Upper Limb on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The upper
 The shoulder girdle or pectoral girdle, composed of the
The shoulder girdle or pectoral girdle, composed of the
 The
The

 The arm proper (''brachium''), sometimes called the upper arm, the region between the shoulder and the elbow, is composed of the
The arm proper (''brachium''), sometimes called the upper arm, the region between the shoulder and the elbow, is composed of the
 The forearm (), composed of the
The forearm (), composed of the
 How muscles act on the wrist is complex to describe. The five muscles acting on the wrist directly —
How muscles act on the wrist is complex to describe. The five muscles acting on the wrist directly —
 The hand (), the
The hand (), the
 The motor and sensory supply of the upper limb is provided by the brachial plexus which is formed by the ventral rami of spinal nerves C5-T1. In the posterior triangle of the neck these rami form three trunks from which fibers enter the axilla region (armpit) to innervate the muscles of the anterior and posterior compartments of the limb. In the axilla, cords are formed to split into branches, including the five terminal branches listed below.
The muscles of the upper limb are innervated segmentally proximal to distal so that the proximal muscles are innervated by higher segments (C5–C6) and the distal muscles are innervated by lower segments (C8–T1).
Motor innervation of upper limb by the five terminal nerves of the
The motor and sensory supply of the upper limb is provided by the brachial plexus which is formed by the ventral rami of spinal nerves C5-T1. In the posterior triangle of the neck these rami form three trunks from which fibers enter the axilla region (armpit) to innervate the muscles of the anterior and posterior compartments of the limb. In the axilla, cords are formed to split into branches, including the five terminal branches listed below.
The muscles of the upper limb are innervated segmentally proximal to distal so that the proximal muscles are innervated by higher segments (C5–C6) and the distal muscles are innervated by lower segments (C8–T1).
Motor innervation of upper limb by the five terminal nerves of the
 Veins of the upper limb:
*
Veins of the upper limb:
*
 The skeletons of all
The skeletons of all
limb
Limb may refer to:
Science and technology
*Limb (anatomy), an appendage of a human or animal
*Limb, a large or main branch of a tree
*Limb, in astronomy, the curved edge of the apparent disk of a celestial body, e.g. lunar limb
*Limb, in botany, t ...
s or upper extremities are the forelimb
A forelimb or front limb is one of the paired articulated appendages ( limbs) attached on the cranial (anterior) end of a terrestrial tetrapod vertebrate's torso. With reference to quadrupeds, the term foreleg or front leg is often used inst ...
s of an upright-postured tetrapod
A tetrapod (; from Ancient Greek :wiktionary:τετρα-#Ancient Greek, τετρα- ''(tetra-)'' 'four' and :wiktionary:πούς#Ancient Greek, πούς ''(poús)'' 'foot') is any four-Limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animal of the clade Tetr ...
vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
, extending from the scapula
The scapula (: scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side ...
e and clavicle
The clavicle, collarbone, or keybone is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately long that serves as a strut between the scapula, shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on each side of the body. The clavic ...
s down to and including the digits, including all the musculature
Skeletal muscle (commonly referred to as muscle) is one of the three types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. They are part of the somatic nervous system, voluntary muscular system and typically are a ...
s and ligament
A ligament is a type of fibrous connective tissue in the body that connects bones to other bones. It also connects flight feathers to bones, in dinosaurs and birds. All 30,000 species of amniotes (land animals with internal bones) have liga ...
s involved with the shoulder
The human shoulder is made up of three bones: the clavicle (collarbone), the scapula (shoulder blade), and the humerus (upper arm bone) as well as associated muscles, ligaments and tendons.
The articulations between the bones of the shoulder m ...
, elbow
The elbow is the region between the upper arm and the forearm that surrounds the elbow joint. The elbow includes prominent landmarks such as the olecranon, the cubital fossa (also called the chelidon, or the elbow pit), and the lateral and t ...
, wrist
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carpal ...
and knuckle
The knuckles are the joints of the fingers. The word is cognate to similar words in other Germanic languages, such as the Dutch "knokkel" (knuckle) or German "Knöchel" (ankle), i.e., ''Knöchlein'', the diminutive of the German word for bone ( ...
joints. In human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
s, each upper limb is divided into the shoulder
The human shoulder is made up of three bones: the clavicle (collarbone), the scapula (shoulder blade), and the humerus (upper arm bone) as well as associated muscles, ligaments and tendons.
The articulations between the bones of the shoulder m ...
, arm
In human anatomy, the arm refers to the upper limb in common usage, although academically the term specifically means the upper arm between the glenohumeral joint (shoulder joint) and the elbow joint. The distal part of the upper limb between ...
, elbow
The elbow is the region between the upper arm and the forearm that surrounds the elbow joint. The elbow includes prominent landmarks such as the olecranon, the cubital fossa (also called the chelidon, or the elbow pit), and the lateral and t ...
, forearm
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, techn ...
, wrist
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carpal ...
and hand
A hand is a prehensile, multi-fingered appendage located at the end of the forearm or forelimb of primates such as humans, chimpanzees, monkeys, and lemurs. A few other vertebrates such as the Koala#Characteristics, koala (which has two thumb#O ...
, and is primarily used for climbing
Climbing is the activity of using one's hands, feet, or other parts of the body to ascend a steep topographical object that can range from the world's tallest mountains (e.g. the eight thousanders) to small boulders. Climbing is done for locom ...
, lifting and manipulating objects. In anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of morphology concerned with the study of the internal structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old scien ...
, just as arm
In human anatomy, the arm refers to the upper limb in common usage, although academically the term specifically means the upper arm between the glenohumeral joint (shoulder joint) and the elbow joint. The distal part of the upper limb between ...
refers to the upper arm
The upper limbs or upper extremities are the forelimbs of an upright-postured tetrapod vertebrate, extending from the scapulae and clavicles down to and including the digits, including all the musculatures and ligaments involved with the should ...
, leg
A leg is a weight-bearing and locomotive anatomical structure, usually having a columnar shape. During locomotion, legs function as "extensible struts". The combination of movements at all joints can be modeled as a single, linear element cap ...
refers to the lower leg
The leg is the entire lower limb (anatomy), limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or Gluteal muscles, buttock region. The major bones of the leg are the femur (thigh bone), tibia (shin bone), and adjacent f ...
.
Definition
In formal usage, the term "arm" only refers to the structures from the shoulder to the elbow, explicitly excluding theforearm
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, techn ...
, and thus "upper limb" and "arm" are not synonymous. However, in casual usage, the terms are often used interchangeably. The term "upper arm" is redundant in anatomy, but in informal usage is used to distinguish between the two terms.
Structure
In thehuman body
The human body is the entire structure of a Human, human being. It is composed of many different types of Cell (biology), cells that together create Tissue (biology), tissues and subsequently Organ (biology), organs and then Organ system, org ...
, the muscles of the upper limb can be classified by origin, topography, function, or innervation. While a grouping by innervation reveals embryological
Embryology (from Greek ἔμβρυον, ''embryon'', "the unborn, embryo"; and -λογία, ''-logia'') is the branch of animal biology that studies the prenatal development of gametes (sex cells), fertilization, and development of embryos an ...
and phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical dat ...
origins, the functional-topographical classification below reflects the similarity in action between muscles (with the exception of the shoulder girdle, where muscles with similar action can vary considerably in their location and orientation.
Musculoskeletal system
Shoulder girdle
clavicle
The clavicle, collarbone, or keybone is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately long that serves as a strut between the scapula, shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on each side of the body. The clavic ...
and the scapula
The scapula (: scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side ...
, connects the upper limb to the axial skeleton
The axial skeleton is the core part of the endoskeleton made of the bones of the head and trunk of vertebrates. In the human skeleton, it consists of 80 bones and is composed of the skull (28 bones, including the cranium, mandible and the midd ...
through the sternoclavicular joint
The sternoclavicular joint or sternoclavicular articulation is a Synovial joint, synovial Saddle joint, saddle joint between the sternum#Manubrium, manubrium of the sternum, and the clavicle bone, clavicle, and the first costal cartilage. The joi ...
(the only joint in the upper limb that directly articulates with the trunk), a ball and socket joint supported by the subclavius muscle
The subclavius is a small triangular muscle, placed between the clavicle and the first rib. Along with the pectoralis major and pectoralis minor muscles, the subclavius muscle makes up the anterior axioappendicular muscles, also known as anteri ...
which acts as a dynamic ligament
A ligament is a type of fibrous connective tissue in the body that connects bones to other bones. It also connects flight feathers to bones, in dinosaurs and birds. All 30,000 species of amniotes (land animals with internal bones) have liga ...
. While this muscle prevents dislocation in the joint, strong forces tend to break the clavicle instead. The acromioclavicular joint
The acromioclavicular joint, or AC joint, is a joint at the top of the shoulder. It is the junction between the acromion (part of the scapula that forms the highest point of the shoulder) and the clavicle. It is a Plane joint, plane synovial joint ...
, the joint between the acromion
In human anatomy, the acromion (from Greek: ''akros'', "highest", ''ōmos'', "shoulder", : acromia) or summit of the shoulder is a bony process on the scapula (shoulder blade). Together with the coracoid process, it extends laterally over the sh ...
process on the scapula and the clavicle, is similarly strengthened by strong ligaments, especially the coracoclavicular ligament
The coracoclavicular ligament is a ligament of the shoulder. It connects the clavicle to the coracoid process of the scapula.
Structure
The coracoclavicular ligament connects the clavicle to the coracoid process of the scapula. It is not part o ...
which prevents excessive lateral and medial movements. Between them these two joints allow a wide range of movements for the shoulder girdle, much because of the lack of a bone-to-bone contact between the scapula and the axial skeleton. The pelvic girdle
The hip bone (os coxae, innominate bone, pelvic bone or coxal bone) is a large flat bone, constricted in the center and expanded above and below. In some vertebrates (including humans before puberty) it is composed of three parts: the Ilium (bone) ...
is, in contrast, firmly fixed to the axial skeleton, which increases stability and load-bearing capabilities.
The mobility of the shoulder girdle is supported by a large number of muscles. The most important of these are muscular sheets rather than fusiform or strap-shaped muscles and they thus never act in isolation but with some fibres acting in coordination with fibres in other muscles.
; Muscles: of shoulder girdle excluding the glenohumeral joint
:; Migrated from head: Trapezius
The trapezius is a large paired trapezoid-shaped surface muscle that extends longitudinally from the occipital bone to the lower thoracic vertebrae of the human spine, spine and laterally to the spine of the scapula. It moves the scapula and ...
, sternocleidomastoideus
The sternocleidomastoid muscle is one of the largest and most superficial cervical muscles. The primary actions of the muscle are rotation of the head to the opposite side and flexion of the neck. The sternocleidomastoid is innervated by the acces ...
, omohyoideus
The omohyoid muscle is a muscle in the neck. It is one of the infrahyoid muscles. It consists of two bellies separated by an intermediate tendon. Its inferior belly is attached to the scapula; its superior belly is attached to the hyoid bone. Its i ...
:; Posterior: Rhomboideus major
The rhomboid major is a skeletal muscle of the back that connects the scapula with the vertebrae of the spinal column. It originates from the spinous processes of the thoracic vertebrae T2–T5 and supraspinous ligament; it inserts onto the lower ...
, rhomboideus minor, levator scapulae
The levator scapulae is a slender skeletal muscle situated at the back and side of the neck. It originates from the transverse processes of the four uppermost cervical vertebrae; it inserts onto the upper portion of the medial border of the scapu ...
:; Anterior: Subclavius
The subclavius is a small triangular muscle, placed between the clavicle and the first rib. Along with the pectoralis major and pectoralis minor muscles, the subclavius muscle makes up the anterior axioappendicular muscles, also known as anteri ...
, pectoralis minor
Pectoralis minor muscle () is a thin, triangular muscle, situated at the upper part of the chest, beneath the pectoralis major in the human body. It arises from ribs III-V; it inserts onto the coracoid process of the scapula. It is innervated by ...
, serratus anterior
The serratus anterior is a muscle of the chest. It originates at the side of the chest from the upper 8 or 9 ribs; it inserts along the entire length of the anterior aspect of the medial border of the scapula. It is innervated by the long thor ...
Shoulder joint
 The
The glenohumeral joint
The shoulder joint (or glenohumeral joint from Greek ''glene'', eyeball, + -''oid'', 'form of', + Latin ''humerus'', shoulder) is structurally classified as a synovial ball-and-socket joint and functionally as a diarthrosis and multiaxial joint ...
(colloquially called the shoulder joint) is the highly mobile ball and socket joint between the glenoid cavity
The glenoid fossa of the scapula or the glenoid cavity is a bone part of the shoulder. The word ''glenoid'' is pronounced or (both are common) and is from , "socket", reflecting the shoulder joint's ball-and-socket form. It is a shallow, pyri ...
of the scapula and the head of the humerus. Lacking the passive stabilisation offered by ligaments in other joints, the glenohumeral joint is actively stabilised by the rotator cuff
The rotator cuff (SITS muscles) is a group of muscles and their tendons that act to stabilize the human shoulder and allow for its extensive range of motion. Of the seven scapulohumeral muscles, four make up the rotator cuff. The four muscles a ...
, a group of short muscles stretching from the scapula to the humerus. Little inferior support is available to the joint and dislocation of the shoulder almost exclusively occurs in this direction.
The large muscles acting at this joint perform multiple actions and seemingly simple movements are often the result of composite antagonist and protagonist actions from several muscles. For example, pectoralis major is the most important arm flexor and latissimus dorsi
The latissimus dorsi () is a large, flat muscle on the back that stretches to the sides, behind the arm, and is partly covered by the trapezius on the back near the midline.
The word latissimus dorsi (plural: ''latissimi dorsi'') comes from L ...
the most important extensor at the glenohumeral joint, but, acting together, these two muscles cancel each other's action leaving only their combined medial rotation component. On the other hand, to achieve pure flexion at the joint the deltoid Deltoid (delta-shaped) can refer to:
* The deltoid muscle, a muscle in the shoulder
* Kite (geometry), also known as a deltoid, a type of quadrilateral
* A deltoid curve, a three-cusped hypocycloid
* A leaf shape
* The deltoid tuberosity, a part o ...
and supraspinatus
The supraspinatus (: supraspinati) is a relatively small muscle of the upper back that runs from the supraspinous fossa superior portion of the scapula (shoulder blade) to the greater tubercle of the humerus. It is one of the four rotator cuff m ...
must cancel the adduction component and the teres minor
The teres minor (Latin ''teres'' meaning 'rounded') is a narrow, elongated muscle of the rotator cuff. The muscle originates from the lateral border and adjacent posterior surface of the corresponding right or left scapula and inserts at both the ...
and infraspinatus
In human anatomy, the infraspinatus muscle is a thick triangular muscle, which occupies the chief part of the infraspinatous fossa.''Gray's Anatomy'', see infobox. As one of the four muscles of the rotator cuff, the main function of the infraspin ...
the medial rotation component of pectoralis major. Similarly, abduction (moving the arm away from the body) is performed by different muscles at different stages. The first 10° is performed entirely by the supraspinatus, but beyond that fibres of the much stronger deltoid are in position to take over the work until 90°. To achieve the full 180° range of abduction the arm must be rotated medially and the scapula most be rotated about itself to direct the glenoid cavity upward.
; Muscles: of shoulder joint proper
:; Posterior: Supraspinatus
The supraspinatus (: supraspinati) is a relatively small muscle of the upper back that runs from the supraspinous fossa superior portion of the scapula (shoulder blade) to the greater tubercle of the humerus. It is one of the four rotator cuff m ...
, infraspinatus
In human anatomy, the infraspinatus muscle is a thick triangular muscle, which occupies the chief part of the infraspinatous fossa.''Gray's Anatomy'', see infobox. As one of the four muscles of the rotator cuff, the main function of the infraspin ...
, teres minor
The teres minor (Latin ''teres'' meaning 'rounded') is a narrow, elongated muscle of the rotator cuff. The muscle originates from the lateral border and adjacent posterior surface of the corresponding right or left scapula and inserts at both the ...
, subscapularis
The subscapularis is a large triangular muscle which fills the subscapular fossa and inserts into the lesser tubercle of the humerus and the front of the capsule of the Glenohumeral joint, shoulder-joint.
Structure
The subscapularis is covere ...
, deltoideus
The deltoid muscle is the muscle forming the rounded contour of the human shoulder. It is also known as the 'common shoulder muscle', particularly in other animals such as the domestic cat. Anatomically, the deltoid muscle is made up of three d ...
, latissimus dorsi
The latissimus dorsi () is a large, flat muscle on the back that stretches to the sides, behind the arm, and is partly covered by the trapezius on the back near the midline.
The word latissimus dorsi (plural: ''latissimi dorsi'') comes from L ...
, teres major
The teres major muscle is a muscle of the upper limb. It attaches to the scapula and the humerus and is one of the seven scapulohumeral muscles. It is a thick but somewhat flattened muscle.
The teres major muscle (from Latin ''teres'', meanin ...
:; Anterior: Pectoralis major, coracobrachialis
The coracobrachialis muscle muscle in the upper medial part of the arm. It is located within the anterior compartment of the arm. It originates from the coracoid process of the scapula; it inserts onto the middle of the medial aspect of the body ...
Bones of upper limb
The bones forming the human upper limb are * Clavicle * Scapula * Humerus * Radius * Ulna * Carpal bones ** Scaphoid ** Lunate ** Triquetral ** Pisiform ** Trapezium ** Trapezoid ** Capitate ** Hamate * 5 Metacarpal bones * 14 PhalangesArm
 The arm proper (''brachium''), sometimes called the upper arm, the region between the shoulder and the elbow, is composed of the
The arm proper (''brachium''), sometimes called the upper arm, the region between the shoulder and the elbow, is composed of the humerus
The humerus (; : humeri) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius (bone), radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extrem ...
with the elbow joint
The elbow is the region between the upper arm and the forearm that surrounds the elbow joint. The elbow includes prominent landmarks such as the olecranon, the cubital fossa (also called the chelidon, or the elbow pit), and the lateral and the ...
at its distal end.
The elbow joint is a complex of three joints — the humeroradial, humeroulnar, and superior radioulnar joint
The proximal radioulnar articulation, also known as the proximal radioulnar joint (PRUJ), is a synovial pivot joint between the circumference of the head of the radius and the ring formed by the radial notch of the ulna and the annular ligament. ...
s — the former two allowing flexion and extension whilst the latter, together with its inferior namesake, allows supination and pronation at the wrist. Triceps
The triceps, or triceps brachii (Latin for "three-headed muscle of the arm"), is a large muscle on the ventral, back of the upper limb of many vertebrates. It consists of three parts: the medial, lateral, and long head. All three heads cross the ...
is the major extensor and brachialis
The brachialis (brachialis anticus) is a muscle in the upper arm that flexes the elbow. It lies beneath the biceps brachii, and makes up part of the floor of the region known as the cubital fossa (elbow pit). It originates from the anterior aspec ...
and biceps
The biceps or biceps brachii (, "two-headed muscle of the arm") is a large muscle that lies on the front of the upper arm between the shoulder and the elbow. Both heads of the muscle arise on the scapula and join to form a single muscle bel ...
the major flexors. Biceps is, however, the major supinator and while performing this action it ceases to be an effective flexor at the elbow.
; Muscles: of the arm
:; Posterior: Triceps brachii
The triceps, or triceps brachii (Latin for "three-headed muscle of the arm"), is a large muscle on the back of the upper limb of many vertebrates. It consists of three parts: the medial, lateral, and long head. All three heads cross the elbow jo ...
, anconeus
The anconeus muscle (or anconaeus/anconæus) is a small muscle on the posterior aspect of the elbow joint.
Some consider anconeus to be a continuation of the triceps brachii muscle. Some sources consider it to be part of the posterior compartment ...
:; Anterior: Brachialis
The brachialis (brachialis anticus) is a muscle in the upper arm that flexes the elbow. It lies beneath the biceps brachii, and makes up part of the floor of the region known as the cubital fossa (elbow pit). It originates from the anterior aspec ...
, biceps brachii
The biceps or biceps brachii (, "two-headed muscle of the arm") is a large muscle that lies on the front of the upper arm between the shoulder and the elbow. Both heads of the muscle arise on the scapula and join to form a single muscle bell ...
Forearm
 The forearm (), composed of the
The forearm (), composed of the radius
In classical geometry, a radius (: radii or radiuses) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its Centre (geometry), center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The radius of a regular polygon is th ...
and ulna
The ulna or ulnar bone (: ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone in the forearm stretching from the elbow to the wrist. It is on the same side of the forearm as the little finger, running parallel to the Radius (bone), radius, the forearm's other long ...
; the latter is the main distal part of the elbow joint, while the former composes the main proximal part of the wrist joint.
Most of the large number of muscles in the forearm are divided into the wrist, hand, and finger extensors on the dorsal side (back of hand) and the ditto flexors in the superficial layers on the ventral side (side of palm). These muscles are attached to either the lateral
Lateral is a geometric term of location which may also refer to:
Biology and healthcare
* Lateral (anatomy), a term of location meaning "towards the side"
* Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle, an intrinsic muscle of the larynx
* Lateral release ( ...
or medial epicondyle of the humerus. They thus act on the elbow, but, because their origins are located close to the centre of rotation of the elbow, they mainly act distally at the wrist and hand. Exceptions to this simple division are brachioradialis
The brachioradialis is a muscle of the forearm that flexes the forearm at the elbow. It is also capable of both pronation and supination, depending on the position of the forearm. It is attached to the distal styloid process of the radius by way ...
— a strong elbow flexor — and palmaris longus
The palmaris longus is a muscle visible as a small tendon located between the flexor carpi radialis and the flexor carpi ulnaris, although it is not always present. Reviews report rates of absence in the general population ranging from 10–20%; h ...
— a weak wrist flexor which mainly acts to tense the palmar aponeurosis
The palmar aponeurosis (palmar fascia) Deep fascia, invests the muscles of the palm, and consists of central, lateral, and medial portions.
Structure
The central portion occupies the middle of the palm, is triangular in shape, and of great strengt ...
. The deeper flexor muscles are extrinsic hand muscles; strong flexors at the finger joints used to produce the important power grip of the hand, whilst forced extension is less useful and the corresponding extensor thus are much weaker.
Biceps is the major supinator (drive a screw in with the right arm) and pronator teres
The pronator teres is a muscle (located mainly in the forearm) that, along with the pronator quadratus, serves to pronate the forearm (turning it so that the palm faces posteriorly when from the anatomical position). It has two origins, at th ...
and pronator quadratus
Pronator quadratus is a square-shaped muscle on the distal forearm that acts to pronate (turn so the palm faces downwards) the hand.
Structure
Its fibres run perpendicular to the direction of the arm, running from the most distal quarter of the ...
the major pronators (unscrewing) — the latter two role the radius around the ulna (hence the name of the first bone) and the former reverses this action assisted by supinator
In human anatomy, the supinator is a broad muscle in the posterior compartment of the forearm, curved around the upper third of the radius (bone), radius. Its function is to supination, supinate the forearm.
Structure
The supinator consists of tw ...
. Because biceps is much stronger than its opponents, supination is a stronger action than pronation (hence the direction of screws).
; Muscles: of the forearm
:; Posterior: (Superficial) extensor digitorum
The extensor digitorum muscle (also known as extensor digitorum communis) is a muscle of the posterior forearm present in humans and other animals. It extends the medial four digits of the hand. Extensor digitorum is innervated by the posterior in ...
, extensor digiti minimi
The extensor digiti minimi (extensor digiti quinti proprius) is a slender muscle of the forearm, placed on the ulnar side of the extensor digitorum communis, with which it is generally connected.
It arises from the common extensor tendon by a t ...
, extensor carpi ulnaris
In human anatomy, the extensor carpi ulnaris is a skeletal muscle located on the ulnar side of the forearm. The extensor carpi ulnaris acts to extend and adduct at the carpus/wrist from anatomical position.
Being an extensor muscle, extensor car ...
, (deep) supinator
In human anatomy, the supinator is a broad muscle in the posterior compartment of the forearm, curved around the upper third of the radius (bone), radius. Its function is to supination, supinate the forearm.
Structure
The supinator consists of tw ...
, abductor pollicis longus
In human anatomy, the abductor pollicis longus (APL) is one of the extrinsic muscles of the hand. Its major function is to abduct the thumb at the wrist. Its tendon forms the anterior border of the anatomical snuffbox.
Structure
The abducto ...
, extensor pollicis brevis
In human anatomy, the extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) is a skeletal muscle on the dorsal side of the forearm. It lies on the medial side of, and is closely connected with, the abductor pollicis longus. The extensor pollicis brevis belongs to t ...
, extensor pollicis longus
In human anatomy, the extensor pollicis longus muscle (EPL) is a skeletal muscle located dorsally on the forearm. It is much larger than the extensor pollicis brevis, the origin of which it partly covers and acts to stretch the thumb together w ...
, extensor indicis
In human anatomy, the extensor indicis (proprius) is a narrow, elongated skeletal muscle in the deep layer of the dorsal forearm, placed medial to, and parallel with, the extensor pollicis longus. Its tendon goes to the index finger, which it ext ...
:; Anterior: (Superficial) pronator teres
The pronator teres is a muscle (located mainly in the forearm) that, along with the pronator quadratus, serves to pronate the forearm (turning it so that the palm faces posteriorly when from the anatomical position). It has two origins, at th ...
, flexor digitorum superficialis
Flexor digitorum superficialis (''flexor digitorum sublimis'') or flexor digitorum communis sublimis is an extrinsic flexor muscle of the fingers at the proximal interphalangeal joints.
It is in the anterior compartment of the forearm. It is s ...
, flexor carpi radialis
In anatomy, flexor carpi radialis is a muscle of the human forearm that acts to flex and (radially) abduct the hand. The Latin ''carpus'' means wrist; hence flexor carpi is a flexor of the wrist.
Origin and insertion
The flexor carpi radialis is ...
, flexor carpi ulnaris
The flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU) is a skeletal muscle, muscle of the forearm that flexion, flexes and Adduction, adducts at the wrist joint.
Structure Origin
The flexor carpi ulnaris has two heads; a humeral head and ulnar head. The humeral head o ...
, palmaris longus
The palmaris longus is a muscle visible as a small tendon located between the flexor carpi radialis and the flexor carpi ulnaris, although it is not always present. Reviews report rates of absence in the general population ranging from 10–20%; h ...
, (deep) flexor digitorum profundus
The flexor digitorum profundus or flexor digitorum communis profundus is a muscle in the forearm of humans that flexes the fingers (also known as digits). It is considered an Muscles of the hand#Extrinsic, extrinsic hand muscle because it acts on ...
, flexor pollicis longus
The flexor pollicis longus (; FPL, Latin ''flexor'', bender; ''pollicis'', of the thumb; ''longus'', long) is a muscle in the forearm and hand that flexes the thumb. It lies in the same plane as the flexor digitorum profundus. This muscle is uniq ...
, pronator quadratus
Pronator quadratus is a square-shaped muscle on the distal forearm that acts to pronate (turn so the palm faces downwards) the hand.
Structure
Its fibres run perpendicular to the direction of the arm, running from the most distal quarter of the ...
:; Radial: Brachioradialis
The brachioradialis is a muscle of the forearm that flexes the forearm at the elbow. It is also capable of both pronation and supination, depending on the position of the forearm. It is attached to the distal styloid process of the radius by way ...
, extensor carpi radialis longus
The extensor carpi radialis longus is one of the five main muscles that control movements at the wrist. This muscle is quite long, starting on the lateral side of the humerus, and attaching to the base of the second metacarpal bone (metacarpal of ...
, extensor carpi radialis brevis
In human anatomy, extensor carpi radialis brevis is a muscle in the forearm that acts to extend and abduct the wrist. It is shorter and thicker than its namesake extensor carpi radialis longus which can be found above the proximal end of the ext ...
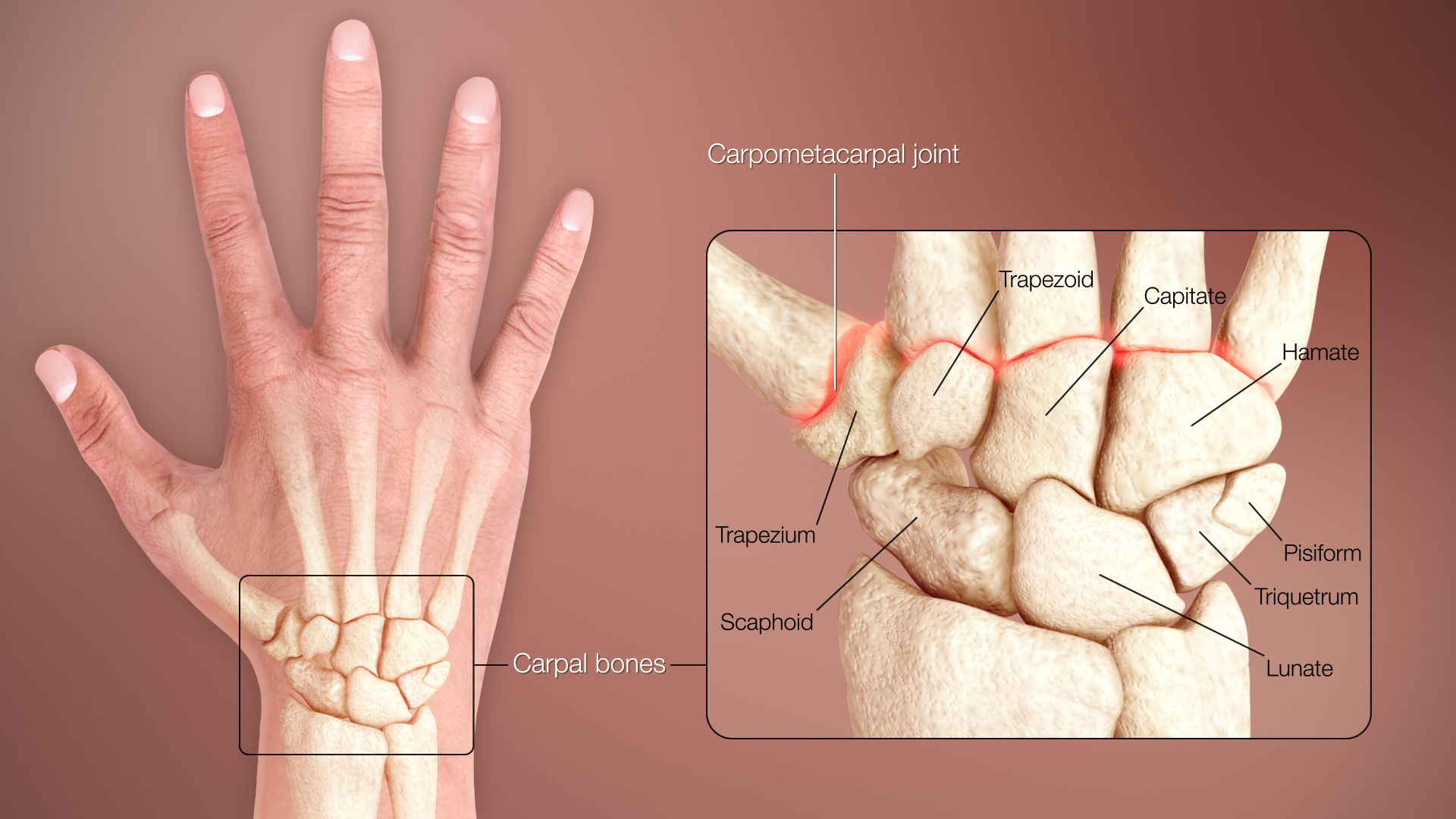
Wrist
Thewrist
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carpal ...
(), composed of the carpal bones
The carpal bones are the eight small bones that make up the wrist (carpus) that connects the hand to the forearm. The terms "carpus" and "carpal" are derived from the Latin wikt:carpus#Latin, carpus and the Greek language, Greek wikt:καρπός ...
, articulates at the wrist joint (or radiocarpal joint
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carpal ...
) proximally and the carpometacarpal joint
The carpometacarpal (CMC) joints are five joints in the wrist that articulate the distal row of carpal bones and the proximal bases of the five metacarpal bones.
The CMC joint of the thumb or the first CMC joint, also known as the trapeziometaca ...
distally. The wrist can be divided into two components separated by the midcarpal joint
The midcarpal joint is formed by the scaphoid, lunate, and triquetral bones in the proximal row, and the trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate bones in the distal row. The distal pole of the scaphoid articulates with two trapezial bones as ...
s. The small movements of the eight carpal bones during composite movements at the wrist are complex to describe, but flexion mainly occurs in the midcarpal joint whilst extension mainly occurs in the radiocarpal joint; the latter joint also providing most of adduction and abduction at the wrist.
 How muscles act on the wrist is complex to describe. The five muscles acting on the wrist directly —
How muscles act on the wrist is complex to describe. The five muscles acting on the wrist directly — flexor carpi radialis
In anatomy, flexor carpi radialis is a muscle of the human forearm that acts to flex and (radially) abduct the hand. The Latin ''carpus'' means wrist; hence flexor carpi is a flexor of the wrist.
Origin and insertion
The flexor carpi radialis is ...
, flexor carpi ulnaris
The flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU) is a skeletal muscle, muscle of the forearm that flexion, flexes and Adduction, adducts at the wrist joint.
Structure Origin
The flexor carpi ulnaris has two heads; a humeral head and ulnar head. The humeral head o ...
, extensor carpi radialis, extensor carpi ulnaris
In human anatomy, the extensor carpi ulnaris is a skeletal muscle located on the ulnar side of the forearm. The extensor carpi ulnaris acts to extend and adduct at the carpus/wrist from anatomical position.
Being an extensor muscle, extensor car ...
, and palmaris longus
The palmaris longus is a muscle visible as a small tendon located between the flexor carpi radialis and the flexor carpi ulnaris, although it is not always present. Reviews report rates of absence in the general population ranging from 10–20%; h ...
— are accompanied by the tendons of the extrinsic hand muscles (i.e. the muscles acting on the fingers). Thus, every movement at the wrist is the work of a group of muscles; because the four primary wrist muscles (FCR, FCU, ECR, and ECU) are attached to the four corners of the wrist, they also produce a secondary movement (i.e. ulnar or radial deviation). To produce pure flexion or extension at the wrist, these muscle therefore must act in pairs to cancel out each other's secondary action. On the other hand, finger movements without the corresponding wrist movements require the wrist muscles to cancel out the contribution from the extrinsic hand muscles at the wrist.
Hand
metacarpals
In human anatomy, the metacarpal bones or metacarpus, also known as the "palm bones", are the appendicular skeleton, appendicular bones that form the intermediate part of the hand between the phalanges (fingers) and the carpal bones (wrist, wris ...
(in the hand proper) and the phalanges
The phalanges (: phalanx ) are digit (anatomy), digital bones in the hands and foot, feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the Thumb, thumbs and Hallux, big toes have two phalanges while the other Digit (anatomy), digits have three phalanges. ...
of the fingers, form the metacarpophalangeal joint
The metacarpophalangeal joints (MCP) are situated between the metacarpal bones and the proximal phalanges of the fingers. These joints are of the condyloid kind, formed by the reception of the rounded heads of the metacarpal bones into shallow ...
s (MCP, including the knuckle
The knuckles are the joints of the fingers. The word is cognate to similar words in other Germanic languages, such as the Dutch "knokkel" (knuckle) or German "Knöchel" (ankle), i.e., ''Knöchlein'', the diminutive of the German word for bone ( ...
s) and interphalangeal joints (IP).
Of the joints between the carpus and metacarpus, the carpometacarpal joint
The carpometacarpal (CMC) joints are five joints in the wrist that articulate the distal row of carpal bones and the proximal bases of the five metacarpal bones.
The CMC joint of the thumb or the first CMC joint, also known as the trapeziometaca ...
s, only the saddle-shaped joint of the thumb offers a high degree of mobility while the opposite is true for the metacarpophalangeal joints. The joints of the fingers are simple hinge joints.
The primary role of the hand itself is grasping and manipulation; tasks for which the hand has been adapted to two main grips — power grip and precision grip. In a power grip an object is held against the palm and in a precision grip an object is held with the fingers, both grips are performed by intrinsic and extrinsic hand muscles together. Most importantly, the relatively strong thenar muscles of the thumb and the thumb's flexible first joint allow the special opposition movement that brings the distal thumb pad in direct contact with the distal pads of the other four digits. Opposition is a complex combination of thumb flexion and abduction that also requires the thumb to be rotated 90° about its own axis. Without this complex movement, humans would not be able to perform a precision grip.
In addition, the central group of intrinsic hand muscles give important contributions to human dexterity. The palmar and dorsal interossei adduct and abduct at the MCP joints and are important in pinching. The lumbricals, attached to the tendons of the flexor digitorum profundus
The flexor digitorum profundus or flexor digitorum communis profundus is a muscle in the forearm of humans that flexes the fingers (also known as digits). It is considered an Muscles of the hand#Extrinsic, extrinsic hand muscle because it acts on ...
(FDP) and extensor digitorum communis
In anatomy, extension is a movement of a joint that increases the angle between two bones or body surfaces at a joint. Extension usually results in straightening of the bones or body surfaces involved. For example, extension is produced by extend ...
(FDC), flex the MCP joints while extending the IP joints and allow a smooth transfer of forces between these two muscles while extending and flexing the fingers.
; Muscles: of the hand
:; Metacarpal: Lumbricals, palmar introssei, dorsal interossei
:; Thenar
The thenar eminence is the mound formed at the base of the thumb on the palm of the hand by the intrinsic group of muscles of the thumb. The skin overlying this region is the area stimulated when trying to elicit a palmomental reflex. The w ...
: Abductor pollicis brevis
The abductor pollicis brevis is a muscle in the hand that functions as an abductor of the thumb.
Structure
The abductor pollicis brevis is a flat, thin muscle located just under the skin. It is a thenar muscle, and therefore contributes to th ...
, adductor pollicis
In human anatomy, the adductor pollicis muscle is a muscle in the hand that functions to Adduction, adduct the thumb. It has two heads: transverse and oblique.
It is a fleshy, flat, triangular, and fan-shaped muscle deep in the Thenar eminence, ...
, flexor pollicis brevis
The flexor pollicis brevis is a muscle in the hand that flexes the thumb. It is one of three thenar muscles. It has both a superficial part and a deep part.
Origin and insertion
The muscle's superficial head arises from the distal edge of the ...
, opponens pollicis
The opponens pollicis is a small, triangular muscle in the hand, which functions to oppose the thumb. It is one of the three thenar muscles. It lies deep to the abductor pollicis brevis and lateral to the flexor pollicis brevis.
Structure
The ...
:; Hypothenar
The hypothenar muscles are a group of three muscles of the hand, palm that control the motion of the little finger.
The three muscles are:
* Abductor minimi digiti muscle (hand), Abductor digiti minimi
* Flexor digiti minimi brevis (hand), Flexor ...
: Abductor digiti minimi, flexor digiti minimi, opponens digiti minimi
The opponens digiti minimi (opponens digiti quinti in older texts) is a muscle in the hand. It is of a triangular form, and placed immediately beneath the palmaris brevis, abductor digiti minimi and flexor digiti minimi brevis. It is one of the ...
, palmaris brevis
Palmaris brevis muscle is a thin, quadrilateral muscle, placed beneath the integument of the ulnar side of the hand. It acts to fold the skin of the hypothenar eminence transversally.
Structure
Origin and insertion
Palmaris brevis muscle is l ...
Neurovascular system
Nerve supply
 The motor and sensory supply of the upper limb is provided by the brachial plexus which is formed by the ventral rami of spinal nerves C5-T1. In the posterior triangle of the neck these rami form three trunks from which fibers enter the axilla region (armpit) to innervate the muscles of the anterior and posterior compartments of the limb. In the axilla, cords are formed to split into branches, including the five terminal branches listed below.
The muscles of the upper limb are innervated segmentally proximal to distal so that the proximal muscles are innervated by higher segments (C5–C6) and the distal muscles are innervated by lower segments (C8–T1).
Motor innervation of upper limb by the five terminal nerves of the
The motor and sensory supply of the upper limb is provided by the brachial plexus which is formed by the ventral rami of spinal nerves C5-T1. In the posterior triangle of the neck these rami form three trunks from which fibers enter the axilla region (armpit) to innervate the muscles of the anterior and posterior compartments of the limb. In the axilla, cords are formed to split into branches, including the five terminal branches listed below.
The muscles of the upper limb are innervated segmentally proximal to distal so that the proximal muscles are innervated by higher segments (C5–C6) and the distal muscles are innervated by lower segments (C8–T1).
Motor innervation of upper limb by the five terminal nerves of the brachial plexus
The brachial plexus is a network of nerves (nerve plexus) formed by the anterior rami of the lower four Spinal nerve#Cervical nerves, cervical nerves and first Spinal nerve#Thoracic nerves, thoracic nerve (cervical spinal nerve 5, C5, Cervical spi ...
:
* The musculocutaneous nerve
The musculocutaneous nerve is a Mixed nerve, mixed branch of the lateral cord of the brachial plexus derived from cervical spinal nerves C5-C7. It arises opposite the lower border of the pectoralis minor. It provides motor innervation to the mus ...
innervates all the muscles of the anterior compartment of the arm
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ...
.
* The median nerve
The median nerve is a nerve in humans and other animals in the upper limb. It is one of the five main nerves originating from the brachial plexus.
The median nerve originates from the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, and has cont ...
innervates all the muscles of the anterior compartment of the forearm
The anterior compartment of the forearm (or flexor compartment) contains the following muscles:
The muscles are largely involved with flexion and supination. The superficial muscles have their origin on the common flexor tendon. The ulnar nerve ...
except flexor carpi ulnaris
The flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU) is a skeletal muscle, muscle of the forearm that flexion, flexes and Adduction, adducts at the wrist joint.
Structure Origin
The flexor carpi ulnaris has two heads; a humeral head and ulnar head. The humeral head o ...
and the ulnar part of the flexor digitorum profundus
The flexor digitorum profundus or flexor digitorum communis profundus is a muscle in the forearm of humans that flexes the fingers (also known as digits). It is considered an Muscles of the hand#Extrinsic, extrinsic hand muscle because it acts on ...
. It also innervates the three thenar
The thenar eminence is the mound formed at the base of the thumb on the palm of the hand by the intrinsic group of muscles of the thumb. The skin overlying this region is the area stimulated when trying to elicit a palmomental reflex. The w ...
muscles and the first and second lumbricals.
* The ulnar nerve
The ulnar nerve is a nerve that runs near the ulna, one of the two long bones in the forearm. The ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint is in relation with the ulnar nerve. The nerve is the largest in the human body unprotected by muscle or ...
innervates the muscles of the forearm and hand not innervated by the median nerve.
* The axillary nerve
The axillary nerve or the circumflex nerve is a nerve of the human body, that originates from the brachial plexus ( upper trunk, posterior division, posterior cord) at the level of the axilla (armpit) and carries nerve fibers from C5 and C6. ...
innervates the deltoid Deltoid (delta-shaped) can refer to:
* The deltoid muscle, a muscle in the shoulder
* Kite (geometry), also known as a deltoid, a type of quadrilateral
* A deltoid curve, a three-cusped hypocycloid
* A leaf shape
* The deltoid tuberosity, a part o ...
and teres minor
The teres minor (Latin ''teres'' meaning 'rounded') is a narrow, elongated muscle of the rotator cuff. The muscle originates from the lateral border and adjacent posterior surface of the corresponding right or left scapula and inserts at both the ...
.
* The radial nerve
The radial nerve is a nerve in the human body that supplies the posterior portion of the upper limb. It innervates the medial and lateral heads of the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, as well as all 12 muscles in the Posterior compartment of the ...
innervates the posterior muscles of the arm and forearm
Collateral branches of the brachial plexus:
* The dorsal scapular nerve
The dorsal scapular nerve is a branch of the brachial plexus, usually derived from the ventral ramus of cervical nerve C5. It provides motor innervation to the rhomboid major muscle, rhomboid minor muscle, and levator scapulae muscle.
Dorsal ...
innervates rhomboid major, minor
Minor may refer to:
Common meanings
* Minor (law), a person not under the age of certain legal activities.
* Academic minor, a secondary field of study in undergraduate education
Mathematics
* Minor (graph theory), a relation of one graph to an ...
and levator scapulae
The levator scapulae is a slender skeletal muscle situated at the back and side of the neck. It originates from the transverse processes of the four uppermost cervical vertebrae; it inserts onto the upper portion of the medial border of the scapu ...
.
* The long thoracic nerve
The long thoracic nerve (also: external respiratory nerve of Bell or posterior thoracic nerve) is a branch of the brachial plexus derived from cervical nerves C5-C7 that innervates the serratus anterior muscle.
Structure
Origin
The long th ...
innervates serratus anterior
The serratus anterior is a muscle of the chest. It originates at the side of the chest from the upper 8 or 9 ribs; it inserts along the entire length of the anterior aspect of the medial border of the scapula. It is innervated by the long thor ...
.
* The suprascapular nerve
The suprascapular nerve is a mixed (sensory and motor) nerve that branches from the upper trunk of the brachial plexus. It is derived from the ventral rami of cervical nerves C5-C6. It provides motor innervation to the supraspinatus muscle, and t ...
innervates supraspinatus
The supraspinatus (: supraspinati) is a relatively small muscle of the upper back that runs from the supraspinous fossa superior portion of the scapula (shoulder blade) to the greater tubercle of the humerus. It is one of the four rotator cuff m ...
and infraspinatus
In human anatomy, the infraspinatus muscle is a thick triangular muscle, which occupies the chief part of the infraspinatous fossa.''Gray's Anatomy'', see infobox. As one of the four muscles of the rotator cuff, the main function of the infraspin ...
* The lateral pectoral nerve
The lateral pectoral nerve (also known as the lateral anterior thoracic nerve) arises from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus, and through it from the C5-7.
It passes across the axillary artery and vein, pierces the clavipectoral (coracocl ...
innervates pectoralis major
* The medial pectoral nerve
The medial pectoral nerve (also known as the medial anterior thoracic nerve) is (typically) a branch of the medial cord of the brachial plexus and is derived from spinal nerve roots C8-T1. It provides motor innervation to the pectoralis minor musc ...
innervates pectoralis major and minor
Minor may refer to:
Common meanings
* Minor (law), a person not under the age of certain legal activities.
* Academic minor, a secondary field of study in undergraduate education
Mathematics
* Minor (graph theory), a relation of one graph to an ...
* The upper subscapular nerve
The upper (superior) subscapular nerve is the first branch of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. The upper subscapular nerve contains axons from the ventral rami of the C5 and C6 cervical spinal nerves. It innervates the superior porti ...
innervates subscapularis
The subscapularis is a large triangular muscle which fills the subscapular fossa and inserts into the lesser tubercle of the humerus and the front of the capsule of the Glenohumeral joint, shoulder-joint.
Structure
The subscapularis is covere ...
* The thoracodorsal nerve
The thoracodorsal nerve is a nerve present in humans and other animals, also known as the middle subscapular nerve or the long subscapular nerve. It supplies the latissimus dorsi muscle.
Anatomy
Origin
The thoracodorsal nerve arises from the ...
innervates latissimus dorsi
The latissimus dorsi () is a large, flat muscle on the back that stretches to the sides, behind the arm, and is partly covered by the trapezius on the back near the midline.
The word latissimus dorsi (plural: ''latissimi dorsi'') comes from L ...
* The lower subscapular nerve
The lower subscapular nerve, also known as the inferior subscapular nerve, is the third branch of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. It innervates the inferior portion of the subscapularis muscle and the teres major muscle.
Structure
The ...
innervates subscapularis
The subscapularis is a large triangular muscle which fills the subscapular fossa and inserts into the lesser tubercle of the humerus and the front of the capsule of the Glenohumeral joint, shoulder-joint.
Structure
The subscapularis is covere ...
and teres major
The teres major muscle is a muscle of the upper limb. It attaches to the scapula and the humerus and is one of the seven scapulohumeral muscles. It is a thick but somewhat flattened muscle.
The teres major muscle (from Latin ''teres'', meanin ...
* The medial brachial cutaneous nerve
The medial brachial cutaneous nerve (lesser internal cutaneous nerve; medial cutaneous nerve of arm) is a sensory branch of the medial cord of the brachial plexus derived from spinal nerves C8-T1. It provides sensory innervation to the medial arm. ...
innervates the skin of medial arm
* The medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve
The medial cutaneous nerve of the forearm (also known as the medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve) is a sensory branch of the medial cord of the brachial plexus derived from the ventral rami of spinal nerves C8-T1. It provides sensory innervation ...
innervates the skin of medial forearm
Blood supply and drainage
Arteries of the upper limb: * The superior thoracic, thoracoacromial, posterior circumflex humeral and subscapular branches of theaxillary artery
In human anatomy, the axillary artery is a large blood vessel that conveys oxygenated blood to the lateral aspect of the thorax, the axilla (armpit) and the upper limb. Its origin is at the lateral margin of the first rib, before which it is c ...
.
* The deep brachial, superior ulnar collateral, inferior ulnar collateral, radial
Radial is a geometric term of location which may refer to:
Mathematics and Direction
* Vector (geometric), a line
* Radius, adjective form of
* Radial distance (geometry), a directional coordinate in a polar coordinate system
* Radial set
* A ...
,
ulnar, nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
and muscular
MUSCULAR (DS-200B), located in the United Kingdom, is the name of a surveillance program jointly operated by Britain's Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ) and the U.S. National Security Agency (NSA) that was revealed by documents release ...
branches of the brachial artery
The brachial artery is the major blood vessel of the (upper) arm. It is the continuation of the axillary artery beyond the lower margin of teres major muscle. It continues down the ventral surface of the arm until it reaches the cubital fossa ...
.
* The radial recurrent, muscular
MUSCULAR (DS-200B), located in the United Kingdom, is the name of a surveillance program jointly operated by Britain's Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ) and the U.S. National Security Agency (NSA) that was revealed by documents release ...
, superficial palmar, dorsal carpal, princeps pollicis and radialis indicis branches of the radial artery
In human anatomy, the radial artery is the main artery of the lateral aspect of the forearm.
Structure
The radial artery arises from the bifurcation of the brachial artery in the antecubital fossa. It runs distally on the anterior part of the ...
.
* The anterior ulnar recurrent, posterior ulnar recurrent, anterior interosseous, posterior interosseous and superficial
Superficial may refer to:
*Superficial anatomy, is the study of the external features of the body
*Superficiality, the discourses in philosophy regarding social relation
* Superficial charm, the tendency to be smooth, engaging, charming, slick and ...
branches of the ulnar artery
The ulnar artery is the main blood vessel, with oxygenated blood, of the Human Anatomical Terms#Anatomical directions, medial aspects of the forearm. It arises from the brachial artery and terminates in the superficial palmar arch, which joins ...
.
 Veins of the upper limb:
*
Veins of the upper limb:
* Basilic vein
The basilic vein is a large superficial vein of the upper limb that helps drain parts of the hand and forearm. It originates on the medial ( ulnar) side of the dorsal venous network of the hand and travels up the base of the forearm, where its ...
* Cephalic vein
In human anatomy, the cephalic vein (also called the antecubital vein) is a superficial vein in the arm. It is the longest vein of the upper limb. It starts at the anatomical snuffbox from the radial end of the dorsal venous network of hand, a ...
* Median cubital vein
In human anatomy, the median cubital vein (or median basilic vein) is a superficial vein of the arm on the anterior aspect of the elbow. It classically shunts blood from the cephalic to the basilic vein at the roof of the cubital fossa. It is ty ...
* Median antebrachial vein
The median antebrachial vein, also known as median vein of forearm, is a superficial vein of the (anterior) forearm. It arises from - and drains - the superficial palmar venous arch, ascending superficially along the anterior forearm before endin ...
* Dorsal venous arch
The dorsal venous arch of the foot is a Superficial anatomy, superficial vein that connects the small saphenous vein and the great saphenous vein. Anatomically, it is defined by where the dorsal veins of the first and fifth toe, digit, respective ...
As for the upper limb blood supply, there are many anatomical variations.
Other animals
Evolutionary variation
 The skeletons of all
The skeletons of all mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s are based on a common pentadactyl ("five-fingered") template but optimised for different functions. While many mammals can perform other tasks using their forelimbs, their primary use in most terrestrial mammals is one of three main modes of locomotion: unguligrade
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Euungulata ("true ungulates"), which primarily consists of large mammals with Hoof, hooves. Once part of the clade "Ungulata" along with the clade Paenungulata, "Ungulata" has since been determined ...
(hoof walkers), digitigrade
In terrestrial vertebrates, digitigrade ( ) locomotion is walking or running on the toes (from the Latin ''digitus'', 'finger', and ''gradior'', 'walk'). A digitigrade animal is one that stands or walks with its toes (phalanges) on the ground, and ...
(toe walkers), and plantigrade
151px, Portion of a human skeleton, showing plantigrade habit
In terrestrial animals, plantigrade locomotion means walking with the toes and metatarsals flat on the ground. It is one of three forms of locomotion adopted by terrestrial mammals. ...
(sole walkers). Generally, the forelimbs are optimised for speed and stamina, but in some mammals some of the locomotion optimisation have been sacrificed for other functions, such as digging and grasping.
In primate
Primates is an order (biology), order of mammals, which is further divided into the Strepsirrhini, strepsirrhines, which include lemurs, galagos, and Lorisidae, lorisids; and the Haplorhini, haplorhines, which include Tarsiiformes, tarsiers a ...
s, the upper limbs provide a wide range of movement which increases manual dexterity. The limbs of chimpanzee
The chimpanzee (; ''Pan troglodytes''), also simply known as the chimp, is a species of Hominidae, great ape native to the forests and savannahs of tropical Africa. It has four confirmed subspecies and a fifth proposed one. When its close rel ...
s, compared to those of humans, reveal their different lifestyle. The chimpanzee primarily uses two modes of locomotion: knuckle-walking
Knuckle-walking is a form of quadrupedal walking in which the forelimbs hold the fingers in a partially flexed posture that allows body weight to press down on the ground through the knuckles. Gorillas and chimpanzees use this style of locomoti ...
, a style of quadrupedalism
Quadrupedalism is a form of locomotion in which animals have four legs that are used to bear weight and move around. An animal or machine that usually maintains a four-legged posture and moves using all four legs is said to be a quadruped (fr ...
in which the body weight is supported on the knuckles (or more properly on the middle phalanges of the fingers), and brachiation
Brachiation (from "brachium", Latin for "arm"), or arm swinging, is a form of arboreal locomotion in which primates swing from tree limb to tree limb using only their arms. During brachiation, the body is alternately supported under each forelimb ...
(swinging from branch to branch), a style of bipedalism
Bipedalism is a form of terrestrial locomotion where an animal moves by means of its two rear (or lower) Limb (anatomy), limbs or legs. An animal or machine that usually moves in a bipedal manner is known as a biped , meaning 'two feet' (from ...
in which flexed fingers are used to grasp branches above the head. To meet the requirements of these styles of locomotion, the chimpanzee's finger phalanges are longer and have more robust insertion areas for the flexor tendons while the metacarpals have transverse ridges to limit dorsiflexion (stretching the fingers towards the back of the hand). The thumb is small enough to facilitate brachiation while maintaining some of the dexterity offered by an opposable thumb. In contrast, virtually all locomotion functionality has been lost in humans while predominant brachiators, such as the gibbon
Gibbons () are apes in the family Hylobatidae (). The family historically contained one genus, but now is split into four extant genera and 20 species. Gibbons live in subtropical and tropical forests from eastern Bangladesh and Northeast Indi ...
s, have very reduced thumbs and inflexible wrists.
In ungulate
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Euungulata ("true ungulates"), which primarily consists of large mammals with Hoof, hooves. Once part of the clade "Ungulata" along with the clade Paenungulata, "Ungulata" has since been determined ...
s the forelimbs are optimised to maximize speed and stamina to the extent that the limbs serve almost no other purpose. In contrast to the skeleton of human limbs, the proximal bones of ungulates are short and the distal bones long to provide length of stride; proximally, large and short muscles provide rapidity of step. The odd-toed ungulate
Perissodactyla (, ), or odd-toed ungulates, is an order of ungulates. The order includes about 17 living species divided into three families: Equidae (horses, asses, and zebras), Rhinocerotidae (rhinoceroses), and Tapiridae (tapirs). They t ...
s, such as the horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 mi ...
, use a single third toe for weight-bearing and have significantly reduced metacarpals. Even-toed ungulate
Artiodactyls are placental mammals belonging to the order Artiodactyla ( , ). Typically, they are ungulates which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes (the third and fourth, often in the form of a hoof). The other t ...
s, such as the giraffe
The giraffe is a large Fauna of Africa, African even-toed ungulate, hoofed mammal belonging to the genus ''Giraffa.'' It is the Largest mammals#Even-toed Ungulates (Artiodactyla), tallest living terrestrial animal and the largest ruminant on ...
, uses both their third and fourth toes but a single completely fused phalanx bone for weight-bearing. Ungulates whose habitat does not require fast running on hard terrain, for example the hippopotamus
The hippopotamus (''Hippopotamus amphibius;'' ; : hippopotamuses), often shortened to hippo (: hippos), further qualified as the common hippopotamus, Nile hippopotamus and river hippopotamus, is a large semiaquatic mammal native to sub-Sahar ...
, have maintained four digits.
In species in the order Carnivora
Carnivora ( ) is an order of placental mammals specialized primarily in eating flesh, whose members are formally referred to as carnivorans. The order Carnivora is the sixth largest order of mammals, comprising at least 279 species. Carnivor ...
, some of which are insectivore
file:Common brown robberfly with prey.jpg, A Asilidae, robber fly eating a hoverfly
An insectivore is a carnivore, carnivorous animal or plant which eats insects. An alternative term is entomophage, which can also refer to the Entomophagy ...
s rather than carnivore
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they ar ...
s, the cat
The cat (''Felis catus''), also referred to as the domestic cat or house cat, is a small domesticated carnivorous mammal. It is the only domesticated species of the family Felidae. Advances in archaeology and genetics have shown that the ...
s are some of the most highly evolved predators designed for speed, power, and acceleration rather than stamina. Compared to ungulates, their limbs are shorter, more muscular in the distal segments, and maintain five metacarpals and digit bones; providing a greater range of movements, a more varied function and agility (e.g. climbing, swatting, and grooming). Some insectivorous species in this order have paws specialised for specific functions. The sloth bear
The sloth bear (''Melursus ursinus''), also known as the Indian bear, is a myrmecophagous bear species native to the Indian subcontinent. It feeds on fruits, ants and termites. It is listed as vulnerable on the IUCN Red List, mainly because of ...
uses their digits and large claws to tear logs open rather than kill prey. Other insectivorous species, such as the giant
In folklore, giants (from Ancient Greek: ''wiktionary:gigas, gigas'', cognate wiktionary:giga-, giga-) are beings of humanoid appearance, but are at times prodigious in size and strength or bear an otherwise notable appearance. The word ''gia ...
and red panda
The red panda (''Ailurus fulgens''), also known as the lesser panda, is a small mammal native to the eastern Himalayas and southwestern China. It has dense reddish-brown fur with a black belly and legs, white-lined ears, a mostly white muzz ...
s, have developed large sesamoid bone
In anatomy, a sesamoid bone () is a bone embedded within a tendon or a muscle. Its name is derived from the Greek word for 'sesame seed', indicating the small size of most sesamoids. Often, these bones form in response to strain, or can be presen ...
s in their paws that serve as an extra "thumb" while others, such as the meerkat
The meerkat (''Suricata suricatta'') or suricate is a small mongoose found in southern Africa. It is characterised by a broad head, large eyes, a pointed snout, long legs, a thin tapering tail, and a brindled coat pattern. The head-and-body ...
, uses their limbs primary for digging and have vestigial
Vestigiality is the retention, during the process of evolution, of genetically determined structures or attributes that have lost some or all of the ancestral function in a given species. Assessment of the vestigiality must generally rely on co ...
first digits.
The arboreal
Arboreal locomotion is the locomotion of animals in trees. In habitats in which trees are present, animals have evolved to move in them. Some animals may scale trees only occasionally (scansorial), but others are exclusively arboreal. The hab ...
two-toed sloth
''Choloepus'' is a genus of xenarthran mammals from Central and South America within the monotypic family Choloepodidae, consisting of two-toed sloths, sometimes also called two-fingered sloths. The two species of ''Choloepus'' (which means "la ...
, a South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
n mammal in the order Pilosa
The Order (biology), order Pilosa is a clade of xenarthran placental mammals, native to the Americas. It includes anteaters and sloths (which include the extinct ground sloths). The name comes from the Latin word for "hairy".
Origins and taxon ...
, have limbs so highly adapted to hanging in branches that it is unable to walk on the ground where it has to drag its own body using the large curved claws on its foredigits.
See also
*Human skeletal changes due to bipedalism
The evolution of human bipedalism, which began in primates approximately four million years ago, or as early as seven million years ago with '' Sahelanthropus'', or approximately twelve million years ago with '' Danuvius guggenmosi'', has led to ...
* Lower limb
Lower may refer to:
*Lower (album), ''Lower'' (album), 2025 album by Benjamin Booker
*Lower (surname)
*Lower Township, New Jersey
*Lower Receiver (firearms)
*Lower Wick Gloucestershire, England
See also
*Nizhny
{{Disambiguation ...
Notes
References
* * * * {{Authority control Limbs (anatomy)