Proteasomes are essential
protein complex
A protein complex or multiprotein complex is a group of two or more associated polypeptide chains. Protein complexes are distinct from multidomain enzymes, in which multiple active site, catalytic domains are found in a single polypeptide chain.
...
es responsible for the degradation of
protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s by
proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Protein degradation is a major regulatory mechanism of gene expression and contributes substantially to shaping mammalian proteomes. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis o ...
, a
chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemistry, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. When chemical reactions occur, the atoms are rearranged and the reaction is accompanied by an Gibbs free energy, ...
that breaks
peptide bond
In organic chemistry, a peptide bond is an amide type of covalent chemical bond linking two consecutive alpha-amino acids from C1 (carbon number one) of one alpha-amino acid and N2 (nitrogen number two) of another, along a peptide or protein cha ...
s.
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
s that help such reactions are called
protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyzes proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the formation of new protein products ...
s. Proteasomes are found inside all
eukaryote
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms ...
s and
archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even thou ...
, and in some
bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
.
In eukaryotes, proteasomes are located both in the
nucleus and in the
cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell a ...
.
The proteasomal degradation pathway is essential for many cellular processes, including the
cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the sequential series of events that take place in a cell (biology), cell that causes it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the growth of the cell, duplication of its DNA (DNA re ...
, the regulation of
gene expression
Gene expression is the process (including its Regulation of gene expression, regulation) by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, proteins or non-coding RNA, ...
, and responses to
oxidative stress
Oxidative stress reflects an imbalance between the systemic manifestation of reactive oxygen species and a biological system's ability to readily detoxify the reactive intermediates or to repair the resulting damage. Disturbances in the normal ...
. The importance of proteolytic degradation inside cells and the role of ubiquitin in proteolytic pathways was acknowledged in the award of the 2004
Nobel Prize in Chemistry
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry () is awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to scientists in the various fields of chemistry. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895, awarded for outst ...
to
Aaron Ciechanover,
Avram Hershko and
Irwin Rose.
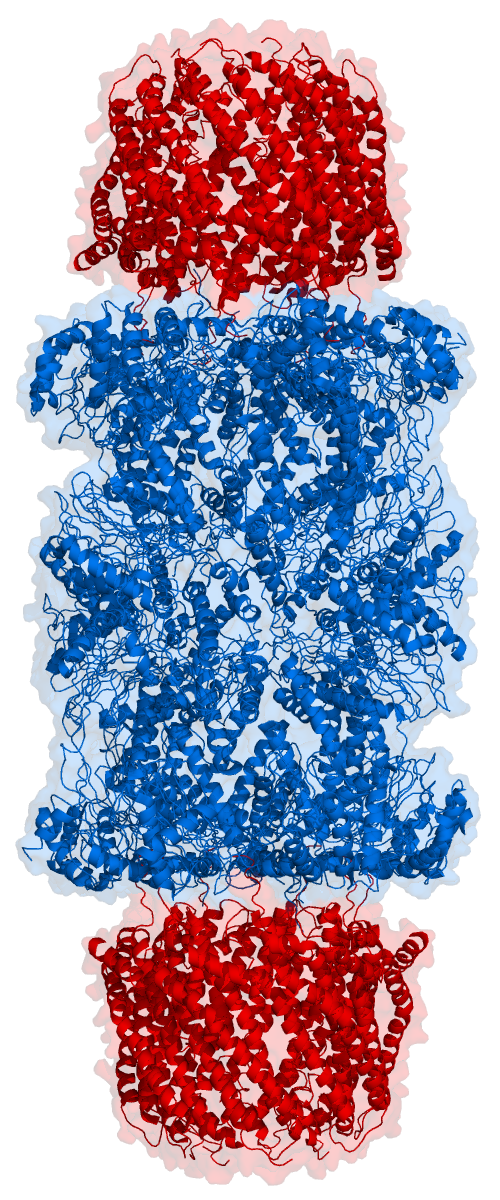
The core 20S proteasome (blue in the adjacent figure) is a cylindrical, compartmental protein complex of four stacked rings forming a central pore. Each ring is composed of seven individual proteins. The inner two rings are made of seven ''β subunits'' that contain three to seven protease
active site
In biology and biochemistry, the active site is the region of an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The active site consists of amino acid residues that form temporary bonds with the substrate, the ''binding s ...
s, within the central chamber of the complex. Access to these proteases is gated on the top of the 20S, and access is regulated by several large protein complexes, including the 19S Regulatory Particle forming the 26S Proteasome. In eukaryotes, proteins that are tagged with
Ubiquitin
Ubiquitin is a small (8.6 kDa) regulatory protein found in most tissues of eukaryotic organisms, i.e., it is found ''ubiquitously''. It was discovered in 1975 by Gideon Goldstein and further characterized throughout the late 1970s and 19 ...
are targeted to the 26S proteasome and is the penultimate step of the Ubiquitin Proteasome System (UPS). Proteasomes are part of a major mechanism by which
cells regulate the
concentration
In chemistry, concentration is the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Several types of mathematical description can be distinguished: '' mass concentration'', '' molar concentration'', '' number concentration'', ...
of particular proteins and degrade
misfolded proteins
Protein folding is the physical process by which a protein, after synthesis by a ribosome as a linear chain of amino acids, changes from an unstable random coil into a more ordered three-dimensional structure. This structure permits the prot ...
.
Protein that are destined for degradation by the 26S proteasome require two main elements: 1) the attachment of a small protein called
ubiquitin
Ubiquitin is a small (8.6 kDa) regulatory protein found in most tissues of eukaryotic organisms, i.e., it is found ''ubiquitously''. It was discovered in 1975 by Gideon Goldstein and further characterized throughout the late 1970s and 19 ...
and 2) an unstructured region of about 25 amino acids. Proteins that lack this unstructured region can have another motor,
cdc48 in yeast or P97 in humans, generate this unstructured region by a unique mechanism where ubiquitin is unfolded by cdc48 and its cofactors Npl4/Ufd1. The tagging of a target protein by ubiquitin is catalyzed by cascade of enzymes consisting of the
Ubiquitin-activating enzyme (E1),
Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme (E2), and
ubiquitin ligases (E3). Once a protein is tagged with a single ubiquitin molecule, this is a signal to other ligases to attach additional ubiquitin molecules. The result is a ''polyubiquitin chain'' that is bound by the proteasome, allowing it to degrade the tagged protein in an ATP dependent manner.
[ The degradation process by the proteasome yields ]peptide
Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides that have a molecular mass of 10,000 Da or more are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty am ...
s of about seven to eight amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
s long, which can then be further degraded into shorter amino acid sequences and used in synthesizing new proteins.
Discovery
Before the discovery of the ubiquitin–proteasome system, protein degradation in cells was thought to rely mainly on lysosome
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle that is found in all mammalian cells, with the exception of red blood cells (erythrocytes). There are normally hundreds of lysosomes in the cytosol, where they function as the cell’s degradation cent ...
s, membrane-bound organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell (biology), cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as Organ (anatomy), organs are to th ...
s with acid
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis ...
ic and protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyzes proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the formation of new protein products ...
-filled interiors that can degrade and then recycle exogenous proteins and aged or damaged organelles.histone
In biology, histones are highly basic proteins abundant in lysine and arginine residues that are found in eukaryotic cell nuclei and in most Archaeal phyla. They act as spools around which DNA winds to create structural units called nucleosomes ...
s led to the identification of an unexpected covalent
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atom ...
modification of the histone protein by a bond between a lysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. Lysine contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated form when the lysine is dissolved in water at physiological pH), an α-carboxylic acid group ( ...
side chain of the histone and the C-terminal
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, carboxy tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When t ...
glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (G ...
residue of ubiquitin
Ubiquitin is a small (8.6 kDa) regulatory protein found in most tissues of eukaryotic organisms, i.e., it is found ''ubiquitously''. It was discovered in 1975 by Gideon Goldstein and further characterized throughout the late 1970s and 19 ...
, a protein that had no known function.Nobel Prize in Chemistry
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry () is awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to scientists in the various fields of chemistry. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895, awarded for outst ...
for their work in discovering this system.[
Although ]electron microscopy
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of electrons as a source of illumination. It uses electron optics that are analogous to the glass lenses of an optical light microscope to control the electron beam, for instance focusing i ...
(EM) data revealing the stacked-ring structure of the proteasome became available in the mid-1980s,X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science of determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to Diffraction, diffract in specific directions. By measuring th ...
until 1994.holoenzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
cryogenic electron microscopy
Cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) is a transmission electron microscopy technique applied to samples cooled to cryogenic temperatures. For biological specimens, the structure is preserved by embedding in an environment of vitreous ice. An ...
, confirming the mechanisms by which the substrate is recognized, deubiquitylated, unfolded and degraded by the 26S proteasome. Detailed biochemistry has provided a general mechanism for ubiquitin-dependent degradation by the proteasome: binding of a substrate to the proteasome, engagement of an unstructured region to the AAA motor accompanied by a major conformational change of the proteasome, translocation dependent de-ubiquitination by Rpn11, followed by unfolding and proteolysis by the 20S core particle.Electron tomography Electron tomography (ET) is a tomography technique for obtaining detailed 3D structures of sub-cellular, macro-molecular, or materials specimens. Electron tomography is an extension of traditional transmission electron microscopy and uses a trans ...
(Cryo-ET) has also provided unique insight into proteasomes within cells. Looking at neurons, proteasomes were found to be in the same ground-state and processing states as determined by cryo-EM. Interestingly, most proteasomes were in the ground state suggesting that they were ready to start working when a cell undergoes proteotoxic stress. In a separate study, when protein aggregates in the form of poly-Gly-Ala repeats are overexpressed, proteasome are captured stalled on these aggregates. Cryo-ET of green algae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii found that 26S proteasomes within the nucleus cluster around the Nuclear pore complex
The nuclear pore complex (NPC), is a large protein complex giving rise to the nuclear pore. A great number of nuclear pores are studded throughout the nuclear envelope that surrounds the eukaryote cell nucleus. The pores enable the nuclear tra ...
and are specifically attached to the membrane.
Structure and organization
 The proteasome subcomponents are often referred to by their
The proteasome subcomponents are often referred to by their Svedberg
In chemistry, a Svedberg unit or svedberg (symbol S, sometimes Sv) is a non- SI metric unit for sedimentation coefficients. The Svedberg unit offers a measure of a particle's size indirectly based on its sedimentation rate under acceleration ...
sedimentation coefficient (denoted ''S''). The proteasome most exclusively used in mammals is the cytosolic 26S proteasome, which is about 2,000 kilodaltons (kDa) in molecular mass
The molecular mass () is the mass of a given molecule, often expressed in units of daltons (Da). Different molecules of the same compound may have different molecular masses because they contain different isotopes of an element. The derived quan ...
containing one 20S protein subcomplex and one 19S regulatory cap subcomplex. Doubly capped proteasomes are referred to as 30S proteasomes also exist in the cell. The 20S core is hollow and provides an enclosed cavity in which proteins are degraded; openings at the two ends of the core are gates that allow the target protein to enter. Each end of the core particle can associate with a 19S regulatory subunit that contains multiple ATPase
ATPases (, Adenosine 5'-TriPhosphatase, adenylpyrophosphatase, ATP monophosphatase, triphosphatase, ATP hydrolase, adenosine triphosphatase) are a class of enzymes that catalyze the decomposition of ATP into ADP and a free phosphate ion or ...
active site
In biology and biochemistry, the active site is the region of an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The active site consists of amino acid residues that form temporary bonds with the substrate, the ''binding s ...
s and ubiquitin binding sites; it is this structure that recognizes polyubiquitinated proteins and transfers them to the catalytic core.
Several alternative caps can also bind the 20S core: 11S (PA26) or Blm10 (PA200) are also known to associate with the core and can bind either one or both sides. An alternative form of regulatory subunit called the 11S particle can associate with the core in essentially the same manner as the 19S particle; the 11S may play a role in degradation of foreign peptides such as those produced after infection by a virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are ...
.
20S core particle
The number and diversity of subunits contained in the 20S core particle depends on the organism; the number of distinct and specialized subunits is larger in multicellular than unicellular organisms and larger in eukaryotes than in prokaryotes. All 20S particles consist of four stacked heptameric ring structures that are themselves composed of two different types of subunits; α subunits are structural in nature, whereas β subunits are predominantly catalytic
Catalysis () is the increase in reaction rate, rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst ...
. The α subunits are pseudoenzymes homologous to β subunits. They are assembled with their N-termini adjacent to that of the β subunits.angstrom
The angstrom (; ) is a unit of length equal to m; that is, one ten-billionth of a metre, a hundred-millionth of a centimetre, 0.1 nanometre, or 100 picometres. The unit is named after the Swedish physicist Anders Jonas Ångström (1814–18 ...
s (Å) by 115 Å. The interior chamber is at most 53 Å wide, though the entrance can be as narrow as 13 Å, suggesting that substrate proteins must be at least partially unfolded to enter.archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even thou ...
such as '' Thermoplasma acidophilum'', all the α and all the β subunits are identical, whereas eukaryotic proteasomes such as those in yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom (biology), kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are est ...
contain seven distinct types of each subunit. In mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s, the β1, β2, and β5 subunits are catalytic; although they share a common mechanism, they have three distinct substrate specificities considered chymotrypsin-like, trypsin
Trypsin is an enzyme in the first section of the small intestine that starts the digestion of protein molecules by cutting long chains of amino acids into smaller pieces. It is a serine protease from the PA clan superfamily, found in the dig ...
-like, and peptidyl-glutamyl peptide-hydrolyzing (PHGH).hematopoietic
Haematopoiesis (; ; also hematopoiesis in American English, sometimes h(a)emopoiesis) is the formation of blood cellular components. All cellular blood components are derived from haematopoietic stem cells. In a healthy adult human, roughly ten ...
cells in response to exposure to pro- inflammatory signal
A signal is both the process and the result of transmission of data over some media accomplished by embedding some variation. Signals are important in multiple subject fields including signal processing, information theory and biology.
In ...
s such as cytokine
Cytokines () are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling.
Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B cell, B lymphocytes, T cell, T lymphocytes ...
s, in particular, interferon gamma
Interferon gamma (IFNG or IFN-γ) is a dimerized soluble cytokine that is the only member of the type II class of interferons. The existence of this interferon, which early in its history was known as immune interferon, was described by E. F. ...
. The proteasome assembled with these alternative subunits is known as the '' immunoproteasome'', whose substrate specificity is altered relative to the normal proteasome.[
Recently an alternative proteasome was identified in human cells that lack the α3 core subunit.]BRD4
Bromodomain-containing protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BRD4'' gene.
BRD4 is a member of the BET (bromodomain and extra terminal domain) family, which also includes BRD2, BRD3, and BRDT. BRD4, similar to other BET fam ...
for degradation, lead to 26S proteasome generated peptides that release Inhibitor of apoptosis
Inhibitors of apoptosis are a group of proteins that mainly act on the intrinsic pathway that block programmed cell death, which can frequently lead to cancer or other effects for the cell if mutated or improperly regulated. Many of these inhibito ...
(IAPs) leading to Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biol ...
,
19S regulatory particle
The 19S particle in eukaryotes consists of 19 individual proteins and is divisible into two subassemblies, a 9-subunit base that binds directly to the α ring of the 20S core particle, and a 10-subunit lid. Six of the nine base proteins are ATPase subunits from the AAA Family, and an evolutionary homolog of these ATPases exists in archaea, called PAN (proteasome-activating nucleotidase). The association of the 19S and 20S particles requires the binding of ATP to the 19S ATPase subunits, and ATP hydrolysis is required for the assembled complex to degrade folded and ubiquitinated proteins. Note that only the step of substrate unfolding requires energy from ATP hydrolysis, while ATP-binding alone can support all the other steps required for protein degradation (e.g., complex assembly, gate opening, translocation, and proteolysis). In 2012, two independent efforts have elucidated the molecular architecture of the 26S proteasome by single particle electron microscopy.
In 2012, two independent efforts have elucidated the molecular architecture of the 26S proteasome by single particle electron microscopy.eIF3
Eukaryotic initiation factor 3 (eIF3) is a multiprotein complex that functions during the initiation phase of eukaryotic translation. It is essential for most forms of Eukaryotic translation#Cap-dependent initiation, cap-dependent and Eukaryotic ...
(hence called PCI subunits) assemble to a horseshoe-like structure enclosing the Rpn8/Rpn11 heterodimer. Rpn11, the deubiquitinating enzyme, is placed at the mouth of the AAA-ATPase hexamer, ideally positioned to remove ubiquitin moieties immediately before translocation of substrates into the 20S. The second ubiquitin receptor identified to date, Rpn10, is positioned at the periphery of the lid, near subunits Rpn8 and Rpn9.
Conformational changes of 19S
These initial structures showed that the 19S RP adopted a number of states (termed s1, s2, s3, and s4 in yeast) which provided a model for how substrates were recruited and subsequently degraded by the proteasome.
Regulation of the 20S by the 19S
The 19S regulatory particle is responsible for stimulating the 20S to degrade proteins. A primary function of the 19S regulatory ATPases is to open the gate in the 20S that blocks the entry of substrates into the degradation chamber. The mechanism by which the proteasomal ATPase open this gate has been recently elucidated.[ 20S gate opening, and thus substrate degradation, requires the C-termini of the proteasomal ATPases, which contains a specific motif (i.e., HbYX motif). The ATPases C-termini bind into pockets in the top of the 20S, and tether the ATPase complex to the 20S proteolytic complex, thus joining the substrate unfolding equipment with the 20S degradation machinery. Binding of these C-termini into these 20S pockets by themselves stimulates opening of the gate in the 20S in much the same way that a "key-in-a-lock" opens a door.][ The precise mechanism by which this "key-in-a-lock" mechanism functions has been structurally elucidated in the context of human 26S proteasome at near-atomic resolution, suggesting that the insertion of five C-termini of ATPase subunits Rpt1/2/3/5/6 into the 20S surface pockets are required to fully open the 20S gate, confirming work previously done on yeast proteasome.]
Other regulatory particles
11S
20S proteasomes can also associate with a second type of regulatory particle, the 11S regulatory particle, a heptameric structure that does not contain any ATPases and can promote the degradation of short peptide
Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides that have a molecular mass of 10,000 Da or more are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty am ...
s but not of complete proteins. It is presumed that this is because the complex cannot unfold larger substrates. This structure is also known as PA28, REG, or PA26.conformational change
In biochemistry, a conformational change is a change in the shape of a macromolecule, often induced by environmental factors.
A macromolecule is usually flexible and dynamic. Its shape can change in response to changes in its environment or othe ...
s to open the 20S gate suggest a similar mechanism for the 19S particle.major histocompatibility complex
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a large Locus (genetics), locus on vertebrate DNA containing a set of closely linked polymorphic genes that code for Cell (biology), cell surface proteins essential for the adaptive immune system. The ...
.[
]
BLM10/PA200
Yet another type of non-ATPase regulatory particle is the Blm10 (yeast) or PA200/ PSME4 (human). It opens only one α subunit in the 20S gate and itself folds into a dome with a very small pore over it.
Archaeal Proteasomes
Archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even thou ...
also contain a proteasome degradation pathway with a 20S core and a regulatory particle consisting of the Proteasome-Activating Nucleotidase (PAN), that shares similarities to the 19S proteasome. Like the eukaryotic 19S, PAN is a AAA-ATPase, containing N-terminal coiled coils, an OB ring, an ATPase domain with an HBXY motif that interacts with the archaeal 20S.
Bacterial Proteasomes
Actinobacteria have acquired a proteasome degradation pathway, including its own 20S core particle and a AAA protein motor, MPA (mycobacterial proteasome activator). Unlike the base subcomplex of the 19S, MPA is a homohexameric motor complex, containing the ATPase sites, a tandem (oligosaccharide/oligonucleotide-binding) OB ring, and Coiled coils that extend off N-termini off the OB ring. The C-terminus contains HBXY motifs that contact the 20S core particle in a similar way as with other regulatory particles. Targeting to MPA requires a prokaryotic protein, Prokaryotic ubiquitin-like protein (or Pup) that functions as ubiquitin as a tag that can be attached to a protein substrate, though the structure of Pup is unrelated to that of ubiquitin. Once attached, a puplyated protein can be targeted to MPA through the coiled-coil and can be directed through the AAA motor into the 20S for degradation.
Assembly
The assembly of the proteasome is a complex process due to the number of subunits that must associate to form an active complex. The β subunits are synthesized with N-terminal
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the amin ...
"propeptides" that are post-translationally modified during the assembly of the 20S particle to expose the proteolytic active site. The 20S particle is assembled from two half-proteasomes, each of which consists of a seven-membered pro-β ring attached to a seven-membered α ring. The association of the β rings of the two half-proteasomes triggers threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form when dissolved in water), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− ...
-dependent autolysis of the propeptides to expose the active site. These β interactions are mediated mainly by salt bridge
In electrochemistry, a salt bridge or ion bridge is an essential laboratory device discovered over 100 years ago. It contains an electrolyte solution, typically an inert solution, used to connect the Redox, oxidation and reduction Half cell, ...
s and hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the chemical property of a molecule (called a hydrophobe) that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water. In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, thu ...
interactions between conserved alpha helices
An alpha helix (or α-helix) is a sequence of amino acids in a protein that are twisted into a coil (a helix).
The alpha helix is the most common structural arrangement in the secondary structure of proteins. It is also the most extreme type of l ...
whose disruption by mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, ...
damages the proteasome's ability to assemble.gankyrin
26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 10 or gankyrin is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PSMD10'' gene. First isolated in 1998 by Tanaka et al.; Gankyrin is an oncogene, oncoprotein that is a component of the 19S regulatory cap ...
(names for yeast/mammals).ATPase
ATPases (, Adenosine 5'-TriPhosphatase, adenylpyrophosphatase, ATP monophosphatase, triphosphatase, ATP hydrolase, adenosine triphosphatase) are a class of enzymes that catalyze the decomposition of ATP into ADP and a free phosphate ion or ...
subunits and their main function seems to be to ensure proper assembly of the heterohexameric AAA-ATPase
ATPases (, Adenosine 5'-TriPhosphatase, adenylpyrophosphatase, ATP monophosphatase, triphosphatase, ATP hydrolase, adenosine triphosphatase) are a class of enzymes that catalyze the decomposition of ATP into ADP and a free phosphate ion or ...
ring. To date it is still under debate whether the base complex assembles separately, whether the assembly is templated by the 20S core particle, or whether alternative assembly pathways exist. In addition to the four assembly chaperones, the deubiquitinating enzyme Ubp6/ Usp14 also promotes base assembly, but it is not essential.
Protein degradation process
Ubiquitination and targeting
Proteins are targeted for degradation by the proteasome with covalent modification of a lysine residue that requires the coordinated reactions of three enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
s. In the first step, a ubiquitin-activating enzyme (known as E1) hydrolyzes ATP and adenylylates a ubiquitin
Ubiquitin is a small (8.6 kDa) regulatory protein found in most tissues of eukaryotic organisms, i.e., it is found ''ubiquitously''. It was discovered in 1975 by Gideon Goldstein and further characterized throughout the late 1970s and 19 ...
molecule. This is then transferred to E1's active-site cysteine
Cysteine (; symbol Cys or C) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the chemical formula, formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine enables the formation of Disulfide, disulfide bonds, and often participates in enzymatic reactions as ...
residue in concert with the adenylylation of a second ubiquitin.ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme
Ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, also known as E2 enzymes and more rarely as ''ubiquitin-carrier enzymes'', perform the second step in the ubiquitination reaction that targets a protein for degradation via the proteasome. The ubiquitination process ...
(E2). In the last step, a member of a highly diverse class of enzymes known as ubiquitin ligase
A ubiquitin ligase (also called an E3 ubiquitin ligase) is a protein that recruits an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme that has been loaded with ubiquitin, recognizes a protein substrate, and assists or directly catalyzes the transfer of ubiquitin ...
s (E3) recognizes the specific protein to be ubiquitinated and catalyzes the transfer of ubiquitin from E2 to this target protein. A target protein must be labeled with at least four ubiquitin monomers (in the form of a polyubiquitin chain) before it is recognized by the proteasome lid.substrate
Substrate may refer to:
Physical layers
*Substrate (biology), the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the surface or medium on which an organism grows or is attached
** Substrate (aquatic environment), the earthy material that exi ...
specificity to this system.ubiquitin
Ubiquitin is a small (8.6 kDa) regulatory protein found in most tissues of eukaryotic organisms, i.e., it is found ''ubiquitously''. It was discovered in 1975 by Gideon Goldstein and further characterized throughout the late 1970s and 19 ...
protein itself is 76 amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
s long and was named due to its ubiquitous nature, as it has a highly conserved sequence and is found in all known eukaryotic organisms.eukaryote
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms ...
s are arranged in tandem repeat
In genetics, tandem repeats occur in DNA when a pattern of one or more nucleotides is repeated and the repetitions are directly adjacent to each other, e.g. ATTCG ATTCG ATTCG, in which the sequence ATTCG is repeated three times.
Several protein ...
s, possibly due to the heavy transcription demands on these genes to produce enough ubiquitin for the cell. It has been proposed that ubiquitin is the slowest- evolving protein identified to date.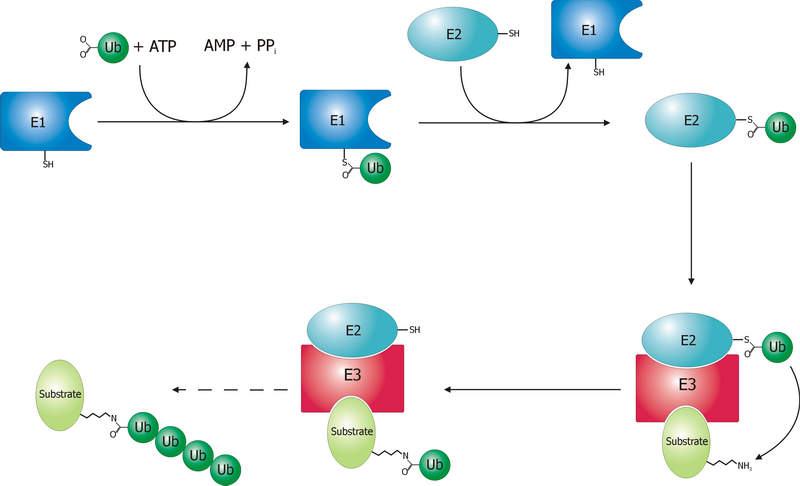
Intrinsic Ubiquitin Receptors of the Proteasome
Polyubiquitinated proteins are targeted to the proteasome through three identified Ubiquitin receptors: Rpn1, Rpn10, and Rpn13, that decorate the 19S RP and can direct an unstructured region of the target substrate into the N-domain of the AAA motor.
= Rpn10
=
Rpn10 was the first ubiquitin receptor identified on the proteasome. Rpn10 has a von Willebrand factor type A (VWA) attached to either a single Ubiquitin Interaction Motif (UIM), in yeast, or two UIMs in higher eukaryotes. The VWA domain binds between the base subcomplex and lid subcomplex of the 19S RP, while the UIM extends into a space over the AAA motor, though the UIM has not been seen in cryo-EM structures. NMR studies have shown that the UIM of Rpn10 binds mono-ubiquitin, and K48 di-ubiquitin with higher affinity. More recently, the C-terminus of Rpn10 in higher eukaryotes has been shown to bind an E3 ligase, UBE3A/E6AP (see Proteasomal Ligases).
= Rpn13
=
Rpn13 was identified as a ubiquitin receptor using a Yeast-2-hybrid screen.
= Rpn1
=
Ubiquitin binds Rpn1 via two sites, termed the T1 and T2 sites that were identified using NMR.
= Potential additional ubiquitin receptors.
=
Interestingly, mutations of Rpn1, Rpn10, and Rpn13 in yeast are not lethal, suggesting that additional sites may exist.
Proteasomal Deubiquitinases
Ubiquitin chains conjugated to a protein targeted for proteasomal degradation are normally removed by any one of the three proteasome-associated deubiquitylating enzymes (DUBs), which are Rpn11, Ubp6/USP14 and UCH37. Rpn11 is the essential DUB responsible for the en block removal of the ubiquitin signal from the substrate, while Ubp6/USP14 and UCH37 have been proposed to edit the ubiquitin code. Ubp6 knockouts in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungal microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have be ...
are viable, and there is no homolog of UCH37 in budding yeast, though they exist in Schizosaccharomyces pombe
''Schizosaccharomyces pombe'', also called "fission yeast", is a species of yeast used in traditional brewing and as a model organism in molecular and cell biology. It is a unicellular eukaryote, whose cells are rod-shaped. Cells typically meas ...
and higher eukaryotes. This process recycles ubiquitin and is essential to maintain the ubiquitin reservoir in cells.
Rpn11 (POH1)
 Rpn11 is an intrinsic, stoichiometric subunit of the 19S regulatory particle and is essential for the function of 26S proteasome. Rpn11 is a zinc-dependent, metalloprotease of the JAB1/MPN/Mov34 metalloenzyme (JAMM) family of DUBs, that was identified to be the essential DUB responsible for the en block removal of the ubiquitin chain from the protein substrate. Rpn11 forms an obligate dimer with Rpn8 forming an active DUB able to cleave all ubiquitin linkages.
Rpn11 is an intrinsic, stoichiometric subunit of the 19S regulatory particle and is essential for the function of 26S proteasome. Rpn11 is a zinc-dependent, metalloprotease of the JAB1/MPN/Mov34 metalloenzyme (JAMM) family of DUBs, that was identified to be the essential DUB responsible for the en block removal of the ubiquitin chain from the protein substrate. Rpn11 forms an obligate dimer with Rpn8 forming an active DUB able to cleave all ubiquitin linkages.
USP14/UBP6
In contrast to Rpn11, USP14 and UCH37 are the DUBs that do not always associated with the proteasome and are not essential for ubiquitin dependent degradation. Instead, these DUBs are proposed to "edit" the ubiquitin code of a substrate that is already engaged with the proteasome. In cells, about 10-40% of the proteasomes were found to have USP14 associated. Ubp6/USP14 is a member of the Ubiquitin Specific Protease (USP) family, utilizing a catalytic cysteine to cleave ubiquitin. Along with the USP, Ubp6/USP14 contains a Ubiquitin-like protein
Ubiquitin-like proteins (UBLs) are a family of small proteins involved in post-translational modification of other proteins in a cell (biology), cell, usually with a regulatory protein, regulatory function. The UBL protein family derives its name ...
(UBL) that binds the proteasome. Ubp6/USP14 is largely activated by the proteasome and exhibit a very low DUB activity alone.
UCH37
UCH37 is a Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase that activated upon binding the 26S proteasome through the ubiquitin receptor Rpn13. UCH37 is activated upon binding the proteasome through the C-terminal DEUBAD (DUB adaptor) domain that binds Rpn2.
Proteasomal Ligases
While Ubp6 and UCH37 can remodel the ubiquitin code on a substrate by removing Ubiquitins, Ubiquitin ligase
A ubiquitin ligase (also called an E3 ubiquitin ligase) is a protein that recruits an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme that has been loaded with ubiquitin, recognizes a protein substrate, and assists or directly catalyzes the transfer of ubiquitin ...
s can also associate with the proteasome and attach ubiquitins. For the 26S, this includes Hul5 in yeast (or UBE3C in humans) and UBE3A
Ubiquitin-protein ligase E3A (UBE3A) also known as E6AP ubiquitin-protein ligase (E6AP) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''UBE3A'' gene. This enzyme is involved in targeting proteins for degradation within cell (biology), cells.
...
/E6AP in humans.
Hul5 was first identified in yeast as a 26S associated ligase along with Ubp6 and they were proposed to remodel ubiquitin chains at the proteasome. Biochemical studies show that Hul5 can attach additional ubiquitins onto a ubiquitinated substrate effectively acting as an Ubiquitin ligase
A ubiquitin ligase (also called an E3 ubiquitin ligase) is a protein that recruits an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme that has been loaded with ubiquitin, recognizes a protein substrate, and assists or directly catalyzes the transfer of ubiquitin ...
. Hul5 has been proposed to bind Rpn2 in yeast, however this interaction has not been shown structurally. Further work needs to be done to understand how Hul5 works and what substrates are processed by Hul5.
UBE3A/E6AP binds the C-terminus of Rpn10 in mammals. NMR has shown that a previously described disordered region of Rpn10 becomes order upon binding E6AP forming a tight interaction in the low nanomolar range.
Proteasomal Chaperones
In addition to DUBs and Ligases, many other proteins associate with the proteasome and are important for degradation. These proteins typically consist of a Ubiquitin-like domain (UBL) and a Ubiquitin associating domain (UBA) with Dsk2, Rad23, and Ddi1 being classified as Proteasomal Chaperones. Dsk2 and Rad23 have UBLs that bind the receptors of the proteasome. Ddi1 has been shown to bind long K48-Ubiquitin chains and act as a protease and is probably not directly interacting with the proteasome.
Unfolding and translocation
After a protein has been ubiquitinated, it is recognized by the 19S regulatory particle in an ATP-dependent binding step.[ The substrate protein must then enter the interior of the 20S subunit to come in contact with the proteolytic active sites. Because the 20S particle's central channel is narrow and gated by the N-terminal tails of the α ring subunits, the substrates must be at least partially unfolded before they enter the core. The passage of the unfolded substrate into the core is called ''translocation'' and necessarily occurs after deubiquitination.][ For an idealized substrate, translocation drives deubiquitination.]tertiary structure
Protein tertiary structure is the three-dimensional shape of a protein. The tertiary structure will have a single polypeptide chain "backbone" with one or more protein secondary structures, the protein domains. Amino acid side chains and the ...
, and in particular nonlocal interactions such as disulfide bond
In chemistry, a disulfide (or disulphide in British English) is a compound containing a functional group or the anion. The linkage is also called an SS-bond or sometimes a disulfide bridge and usually derived from two thiol groups.
In inor ...
s, are sufficient to inhibit degradation.hydrolyzed
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysi ...
before translocation. While energy is needed for substrate unfolding, it is not required for translocation.[ Passage of the unfolded substrate through the opened gate occurs via ]facilitated diffusion
Facilitated diffusion (also known as facilitated transport or passive-mediated transport) is the process of spontaneous passive transport (as opposed to active transport) of molecules or ions across a biological membrane via specific transmembr ...
if the 19S cap is in the ATP-bound state.globular protein
In biochemistry, globular proteins or spheroproteins are spherical ("globe-like") proteins and are one of the common protein types (the others being fibrous, disordered and membrane proteins). Globular proteins are somewhat water-soluble (form ...
s is necessarily general, but somewhat dependent on the amino acid sequence
Protein primary structure is the linear sequence of amino acids in a peptide or protein. By convention, the primary structure of a protein is reported starting from the amino-terminal (N) end to the carboxyl-terminal (C) end. Protein biosynthe ...
. Long sequences of alternating glycine and alanine
Alanine (symbol Ala or A), or α-alanine, is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an amine group and a carboxylic acid group, both attached to the central carbon atom which also carries a methyl group sid ...
have been shown to inhibit substrate unfolding, decreasing the efficiency of proteasomal degradation; this results in the release of partially degraded byproducts, possibly due to the decoupling of the ATP hydrolysis and unfolding steps.silk
Silk is a natural fiber, natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be weaving, woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is most commonly produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoon (silk), c ...
fibroin
Fibroin is an insoluble protein present in silk produced by numerous insects, such as the larvae of ''Bombyx mori'', and other moth genera such as ''Antheraea'', ''Cricula trifenestrata, Cricula'', ''Samia (moth), Samia'' and ''Gonometa''. Sil ...
; in particular, certain Epstein–Barr virus
The Epstein–Barr virus (EBV), also known as human herpesvirus 4 (HHV-4), is one of the nine known Herpesviridae#Human herpesvirus types, human herpesvirus types in the Herpesviridae, herpes family, and is one of the most common viruses in ...
gene products bearing this sequence can stall the proteasome, helping the virus propagate by preventing antigen presentation
Antigen presentation is a vital immune process that is essential for T cell immune response triggering. Because T cells recognize only fragmented antigens displayed on cell surfaces, antigen processing must occur before the antigen fragment can ...
on the major histocompatibility complex.
Proteolysis
The proteasome functions as an endoprotease. The mechanism of proteolysis by the β subunits of the 20S core particle is through a threonine-dependent nucleophilic attack
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they a ...
. This mechanism may depend on an associated water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
molecule for deprotonation of the reactive threonine hydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy ...
. Degradation occurs within the central chamber formed by the association of the two β rings and normally does not release partially degraded products, instead reducing the substrate to short polypeptides typically 7–9 residues long, though they can range from 4 to 25 residues, depending on the organism and substrate. The biochemical mechanism that determines product length is not fully characterized.[
Although the proteasome normally produces very short peptide fragments, in some cases these products are themselves biologically active and functional molecules. Certain ]transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription (genetics), transcription of genetics, genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding t ...
s regulating the expression of specific genes, including one component of the mammalian complex NF-κB
Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) is a family of transcription factor protein complexes that controls transcription (genetics), transcription of DNA, cytokine production and cell survival. NF-κB is found i ...
, are synthesized as inactive precursors whose ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation converts them to an active form. Such activity requires the proteasome to cleave the substrate protein internally, rather than processively degrading it from one terminus. It has been suggested that long loops on these proteins' surfaces serve as the proteasomal substrates and enter the central cavity, while the majority of the protein remains outside.
Ubiquitin-independent degradation
Although most substrates must be ubiquitinated before being degraded by the 26S proteasome, there are some exceptions to this general rule, especially when the proteasome plays a normal role in the post- translational processing of the protein. The proteasomal activation of NF-κB by processing p105 into p50 via internal proteolysis is one major example.[ Some proteins that are hypothesized to be unstable due to intrinsically unstructured regions,]cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the sequential series of events that take place in a cell (biology), cell that causes it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the growth of the cell, duplication of its DNA (DNA re ...
regulators such as p53
p53, also known as tumor protein p53, cellular tumor antigen p53 (UniProt name), or transformation-related protein 53 (TRP53) is a regulatory transcription factor protein that is often mutated in human cancers. The p53 proteins (originally thou ...
have also been reported, although p53 is also subject to ubiquitin-dependent degradation.ornithine decarboxylase
The enzyme ornithine decarboxylase (, ODC) catalyzes the decarboxylation of ornithine (a product of the urea cycle) to form putrescine. This reaction is the committed step in polyamine synthesis. In humans, this protein has 461 amino acids ...
(ODC).
Evolution
 The 20S proteasome is both ubiquitous and essential in eukaryotes and archaea. The
The 20S proteasome is both ubiquitous and essential in eukaryotes and archaea. The bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
l order Actinomycetales
The Actinomycetales is an order of Actinomycetota. A member of the order is often called an actinomycete. Actinomycetales are generally gram-positive and anaerobic and have mycelia in a filamentous and branching growth pattern. Some actinomycet ...
, also share homologs of the 20S proteasome, whereas most bacteria possess heat shock genes hslV and hslU
The heat shock proteins HslV and HslU (HslVU complex; also known as ClpQ and ClpY respectively, or ClpQY) are expressed in many bacteria such as '' E. coli'' in response to cell stress.Ramachandran R, Hartmann C, Song HK, Huber R, Bochtler M. ( ...
, whose gene products are a multimeric protease arranged in a two-layered ring and an ATPase.protist
A protist ( ) or protoctist is any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a natural group, or clade, but are a paraphyletic grouping of all descendants of the last eukaryotic common ancest ...
s possess both the 20S and the hslV systems.[ Many bacteria also possess other homologs of the proteasome and an associated ATPase, most notably ClpP and ClpX. This redundancy explains why the HslUV system is not essential.
Sequence analysis suggests that the catalytic β subunits diverged earlier in evolution than the predominantly structural α subunits. In bacteria that express a 20S proteasome, the β subunits have high sequence identity to archaeal and eukaryotic β subunits, whereas the α sequence identity is much lower. The presence of 20S proteasomes in bacteria may result from lateral gene transfer, while the diversification of subunits among eukaryotes is ascribed to multiple ]gene duplication
Gene duplication (or chromosomal duplication or gene amplification) is a major mechanism through which new genetic material is generated during molecular evolution. It can be defined as any duplication of a region of DNA that contains a gene ...
events.[
]
Cell cycle control
Cell cycle progression is controlled by ordered action of cyclin-dependent kinase
Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are a predominant group of serine/threonine protein kinases involved in the regulation of the cell cycle and its progression, ensuring the integrity and functionality of cellular machinery. These regulatory enzym ...
s (CDKs), activated by specific cyclin
Cyclins are proteins that control the progression of a cell through the cell cycle by activating cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK).
Etymology
Cyclins were originally discovered by R. Timothy Hunt in 1982 while studying the cell cycle of sea urch ...
s that demarcate phases of the cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the sequential series of events that take place in a cell (biology), cell that causes it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the growth of the cell, duplication of its DNA (DNA re ...
. Mitotic cyclins, which persist in the cell for only a few minutes, have one of the shortest life spans of all intracellular proteins.[ After a CDK-cyclin complex has performed its function, the associated cyclin is polyubiquitinated and destroyed by the proteasome, which provides directionality for the cell cycle. In particular, exit from ]mitosis
Mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new Cell nucleus, nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives rise to genetically identic ...
requires the proteasome-dependent dissociation of the regulatory component cyclin B
Cyclin B is a member of the cyclin family. Cyclin B is a mitotic cyclin. The amount of cyclin B (which binds to Cdk1) and the activity of the cyclin B-Cdk complex rise through the cell cycle until mitosis, where they fall abruptly due to degr ...
from the mitosis promoting factor complex.vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
cells, "slippage" through the mitotic checkpoint leading to premature M phase
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the sequential series of events that take place in a cell that causes it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the growth of the cell, duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and ...
exit can occur despite the delay of this exit by the spindle checkpoint
The spindle checkpoint, also known as the metaphase-to-anaphase transition, the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC), the metaphase checkpoint, or the mitotic checkpoint, is a cell cycle checkpoint during metaphase of mitosis or meiosis that preven ...
.restriction point
The restriction point (R), also known as the Start or G1/S checkpoint, is a cell cycle checkpoint in the G1 phase of the animal cell cycle at which the cell becomes "committed" to the cell cycle, and after which extracellular signals are no lon ...
check between G1 phase and S phase
S phase (Synthesis phase) is the phase of the cell cycle in which DNA is replicated, occurring between G1 phase and G2 phase. Since accurate duplication of the genome is critical to successful cell division, the processes that occur during S ...
similarly involve proteasomal degradation of cyclin A, whose ubiquitination is promoted by the anaphase promoting complex (APC), an E3 ubiquitin ligase
A ubiquitin ligase (also called an E3 ubiquitin ligase) is a protein that recruits an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme that has been loaded with ubiquitin, recognizes a protein substrate, and assists or directly catalyzes the transfer of ubiquitin ...
.Gankyrin
26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 10 or gankyrin is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PSMD10'' gene. First isolated in 1998 by Tanaka et al.; Gankyrin is an oncogene, oncoprotein that is a component of the 19S regulatory cap ...
, a recently identified oncoprotein, is one of the 19S subcomponents that also tightly binds the cyclin-dependent kinase
Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are a predominant group of serine/threonine protein kinases involved in the regulation of the cell cycle and its progression, ensuring the integrity and functionality of cellular machinery. These regulatory enzym ...
CDK4 and plays a key role in recognizing ubiquitinated p53
p53, also known as tumor protein p53, cellular tumor antigen p53 (UniProt name), or transformation-related protein 53 (TRP53) is a regulatory transcription factor protein that is often mutated in human cancers. The p53 proteins (originally thou ...
, via its affinity for the ubiquitin ligase MDM2. Gankyrin is anti- apoptotic and has been shown to be overexpressed in some tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
cell types such as hepatocellular carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer in adults and is currently the most common cause of death in people with cirrhosis. HCC is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide.
HCC most common ...
.
Regulation of plant growth
In plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
s, signaling by auxin
Auxins (plural of auxin ) are a class of plant hormones (or plant-growth regulators) with some morphogen-like characteristics. Auxins play a cardinal role in coordination of many growth and behavioral processes in plant life cycles and are essent ...
s, or phytohormone
Plant hormones (or phytohormones) are signal molecules, produced within plants, that occur in extremely low concentrations. Plant hormones control all aspects of plant growth and development, including embryogenesis, the regulation of organ si ...
s that order the direction and tropism
In biology, a tropism is a phenomenon indicating the growth or turning movement of an organism, usually a plant, in response to an environmental stimulus (physiology), stimulus. In tropisms, this response is dependent on the direction of the s ...
of plant growth, induces the targeting of a class of transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription (genetics), transcription of genetics, genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding t ...
repressors known as Aux/IAA proteins for proteasomal degradation. These proteins are ubiquitinated by SCFTIR1, or SCF in complex with the auxin receptor TIR1. Degradation of Aux/IAA proteins derepresses transcription factors in the auxin-response factor (ARF) family and induces ARF-directed gene expression.
Apoptosis
Both internal and external signals
A signal is both the process and the result of Signal transmission, transmission of data over some transmission media, media accomplished by embedding some variation. Signals are important in multiple subject fields including signal processin ...
can lead to the induction of apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biol ...
, or programmed cell death. The resulting deconstruction of cellular components is primarily carried out by specialized proteases known as caspases, but the proteasome also plays important and diverse roles in the apoptotic process. The involvement of the proteasome in this process is indicated by both the increase in protein ubiquitination, and of E1, E2, and E3 enzymes that is observed well in advance of apoptosis.thymocyte
A thymocyte is an immune cell present in the thymus, before it undergoes transformation into a T cell. Thymocytes are produced as stem cells in the bone marrow and reach the thymus via the blood.
Thymopoiesis describes the process which turns thy ...
s and neuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural net ...
s — are prevented from undergoing apoptosis on exposure to proteasome inhibitors. The mechanism for this effect is not clear, but is hypothesized to be specific to cells in quiescent states, or to result from the differential activity of the pro-apoptotic kinase
In biochemistry, a kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule don ...
JNK.chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
agents such as bortezomib and .
Response to cellular stress
In response to cellular stresses – such as infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
, heat shock, or oxidative damage
Oxidative stress reflects an imbalance between the systemic manifestation of reactive oxygen species and a biological system's ability to readily detoxify the reactive intermediates or to repair the resulting damage. Disturbances in the normal r ...
– heat shock protein
Heat shock proteins (HSPs) are a family of proteins produced by cells in response to exposure to stressful conditions. They were first described in relation to heat shock, but are now known to also be expressed during other stresses including ex ...
s that identify misfolded or unfolded proteins and target them for proteasomal degradation are expressed. Both Hsp27
Heat shock protein 27 (Hsp27) also known as heat shock protein beta-1 (HSPB1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HSPB1'' gene.
Hsp27 is a chaperone of the sHsp (small heat shock protein) group among α- crystallin, Hsp20, and ot ...
and Hsp90
Hsp90 (heat shock protein 90) is a chaperone (protein), chaperone protein that assists other proteins to protein folding, fold properly, stabilizes proteins against heat stress, and aids in protein degradation. It also stabilizes a number of ...
— chaperone proteins have been implicated in increasing the activity of the ubiquitin-proteasome system, though they are not direct participants in the process.Hsp70
The 70 kilodalton heat shock proteins (Hsp70s or DnaK) are a family of conserved ubiquitously expressed heat shock proteins. Proteins with similar structure exist in virtually all living organisms and play crucial roles in the development of can ...
, on the other hand, binds exposed hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the chemical property of a molecule (called a hydrophobe) that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water. In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, thu ...
patches on the surface of misfolded proteins and recruits E3 ubiquitin ligases such as CHIP to tag the proteins for proteasomal degradation.histone
In biology, histones are highly basic proteins abundant in lysine and arginine residues that are found in eukaryotic cell nuclei and in most Archaeal phyla. They act as spools around which DNA winds to create structural units called nucleosomes ...
s.aging
Ageing (or aging in American English) is the process of becoming Old age, older until death. The term refers mainly to humans, many other animals, and fungi; whereas for example, bacteria, perennial plants and some simple animals are potentiall ...
.Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease primarily of the central nervous system, affecting both motor system, motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually and non-motor issues become ...
and Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease and the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems wit ...
, large insoluble aggregates of misfolded proteins can form and then result in neurotoxicity
Neurotoxicity is a form of toxicity in which a biological, chemical, or physical agent produces an adverse effect on the structure or function of the central and/or peripheral nervous system. It occurs when exposure to a substance – specifical ...
, through mechanisms that are not yet well understood. Decreased proteasome activity has been suggested as a cause of aggregation and Lewy body
Lewy bodies are the inclusion bodies – abnormal aggregations of protein – that develop inside neurons affected by Parkinson's disease (PD), the Lewy body dementias ( Parkinson's disease dementia and dementia with Lewy bodies (DL ...
formation in Parkinson's.yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom (biology), kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are est ...
models of Parkinson's are more susceptible to toxicity from α-synuclein, the major protein component of Lewy bodies, under conditions of low proteasome activity.autism spectrum disorder
Autism, also known as autism spectrum disorder (ASD), is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by differences or difficulties in social communication and interaction, a preference for predictability and routine, sensory processing di ...
s, and muscle and nerve diseases such as inclusion body myopathy.[
]
Role in the immune system
The proteasome plays a straightforward but critical role in the function of the adaptive immune system
The adaptive immune system (AIS), also known as the acquired immune system, or specific immune system is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized cells, organs, and processes that eliminate pathogens specifically. The ac ...
. Peptide antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule, moiety, foreign particulate matter, or an allergen, such as pollen, that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response.
...
s are displayed by the major histocompatibility complex
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a large Locus (genetics), locus on vertebrate DNA containing a set of closely linked polymorphic genes that code for Cell (biology), cell surface proteins essential for the adaptive immune system. The ...
class I (MHC) proteins on the surface of antigen-presenting cell
An antigen-presenting cell (APC) or accessory cell is a Cell (biology), cell that displays an antigen bound by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins on its surface; this process is known as antigen presentation. T cells may recognize the ...
s. These peptides are products of proteasomal degradation of proteins originated by the invading pathogen
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a Germ theory of d ...
. Although constitutively expressed proteasomes can participate in this process, a specialized complex composed of proteins, whose expression is induced by interferon gamma
Interferon gamma (IFNG or IFN-γ) is a dimerized soluble cytokine that is the only member of the type II class of interferons. The existence of this interferon, which early in its history was known as immune interferon, was described by E. F. ...
, are the primary producers of peptides which are optimal in size and composition for MHC binding. These proteins whose expression increases during the immune response include the 11S regulatory particle, whose main known biological role is regulating the production of MHC ligands, and specialized β subunits called β1i, β2i, and β5i with altered substrate specificity. The complex formed with the specialized β subunits is known as the '' immunoproteasome''.thymoproteasome
Thymoproteasome is a special kind of proteasome, which is present in vertebrates. In the body it is located in thymus, exclusively in cortical thymic epithelial cells (cTECs). But in thymus we can also find another type of specific proteasome, im ...
" whose function is as yet unclear.C-terminus
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, carboxy tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comp ...
, as peptides bind by hydrogen bond
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (H-bond) is a specific type of molecular interaction that exhibits partial covalent character and cannot be described as a purely electrostatic force. It occurs when a hydrogen (H) atom, Covalent bond, covalently b ...
ing and by close contacts with a region called the "B pocket" on the MHC surface. Many MHC class I alleles prefer hydrophobic C-terminal residues, and the immunoproteasome complex is more likely to generate hydrophobic C-termini.NF-κB
Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) is a family of transcription factor protein complexes that controls transcription (genetics), transcription of DNA, cytokine production and cell survival. NF-κB is found i ...
, an anti- apoptotic and pro- inflammatory regulator of cytokine
Cytokines () are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling.
Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B cell, B lymphocytes, T cell, T lymphocytes ...
expression, proteasomal activity has been linked to inflammatory and autoimmune disease
An autoimmune disease is a condition that results from an anomalous response of the adaptive immune system, wherein it mistakenly targets and attacks healthy, functioning parts of the body as if they were foreign organisms. It is estimated tha ...
s. Increased levels of proteasome activity correlate with disease activity and have been implicated in autoimmune diseases including systemic lupus erythematosus
Lupus, formally called systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Common ...
and rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and h ...
.Intracellular antibody-mediated proteolysis Intracellular antibody-mediated degradation (IAMD) is a neutralization mechanism of intracellular antibody-mediated immunity whereby an effector protein, TRIM21, directs antibody bound virus, virions to the proteasome where they are degraded. As yet ...
of antibody-bound virions. In this neutralisation pathway, TRIM21
Tripartite motif-containing protein 21, also known as E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM21, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TRIM21'' gene. Alternatively spliced transcript variants for this gene have been described but the full-lengt ...
(a protein of the tripartite motif family) binds with immunoglobulin G
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a type of antibody. Representing approximately 75% of serum antibodies in humans, IgG is the most common type of antibody found in blood circulation. IgG molecules are created and released by plasma B cells. Each IgG ...
to direct the virion to the proteasome where it is degraded.
Proteasome inhibitors
 Proteasome inhibitors have effective anti-
Proteasome inhibitors have effective anti-tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
activity in cell culture
Cell culture or tissue culture is the process by which cell (biology), cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. After cells of interest have been Cell isolation, isolated from living tissue, ...
, inducing apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biol ...
by disrupting the regulated degradation of pro-growth cell cycle proteins.Streptomyces
''Streptomyces'', from στρεπτός (''streptós''), meaning "twisted", and μύκης (''múkés''), meaning "fungus", is the largest genus of Actinomycetota, and the type genus of the family Streptomycetaceae. Over 700 species of ''St ...
'' bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
, was the first non-peptidic proteasome inhibitor discoveredMillennium Pharmaceuticals
Takeda Oncology (originally Millennium Pharmaceuticals) is a biopharmaceutical company based in Cambridge, Massachusetts. It is a fully owned subsidiary of Takeda Pharmaceutical.
Takeda Oncology's research, development and commercialization ac ...
, now part of Takeda Pharmaceuticals. Lactacystin covalently modifies the amino-terminal threonine of catalytic β subunits of the proteasome, particularly the β5 subunit responsible for the proteasome's chymotrypsin-like activity. This discovery helped to establish the proteasome as a mechanistically novel class of protease: an amino-terminal threonine protease.
Bortezomib (Boronated MG132), a molecule developed by Millennium Pharmaceuticals
Takeda Oncology (originally Millennium Pharmaceuticals) is a biopharmaceutical company based in Cambridge, Massachusetts. It is a fully owned subsidiary of Takeda Pharmaceutical.
Takeda Oncology's research, development and commercialization ac ...
and marketed as Velcade, is the first proteasome inhibitor to reach clinical use as a chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
agent.[United States Food and Drug Administration press release](_blank)
13 May 2003. Access date 29 December 2006. See als
FDA Velcade information page
Bortezomib is used in the treatment of multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma (MM), also known as plasma cell myeloma and simply myeloma, is a cancer of plasma cells, a type of white blood cell that normally produces antibody, antibodies. Often, no symptoms are noticed initially. As it progresses, bone ...
.blood serum
Serum () is the fluid and solvent component of blood which does not play a role in clotting. It may be defined as blood plasma without the clotting factors, or as blood with all cells and clotting factors removed. Serum contains all proteins ex ...
that decrease to normal levels in response to successful chemotherapy.pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer arises when cell (biology), cells in the pancreas, a glandular organ behind the stomach, begin to multiply out of control and form a Neoplasm, mass. These cancerous cells have the malignant, ability to invade other parts of ...
.non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), also known as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, is a group of blood cancers that includes all types of lymphomas except Hodgkin lymphomas. Symptoms include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and tire ...
.ritonavir
Ritonavir, sold under the brand name Norvir, is an antiretroviral medication used along with other medications to treat HIV/AIDS. This combination treatment is known as highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). Ritonavir is a protease inhi ...
, marketed as Norvir, was developed as a protease inhibitor and used to target HIV infection. However, it has been shown to inhibit proteasomes as well as free proteases; to be specific, the chymotrypsin-like activity of the proteasome is inhibited by ritonavir, while the trypsin
Trypsin is an enzyme in the first section of the small intestine that starts the digestion of protein molecules by cutting long chains of amino acids into smaller pieces. It is a serine protease from the PA clan superfamily, found in the dig ...
-like activity is somewhat enhanced.glioma
A glioma is a type of primary tumor that starts in the glial cells of the brain or spinal cord. They are malignant but some are extremely slow to develop. Gliomas comprise about 30% of all brain and central nervous system tumors and 80% of ...
cells.skin graft
Skin grafting, a type of graft (surgery), graft surgery, involves the organ transplant, transplantation of skin without a defined circulation. The transplanted biological tissue, tissue is called a skin graft.
Surgeons may use skin grafting to ...
s found a reduction in the size of lesions from psoriasis
Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by patches of abnormal skin. These areas are red, pink, or purple, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small localized patches to complete b ...
after treatment with a proteasome inhibitor.rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the Order (biology), order Rodentia ( ), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and Mandible, lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal specie ...
models of asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wh ...
.Fluorescent
Fluorescence is one of two kinds of photoluminescence, the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. When exposed to ultraviolet radiation, many substances will glow (fluoresce) with color ...
inhibitors have also been developed to specifically label the active sites of the assembled proteasome.
Clinical significance
The proteasome and its subunits are of clinical significance for at least two reasons: (1) a compromised complex assembly or a dysfunctional proteasome can be associated with the underlying pathophysiology of specific diseases, and (2) they can be exploited as drug targets for therapeutic interventions. More recently, more effort has been made to consider the proteasome for the development of novel diagnostic markers and strategies. An improved and comprehensive understanding of the pathophysiology of the proteasome should lead to clinical applications in the future.
The proteasomes form a pivotal component for the ubiquitin–proteasome system (UPS) and corresponding cellular Protein Quality Control (PQC). Protein ubiquitination
Ubiquitin is a small (8.6 kDa) regulatory protein found in most tissues of eukaryotic organisms, i.e., it is found ''ubiquitously''. It was discovered in 1975 by Gideon Goldstein and further characterized throughout the late 1970s and 19 ...
and subsequent proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Protein degradation is a major regulatory mechanism of gene expression and contributes substantially to shaping mammalian proteomes. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis o ...
and degradation by the proteasome are important mechanisms in the regulation of the cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the sequential series of events that take place in a cell (biology), cell that causes it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the growth of the cell, duplication of its DNA (DNA re ...
, cell growth
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
* Cellphone, a phone connected to a cellular network
* Clandestine cell, a penetration-resistant form of a secret or outlawed organization
* Electrochemical cell, a de ...
and differentiation, gene transcription, signal transduction and apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biol ...
. Proteasome defects lead to reduced proteolytic activity and the accumulation of damaged or misfolded proteins, which may contribute to neurodegenerative disease, cardiovascular diseases, inflammatory responses and autoimmune diseases,malignancies
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse; the term is most familiar as a characterization of cancer.
A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous ''benign'' tumor in that a malignancy is not ...
.
Research has implicated UPS defects in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative and myodegenerative disorders, including Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease and the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems wit ...
, Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease primarily of the central nervous system, affecting both motor system, motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually and non-motor issues become ...
Pick's disease
Frontotemporal dementia (FTD), also called frontotemporal degeneration disease or frontotemporal neurocognitive disorder, encompasses several types of dementia involving the progressive degeneration of the brain's frontal and temporal lobes. Men ...
,amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or—in the United States—Lou Gehrig's disease (LGD), is a rare, Terminal illness, terminal neurodegenerative disease, neurodegenerative disorder that results i ...
(ALS),Huntington's disease
Huntington's disease (HD), also known as Huntington's chorea, is an incurable neurodegenerative disease that is mostly Genetic disorder#Autosomal dominant, inherited. It typically presents as a triad of progressive psychiatric, cognitive, and ...
,Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease
Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (CJD) is an incurable, always fatal neurodegenerative disease belonging to the transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (TSE) group. Early symptoms include memory problems, behavioral changes, poor coordination, visu ...
, and motor neuron diseases, polyglutamine (PolyQ) diseases, muscular dystrophies
Muscular dystrophies (MD) are a genetically and clinically heterogeneous group of rare neuromuscular diseases that cause progressive weakness and breakdown of skeletal muscles over time. The disorders differ as to which muscles are primarily aff ...
and several rare forms of neurodegenerative diseases associated with dementia
Dementia is a syndrome associated with many neurodegenerative diseases, characterized by a general decline in cognitive abilities that affects a person's ability to perform activities of daily living, everyday activities. This typically invo ...
. As part of the ubiquitin–proteasome system (UPS), the proteasome maintains cardiac protein homeostasis and thus plays a significant role in cardiac ischemic
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems ...
injury, ventricular hypertrophy
Ventricular hypertrophy (VH) is thickening of the walls of a ventricle (lower chamber) of the heart. Although left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is more common, right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH), as well as concurrent hypertrophy of both vent ...
and heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome caused by an impairment in the heart's ability to Cardiac cycle, fill with and pump blood.
Although symptoms vary based on which side of the heart is affected, HF ...
. Additionally, evidence is accumulating that the UPS plays an essential role in malignant transformation. UPS proteolysis plays a major role in responses of cancer cells to stimulatory signals that are critical for the development of cancer. Accordingly, gene expression by degradation of transcription factors
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The fun ...
, such as p53
p53, also known as tumor protein p53, cellular tumor antigen p53 (UniProt name), or transformation-related protein 53 (TRP53) is a regulatory transcription factor protein that is often mutated in human cancers. The p53 proteins (originally thou ...
, c-jun, c-Fos
Protein c-Fos is a proto-oncogene that is the human homolog of the retroviral oncogene v-fos. It is encoded in humans by the ''FOS'' gene. It was first discovered in rat fibroblasts as the transforming gene of the FBJ MSV (Finkel–Biskis–Ji ...
, NF-κB
Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) is a family of transcription factor protein complexes that controls transcription (genetics), transcription of DNA, cytokine production and cell survival. NF-κB is found i ...
, c-Myc
''Myc'' is a family of regulator genes and proto-oncogenes that code for transcription factors. The ''Myc'' family consists of three related human genes: ''c-myc'' ( MYC), ''l-myc'' ( MYCL), and ''n-myc'' ( MYCN). ''c-myc'' (also sometimes ...
, HIF-1α, MATα2, STAT3
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is a transcription factor which in humans is encoded by the ''STAT3'' gene. It is a member of the STAT protein family.
Function
STAT3 is a member of the STAT protein family. In respon ...
, sterol-regulated element-binding proteins and androgen receptors
The androgen receptor (AR), also known as NR3C4 (nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 4), is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by binding any of the androgenic hormones, including testosterone and dihydrotestosterone, in th ...
are all controlled by the UPS and thus involved in the development of various malignancies. Moreover, the UPS regulates the degradation of tumor suppressor gene products such as adenomatous polyposis coli
Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) also known as deleted in polyposis 2.5 (DP2.5) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''APC'' gene. The APC protein is a Down-regulation, negative regulator that controls beta-catenin concentrations and i ...
(APC) in colorectal cancer, retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma (Rb) is a rare form of cancer that rapidly develops from the immature cells of a retina, the light-detecting tissue of the eye. It is the most common primary malignant intraocular cancer in children, and 80% of retinoblastoma cas ...
(Rb). and von Hippel–Lindau tumor suppressor (VHL), as well as a number of proto-oncogenes ( Raf, Myc, Myb, Rel, Src, Mos, ABL). The UPS is also involved in the regulation of inflammatory responses. This activity is usually attributed to the role of proteasomes in the activation of NF-κB which further regulates the expression of pro inflammatory cytokines
Cytokines () are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling.
Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B cell, B lymphocytes, T cell, T lymphocytes ...
such as TNF-α, IL-β, IL-8, adhesion molecules (ICAM-1
ICAM-1 (Intercellular adhesion molecule, Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1) also known as CD54 (Cluster of Differentiation 54) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ICAM1'' gene. This gene encodes a cell surface glycoprotein which is ty ...
, VCAM-1, P-selectin
P-selectin is a type-1 transmembrane protein that in humans is encoded by the SELP gene.
P-selectin functions as a cell adhesion molecule (CAM) on the surfaces of activated endothelial cells, which line the inner surface of blood vessels, and a ...
) and prostaglandins
Prostaglandins (PG) are a group of physiologically active lipid compounds called eicosanoids that have diverse hormone-like effects in animals. Prostaglandins have been found in almost every tissue in humans and other animals. They are derive ...
and nitric oxide
Nitric oxide (nitrogen oxide, nitrogen monooxide, or nitrogen monoxide) is a colorless gas with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes den ...
(NO).autoimmune disease
An autoimmune disease is a condition that results from an anomalous response of the adaptive immune system, wherein it mistakenly targets and attacks healthy, functioning parts of the body as if they were foreign organisms. It is estimated tha ...
patients with SLE, Sjögren syndrome Sjögren is a Swedish surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Anders Johan Sjögren (1794–1855), Finnish linguist, historian, ethnographer and explorer
* Ann Mari Sjögren, Swedish fantasy artist and illustrator
* Christer Sjögren, ...
and rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and h ...
(RA) predominantly exhibit circulating proteasomes which can be applied as clinical biomarkers.
See also
* The Proteolysis Map
* DSS1/SEM1 protein family
* Exosome complex
The exosome complex (or PM/Scl complex, often just called the exosome) is a multi-protein intracellular complex capable of degrading various types of RNA (ribonucleic acid) molecules. Exosome complexes are found in both eukaryotic cells and ar ...
* Endoplasmic-reticulum-associated protein degradation
Endoplasmic-reticulum-associated protein degradation (ERAD) designates a Cell (biology), cellular pathway which targets misfolded proteins of the endoplasmic reticulum for ubiquitination and subsequent degradation by a protein-degrading complex, c ...
* JUNQ and IPOD
References
Further reading
*
The Yeast 26S Proteasome with list of subunits and pictures
*
*
*
*
External links
Proteasome subunit nomenclature guide3D proteasome structures in the EM Data Bank(EMDB)
*Key points o
proteasome function
{{Authority control
Proteins
Protein complexes
Organelles
Apoptosis
 Proteasomes are essential
Proteasomes are essential  The proteasome subcomponents are often referred to by their
The proteasome subcomponents are often referred to by their  In 2012, two independent efforts have elucidated the molecular architecture of the 26S proteasome by single particle electron microscopy. In 2016, three independent efforts have determined the first near-atomic resolution structure of the human 26S proteasome in the absence of substrates by cryo-EM. In the heart of the 19S, directly adjacent to the 20S, are the AAA-ATPases ( AAA proteins) that assemble to a heterohexameric ring of the order Rpt1/Rpt2/Rpt6/Rpt3/Rpt4/Rpt5. This ring is a trimer of dimers: Rpt1/Rpt2, Rpt6/Rpt3, and Rpt4/Rpt5 dimerize via their N-terminal coiled-coils. These coiled-coils protrude from the hexameric ring. The largest regulatory particle non-ATPases Rpn1 and Rpn2 bind to the tips of Rpt1/2 and Rpt6/3, respectively. The ubiquitin receptor Rpn13 binds to Rpn2 and completes the base sub-complex. The lid covers one half of the AAA-ATPase hexamer (Rpt6/Rpt3/Rpt4) and, unexpectedly, directly contacts the 20S via Rpn6 and to lesser extent Rpn5. The subunits Rpn9, Rpn5, Rpn6, Rpn7, Rpn3, and Rpn12, which are structurally related among themselves and to subunits of the COP9 complex and
In 2012, two independent efforts have elucidated the molecular architecture of the 26S proteasome by single particle electron microscopy. In 2016, three independent efforts have determined the first near-atomic resolution structure of the human 26S proteasome in the absence of substrates by cryo-EM. In the heart of the 19S, directly adjacent to the 20S, are the AAA-ATPases ( AAA proteins) that assemble to a heterohexameric ring of the order Rpt1/Rpt2/Rpt6/Rpt3/Rpt4/Rpt5. This ring is a trimer of dimers: Rpt1/Rpt2, Rpt6/Rpt3, and Rpt4/Rpt5 dimerize via their N-terminal coiled-coils. These coiled-coils protrude from the hexameric ring. The largest regulatory particle non-ATPases Rpn1 and Rpn2 bind to the tips of Rpt1/2 and Rpt6/3, respectively. The ubiquitin receptor Rpn13 binds to Rpn2 and completes the base sub-complex. The lid covers one half of the AAA-ATPase hexamer (Rpt6/Rpt3/Rpt4) and, unexpectedly, directly contacts the 20S via Rpn6 and to lesser extent Rpn5. The subunits Rpn9, Rpn5, Rpn6, Rpn7, Rpn3, and Rpn12, which are structurally related among themselves and to subunits of the COP9 complex and 


 Rpn11 is an intrinsic, stoichiometric subunit of the 19S regulatory particle and is essential for the function of 26S proteasome. Rpn11 is a zinc-dependent, metalloprotease of the JAB1/MPN/Mov34 metalloenzyme (JAMM) family of DUBs, that was identified to be the essential DUB responsible for the en block removal of the ubiquitin chain from the protein substrate. Rpn11 forms an obligate dimer with Rpn8 forming an active DUB able to cleave all ubiquitin linkages. The active site of Rpn11 is formed through metal coordination of the catalytic zinc and this site is covered by an Insert-1 loop that covers this active site. The structure is very similar to that of a related JAMM DUB, AMSH, that is responsible for K63 ubiquitin cleavage, however it lacks the residues that are key for AMSH's linkage specificity. The structure of Rpn11 bound to ubiquitin revealed that the C-terminus of Ubiquitin pushes the insert-1 loop into an beta-sheet providing access to the catalytic zinc. This structure combined with detailed biochemistry revealed that the DUB activity of Rpn11 was accelerated at least 10-fold by the translocation of the protein substrate, suggesting that the translocation delivered the Ub substrate to the active site of Rpn11. This model of translocation-dependent deubiquitination was later confirmed by cryoEM of both the yeast and human proteasome bound to a substrate, both of which recapitulated the crystal structure of Ubiquitin bound to Rpn11. Single molecule studies on the yeast proteasome confirmed that the DUB rates measured by biochemistry were indeed stimulated by translocation. More recent biochemical and single molecule studies have shown that on top of being the essential DUB, Rpn11 is also a ubiquitin receptor that acts as an allosteric sensor to enable proper engagement of a substrate by the proteasome.
In addition to binding Ubiquitin, Rpn11 has also recently been shown to be a binding spot for many proteasome associated factors. Three recent cryo-EM studies have shown that PITHD1 (Proteasome Interacting Thioredoxin Domain 1) and TXNL1 (Thioredoxin-like protein 1) bind the proteasome by binding Rpn2/Rpn10 and making an interaction with the insert-1 loop of Rpn11. PITHD1 binds the proteasome in a resting state and has been proposed to be a dormancy factor, while TXNL1 binds in a processing state, suggesting that it may have an active role in aiding protein degradation. Cryo-EM has also shown that Rpn11 can bind the Ubiquitin-like domain of midnolin, a protein that enables ubiquitin-independent degradation of transcription factors (see the section on ubiquitin-independent degradation).
Rpn11 is an intrinsic, stoichiometric subunit of the 19S regulatory particle and is essential for the function of 26S proteasome. Rpn11 is a zinc-dependent, metalloprotease of the JAB1/MPN/Mov34 metalloenzyme (JAMM) family of DUBs, that was identified to be the essential DUB responsible for the en block removal of the ubiquitin chain from the protein substrate. Rpn11 forms an obligate dimer with Rpn8 forming an active DUB able to cleave all ubiquitin linkages. The active site of Rpn11 is formed through metal coordination of the catalytic zinc and this site is covered by an Insert-1 loop that covers this active site. The structure is very similar to that of a related JAMM DUB, AMSH, that is responsible for K63 ubiquitin cleavage, however it lacks the residues that are key for AMSH's linkage specificity. The structure of Rpn11 bound to ubiquitin revealed that the C-terminus of Ubiquitin pushes the insert-1 loop into an beta-sheet providing access to the catalytic zinc. This structure combined with detailed biochemistry revealed that the DUB activity of Rpn11 was accelerated at least 10-fold by the translocation of the protein substrate, suggesting that the translocation delivered the Ub substrate to the active site of Rpn11. This model of translocation-dependent deubiquitination was later confirmed by cryoEM of both the yeast and human proteasome bound to a substrate, both of which recapitulated the crystal structure of Ubiquitin bound to Rpn11. Single molecule studies on the yeast proteasome confirmed that the DUB rates measured by biochemistry were indeed stimulated by translocation. More recent biochemical and single molecule studies have shown that on top of being the essential DUB, Rpn11 is also a ubiquitin receptor that acts as an allosteric sensor to enable proper engagement of a substrate by the proteasome.
In addition to binding Ubiquitin, Rpn11 has also recently been shown to be a binding spot for many proteasome associated factors. Three recent cryo-EM studies have shown that PITHD1 (Proteasome Interacting Thioredoxin Domain 1) and TXNL1 (Thioredoxin-like protein 1) bind the proteasome by binding Rpn2/Rpn10 and making an interaction with the insert-1 loop of Rpn11. PITHD1 binds the proteasome in a resting state and has been proposed to be a dormancy factor, while TXNL1 binds in a processing state, suggesting that it may have an active role in aiding protein degradation. Cryo-EM has also shown that Rpn11 can bind the Ubiquitin-like domain of midnolin, a protein that enables ubiquitin-independent degradation of transcription factors (see the section on ubiquitin-independent degradation).

 The 20S proteasome is both ubiquitous and essential in eukaryotes and archaea. The
The 20S proteasome is both ubiquitous and essential in eukaryotes and archaea. The