|
Abductor Pollicis Longus
In human anatomy, the abductor pollicis longus (APL) is one of the extrinsic muscles of the hand. Its major function is to abduct the thumb at the wrist. Its tendon forms the anterior border of the anatomical snuffbox. Structure The abductor pollicis longus lies immediately below the supinator and is sometimes united with it. It arises from the lateral part of the dorsal surface of the body of the ulna, below the insertion of the anconeus, from the interosseous membrane, and from the middle third of the dorsal surface of the body of the radius.'' Gray's Anatomy'' (1918), see infobox Passing obliquely downward and lateralward, it ends in a tendon, which runs through a groove on the lateral side of the lower end of the radius, accompanied by the tendon of the extensor pollicis brevis. The insertion is divided into a distal, superficial part and a proximal, deep part. The superficial part is inserted with one or more tendons into the radial side of the base of the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulna
The ulna or ulnar bone (: ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone in the forearm stretching from the elbow to the wrist. It is on the same side of the forearm as the little finger, running parallel to the Radius (bone), radius, the forearm's other long bone. Longer and thinner than the radius, the ulna is considered to be the smaller long bone of the lower arm. The corresponding bone in the Human leg#Structure, lower leg is the fibula. Structure The ulna is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the wrist, and when in standard anatomical position, is found on the Medial (anatomy), medial side of the forearm. It is broader close to the elbow, and narrows as it approaches the wrist. Close to the elbow, the ulna has a bony Process (anatomy), process, the olecranon process, a hook-like structure that fits into the olecranon fossa of the humerus. This prevents hyperextension and forms a hinge joint with the trochlea of the humerus. There is also a radial notch for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anconeus Muscle
The anconeus muscle (or anconaeus/anconæus) is a small muscle on the posterior aspect of the elbow joint. Some consider anconeus to be a continuation of the triceps brachii muscle. Some sources consider it to be part of the posterior compartment of the arm, while others consider it part of the posterior compartment of the forearm. The anconeus muscle can easily be palpated just lateral to the olecranon process of the ulna. Structure Anconeus originates on the posterior surface of the lateral epicondyle of the humerus and inserts distally on the superior posterior surface of the ulna and the lateral aspect of the olecranon. Innervation Anconeus is innervated by a branch of the radial nerve (cervical roots 7 and 8) from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus called the nerve to the anconeus. The somatomotor portion of radial nerve innervating anconeus bifurcates from the main branch in the radial groove of the humerus. This innervation pattern follows the rules of innervat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Interosseous Artery
The posterior interosseous artery (dorsal interosseous artery) is an artery of the forearm. It is a branch of the common interosseous artery, which is a branch of the ulnar artery. Structure The posterior interosseous artery passes backward between the oblique cord and the upper border of the interosseous membrane. It appears between the contiguous borders of supinator muscle and the abductor pollicis longus muscle, and runs down the back of the forearm between the superficial and deep layers of muscles, to both of which it distributes branches. Where it lies on abductor pollicis longus muscle and the extensor pollicis brevis muscle, it is accompanied by the dorsal interosseous nerve. At the lower part of the forearm it anastomoses with the termination of the volar interosseous artery, and with the dorsal carpal network. Branches Near its origin, it gives off the interosseous recurrent artery. This ascends to the interval between the lateral epicondyle and olecranon, on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPnotebook
GPnotebook is a British medical database for general practitioners (GPs). It is an online encyclopaedia of medicine that provides an immediate reference resource for clinician A clinician is a health care professional typically employed at a skilled nursing facility or clinic. Clinicians work directly with patients rather than in a laboratory, community health setting or in research. A clinician may diagnose, treat a ...s worldwide. The database consists of over 30,000 index terms and over two million words of information. GPnotebook is provided online by Oxbridge Solutions Limited. GPnotebook website is primarily designed with the needs of general practitioners (GPs) in mind, and written by a variety of specialists, ranging from paediatrics to accident and emergency. The original idea for the database began in the canteen of John Radcliffe Hospital in 1990 while James McMorran, a first-year Oxford University clinical student, was writing up his medical notes. Instead of wr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supinator Muscle
In human anatomy, the supinator is a broad muscle in the posterior compartment of the forearm, curved around the upper third of the radius. Its function is to supinate the forearm. Structure The supinator consists of two planes of fibers, between which passes the deep branch of the radial nerve. The two planes arise in common—the superficial one originating as tendons and the deeper by muscular fibers—from the supinator crest of the ulna, the lateral epicondyle of the humerus, the radial collateral ligament, and the annular radial ligament. The superficial fibers (''pars superficialis'') surround the upper part of the radius, and are inserted into the lateral edge of the radial tuberosity and the oblique line of the radius, as low down as the insertion of the pronator teres. The upper fibers (''pars profunda'') of the deeper plane form a sling-like fasciculus, which encircles the neck of the radius above the tuberosity and is attached to the back part of its medial surfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
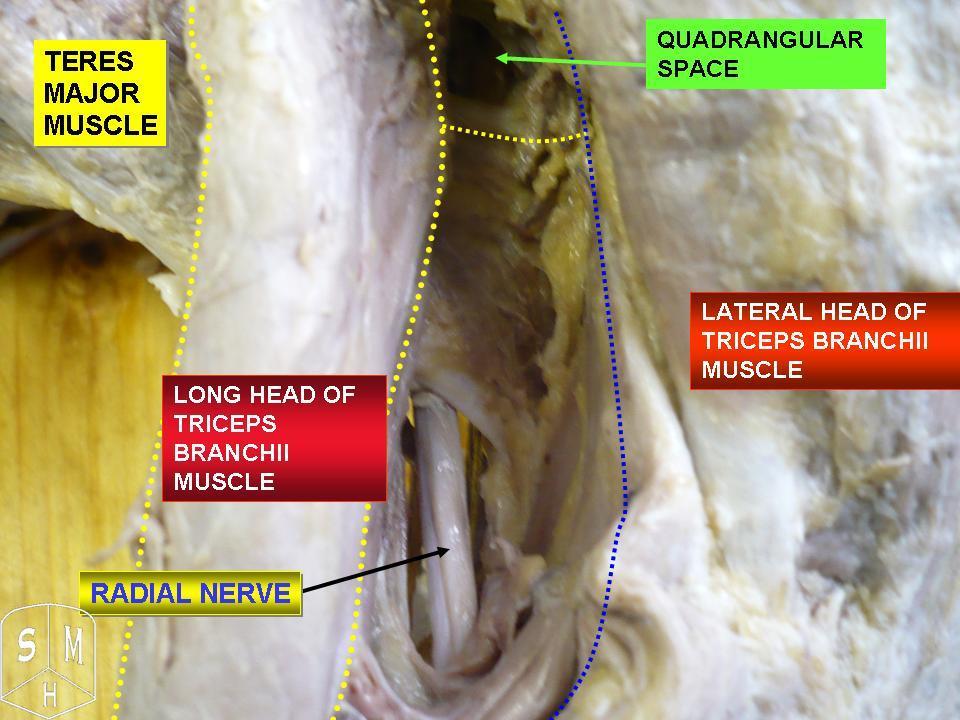
Radial Nerve
The radial nerve is a nerve in the human body that supplies the posterior portion of the upper limb. It innervates the medial and lateral heads of the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, as well as all 12 muscles in the Posterior compartment of the forearm, posterior osteofascial compartment of the forearm and the associated joints and overlying skin. It originates from the brachial plexus, carrying fibers from the posterior roots of spinal nerves C5, C6, C7, C8 and T1. The radial nerve and its branches provide Motor neuron, motor innervation to the dorsal arm muscles (the triceps brachii and the anconeus) and the extrinsic extensors of the wrists and hands; it also provides cutaneous Nerve supply to the skin, sensory innervation to most of the back of the hand, except for the back of the little finger and adjacent half of the ring finger (which are innervated by the ulnar nerve). The radial nerve divides into a deep branch, which becomes the posterior interosseous nerve, and a su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Interosseous Nerve
The posterior interosseous nerve (or dorsal interosseous nerve/deep radial nerve) is a nerve in the forearm. It is the continuation of the deep branch of the radial nerve, after this has crossed the supinator muscle. It is considerably diminished in size compared to the deep branch of the radial nerve. The nerve fibers originate from cervical segments C7 and C8 in the spinal column. Structure Course It descends along the interosseous membrane, anterior to the extensor pollicis longus muscle, to the back of the carpus, where it presents a gangliform enlargement from which filaments are distributed to the ligaments and articulations of the carpus. Supply The posterior interosseous nerve supplies all the muscles of the posterior compartment of the forearm, except anconeus muscle, brachioradialis muscle, and extensor carpi radialis longus muscle. In other words, it supplies the following muscles: * Extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle — deep branch of radial nerve * Ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Innervated
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons). Nerves have historically been considered the basic units of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the electrochemical nerve impulses called action potentials that are transmitted along each of the axons to peripheral organs or, in the case of sensory nerves, from the periphery back to the central nervous system. Each axon is an extension of an individual neuron, along with other supportive cells such as some Schwann cells that coat the axons in myelin. Each axon is surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called the endoneurium. The axons are bundled together into groups called fascicles, and each fascicle is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the perineurium. The entire nerve is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the epineurium. Nerve cells (often called neurons) are further classified as either sensory or motor. In the central nervous system, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opponens Pollicis Muscle
The opponens pollicis is a small, triangular muscle in the hand, which functions to oppose the thumb. It is one of the three thenar muscles. It lies deep to the abductor pollicis brevis and lateral to the flexor pollicis brevis. Structure The opponens pollicis muscle is one of the three thenar muscles. It originates from the flexor retinaculum of the hand and the tubercle of the trapezium. It passes downward and laterally, and is inserted into the whole length of the metacarpal bone of the thumb on its radial side. Innervation Like the other thenar muscles, the opponens pollicis is innervated by the recurrent branch of the median nerve. In 20% of the population, opponens pollicis is innervated by the ulnar nerve. Blood supply The opponens pollicis receives its blood supply from the superficial palmar arch. Function ''Opposition of the thumb'' is a combination of actions that allows the tip of the thumb to touch the tips of other fingers. The part of apposition that this m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abductor Pollicis Brevis Muscle
The abductor pollicis brevis is a muscle in the hand that functions as an abductor of the thumb. Structure The abductor pollicis brevis is a flat, thin muscle located just under the skin. It is a thenar muscle, and therefore contributes to the bulk of the palm's thenar eminence. It originates from the flexor retinaculum of the hand, the tubercle of the scaphoid bone, and additionally sometimes from the tubercle of the trapezium. Running lateralward and downward, it is inserted by a thin, flat tendon into the lateral side of the base of the first phalanx of the thumb, and the capsule of the metacarpophalangeal joint. Nerve supply The abductor pollicis brevis is supplied by the recurrent branch of the median nerve (Roots C8-T1). Function Abduction of the thumb is defined as the movement of the thumb anteriorly, a direction perpendicular to the palm. The abductor pollicis brevis does this by acting across both the carpometacarpal joint and the metacarpophalangeal joint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distal
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether a vertebrate is a biped or a quadruped, due to the difference in the neuraxis, or if an invertebrate is a non-bilaterian. A non-bilaterian has no anterior or posterior surface for example but can still have a descriptor used such as proximal or distal in relation to a body part that is nearest to, or furthest from its middle. International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standards for subdisciplines of anatomy. For example, '' Terminologia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensor Pollicis Brevis Muscle
In human anatomy, the extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) is a skeletal muscle on the dorsal side of the forearm. It lies on the medial side of, and is closely connected with, the abductor pollicis longus. The extensor pollicis brevis belongs to the deep group of the posterior fascial compartment of the forearm. It is a part of the lateral border of the anatomical snuffbox. Structure The extensor pollicis brevis arises from the ulna distal to the abductor pollicis longus, from the interosseous membrane, and from the dorsal surface of the radius. Its direction is similar to that of the abductor pollicis longus, its tendon passing the same groove on the lateral side of the lower end of the radius, to be inserted into the base of the first phalanx of the thumb. Variation Absence; fusion of tendon with that of the extensor pollicis longus or abductor pollicis longus muscle. Function In a close relationship to the abductor pollicis longus, the extensor pollicis brevis both ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |