|
Borehole Mining
Borehole Mining (BHM) is a remotely operated method of extraction (mining) of mineral resources through boreholes based on in-situ conversion of ores into a mobile form (slurry) using high-pressure water jetting (hydraulicking). This process is carried out from a land surface, open pit floor, underground mine or floating vessel through pre-drilled boreholes. History Based on the US Patent database, the method history can be traced back to the beginning of the 20th century (1906). The most advanced BHM tool design was patented in 1926. With a few improvements, this design concept remains a base for the modern BHM tools and technologies. In the US, the major R&D were conducted by USBM in the 1970 and 1980s. Borehole mining of Uranium in Kazakhstan remains the most advanced BHM project in the world.G. Abramov, Geotechnology - A Solution For Unconventional Uranium, IJSRED Volume 3 Issue 3 June 2020 The process # A borehole is drilled to a required depth; # A casing column is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Borehole Miming Tool And Technology Principle Schematic
A borehole is a narrow shaft bored in the ground, either vertically or horizontally. A borehole may be constructed for many different purposes, including the extraction of water ( drilled water well and tube well), other liquids (such as petroleum), or gases (such as natural gas). It may also be part of a geotechnical investigation, environmental site assessment, mineral exploration, temperature measurement, as a pilot hole for installing piers or underground utilities, for geothermal installations, or for underground storage of unwanted substances, e.g. in carbon capture and storage. Importance Engineers and environmental consultants use the term ''borehole'' to collectively describe all of the various types of holes drilled as part of a geotechnical investigation or environmental site assessment (a so-called Phase II ESA). This includes holes advanced to collect soil samples, water samples or rock cores, to advance ''in situ'' sampling equipment, or to install monitoring w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hydraulic Mining
Hydraulic mining is a form of mining that uses high-pressure jets of water to dislodge rock material or move sediment.Paul W. Thrush, ''A Dictionary of Mining, Mineral, and Related Terms'', US Bureau of Mines, 1968, p.560. In the placer mining of gold or tin, the resulting water-sediment slurry is directed through Sluice boxes to remove the gold or tin. It is also used in mining kaolin and coal. Hydraulic mining developed from ancient Roman techniques that used water to excavate soft underground deposits. Its modern form, using pressurized water Jet (fluid), jets produced by a nozzle called a "monitor", came about in the 1850s during the California Gold Rush in the United States. Though successful in extracting gold-rich minerals, the widespread use of the process resulted in extensive environmental damage, such as increased flooding and erosion, and sediment blocking waterways and covering farm fields. These problems led to its legal regulation. Hydraulic mining has been used in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
United States Bureau Of Mines
The United States Bureau of Mines (USBM) was the primary Federal government of the United States, United States government agency in the 20th century that conducted scientific research and disseminated information on the extraction, processing, use, and conservation of mineral natural resource, resources. The Bureau was abolished in 1996. History The U.S. Bureau of Mines was established in the United States Department of the Interior, U.S. States Department of the Interior on May 16, 1910, pursuant to the Organic Act (Public Law 179), to deal with a wave of catastrophic Mining, mine disasters. The Bureau's mission was gradually expanded to include: * The conduct of research to enhance the safety, health, and environmental impact of mining and processing of minerals and materials. * The collection, analysis, and dissemination of information about mining and processing of more than 100 mineral commodities across the Nation and in more than 185 countries around the world. * Analy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Uranium
Uranium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium radioactive decay, radioactively decays, usually by emitting an alpha particle. The half-life of this decay varies between 159,200 and 4.5 billion years for different isotopes of uranium, isotopes, making them useful for dating the age of the Earth. The most common isotopes in natural uranium are uranium-238 (which has 146 neutrons and accounts for over 99% of uranium on Earth) and uranium-235 (which has 143 neutrons). Uranium has the highest atomic weight of the primordial nuclide, primordially occurring elements. Its density is about 70% higher than that of lead and slightly lower than that of gold or tungsten. It occurs naturally in low concentrations of a few Parts-per notation#Parts-per expressions, parts per million in soil, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Borehole
A borehole is a narrow shaft bored in the ground, either vertically or horizontally. A borehole may be constructed for many different purposes, including the extraction of water ( drilled water well and tube well), other liquids (such as petroleum), or gases (such as natural gas). It may also be part of a geotechnical investigation, environmental site assessment, mineral exploration, temperature measurement, as a pilot hole for installing piers or underground utilities, for geothermal installations, or for underground storage of unwanted substances, e.g. in carbon capture and storage. Importance Engineers and environmental consultants use the term ''borehole'' to collectively describe all of the various types of holes drilled as part of a geotechnical investigation or environmental site assessment (a so-called Phase II ESA). This includes holes advanced to collect soil samples, water samples or rock cores, to advance ''in situ'' sampling equipment, or to install monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Offshore BHM
Offshore may refer to: Science and technology * Offshore (hydrocarbons) * Offshore construction, construction out at sea * Offshore drilling, discovery and development of oil and gas resources which lie underwater through drilling a well * Offshore hosting, server * Offshore wind power, wind power in a body of water * Offshore geotechnical engineering * Offshore aquaculture Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Offshore'' (novel), a 1979 British novel by Penelope Fitzgerald *The Offshore, an elite enclave of the chosen, in '' 3%'' * ''Offshore'' (album), a 2006 album by Indiana-based post-rock band Early Day Miners * "Offshore" (song), a 1996 song by British electronic dance music act Chicane Finance and law * Offshore bank, relates to the banking industry in offshore centers * Offshore company * Offshore financial centre, jurisdictions which transact financial business with non-residents * Offshore fund, collective investment in offshore centers * Offshore investment, re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
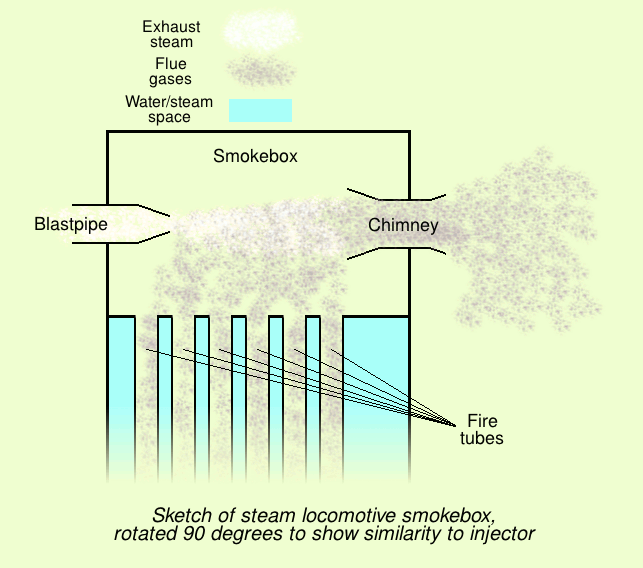
Injector
An injector is a system of ducting and nozzles used to direct the flow of a high-pressure fluid in such a way that a lower pressure fluid is Entrainment (hydrodynamics), entrained in the jet and carried through a duct to a region of higher pressure. It is a fluid-dynamic pump with no moving parts except a valve to control inlet flow. Depending on the application, an injector can also take the form of an ''eductor-jet pump'', a ''water eductor'' or an ''aspirator''. An ''Vacuum ejector, ejector'' operates on similar principles to create a vacuum feed connection for braking systems etc. The motive fluid may be a liquid, steam or any other gas. The entrained suction fluid may be a gas, a liquid, a slurry, or a dust-laden gas stream. Steam injector The steam injector is a common device used for delivering water to steam boilers, especially in steam locomotives. It is a typical application of the injector principle used to deliver cold boiler feedwater, water to a boiler against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Airlift Pump
An airlift pump is a pump that has low suction and moderate discharge of liquid and entrained solids. The pump injects compressed air at the bottom of the discharge pipe which is immersed in the liquid. The compressed air mixes with the liquid causing the air-water mixture to be less dense than the rest of the liquid around it and therefore is displaced upwards through the discharge pipe by the surrounding liquid of higher density. Solids may be entrained in the flow and if small enough to fit through the pipe, will be discharged with the rest of the flow at a shallower depth or above the surface. Airlift pumps are widely used in aquaculture to pump, circulate and aerate water in closed, recirculating systems and ponds. Other applications include dredging, underwater archaeology, salvage operations and collection of Biological specimen, scientific specimens. Principle The only energy required is provided by compressed air. This air is usually compressed by a gas compressor, compr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
1K PIC-2
1K or 1-K may refer to: *Astra 1K satellite *Astra 1KR satellite *1K ZX Chess computer program * Southern Cross Distribution (IATA code) * Sutra (air company) (IATA code) *BMP-1K, see BMP-1 *BRM-1K, see BMP-1 variants *HH-1K, see Bell UH-1 Iroquois variants *XMODEM-1K, a model of XMODEM *YMODEM-1K, a model of YMODEM *GSXR 1K, or Suzuki GSX-R1000 *Typ 1K, a chassis code of Volkswagen Golf Mk5 *SSH 1K (WA), see Washington State Route 509 *Premier 1K, a membership level of United Airlines MileagePlus program *1k as one thousand See also *Kelvin *Kilobyte *K (other) *K1 (other) *IK (other) IK or Ik may refer to: Businesses and organizations * IK Investment Partners, a European private equity firm * Imair Airlines (IATA code IK) * Iparretarrak, a Basque nationalist organization Languages * Ik language (ISO 639 alpha-3 ikx), spoken ... * lK (other) * 1000 (other) * * {{Letter-NumberCombDisambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mining Techniques
Mining is the extraction of valuable geological materials and minerals from the surface of the Earth. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agricultural processes, or feasibly created artificially in a laboratory or factory. Ores recovered by mining include metals, coal, oil shale, gemstones, limestone, chalk, dimension stone, rock salt, potash, gravel, and clay. The ore must be a rock or mineral that contains valuable constituent, can be extracted or mined and sold for profit. Mining in a wider sense includes extraction of any non-renewable resource such as petroleum, natural gas, or even water. Modern mining processes involve prospecting for ore bodies, analysis of the profit potential of a proposed mine, extraction of the desired materials, and final reclamation or restoration of the land after the mine is closed. Mining materials are often obtained from ore bodies, lodes, veins, seams, reefs, or placer deposits. The exploitation of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Drilling Technology
Drilling is a cutting process where a drill bit is spun to cut a hole of circular cross-section in solid materials. The drill bit is usually a rotary cutting tool, often multi-point. The bit is pressed against the work-piece and rotated at rates from hundreds to thousands of revolutions per minute. This forces the cutting edge against the work-piece, cutting off chips (swarf) from the hole as it is drilled. In rock drilling, the hole is usually not made through a circular cutting motion, though the bit is usually rotated. Instead, the hole is usually made by hammering a drill bit into the hole with quickly repeated short movements. The hammering action can be performed from outside the hole ( top-hammer drill) or within the hole ( down-the-hole drill, DTH). Drills used for horizontal drilling are called drifter drills. In rare cases, specially-shaped bits are used to cut holes of non-circular cross-section; a square cross-section is possible. Process Drilled holes are c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |