|
Substituted β-carboline
A substituted β-carboline is a chemical compound featuring a β-carboline moiety (chemistry), moiety with one or more chemical substituent, substitutions. β-Carbolines include more than one hundred alkaloids and synthetic compounds. The effects of these substances depend on their respective substituent. Natural β-carbolines primarily influence brain functions but can also exhibit antioxidant effects. Synthetically designed β-carboline Derivative (chemistry), derivatives have recently been shown to have Neuroprotection, neuroprotective, Neuroenhancement, cognitive enhancing and anti-cancer properties. β-Carbolines are indole alkaloids featuring a fused pyridine and indole ring structure similar to tryptamine, forming a three-ringed system with variable saturation in the third ring. β-Carboline alkaloids naturally occur widely in prokaryotes, plants, animals, certain marine tunicates, and foods like coffee and smoked meats, and are also responsible for the fluorescence of sco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prokaryote
A prokaryote (; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a unicellular organism, single-celled organism whose cell (biology), cell lacks a cell nucleus, nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'before', and (), meaning 'nut' or 'kernel'. In the earlier two-empire system arising from the work of Édouard Chatton, prokaryotes were classified within the empire Prokaryota. However, in the three-domain system, based upon molecular phylogenetics, prokaryotes are divided into two domain (biology), domains: Bacteria and Archaea. A third domain, Eukaryote, Eukaryota, consists of organisms with nuclei. Prokaryotes evolution, evolved before eukaryotes, and lack nuclei, mitochondria, and most of the other distinct organelles that characterize the eukaryotic cell. Some unicellular prokaryotes, such as cyanobacteria, form colony (biology), colonies held together by biofilms, and large colonies can create multilayered microbial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
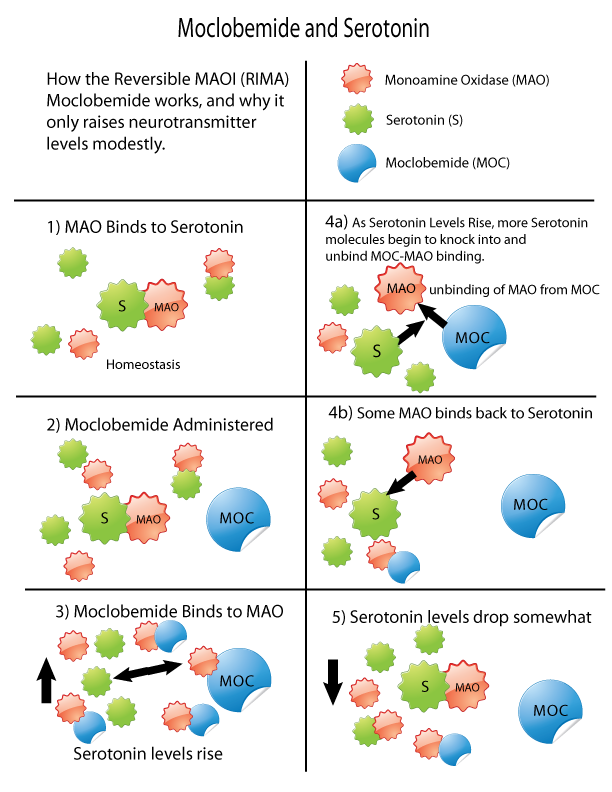
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a drug class, class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressants, especially for treatment-resistant depression and atypical depression. They are also used to treat panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, Parkinson's disease, and several other disorders. Reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A (RIMAs) are a subclass of MAOIs that binding selectivity, selectively and Enzyme inhibitor#Reversible inhibitors, reversibly enzyme inhibitor, inhibit the MAO-A enzyme. RIMAs are used clinically in the medication, treatment of major depressive disorder, depression and dysthymia. Due to their reversibility, they are safer in single-drug overdose than the older, irreversible MAOIs, and weaker in increasing the monoamines important in depressive disorder. RIMAs have not gained widespread market share in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Shulgin
Alexander Theodore "Sasha" Shulgin (June 17, 1925 – June 2, 2014) was an American biochemist, broad researcher of synthetic psychoactive compounds, and author of works regarding these, who independently explored the organic chemistry and pharmacology of such agents—in his mid-life and later, many through preparation in his home laboratory, and testing on himself. He is acknowledged to have introduced to broader use, in the late 1970s, the previously-synthesized compound MDMA ("ecstasy"), in research psychopharmacology and in combination with conventional therapy, the latter through presentations and academic publications, including to psychologists; and for the rediscovery, occasional discovery, and regular synthesis and personal use and distribution, of possibly hundreds of Psychoactive drug, psychoactive compounds (for their Psychedelic drug, psychedelic and MDMA-like empathogenic bioactivity, bioactivities). As such, Shulgin is seen both as a pioneering and a controversi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hallucinogen
Hallucinogens, also known as psychedelics, entheogens, or historically as psychotomimetics, are a large and diverse class of psychoactive drugs that can produce altered states of consciousness characterized by major alterations in thought, mood, and perception as well as other changes. Hallucinogens are often categorized as either being psychedelics, dissociatives, or deliriants, but not all hallucinogens fall into these three classes. Examples of hallucinogens include psychedelics or serotonin 5-HT2A receptor agonists like LSD, psilocybin, mescaline, and DMT; dissociatives or NMDA receptor antagonists like ketamine, PCP, DXM, and nitrous oxide; deliriants or antimuscarinics like scopolamine and diphenhydramine; cannabinoids or cannabinoid CB1 receptor agonists like THC, nabilone, and JWH-018; κ-opioid receptor agonists like salvinorin A and pentazocine; GABAA receptor agonists like muscimol and gaboxadol; and oneirogens like ibogaine and harmaline, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmaline
Harmaline, also known as 7-methoxyharmalan or as 3,4-dihydro-7-methoxy-1-methyl-β-carboline, is a fluorescent indole alkaloid from the group of harmala alkaloids and β-carbolines. It is the partly hydrogenated form of harmine. It is a reversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (RIMA). It produces vivid dream-like visual effects and physical discomfort at oral doses of 300 to 400mg, often leading users to seek solitude in a quiet, dark environment. Plants containing harmaline are combined in ayahuasca to inhibit monoamine oxidase, allowing orally ingested DMT to remain active in the brain and produce psychoactive effects. Harmala alkaloids, including harmaline, are psychoactive on their own in humans, with harmaline being particularly hallucinogenic, although other compounds such as harmine and tetrahydroharmine have also been reported to produce hallucinogenic effects as well. Harmaline exhibits weak affinity for 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors, partially substitutes for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmala Alkaloid
Harmala alkaloids are several alkaloids that act as monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). These alkaloids are found in the seeds of ''Peganum harmala'' (also known as harmal or Syrian rue), as well as ''Banisteriopsis caapi'' (ayahuasca), leaves of tobacco and coffee beans. The alkaloids include harmine, harmaline, harmalol, and their derivatives, which have similar chemical structures, hence the name "harmala alkaloids". These alkaloids are of interest for their use in Amazonian shamanism, where they are derived from other plants. Harmine, once known as telepathine and banisterine, is a naturally occurring substituted β-carboline, β-carboline alkaloid that is structurally related to harmaline, and also found in the vine ''Banisteriopsis caapi''. Tetrahydroharmine is also found in ''B. caapi'' and ''P. harmala''. Dr. Alexander Shulgin has suggested that harmine may be a breakdown product of harmaline. Harmine and harmaline are reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A (RIMA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
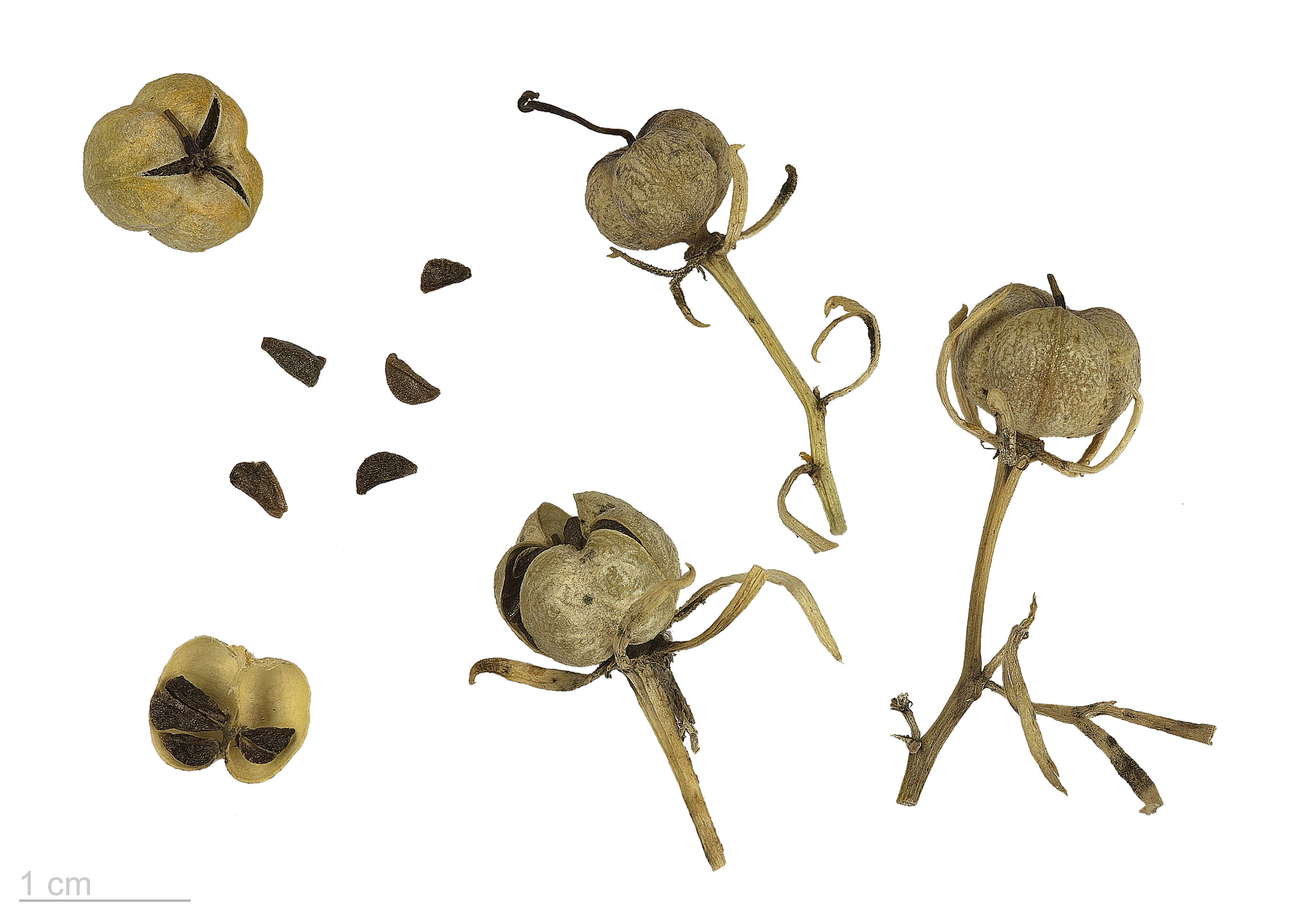
Peganum Harmala
''Peganum harmala'', commonly called wild rue, Syrian rue, African rue, esfand or espand,Mahmoud OmidsalaEsfand: a common weed found in Persia, Central Asia, and the adjacent areasEncyclopædia Iranica Vol. VIII, Fasc. 6, pp. 583–584. Originally published: 15 December 1998. Online version last updated 19 January 2012 or harmel (among other similar pronunciations and spellings), is a perennial, herbaceous plant, with a woody underground rootstock, of the family (biology), family Nitrariaceae, usually growing in saline soils in Desert#Classification, temperate desert and Mediterranean climate, Mediterranean regions. Its common English-language name came about because of a resemblance to rue (to which it is not related). Its seeds contain a high concentration (at least 5.9% by weight) of diverse beta-carboline alkaloids. It has deep roots and a strong smell, finely divided leaves, white flowers rich in alkaloids, and small Capsule (fruit), seed capsules containing numerous dark, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs, Cherenkov radiation, and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. The photons of ultraviolet have greater energy than those of visible light, from about 3.1 to 12 electron volts, around the minimum energy required to ionize atoms. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack sufficient energy, it can induce chemical reactions and cause many substances to glow or fluoresce. Many practical applications, including chemical and biological effects, are derived from the way that UV radiation can interact with organic molecules. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scorpion
Scorpions are predatory arachnids of the Order (biology), order Scorpiones. They have eight legs and are easily recognized by a pair of Chela (organ), grasping pincers and a narrow, segmented tail, often carried in a characteristic forward curve over the back and always ending with a stinger. The evolutionary history of scorpions goes back Silurian, 435 million years. They mainly live in deserts but have adapted to a wide range of environmental conditions, and can be found on all continents except Antarctica. There are over 2,500 described species, with 22 extant (living) families recognized to date. Their Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy is being revised to account for 21st-century genomic studies. Scorpions primarily prey on insects and other invertebrates, but some species hunt vertebrates. They use their pincers to restrain and kill prey, or to prevent their own predation. The Scorpion sting, venomous sting is used for offense and defense. During courtship, the male and female ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meat
Meat is animal Tissue (biology), tissue, often muscle, that is eaten as food. Humans have hunted and farmed other animals for meat since prehistory. The Neolithic Revolution allowed the domestication of vertebrates, including chickens, sheep, goats, pigs, horses, and cattle, starting around 11,000 years ago. Since then, selective breeding has enabled farmers to produce meat with the qualities desired by producers and consumers. Meat is mainly composed of water, protein, and fat. Its quality is affected by many factors, including the genetics, health, and nutritional status of the animal involved. Without preservation, bacteria and fungi decompose and Meat spoilage, spoil unprocessed meat within hours or days. Meat is Raw meat, edible raw, but it is mostly eaten cooked, such as by stewing or roasting, or Processed meat, processed, such as by Smoking (cooking), smoking or Salting (food), salting. The consumption of meat (especially Red meat, red and processed meat, as opposed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
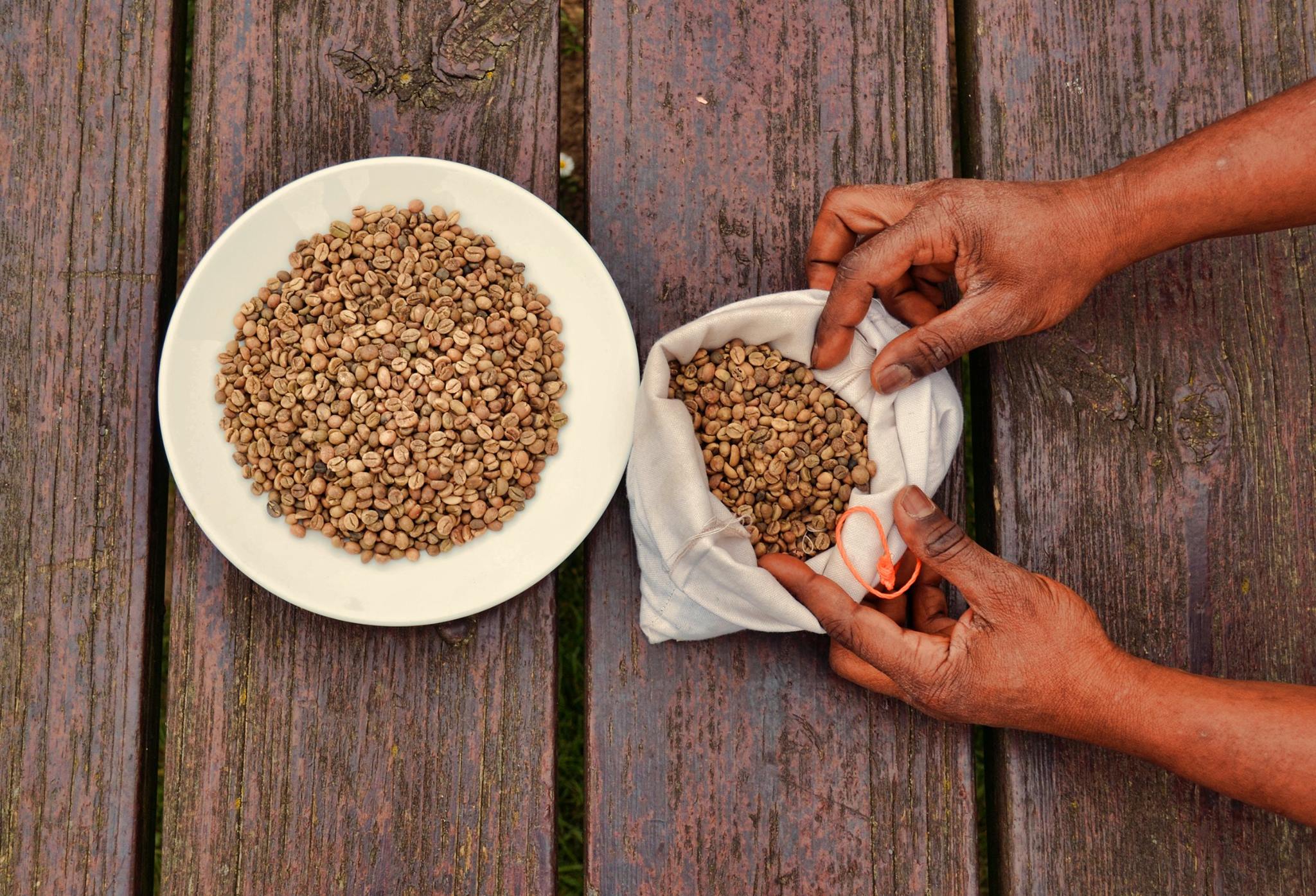
Coffee
Coffee is a beverage brewed from roasted, ground coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content, but decaffeinated coffee is also commercially available. There are also various coffee substitutes. Typically served hot, coffee has the highest sales in the world market for hot drinks. Coffee production begins when the seeds from coffee cherries (the '' Coffea'' plant's fruits) are separated to produce unroasted green coffee beans. The "beans" are roasted and then ground into fine particles. Coffee is brewed from the ground roasted beans, which are typically steeped in hot water before being filtered out. It is usually served hot, although chilled or iced coffee is common. Coffee can be prepared and presented in a variety of ways (e.g., espresso, French press, caffè latte, or already-brewed canned coffee). Sugar, sugar substitutes, milk, and cream are often added to mask ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |