|
Bromine
Bromine is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a similarly coloured vapour. Its properties are intermediate between those of chlorine and iodine. Isolated independently by two chemists, Carl Jacob Löwig (in 1825) and Antoine Jérôme Balard (in 1826), its name was derived , referring to its sharp and pungent smell. Elemental bromine is very reactive and thus does not occur as a free element in nature. Instead, it can be isolated from colourless soluble crystalline mineral halide Ionic salt, salts analogous to table salt, a property it shares with the other halogens. While it is rather rare in the Earth's crust, the high solubility of the bromide ion (Br) has caused its Bromine cycle, accumulation in the oceans. Commercially the element is easily extracted from brine evaporation ponds, mostly in the United States and Israel. The mass of bromine in the oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
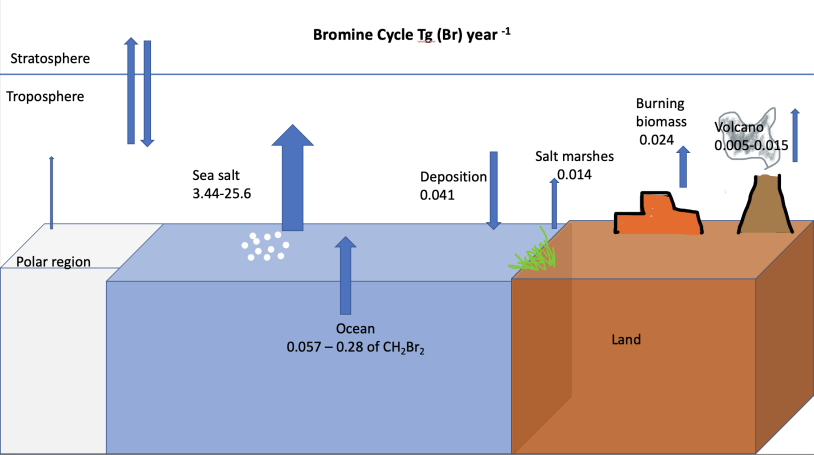
Bromine Cycle
The bromine cycle is a biogeochemical cycle of bromine through the atmosphere, biosphere, and hydrosphere. Bromine has natural and anthropogenic sources, impacting each sphere as bromine is stored, released, or taken up. Ozone depletion and health hazards to humans, animals, and plants are effects of bromine throughout the environment. Sources Natural sources Bromine is present naturally as bromide salts in evaporite deposits. Bromine is also present in soils and marine algae that synthesize organic bromine compounds. Other natural sources of bromine come from polar ice and snow, salt lakes, and volcanoes. The primary natural source of bromine to the atmosphere is sea spray aerosols. Oceans contain small amounts of bromine due to waves perturbing gas bubbles containing bromine, as well as marine biota producing bromine containing compounds. The lifetime of bromine from sea spray aerosols is determined by the time it takes for photolysis to release bromine from sea spray aer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromide
A bromide ion is the negatively charged form (Br−) of the element bromine, a member of the halogens group on the periodic table. Most bromides are colorless. Bromides have many practical roles, being found in anticonvulsants, flame-retardant materials, and cell stains. Although uncommon, chronic toxicity from bromide can result in bromism, a syndrome with multiple neurological symptoms. Bromide toxicity can also cause a type of skin eruption, see potassium bromide. The bromide ion has an ionic radius of 196 pm. Natural occurrence Bromide is present in typical seawater (35 PSU) with a concentration of around 65 mg/L, which is about 0.2% of all dissolved salts. Seafood and deep sea plants generally have higher levels than land-derived foods. Bromargyrite—natural, crystalline silver bromide—is the most common bromide mineral known but is still very rare. In addition to silver, bromine is also in minerals combined with mercury and copper. Formation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halogen
The halogens () are a group in the periodic table consisting of six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and the radioactive elements astatine (At) and tennessine (Ts), though some authors would exclude tennessine as its chemistry is unknown and is theoretically expected to be more like that of gallium. In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, this group is known as group 17. The word "halogen" means "salt former" or "salt maker". When halogens react with metals, they produce a wide range of salts, including calcium fluoride, sodium chloride (common table salt), silver bromide and potassium iodide. The group of halogens is the only periodic table group that contains elements in three of the main states of matter at standard temperature and pressure, though not far above room temperature the same becomes true of groups 1 and 15, assuming white phosphorus is taken as the standard state.This could also be the case for group 12, al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organobromine Compound
Organobromine chemistry is the study of the synthesis and properties of organobromine compounds, also called organobromides, which are organic compounds that contain carbon bonded to bromine. The most pervasive is the naturally produced bromomethane. One prominent application of synthetic organobromine compounds is the use of polybrominated diphenyl ethers as fire-retardants, and in fact fire-retardant manufacture is currently the major industrial use of the element bromine. A variety of minor organobromine compounds are found in nature, but none are biosynthesized or required by mammals. Organobromine compounds have fallen under increased scrutiny for their environmental impact. General properties Most organobromine compounds, like most organohalide compounds, are relatively nonpolar. Bromine is more electronegative than carbon (2.9 vs 2.5). Consequently, the carbon in a carbon–bromine bond is electrophilic, i.e. alkyl bromides are alkylating agents. Carbon–haloge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromomethane
Bromomethane, commonly known as methyl bromide, is an organobromine compound with formula C H3 Br. This colorless, odorless, nonflammable gas is produced both industrially and biologically. It is a recognized ozone-depleting chemical. According to the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report, it has a global warming potential of 2. The compound was used extensively as a pesticide until being phased out by most countries in the early 2000s. From a chemistry perspective, it is one of the halomethanes. Occurrence and manufacture Marine organisms are estimated to produce 56,000 tonnes annually. It is also produced in small quantities by certain terrestrial plants, such as members of the family Brassicaceae. In 2009, an estimated 24,000 tonnes of methyl bromide were produced. Its production was curtailed by the Montreal Protocol, such that in 1983, production was nearly twice that of 2009 levels. It is manufactured by treating methanol with bromine in the presence of sulfur or hydrogen sulf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antoine Jérôme Balard
Antoine Jérôme Balard (; 30 September 1802 – 30 April 1876) was a French chemist and one of the discoverers of bromine. Career Born at Montpellier, France, on 30 September 1802, he started as an apothecary ''Apothecary'' () is an Early Modern English, archaic English term for a medicine, medical professional who formulates and dispenses ''materia medica'' (medicine) to physicians, surgeons and patients. The modern terms ''pharmacist'' and, in Brit ..., but taking up teaching he acted as chemical assistant at the faculty of sciences of his native town, and then became professor of chemistry at the royal college and school of pharmacy and at the faculty of sciences. In 1826 he discovered in seawater a substance which he recognized as a previously unknown element and named it bromine. It had been independently prepared by Carl Jacob Löwig the previous year and the two are both regarded as having discovered the element. This achievement brought him the reputation that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromism
Bromism is the syndrome which results from the long-term consumption of bromine, usually through bromine-based sedatives such as potassium bromide and lithium bromide. Bromism was once a very common disorder, being responsible for 5 to 10% of psychiatric hospital admissions, but is now uncommon since bromide was withdrawn from clinical use in many countries and was severely restricted in others. Presentation Neurological and psychiatric :Neurological and psychiatric symptoms are widely variable. Common symptoms may include restlessness, irritability, ataxia, confusion, hallucinations, psychosis, weakness, stupor, and, in severe cases, coma. Gastrointestinal :Gastrointestinal effects include nausea and vomiting as acute adverse effects. Chronic exposure may lead to anorexia or constipation. Dermatological :Dermatological effects include cherry angiomas, acneiform, and pustular and erythematous rashes. Cause High levels of bromide chronically impair the membrane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Symbol
Chemical symbols are the abbreviations used in chemistry, mainly for chemical elements; but also for functional groups, chemical compounds, and other entities. Element symbols for chemical elements, also known as atomic symbols, normally consist of one or two letters from the Latin alphabet and are written with the first letter capitalised. History Earlier symbols for chemical elements stem from classical Latin and Greek language, Greek words. For some elements, this is because the material was known in ancient times, while for others, the name is a more recent invention. For example, Pb is the symbol for lead (''plumbum'' in Latin); Hg is the symbol for mercury (element), mercury (''hydrargyrum'' in Greek); and He is the symbol for helium (a Neo-Latin name) because helium was not known in ancient Roman times. Some symbols come from other sources, like W for tungsten (''Wolfram'' in German) which was not known in Roman times. A three-letter Systematic element name, temporary sym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ozone Depletion
Ozone depletion consists of two related events observed since the late 1970s: a lowered total amount of ozone in Earth, Earth's upper atmosphere, and a much larger springtime decrease in stratospheric ozone (the ozone layer) around Earth's polar regions. The latter phenomenon is referred to as the #Ozone hole and its causes, ozone hole. There are also springtime polar tropospheric ozone depletion events in addition to these stratospheric events. The main causes of ozone depletion and the ozone hole are manufactured chemicals, especially manufactured halocarbon refrigerants, solvents, propellants, and foam-blowing agents (chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), HCFCs, Haloalkanes, halons), referred to as ''ozone-depleting substances'' (ODS). These compounds are transported into the stratosphere by Turbulence, turbulent mixing after being emitted from the surface, mixing much faster than the molecules can settle. Once in the stratosphere, they release atoms from the halogen group through photod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Jacob Löwig
Carl Jacob Löwig (17 March 1803 – 27 March 1890) was a German chemist and discovered bromine independently of Antoine Jérôme Balard. He received his PhD at the University of Heidelberg for his work with Leopold Gmelin. During his research on mineral salts he discovered bromine in 1825, as a brown gas evolving after the salt was treated with chlorine.Carl Löwig, ''Das Brom und seine chemischen Verhältnisse'' (Bromine and its chemical relationships) (Heidelberg: Carl Winter, 1829). After working at the University of Heidelberg and the University of Zurich The University of Zurich (UZH, ) is a public university, public research university in Zurich, Switzerland. It is the largest university in Switzerland, with its 28,000 enrolled students. It was founded in 1833 from the existing colleges of the ... he became the successor to Robert Wilhelm Bunsen at the University of Breslau. He worked and lived in Breslau until his death in 1890. References * 19th-century G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for approximately 50% of all pesticide use globally. Most pesticides are used as plant protection products (also known as crop protection products), which in general protect plants from weeds, fungi, or insects. In general, a pesticide is a chemical or biological agent (such as a virus, bacterium, or fungus) that deters, incapacitates, kills, or otherwise discourages pests. Target pests can include insects, plant pathogens, weeds, molluscs, birds, mammals, fish, nematodes (roundworms), and microbes that destroy property, cause nuisance, spread disease, or are disease vectors. Along with these benefits, pesticides also have drawbacks, such as potential toxicity to humans and other species. Definition The word pesticide derives from the Latin ''pestis'' (plagu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosphere is the outer region of a star, which includes the layers above the opaque photosphere; stars of low temperature might have outer atmospheres containing compound molecules. The atmosphere of Earth is composed of nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), argon (0.9%), carbon dioxide (0.04%) and trace gases. Most organisms use oxygen for respiration; lightning and bacteria perform nitrogen fixation which produces ammonia that is used to make nucleotides and amino acids; plants, algae, and cyanobacteria use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. The layered composition of the atmosphere minimises the harmful effects of sunlight, ultraviolet radiation, solar wind, and cosmic rays and thus protects the organisms from genetic damage. The curr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |