|
Clavicle
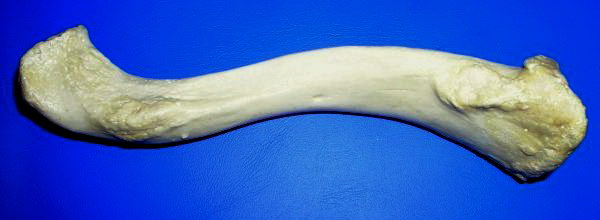
The clavicle, or collarbone, is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately 6 inches (15 cm) long that serves as a strut between the shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on the left and one on the right. The clavicle is the only long bone in the body that lies horizontally. Together with the shoulder blade, it makes up the shoulder girdle. It is a palpable bone and, in people who have less fat in this region, the location of the bone is clearly visible. It receives its name from the Latin ''clavicula'' ("little key"), because the bone rotates along its axis like a key when the shoulder is abducted. The clavicle is the most commonly fractured bone. It can easily be fractured by impacts to the shoulder from the force of falling on outstretched arms or by a direct hit. Structure The collarbone is a thin doubly curved long bone that connects the arm to the trunk of the body. Located directly above the first rib, it acts as a strut t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clavicle 3d Model
The clavicle, or collarbone, is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately 6 inches (15 cm) long that serves as a strut between the shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on the left and one on the right. The clavicle is the only long bone in the body that lies horizontally. Together with the shoulder blade, it makes up the shoulder girdle. It is a palpable bone and, in people who have less fat in this region, the location of the bone is clearly visible. It receives its name from the Latin ''clavicula'' ("little key"), because the bone rotates along its axis like a key when the shoulder is abducted. The clavicle is the most commonly fractured bone. It can easily be fractured by impacts to the shoulder from the force of falling on outstretched arms or by a direct hit. Structure The collarbone is a thin doubly curved long bone that connects the arm to the trunk of the body. Located directly above the first rib, it acts as a strut to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoulder Girdle
The shoulder girdle or pectoral girdle is the set of bones in the appendicular skeleton which connects to the arm on each side. In humans it consists of the clavicle and scapula; in those species with three bones in the shoulder, it consists of the clavicle, scapula, and coracoid. Some mammalian species (such as the dog and the horse) have only the scapula. The pectoral girdles are to the upper limbs as the pelvic girdle is to the lower limbs; the girdles are the parts of the appendicular skeleton that anchor the appendages to the axial skeleton. In humans, the only true anatomical joints between the shoulder girdle and the axial skeleton are the sternoclavicular joints on each side. No anatomical joint exists between each scapula and the rib cage; instead the muscular connection or physiological joint between the two permits great mobility of the shoulder girdle compared to the compact pelvic girdle; because the upper limb is not usually involved in weight bear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acromioclavicular Joint
The acromioclavicular joint, or AC joint, is a joint at the top of the shoulder. It is the junction between the acromion (part of the scapula that forms the highest point of the shoulder) and the clavicle. It is a plane synovial joint. Structure Ligaments The joint is stabilized by three ligaments: * The acromioclavicular ligament, which attaches the clavicle to the acromion of the scapula. Superior Acromioclavicular Ligament This ligament is a quadrilateral band, covering the superior part of the articulation, and extending between the upper part of the lateral end of the clavicle and the adjoining part of the upper surface of the acromion. It is composed of parallel fibers, which interlace with the aponeuroses of the Trapezius and Deltoideus; below, it is in contact with the articular disk when this is present. Inferior Acromioclavicular Ligament This ligament is somewhat thinner than the preceding; it covers the under part of the articulation, and is attached to the adjoin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternoclavicular Joint
The sternoclavicular joint or sternoclavicular articulation is a synovial saddle joint between the manubrium of the sternum, and the clavicle, as well as the first rib. The joint possesses a joint capsule, and an articular disk, and is reinforced by multiple ligaments. Structure The joint is structurally classed as a synovial plane joint and functionally classed as a diarthrosis and multiaxial joint. It is composed of two portions separated by an articular disc of fibrocartilage. The joint is formed by the sternal end of the clavicle, the clavicular notch (the superior and lateral part of the sternum), and (the superior surface of) the cartilage of the first rib (visible from the outside as the suprasternal notch). The articular surface of the clavicle is larger than that of the sternum, and is invested with a layer of cartilage, which is considerably thicker than that of the sternum. The joint receives arterial supply via branches of the internal thoracic artery, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manubrium
The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Shaped roughly like a necktie, it is one of the largest and longest flat bones of the body. Its three regions are the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process. The word "sternum" originates from the Ancient Greek στέρνον (stérnon), meaning "chest". Structure The sternum is a narrow, flat bone, forming the middle portion of the front of the chest. The top of the sternum supports the clavicles (collarbones) and its edges join with the costal cartilages of the first two pairs of ribs. The inner surface of the sternum is also the attachment of the sternopericardial ligaments. Its top is also connected to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The sternum consists of three main parts, listed from the top: * Manubrium * Body (gladiolu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternum
The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Shaped roughly like a necktie, it is one of the largest and longest flat bones of the body. Its three regions are the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process. The word "sternum" originates from the Ancient Greek στέρνον (stérnon), meaning "chest". Structure The sternum is a narrow, flat bone, forming the middle portion of the front of the chest. The top of the sternum supports the clavicles (collarbones) and its edges join with the costal cartilages of the first two pairs of ribs. The inner surface of the sternum is also the attachment of the sternopericardial ligaments. Its top is also connected to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The sternum consists of three main parts, listed from the top: * Manubrium * Body (gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scapula
The scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the other. The name derives from the Classical Latin word for trowel or small shovel, which it was thought to resemble. In compound terms, the prefix omo- is used for the shoulder blade in medical terminology. This prefix is derived from ὦμος (ōmos), the Ancient Greek word for shoulder, and is cognate with the Latin , which in Latin signifies either the shoulder or the upper arm bone. The scapula forms the back of the shoulder girdle. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage. Structure The scapula is a thick, flat bone lying on the thoracic wall that provides an attachment for three groups of muscles: i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coracoclavicular Ligament
The coracoclavicular ligament is a ligament of the shoulder. It connects the clavicle to the coracoid process of the scapula. Structure The coracoclavicular ligament connects the clavicle to the coracoid process of the scapula. It it is not part of the acromioclavicular joint articulation, but is usually described with it, since it keeps the clavicle in contact with the acromion. It consists of two fasciculi, the trapezoid ligament in front, and the conoid ligament behind. These ligaments are in relation, in front, with the subclavius muscle and the deltoid muscle; behind, with the trapezius. Variation The insertions of the coracoclavicular ligament can occur in slightly different places in different people. It may contain three fascicles rather than two. Function The coracoclavicular ligament is a strong stabilizer of the acromioclavicular joint. It is also important in the transmission of weight of the upper limb to the axial skeleton. There is very little movement at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coracoid Process
The coracoid process (from Greek κόραξ, raven) is a small hook-like structure on the lateral edge of the superior anterior portion of the scapula (hence: coracoid, or "like a raven's beak"). Pointing laterally forward, it, together with the acromion, serves to stabilize the shoulder joint. It is palpable in the deltopectoral groove between the deltoid and pectoralis major muscles. Structure The coracoid process is a thick curved process attached by a broad base to the upper part of the neck of the scapula; it runs at first upward and medialward; then, becoming smaller, it changes its direction, and projects forward and lateralward. Anatomically it is divided into intervals of: base of coracoid process, angle of coracoid process, shaft and the apex of the coracoid process. The coracoglenoid notch is an indentation localized between the coracoid process and the glenoid. As the coracoid process projects laterally, it house underneath it the subcoracoid space. The ''as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strut
A strut is a structural component commonly found in engineering, aeronautics, architecture and anatomy. Struts generally work by resisting longitudinal compression, but they may also serve in tension. Human anatomy Part of the functionality of the clavicle is to serve as a strut between the scapula and sternum, resisting forces that would otherwise bring the upper limb close to the thorax. Keeping the upper limb away from the thorax is vital for its range of motion. Complete lack of clavicles may be seen in cleidocranial dysostosis, and the abnormal proximity of the shoulders to the median plane exemplifies the clavicle's importance as a strut. Architecture and construction Strut is a common name in timber framing for a support or brace of scantlings lighter than a post. Frequently struts are found in roof framing from either a tie beam or a king post to a principal rafter. Struts may be vertically plumb or leaning (then called canted, raking, or angled) and may be straight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acromion
In human anatomy, the acromion (from Greek: ''akros'', "highest", ''ōmos'', "shoulder", plural: acromia) is a bony process on the scapula (shoulder blade). Together with the coracoid process it extends laterally over the shoulder joint. The acromion is a continuation of the scapular spine, and hooks over anteriorly. It articulates with the clavicle (collar bone) to form the acromioclavicular joint. Structure The acromion forms the summit of the shoulder, and is a large, somewhat triangular or oblong process, flattened from behind forward, projecting at first lateralward, and then curving forward and upward, so as to overhang the glenoid fossa.'' Gray's Anatomy'' 1918, see infobox It starts from the base of acromion which marks its projecting point emerging from the spine of scapula. Surfaces Its superior surface, directed upward, backward, and lateralward, is convex, rough, and gives attachment to some fibers of the deltoideus, and in the rest of its extent is subcuta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
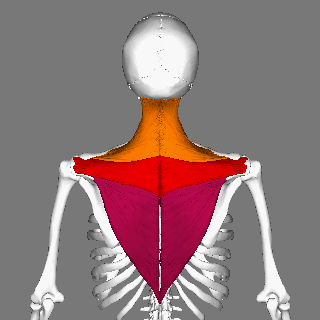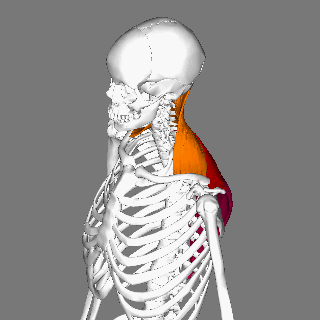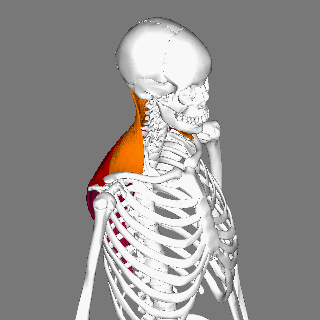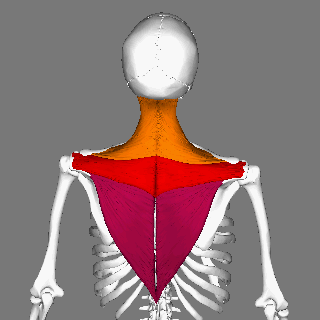
Trapezius Muscle
The trapezius is a large paired trapezoid-shaped surface muscle that extends longitudinally from the occipital bone to the lower thoracic vertebrae of the spine and laterally to the spine of the scapula. It moves the scapula and supports the arm. The trapezius has three functional parts: an upper (descending) part which supports the weight of the arm; a middle region (transverse), which retracts the scapula; and a lower (ascending) part which medially rotates and depresses the scapula. Name and history The trapezius muscle resembles a trapezium, also known as a trapezoid, or diamond-shaped quadrilateral. The word "spinotrapezius" refers to the human trapezius, although it is not commonly used in modern texts. In other mammals, it refers to a portion of the analogous muscle. Similarly, the term "tri-axle back plate" was historically used to describe the trapezius muscle. Structure The ''superior'' or ''upper'' (or descending) fibers of the trapezius originate from the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |