|
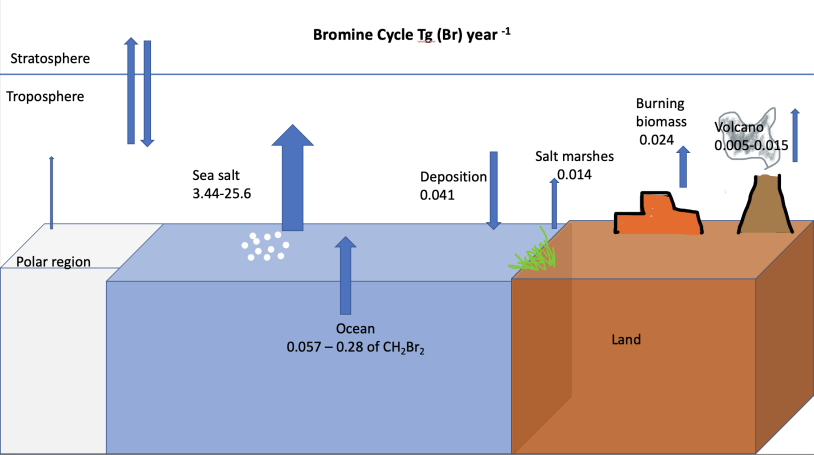
Bromine Cycle
The bromine cycle is a biogeochemical cycle of bromine through the atmosphere, biosphere, and hydrosphere. Sources Natural sources Bromine is present naturally as bromide salts in evaporite deposits. Bromine is also present in soils and in marine algae that synthesize organic bromine compounds. Other natural sources of bromine come from polar regions, salt lakes, and volcanoes. The primary natural source of bromine to the atmosphere is sea spray aerosols. Smaller fluxes originate from volcanic emissions and biomass burning. The primary atmospheric sinks are sea spray deposition and photochemical reactions, which release gaseous bromine. Anthropogenic sources Bromine is used in flame retardants, pesticides, lighter fuel, antiknocking agents, and for water purification. The organic form of this element is used as flame retardants commercially and in pesticides. These chemicals have led to an increase in the depletion of the stratospheric ozone layer. Some countries use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromine Biogeochemical Cycle
Bromine is a chemical element with the symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is the third-lightest element in group 17 of the periodic table ( halogens) and is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a similarly coloured vapour. Its properties are intermediate between those of chlorine and iodine. Isolated independently by two chemists, Carl Jacob Löwig (in 1825) and Antoine Jérôme Balard (in 1826), its name was derived from the Ancient Greek (bromos) meaning "stench", referring to its sharp and pungent smell. Elemental bromine is very reactive and thus does not occur as a native element in nature but it occurs in colourless soluble crystalline mineral halide salts, analogous to table salt. In fact, bromine and all the halogens are so reactive that they form bonds in pairs—never in single atoms. While it is rather rare in the Earth's crust, the high solubility of the bromide ion (Br) has caused its accumulation in the oceans. Commercial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratosphere
The stratosphere () is the second layer of the atmosphere of the Earth, located above the troposphere and below the mesosphere. The stratosphere is an atmospheric layer composed of stratified temperature layers, with the warm layers of air high in the sky and the cool layers of air in the low sky, close to the planetary surface of the Earth. The increase of temperature with altitude is a result of the absorption of the Sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation by the ozone layer. The temperature inversion is in contrast to the troposphere, near the Earth's surface, where temperature decreases with altitude. Between the troposphere and stratosphere is the tropopause border that demarcates the beginning of the temperature inversion. Near the equator, the lower edge of the stratosphere is as high as , at midlatitudes around , and at the poles about . Temperatures range from an average of near the tropopause to an average of near the mesosphere. Stratospheric temperatures also var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropospheric
The troposphere is the first and lowest layer of the atmosphere of the Earth, and contains 75% of the total mass of the planetary atmosphere, 99% of the total mass of water vapour and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From the planetary surface of the Earth, the average height of the troposphere is in the tropics; in the middle latitudes; and in the high latitudes of the polar regions in winter; thus the average height of the troposphere is . The term ''troposphere'' derives from the Greek words ''tropos'' (rotating) and '' sphaira'' (sphere) indicating that rotational turbulence mixes the layers of air and so determines the structure and the phenomena of the troposphere. The rotational friction of the troposphere against the planetary surface affects the flow of the air, and so forms the planetary boundary layer (PBL) that varies in height from hundreds of meters up to . The measures of the PBL vary according to the latitude, the landform, and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dead Sea
The Dead Sea ( he, יַם הַמֶּלַח, ''Yam hamMelaḥ''; ar, اَلْبَحْرُ الْمَيْتُ, ''Āl-Baḥrū l-Maytū''), also known by other names, is a salt lake bordered by Jordan to the east and Israel and the West Bank to the west. It lies in the Jordan Rift Valley, and its main tributary is the Jordan River. As of 2019, the lake's surface is below sea level, making its shores the lowest land-based elevation on Earth. It is deep, the deepest hypersaline lake in the world. With a salinity of 342 g/kg, or 34.2% (in 2011), it is one of the world's saltiest bodies of water – 9.6 times as salty as the ocean – and has a density of 1.24 kg/litre, which makes swimming similar to floating. This salinity makes for a harsh environment in which plants and animals cannot flourish, hence its name. The Dead Sea's main, northern basin is long and wide at its widest point. The Dead Sea has attracted visitors from around the Mediterranean Basin for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
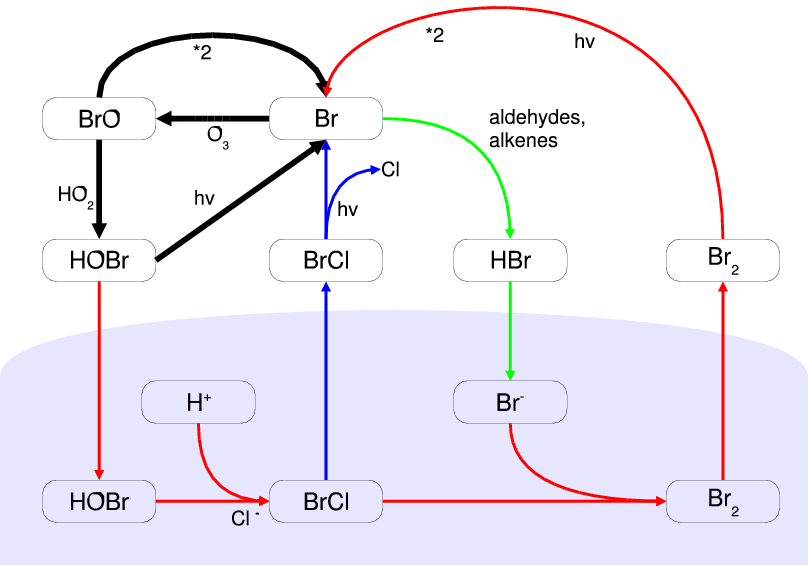
Bromine Explosion
During springtime in the polar regions of Earth, unique photochemistry converts inert halide salt ions (e.g. Br−) into reactive halogen species (e.g. Br atoms and BrO) that episodically deplete ozone in the atmospheric boundary layer to near zero levels. Since their discovery in the late 1980s, research on these ozone depletion events (ODEs) has shown the central role of bromine photochemistry. Due to the autocatalytic nature of the reaction mechanism, it has been called bromine explosion. It is still not fully understood how salts are transported from the ocean and oxidized to become reactive halogen species in the air. Other halogens ( chlorine and iodine) are also activated through mechanisms coupled to bromine chemistry. The main consequence of halogen activation is chemical destruction of ozone, which removes the primary precursor of atmospheric oxidation, and generation of reactive halogen atoms/oxides that become the primary oxidizing species. The different reactiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autocatalysis
A single chemical reaction is said to be autocatalytic if one of the reaction products is also a catalyst for the same or a coupled reaction.Steinfeld J.I., Francisco J.S. and Hase W.L. ''Chemical Kinetics and Dynamics'' (2nd ed., Prentice-Hall 1999) p.151-2 Such a reaction is called an autocatalytic reaction. A ''set'' of chemical reactions can be said to be "collectively autocatalytic" if a number of those reactions produce, as reaction products, catalysts for enough of the other reactions that the entire set of chemical reactions is self-sustaining given an input of energy and food molecules (see autocatalytic set). Chemical reactions A chemical reaction of two reactants and two products can be written as : \alpha A + \beta B \rightleftharpoons \sigma S + \tau T where the Greek letters are stoichiometric coefficients and the capital Latin letters represent chemical species. The chemical reaction proceeds in both the forward and reverse direction. This equation is easily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boundary Layer
In physics and fluid mechanics, a boundary layer is the thin layer of fluid in the immediate vicinity of a bounding surface formed by the fluid flowing along the surface. The fluid's interaction with the wall induces a no-slip boundary condition (zero velocity at the wall). The flow velocity then monotonically increases above the surface until it returns to the bulk flow velocity. The thin layer consisting of fluid whose velocity has not yet returned to the bulk flow velocity is called the velocity boundary layer. The air next to a human is heated resulting in gravity-induced convective airflow, airflow which results in both a velocity and thermal boundary layer. A breeze disrupts the boundary layer, and hair and clothing protect it, making the human feel cooler or warmer. On an aircraft wing, the velocity boundary layer is the part of the flow close to the wing, where viscous forces distort the surrounding non-viscous flow. In the Earth's atmosphere, the atmospheric b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dibromomethane
Preparation Dibromomethane is prepared commercially from dichloromethane via bromochloromethane: :6 CH2Cl2 + 3 Br2 + 2 Al → 6 CH2BrCl + 2 AlCl3 :CH2Cl2 + HBr → CH2BrCl + HCl The latter route requires aluminium trichloride as a catalyst. The bromochloromethane product from either reaction can further react in a similar manner: :6 CH2BrCl + 3 Br2 + 2 Al → 6 CH2Br2 + 2 AlCl3 :CH2BrCl + HBr → CH2Br2 + HCl In the laboratory, it is prepared from bromoform: :CHBr3 + Na3AsO3 + NaOH → CH2Br2 + Na3AsO4 + NaBr using sodium arsenite and sodium hydroxide. Another way is to prepare it from diiodomethane and bromine. Uses Dibromomethane is used as a solvent, gauge fluid, and in organic synthesis (often as 1H-NMR internal standard). It is a convenient agent for converting catechols to their methylenedioxy derivatives. Natural occurrence It is naturally produced by marine algae and liberated to the oceans. Releasing on soil causes it to evaporate and leach into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromomethane
Bromomethane, commonly known as methyl bromide, is an organobromine compound with formula C H3 Br. This colorless, odorless, nonflammable gas is produced both industrially and biologically. It has a tetrahedral shape and it is a recognized ozone-depleting chemical. It was used extensively as a pesticide until being phased out by most countries in the early 2000s. Occurrence and manufacture Bromomethane originates from both natural and human sources. In the ocean, marine organisms are estimated to produce 56,000 tonnes annually. It is also produced in small quantities by certain terrestrial plants, such as members of the family Brassicaceae. It is manufactured for agricultural and industrial use by treating methanol with bromine in the presence of sulfur or hydrogen sulfide: :6 CH3OH + 3 Br2 + S → 6 CH3Br + 2 H2O + H2SO4 Uses In 1999, an estimated 71,500 tonnes of synthetic methyl bromide were used annually worldwide. 97% of this estimate was used for fumigation purposes, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooling Tower
A cooling tower is a device that rejects waste heat to the atmosphere through the cooling of a coolant stream, usually a water stream to a lower temperature. Cooling towers may either use the evaporation of water to remove process heat and cool the working fluid to near the wet-bulb air temperature or, in the case of ''dry cooling towers'', rely solely on air to cool the working fluid to near the dry-bulb air temperature using radiators. Common applications include cooling the circulating water used in oil refineries, petrochemical and other chemical plants, thermal power stations, nuclear power stations and HVAC systems for cooling buildings. The classification is based on the type of air induction into the tower: the main types of cooling towers are natural draft and induced draft cooling towers. Cooling towers vary in size from small roof-top units to very large hyperboloid structures (as in the adjacent image) that can be up to tall and in diameter, or recta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
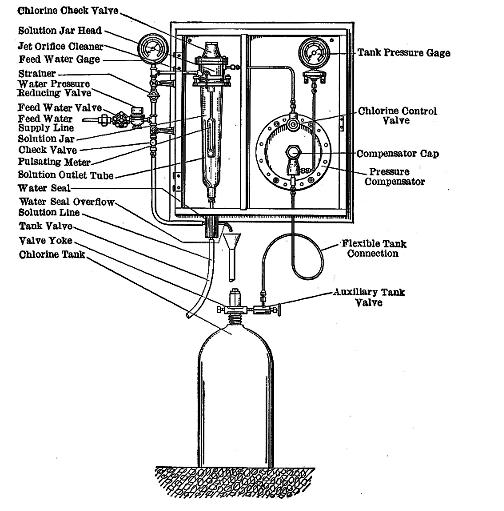
Water Chlorination
Water chlorination is the process of adding chlorine or chlorine compounds such as sodium hypochlorite to water. This method is used to kill bacteria, viruses and other microbes in water. In particular, chlorination is used to prevent the spread of waterborne diseases such as cholera, dysentery, and typhoid. History In a paper published in 1894, it was formally proposed to add chlorine to water to render it "germ-free". Two other authorities endorsed this proposal and published it in many other papers in 1895. Early attempts at implementing water chlorination at a water treatment plant were made in 1893 in Hamburg, Germany. In 1897 the town of Maidstone, England was the first to have its entire water supply treated with chlorine. Permanent water chlorination began in 1905, when a faulty slow sand filter and a contaminated water supply caused a serious typhoid fever epidemic in Lincoln, England. Alexander Cruickshank Houston used chlorination of the water to stop the epidem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ozone Depletion
Ozone depletion consists of two related events observed since the late 1970s: a steady lowering of about four percent in the total amount of ozone in Earth's atmosphere, and a much larger springtime decrease in stratospheric ozone (the ozone layer) around Earth's polar regions. The latter phenomenon is referred to as the ozone hole. There are also springtime polar tropospheric ozone depletion events in addition to these stratospheric events. The main causes of ozone depletion and the ozone hole are manufactured chemicals, especially manufactured halocarbon refrigerants, solvents, propellants, and foam- blowing agents ( chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), HCFCs, halons), referred to as ozone-depleting substances (ODS). These compounds are transported into the stratosphere by turbulent mixing after being emitted from the surface, mixing much faster than the molecules can settle. Once in the stratosphere, they release atoms from the halogen group through photodissociation, which catal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |