported by the surrounding soft and hard tissues of the oral cavity. Conventional dentures are removable ( removable partial denture or comp ...
, and in the leather and wood industries for stains and dyes. Uranium salts are mordants of silk or wool. Uranyl acetate and uranyl formate are used as electron-dense "stains" in transmission electron microscopy
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is a microscopy technique in which a beam of electrons is transmitted through a specimen to form an image. The specimen is most often an ultrathin section less than 100 nm thick or a suspension on a g ...
, to increase the contrast of biological specimens in ultrathin sections and in negative staining of virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are ...
es, isolated cell organelles and macromolecule
A macromolecule is a "molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass." Polymers are physi ...
s.
The discovery of the radioactivity of uranium ushered in additional scientific and practical uses of the element. The long half-life Half-life is a mathematical and scientific description of exponential or gradual decay.
Half-life, half life or halflife may also refer to:
Film
* Half-Life (film), ''Half-Life'' (film), a 2008 independent film by Jennifer Phang
* ''Half Life: ...
of uranium-238 (4.47 years) makes it well-suited for use in estimating the age of the earliest igneous rock
Igneous rock ( ), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava.
The magma can be derived from partial ...
s and for other types of radiometric dating
Radiometric dating, radioactive dating or radioisotope dating is a technique which is used to Chronological dating, date materials such as Rock (geology), rocks or carbon, in which trace radioactive impurity, impurities were selectively incorporat ...
, including uranium–thorium dating, uranium–lead dating
Uranium–lead dating, abbreviated U–Pb dating, is one of the oldest and most refined of the radiometric dating schemes. It can be used to date rocks that formed and crystallised from about 1 million years to over 4.5 billion years ago with routi ...
and uranium–uranium dating. Uranium metal is used for X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
targets in the making of high-energy X-rays.
History
Pre-discovery use
The use ofpitchblende
Uraninite, also known as pitchblende, is a radioactive, uranium-rich mineral and ore with a chemical composition that is largely UO2 but because of oxidation typically contains variable proportions of U3O8. Radioactive decay of the urani ...
, uranium in its natural oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound containing at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion (anion bearing a net charge of −2) of oxygen, an O2− ion with oxygen in the oxidation st ...
form, dates back to at least the year 79 AD, when it was used in the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
to add a yellow color to ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant, and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcela ...
glazes. Yellow glass with 1% uranium oxide was found in a Roman villa on Cape Posillipo
Posillipo (; ) is an affluent residential quarter of Naples, southern Italy, located along the northern coast of the Gulf of Naples.
From the 1st century BC the Bay of Naples witnessed the rise of villas constructed by elite Romans along the mo ...
in the Gulf of Naples
The Gulf of Naples (), also called the Bay of Naples, is a roughly 15-kilometer-wide (9.3 mi) gulf located along the south-western coast of Italy (Metropolitan City of Naples, Campania region). It opens to the west into the Mediterranean ...
, Italy, by R. T. Gunther of the University of Oxford
The University of Oxford is a collegiate university, collegiate research university in Oxford, England. There is evidence of teaching as early as 1096, making it the oldest university in the English-speaking world and the List of oldest un ...
in 1912. Starting in the late Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, pitchblende was extracted from the Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (; ), also known as the House of Austria, was one of the most powerful dynasties in the history of Europe and Western civilization. They were best known for their inbreeding and for ruling vast realms throughout Europe d ...
silver mines in Joachimsthal, Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
(now Jáchymov in the Czech Republic) in the Ore Mountains
The Ore Mountains (, or ; ) lie along the Czech–German border, separating the historical regions of Bohemia in the Czech Republic and Saxony in Germany. The highest peaks are the Klínovec in the Czech Republic (German: ''Keilberg'') at ab ...
, and was used as a coloring agent in the local glass
Glass is an amorphous (non-crystalline solid, non-crystalline) solid. Because it is often transparency and translucency, transparent and chemically inert, glass has found widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in window pane ...
making industry. In the early 19th century, the world's only known sources of uranium ore were these mines.
Discovery
 The
The discovery
Discovery may refer to:
* Discovery (observation), observing or finding something unknown
* Discovery (fiction), a character's learning something unknown
* Discovery (law), a process in courts of law relating to evidence
Discovery, The Discovery ...
of the element is credited to the German chemist Martin Heinrich Klaproth. While he was working in his experimental laboratory in Berlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population withi ...
in 1789, Klaproth was able to precipitate a yellow compound (likely sodium diuranate) by dissolving pitchblende
Uraninite, also known as pitchblende, is a radioactive, uranium-rich mineral and ore with a chemical composition that is largely UO2 but because of oxidation typically contains variable proportions of U3O8. Radioactive decay of the urani ...
in nitric acid
Nitric acid is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but samples tend to acquire a yellow cast over time due to decomposition into nitrogen oxide, oxides of nitrogen. Most com ...
and neutralizing the solution with sodium hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions .
Sodium hydroxide is a highly corrosive base (chemistry), ...
. Klaproth assumed the yellow substance was the oxide of a yet-undiscovered element and heated it with charcoal
Charcoal is a lightweight black carbon residue produced by strongly heating wood (or other animal and plant materials) in minimal oxygen to remove all water and volatile constituents. In the traditional version of this pyrolysis process, ca ...
to obtain a black powder, which he thought was the newly discovered metal itself (in fact, that powder was an oxide of uranium). He named the newly discovered element after the planet Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It is a gaseous cyan-coloured ice giant. Most of the planet is made of water, ammonia, and methane in a Supercritical fluid, supercritical phase of matter, which astronomy calls "ice" or Volatile ( ...
(named after the primordial Greek god of the sky), which had been discovered eight years earlier by William Herschel
Frederick William Herschel ( ; ; 15 November 1738 – 25 August 1822) was a German-British astronomer and composer. He frequently collaborated with his younger sister and fellow astronomer Caroline Herschel. Born in the Electorate of Hanover ...
.
In 1841, Eugène-Melchior Péligot
Eugène-Melchior Péligot (24 March 1811 – 15 April 1890), also known as Eugène Péligot, was a French chemist who isolated the first sample of uranium metal in 1841.
Péligot proved that the black powder of Martin Heinrich Klaproth was not ...
, Professor of Analytical Chemistry at the Conservatoire National des Arts et Métiers
The (; ; abbr. CNAM) is an AMBA-accredited French ''grande école'' and '' grand établissement''. It is a member of the '' Conférence des Grandes écoles'', which is an equivalent to the Ivy League schools in the United States, Oxbridge in th ...
(Central School of Arts and Manufactures) in Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
, isolated the first sample of uranium metal by heating uranium tetrachloride with potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to ...
.

Henri Becquerel
Antoine Henri Becquerel ( ; ; 15 December 1852 – 25 August 1908) was a French nuclear physicist who shared the 1903 Nobel Prize in Physics with Marie and Pierre Curie for his discovery of radioactivity.
Biography
Family and education
Becq ...
discovered radioactivity by using uranium in 1896. Becquerel made the discovery in Paris by leaving a sample of a uranium salt, KUO(SO) (potassium uranyl sulfate), on top of an unexposed photographic plate in a drawer and noting that the plate had become "fogged". He determined that a form of invisible light or rays emitted by uranium had exposed the plate.
During World War I when the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,; ; , ; were one of the two main coalitions that fought in World War I (1914–1918). It consisted of the German Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulga ...
suffered a shortage of molybdenum to make artillery gun barrels and high speed tool steels, they routinely used ferrouranium alloy as a substitute, as it presents many of the same physical characteristics as molybdenum. When this practice became known in 1916 the US government requested several prominent universities to research the use of uranium in manufacturing and metalwork. Tools made with these formulas remained in use for several decades, until the Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development program undertaken during World War II to produce the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States in collaboration with the United Kingdom and Canada.
From 1942 to 1946, the ...
and the Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
placed a large demand on uranium for fission research and weapon development.
Fission research
 A team led by Enrico Fermi in 1934 found that bombarding uranium with neutrons produces beta rays (
A team led by Enrico Fermi in 1934 found that bombarding uranium with neutrons produces beta rays (electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
s or positron
The positron or antielectron is the particle with an electric charge of +1''elementary charge, e'', a Spin (physics), spin of 1/2 (the same as the electron), and the same Electron rest mass, mass as an electron. It is the antiparticle (antimatt ...
s from the elements produced; see beta particle
A beta particle, also called beta ray or beta radiation (symbol β), is a high-energy, high-speed electron or positron emitted by the radioactive decay of an atomic nucleus, known as beta decay. There are two forms of beta decay, β− decay and � ...
). The fission products were at first mistaken for new elements with atomic numbers 93 and 94, which the Dean of the Sapienza University of Rome
The Sapienza University of Rome (), formally the Università degli Studi di Roma "La Sapienza", abbreviated simply as Sapienza ('Wisdom'), is a Public university, public research university located in Rome, Italy. It was founded in 1303 and is ...
, Orso Mario Corbino, named ausenium and hesperium, respectively. The experiments leading to the discovery of uranium's ability to fission (break apart) into lighter elements and release binding energy
In physics and chemistry, binding energy is the smallest amount of energy required to remove a particle from a system of particles or to disassemble a system of particles into individual parts. In the former meaning the term is predominantly use ...
were conducted by Otto Hahn
Otto Hahn (; 8 March 1879 – 28 July 1968) was a German chemist who was a pioneer in the field of radiochemistry. He is referred to as the father of nuclear chemistry and discoverer of nuclear fission, the science behind nuclear reactors and ...
and Fritz Strassmann in Hahn's laboratory in Berlin. Lise Meitner
Elise Lise Meitner ( ; ; 7 November 1878 – 27 October 1968) was an Austrian-Swedish nuclear physicist who was instrumental in the discovery of nuclear fission.
After completing her doctoral research in 1906, Meitner became the second woman ...
and her nephew, physicist Otto Robert Frisch, published the physical explanation in February 1939 and named the process "nuclear fission
Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei. The fission process often produces gamma photons, and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radioactiv ...
". Soon after, Fermi hypothesized that fission of uranium might release enough neutrons to sustain a fission reaction. Confirmation of this hypothesis came in 1939, and later work found that on average about 2.5 neutrons are released by each fission of uranium-235. Fermi urged Alfred O. C. Nier to separate uranium isotopes for determination of the fissile component, and on 29 February 1940, Nier used an instrument he built at the University of Minnesota
The University of Minnesota Twin Cities (historically known as University of Minnesota) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in the Minneapolis–Saint Paul, Twin Cities of Minneapolis and Saint ...
to separate the world's first uranium-235
Uranium-235 ( or U-235) is an isotope of uranium making up about 0.72% of natural uranium. Unlike the predominant isotope uranium-238, it is fissile, i.e., it can sustain a nuclear chain reaction. It is the only fissile isotope that exists in nat ...
sample in the Tate Laboratory. Using Columbia University
Columbia University in the City of New York, commonly referred to as Columbia University, is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Churc ...
's cyclotron
A cyclotron is a type of particle accelerator invented by Ernest Lawrence in 1929–1930 at the University of California, Berkeley, and patented in 1932. Lawrence, Ernest O. ''Method and apparatus for the acceleration of ions'', filed: Januar ...
, John Dunning confirmed the sample to be the isolated fissile material on 1 March. Further work found that the far more common uranium-238 isotope can be transmuted into plutonium, which, like uranium-235, is also fissile by thermal neutrons. These discoveries led numerous countries to begin working on the development of nuclear weapons and nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced by ...
. Despite fission having been discovered in Germany, the '' Uranverein'' ("uranium club") Germany's wartime project to research nuclear power and/or weapons was hampered by limited resources, infighting, the exile or non-involvement of several prominent scientists in the field and several crucial mistakes such as failing to account for impurities in available graphite samples which made it appear less suitable as a neutron moderator
In nuclear engineering, a neutron moderator is a medium that reduces the speed of fast neutrons, ideally without capturing any, leaving them as thermal neutrons with only minimal (thermal) kinetic energy. These thermal neutrons are immensely ...
than it is in reality. Germany's attempts to build a natural uranium / heavy water
Heavy water (deuterium oxide, , ) is a form of water (molecule), water in which hydrogen atoms are all deuterium ( or D, also known as ''heavy hydrogen'') rather than the common hydrogen-1 isotope (, also called ''protium'') that makes up most o ...
reactor had not come close to reaching criticality by the time the Americans reached Haigerloch, the site of the last German wartime reactor experiment.
On 2 December 1942, as part of the Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development program undertaken during World War II to produce the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States in collaboration with the United Kingdom and Canada.
From 1942 to 1946, the ...
, another team led by Enrico Fermi was able to initiate the first artificial self-sustained nuclear chain reaction, Chicago Pile-1
Chicago Pile-1 (CP-1) was the first artificial nuclear reactor. On 2 December 1942, the first human-made self-sustaining nuclear chain reaction was initiated in CP-1 during an experiment led by Enrico Fermi. The secret development of the react ...
. An initial plan using enriched uranium-235 was abandoned as it was as yet unavailable in sufficient quantities. Working in a lab below the stands of Stagg Field
Amos Alonzo Stagg Field is the name of two successive football fields for the University of Chicago. Beyond sports, the first Stagg Field (1893–1957), named for famed coach, Alonzo Stagg, is remembered for its role in a landmark scientific ac ...
at the University of Chicago
The University of Chicago (UChicago, Chicago, or UChi) is a Private university, private research university in Chicago, Illinois, United States. Its main campus is in the Hyde Park, Chicago, Hyde Park neighborhood on Chicago's South Side, Chic ...
, the team created the conditions needed for such a reaction by piling together 360 tonnes of graphite
Graphite () is a Crystallinity, crystalline allotrope (form) of the element carbon. It consists of many stacked Layered materials, layers of graphene, typically in excess of hundreds of layers. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable ...
, 53 tonnes of uranium oxide, and 5.5 tonnes of uranium metal, most of which was supplied by Westinghouse Lamp Plant in a makeshift production process.
Nuclear weaponry
 Two types of atomic bomb were developed by the United States during
Two types of atomic bomb were developed by the United States during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
: a uranium-based device (codenamed "Little Boy") whose fissile material was highly enriched uranium, and a plutonium-based device (see Trinity test and "Fat Man") whose plutonium was derived from uranium-238. Little Boy became the first nuclear weapon used in war when it was detonated over Hiroshima
is the capital of Hiroshima Prefecture in Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 1,199,391. The gross domestic product (GDP) in Greater Hiroshima, Hiroshima Urban Employment Area, was US$61.3 billion as of 2010. Kazumi Matsui has b ...
, Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
, on 6 August 1945. Exploding with a yield equivalent to 12,500 tonnes of TNT, the blast and thermal wave of the bomb destroyed nearly 50,000 buildings and killed about 75,000 people (see Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki
On 6 and 9 August 1945, the United States detonated two atomic bombs over the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, respectively, during World War II. The aerial bombings killed between 150,000 and 246,000 people, most of whom were civili ...
). Initially it was believed that uranium was relatively rare, and that nuclear proliferation
Nuclear proliferation is the spread of nuclear weapons to additional countries, particularly those not recognized as List of states with nuclear weapons, nuclear-weapon states by the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons, commonl ...
could be avoided by simply buying up all known uranium stocks, but within a decade large deposits of it were discovered in many places around the world.
Reactors
 The X-10 Graphite Reactor at
The X-10 Graphite Reactor at Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) is a federally funded research and development centers, federally funded research and development center in Oak Ridge, Tennessee, United States. Founded in 1943, the laboratory is sponsored by the United Sta ...
(ORNL) in Oak Ridge, Tennessee, formerly known as the Clinton Pile and X-10 Pile, was the world's second artificial nuclear reactor (after Enrico Fermi's Chicago Pile) and was the first reactor designed and built for continuous operation. Argonne National Laboratory
Argonne National Laboratory is a Federally funded research and development centers, federally funded research and development center in Lemont, Illinois, Lemont, Illinois, United States. Founded in 1946, the laboratory is owned by the United Sta ...
's Experimental Breeder Reactor I
Experimental Breeder Reactor I (EBR-I) is a decommissioned research reactor and U.S. National Historic Landmark located in the desert about southeast of Arco, Idaho. It was the world's first breeder reactor. At 1:50 p.m. on December 2 ...
, located at the Atomic Energy Commission's National Reactor Testing Station near Arco, Idaho, became the first nuclear reactor to create electricity on 20 December 1951. Initially, four 150-watt light bulbs were lit by the reactor, but improvements eventually enabled it to power the whole facility (later, the town of Arco became the first in the world to have all its electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwel ...
come from nuclear power generated by BORAX-III, another reactor designed and operated by Argonne National Laboratory
Argonne National Laboratory is a Federally funded research and development centers, federally funded research and development center in Lemont, Illinois, Lemont, Illinois, United States. Founded in 1946, the laboratory is owned by the United Sta ...
). The world's first commercial scale nuclear power station, Obninsk in the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
, began generation with its reactor AM-1 on 27 June 1954. Other early nuclear power plants were Calder Hall in England, which began generation on 17 October 1956, and the Shippingport Atomic Power Station in Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
, which began on 26 May 1958. Nuclear power was used for the first time for propulsion by a submarine
A submarine (often shortened to sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. (It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability.) The term "submarine" is also sometimes used historically or infor ...
, the USS ''Nautilus'', in 1954.
Prehistoric naturally occurring fission
In 1972, French physicist Francis Perrin discovered fifteen ancient and no longer active natural nuclear fission reactors in three separate ore deposits at the Oklo mine inGabon
Gabon ( ; ), officially the Gabonese Republic (), is a country on the Atlantic coast of Central Africa, on the equator, bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the north, the Republic of the Congo to the east and south, and ...
, Africa, collectively known as the Oklo Fossil Reactors. The ore deposit is 1.7 billion years old; then, uranium-235 constituted about 3% of uranium on Earth. This is high enough to permit a sustained chain reaction, if other supporting conditions exist. The capacity of the surrounding sediment to contain the health-threatening nuclear waste
Radioactive waste is a type of hazardous waste that contains radioactive material. It is a result of many activities, including nuclear medicine, nuclear research, nuclear power generation, nuclear decommissioning, rare-earth mining, and nuclear ...
products has been cited by the U.S. federal government as supporting evidence for the feasibility to store spent nuclear fuel at the Yucca Mountain nuclear waste repository.
Contamination and the Cold War legacy
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
into the 1970s and 1980s spread a significant amount of fallout from uranium daughter isotopes around the world. Additional fallout and pollution occurred from several nuclear accidents.
Uranium miners have a higher incidence of cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
. An excess risk of lung cancer among Navajo
The Navajo or Diné are an Indigenous people of the Southwestern United States. Their traditional language is Diné bizaad, a Southern Athabascan language.
The states with the largest Diné populations are Arizona (140,263) and New Mexico (1 ...
uranium miners, for example, has been documented and linked to their occupation. The Radiation Exposure Compensation Act, a 1990 law in the US, required $100,000 in "compassion payments" to uranium miners diagnosed with cancer or other respiratory ailments.
During the Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
between the Soviet Union and the United States, huge stockpiles of uranium were amassed and tens of thousands of nuclear weapons were created using enriched uranium and plutonium made from uranium. After the break-up of the Soviet Union in 1991, an estimated 600 short tons (540 metric tons) of highly enriched weapons grade uranium (enough to make 40,000 nuclear warheads) had been stored in often inadequately guarded facilities in the Russian Federation
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
and several other former Soviet states. Police in Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
, Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
, and South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
on at least 16 occasions from 1993 to 2005 have intercepted shipments of smuggled bomb-grade uranium or plutonium, most of which was from ex-Soviet sources. From 1993 to 2005 the Material Protection, Control, and Accounting Program, operated by the federal government of the United States
The Federal Government of the United States of America (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the Federation#Federal governments, national government of the United States.
The U.S. federal government is composed of three distinct ...
, spent about US$550 million to help safeguard uranium and plutonium stockpiles in Russia. This money was used for improvements and security enhancements at research and storage facilities.
Safety of nuclear facilities in Russia has been significantly improved since the stabilization of political and economical turmoil of the early 1990s. For example, in 1993 there were 29 incidents ranking above level 1 on the International Nuclear Event Scale, and this number dropped under four per year in 1995–2003. The number of employees receiving annual radiation doses above 20 mSv, which is equivalent to a single full-body CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
, saw a strong decline around 2000. In November 2015, the Russian government approved a federal program for nuclear and radiation safety for 2016 to 2030 with a budget of 562 billion rubles (ca. 8 billion USD
The United States dollar (symbol: $; currency code: USD) is the official currency of the United States and several other countries. The Coinage Act of 1792 introduced the U.S. dollar at par with the Spanish silver dollar, divided it int ...
). Its key issue is "the deferred liabilities accumulated during the 70 years of the nuclear industry, particularly during the time of the Soviet Union". About 73% of the budget will be spent on decommissioning aged and obsolete nuclear reactors and nuclear facilities, especially those involved in state defense programs; 20% will go in processing and disposal of nuclear fuel and radioactive waste, and 5% into monitoring and ensuring of nuclear and radiation safety.
Occurrence
Uranium is anaturally occurring
A natural product is a natural compound or substance produced by a living organism—that is, found in nature. In the broadest sense, natural products include any substance produced by life. Natural products can also be prepared by chemical ...
element found in low levels in all rock, soil, and water. It is the highest-numbered element found naturally in significant quantities on Earth and is almost always found combined with other elements. Uranium is the 48th most abundant element in the Earth’s crust. The decay of uranium, thorium
Thorium is a chemical element; it has symbol Th and atomic number 90. Thorium is a weakly radioactive light silver metal which tarnishes olive grey when it is exposed to air, forming thorium dioxide; it is moderately soft, malleable, and ha ...
, and potassium-40
Potassium-40 (K) is a long lived and the main naturally occurring radioactive isotope of potassium. Its half-life is 1.25 billion years. It makes up about 0.012% (120 parts-per notation, ppm) of natural potassium.
Potassium-40 undergoes four dif ...
in Earth's mantle is thought to be the main source of heat that keeps the Earth's outer core
Earth's outer core is a fluid layer about thick, composed of mostly iron and nickel that lies above Earth's solid Earth's inner core, inner core and below its Earth's mantle, mantle. The outer core begins approximately beneath Earth's surface ...
in the liquid state and drives mantle convection
Mantle convection is the very slow creep of Earth's solid silicate mantle as convection currents carry heat from the interior to the planet's surface. Mantle convection causes tectonic plates to move around the Earth's surface.
The Earth's l ...
, which in turn drives plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (, ) is the scientific theory that the Earth's lithosphere comprises a number of large tectonic plates, which have been slowly moving since 3–4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of , an idea developed durin ...
.
Uranium's concentration in the Earth's crust is (depending on the reference) 2 to 4 parts per million, or about 40 times as abundant as silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
. The Earth's crust from the surface to 25 km (15 mi) down is calculated to contain 10 kg (2 lb) of uranium while the ocean
The ocean is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of Earth. The ocean is conventionally divided into large bodies of water, which are also referred to as ''oceans'' (the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian Ocean, Indian, Southern Ocean ...
s may contain 10 kg (2 lb). The concentration of uranium in soil ranges from 0.7 to 11 parts per million (up to 15 parts per million in farmland soil due to use of phosphate fertilizer
A fertilizer or fertiliser is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from liming materials or other non-nutrient soil amendments. Man ...
s), and its concentration in sea water is 3 parts per billion.
Uranium is more plentiful than antimony
Antimony is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Sb () and atomic number 51. A lustrous grey metal or metalloid, it is found in nature mainly as the sulfide mineral stibnite (). Antimony compounds have been known since ancient t ...
, tin, cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, silvery-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12 element, group 12, zinc and mercury (element), mercury. Like z ...
, mercury, or silver, and it is about as abundant as arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a metalloid and one of the pnictogens, and therefore shares many properties with its group 15 neighbors phosphorus and antimony. Arsenic is not ...
or molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mo (from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'') and atomic number 42. The name derived from Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ores. Molybdenum minerals hav ...
. Uranium is found in hundreds of minerals, including uraninite (the most common uranium ore), carnotite, autunite, uranophane, torbernite
Torbernite, also known as chalcolite, is a relatively common mineral with the chemical formula Cu UO2)(PO4)sub>2(H2O)12. It is a radioactive, hydrated green copper uranyl phosphate, found in granites and other uranium-bearing deposits as a s ...
, and coffinite. Significant concentrations of uranium occur in some substances such as phosphate
Phosphates are the naturally occurring form of the element phosphorus.
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthop ...
rock deposits, and minerals such as lignite, and monazite sands in uranium-rich ores (it is recovered commercially from sources with as little as 0.1% uranium).
Origin
Like all elements withatomic weight
Relative atomic mass (symbol: ''A''; sometimes abbreviated RAM or r.a.m.), also known by the deprecated synonym atomic weight, is a dimensionless physical quantity defined as the ratio of the average mass of atoms of a chemical element in a giv ...
s higher than that of iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
, uranium is only naturally formed by the r-process
In nuclear astrophysics, the rapid neutron-capture process, also known as the ''r''-process, is a set of nuclear reactions that is responsible for nucleosynthesis, the creation of approximately half of the Atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei Heavy meta ...
(rapid neutron capture) in supernova
A supernova (: supernovae or supernovas) is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. A supernova occurs during the last stellar evolution, evolutionary stages of a massive star, or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion ...
e and neutron star merger
A neutron star merger is the stellar collision of neutron stars. When two neutron stars fall into mutual orbit, they gradually inspiral, spiral inward due to the loss of energy emitted as gravitational radiation. When they finally meet, their me ...
s. Primordial thorium and uranium are only produced in the r-process, because the s-process
The slow neutron-capture process, or ''s''-process, is a series of nuclear reactions, reactions in nuclear astrophysics that occur in stars, particularly asymptotic giant branch stars. The ''s''-process is responsible for the creation (nucleosynt ...
(slow neutron capture) is too slow and cannot pass the gap of instability after bismuth. Besides the two extant primordial uranium isotopes, U and U, the r-process also produced significant quantities of U, which has a shorter half-life and so is an extinct radionuclide, having long since decayed completely to Th. Further uranium-236 was produced by the decay of Pu, accounting for the observed higher-than-expected abundance of thorium and lower-than-expected abundance of uranium. While the natural abundance of uranium has been supplemented by the decay of extinct Pu (half-life 375,000 years) and Cm (half-life 16 million years), producing U and U respectively, this occurred to an almost negligible extent due to the shorter half-lives of these parents and their lower production than U and Pu, the parents of thorium: the Cm/U ratio at the formation of the Solar System was .
Biotic and abiotic
 Some bacteria, such as '' Shewanella putrefaciens'', '' Geobacter metallireducens'' and some strains of '' Burkholderia fungorum'', can use uranium for their growth and convert U(VI) to U(IV). Recent research suggests that this pathway includes reduction of the soluble U(VI) via an intermediate U(V) pentavalent state.
Other organisms, such as the
Some bacteria, such as '' Shewanella putrefaciens'', '' Geobacter metallireducens'' and some strains of '' Burkholderia fungorum'', can use uranium for their growth and convert U(VI) to U(IV). Recent research suggests that this pathway includes reduction of the soluble U(VI) via an intermediate U(V) pentavalent state.
Other organisms, such as the lichen
A lichen ( , ) is a hybrid colony (biology), colony of algae or cyanobacteria living symbiotically among hypha, filaments of multiple fungus species, along with yeasts and bacteria embedded in the cortex or "skin", in a mutualism (biology), m ...
''Trapelia involuta'' or microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic scale, microscopic size, which may exist in its unicellular organism, single-celled form or as a Colony (biology)#Microbial colonies, colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen ...
s such as the bacterium
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the ...
'' Citrobacter'', can absorb concentrations of uranium that are up to 300 times the level of their environment. ''Citrobacter'' species absorb uranyl ions when given glycerol phosphate (or other similar organic phosphates). After one day, one gram of bacteria can encrust themselves with nine grams of uranyl phosphate crystals; this creates the possibility that these organisms could be used in bioremediation
Bioremediation broadly refers to any process wherein a biological system (typically bacteria, microalgae, fungi in mycoremediation, and plants in phytoremediation), living or dead, is employed for removing environmental pollutants from air, wate ...
to decontaminate uranium-polluted water.
The proteobacterium '' Geobacter'' has also been shown to bioremediate uranium in ground water. The mycorrhizal fungus '' Glomus intraradices'' increases uranium content in the roots of its symbiotic plant.
In nature, uranium(VI) forms highly soluble carbonate complexes at alkaline pH. This leads to an increase in mobility and availability of uranium to groundwater and soil from nuclear wastes which leads to health hazards. However, it is difficult to precipitate uranium as phosphate in the presence of excess carbonate at alkaline pH. A '' Sphingomonas'' sp. strain BSAR-1 has been found to express a high activity alkaline phosphatase (PhoK) that has been applied for bioprecipitation of uranium as uranyl phosphate species from alkaline solutions. The precipitation ability was enhanced by overexpressing PhoK protein in '' E. coli''.
Plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
s absorb some uranium from soil. Dry weight concentrations of uranium in plants range from 5 to 60 parts per billion, and ash from burnt wood can have concentrations up to 4 parts per million. Dry weight concentrations of uranium in food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for Nutrient, nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or Fungus, fungal origin and contains essential nutrients such as carbohydrates, fats, protein (nutrient), proteins, vitamins, ...
plants are typically lower with one to two micrograms per day ingested through the food people eat.
Production and mining
Worldwide production of uranium in 2021 was 48,332tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1,000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton in the United States to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the s ...
s, of which 21,819 t (45%) was mined in Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
. Other important uranium mining countries are Namibia
Namibia, officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country on the west coast of Southern Africa. Its borders include the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Angola and Zambia to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south; in the no ...
(5,753 t), Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
(4,693 t), Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
(4,192 t), Uzbekistan
, image_flag = Flag of Uzbekistan.svg
, image_coat = Emblem of Uzbekistan.svg
, symbol_type = Emblem of Uzbekistan, Emblem
, national_anthem = "State Anthem of Uzbekistan, State Anthem of the Republ ...
(3,500 t), and Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
(2,635 t).
Uranium ore is mined in several ways: open pit, underground, in-situ leaching, and borehole mining. Low-grade uranium ore mined typically contains 0.01 to 0.25% uranium oxides. Extensive measures must be employed to extract the metal from its ore. High-grade ores found in Athabasca Basin
The Athabasca Basin is a region in the Canadian Shield of northern Saskatchewan and Alberta, Canada. It is best known as the world's leading source of high-grade uranium and currently supplies about 20% of the world's uranium.
The basin i ...
deposits in Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Western Canada. It is bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and to the south by the ...
, Canada can contain up to 23% uranium oxides on average. Uranium ore is crushed and rendered into a fine powder and then leached with either an acid
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis ...
or alkali
In chemistry, an alkali (; from the Arabic word , ) is a basic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7.0. The a ...
. The leachate
A leachate is any liquid that, in the course of passing through matter, extracts soluble or suspended solids, or any other component of the material through which it has passed.
Leachate is a widely used term in the environmental sciences wh ...
is subjected to one of several sequences of precipitation, solvent extraction, and ion exchange. The resulting mixture, called yellowcake, contains at least 75% uranium oxides UO. Yellowcake is then calcined to remove impurities from the milling process before refining and conversion.
Commercial-grade uranium can be produced through the reduction of uranium halides with alkali
In chemistry, an alkali (; from the Arabic word , ) is a basic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7.0. The a ...
or alkaline earth metal
The alkaline earth metals are six chemical elements in group (periodic table), group 2 of the periodic table. They are beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra).. The elements have very similar p ...
s. Uranium metal can also be prepared through electrolysis
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a technique that uses Direct current, direct electric current (DC) to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Electrolysis is commercially important as a stage in the separation of c ...
of or
, dissolved in molten calcium chloride
Calcium chloride is an inorganic compound, a Salt (chemistry), salt with the chemical formula . It is a white crystalline solid at room temperature, and it is highly soluble in water. It can be created by neutralising hydrochloric acid with cal ...
() and sodium chloride
Sodium chloride , commonly known as Salt#Edible salt, edible salt, is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. It is transparent or translucent, brittle, hygroscopic, and occurs a ...
( NaCl) solution. Very pure uranium is produced through the thermal decomposition of uranium halides on a hot filament.
Resources and reserves
 It is estimated that 6.1 million tonnes of uranium exists in ores that are economically viable at US$130 per kg of uranium, while 35 million tonnes are classed as mineral resources (reasonable prospects for eventual economic extraction).
Australia has 28% of the world's known uranium ore reserves and the world's largest single uranium deposit is located at the Olympic Dam Mine in
It is estimated that 6.1 million tonnes of uranium exists in ores that are economically viable at US$130 per kg of uranium, while 35 million tonnes are classed as mineral resources (reasonable prospects for eventual economic extraction).
Australia has 28% of the world's known uranium ore reserves and the world's largest single uranium deposit is located at the Olympic Dam Mine in South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a States and territories of Australia, state in the southern central part of Australia. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories by area, which in ...
. There is a significant reserve of uranium in Bakouma, a sub-prefecture in the prefecture
A prefecture (from the Latin word, "''praefectura"'') is an administrative jurisdiction traditionally governed by an appointed prefect. This can be a regional or local government subdivision in various countries, or a subdivision in certain inter ...
of Mbomou in the Central African Republic
The Central African Republic (CAR) is a landlocked country in Central Africa. It is bordered by Chad to Central African Republic–Chad border, the north, Sudan to Central African Republic–Sudan border, the northeast, South Sudan to Central ...
.
Some uranium also originates from dismantled nuclear weapons. For example, in 1993–2013 Russia supplied the United States with 15,000 tonnes of low-enriched uranium within the Megatons to Megawatts Program.
An additional 4.6 billion tonnes of uranium are estimated to be dissolved in sea water (Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
ese scientists in the 1980s showed that extraction of uranium from sea water using ion exchangers was technically feasible). There have been experiments to extract uranium from sea water, but the yield has been low due to the carbonate present in the water. In 2012, ORNL researchers announced the successful development of a new absorbent material dubbed HiCap which performs surface retention of solid or gas molecules, atoms or ions and also effectively removes toxic metals from water, according to results verified by researchers at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory.
Supplies
 In 2005, ten countries accounted for the majority of the world's concentrated uranium oxides:
In 2005, ten countries accounted for the majority of the world's concentrated uranium oxides: Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
(27.9%), Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
(22.8%), Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
(10.5%), Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
(8.0%), Namibia
Namibia, officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country on the west coast of Southern Africa. Its borders include the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Angola and Zambia to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south; in the no ...
(7.5%), Niger
Niger, officially the Republic of the Niger, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is a unitary state Geography of Niger#Political geography, bordered by Libya to the Libya–Niger border, north-east, Chad to the Chad–Niger border, east ...
(7.4%), Uzbekistan
, image_flag = Flag of Uzbekistan.svg
, image_coat = Emblem of Uzbekistan.svg
, symbol_type = Emblem of Uzbekistan, Emblem
, national_anthem = "State Anthem of Uzbekistan, State Anthem of the Republ ...
(5.5%), the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
(2.5%), Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
(2.1%) and Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
(1.9%). In 2008, Kazakhstan was forecast to increase production and become the world's largest supplier of uranium by 2009; Kazakhstan has dominated the world's uranium market since 2010. In 2021, its share was 45.1%, followed by Namibia (11.9%), Canada (9.7%), Australia (8.7%), Uzbekistan (7.2%), Niger (4.7%), Russia (5.5%), China (3.9%), India (1.3%), Ukraine (0.9%), and South Africa (0.8%), with a world total production of 48,332 tonnes. Most uranium was produced not by conventional underground mining of ores (29% of production), but by in situ leach
In-situ leaching (ISL), also called in-situ recovery (ISR) or solution mining, is a mining process used to recover minerals such as copper and uranium through boreholes drilled into a deposit, '' in situ''. In-situ leach works by artificially di ...
ing (66%).
In the late 1960s, UN geologists discovered major uranium deposits and other rare mineral reserves in Somalia
Somalia, officially the Federal Republic of Somalia, is the easternmost country in continental Africa. The country is located in the Horn of Africa and is bordered by Ethiopia to the west, Djibouti to the northwest, Kenya to the southwest, th ...
. The find was the largest of its kind, with industry experts estimating the deposits at over 25% of the world's then known uranium reserves of 800,000 tons.
The ultimate available supply is believed to be sufficient for at least the next 85 years, though some studies indicate underinvestment in the late twentieth century may produce supply problems in the 21st century.
Uranium deposits seem to be log-normal distributed. There is a 300-fold increase in the amount of uranium recoverable for each tenfold decrease in ore grade.
In other words, there is little high grade ore and proportionately much more low grade ore available.
Compounds
Oxidation states and oxides
Oxides
Calcined uranium yellowcake, as produced in many large mills, contains a distribution of uranium oxidation species in various forms ranging from most oxidized to least oxidized. Particles with short residence times in a calciner will generally be less oxidized than those with long retention times or particles recovered in the stack scrubber. Uranium content is usually referenced to , which dates to the days of theManhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development program undertaken during World War II to produce the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States in collaboration with the United Kingdom and Canada.
From 1942 to 1946, the ...
when was used as an analytical chemistry reporting standard.
Phase relationships in the uranium-oxygen system are complex. The most important oxidation states of uranium are uranium(IV) and uranium(VI), and their two corresponding oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound containing at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion (anion bearing a net charge of −2) of oxygen, an O2− ion with oxygen in the oxidation st ...
s are, respectively, uranium dioxide () and uranium trioxide (). Other uranium oxides such as uranium monoxide (UO), diuranium pentoxide (), and uranium peroxide () also exist.
The most common forms of uranium oxide are triuranium octoxide () and . Both oxide forms are solids that have low solubility in water and are relatively stable over a wide range of environmental conditions. Triuranium octoxide is (depending on conditions) the most stable compound of uranium and is the form most commonly found in nature. Uranium dioxide is the form in which uranium is most commonly used as a nuclear reactor fuel. At ambient temperatures, will gradually convert to . Because of their stability, uranium oxides are generally considered the preferred chemical form for storage or disposal.
Aqueous chemistry
 Salts of many
Salts of many oxidation state
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical Electrical charge, charge of an atom if all of its Chemical bond, bonds to other atoms are fully Ionic bond, ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons ...
s of uranium are water- soluble and may be studied in aqueous solution
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, also known as sodium chloride (NaCl), in water ...
s. The most common ionic forms are (brown-red), (green), (unstable), and (yellow), for U(III), U(IV), U(V), and U(VI), respectively. A few solid
Solid is a state of matter where molecules are closely packed and can not slide past each other. Solids resist compression, expansion, or external forces that would alter its shape, with the degree to which they are resisted dependent upon the ...
and semi-metallic compounds such as UO and US exist for the formal oxidation state uranium(II), but no simple ions are known to exist in solution for that state. Ions of liberate hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
from water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
and are therefore considered to be highly unstable. The ion represents the uranium(VI) state and is known to form compounds such as uranyl carbonate, uranyl chloride and uranyl sulfate. also forms complexes with various organic chelating agents, the most commonly encountered of which is uranyl acetate.
Unlike the uranyl salts of uranium and polyatomic ion
A polyatomic ion (also known as a molecular ion) is a covalent bonded set of two or more atoms, or of a metal complex, that can be considered to behave as a single unit and that usually has a net charge that is not zero, or in special c ...
uranium-oxide cationic forms, the uranates, salts containing a polyatomic uranium-oxide anion, are generally not water-soluble.
Carbonates
The interactions of carbonate anions with uranium(VI) cause the Pourbaix diagram to change greatly when the medium is changed from water to a carbonate containing solution. While the vast majority of carbonates are insoluble in water (students are often taught that all carbonates other than those of alkali metals are insoluble in water), uranium carbonates are often soluble in water. This is because a U(VI) cation is able to bind two terminal oxides and three or more carbonates to form anionic complexes.Effects of pH
The uranium fraction diagrams in the presence of carbonate illustrate this further: when the pH of a uranium(VI) solution increases, the uranium is converted to a hydrated uranium oxide hydroxide and at high pHs it becomes an anionic hydroxide complex. When carbonate is added, uranium is converted to a series of carbonate complexes if the pH is increased. One effect of these reactions is increased solubility of uranium in the pH range 6 to 8, a fact that has a direct bearing on the long term stability of spent uranium dioxide nuclear fuels.Hydrides, carbides and nitrides
Uranium metal heated to reacts withhydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
to form uranium hydride. Even higher temperatures will reversibly remove the hydrogen. This property makes uranium hydrides convenient starting materials to create reactive uranium powder along with various uranium carbide
In chemistry, a carbide usually describes a compound composed of carbon and a metal. In metallurgy, carbiding or carburizing is the process for producing carbide coatings on a metal piece.
Interstitial / Metallic carbides
The carbides of th ...
, nitride, and halide compounds. Two crystal modifications of uranium hydride exist: an α form that is obtained at low temperatures and a β form that is created when the formation temperature is above 250 °C.
Uranium carbides and uranium nitrides are both relatively inert semimetallic compounds that are minimally soluble in acid
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis ...
s, react with water, and can ignite in air
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
to form . Carbides of uranium include uranium monocarbide (U C), uranium dicarbide (), and diuranium tricarbide (). Both UC and are formed by adding carbon to molten uranium or by exposing the metal to carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the si ...
at high temperatures. Stable below 1800 °C, is prepared by subjecting a heated mixture of UC and to mechanical stress. Uranium nitrides obtained by direct exposure of the metal to nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
include uranium mononitride (UN), uranium dinitride (), and diuranium trinitride ().
Halides
 All uranium fluorides are created using uranium tetrafluoride (); itself is prepared by hydrofluorination of uranium dioxide. Reduction of with hydrogen at 1000 °C produces uranium trifluoride (). Under the right conditions of temperature and pressure, the reaction of solid with gaseous uranium hexafluoride () can form the intermediate fluorides of , , and .
At room temperatures, has a high
All uranium fluorides are created using uranium tetrafluoride (); itself is prepared by hydrofluorination of uranium dioxide. Reduction of with hydrogen at 1000 °C produces uranium trifluoride (). Under the right conditions of temperature and pressure, the reaction of solid with gaseous uranium hexafluoride () can form the intermediate fluorides of , , and .
At room temperatures, has a high vapor pressure
Vapor pressure or equilibrium vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases (solid or liquid) at a given temperature in a closed system. The equilibrium vapor pressure is an indicat ...
, making it useful in the gaseous diffusion process to separate the rare uranium-235 from the common uranium-238 isotope. This compound can be prepared from uranium dioxide and uranium hydride by the following process:
: + 4 HF → + 2 (500 °C, endothermic)
: + → (350 °C, endothermic)
The resulting , a white solid, is highly reactive (by fluorination), easily sublimes (emitting a vapor that behaves as a nearly ideal gas
An ideal gas is a theoretical gas composed of many randomly moving point particles that are not subject to interparticle interactions. The ideal gas concept is useful because it obeys the ideal gas law, a simplified equation of state, and is ...
), and is the most volatile compound of uranium known to exist.
One method of preparing uranium tetrachloride () is to directly combine chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between ...
with either uranium metal or uranium hydride. The reduction of by hydrogen produces uranium trichloride () while the higher chlorides of uranium are prepared by reaction with additional chlorine. All uranium chlorides react with water and air.
Bromides and iodides of uranium are formed by direct reaction of, respectively, bromine
Bromine is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a similarly coloured vapour. Its properties are intermediate between th ...
and iodine
Iodine is a chemical element; it has symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists at standard conditions as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a vi ...
with uranium or by adding to those element's acids. Known examples include: , , , and . has never been prepared. Uranium oxyhalides are water-soluble and include , , , and . Stability of the oxyhalides decrease as the atomic weight
Relative atomic mass (symbol: ''A''; sometimes abbreviated RAM or r.a.m.), also known by the deprecated synonym atomic weight, is a dimensionless physical quantity defined as the ratio of the average mass of atoms of a chemical element in a giv ...
of the component halide increases.
Isotopes
Uranium, like all elements with an atomic number greater than 82, has nostable isotope
Stable nuclides are Isotope, isotopes of a chemical element whose Nucleon, nucleons are in a configuration that does not permit them the surplus energy required to produce a radioactive emission. The Atomic nucleus, nuclei of such isotopes are no ...
s. All isotopes of uranium are radioactive
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is conside ...
because the strong nuclear force does not prevail over electromagnetic repulsion in nuclides containing more than 82 protons. Nevertheless, the two most stable isotopes, U and U, have half-lives long enough to occur in nature as primordial radionuclide
In geochemistry, geophysics and nuclear physics, primordial nuclides, also known as primordial isotopes, are nuclides found on Earth that have existed in their current form since before Earth was formed. Primordial nuclides were present in the ...
s, with measurable quantities having survived since the formation of the Earth. These two nuclide
Nuclides (or nucleides, from nucleus, also known as nuclear species) are a class of atoms characterized by their number of protons, ''Z'', their number of neutrons, ''N'', and their nuclear energy state.
The word ''nuclide'' was coined by the A ...
s, along with thorium-232
Thorium-232 () is the main naturally occurring isotope of thorium, with a relative abundance of 99.98%. It has a half life of 14.05 billion years, which makes it the longest-lived isotope of thorium. It decays by alpha decay to radium-228; its de ...
, are the only confirmed primordial nuclides heavier than nearly-stable bismuth-209
Bismuth-209 (Bi) is an isotope of bismuth, with the longest known half-life of any radioisotope that undergoes α-decay (alpha decay). It has 83 protons and a magic number of 126 neutrons, and an atomic mass of 208.9803987 amu (atomic mass unit ...
.
Natural uranium consists of three major isotopes: uranium-238 (99.28% natural abundance), uranium-235 (0.71%), and uranium-234 (0.0054%). There are also five other trace isotopes: uranium-240, a decay product of plutonium-244; uranium-239, which is formed when U undergoes spontaneous fission, releasing neutrons that are captured by another U atom; uranium-237, which is formed when U captures a neutron but emits two more, which then decays to neptunium-237; uranium-236
Uranium-236 ( or U-236) is an isotope of uranium that is neither fissile with thermal neutrons, nor very good fertile material, but is generally considered a nuisance and long-lived radioactive waste. It is found in spent nuclear fuel and in ...
, which occurs in trace quantities due to neutron capture on U and as a decay product of plutonium-244; and finally, uranium-233
Uranium-233 ( or U-233) is a fissile isotope of uranium that is bred from thorium-232 as part of the thorium fuel cycle. Uranium-233 was investigated for use in nuclear weapons and as a Nuclear fuel, reactor fuel. It has been used successfully ...
, which is formed in the decay chain
In nuclear science a decay chain refers to the predictable series of radioactive disintegrations undergone by the nuclei of certain unstable chemical elements.
Radioactive isotopes do not usually decay directly to stable isotopes, but rather ...
of neptunium-237. Additionally, uranium-232 would be produced by the double beta decay
In nuclear physics, double beta decay is a type of radioactive decay in which two neutrons are simultaneously transformed into two protons, or vice versa, inside an atomic nucleus. As in single beta decay, this process allows the atom to move cl ...
of natural thorium-232
Thorium-232 () is the main naturally occurring isotope of thorium, with a relative abundance of 99.98%. It has a half life of 14.05 billion years, which makes it the longest-lived isotope of thorium. It decays by alpha decay to radium-228; its de ...
, though this energetically possible process has never been observed.
Uranium-238 is the most stable isotope of uranium, with a half-life of about years, roughly the age of the Earth
The age of Earth is estimated to be 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years. This age may represent the age of Earth's accretion (astrophysics), accretion, or Internal structure of Earth, core formation, or of the material from which Earth formed. This dating ...
. Uranium-238 is predominantly an alpha emitter, decaying to thorium-234. It ultimately decays through the uranium series
In nuclear science a decay chain refers to the predictable series of radioactive disintegrations undergone by the nuclei of certain unstable chemical elements.
Radioactive isotopes do not usually decay directly to stable isotopes, but rather ...
, which has 18 members, into lead-206. Uranium-238 is not fissile, but is a fertile isotope, because after neutron activation it can be converted to plutonium-239, another fissile isotope. Indeed, the U nucleus can absorb one neutron to produce the radioactive isotope uranium-239. U decays by beta emission to neptunium
Neptunium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactivity, radioactive actinide metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element. It is named after Neptune, the planet beyond Uranus in the Solar Syste ...
-239, also a beta-emitter, that decays in its turn, within a few days into plutonium-239. Pu was used as fissile material in the first atomic bomb detonated in the " Trinity test" on 16 July 1945 in New Mexico
New Mexico is a state in the Southwestern United States, Southwestern region of the United States. It is one of the Mountain States of the southern Rocky Mountains, sharing the Four Corners region with Utah, Colorado, and Arizona. It also ...
.
Uranium-235 has a half-life of about years; it is the next most stable uranium isotope after U and is also predominantly an alpha emitter, decaying to thorium-231. Uranium-235 is important for both nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a Nuclear fission, fission nuclear chain reaction. They are used for Nuclear power, commercial electricity, nuclear marine propulsion, marine propulsion, Weapons-grade plutonium, weapons ...
s and nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission or atomic bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear weapon), producing a nuclear exp ...
s, because it is the only uranium isotope existing in nature on Earth in significant amounts that is fissile. This means that it can be split into two or three fragments ( fission products) by thermal neutrons. The decay chain of U, which is called the actinium series
In nuclear science a decay chain refers to the predictable series of radioactive disintegrations undergone by the nuclei of certain unstable chemical elements.
Radioactive isotopes do not usually decay directly to stable isotopes, but rather ...
, has 15 members and eventually decays into lead-207. The constant rates of decay in these decay series makes the comparison of the ratios of parent to daughter elements useful in radiometric dating.
Uranium-236 has a half-life of years and is not found in significant quantities in nature. The half-life of uranium-236 is too short for it to be primordial, though it has been identified as an extinct
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
progenitor of its alpha decay daughter, thorium-232. Uranium-236 occurs in spent nuclear fuel
Spent nuclear fuel, occasionally called used nuclear fuel, is nuclear fuel that has been irradiated in a nuclear reactor (usually at a nuclear power plant). It is no longer useful in sustaining a nuclear reaction in an ordinary thermal reactor and ...
when neutron capture on U does not induce fission, or as a decay product of plutonium-240
Plutonium-240 ( or Pu-240) is an isotope of plutonium formed when plutonium-239 captures a neutron. The detection of its spontaneous fission led to its discovery in 1944 at Los Alamos and had important consequences for the Manhattan Project.
...
. Uranium-236 is not fertile, as three more neutron captures are required to produce fissile Pu, and is not itself fissile; as such, it is considered long-lived radioactive waste.
Uranium-234 is a member of the uranium series and occurs in equilibrium with its progenitor, U; it undergoes alpha decay with a half-life of 245,500 years and decays to lead-206 through a series of relatively short-lived isotopes.
Uranium-233 undergoes alpha decay with a half-life of 160,000 years and, like U, is fissile. It can be bred from thorium-232
Thorium-232 () is the main naturally occurring isotope of thorium, with a relative abundance of 99.98%. It has a half life of 14.05 billion years, which makes it the longest-lived isotope of thorium. It decays by alpha decay to radium-228; its de ...
via neutron bombardment, usually in a nuclear reactor; this process is known as the thorium fuel cycle. Owing to the fissility of U and the greater natural abundance of thorium (three times that of uranium), U has been investigated for use as nuclear fuel as a possible alternative to U and Pu, though is not in widespread use . The decay chain of uranium-233 forms part of the neptunium series
In nuclear science a decay chain refers to the predictable series of radioactive decay, radioactive disintegrations undergone by the nuclei of certain unstable chemical elements.
Radionuclide, Radioactive isotopes do not usually decay directly ...
and ends at nearly-stable bismuth-209 (half-life ) and stable thallium
Thallium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Tl and atomic number 81. It is a silvery-white post-transition metal that is not found free in nature. When isolated, thallium resembles tin, but discolors when exposed to air. Che ...
-205.
Uranium-232 is an alpha emitter with a half-life of 68.9 years. This isotope is produced as a byproduct in production of U and is considered a nuisance, as it is not fissile and decays through short-lived alpha and gamma emitters such as Tl. It is also expected that thorium-232 should be able to undergo double beta decay
In nuclear physics, double beta decay is a type of radioactive decay in which two neutrons are simultaneously transformed into two protons, or vice versa, inside an atomic nucleus. As in single beta decay, this process allows the atom to move cl ...
, which would produce uranium-232, but this has not yet been observed experimentally.
All isotopes from U to U inclusive have minor cluster decay
Cluster decay, also named heavy particle radioactivity, heavy ion radioactivity or heavy cluster decay," is a rare type of nuclear decay in which an atomic nucleus emits a small "cluster" of neutrons and protons, more than in an alpha particle, ...
branches (less than %), and all these bar U, in addition to U, have minor spontaneous fission branches; the greatest branching ratio for spontaneous fission is about % for U, or about one in every two million decays. The shorter-lived trace isotopes U and U exclusively undergo beta decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits a beta particle (fast energetic electron or positron), transforming into an isobar of that nuclide. For example, beta decay of a neutron ...
, with respective half-lives of 6.752 days and 23.45 minutes.
In total, 28 isotopes of uranium have been identified, ranging in mass number
The mass number (symbol ''A'', from the German word: ''Atomgewicht'', "atomic weight"), also called atomic mass number or nucleon number, is the total number of protons and neutrons (together known as nucleons) in an atomic nucleus. It is appro ...
from 214 to 242, with the exception of 220. Among the uranium isotopes not found in natural samples or nuclear fuel, the longest-lived is U, an alpha emitter with a half-life of 20.23 days. This isotope has been considered for use in targeted alpha-particle therapy (TAT). All other isotopes have half-lives shorter than one hour, except for U (half-life 4.2 days) and U (half-life 14.1 hours). The shortest-lived known isotope is U, with a half-life of 660 nanoseconds, and it is expected that the hitherto unknown U has an even shorter half-life. The proton-rich isotopes lighter than U primarily undergo alpha decay, except for U and U, which decay to protactinium isotopes via positron emission
Positron emission, beta plus decay, or β+ decay is a subtype of radioactive decay called beta decay, in which a proton inside a radionuclide nucleus is converted into a neutron while releasing a positron and an electron neutrino (). Positron emi ...
and electron capture
Electron capture (K-electron capture, also K-capture, or L-electron capture, L-capture) is a process in which the proton-rich nucleus of an electrically neutral atom absorbs an inner atomic electron, usually from the K or L electron shells. Th ...
, respectively; the neutron-rich U, U, and U undergo beta decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits a beta particle (fast energetic electron or positron), transforming into an isobar of that nuclide. For example, beta decay of a neutron ...
to form neptunium isotopes.
Enrichment
 In nature, uranium is found as uranium-238 (99.2742%) and uranium-235 (0.7204%). Isotope separation concentrates (enriches) the fissile uranium-235 for nuclear weapons and most nuclear power plants, except for gas cooled reactors and pressurized heavy water reactors. Most neutrons released by a fissioning atom of uranium-235 must impact other uranium-235 atoms to sustain the nuclear chain reaction. The concentration and amount of uranium-235 needed to achieve this is called a ' critical mass'.
To be considered 'enriched', the uranium-235 fraction should be between 3% and 5%. This process produces huge quantities of uranium that is depleted of uranium-235 and with a correspondingly increased fraction of uranium-238, called depleted uranium or 'DU'. To be considered 'depleted', the U concentration should be no more than 0.3%. The price of uranium has risen since 2001, so enrichment tailings containing more than 0.35% uranium-235 are being considered for re-enrichment, driving the price of depleted uranium hexafluoride above $130 per kilogram in July 2007 from $5 in 2001.
The gas centrifuge process, where gaseous uranium hexafluoride () is separated by the difference in molecular weight between UF and UF using high-speed centrifuges, is the cheapest and leading enrichment process. The gaseous diffusion process had been the leading method for enrichment and was used in the
In nature, uranium is found as uranium-238 (99.2742%) and uranium-235 (0.7204%). Isotope separation concentrates (enriches) the fissile uranium-235 for nuclear weapons and most nuclear power plants, except for gas cooled reactors and pressurized heavy water reactors. Most neutrons released by a fissioning atom of uranium-235 must impact other uranium-235 atoms to sustain the nuclear chain reaction. The concentration and amount of uranium-235 needed to achieve this is called a ' critical mass'.
To be considered 'enriched', the uranium-235 fraction should be between 3% and 5%. This process produces huge quantities of uranium that is depleted of uranium-235 and with a correspondingly increased fraction of uranium-238, called depleted uranium or 'DU'. To be considered 'depleted', the U concentration should be no more than 0.3%. The price of uranium has risen since 2001, so enrichment tailings containing more than 0.35% uranium-235 are being considered for re-enrichment, driving the price of depleted uranium hexafluoride above $130 per kilogram in July 2007 from $5 in 2001.
The gas centrifuge process, where gaseous uranium hexafluoride () is separated by the difference in molecular weight between UF and UF using high-speed centrifuges, is the cheapest and leading enrichment process. The gaseous diffusion process had been the leading method for enrichment and was used in the Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development program undertaken during World War II to produce the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States in collaboration with the United Kingdom and Canada.
From 1942 to 1946, the ...
. In this process, uranium hexafluoride is repeatedly diffused through a silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
-zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
membrane, and the different isotopes of uranium are separated by diffusion rate (since uranium-238 is heavier it diffuses slightly slower than uranium-235). The molecular laser isotope separation method employs a laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ...
beam of precise energy to sever the bond between uranium-235 and fluorine. This leaves uranium-238 bonded to fluorine and allows uranium-235 metal to precipitate from the solution. An alternative laser method of enrichment is known as atomic vapor laser isotope separation (AVLIS) and employs visible tunable laser
A tunable laser is a laser whose wavelength of operation can be altered in a controlled manner. While all active laser medium, laser gain media allow small shifts in output wavelength, only a few types of lasers allow continuous tuning over a sign ...
s such as dye lasers. Another method used is liquid thermal diffusion.
The only significant deviation from the U to U ratio in any known natural samples occurs in Oklo, Gabon
Gabon ( ; ), officially the Gabonese Republic (), is a country on the Atlantic coast of Central Africa, on the equator, bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the north, the Republic of the Congo to the east and south, and ...
, where natural nuclear fission reactors consumed some of the U some two billion years ago when the ratio of U to U was more akin to that of low enriched uranium allowing regular ("light") water to act as a neutron moderator
In nuclear engineering, a neutron moderator is a medium that reduces the speed of fast neutrons, ideally without capturing any, leaving them as thermal neutrons with only minimal (thermal) kinetic energy. These thermal neutrons are immensely ...
akin to the process in humanmade light water reactors. The existence of such natural fission reactors which had been theoretically predicted beforehand was proven as the slight deviation of U concentration from the expected values were discovered during uranium enrichment in France. Subsequent investigations to rule out any nefarious human action (such as stealing of U) confirmed the theory by finding isotope ratios of common fission products (or rather their stable daughter nuclides) in line with the values expected for fission but deviating from the values expected for non-fission derived samples of those elements.
Human exposure
A person can be exposed to uranium (or its radioactive daughters, such asradon
Radon is a chemical element; it has symbol Rn and atomic number 86. It is a radioactive noble gas and is colorless and odorless. Of the three naturally occurring radon isotopes, only Rn has a sufficiently long half-life (3.825 days) for it to b ...
) by inhaling dust in air or by ingesting contaminated water and food. The amount of uranium in air is usually very small; however, people who work in factories that process phosphate
Phosphates are the naturally occurring form of the element phosphorus.
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthop ...
fertilizer
A fertilizer or fertiliser is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from liming materials or other non-nutrient soil amendments. Man ...
s, live near government facilities that made or tested nuclear weapons, live or work near a modern battlefield where depleted uranium weapons
A weapon, arm, or armament is any implement or device that is used to deter, threaten, inflict physical damage, harm, or kill. Weapons are used to increase the efficacy and efficiency of activities such as hunting, crime (e.g., murder), law ...
have been used, or live or work near a coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal i ...
-fired power plant, facilities that mine or process uranium ore, or enrich uranium for reactor fuel, may have increased exposure to uranium. Houses or structures that are over uranium deposits (either natural or man-made slag deposits) may have an increased incidence of exposure to radon gas. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA; ) is a regulatory agency of the United States Department of Labor that originally had federal visitorial powers to inspect and examine workplaces. The United States Congress established ...
(OSHA) has set the permissible exposure limit for uranium exposure in the workplace as 0.25 mg/m over an 8-hour workday. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) has set a recommended exposure limit (REL) of 0.2 mg/m over an 8-hour workday and a short-term limit of 0.6 mg/m. At 10 mg/m, uranium is immediately dangerous to life and health.
Most ingested uranium is excreted during digestion
Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food compounds into small water-soluble components so that they can be absorbed into the blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intestine into th ...
. Only 0.5% is absorbed when insoluble forms of uranium, such as its oxide, are ingested, whereas absorption of the more soluble uranyl ion can be up to 5%. However, soluble uranium compounds tend to quickly pass through the body, whereas insoluble uranium compounds, especially when inhaled by way of dust into the lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their ...
s, pose a more serious exposure hazard. After entering the bloodstream, the absorbed uranium tends to bioaccumulate and stay for many years in bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
tissue because of uranium's affinity for phosphates. Incorporated uranium becomes uranyl ions, which accumulate in bone, liver, kidney, and reproductive tissues.
Radiological and chemical toxicity of uranium combine by the fact that elements of high atomic number like uranium exhibit phantom or secondary radiotoxicity through absorption of natural background gamma and X-rays and re-emission of photoelectrons, which in combination with the high affinity of uranium to the phosphate moiety of DNA cause increased single and double strand DNA breaks.
Uranium is not absorbed through the skin, and alpha particle
Alpha particles, also called alpha rays or alpha radiation, consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus. They are generally produced in the process of alpha decay but may also be produce ...
s released by uranium cannot penetrate the skin.
Uranium can be decontaminated from steel surfaces and aquifers.
Effects and precautions
Normal functioning of the kidney, brain, liver, heart, and other systems can be affected by uranium exposure, because, besides being weakly radioactive, uranium is a Metal toxicity, toxic metal. Uranium is also a reproductive toxicant. Radiological effects are generally local because alpha radiation, the primary form of U decay, has a very short range, and will not penetrate skin. Alpha radiation from inhaled uranium has been demonstrated to cause lung cancer in exposed nuclear workers. While the CDC has published one study that no humancancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
has been seen as a result of exposure to natural or depleted uranium, exposure to uranium and its decay products, especially radon
Radon is a chemical element; it has symbol Rn and atomic number 86. It is a radioactive noble gas and is colorless and odorless. Of the three naturally occurring radon isotopes, only Rn has a sufficiently long half-life (3.825 days) for it to b ...
, is a significant health threat. Exposure to strontium-90, iodine-131, and other fission products is unrelated to uranium exposure, but may result from medical procedures or exposure to spent reactor fuel or fallout from nuclear weapons.
Although accidental inhalation exposure to a high concentration of uranium hexafluoride has resulted in human fatalities, those deaths were associated with the generation of highly toxic hydrofluoric acid and uranyl fluoride rather than with uranium itself. Finely divided uranium metal presents a fire hazard because uranium is pyrophoricity, pyrophoric; small grains will ignite spontaneously in air at room temperature.
Uranium metal is commonly handled with gloves as a sufficient precaution. Uranium concentrate is handled and contained so as to ensure that people do not inhale or ingest it.
See also
* K-65 residues * List of countries by uranium production * List of countries by uranium reserves * List of uranium projects * Lists of nuclear disasters and radioactive incidents * Nuclear and radiation accidents and incidents * Nuclear engineering * Nuclear fuel cycle * Nuclear physics * Quintuple bond (earlier thought to be a phi bond), in the molecule U * Thorium fuel cycle * World Uranium HearingNotes
References
Sources cited
* *External links
Nuclear fuel data and analysis
from the U.S. Energy Information Administration
World Uranium deposit maps
*
Annotated bibliography for uranium from the Alsos Digital Library
NLM Hazardous Substances Databank – Uranium, Radioactive
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
Uranium
at ''The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham) {{Authority control Uranium, Chemical elements Actinides Nuclear fuels Nuclear materials Suspected male-mediated teratogens Manhattan Project Pyrophoric materials