Fish net on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic, anamniotic,
 About 530 million years ago during the Cambrian explosion, fishlike animals with a
About 530 million years ago during the Cambrian explosion, fishlike animals with a
Number of species evaluated in relation to the overall number of described species, and numbers of threatened species by major groups of organisms
/ref>
File:Rhincodon typus fgbnms (cropped).jpg, Largest:
Swimming performance varies from fish such as tuna,
File:Salmo salar.jpg, Fastest: e.g.
A typical fish is cold-blooded, has a
File:Humpback anglerfish.png,
 Fish species are roughly divided equally between
Fish species are roughly divided equally between
File:Initial phase parrotfish feeding at Shaab Marsa Alam, Red Sea, Egypt -SCUBA (6336981391).jpg, A parrotfish feeding on
File:Lampanyctodes hectoris (Hector's lanternfish).svg, Anatomy of a typical fish (
1)
5) caudal peduncle 6) caudal fin 7) anal fin 8)
Since body tissue is denser than water, fish must compensate for the difference or they will sink. Many bony fish have an internal organ called a
File:Swim bladder.jpg, Gas-filled
 Fish have a closed-loop circulatory system. The
Fish have a closed-loop circulatory system. The
 Fish have small brains relative to body size compared with other vertebrates, typically one-fifteenth the brain mass of a similarly sized bird or mammal. However, some fish have relatively large brains, notably mormyrids and
Fish have small brains relative to body size compared with other vertebrates, typically one-fifteenth the brain mass of a similarly sized bird or mammal. However, some fish have relatively large brains, notably mormyrids and
Lamb et al.'s "The origin of the Vertebrate Eye", 2008.
/ref>

 The primary reproductive organs are paired
The primary reproductive organs are paired
 Some fish produce sounds by rubbing or grinding their bones together. These sounds are stridulatory. In ''Haemulon flavolineatum'', the French grunt fish, as it produces a grunting noise by grinding its teeth together, especially when in distress. The grunts are at a frequency of around 700 Hz, and last approximately 47 milliseconds. The longsnout seahorse, ''Hippocampus reidi'' produces two categories of sounds, 'clicks' and 'growls', by rubbing their coronet bone across the grooved section of their neurocranium. Clicks are produced during courtship and feeding, and the frequencies of clicks were within the range of 50 Hz-800 Hz. The frequencies are at the higher end of the range during spawning, when the female and male fishes were less than fifteen centimeters apart. Growls are produced when the ''H. reidi'' are stressed. The 'growl' sounds consist of a series of sound pulses and are emitted simultaneously with body vibrations.
Some fish species create noise by engaging specialized muscles that contract and cause swimbladder vibrations. Oyster toadfish produce loud grunts by contracting sonic muscles along the sides of the swim bladder. Female and male toadfishes emit short-duration grunts, often as a fright response. In addition to short-duration grunts, male toadfishes produce "boat whistle calls". These calls are longer in duration, lower in frequency, and are primarily used to attract mates. The various sounds have frequency range of 140 Hz to 260 Hz. The frequencies of the calls depend on the rate at which the sonic muscles contract.
The red drum, ''Sciaenops ocellatus'', produces drumming sounds by vibrating its swimbladder. Vibrations are caused by the rapid contraction of sonic muscles that surround the dorsal aspect of the swimbladder. These vibrations result in repeated sounds with frequencies from 100 to >200 Hz. ''S. ocellatus'' produces different calls depending on the stimuli involved, such as courtship or a predator's attack. Females do not produce sounds, and lack sound-producing (sonic) muscles.
Some fish produce sounds by rubbing or grinding their bones together. These sounds are stridulatory. In ''Haemulon flavolineatum'', the French grunt fish, as it produces a grunting noise by grinding its teeth together, especially when in distress. The grunts are at a frequency of around 700 Hz, and last approximately 47 milliseconds. The longsnout seahorse, ''Hippocampus reidi'' produces two categories of sounds, 'clicks' and 'growls', by rubbing their coronet bone across the grooved section of their neurocranium. Clicks are produced during courtship and feeding, and the frequencies of clicks were within the range of 50 Hz-800 Hz. The frequencies are at the higher end of the range during spawning, when the female and male fishes were less than fifteen centimeters apart. Growls are produced when the ''H. reidi'' are stressed. The 'growl' sounds consist of a series of sound pulses and are emitted simultaneously with body vibrations.
Some fish species create noise by engaging specialized muscles that contract and cause swimbladder vibrations. Oyster toadfish produce loud grunts by contracting sonic muscles along the sides of the swim bladder. Female and male toadfishes emit short-duration grunts, often as a fright response. In addition to short-duration grunts, male toadfishes produce "boat whistle calls". These calls are longer in duration, lower in frequency, and are primarily used to attract mates. The various sounds have frequency range of 140 Hz to 260 Hz. The frequencies of the calls depend on the rate at which the sonic muscles contract.
The red drum, ''Sciaenops ocellatus'', produces drumming sounds by vibrating its swimbladder. Vibrations are caused by the rapid contraction of sonic muscles that surround the dorsal aspect of the swimbladder. These vibrations result in repeated sounds with frequencies from 100 to >200 Hz. ''S. ocellatus'' produces different calls depending on the stimuli involved, such as courtship or a predator's attack. Females do not produce sounds, and lack sound-producing (sonic) muscles.
 The Food and Agriculture Organization reports that "in 2017, 34 percent of the fish stocks of the world's marine fisheries were classified as overfished". Overfishing is a major threat to edible fish such as cod and
The Food and Agriculture Organization reports that "in 2017, 34 percent of the fish stocks of the world's marine fisheries were classified as overfished". Overfishing is a major threat to edible fish such as cod and
 Throughout history, humans have used fish as food, fish as a food source for dietary protein. Historically and today, most fish harvested for human consumption has come by means of catching wild fish. However, fish farming, which has been practiced since about 3,500 BCE in ancient China, is becoming increasingly important in many nations. Overall, about one-sixth of the world's protein is estimated to be provided by fish. Fishing is accordingly a large global business which provides income for millions of people. The Environmental Defense Fund has a guide on which fish are safe to eat, given the state of pollution in today's world, and which fish are obtained in a sustainable way. As of 2020, over 65 million tonnes (Mt) of marine fish and 10 Mt of freshwater fish were captured, while some 50 Mt of fish, mainly freshwater, were farmed. Of the marine species captured in 2020, anchoveta represented 4.9 Mt, Alaska pollock 3.5 Mt, skipjack tuna 2.8 Mt, and Atlantic herring and yellowfin tuna 1.6 Mt each; eight more species had catches over 1 Mt.
Throughout history, humans have used fish as food, fish as a food source for dietary protein. Historically and today, most fish harvested for human consumption has come by means of catching wild fish. However, fish farming, which has been practiced since about 3,500 BCE in ancient China, is becoming increasingly important in many nations. Overall, about one-sixth of the world's protein is estimated to be provided by fish. Fishing is accordingly a large global business which provides income for millions of people. The Environmental Defense Fund has a guide on which fish are safe to eat, given the state of pollution in today's world, and which fish are obtained in a sustainable way. As of 2020, over 65 million tonnes (Mt) of marine fish and 10 Mt of freshwater fish were captured, while some 50 Mt of fish, mainly freshwater, were farmed. Of the marine species captured in 2020, anchoveta represented 4.9 Mt, Alaska pollock 3.5 Mt, skipjack tuna 2.8 Mt, and Atlantic herring and yellowfin tuna 1.6 Mt each; eight more species had catches over 1 Mt.
File:Matsya painting.jpg, Avatar of Vishnu as a Matsya, India
File:Bartolomeo Passerotti - The Fishmonger's Shop - WGA17072.jpg, ''The Fishmonger's Shop'', Bartolomeo Passerotti, 1580s
File:Goldfish Matisse.jpg, ''Goldfish (Matisse), Goldfish'' by Henri Matisse, 1912
''Fish: An Enthusiast's Guide''
University of California Press. – good lay text. * * *
''UCTV'' interview
ANGFA
– Illustrated database of freshwater fishes of Australia and New Guinea
FishBase online
– Comprehensive database with information on over 29,000 fish species * *
United Nation
– Fisheries and Aquaculture Department: Fish and seafood utilization {{Authority control Fish, Aquatic ecology Fishing, Fish Ichthyology Obsolete vertebrate taxa Seafood Paraphyletic groups
gill
A gill () is a respiration organ, respiratory organ that many aquatic ecosystem, aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow r ...
-bearing vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, ...
with swimming fins
A fin is a thin component or appendage attached to a larger body or structure. Fins typically function as foil (fluid mechanics), foils that produce lift (force), lift or thrust, or provide the ability to steer or stabilize motion while travelin ...
and a hard skull, but lacking limbs with digits. Fish can be grouped into the more basal jawless fish
Agnatha (; ) or jawless fish is a paraphyletic infraphylum of animals in the subphylum Vertebrata of the phylum Chordata, characterized by the lack of jaws. The group consists of both extant taxon, living (Cyclostomi, cyclostomes such as hagfish ...
and the more common jawed fish
Gnathostomata (; from Ancient Greek: (') 'jaw' + (') 'mouth') are jawed vertebrates. Gnathostome diversity comprises roughly 60,000 species, which accounts for 99% of all extant taxon, extant vertebrates, including all living bony fishes (bot ...
, the latter including all living
Living or The Living may refer to:
Common meanings
*Life, a condition that distinguishes organisms from inorganic objects and dead organisms
** Living species, one that is not extinct
*Personal life, the course of an individual human's life
* ...
cartilaginous
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. Semi-transparent and non-porous, it is usually covered by a tough and fibrous membrane called perichondrium. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints ...
and bony fish
Osteichthyes ( ; ), also known as osteichthyans or commonly referred to as the bony fish, is a Biodiversity, diverse clade of vertebrate animals that have endoskeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. They can be contrasted with the Chondricht ...
, as well as the extinct placoderm
Placoderms (from Ancient Greek πλάξ 'plax'', ''plakos'''Plate (animal anatomy), plate' and δέρμα 'derma'''skin') are vertebrate animals of the class (biology), class Placodermi, an extinct group of prehistoric fish known from Pal ...
s and acanthodian
Acanthodii or acanthodians is an extinct class of Gnathostomata, gnathostomes (jawed fishes). They are currently considered to represent a paraphyletic Evolutionary grade, grade of various fish lineages Basal (phylogenetics), basal to extant tax ...
s. In a break to the long tradition of grouping all fish into a single class
Class, Classes, or The Class may refer to:
Common uses not otherwise categorized
* Class (biology), a taxonomic rank
* Class (knowledge representation), a collection of individuals or objects
* Class (philosophy), an analytical concept used d ...
(Pisces), modern phylogenetics
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical dat ...
views fish as a paraphyletic
Paraphyly is a taxonomic term describing a grouping that consists of the grouping's last common ancestor and some but not all of its descendant lineages. The grouping is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In co ...
group.
Most fish are cold-blooded, their body temperature varying with the surrounding water, though some large active swimmers like white shark and tuna
A tuna (: tunas or tuna) is a saltwater fish that belongs to the tribe Thunnini, a subgrouping of the Scombridae ( mackerel) family. The Thunnini comprise 15 species across five genera, the sizes of which vary greatly, ranging from the bul ...
can hold a higher core temperature
Normal human body temperature (normothermia, euthermia) is the typical temperature range found in humans. The normal human body temperature range is typically stated as .
Human body temperature varies. It depends on sex, age, time of day, exert ...
. Many fish can communicate acoustically with each other, such as during courtship display
A courtship display is a set of display behaviors in which an animal, usually a male, attempts to attract a mate; the mate exercises choice, so sexual selection acts on the display. These behaviors often include ritualized movement ("dances"), ...
s. The study of fish is known as ichthyology
Ichthyology is the branch of zoology devoted to the study of fish, including bony fish (Osteichthyes), cartilaginous fish (Chondrichthyes), and jawless fish (Agnatha). According to FishBase, 35,800 species of fish had been described as of March 2 ...
.
The earliest fish appeared during the Cambrian
The Cambrian ( ) is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 51.95 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Ordov ...
as small filter feeder
Filter feeders are aquatic animals that acquire nutrients by feeding on organic matters, food particles or smaller organisms (bacteria, microalgae and zooplanktons) suspended in water, typically by having the water pass over or through a s ...
s; they continued to evolve through the Paleozoic
The Paleozoic ( , , ; or Palaeozoic) Era is the first of three Era (geology), geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Beginning 538.8 million years ago (Ma), it succeeds the Neoproterozoic (the last era of the Proterozoic Eon) and ends 251.9 Ma a ...
, diversifying into many forms. The earliest fish with dedicated respiratory gills and paired fins
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the back bone and are supported only b ...
, the ostracoderm
Ostracodermi () or ostracoderms is an informal group of vertebrate animals that include all armored jawless fish of the Paleozoic Era. The term does not often appear in classifications today because it is paraphyletic (excluding jawed fishes and ...
s, had heavy bony plates that served as protective exoskeleton
An exoskeleton () . is a skeleton that is on the exterior of an animal in the form of hardened integument, which both supports the body's shape and protects the internal organs, in contrast to an internal endoskeleton (e.g. human skeleton, that ...
s against invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate s ...
predator
Predation is a biological interaction in which one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common List of feeding behaviours, feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation ...
s. The first fish with jaw
The jaws are a pair of opposable articulated structures at the entrance of the mouth, typically used for grasping and manipulating food. The term ''jaws'' is also broadly applied to the whole of the structures constituting the vault of the mouth ...
s, the placoderms, appeared in the Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 23.5 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the third and shortest period of t ...
and greatly diversified during the Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a period (geology), geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era during the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian per ...
, the "Age of Fishes".
Bony fish, distinguished by the presence of swim bladder
The swim bladder, gas bladder, fish maw, or air bladder is an internal gas-filled organ (anatomy), organ in bony fish that functions to modulate buoyancy, and thus allowing the fish to stay at desired water depth without having to maintain lift ...
s and later ossified
Ossification (also called osteogenesis or bone mineralization) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in t ...
endoskeleton
An endoskeleton (From Ancient Greek ἔνδον, éndon = "within", "inner" + σκελετός, skeletos = "skeleton") is a structural frame (skeleton) — usually composed of mineralized tissue — on the inside of an animal, overlaid by soft ...
s, emerged as the dominant group of fish after the end-Devonian extinction
The Hangenberg event, also known as the Hangenberg crisis or end-Devonian extinction, is a mass extinction that occurred at the end of the Famennian stage, the last stage in the Devonian Period (roughly 358.9 ± 0.4 million years ago). It is usu ...
wiped out the apex predator
An apex predator, also known as a top predator or superpredator, is a predator at the top of a food chain, without natural predators of its own.
Apex predators are usually defined in terms of trophic dynamics, meaning that they occupy the hig ...
s, the placoderms. Bony fish are further divided into the lobe-finned and ray-finned fish
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fish or actinopterygians, is a class of bony fish that comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species. They are so called because of their lightly built fins made of webbings of sk ...
. About 96% of all living fish species today are teleost
Teleostei (; Ancient Greek, Greek ''teleios'' "complete" + ''osteon'' "bone"), members of which are known as teleosts (), is, by far, the largest group of ray-finned fishes (class Actinopterygii), with 96% of all neontology, extant species of f ...
s, a crown group
In phylogenetics, the crown group or crown assemblage is a collection of species composed of the living representatives of the collection, the most recent common ancestor of the collection, and all descendants of the most recent common ancestor ...
of ray-finned fish that can protrude their jaws. The tetrapods
A tetrapod (; from Ancient Greek τετρα- ''(tetra-)'' 'four' and πούς ''(poús)'' 'foot') is any four- limbed vertebrate animal of the clade Tetrapoda (). Tetrapods include all extant and extinct amphibians and amniotes, with the lat ...
, a mostly terrestrial clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach t ...
of vertebrates that have dominated the top trophic level
The trophic level of an organism is the position it occupies in a food web. Within a food web, a food chain is a succession of organisms that eat other organisms and may, in turn, be eaten themselves. The trophic level of an organism is the ...
s in both aquatic and terrestrial ecosystem
Terrestrial ecosystems are ecosystems that are found on land. Examples include tundra, taiga, temperate deciduous forest, tropical rain forest, grassland, deserts.
Terrestrial ecosystems differ from aquatic ecosystems by the predominant presen ...
s since the Late Paleozoic
The Paleozoic ( , , ; or Palaeozoic) Era is the first of three Era (geology), geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Beginning 538.8 million years ago (Ma), it succeeds the Neoproterozoic (the last era of the Proterozoic Eon) and ends 251.9 Ma a ...
, evolved from lobe-finned fish during the Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a Geologic time scale, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era that spans 60 million years, from the end of the Devonian Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the ...
, developing air-breathing lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their ...
s homologous to swim bladders. Despite the cladistic
Cladistics ( ; from Ancient Greek 'branch') is an approach to biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups ("clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesized relationships is ...
lineage, tetrapods are usually not considered to be fish.
Fish have been an important natural resource
Natural resources are resources that are drawn from nature and used with few modifications. This includes the sources of valued characteristics such as commercial and industrial use, aesthetic value, scientific interest, and cultural value. ...
for human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
s since prehistoric
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use o ...
times, especially as food. Commercial
Commercial may refer to:
* (adjective for) commerce, a system of voluntary exchange of products and services
** (adjective for) trade, the trading of something of economic value such as goods, services, information or money
* a dose of advertising ...
and subsistence fishers harvest fish in wild fisheries
A wild fishery is a natural body of water with a sizeable free-ranging fish or other aquatic animal (crustaceans and molluscs) population that can be harvested for its commercial value. Wild fisheries can be marine ( saltwater) or lacustrine/ ...
or farm
A farm (also called an agricultural holding) is an area of land that is devoted primarily to agricultural processes with the primary objective of producing food and other crops; it is the basic facility in food production. The name is used fo ...
them in pond
A pond is a small, still, land-based body of water formed by pooling inside a depression (geology), depression, either naturally or artificiality, artificially. A pond is smaller than a lake and there are no official criteria distinguishing ...
s or in breeding cages in the ocean. Fish are caught for recreation
Recreation is an activity of leisure, leisure being discretionary time. The "need to do something for recreation" is an essential element of human biology and psychology. Recreational activities are often done for happiness, enjoyment, amusement, ...
, or raised by fishkeepers as ornaments
An ornament is something used for decoration.
Ornament may also refer to:
Decoration
*Ornament (art), any purely decorative element in architecture and the decorative arts
*Ornamental turning
*Biological ornament, a characteristic of animals tha ...
for private and public exhibition in aquaria and garden ponds. Fish have had a role in human culture
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
through the ages, serving as deities
A deity or god is a supernatural being considered to be sacred and worthy of worship due to having authority over some aspect of the universe and/or life. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines ''deity'' as a God (male deity), god or god ...
, religious symbols, and as the subjects of art, books and movies.
Etymology
The word ''fish'' is inherited fromProto-Germanic
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the linguistic reconstruction, reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic languages, Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages.
Proto-Germanic eventually developed from ...
, and is related to German , the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
and Old Irish
Old Irish, also called Old Gaelic (, Ogham, Ogham script: ᚌᚑᚔᚇᚓᚂᚉ; ; ; or ), is the oldest form of the Goidelic languages, Goidelic/Gaelic language for which there are extensive written texts. It was used from 600 to 900. The ...
, though the exact root is unknown; some authorities reconstruct a Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. No direct record of Proto-Indo-European exists; its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-Euro ...
root , attested only in Italic, Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foot ...
, and Germanic.
Evolution
Fossil history
 About 530 million years ago during the Cambrian explosion, fishlike animals with a
About 530 million years ago during the Cambrian explosion, fishlike animals with a notochord
The notochord is an elastic, rod-like structure found in chordates. In vertebrates the notochord is an embryonic structure that disintegrates, as the vertebrae develop, to become the nucleus pulposus in the intervertebral discs of the verteb ...
and eyes at the front of the body, such as '' Haikouichthys'', appear in the fossil record
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
. During the late Cambrian
The Cambrian ( ) is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 51.95 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Ordov ...
, other jawless forms such as conodont
Conodonts, are an extinct group of marine jawless vertebrates belonging to the class Conodonta (from Ancient Greek κῶνος (''kōnos''), meaning " cone", and ὀδούς (''odoús''), meaning "tooth"). They are primarily known from their hard ...
s appear.
Jawed vertebrates appear in the Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 23.5 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the third and shortest period of t ...
, with giant armoured placoderms such as ''Dunkleosteus
''Dunkleosteus'' is an extinct genus of large arthrodira, arthrodire ("jointed-neck") fish that existed during the Late Devonian period, about 382–358 million years ago. It was a pelagic fish inhabiting open waters, and one of the first verteb ...
''. Jawed fish, too, appeared during the Silurian: the cartilaginous Chondrichthyes
Chondrichthyes (; ) is a class of jawed fish that contains the cartilaginous fish or chondrichthyans, which all have skeletons primarily composed of cartilage. They can be contrasted with the Osteichthyes or ''bony fish'', which have skeleto ...
and the bony Osteichthyes
Osteichthyes ( ; ), also known as osteichthyans or commonly referred to as the bony fish, is a Biodiversity, diverse clade of vertebrate animals that have endoskeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. They can be contrasted with the Chondricht ...
.
During the Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a period (geology), geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era during the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian per ...
, fish diversity greatly increased, including among the placoderms, lobe-finned fishes, and early sharks, earning the Devonian the epithet "the age of fishes".
Phylogeny
Fishes are aparaphyletic
Paraphyly is a taxonomic term describing a grouping that consists of the grouping's last common ancestor and some but not all of its descendant lineages. The grouping is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In co ...
group, since any clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach t ...
containing all fish, such as the Gnathostomata
Gnathostomata (; from Ancient Greek: (') 'jaw' + (') 'mouth') are jawed vertebrates. Gnathostome diversity comprises roughly 60,000 species, which accounts for 99% of all extant vertebrates, including all living bony fishes (both ray-finned ...
or (for bony fish) Osteichthyes
Osteichthyes ( ; ), also known as osteichthyans or commonly referred to as the bony fish, is a Biodiversity, diverse clade of vertebrate animals that have endoskeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. They can be contrasted with the Chondricht ...
, also contains the clade of tetrapod
A tetrapod (; from Ancient Greek :wiktionary:τετρα-#Ancient Greek, τετρα- ''(tetra-)'' 'four' and :wiktionary:πούς#Ancient Greek, πούς ''(poús)'' 'foot') is any four-Limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animal of the clade Tetr ...
s (four-limbed vertebrates, mostly terrestrial), which are usually not considered fish. Some tetrapods, such as cetacea
Cetacea (; , ) is an infraorder of aquatic mammals belonging to the order Artiodactyla that includes whales, dolphins and porpoises. Key characteristics are their fully aquatic lifestyle, streamlined body shape, often large size and exclusively c ...
ns and ichthyosaurs
Ichthyosauria is an taxonomy (biology), order of large extinction, extinct marine reptiles sometimes referred to as "ichthyosaurs", although the term is also used for wider clades in which the order resides.
Ichthyosaurians thrived during much of ...
, have secondarily acquired a fish-like body shape through convergent evolution
Convergent evolution is the independent evolution of similar features in species of different periods or epochs in time. Convergent evolution creates analogous structures that have similar form or function but were not present in the last comm ...
. On the other hand, ''Fishes of the World
''Fishes of the World'' is a standard reference for the systematics of fishes. It was first written in 1976 by the American ichthyologist Joseph S. Nelson (1937–2011). Now in its fifth edition (2016), the work is a comprehensive overview of t ...
'' comments that "it is increasingly widely accepted that tetrapods, including ourselves, are simply modified bony fishes, and so we are comfortable with using the taxon Osteichthyes as a clade, which now includes all tetrapods". The biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variability of life, life on Earth. It can be measured on various levels. There is for example genetic variability, species diversity, ecosystem diversity and Phylogenetics, phylogenetic diversity. Diversity is not distribut ...
of extant fish is unevenly distributed among the various groups; teleosts, bony fishes able to protrude their jaws, make up 96% of fish species. The cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an Phylogenetic tree, evolutionary tree because it does not s ...
shows the evolutionary relationships of all groups of living fishes (with their respective diversity) and the tetrapods. Table 1aNumber of species evaluated in relation to the overall number of described species, and numbers of threatened species by major groups of organisms
/ref>
Extinct
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
groups are marked with a dagger
A dagger is a fighting knife with a very sharp point and usually one or two sharp edges, typically designed or capable of being used as a cutting or stabbing, thrusting weapon.State v. Martin, 633 S.W.2d 80 (Mo. 1982): This is the dictionary or ...
(†); groups of uncertain placement are labelled with a question mark (?) and dashed lines (- - - - -).
Taxonomy
Fishes (without tetrapods) are aparaphyletic
Paraphyly is a taxonomic term describing a grouping that consists of the grouping's last common ancestor and some but not all of its descendant lineages. The grouping is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In co ...
group and for this reason, the class ''Pisces'' seen in older reference works is no longer used in formal classifications. Traditional classification divides fish into three extant
Extant or Least-concern species, least concern is the opposite of the word extinct. It may refer to:
* Extant hereditary titles
* Extant literature, surviving literature, such as ''Beowulf'', the oldest extant manuscript written in English
* Exta ...
classes ("Agnatha
Agnatha (; ) or jawless fish is a paraphyletic infraphylum of animals in the subphylum Vertebrata of the phylum Chordata, characterized by the lack of jaws. The group consists of both extant taxon, living (Cyclostomi, cyclostomes such as hagfish ...
", Chondrichthyes
Chondrichthyes (; ) is a class of jawed fish that contains the cartilaginous fish or chondrichthyans, which all have skeletons primarily composed of cartilage. They can be contrasted with the Osteichthyes or ''bony fish'', which have skeleto ...
, and "Osteichthyes
Osteichthyes ( ; ), also known as osteichthyans or commonly referred to as the bony fish, is a Biodiversity, diverse clade of vertebrate animals that have endoskeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. They can be contrasted with the Chondricht ...
"), and with extinct forms sometimes classified within those groups, sometimes as their own classes.
Fish account for more than half of vertebrate species. As of 2016, there are over 32,000 described species of bony fish, over 1,100 species of cartilaginous fish, and over 100 hagfish and lampreys. A third of these fall within the nine largest families; from largest to smallest, these are Cyprinidae
Cyprinidae is a family of freshwater fish commonly called the carp or minnow family, including the carps, the true minnows, and their relatives the barbs and barbels, among others. Cyprinidae is the largest and most diverse fish family, and t ...
, Gobiidae
Gobiidae or gobies is a family (biology), family of bony fish in the order (biology), order Gobiiformes, one of the largest fish families comprising over 2,000 species in more than 200 genus, genera. Most of gobiid fish are relatively small, typ ...
, Cichlidae
Cichlids ()
are a large, diverse, and widespread family of percomorph fish in the family Cichlidae, order Cichliformes. At least 1,760 species have been scientifically described, making it one of the largest vertebrate families, with on ...
, Characidae
Characidae, the characids, is a family of freshwater subtropical and tropical fish belonging to the order Characiformes. They are found throughout much of Central and South America, including such major waterways as the Amazon and Orinoco Riv ...
, Loricariidae
Loricariidae is the largest family (biology), family of catfish (order Siluriformes), with over 90 genus, genera and just over 680 species. Loricariids originate from freshwater habitats of Costa Rica, Panama, and tropical and subtropical South A ...
, Balitoridae, Serranidae
Serranidae is a large family (biology), family of fishes belonging to the order Perciformes. The family contains about 450 species in 65 genera, including the sea basses and the groupers (subfamily Epinephelinae). Although many species are small, ...
, Labridae, and Scorpaenidae
The Scorpaenidae (also known as scorpionfish) are a family (biology), family of mostly ocean, marine fish that includes many of the world's most venomous species. As their name suggests, scorpionfish have a type of "sting" in the form of sharp ...
. About 64 families are monotypic
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unisp ...
, containing only one species.
Diversity
Fish range in size from the hugewhale shark
The whale shark (''Rhincodon typus'') is a slow-moving, filter feeder, filter-feeding carpet shark and the largest known Extant taxon, extant fish species. The largest confirmed individual had a length of . The whale shark holds many records for ...
to some tiny teleosts only long, such as the cyprinid '' Paedocypris progenetica'' and the stout infantfish.
whale shark
The whale shark (''Rhincodon typus'') is a slow-moving, filter feeder, filter-feeding carpet shark and the largest known Extant taxon, extant fish species. The largest confirmed individual had a length of . The whale shark holds many records for ...
File:Paedocypris progenetica 001.jpg, Smallest: e.g. '' Paedocypris progenetica''
salmon
Salmon (; : salmon) are any of several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the genera ''Salmo'' and ''Oncorhynchus'' of the family (biology), family Salmonidae, native ...
, and jacks that can cover 10–20 body-lengths per second to species such as eels and rays that swim no more than 0.5 body-lengths per second.
salmon
Salmon (; : salmon) are any of several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the genera ''Salmo'' and ''Oncorhynchus'' of the family (biology), family Salmonidae, native ...
, 10–20 body lengths/second
File:Anguilla japonica 1856.jpg, Slowest: e.g. eel, 0.5 body lengths/second
streamlined
Streamlines, streaklines and pathlines are field lines in a fluid flow.
They differ only when the flow changes with time, that is, when the flow is not steady flow, steady.
Considering a velocity vector field in three-dimensional space in the f ...
body for rapid swimming, extracts oxygen from water using gills, has two sets of paired fins, one or two dorsal fins, an anal fin and a tail fin, jaws, skin covered with scales
Scale or scales may refer to:
Mathematics
* Scale (descriptive set theory), an object defined on a set of points
* Scale (ratio), the ratio of a linear dimension of a model to the corresponding dimension of the original
* Scale factor, a number ...
, and lays eggs. Each criterion has exceptions, creating a wide diversity in body shape and way of life. For example, some fast-swimming fish are warm-blooded, while some slow-swimming fish have abandoned streamlining in favour of other body shapes.
Ambush predator
Ambush predators or sit-and-wait predators are carnivorous animals that capture their prey via stealth, luring or by (typically instinctive) strategies utilizing an element of surprise. Unlike pursuit predators, who chase to capture prey u ...
:anglerfish
The anglerfish are ray-finned fish in the order Lophiiformes (). Both the order's common name, common and scientific name comes from the characteristic mode of predation, in which a modified dorsal Fish fin#Ray-fins, fin ray acts as a Aggressiv ...
File:Atl mackerel photo3 exp.jpg, Streamlined
Streamlines, streaklines and pathlines are field lines in a fluid flow.
They differ only when the flow changes with time, that is, when the flow is not steady flow, steady.
Considering a velocity vector field in three-dimensional space in the f ...
, somewhat warm-blooded
Warm-blooded is a term referring to animal species whose bodies maintain a temperature higher than that of their environment. In particular, homeothermic species (including birds and mammals) maintain a stable body temperature by regulating ...
:mackerel
Mackerel is a common name applied to a number of different species of pelagic fish, mostly from the family Scombridae. They are found in both temperate and tropical seas, mostly living along the coast or offshore in the oceanic environment.
...
File:Hippocampus hippocampus (cropped).jpg, Tail not used for swimming:seahorse
A seahorse (also written ''sea-horse'' and ''sea horse'') is any of 46 species of small marine Osteichthyes, bony fish in the genus ''Hippocampus''. The genus name comes from the Ancient Greek (), itself from () meaning "horse" and () meanin ...
File:Phycodurus eques P2023146 (cropped).JPG, Camouflage
Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. Examples include the leopard's spotted coat, the b ...
d:leafy seadragon
The leafy seadragon (''Phycodurus eques'') or Glauert's seadragon, is a marine fish. It is the only member of the genus ''Phycodurus'' in the family Syngnathidae, which includes seadragons, pipefish, and seahorses.
It is found along the s ...
File:Eastern Cleaner Clingfish (cropped).jpg, No scales
Scale or scales may refer to:
Mathematics
* Scale (descriptive set theory), an object defined on a set of points
* Scale (ratio), the ratio of a linear dimension of a model to the corresponding dimension of the original
* Scale factor, a number ...
:clingfish
Clingfishes are ray-finned fishes of the family Gobiesocidae, the only family in the suborder Gobiesocoidei of the order Blenniiformes. These fairly small to very small fishes are widespread in tropical and temperate regions, mostly near the coa ...
File:Cyphotilapia frontosa mouthbrooding.jpg, Mouthbrooder: front cichlid with young in mouth
Ecology
Habitats
freshwater
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. The term excludes seawater and brackish water, but it does include non-salty mi ...
and marine (oceanic) ecosystems; there are some 15,200 freshwater species and around 14,800 marine species. Coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in group ...
s in the Indo-Pacific
The Indo-Pacific is a vast biogeographic region of Earth. In a narrow sense, sometimes known as the Indo-West Pacific or Indo-Pacific Asia, it comprises the tropical waters of the Indian Ocean, the western and central Pacific Ocean, and the ...
constitute the center of diversity for marine fishes, whereas continental freshwater fishes are most diverse in large river basin
A drainage basin is an area of land in which all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, th ...
s of tropical rainforest
Tropical rainforests are dense and warm rainforests with high rainfall typically found between 10° north and south of the Equator. They are a subset of the tropical forest biome that occurs roughly within the 28° latitudes (in the torrid zo ...
s, especially the Amazon
Amazon most often refers to:
* Amazon River, in South America
* Amazon rainforest, a rainforest covering most of the Amazon basin
* Amazon (company), an American multinational technology company
* Amazons, a tribe of female warriors in Greek myth ...
, Congo, and Mekong
The Mekong or Mekong River ( , ) is a transboundary river in East Asia and Southeast Asia. It is the world's twelfth-longest river and the third-longest in Asia with an estimated length of and a drainage area of , discharging of wat ...
basins. More than 5,600 fish species inhabit Neotropic
The Neotropical realm is one of the eight biogeographic realms constituting Earth's land surface. Physically, it includes the tropical terrestrial ecoregions of the Americas and the entire South American temperate zone.
Definition
In biogeogra ...
al freshwaters alone, such that Neotropical fishes represent about 10% of all vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
species on the Earth.
Fish are abundant in most bodies of water. They can be found in nearly all aquatic environments, from high mountain streams (e.g., char and gudgeon) to the abyssal and even hadal
The hadal zone, also known as the hadopelagic zone, is the deepest region of the ocean, lying within oceanic trenches. The hadal zone ranges from around below sea level, and exists in long, narrow, topographic V-shaped depressions.
The cumula ...
depths of the deepest oceans (e.g., cusk-eels
The cusk-eel family, Ophidiidae, is a group of marine bony fishes in the Ophidiiformes order. The scientific name is from the Greek ''ophis'' meaning "snake", and refers to their eel-like appearance. True eels diverged from other ray-finn ...
and snailfish), although none have been found in the deepest 25% of the ocean. The deepest living fish in the ocean so far found is a cusk-eel, '' Abyssobrotula galatheae'', recorded at the bottom of the Puerto Rico Trench
The Puerto Rico Trench is located on the boundary between the North Atlantic Ocean and Caribbean Sea, parallel to and north of Puerto Rico, where the oceanic trench reaches the deepest points in the Atlantic Ocean. The trench is associated with ...
at .
In terms of temperature, Jonah's icefish live in cold waters of the Southern Ocean, including under the Filchner–Ronne Ice Shelf
The Filchner–Ronne Ice Shelf or Ronne–Filchner Ice Shelf is an List of Antarctic ice shelves, Antarctic ice shelf bordering the Weddell Sea.
Description
The seaward side of the Filchner–Ronne ice shelf is divided into Eastern (Filchne ...
at a latitude of 79°S, while desert pupfish
The desert pupfish (''Cyprinodon macularius'') is a rare species of teleost, bony fish in the family Cyprinodontidae. It is a small fish, typically less than 7.62 cm (3 in) in length. Males are generally larger than females, and have br ...
live in desert springs, streams, and marshes, sometimes highly saline, with water temperatures as high as 36 C.
A few fish live mostly on land or lay their eggs on land near water. Mudskipper
Mudskippers are any of the 23 extant species of amphibious fish from the subfamily Oxudercinae of the goby family (biology), family Oxudercidae. They are known for their unusual body shapes, preferences for semiaquatic habitats, limited terrestria ...
s feed and interact with one another on mudflats and go underwater to hide in their burrows. A single undescribed species
In taxonomy, an undescribed taxon is a taxon (for example, a species) that has been discovered, but not yet formally described and named. The various Nomenclature Codes specify the requirements for a new taxon to be validly described and named. U ...
of '' Phreatobius'' has been called a true "land fish" as this worm-like catfish strictly lives among waterlogged leaf litter
Plant litter (also leaf litter, tree litter, soil litter, litterfall, or duff) is dead plant material (such as leaves, bark, needles, twigs, and cladodes) that has fallen to the ground. This detritus or dead organic material and its constituen ...
. Cavefish
Cavefish or cave fish is a generic term for fresh and brackish water fish adapted to life in caves and other underground habitats. Related terms are subterranean fish, Troglomorphism, troglomorphic fish, troglobitic fish, stygobitic fish, phreat ...
of multiple families live in underground lake
An underground lake or subterranean lake is a lake underneath the surface of the Earth. Most naturally occurring underground lakes are found in areas of karst topography, where limestone or other soluble rock has been weathered away, leaving a ca ...
s, underground rivers or aquifer
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing material, consisting of permeability (Earth sciences), permeable or fractured rock, or of unconsolidated materials (gravel, sand, or silt). Aquifers vary greatly in their characteristics. The s ...
s.
Parasites and predators
Like other animals, fish suffer fromparasitism
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The en ...
. Some species use cleaner fish to remove external parasites. The best known of these are the bluestreak cleaner wrasses of coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in group ...
s in the Indian and Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
oceans. These small fish maintain cleaning stations where other fish congregate and perform specific movements to attract the attention of the cleaners. Cleaning behaviors have been observed in a number of fish groups, including an interesting case between two cichlids of the same genus, '' Etroplus maculatus'', the cleaner, and the much larger '' E. suratensis''.
Fish occupy many trophic level
The trophic level of an organism is the position it occupies in a food web. Within a food web, a food chain is a succession of organisms that eat other organisms and may, in turn, be eaten themselves. The trophic level of an organism is the ...
s in freshwater and marine food web
A food web is the natural interconnection of food chains and a graphical representation of what-eats-what in an ecological community. Position in the food web, or trophic level, is used in ecology to broadly classify organisms as autotrophs or he ...
s. Fish at the higher levels are predatory, and a substantial part of their prey consists of other fish. In addition, mammals such as dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal in the cetacean clade Odontoceti (toothed whale). Dolphins belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontopori ...
s and seal
Seal may refer to any of the following:
Common uses
* Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly:
** Earless seal, also called "true seal"
** Fur seal
** Eared seal
* Seal ( ...
s feed on fish, alongside birds such as gannet
Gannets are seabirds comprising the genus ''Morus'' in the family Sulidae, closely related to boobies. They are known as 'solan' or 'solan goose' in Scotland. A common misconception is that the Scottish name is 'guga' but this is the Gaelic n ...
s and cormorant
Phalacrocoracidae is a family of approximately 40 species of aquatic birds commonly known as cormorants and shags. Several different classifications of the family have been proposed, but in 2021 the International Ornithologists' Union (IOU) ado ...
s.
algae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) is an informal term for any organisms of a large and diverse group of photosynthesis, photosynthetic organisms that are not plants, and includes species from multiple distinct clades. Such organisms range from unicellular ...
on a coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in group ...
File:Arothron hispidus is being cleaned by Hawaiian cleaner wrasses, Labroides phthirophagus 1.jpg, A cleaner fish removing parasite
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted str ...
s from its client, a pufferfish
Tetraodontidae is a family of marine and freshwater fish in the order Tetraodontiformes. The family includes many familiar species variously called pufferfish, puffers, balloonfish, blowfish, blowers, blowies, bubblefish, globefish, swellfis ...
File:Barracuda with prey.jpg, A barracuda
A barracuda is a large, predatory, ray-finned, saltwater fish of the genus ''Sphyraena'', the only genus in the family Sphyraenidae, which was named by Constantine Samuel Rafinesque in 1815. It is found in tropical and subtropical oceans worldw ...
preying on a smaller fish
File:1031 california sealion wright odfw (35281910502).jpg, Sea lion
Sea lions are pinnipeds characterized by external ear flaps, long foreflippers, the ability to walk on all fours, short and thick hair, and a big chest and belly. Together with the fur seals, they make up the family Otariidae, eared seals. ...
, a predatory mammal, eating a large salmonid
Salmonidae (, ) is a family of ray-finned fish, the only extant member of the suborder Salmonoidei, consisting of 11 extant genera and over 200 species collectively known as "salmonids" or "salmonoids". The family includes salmon (both Atlantic a ...
File:Cormorant with fish (cropped).jpg, Cormorant
Phalacrocoracidae is a family of approximately 40 species of aquatic birds commonly known as cormorants and shags. Several different classifications of the family have been proposed, but in 2021 the International Ornithologists' Union (IOU) ado ...
with fish prey
Anatomy and physiology
Locomotion
The body of a typical fish is adapted for efficient swimming by alternately contracting paired sets ofmuscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contra ...
s on either side of the backbone. These contractions form S-shaped curves that move down the body. As each curve reaches the tail fin, force is applied to the water, moving the fish forward. The other fins act as control surfaces like an aircraft's flaps, enabling the fish to steer in any direction.
lanternfish
Lanternfish (or myctophids, from the Greek language, Greek μυκτήρ ''myktḗr'', "nose" and ''ophis'', "serpent") are small mesopelagic fish of the large family (biology), family Myctophidae. One of two families in the order Myctophiformes, ...
shown):1)
gill cover
The operculum is a series of bones found in bony fish and Chimaera, chimaeras that serves as a facial support structure and a protective covering for the gills; it is also used for respiration and feeding.
Anatomy
The opercular series contain ...
2) lateral line
The lateral line, also called the lateral line organ (LLO), is a system of sensory organs found in fish, used to detect movement, vibration, and pressure gradients in the surrounding water. The sensory ability is achieved via modified epithelia ...
3) dorsal fin 4) fat fin5) caudal peduncle 6) caudal fin 7) anal fin 8)
photophore
A photophore is a specialized anatomical structure found in a variety of organisms that emits light through the process of boluminescence. This light may be produced endogenously by the organism itself (symbiotic) or generated through a mut ...
s 9) pelvic fins 10) pectoral fins
swim bladder
The swim bladder, gas bladder, fish maw, or air bladder is an internal gas-filled organ (anatomy), organ in bony fish that functions to modulate buoyancy, and thus allowing the fish to stay at desired water depth without having to maintain lift ...
that allows them to adjust their buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is the force exerted by a fluid opposing the weight of a partially or fully immersed object (which may be also be a parcel of fluid). In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of t ...
by increasing or decreasing the amount of gas it contains.
The scales of fish provide protection from predator
Predation is a biological interaction in which one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common List of feeding behaviours, feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation ...
s at the cost of adding stiffness and weight. Fish scales are often highly reflective; this silvering provides camouflage in the open ocean. Because the water all around is the same colour, reflecting an image of the water offers near-invisibility.
swim bladder
The swim bladder, gas bladder, fish maw, or air bladder is an internal gas-filled organ (anatomy), organ in bony fish that functions to modulate buoyancy, and thus allowing the fish to stay at desired water depth without having to maintain lift ...
of a rudd helps maintain neutral buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is the force exerted by a fluid opposing the weight of a partially or fully immersed object (which may be also be a parcel of fluid). In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of t ...
.
File:Fish scales.jpg, Silvered scales
Scale or scales may refer to:
Mathematics
* Scale (descriptive set theory), an object defined on a set of points
* Scale (ratio), the ratio of a linear dimension of a model to the corresponding dimension of the original
* Scale factor, a number ...
of a rohu provide protection and camouflage.
Circulation
 Fish have a closed-loop circulatory system. The
Fish have a closed-loop circulatory system. The heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrie ...
pumps the blood in a single loop throughout the body; for comparison, the mammal heart has two loops, one for the lungs to pick up oxygen, one for the body to deliver the oxygen. In fish, the heart pumps blood through the gills. Oxygen-rich blood then flows without further pumping, unlike in mammals, to the body tissues. Finally, oxygen-depleted blood returns to the heart.
Respiration
Gills
Fish exchange gases usinggill
A gill () is a respiration organ, respiratory organ that many aquatic ecosystem, aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow r ...
s on either side of the pharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the human mouth, mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates ...
. Gills consist of comblike structures called filaments. Each filament contains a capillary
A capillary is a small blood vessel, from 5 to 10 micrometres in diameter, and is part of the microcirculation system. Capillaries are microvessels and the smallest blood vessels in the body. They are composed of only the tunica intima (the inn ...
network that provides a large surface area
The surface area (symbol ''A'') of a solid object is a measure of the total area that the surface of the object occupies. The mathematical definition of surface area in the presence of curved surfaces is considerably more involved than the d ...
for exchanging oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
and carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
. Fish exchange gases by pulling oxygen-rich water through their mouths and pumping it over their gills. Capillary blood in the gills flows in the opposite direction to the water, resulting in efficient countercurrent exchange
Countercurrent exchange is a mechanism between two flowing bodies flowing in opposite directions to each other, in which there is a transfer of some property, usually heat or some chemical. The flowing bodies can be liquids, gases, or even solid ...
. The gills push the oxygen-poor water out through openings in the sides of the pharynx. Cartilaginous fish have multiple gill openings: sharks usually have five, sometimes six or seven pairs; they often have to swim to oxygenate their gills. Bony fish have a single gill opening on each side, hidden beneath a protective bony cover or operculum. They are able to oxygenate their gills using muscles in the head.
Air breathing
Some 400 species of fish in 50 families can breathe air, enabling them to live in oxygen-poor water or to emerge on to land. The ability of fish to do this is potentially limited by their single-loop circulation, as oxygenated blood from their air-breathing organ will mix with deoxygenated blood returning to the heart from the rest of the body. Lungfish, bichirs, ropefish, bowfins, snakefish, and the African knifefish have evolved to reduce such mixing, and to reduce oxygen loss from the gills to oxygen-poor water. Bichirs and lungfish have tetrapod-like paired lungs, requiring them to surface to gulp air, and making them obligate air breathers. Many other fish, including inhabitants of rock pools and theintertidal zone
The intertidal zone or foreshore is the area above water level at low tide and underwater at high tide; in other words, it is the part of the littoral zone within the tidal range. This area can include several types of habitats with various ...
, are facultative air breathers, able to breathe air when out of water, as may occur daily at low tide, and to use their gills when in water. Some coastal fish like rockskippers and mudskipper
Mudskippers are any of the 23 extant species of amphibious fish from the subfamily Oxudercinae of the goby family (biology), family Oxudercidae. They are known for their unusual body shapes, preferences for semiaquatic habitats, limited terrestria ...
s choose to leave the water to feed in habitats temporarily exposed to the air. Some catfish absorb air through their digestive tracts.
Digestion
The digestive system consists of a tube, the gut, leading from the mouth to the anus. The mouth of most fishes contains teeth to grip prey, bite off or scrape plant material, or crush the food. Anesophagus
The esophagus (American English), oesophagus (British English), or œsophagus (Œ, archaic spelling) (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, see spelling difference) all ; : ((o)e)(œ)sophagi or ((o)e)(œ)sophaguses), c ...
carries food to the stomach where it may be stored and partially digested. A sphincter, the pylorus, releases food to the intestine at intervals. Many fish have finger-shaped pouches, pyloric caeca, around the pylorus, of doubtful function. The pancreas
The pancreas (plural pancreases, or pancreata) is an Organ (anatomy), organ of the Digestion, digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity, abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a ...
secretes enzymes into the intestine to digest the food; other enzymes are secreted directly by the intestine itself. The liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
produces bile
Bile (from Latin ''bilis''), also known as gall, is a yellow-green/misty green fluid produced by the liver of most vertebrates that aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine. In humans, bile is primarily composed of water, is pro ...
which helps to break up fat into an emulsion which can be absorbed in the intestine.
Excretion
Most fish release their nitrogenous wastes asammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pu ...
. This may be excreted through the gills or filtered by the kidney
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organ (anatomy), organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and rig ...
s. Salt is excreted by the rectal gland. Saltwater fish tend to lose water by osmosis
Osmosis (, ) is the spontaneous net movement or diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane, selectively-permeable membrane from a region of high water potential (region of lower solute concentration) to a region of ...
; their kidneys return water to the body, and produce a concentrated urine. The reverse happens in freshwater fish
Freshwater fish are fish species that spend some or all of their lives in bodies of fresh water such as rivers, lakes, ponds and inland wetlands, where the salinity is less than 1.05%. These environments differ from marine habitats in many wa ...
: they tend to gain water osmotically, and produce a dilute urine. Some fish have kidneys able to operate in both freshwater and saltwater.
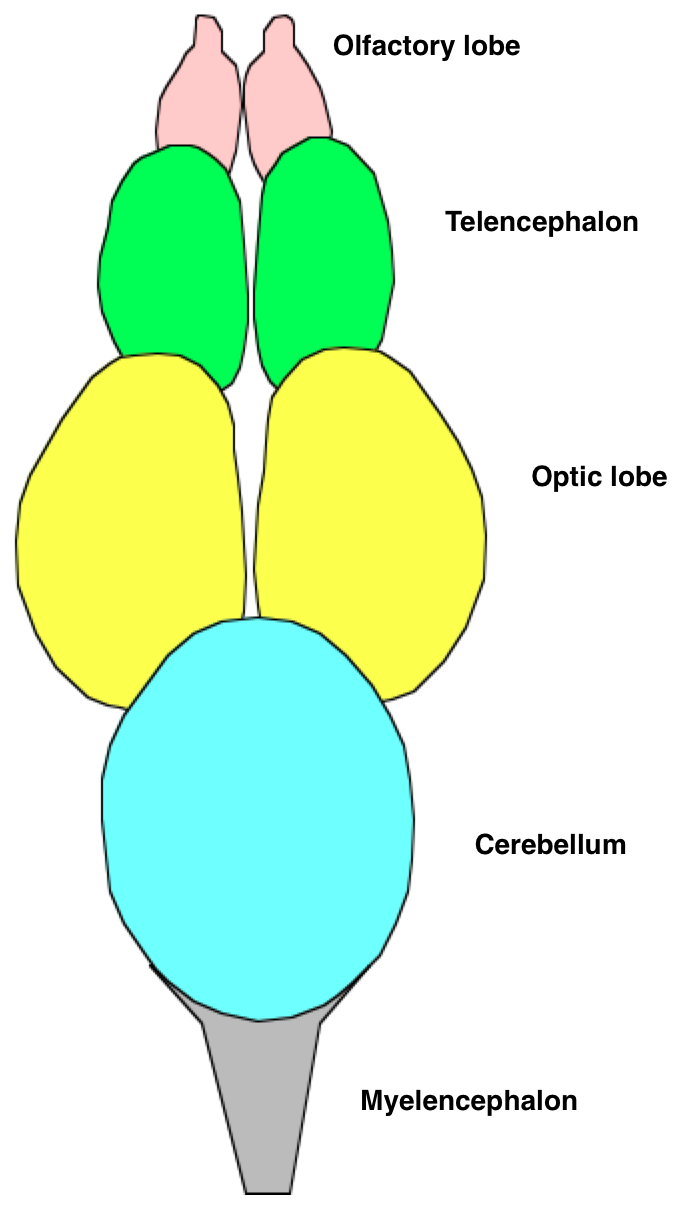
Brain
 Fish have small brains relative to body size compared with other vertebrates, typically one-fifteenth the brain mass of a similarly sized bird or mammal. However, some fish have relatively large brains, notably mormyrids and
Fish have small brains relative to body size compared with other vertebrates, typically one-fifteenth the brain mass of a similarly sized bird or mammal. However, some fish have relatively large brains, notably mormyrids and shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch cartilaginous fish characterized by a ribless endoskeleton, dermal denticles, five to seven gill slits on each side, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the ...
s, which have brains about as large for their body weight as birds and marsupial
Marsupials are a diverse group of mammals belonging to the infraclass Marsupialia. They are natively found in Australasia, Wallacea, and the Americas. One of marsupials' unique features is their reproductive strategy: the young are born in a r ...
s. At the front of the brain are the olfactory lobes, a pair of structures that receive and process signals from the nostril
A nostril (or naris , : nares ) is either of the two orifices of the nose. They enable the entry and exit of air and other gasses through the nasal cavities. In birds and mammals, they contain branched bones or cartilages called turbinates ...
s via the two olfactory nerve
The olfactory nerve, also known as the first cranial nerve, cranial nerve I, or simply CN I, is a cranial nerve that contains sensory nerve fibers relating to the sense of smell.
The afferent nerve fibers of the olfactory receptor neurons t ...
s. Fish that hunt primarily by smell, such as hagfish and sharks, have very large olfactory lobes. Behind these is the telencephalon
The cerebrum (: cerebra), telencephalon or endbrain is the largest part of the brain, containing the cerebral cortex (of the two cerebral hemispheres) as well as several subcortical structures, including the hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olf ...
, which in fish deals mostly with olfaction. Together these structures form the forebrain. Connecting the forebrain to the midbrain is the diencephalon
In the human brain, the diencephalon (or interbrain) is a division of the forebrain (embryonic ''prosencephalon''). It is situated between the telencephalon and the midbrain (embryonic ''mesencephalon''). The diencephalon has also been known as t ...
; it works with hormone
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physio ...
s and homeostasis
In biology, homeostasis (British English, British also homoeostasis; ) is the state of steady internal physics, physical and chemistry, chemical conditions maintained by organism, living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning fo ...
. The pineal body
The pineal gland (also known as the pineal body or epiphysis cerebri) is a small endocrine gland in the brain of most vertebrates. It produces melatonin, a serotonin-derived hormone, which modulates sleep patterns following the diurnal cycles. ...
is just above the diencephalon; it detects light, maintains circadian
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural oscillation that repeats roughly every 24 hours. Circadian rhythms can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., endogenous) and responds to the environment (is entrai ...
rhythms, and controls color changes. The midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the uppermost portion of the brainstem connecting the diencephalon and cerebrum with the pons. It consists of the cerebral peduncles, tegmentum, and tectum.
It is functionally associated with vision, hearing, mo ...
contains the two optic lobes. These are very large in species that hunt by sight, such as rainbow trout
The rainbow trout (''Oncorhynchus mykiss'') is a species of trout native to cold-water tributary, tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in North America and Asia. The steelhead (sometimes called steelhead trout) is an Fish migration#Classification, ...
and cichlid
Cichlids ()
are a large, diverse, and widespread family of percomorph fish in the family Cichlidae, order Cichliformes. At least 1,760 species have been scientifically described, making it one of the largest vertebrate families, with on ...
s. The hindbrain
The hindbrain, rhombencephalon (shaped like a rhombus) is a developmental categorization of portions of the central nervous system in vertebrates. It includes the medulla, pons, and cerebellum. Together they support vital bodily processes.
Met ...
controls swimming and balance.The single-lobed cerebellum is the biggest part of the brain; it is small in hagfish and lamprey
Lampreys (sometimes inaccurately called lamprey eels) are a group of Agnatha, jawless fish comprising the order (biology), order Petromyzontiformes , sole order in the Class (biology), class Petromyzontida. The adult lamprey is characterize ...
s, but very large in mormyrids, processing their electrical sense. The brain stem or myelencephalon
The myelencephalon or afterbrain is the most posterior region of the embryonic hindbrain, from which the medulla oblongata develops.
Myelencephalon is from myel- (bone marrow or spinal cord) and encephalon (the vertebrate brain).
Development
...
controls some muscles and body organs, and governs respiration and osmoregulation
Osmoregulation is the active regulation of the osmotic pressure of an organism's body fluids, detected by osmoreceptors, to maintain the homeostasis of the organism's water content; that is, it maintains the fluid balance and the concentration ...
.
Sensory systems
Thelateral line
The lateral line, also called the lateral line organ (LLO), is a system of sensory organs found in fish, used to detect movement, vibration, and pressure gradients in the surrounding water. The sensory ability is achieved via modified epithelia ...
system is a network of sensors in the skin which detects gentle currents and vibrations, and senses the motion of nearby fish, whether predators or prey. This can be considered both a sense of touch
The somatosensory system, or somatic sensory system is a subset of the sensory nervous system. The main functions of the somatosensory system are the perception of external stimuli, the perception of internal stimuli, and the regulation of bo ...
and of hearing
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is auditory sci ...
. Blind cave fish navigate almost entirely through the sensations from their lateral line system. Some fish, such as catfish and sharks, have the ampullae of Lorenzini, electroreceptors that detect weak electric currents on the order of millivolt.
Vision
Vision, Visions, or The Vision may refer to:
Perception Optical perception
* Visual perception, the sense of sight
* Visual system, the physical mechanism of eyesight
* Computer vision, a field dealing with how computers can be made to gain und ...
is an important sensory system
The sensory nervous system is a part of the nervous system responsible for processing sensory information. A sensory system consists of sensory neurons (including the sensory receptor cells), neural pathways, and parts of the brain involved ...
in fish. Fish eyes are similar to those of terrestrial vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
s like birds
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
and mammals, but have a more spherical lens
A lens is a transmissive optical device that focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements'') ...
. Their retina
The retina (; or retinas) is the innermost, photosensitivity, light-sensitive layer of tissue (biology), tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some Mollusca, molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focus (optics), focused two-dimensional ...
s generally have both rods and cones (for scotopic and photopic vision
Photopic vision is the vision of the eye under well-lit conditions (luminance levels from 10 to 108 cd/m2). In humans and many other animals, photopic vision allows color perception, mediated by cone cells, and a significantly higher vis ...
); many species have colour vision
Color vision, a feature of visual perception, is an ability to perceive differences between light composed of different frequencies independently of light intensity.
Color perception is a part of the larger visual system and is mediated by a co ...
, often with three types of cone. Teleosts can see polarized light
, or , is a property of transverse waves which specifies the geometrical orientation of the oscillations. In a transverse wave, the direction of the oscillation is perpendicular to the direction of motion of the wave. One example of a polarize ...
; some such as cyprinids have a fourth type of cone that detects ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
. Amongst jawless fish
Agnatha (; ) or jawless fish is a paraphyletic infraphylum of animals in the subphylum Vertebrata of the phylum Chordata, characterized by the lack of jaws. The group consists of both extant taxon, living (Cyclostomi, cyclostomes such as hagfish ...
, the lamprey
Lampreys (sometimes inaccurately called lamprey eels) are a group of Agnatha, jawless fish comprising the order (biology), order Petromyzontiformes , sole order in the Class (biology), class Petromyzontida. The adult lamprey is characterize ...
has well-developed eyes, while the hagfish
Hagfish, of the Class (biology), class Myxini (also known as Hyperotreti) and Order (biology), order Myxiniformes , are eel-shaped Agnatha, jawless fish (occasionally called slime eels). Hagfish are the only known living Animal, animals that h ...
has only primitive eyespots. See alsLamb et al.'s "The origin of the Vertebrate Eye", 2008.
/ref>
Hearing
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is auditory sci ...
too is an important sensory system in fish. Fish sense sound using their lateral lines and otolith
An otolith (, ' ear + , ', a stone), also called otoconium, statolith, or statoconium, is a calcium carbonate structure in the saccule or utricle (ear), utricle of the inner ear, specifically in the vestibular system of vertebrates. The saccule ...
s in their ears, inside their heads. Some can detect sound through the swim bladder.
Some fish, including salmon, are capable of magnetoreception; when the axis of a magnetic field is changed around a circular tank of young fish, they reorient themselves in line with the field. The mechanism of fish magnetoreception remains unknown; experiments in birds imply a quantum radical pair mechanism.
Cognition
The cognitive capacities of fish includeself-awareness
In philosophy of self, philosophy, self-awareness is the awareness and reflection of one's own personality or individuality, including traits, feelings, and behaviors. It is not to be confused with consciousness in the sense of qualia. While ...
, as seen in mirror test
The mirror test—sometimes called the mark test, mirror self-recognition (MSR) test, red spot technique, or rouge test—is a behavioral technique developed in 1970 by American psychologist Gordon Gallup Jr. to determine whether an animal posse ...
s. Manta rays
Manta rays are large Batoidea, rays belonging to the genus ''Mobula'' (formerly its own genus ''Manta''). The larger species, ''Giant oceanic manta ray, M. birostris'', reaches in width, while the smaller, ''Reef manta ray, M. alfredi'', reac ...
and wrasse
The wrasses are a family, Labridae, of marine ray-finned fish, many of which are brightly colored. The family is large and diverse, with over 600 species in 81 genera, which are divided into nine subgroups or tribes.
They are typically small, ...
s placed in front of a mirror repeatedly check whether their reflection's behavior mimics their body movement. '' Choerodon'' wrasse, archerfish, and Atlantic cod
The Atlantic cod (: cod; ''Gadus morhua'') is a fish of the family Gadidae, widely consumed by humans. It is also commercially known as '' cod'' or ''codling''.monogamous
Monogamy ( ) is a relationship of two individuals in which they form a mutual and exclusive intimate partnership. Having only one partner at any one time, whether for life or serial monogamy, contrasts with various forms of non-monogamy (e.g. ...
cichlid '' Amatitlania siquia'' exhibits pessimistic behavior when prevented from being with its partner. Fish orient themselves using landmarks; they may use mental maps based on multiple landmarks. Fish are able to learn to traverse mazes, showing that they possess spatial memory and visual discrimination. Behavioral research suggests that fish are sentient, capable of experiencing pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging Stimulus (physiology), stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sense, sensory and emotional experience associated with, or res ...
.
Electrogenesis
Electric fish
An electric fish is any fish that can Bioelectrogenesis, generate electric fields, whether to sense things around them, for defence, or to stun prey. Most fish able to produce shocks are also electroreceptive, meaning that they can sense electric ...
such as elephantfishes, the African knifefish, and electric eels have some of their muscles adapted to generate electric fields. They use the field to locate and identify objects such as prey in the waters around them, which may be turbid or dark. Strongly electric fish like the electric eel can in addition use their electric organs to generate shocks powerful enough to stun their prey.
Endothermy
Most fish are exclusively cold-blooded or ectothermic. However, the Scombroidei arewarm-blooded
Warm-blooded is a term referring to animal species whose bodies maintain a temperature higher than that of their environment. In particular, homeothermic species (including birds and mammals) maintain a stable body temperature by regulating ...
(endothermic), including the billfish
The billfish are a group (Xiphioidea) of saltwater fish, saltwater predatory fish characterised by prominent pointed beak, bills (rostrum (anatomy), rostra), and by their large size; some are longer than . Extant billfish include sailfish and m ...
es and tunas. The opah, a lampriform, uses whole-body endothermy, generating heat with its swimming muscles to warm its body while countercurrent exchange minimizes heat loss. Among the cartilaginous fishes, sharks of the families Lamnidae
The Lamnidae are the family of mackerel sharks known as white sharks. They are large, fast-swimming predatory fish found in oceans worldwide, though they prefer environments with colder water. The name of the family is formed from the Greek word ...
(such as the great white shark) and Alopiidae (thresher sharks) are endothermic. The degree of endothermy varies from the billfishes, which warm only their eyes and brain, to the bluefin tuna Bluefin tuna is a common name used to refer to several species of tuna of the genus ''Thunnus''.
{{Animal common name
Commercial fish
Thunnus
Fish common names ...
and the porbeagle shark, which maintain body temperatures more than above the ambient water.
Reproduction and life-cycle
 The primary reproductive organs are paired
The primary reproductive organs are paired testicle
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is Homology (biology), homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of Androgen, androgens, p ...
s and ovaries
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are endocr ...
. Eggs are released from the ovary to the oviduct
The oviduct in vertebrates is the passageway from an ovary. In human females, this is more usually known as the fallopian tube. The eggs travel along the oviduct. These eggs will either be fertilized by spermatozoa to become a zygote, or will dege ...
s. Over 97% of fish, including salmon and goldfish, are oviparous
Oviparous animals are animals that reproduce by depositing fertilized zygotes outside the body (i.e., by laying or spawning) in metabolically independent incubation organs known as eggs, which nurture the embryo into moving offsprings kno ...
, meaning that the eggs are shed into the water and develop outside the mother's body. The eggs are usually fertilized outside the mother's body, with the male and female fish shedding their gamete
A gamete ( ) is a Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as s ...
s into the surrounding water. In a few oviparous fish, such as the skates, fertilization is internal: the male uses an intromittent organ
An intromittent organ is any external organ of a male organism that is specialized to deliver sperm during copulation. Intromittent organs are found most often in terrestrial species, as most non-mammalian aquatic species fertilize their eggs ...
to deliver sperm into the female's genital opening of the female. Marine fish release large numbers of small eggs into the open water column. Newly hatched young of oviparous fish are planktonic larvae. They have a large yolk sac
The yolk sac is a membranous wikt:sac, sac attached to an embryo, formed by cells of the hypoblast layer of the bilaminar embryonic disc. This is alternatively called the umbilical vesicle by the Terminologia Embryologica (TE), though ''yolk sac' ...
and do not resemble juvenile or adult fish. The larval period in oviparous fish is usually only some weeks, and larvae rapidly grow and change in structure to become juveniles. During this transition, larvae must switch from their yolk sac to feeding on zooplankton
Zooplankton are the heterotrophic component of the planktonic community (the " zoo-" prefix comes from ), having to consume other organisms to thrive. Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents. Consequent ...
prey. Some fish such as surf-perches, splitfins, and lemon shark
The lemon shark (''Negaprion brevirostris'') is a species of shark from the family Requiem shark, Carcharhinidae, known for its yellowish skin, which inspires its common name. It is classified as a Vulnerable species by the International Union for ...
s are viviparous
In animals, viviparity is development of the embryo inside the body of the mother, with the maternal circulation providing for the metabolic needs of the embryo's development, until the mother gives birth to a fully or partially developed juve ...
or live-bearing, meaning that the mother retains the eggs and nourishes the embryos via a structure analogous to the placenta
The placenta (: placentas or placentae) is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas, and waste exchange between ...
to connect the mother's blood supply with the embryo's.
DNA repair
Embryos of externally fertilized fish species are directly exposed during their development to environmental conditions that may DNA damage (naturally occurring), damage their DNA, such as pollutants, ultraviolet, UV light and reactive oxygen species.Dey A, Flajšhans M, Pšenička M, Gazo I. DNA repair genes play a variety of roles in the development of fish embryos. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Mar 1;11:1119229. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1119229. PMID 36936683; PMCID: PMC10014602 To deal with such DNA damages, a variety of different DNA repair pathways are employed by fish embryos during their development. In recent years zebrafish have become a useful model for assessing environmental pollutants that might be genotoxic, i.e. cause DNA damage.Defenses against disease
Fish have both non-specific and immune defenses against disease. Non-specific defenses include the skin and scales, as well as the mucus layer secreted by the Epidermis (skin), epidermis that traps and inhibits the growth of microorganisms. If pathogens breach these defenses, the innate immune system can mount an inflammation, inflammatory response that increases blood flow to the infected region and delivers white blood cells that attempt to destroy pathogens, non-specifically. Specific defenses respond to particular antigens, such as proteins on the surfaces of pathogenic bacteria, recognised by the adaptive immune system. Immune systems evolved in deuterostomes as shown in the cladogram. Immune organs vary by type of fish. The jawless fish have lymphoid tissue within the pronephros, anterior kidney, and granulocytes in the gut. They have Adaptive immunity in jawless fish, their own type of adaptive immune system; it makes use of variable lymphocyte receptors (VLR) to generate immunity to a wide range of antigens, The result is much like that of jawed fishes and tetrapods, but it may have Convergent evolution, evolved separately. All jawed fishes have an adaptive immune system with B and T lymphocytes bearing immunoglobulins and T cell receptors respectively. This makes use of V(D)J recombination, Variable–Diversity–Joining rearrangement (V(D)J) to create immunity to a wide range of antigens. This system evolved once and is basal to the jawed vertebrate clade. Cartilaginous fish have three specialized organs that contain immune system cells: the epigonal organs around the gonads, Leydig's organ within the esophagus, and a spiral valve in their intestine, while their thymus and spleen have similar functions to those of the same organs in the immune systems of tetrapods. Teleosts have lymphocytes in the thymus, and other immune cells in the spleen and other organs.Behavior
Shoaling and schooling
A ''shoal'' is a loosely organised group where each fish swims and forages independently but is attracted to other members of the group and adjusts its behaviour, such as swimming speed, so that it remains close to the other members of the group. A ''school'' is a much more tightly organised group, synchronising its swimming so that all fish move at the same speed and in the same direction. Schooling is sometimes an antipredator adaptation, offering improved vigilance against predators. It is often more efficient to gather food by working as a group, and individual fish optimise their strategies by choosing to join or leave a shoal. When a predator has been noticed, prey fish respond defensively, resulting in collective shoal behaviours such as synchronised movements. Responses do not consist only of attempting to hide or flee; antipredator tactics include for example scattering and reassembling. Fish also aggregate in shoals to spawn. The capelin migrates annually in large schools between its feeding areas and its spawning grounds.Communication
Fish communicate by transmitting acoustic signals (sounds) to each other. This is most often in the context of feeding, aggression or courtship. The sounds emitted vary with the species and stimulus involved. Fish can produce either stridulatory sounds by moving components of the skeletal system, or can produce non-stridulatory sounds by manipulating specialized organs such as the swimbladder. Some fish produce sounds by rubbing or grinding their bones together. These sounds are stridulatory. In ''Haemulon flavolineatum'', the French grunt fish, as it produces a grunting noise by grinding its teeth together, especially when in distress. The grunts are at a frequency of around 700 Hz, and last approximately 47 milliseconds. The longsnout seahorse, ''Hippocampus reidi'' produces two categories of sounds, 'clicks' and 'growls', by rubbing their coronet bone across the grooved section of their neurocranium. Clicks are produced during courtship and feeding, and the frequencies of clicks were within the range of 50 Hz-800 Hz. The frequencies are at the higher end of the range during spawning, when the female and male fishes were less than fifteen centimeters apart. Growls are produced when the ''H. reidi'' are stressed. The 'growl' sounds consist of a series of sound pulses and are emitted simultaneously with body vibrations.
Some fish species create noise by engaging specialized muscles that contract and cause swimbladder vibrations. Oyster toadfish produce loud grunts by contracting sonic muscles along the sides of the swim bladder. Female and male toadfishes emit short-duration grunts, often as a fright response. In addition to short-duration grunts, male toadfishes produce "boat whistle calls". These calls are longer in duration, lower in frequency, and are primarily used to attract mates. The various sounds have frequency range of 140 Hz to 260 Hz. The frequencies of the calls depend on the rate at which the sonic muscles contract.
The red drum, ''Sciaenops ocellatus'', produces drumming sounds by vibrating its swimbladder. Vibrations are caused by the rapid contraction of sonic muscles that surround the dorsal aspect of the swimbladder. These vibrations result in repeated sounds with frequencies from 100 to >200 Hz. ''S. ocellatus'' produces different calls depending on the stimuli involved, such as courtship or a predator's attack. Females do not produce sounds, and lack sound-producing (sonic) muscles.
Some fish produce sounds by rubbing or grinding their bones together. These sounds are stridulatory. In ''Haemulon flavolineatum'', the French grunt fish, as it produces a grunting noise by grinding its teeth together, especially when in distress. The grunts are at a frequency of around 700 Hz, and last approximately 47 milliseconds. The longsnout seahorse, ''Hippocampus reidi'' produces two categories of sounds, 'clicks' and 'growls', by rubbing their coronet bone across the grooved section of their neurocranium. Clicks are produced during courtship and feeding, and the frequencies of clicks were within the range of 50 Hz-800 Hz. The frequencies are at the higher end of the range during spawning, when the female and male fishes were less than fifteen centimeters apart. Growls are produced when the ''H. reidi'' are stressed. The 'growl' sounds consist of a series of sound pulses and are emitted simultaneously with body vibrations.
Some fish species create noise by engaging specialized muscles that contract and cause swimbladder vibrations. Oyster toadfish produce loud grunts by contracting sonic muscles along the sides of the swim bladder. Female and male toadfishes emit short-duration grunts, often as a fright response. In addition to short-duration grunts, male toadfishes produce "boat whistle calls". These calls are longer in duration, lower in frequency, and are primarily used to attract mates. The various sounds have frequency range of 140 Hz to 260 Hz. The frequencies of the calls depend on the rate at which the sonic muscles contract.
The red drum, ''Sciaenops ocellatus'', produces drumming sounds by vibrating its swimbladder. Vibrations are caused by the rapid contraction of sonic muscles that surround the dorsal aspect of the swimbladder. These vibrations result in repeated sounds with frequencies from 100 to >200 Hz. ''S. ocellatus'' produces different calls depending on the stimuli involved, such as courtship or a predator's attack. Females do not produce sounds, and lack sound-producing (sonic) muscles.
Conservation
The 2024 International Union for Conservation of Nature, IUCN IUCN Red List, Red List names 2,168 fish species that are endangered or critically endangered. Included are species such as Gadus morhua, Atlantic cod, Cyprinodon diabolis, Devil's Hole pupfish, coelacanths, and great white sharks. Because fish live underwater they are more difficult to study than terrestrial animals and plants, and information about fish populations is often lacking. However, freshwater fish seem particularly threatened because they often live in relatively small water bodies. For example, the Devil's Hole pupfish occupies only a single pool.Overfishing
 The Food and Agriculture Organization reports that "in 2017, 34 percent of the fish stocks of the world's marine fisheries were classified as overfished". Overfishing is a major threat to edible fish such as cod and
The Food and Agriculture Organization reports that "in 2017, 34 percent of the fish stocks of the world's marine fisheries were classified as overfished". Overfishing is a major threat to edible fish such as cod and tuna
A tuna (: tunas or tuna) is a saltwater fish that belongs to the tribe Thunnini, a subgrouping of the Scombridae ( mackerel) family. The Thunnini comprise 15 species across five genera, the sizes of which vary greatly, ranging from the bul ...
. Overfishing eventually causes fish stocks to collapse, because the survivors cannot produce enough young to replace those removed. Such commercial extinction does not mean that the species is extinct, merely that it can no longer sustain a fishery. In the case of the Pacific sardine fishery off the California coast, the catch steadily declined from a 1937 peak of 800,000 tonnes to an economically inviable 24,000 tonnes in 1968. In the Collapse of the Atlantic northwest cod fishery, case of the Atlantic northwest cod fishery, overfishing reduced the fish population to 1% of its historical level by 1992.
Fisheries science, Fisheries scientists and the fishing industry have sharply differing views on the resiliency of fisheries to intensive fishing. In many coastal regions the fishing industry is a major employer, so governments are predisposed to support it. On the other hand, scientists and conservationists push for stringent protection, warning that many stocks could be destroyed within fifty years.
Other threats
A key stress on both freshwater and marine ecosystems is habitat degradation including water pollution, the building of dams, removal of water for use by humans, and the introduction of invasive species, exotic species including predators. Freshwater fish, especially if Endemism, endemic to a region (occurring nowhere else), may be threatened with extinction for all these reasons, as is the case for three of Spain's ten endemic freshwater fishes. River dams, especially major schemes like the Kariba Dam (Zambezi river) and the Aswan Dam (River Nile) on rivers with economically important fisheries, have caused large reductions in fish catch. Industrial bottom trawling Environmental impact of fishing, can damage seabed habitats, as has occurred on the Georges Bank in the North Atlantic. Introduction of aquatic invasive species is widespread. It modifies ecosystems, causing biodiversity loss, and can harm fisheries. Harmful species include fish but are not limited to them; the arrival of a comb jelly in the Black Sea damaged the anchovy fishery there. The opening of the Suez Canal in 1869 made possible Lessepsian migration, facilitating the arrival of hundreds of Indo-Pacific marine species of fish, algae and invertebrates in the Mediterranean Sea, deeply impacting its overall biodiversity and ecology. The predatory Nile perch was deliberately introduced to Lake Victoria in the 1960s as a commercial and sports fish. The lake had high biodiversity, with some 500 Endemism, endemic species ofcichlid
Cichlids ()
are a large, diverse, and widespread family of percomorph fish in the family Cichlidae, order Cichliformes. At least 1,760 species have been scientifically described, making it one of the largest vertebrate families, with on ...
fish. It drastically altered the lake's ecology, and Fishing on Lake Victoria, simplified the fishery from multi-species to just three: the Nile perch, the silver cyprinid, and another introduced fish, the Nile tilapia. The haplochromine cichlid populations have collapsed.
Importance to humans
Economic
 Throughout history, humans have used fish as food, fish as a food source for dietary protein. Historically and today, most fish harvested for human consumption has come by means of catching wild fish. However, fish farming, which has been practiced since about 3,500 BCE in ancient China, is becoming increasingly important in many nations. Overall, about one-sixth of the world's protein is estimated to be provided by fish. Fishing is accordingly a large global business which provides income for millions of people. The Environmental Defense Fund has a guide on which fish are safe to eat, given the state of pollution in today's world, and which fish are obtained in a sustainable way. As of 2020, over 65 million tonnes (Mt) of marine fish and 10 Mt of freshwater fish were captured, while some 50 Mt of fish, mainly freshwater, were farmed. Of the marine species captured in 2020, anchoveta represented 4.9 Mt, Alaska pollock 3.5 Mt, skipjack tuna 2.8 Mt, and Atlantic herring and yellowfin tuna 1.6 Mt each; eight more species had catches over 1 Mt.
Throughout history, humans have used fish as food, fish as a food source for dietary protein. Historically and today, most fish harvested for human consumption has come by means of catching wild fish. However, fish farming, which has been practiced since about 3,500 BCE in ancient China, is becoming increasingly important in many nations. Overall, about one-sixth of the world's protein is estimated to be provided by fish. Fishing is accordingly a large global business which provides income for millions of people. The Environmental Defense Fund has a guide on which fish are safe to eat, given the state of pollution in today's world, and which fish are obtained in a sustainable way. As of 2020, over 65 million tonnes (Mt) of marine fish and 10 Mt of freshwater fish were captured, while some 50 Mt of fish, mainly freshwater, were farmed. Of the marine species captured in 2020, anchoveta represented 4.9 Mt, Alaska pollock 3.5 Mt, skipjack tuna 2.8 Mt, and Atlantic herring and yellowfin tuna 1.6 Mt each; eight more species had catches over 1 Mt.
Recreation
Fish have been recognized as a source of beauty for almost as long as used for food, appearing in cave art, being raised as ornamental fish in ponds, and displayed in aquariums in homes, offices, or public settings. Recreational fishing is fishing primarily for pleasure or competition; it can be contrasted with commercial fishing, which is fishing for profit, or artisanal fishing, which is fishing primarily for food. The most common form of recreational fishing employs a fishing rod, rod, fishing reel, reel, fishing line, line, fish hook, hooks, and a wide range of bait (luring substance), baits. Recreational fishing is particularly popular in North America and Europe; government agencies often actively manage target fish species.Culture
Fish themes have symbolic significance in many religions. In ancient Mesopotamia, fish offerings were made to the gods from the very earliest times. Fish were also a major symbol of Enki, the god of water. Fish frequently appear as filling motifs in cylinder seals from the First Babylonian dynasty, Old Babylonian ( 1830 BC – 1531 BC) and Neo-Assyrian Empire, Neo-Assyrian (911–609 BC) periods. Starting during the Kassites, Kassite Period ( 1600 BC – 1155 BC) and lasting until the early Achaemenid Empire, Persian Period (550–30 BC), healers and exorcists dressed in ritual garb resembling the bodies of fish. During the Seleucid Empire, Seleucid Period (312–63 BC), the legendary Babylonian culture hero Oannes (mythology), Oannes was said to have dressed in the skin of a fish. Fish were sacred to the Syrian goddess Atargatis and, during her festivals, only her priests were permitted to eat them. In the Book of Jonah, the central figure, a prophet named Jonah, is swallowed by a giant fish after being thrown overboard by the crew of the ship he is travelling on. Early Christianity, Early Christians used the ''ichthys'', a symbol of a fish, to represent Jesus. Among the deity, deities said to take the form of a fish are Ikatere of the Polynesians, the shark-god Kāmohoaliʻi of Hawaii, Hawaii, and Matsya of the Hindus. The constellation Pisces (constellation), Pisces ("The Fishes") is associated with a legend from Ancient Rome that Venus (mythology), Venus and her son Cupid were rescued by two fishes. Fish feature prominently in art, in films such as ''Finding Nemo'' and books such as ''The Old Man and the Sea''. Large fish, particularly sharks, have frequently been the subject of Horror film, horror movies and Thriller (genre), thrillers, notably the novel ''Jaws (novel), Jaws'', made into a film which in turn has been parodied and imitated many times. Piranhas are shown in a similar light to sharks in films such as ''Piranha (1978 film), Piranha''.See also
Notes
References
Sources
* * *Further reading
* * * Moyle, Peter B. (1993''Fish: An Enthusiast's Guide''
University of California Press. – good lay text. * * *
''UCTV'' interview
External links
ANGFA
– Illustrated database of freshwater fishes of Australia and New Guinea
FishBase online
– Comprehensive database with information on over 29,000 fish species * *
United Nation
– Fisheries and Aquaculture Department: Fish and seafood utilization {{Authority control Fish, Aquatic ecology Fishing, Fish Ichthyology Obsolete vertebrate taxa Seafood Paraphyletic groups