|
18-Methylaminocoronaridine
(−)-18-Methylaminocoronaridine (18-MAC) is a second generation synthetic derivative of ibogaine developed by the research team led by the pharmacologist Stanley D. Glick from the Albany Medical College and the chemist Martin E. Kuehne from the University of Vermont. See also * 2-Methoxyethyl-18-methoxycoronaridinate * 18-Methoxycoronaridine * Coronaridine * Ibogaine * Noribogaine * Voacangine Voacangine (12-methoxyibogamine-18-carboxylic acid methyl ester) is an alkaloid found predominantly in the root bark of the ''Voacanga africana'' tree, as well as in other plants such as '' Tabernanthe iboga'', ''Tabernaemontana africana'', '' Tra ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Methylaminocoronaridine, 18- Drug rehabilitation Iboga Nicotinic antagonists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18-Methoxycoronaridine
18-Methoxycoronaridine (18-MC; developmental code name MM-110), also known as zolunicant (), is a derivative of ibogaine invented in 1996 by the research team around the pharmacologist Stanley D. Glick from the Albany Medical College and the chemists Upul K. Bandarage and Martin E. Kuehne from the University of Vermont. In animal studies it has proven to be effective at reducing self-administration of morphine, cocaine, methamphetamine, nicotine and sucrose. It has also been shown to produce anorectic effects in obese rats, most likely due to the same actions on the reward system which underlie its anti-addictive effects against drug addiction. 18-MC was in the early stages of human testing by the California-based drug development company Savant HWP before being acquired by MindMed, a Canadian pharmaceutical company newly listed on the NASDAQ in April 2021. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-Methoxyethyl-18-methoxycoronaridinate
(−)-2-Methoxyethyl-18-methoxycoronaridinate (ME-18-MC) is a second generation synthetic derivative of ibogaine developed by the research team led by the pharmacologist Stanley D. Glick from the Albany Medical College and the chemist Martin E. Kuehne from the University of Vermont. In animal studies it has shown similar efficacy to the related compound 18-methoxycoronaridine (18-MC) at reducing self-administration of morphine and methamphetamine but with higher potency by weight, showing anti-addictive effects at the equivalent of half the minimum effective dose of 18-MC. Similarly to 18-MC itself, ME-18-MC acts primarily as a selective α3β4 nicotinic acetylcholine antagonist, although it has a slightly stronger effect than 18-MC as an NMDA antagonist, and its effects on opioid receptors are weaker than those of 18-MC at all except the kappa opioid receptor, at which it has slightly higher affinity than 18-MC. See also * 18-Methylaminocoronaridine * 18-Methoxycoronaridine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
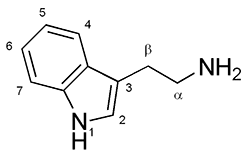
Ibogaine
Ibogaine is a psychoactive indole alkaloid derived from plants such as '' Tabernanthe iboga'', characterized by hallucinogenic and oneirogenic effects. Traditionally used by Central African foragers, it has undergone controversial research for the treatment of substance use disorders. Ibogaine exhibits complex pharmacology by interacting with multiple neurotransmitter systems, notably affecting opioid, serotonin, sigma, and NMDA receptors, while its metabolite noribogaine primarily acts as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor and κ-opioid receptor agonist. The psychoactivity of the root bark of the iboga tree, ''T. iboga'', one of the plants from which ibogaine is extracted, was first discovered by forager tribes in Central Africa, who passed the knowledge to the Bwiti tribe of Gabon. It was first documented in the 19th century for its spiritual use, later isolated and synthesized for its psychoactive properties, briefly marketed in Europe as a stimulant, and ultimately rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanley D
Stanley may refer to: Arts and entertainment Film and television * ''Stanley'' (1972 film), an American horror film * ''Stanley'' (1984 film), an Australian comedy * ''Stanley'' (1999 film), an animated short * ''Stanley'' (1956 TV series), an American situation comedy * ''Stanley'' (2001 TV series), an American animated series Other uses in arts and entertainment * ''Stanley'' (play), by Pam Gems, 1996 * Stanley Award, an Australian Cartoonists' Association award * '' Stanley: The Search for Dr. Livingston'', a video game Businesses * Stanley, Inc., an American information technology company * Stanley Aviation, an American aerospace company * Stanley Black & Decker, formerly The Stanley Works, an American hardware manufacturer ** Stanley Hand Tools, a division of Stanley Black & Decker * Stanley bottle, a brand of food and beverage containers * Stanley Electric, a Japanese manufacturer of electric lights * Stanley Furniture, an American furniture manufacturer * The Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albany Medical College
Albany Medical College (AMC) is a Private university, private medical school in Albany, New York. It was founded in 1839 by Alden March and James H. Armsby and is one of the oldest medical schools in the nation. The college is part of the Albany Medical Center, which includes the Albany Medical Center Hospital. Over its 170-year history, Albany Medical College has attracted and produced many leaders in medicine and research. Among its present and past faculty, researchers, and alumni there are two Nobel Prize winners, two Lasker Award winners, two MacArthur Fellowship recipients, one Gairdner Foundation International Award winner, former Surgeon General of the United States Army, former Surgeon General of the United States Air Force, several presidents and CEOs of major academic hospitals, as well as an early president and co-founder of the American Medical Association. AMC is attributed as the site where David S. Sheridan perfected the modern-day disposable catheter, among other m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin E
Martin may refer to: Places Antarctica * Martin Peninsula, Marie Byrd Land * Port Martin Port Martin, or Port-Martin, is an abandoned French research base at Cape Margerie on the coast of Adélie Land, Antarctica, as well as the name of the adjacent anchorage. History The site was discovered in 1950 by the Fifth French Antarctic Ex ..., Adelie Land * Point Martin, South Orkney Islands Europe * Martin, Croatia, a village * Martin, Slovakia, a city * Martín del Río, Aragón, Spain * Martín River, a tributary of the Ebro river in Spain * Martin (Val Poschiavo), Switzerland England * Martin, Hampshire * Martin, Kent * Martin, East Lindsey, Lincolnshire, a hamlet and former parish * Martin, North Kesteven, Lincolnshire, a village and parish * Martin Hussingtree, Worcestershire * Martin Mere, a lake in Lancashire ** WWT Martin Mere, a wetland nature reserve that includes the lake and surrounding areas North America Canada * Rural Municipality of Martin No. 122, Saskatchewan, Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Vermont
The University of Vermont and State Agricultural College, commonly referred to as the University of Vermont (UVM), is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Burlington, Vermont, United States. Founded in 1791, UVM is the oldest university in Vermont and the fifth-oldest in New England. UVM comprises ten colleges and schools, including the Robert Larner College of Medicine, and offers more than 100 undergraduate majors along with various graduate and professional programs. The University of Vermont Medical Center, has its primary facility on the UVM campus. It is Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education, classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities—Very high research activity". In athletics, UVM's teams, known as the Vermont Catamounts, Catamounts, compete in NCAA Division I, primarily in the America East Conference and Hockey East, Hockey East Association. History The University of Vermont was founded as a pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronaridine
Coronaridine, also known as 18-carbomethoxyibogamine, is an alkaloid found in '' Tabernanthe iboga'' and related species, including '' Tabernaemontana divaricata'' for which (under the now obsolete synonym ''Ervatamia coronaria'') it was named. Like ibogaine, (''R'')-coronaridine and (''S'')-coronaridine can decrease intake of cocaine and morphine in animals and it may have muscle relaxant and hypotensive activity. Chemistry Congeners Coronaridine congers are important in drug discovery and development due to multiple actions on different targets. They have ability to inhibit Cav2.2 channel, modulate and inhibit subunits of nAChr selectively such as α9α10, α3β4 and potentiate GABAA activity. Pharmacology Coronaridine has been reported to bind to an assortment of molecular sites, including: μ-opioid (Ki = 2.0 μM), δ-opioid (Ki = 8.1 μM), and κ-opioid receptors (Ki = 4.3 μM), NMDA receptor (Ki = 6.24 μM) (as an antagonist), and nAChRs (as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibogaine
Ibogaine is a psychoactive indole alkaloid derived from plants such as '' Tabernanthe iboga'', characterized by hallucinogenic and oneirogenic effects. Traditionally used by Central African foragers, it has undergone controversial research for the treatment of substance use disorders. Ibogaine exhibits complex pharmacology by interacting with multiple neurotransmitter systems, notably affecting opioid, serotonin, sigma, and NMDA receptors, while its metabolite noribogaine primarily acts as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor and κ-opioid receptor agonist. The psychoactivity of the root bark of the iboga tree, ''T. iboga'', one of the plants from which ibogaine is extracted, was first discovered by forager tribes in Central Africa, who passed the knowledge to the Bwiti tribe of Gabon. It was first documented in the 19th century for its spiritual use, later isolated and synthesized for its psychoactive properties, briefly marketed in Europe as a stimulant, and ultimately rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noribogaine
Noribogaine (actually ''O''-desmethylibogaine), or 12-hydroxyibogamine, is the principal psychoactive metabolite of the oneirogen ibogaine. It is thought to be involved in the antiaddictive effects of ibogaine-containing plant extracts, such as '' Tabernanthe iboga''. Pharmacology Noribogaine is a potent serotonin reuptake inhibitor, but does not affect the reuptake of dopamine. Unlike ibogaine, noribogaine does not bind to the sigma-2 receptor. Similarly to ibogaine, noribogaine acts as a weak NMDA receptor antagonist and binds to opioid receptors. It has greater affinity for each of the opioid receptors than does ibogaine. Noribogaine is a hERG inhibitor and appears at least as potent as ibogaine. The inhibition of the hERG potassium channel delays the repolarization of cardiac action potentials, resulting in QT interval prolongation and, subsequently, in arrhythmias and sudden cardiac arrest. κ-Opioid receptor Noribogaine has been determined to act as a biased agonist of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voacangine
Voacangine (12-methoxyibogamine-18-carboxylic acid methyl ester) is an alkaloid found predominantly in the root bark of the ''Voacanga africana'' tree, as well as in other plants such as '' Tabernanthe iboga'', ''Tabernaemontana africana'', '' Trachelospermum jasminoides'', ''Tabernaemontana divaricata'' and '' Ervatamia yunnanensis''. It is an iboga alkaloid which commonly serves as a precursor for the semi-synthesis of ibogaine. It has been demonstrated in animals to have similar anti-addictive properties to ibogaine itself. It also potentiates the effects of barbiturates. Under UV-A and UV-B light its crystals fluoresce blue-green, and it is soluble in ethanol. Pharmacology Pharmacodynamics Voacangine exhibits AChE inhibitory activity. Docking simulation reveals that it has inhibitory effect on VEGF2 kinase and reduces angiogenesis. Like ibogaine, its a potent HERG blocker in vitro. It also acts as antagonist to TRPM8 and TRPV1 receptor, but agonist of TRPA1. Pharmacokinetics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drug Rehabilitation
Drug rehabilitation is the process of medical or psychotherapeutic treatment for dependency on psychoactive substances such as alcohol, prescription drugs, and street drugs such as cannabis, cocaine, heroin, and amphetamines. The general intent is to enable the patient to confront substance dependence, if present, and stop substance misuse to avoid the psychological, legal, financial, social, and medical consequences that can be caused. Treatment includes medication for comorbidities, counseling by experts, and sharing of experience with other recovering individuals. Psychological dependency Psychological dependency is addressed in many drug rehabilitation programs by attempting to teach patients new methods of interacting in a drug-free environment. In particular, patients are generally encouraged, or possibly even required, to not associate with peers who still use addictive substances. Twelve-step programs encourage addicts not only to stop using alcohol or other drugs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |