Iboga-type Alkaloid on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Iboga-type alkaloids are a set of
(16R,20S)-Ibogaine Structural Formula V2.svg,

CID:21589055
and voaluteine
CID:633439
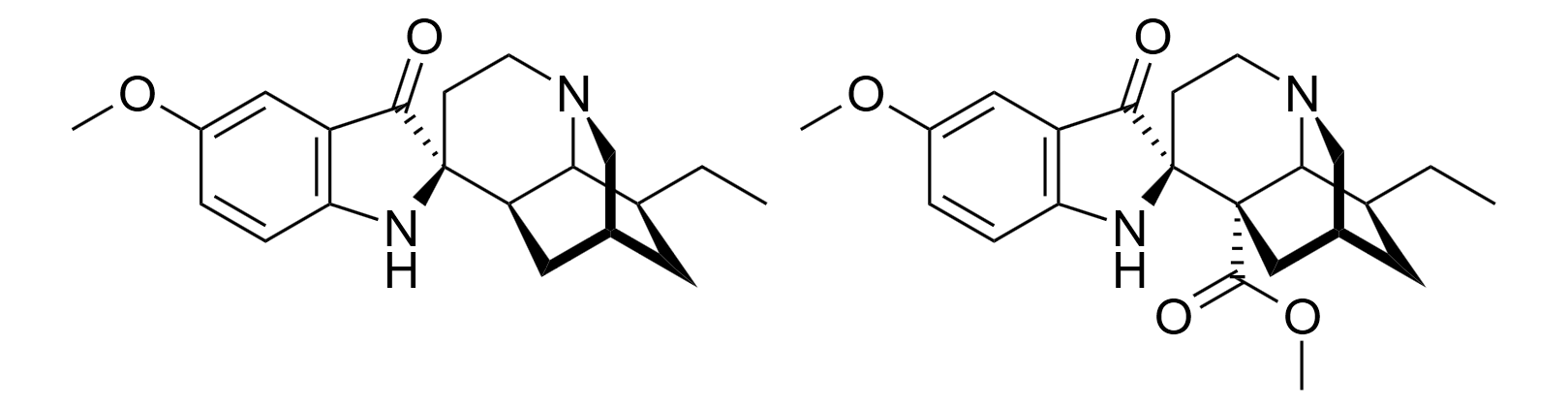
.
monoterpene
Monoterpenes are a class of terpenes that consist of two isoprene units and have the molecular formula C10H16. Monoterpenes may be linear (acyclic) or contain rings (monocyclic and bicyclic). Modified terpenes, such as those containing oxygen func ...
indole alkaloid
Indole alkaloids are a class of alkaloids containing a structural moiety of indole; many indole alkaloids also include isoprene groups and are thus called terpene indole or secologanin tryptamine alkaloids. Containing more than 4100 known differ ...
s comprising naturally occurring compounds found in '' Tabernanthe'' and ''Tabernaemontana
''Tabernaemontana'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae. It has a pan-tropical distribution, found in Asia, Africa, Australia, North America, South America, and islands of the Indian and Pacific Oceans. These plants are everg ...
'', as well as synthetic structural analog
A structural analog, also known as a chemical analog or simply an analog, is a chemical compound, compound having a chemical structure, structure similar to that of another compound, but differing from it in respect to a certain component.
It can ...
s. Naturally occurring iboga-type alkaloids include ibogamine
Ibogamine is an anti-convulsant, anti-addictive, CNS stimulant alkaloid found in '' Tabernanthe iboga'' and Crepe Jasmine ('' Tabernaemontana divaricata''). Basic research related to how addiction affects the brain has used this chemical.
Iboga ...
, ibogaine
Ibogaine is a psychoactive indole alkaloid derived from plants such as '' Tabernanthe iboga'', characterized by hallucinogenic and oneirogenic effects. Traditionally used by Central African foragers, it has undergone controversial research ...
, tabernanthine
Tabernanthine is an alkaloid found in ''Tabernanthe iboga''.
It has been used in laboratory experiments to study how addiction affects the brain.
Tabernanthine persistently reduced the self-administration of cocaine and morphine in rats.
Phar ...
, and other substituted ibogamines . Many iboga-type alkaloids display biological activities such as cardiac toxicity
Cardiotoxicity is the occurrence of heart dysfunction as electric or muscle damage, resulting in heart toxicity. This can cause heart failure, arrhythmia, myocarditis, and cardiomyopathy in patients. Some effects are reversible, while in others, p ...
and psychoactive effects, and some have been studied as potential treatments for drug addiction
Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to use a drug or engage in a behavior that produces natural reward, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use can ...
.
Naturally-occurring
Ibogaine
Ibogaine is a psychoactive indole alkaloid derived from plants such as '' Tabernanthe iboga'', characterized by hallucinogenic and oneirogenic effects. Traditionally used by Central African foragers, it has undergone controversial research ...
(16R,20S)-Ibogamine Structural Formula V2.svg, Ibogamine
Ibogamine is an anti-convulsant, anti-addictive, CNS stimulant alkaloid found in '' Tabernanthe iboga'' and Crepe Jasmine ('' Tabernaemontana divaricata''). Basic research related to how addiction affects the brain has used this chemical.
Iboga ...
(16R,20S)-Tabernanthine Structural Formula V2.svg, Tabernanthine
Tabernanthine is an alkaloid found in ''Tabernanthe iboga''.
It has been used in laboratory experiments to study how addiction affects the brain.
Tabernanthine persistently reduced the self-administration of cocaine and morphine in rats.
Phar ...
(16S,20S)-Coronaridine Structural Formula V2.svg, Coronaridine
Coronaridine, also known as 18-carbomethoxyibogamine, is an alkaloid found in '' Tabernanthe iboga'' and related species, including '' Tabernaemontana divaricata'' for which (under the now obsolete synonym ''Ervatamia coronaria'') it was named.
...
Substituted ibogamines

Catharanthine
Catharanthine is a terpene indole alkaloid produced by the medicinal plant '' Catharanthus roseus'' and '' Tabernaemontana divaricata''. Catharanthine is derived from strictosidine, but the exact mechanism by which this happens is currently unkn ...
is an unsaturated analog of coronaridine
Coronaridine, also known as 18-carbomethoxyibogamine, is an alkaloid found in '' Tabernanthe iboga'' and related species, including '' Tabernaemontana divaricata'' for which (under the now obsolete synonym ''Ervatamia coronaria'') it was named.
...
.
Oxidation products
Similarly to other ring-constrainedtryptamines
Substituted tryptamines, or simply tryptamines, also known as serotonin analogues (i.e., 5-hydroxytryptamine analogues), are organic compounds which may be thought of as being derived from tryptamine itself. The molecular structures of all trypt ...
such as yohimbine
Yohimbine, also known as quebrachine, is an indole alkaloid derived from the bark of the African tree '' Pausinystalia johimbe'' (yohimbe); also from the bark of the unrelated South American tree '' Aspidosperma quebracho-blanco''. Yohimbine is ...
and mitragynine
Mitragynine is an indole-based alkaloid and is one of the main Psychoactive drug, psychoactive constituents in the Southeast Asian plant ''Mitragyna speciosa'', commonly known as kratom. It is an atypical opioid that is typically consumed as a p ...
(see mitragynine pseudoindoxyl), oxidation
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is ...
and rearrangement products of substituted ibogamines have been reported, such as iboluteine (ibogaine pseudoindoxyl)CID:21589055
and voaluteine
CID:633439
.

Other alkaloids
*Vobasine
Vobasine is a naturally occurring monoterpene indole alkaloid found in several species in the genus ''Tabernaemontana'' including ''Tabernaemontana divaricata''.
History
Vobasine was first reported by Renner in 1959 after its isolation from ''Voa ...
* Ervaticine
Conolidine is an indole alkaloid. Preliminary reports suggest that it could provide analgesic effects with few of the detrimental side-effects associated with opioids such as morphine, though at present it has only been evaluated in mouse mod ...
* Dregamine
* Vinblastine
Vinblastine, sold under the brand name Velban among others, is a chemotherapy medication, typically used with other medications, to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes Hodgkin's lymphoma, non-small-cell lung cancer, bladder canc ...
Treatment of drug dependence
Ibogaine and related alkaloids reduce the craving for subsequent doses in individuals experiencingwithdrawal symptoms
Withdrawal means "an act of taking out" and may refer to:
* Anchoresis (withdrawal from the world for religious or ethical reasons)
* ''Coitus interruptus'' (the withdrawal method)
* Drug withdrawal
* Social withdrawal
* Taking of money from a ban ...
associated with drug addiction
Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to use a drug or engage in a behavior that produces natural reward, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use can ...
. Their use has been investigated in several clinical studies involving individuals dependent on opioid
Opioids are a class of Drug, drugs that derive from, or mimic, natural substances found in the Papaver somniferum, opium poppy plant. Opioids work on opioid receptors in the brain and other organs to produce a variety of morphine-like effects, ...
s, cocaine
Cocaine is a tropane alkaloid and central nervous system stimulant, derived primarily from the leaves of two South American coca plants, ''Erythroxylum coca'' and ''Erythroxylum novogranatense, E. novogranatense'', which are cultivated a ...
, and other substances. While positive effects—such as alleviation of withdrawal symptoms, improvement in depression, and mitigation of post-traumatic symptoms—have been confirmed, severe medical complications, including fatal cases, have also been reported due to neurotoxic and cardiotoxic side effects.
Synthetic analogues
18-MC, ME-18-MC, and 18-MAC arecoronaridine
Coronaridine, also known as 18-carbomethoxyibogamine, is an alkaloid found in '' Tabernanthe iboga'' and related species, including '' Tabernaemontana divaricata'' for which (under the now obsolete synonym ''Ervatamia coronaria'') it was named.
...
analogs with similar anti-addictive effects.
More distantly related synthetic analogs include:
* Varenicline
Varenicline, sold under the brand names Chantix and Champix among others, is a medication used for smoking cessation and for the treatment of dry eye syndrome. It is a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor partial agonist. When activated, this recep ...
, a polycyclic azepine
Azepine is unsaturated heterocycle of seven atoms, with a nitrogen replacing a carbon at one position.
The atoms are numbered starting with the nitrogen. The 1H form shown to the right is unstable and converts to the 3H form.nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, or nAChRs, are Receptor (biochemistry), receptor polypeptides that respond to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Nicotinic receptors also respond to drugs such as the agonist nicotine. They are found in the c ...
s, but acts as a partial agonist
In pharmacology, partial agonists are drugs that bind to and activate a given Receptor (biochemistry), receptor, but have only partial Intrinsic activity, efficacy at the receptor relative to a full agonist. They may also be considered Ligand (bio ...
instead.
* Tabernanthalog
Tabernanthalog (TBG, DLX-007) is a novel water-soluble, non-toxic ibogalog or simplified analogue of the psychoactive drug tabernanthine first synthesized by David E. Olson at UC Davis.
Tabernanthalog is a non-hallucinogenic serotonin 5-HT2A ...
is a structural simplification of tabernanthine
Tabernanthine is an alkaloid found in ''Tabernanthe iboga''.
It has been used in laboratory experiments to study how addiction affects the brain.
Tabernanthine persistently reduced the self-administration of cocaine and morphine in rats.
Phar ...
and "non-hallucinogenic psychoplastogen
Psychoplastogens, also known as neuroplastogens, are a group of Small molecule#Drugs, small molecule drugs that produce rapid and sustained effects on neuronal structure and function, intended to manifest therapeutic benefit after a single admin ...
".
See also
*Strictosidine
Strictosidine is a natural chemical compound and is classified as a glucoalkaloid and a vinca alkaloid. It is formed by the Pictet–Spengler condensation reaction of tryptamine with secologanin, catalyzed by the enzyme strictosidine synthase. ...
* Bwiti
Bwiti is a spiritual discipline of the forest-dwelling Punu people and Mitsogo peoples of Gabon (where it is recognized as one of three official religions) and by the Fang people of Gabon. Modern Bwiti incorporates animism, ancestor worship, an ...
* Ibogalog
Noribogaminalog, or ''N''-desmethylibogaminalog, also known as 1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydroazepino ,5-bndole, is a chemical compound and parent structure of the ibogalog group of compounds. The ibogalogs that have been described include ibogaminalog, ...
* Substituted β-carboline
A substituted β-carboline is a chemical compound featuring a β-carboline moiety (chemistry), moiety with one or more chemical substituent, substitutions. β-Carbolines include more than one hundred alkaloids and synthetic compounds. The effect ...
and harmala alkaloid
Harmala alkaloids are several alkaloids that act as monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). These alkaloids are found in the seeds of ''Peganum harmala'' (also known as harmal or Syrian rue), as well as ''Banisteriopsis caapi'' (ayahuasca), leave ...
References
{{Chemical classes of psychoactive drugs Alkaloids found in Iboga Chemical classes of psychoactive drugs Entheogens Hallucinogens Indole alkaloids Plant toxins Tryptamines