|
Thymoproteasome
Thymoproteasome is a special kind of proteasome, which is present in vertebrates. In the body it is located in thymus, exclusively in cortical thymic epithelial cells (cTECs). But in thymus we can also find another type of specific proteasome, immunoproteasome, which is present in thymocytes, dendritic cells and medular thymic epithelial cells. It was first described in 2007 during a search for non-intronic sequence proximal to PSMB5 locus in mouse genome. The PSMB5 locus encodes the standard β5 proteasome subunit, while this sequence encodes a variant subunit β5t (PSMB11) specific to thymoproteasome. The importance of this protein complex is its involvement in positive selection of T cells. Generally proteasomes are protein complexes in cells, which degrade proteins marked by ubiquitin systems. Proteasomes are present in all eukaryotes. It has been shown that there exist modifications, which have different catalytic subunits. The first type of proteasome which was described is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cortical Thymic Epithelial Cells
Cortical thymic epithelial cells (cTECs) form unique parenchyma cell population of the thymus which critically contribute to the development of T cells. Thymus Tissue (biology), tissue is compartmentalized into cortex and medulla and each of these two compartments comprises its specific thymic epithelial cell subset. cTECs reside in the outer part- cortex, which mostly serves as a developmental site for T cells. Precursor cell, Precursors of T cells originate in the bone marrow from which they migrate via bloodstream into thymic cortex, where they encounter stromal cells including cTECs, which form the microenvironment crucial for proliferation and development of T cells by expression of DLL4 (delta-like notch ligand 4), cytokines Interleukin 7, IL-7, Transforming growth factor beta, TGFβ or stem cell factor and chemokines CCL25, Stromal cell-derived factor 1, CXCL12 or CCRL1 etc. Essential part of T cell development forms process called V(D)J recombination, VDJ recombination, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunoproteasome
An immunoproteasome is a type of proteasome that degrades ubiquitin-labeled proteins found in the cytoplasm in cells exposed to oxidative stress and proinflammatory stimuli. In general, proteasomes consist of a regulatory and a catalytic part. Immunoproteasomes are induced by interferon gamma (but also by other proinflammatory cytokines) and oxidative stress, which in the cell triggers the transcription of three catalytic subunits that do not occur in the classical proteasome. Another possible variation of proteasome is the thymoproteasome, which is located in the thymus and folds to present peptides to naive T cells. Structure Structurally, immunoproteasome is a cylindrical protein complex composed of a catalytic 20S subunit and a 19S regulatory subunit. The catalytic subunit consists of four outer alpha rings and four inner beta rings. In the classical proteasome, the beta (β) 1, β2 and β5 subunits have catalytic activity, which, however, in the immunoproteasome are replaced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
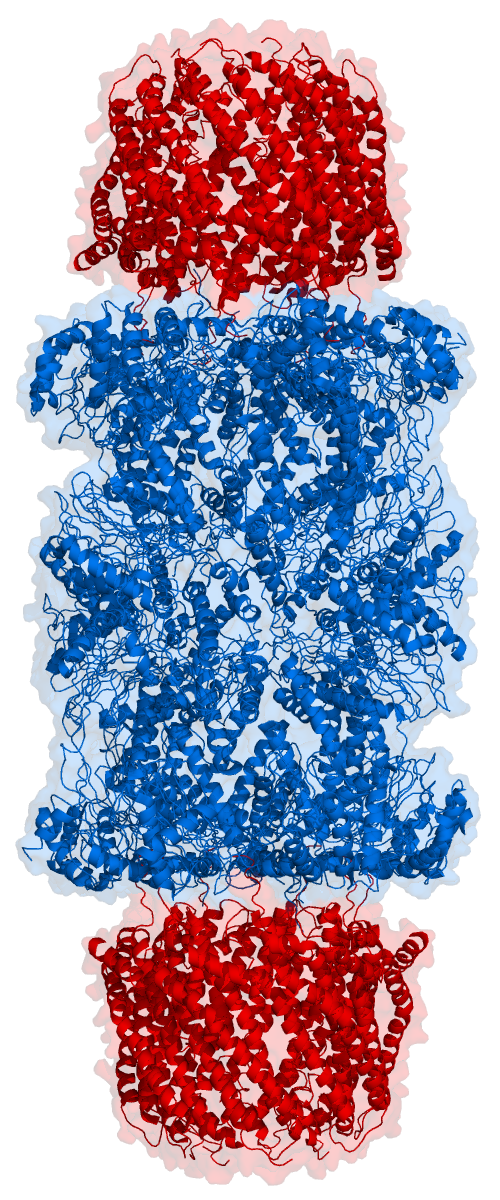
Proteasome
Proteasomes are essential protein complexes responsible for the degradation of proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds. Enzymes that help such reactions are called proteases. Proteasomes are found inside all eukaryotes and archaea, and in some bacteria. In eukaryotes, proteasomes are located both in the nucleus and in the cytoplasm. The proteasomal degradation pathway is essential for many cellular processes, including the cell cycle, the regulation of gene expression, and responses to oxidative stress. The importance of proteolytic degradation inside cells and the role of ubiquitin in proteolytic pathways was acknowledged in the award of the 2004 Nobel Prize in Chemistry to Aaron Ciechanover, Avram Hershko and Irwin Rose. The core 20S proteasome (blue in the adjacent figure) is a cylindrical, compartmental protein complex of four stacked rings forming a central pore. Each ring is composed of seven individual proteins. The inner two rings a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thymus
The thymus (: thymuses or thymi) is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, T cells mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. The thymus is located in the upper front part of the chest, in the anterior superior mediastinum, behind the sternum, and in front of the heart. It is made up of two lobes, each consisting of a central medulla and an outer cortex, surrounded by a capsule. The thymus is made up of immature T cells called thymocytes, as well as lining cells called epithelial cells which help the thymocytes develop. T cells that successfully develop react appropriately with Major histocompatibility complex, MHC immune receptors of the body (called ''positive selection'') and not against proteins of the body (called ''negative selection''). The thymus is the largest and most active during the neonatal and pre-adolescent periods. By the early teens, the Thymic involuti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thymocyte
A thymocyte is an immune cell present in the thymus, before it undergoes transformation into a T cell. Thymocytes are produced as stem cells in the bone marrow and reach the thymus via the blood. Thymopoiesis describes the process which turns thymocytes into mature T cells according to either negative or positive selection. This selection process is vitally important in shaping the population of thymocytes into a peripheral pool of T cells that are able to respond to foreign pathogens but remain tolerant towards the body's own antigens. Positive selection selects cells which are able to bind MHC class I or II molecules with at least a weak affinity. This eliminates (by a process called "death by neglect") those T cells which would be non-functional due to an inability to bind MHC. Negative selection destroys thymocytes with a high affinity for self peptides or MHC. This eliminates cells which would direct immune responses towards self-proteins in the periphery. Negative selection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendritic Cell
A dendritic cell (DC) is an antigen-presenting cell (also known as an ''accessory cell'') of the mammalian immune system. A DC's main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. They act as messengers between the innate and adaptive immune systems. Dendritic cells are present in tissues that are in contact with the body's external environment, such as the skin, and the inner lining of the nose, lungs, stomach and intestines. They can also be found in an immature and mature state in the blood. Once activated, they migrate to the lymph nodes, where they interact with T cells and B cells to initiate and shape the adaptive immune response. At certain development stages they grow branched projections, the '' dendrites,'' that give the cell its name (δένδρον or déndron being Greek for 'tree'). While similar in appearance to the dendrites of neurons, these are structures distinct from them. Immature dendr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PSMB5
Proteasome subunit beta type-5 also known as 20S proteasome subunit beta-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PSMB5'' gene. This protein is one of the 17 essential subunits (alpha subunits 1–7, constitutive beta subunits 1–7, and inducible subunits including beta1i, beta2i, beta5i) that contributes to the complete assembly of 20S proteasome complex. In particular, proteasome subunit beta type-5, along with other beta subunits, assemble into two heptameric rings and subsequently a proteolytic chamber for substrate degradation. This protein contains "chymotrypsin-like" activity and is capable of cleaving after large hydrophobic residues of peptide. The eukaryotic proteasome recognized degradable proteins, including damaged proteins for protein quality control purpose or key regulatory protein components for dynamic biological processes. An essential function of a modified proteasome, the immunoproteasome, is the processing of class I MHC peptides. Structure Prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Cell
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell surface receptor, cell surface. T cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells, found in the bone marrow. Developing T cells then migrate to the thymus gland to develop (or mature). T cells derive their name from the thymus. After migration to the thymus, the precursor cells mature into several distinct types of T cells. T cell differentiation also continues after they have left the thymus. Groups of specific, differentiated T cell subtypes have a variety of important functions in controlling and shaping the immune response. One of these functions is immune-mediated cell death, and it is carried out by two major subtypes: Cytotoxic T cell, CD8+ "killer" (cytotoxic) and T helper cell, CD4+ "helper" T cells. (These are named for the presen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryote
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms are eukaryotes. They constitute a major group of Outline of life forms, life forms alongside the two groups of prokaryotes: the Bacteria and the Archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but given their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is much larger than that of prokaryotes. The eukaryotes emerged within the archaeal Kingdom (biology), kingdom Asgard (Archaea), Promethearchaeati and its sole phylum Promethearchaeota. This implies that there are only Two-domain system, two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among the Archaea. Eukaryotes first emerged during the Paleoproterozoic, likely as Flagellated cell, flagellated cells. The leading evolutiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MHC Class I
MHC class I molecules are one of two primary classes of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules (the other being MHC class II) and are found on the cell surface of all nucleated cells in the bodies of vertebrates. They also occur on platelets, but not on red blood cells. Their function is to display peptide fragments of proteins from within the cell to cytotoxic T cells; this will trigger an immediate response from the immune system against a particular non-self antigen displayed with the help of an MHC class I protein. Because MHC class I molecules present peptides derived from cytosolic proteins, the pathway of MHC class I presentation is often called ''cytosolic'' or ''endogenous pathway''. In humans, the HLAs corresponding to MHC class I are HLA-A, HLA-B, and HLA-C. Function Class I MHC molecules bind peptides generated mainly from the degradation of cytosolic proteins by the proteasome. The MHC I: peptide complex is then inserted via the endoplasmic re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interferon Gamma
Interferon gamma (IFNG or IFN-γ) is a dimerized soluble cytokine that is the only member of the type II class of interferons. The existence of this interferon, which early in its history was known as immune interferon, was described by E. F. Wheelock as a product of human leukocytes stimulated with phytohemagglutinin, and by others as a product of antigen-stimulated lymphocytes. It was also shown to be produced in human lymphocytes. or tuberculin-sensitized mouse peritoneal lymphocytes challenged with Mantoux test (PPD); the resulting supernatants were shown to inhibit growth of vesicular stomatitis virus. Those reports also contained the basic observation underlying the now widely employed interferon gamma release assay used to test for tuberculosis. In humans, the IFNG protein is encoded by the ''IFNG'' gene. Through cell signaling, interferon gamma plays a role in regulating the immune response of its target cell. A key signaling pathway that is activated by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |