CN X on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth
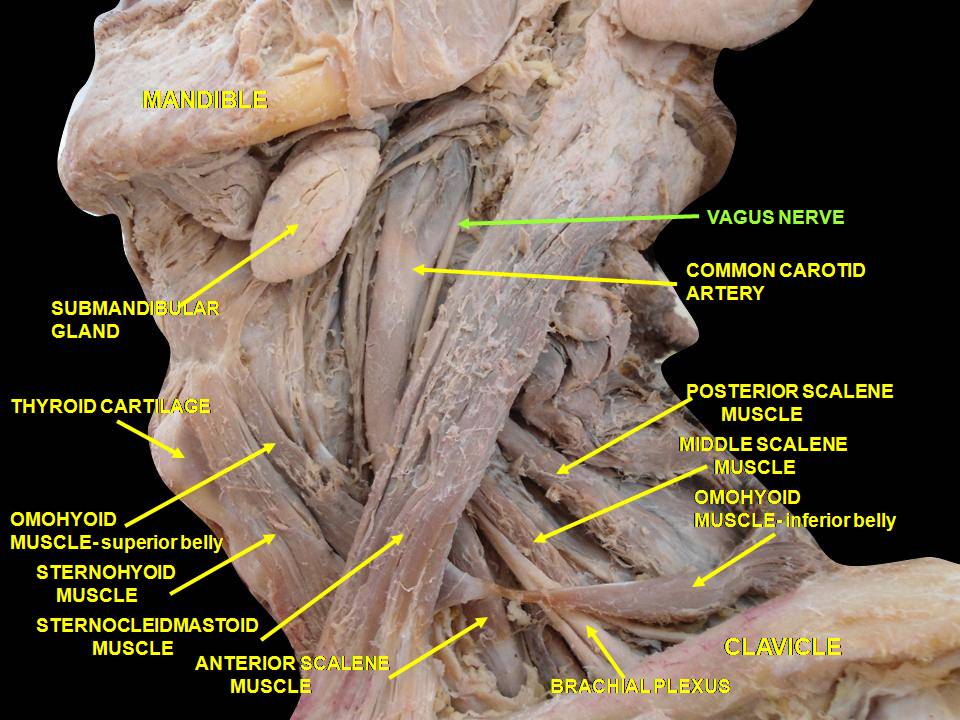
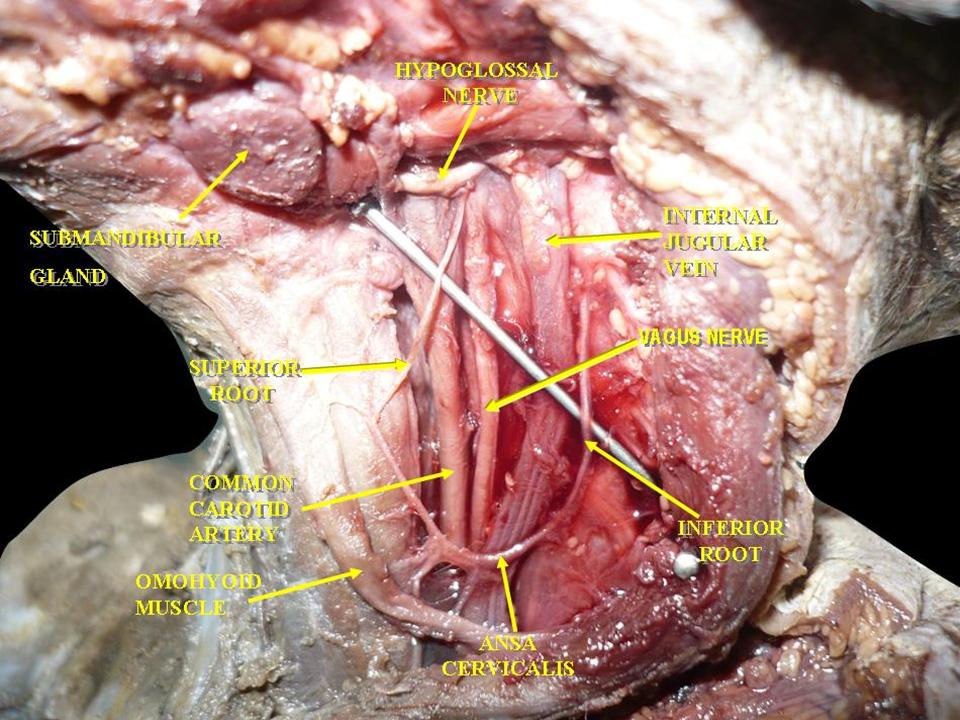 Right Vagus Nerve: The right vagus nerve gives rise to the right
Right Vagus Nerve: The right vagus nerve gives rise to the right
 Parasympathetic innervation of the heart is partially controlled by the vagus nerve and is shared by the
Parasympathetic innervation of the heart is partially controlled by the vagus nerve and is shared by the
File:Brain human normal inferior view with labels en.svg, Inferior view of the human brain, with the cranial nerves labeled.
File:Gray384.png, Section of the neck at about the level of the sixth cervical vertebra
File:Gray503.png, Transverse section of thorax, showing relations of pulmonary artery
File:Gray505.png, The arch of the aorta, and its branches
File:Gray567.png, Dura mater and its processes exposed by removing part of the right half of the skull, and the brain
File:Gray622.png, The tracheobronchial lymph glands
File:Gray694.png, Section of the medulla oblongata at about the middle of the olive
File:Gray719.png, Hind- and mid-brains; postero-lateral view
File:Gray792.png, Upper part of medulla spinalis and hind- and mid-brains; posterior aspect, exposed in situ
File:Gray838.png, The right sympathetic chain and its connections with the thoracic, abdominal, and pelvic plexuses
File:Gray848.png, The celiac ganglia with the sympathetic plexuses of the abdominal viscera radiating from the ganglia
File:Gray1032.png, The position and relation of the esophagus in the cervical region and in the posterior mediastinum, seen from behind
File:Gray1174.png, The thyroid gland and its relations
File:Gray1178.png, The thymus of a full-term fetus, exposed in situ
File:Internal carotid artery.jpg, Vagus nerve – dissection
cranial nerve
Cranial nerves are the nerves that emerge directly from the brain (including the brainstem), of which there are conventionally considered twelve pairs. Cranial nerves relay information between the brain and parts of the body, primarily to and f ...
(CN X), plays a crucial role in the autonomic nervous system
The autonomic nervous system (ANS), sometimes called the visceral nervous system and formerly the vegetative nervous system, is a division of the nervous system that operates viscera, internal organs, smooth muscle and glands. The autonomic nervo ...
, which is responsible for regulating involuntary functions within the human body. This nerve carries both sensory and motor fibers and serves as a major pathway that connects the brain to various organs, including the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. As a key part of the parasympathetic nervous system
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system.
The autonomic nervous system is responsible for regulat ...
, the vagus nerve helps regulate essential involuntary functions like heart rate, breathing, and digestion. By controlling these processes, the vagus nerve contributes to the body's "rest and digest" response, helping to calm the body after stress, lower heart rate, improve digestion, and maintain homeostasis.
The vagus nerve consists of two branches: the right and left vagus nerves. In the neck, the right vagus nerve contains approximately 105,000 fibers, while the left vagus nerve has about 87,000 fibers, according to one source. However, other sources report slightly different figures, with around 25,000 fibers in the right vagus nerve and 23,000 fibers in the left.
The vagus nerve is the longest nerve of the autonomic nervous system
The autonomic nervous system (ANS), sometimes called the visceral nervous system and formerly the vegetative nervous system, is a division of the nervous system that operates viscera, internal organs, smooth muscle and glands. The autonomic nervo ...
in the human body, consisting of both sensory and motor fibers. The sensory fibers originate from the jugular
The jugular veins () are veins that take blood from the head back to the heart via the superior vena cava. The internal jugular vein descends next to the internal carotid artery and continues posteriorly to the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
Struc ...
and nodose ganglion, while the motor fibers are derived from neurons in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus and the nucleus ambiguus
The nucleus ambiguus ("ambiguous nucleus" in English) is a group of large motor neurons, situated deep in the medullary part of the reticular formation named by Jacob Clarke. The nucleus ambiguus contains the cell bodies of neurons that innerva ...
. Historically, the vagus nerve was also known as the pneumogastric nerve, reflecting its role in regulating both the lungs and digestive system.
Structure
Upon leaving themedulla oblongata
The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involun ...
between the olive
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'' ("European olive"), is a species of Subtropics, subtropical evergreen tree in the Family (biology), family Oleaceae. Originating in Anatolia, Asia Minor, it is abundant throughout the Mediterranean ...
and the inferior cerebellar peduncle
The inferior cerebellar peduncle is formed by fibers of the restiform body that join with fibers from the much smaller juxtarestiform body. The inferior cerebellar peduncle is the smallest of the three cerebellar peduncles.
The upper part of t ...
, the vagus nerve extends through the jugular foramen
A jugular foramen is one of the two (left and right) large foramina (openings) in the base of the skull, located behind the carotid canal. It is formed by the temporal bone and the occipital bone. It allows many structures to pass, including the ...
, then passes into the carotid sheath
The carotid sheath is a condensation of the deep cervical fascia enveloping multiple vital neurovascular structures of the neck, including the common and internal carotid arteries, the internal jugular vein, the vagus nerve (CN X), and ansa c ...
between the internal carotid artery
The internal carotid artery is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior cerebral artery, anterior and middle cerebral artery, middle cerebral circulation.
In human anatomy, the internal and external carotid artery, external carotid ari ...
and the internal jugular vein
The internal jugular vein is a paired jugular vein that collects blood from the brain and the superficial parts of the face and neck. This vein runs in the carotid sheath with the common carotid artery and vagus nerve.
It begins in the posteri ...
down to the neck
The neck is the part of the body in many vertebrates that connects the head to the torso. It supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that transmit sensory and motor information between the brain and the rest of the body. Addition ...
, chest
The thorax (: thoraces or thoraxes) or chest is a part of the anatomy of mammals and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen.
In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main di ...
, and abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the gut, belly, tummy, midriff, tucky, or stomach) is the front part of the torso between the thorax (chest) and pelvis in humans and in other vertebrates. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal ...
, where it contributes to the innervation of the viscera
In a multicellular organism, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to a ...
, reaching all the way to the colon. Besides giving some output to various organs, the vagus nerve comprises between 80% and 90% of afferent nerve fiber
Afferent nerve fibers are axons (nerve fibers) of sensory neurons that carry sensory information from sensory receptors to the central nervous system. Many afferent projections ''arrive'' at a particular brain region.
In the peripheral nerv ...
s conveying sensory information about the state of the body's organs to the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
.
The right and left vagus nerves descend from the cranial vault through the jugular foramina, penetrating the carotid sheath between the internal and external carotid arteries, then passing posterolateral to the common carotid artery. The cell bodies of visceral afferent fibers of the vagus nerve are located bilaterally in the inferior ganglion of the vagus nerve (nodose ganglia).The vagus runs parallel to the common carotid artery and internal jugular vein inside the carotid sheath.
recurrent laryngeal nerve
The recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN), also known as nervus recurrens, is a branch of the vagus nerve ( cranial nerve X) that supplies all the intrinsic muscles of the larynx, with the exception of the cricothyroid muscles. There are two recur ...
, which hooks around the right subclavian artery
In human anatomy, the subclavian arteries are paired major arteries of the upper thorax, below the clavicle. They receive blood from the aortic arch. The left subclavian artery supplies blood to the left arm and the right subclavian artery suppli ...
and ascends into the neck between the trachea
The trachea (: tracheae or tracheas), also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all animals' lungs. The trachea extends from ...
and esophagus
The esophagus (American English), oesophagus (British English), or œsophagus (Œ, archaic spelling) (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, see spelling difference) all ; : ((o)e)(œ)sophagi or ((o)e)(œ)sophaguses), c ...
. The right vagus then crosses anterior to the right subclavian artery, runs posterior to the superior vena cava
The superior vena cava (SVC) is the superior of the two venae cavae, the great venous trunks that return deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation to the right atrium of the heart. It is a large-diameter (24 mm) short length vei ...
, descends posterior to the right main bronchus
A bronchus ( ; : bronchi, ) is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus. Thes ...
, and contributes to cardiac
The heart is a muscular organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the tissu ...
, pulmonary
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory syste ...
, and esophageal plexuses. It forms the posterior vagal trunk at the lower part of the esophagus and passes through the diaphragm to enter the abdomen through the esophageal hiatus.
Left Vagus Nerve: The left vagus nerve enters the thorax
The thorax (: thoraces or thoraxes) or chest is a part of the anatomy of mammals and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen.
In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main di ...
between left common carotid artery and left subclavian artery
In human anatomy, the subclavian arteries are paired major arteries of the upper thorax, below the clavicle. They receive blood from the aortic arch. The left subclavian artery supplies blood to the left arm and the right subclavian artery suppli ...
and descends on the aortic arch
The aortic arch, arch of the aorta, or transverse aortic arch () is the part of the aorta between the ascending and descending aorta. The arch travels backward, so that it ultimately runs to the left of the trachea.
Structure
The aorta begins ...
. It gives rise to the left recurrent laryngeal nerve
The recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN), also known as nervus recurrens, is a branch of the vagus nerve ( cranial nerve X) that supplies all the intrinsic muscles of the larynx, with the exception of the cricothyroid muscles. There are two recur ...
, which hooks around the aortic arch
The aortic arch, arch of the aorta, or transverse aortic arch () is the part of the aorta between the ascending and descending aorta. The arch travels backward, so that it ultimately runs to the left of the trachea.
Structure
The aorta begins ...
to the left of the ligamentum arteriosum
The ligamentum arteriosum (arterial ligament), also known as Botallo's ligament, Harvey's ligament, and Botallo's duct, is a small ligament attaching the aorta to the pulmonary artery. It serves no function in adults but is the remnant of the duct ...
and ascends between the trachea and esophagus. The left vagus further gives off thoracic cardiac branches, breaks up into the pulmonary plexus, continues into the esophageal plexus, and enters the abdomen as the anterior vagal trunk by way of the esophageal hiatus of the diaphragm.
Branches
*Pharyngeal nerve
The pharyngeal nerve is a small branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V2), arising at the posterior part of the pterygopalatine ganglion. It passes through the palatovaginal canal with the pharyngeal branch of the maxillary artery.
It is distribute ...
* Superior laryngeal nerve
The superior laryngeal nerve is a branch of the vagus nerve. It arises from the middle of the inferior ganglion of the vagus nerve and additionally receives a sympathetic branch from the superior cervical ganglion.
The superior laryngeal nerve ...
* Aortic nerve
* Superior cervical cardiac branches of vagus nerve
* Inferior cervical cardiac branch
* Recurrent laryngeal nerve
The recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN), also known as nervus recurrens, is a branch of the vagus nerve ( cranial nerve X) that supplies all the intrinsic muscles of the larynx, with the exception of the cricothyroid muscles. There are two recur ...
* Thoracic cardiac branches
* Branches to the pulmonary plexus
* Branches to the esophageal plexus
* Anterior vagal trunk
* Posterior vagal trunk
Nuclei
The vagus nerve includesaxon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis) or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see American and British English spelling differences#-re, -er, spelling differences) is a long, slender cellular extensions, projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, ...
s which emerge from or converge onto four nuclei of the medulla:
# The dorsal nucleus of vagus nerve
The dorsal nucleus of vagus nerve (or posterior nucleus of vagus nerve or dorsal vagal nucleus or nucleus dorsalis nervi vagi or nucleus posterior nervi vagi) is a cranial nerve nucleus of the vagus nerve (CN X) situated in the medulla oblongata ...
– sends parasympathetic
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system.
The autonomic nervous system is responsible for regulat ...
output to the viscera, especially the intestines
# The nucleus ambiguus
The nucleus ambiguus ("ambiguous nucleus" in English) is a group of large motor neurons, situated deep in the medullary part of the reticular formation named by Jacob Clarke. The nucleus ambiguus contains the cell bodies of neurons that innerva ...
– gives rise to the branchial efferent motor fibers of the vagus nerve and preganglionic parasympathetic neurons that innervate the heart
# The solitary nucleus
The solitary nucleus (SN) (nucleus of the solitary tract, nucleus solitarius, or nucleus tractus solitarii) is a series of neurons whose cell bodies form a roughly vertical column of grey matter in the medulla oblongata of the brainstem. Their a ...
– receives afferent taste information and primary afferents from visceral organs
# The spinal trigeminal nucleus
The spinal trigeminal nucleus is a nucleus in the medulla that receives information about deep/crude touch, pain, and temperature from the ipsilateral face. In addition to the trigeminal nerve (CN V), the facial (CN VII), glossopharyngeal (CN ...
– receives information about deep/crude touch, pain, and temperature of the outer ear, the dura of the posterior cranial fossa
The posterior cranial fossa is the part of the cranial cavity located between the foramen magnum, and tentorium cerebelli. It is formed by the sphenoid bones, temporal bones, and occipital bone. It lodges the cerebellum, and parts of the brai ...
and the mucosa of the larynx
Development
Themotor
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy.
Available energy sources include potential energy (e.g. energy of the Earth's gravitational field as exploited in hydroelectric power gene ...
division of the glossopharyngeal nerve is derived from the basal plate of the embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sp ...
nic medulla oblongata
The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involun ...
, while the sensory division originates from the cranial neural crest
The cranial neural crest is one of the four regions of the neural crest.
The cranial neural crest arises in the anterior and populates the face and the pharyngeal arches giving rise to bones, cartilage, nerves and connective tissue. The endocraniu ...
. The development of the vagus nerve begins early in embryonic life, around the third to fourth week of gestation. It forms from two key structures: neural crest
The neural crest is a ridge-like structure that is formed transiently between the epidermal ectoderm and neural plate during vertebrate development. Neural crest cells originate from this structure through the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, ...
cells, which contribute to its sensory components, and the neural tube
In the developing chordate (including vertebrates), the neural tube is the embryonic precursor to the central nervous system, which is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The neural groove gradually deepens as the neural folds become elevated, ...
, which forms its motor components in the brainstem (specifically in the medulla oblongata
The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involun ...
). By weeks 4 to 5, the vagus nerve begins to connect with the fourth and sixth pharyngeal arches
The pharyngeal arches, also known as visceral arches'','' are transient structures seen in the Animal embryonic development, embryonic development of humans and other vertebrates, that are recognisable precursors for many structures. In fish, t ...
, which give rise to muscles involved in swallowing and speaking. Around weeks 5 to 6, specialized nuclei in the brainstem develop to manage the nerve’s motor and sensory functions. These centers are essential for regulating vital automatic processes like breathing, digestion, and heart rate. Between weeks 6 and 9, the vagus nerve extends its branches to various organs, including the heart, lungs, and gastrointestinal tract, as well as sensory areas like the ear and throat. As the fetus
A fetus or foetus (; : fetuses, foetuses, rarely feti or foeti) is the unborn offspring of a viviparous animal that develops from an embryo. Following the embryonic development, embryonic stage, the fetal stage of development takes place. Pren ...
grows, the vagus nerve matures into a crucial part of the parasympathetic nervous system, helping maintain the body's internal balance. This process shows how a single nerve can become so important for multiple systems in the body.
Function
The vagus nerve supplies motorparasympathetic
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system.
The autonomic nervous system is responsible for regulat ...
fibers to all the organs (except the adrenal
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex which ...
glands) from the neck
The neck is the part of the body in many vertebrates that connects the head to the torso. It supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that transmit sensory and motor information between the brain and the rest of the body. Addition ...
down to the second segment of the transverse colon
In human anatomy, the transverse colon is the longest and most movable part of the Large intestine#Structure, colon.
Anatomical position
It crosses the abdomen from the ascending colon at the right colic flexure (hepatic flexure) with a downward ...
. The vagus also controls a few skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscle (commonly referred to as muscle) is one of the three types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. They are part of the somatic nervous system, voluntary muscular system and typically are a ...
s, including:
* Cricothyroid muscle
The cricothyroid muscle is the only tensor muscle of the larynx aiding with phonation. It is innervated by the superior laryngeal nerve. Its action tilts the thyroid forward to help tense the vocal cords, thus increasing the pitch of the voice ...
* Levator veli palatini muscle
* Salpingopharyngeus muscle
* Palatoglossus muscle
The palatoglossal muscle is a muscle of the soft palate and an extrinsic muscle of the tongue. Its surface is covered by oral mucosa and forms the visible palatoglossal arch.
Structure
From its origin, it passes anteroinferiorly and laterally. I ...
* Palatopharyngeus muscle
* Superior, middle and inferior pharyngeal constrictors
* Muscles of the larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ (anatomy), organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal ...
(speech
Speech is the use of the human voice as a medium for language. Spoken language combines vowel and consonant sounds to form units of meaning like words, which belong to a language's lexicon. There are many different intentional speech acts, suc ...
).
This means that the vagus nerve is responsible for such varied tasks as heart rate
Heart rate is the frequency of the cardiac cycle, heartbeat measured by the number of contractions of the heart per minute (''beats per minute'', or bpm). The heart rate varies according to the body's Human body, physical needs, including the nee ...
, gastrointestinal peristalsis
Peristalsis ( , ) is a type of intestinal motility, characterized by symmetry in biology#Radial symmetry, radially symmetrical contraction and relaxation of muscles that propagate in a wave down a tube, in an wikt:anterograde, anterograde dir ...
, sweating
Perspiration, also known as sweat, is the fluid secreted by sweat glands in the skin of mammals.
Two types of sweat glands can be found in humans: eccrine glands and apocrine glands. The eccrine sweat glands are distributed over much of the ...
, and quite a few muscle movements in the mouth, including speech
Speech is the use of the human voice as a medium for language. Spoken language combines vowel and consonant sounds to form units of meaning like words, which belong to a language's lexicon. There are many different intentional speech acts, suc ...
(via the recurrent laryngeal nerve
The recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN), also known as nervus recurrens, is a branch of the vagus nerve ( cranial nerve X) that supplies all the intrinsic muscles of the larynx, with the exception of the cricothyroid muscles. There are two recur ...
). It also has some afferent fibers that innervate the inner (canal) portion of the outer ear
The outer ear, external ear, or auris externa is the external part of the ear, which consists of the auricle (also pinna) and the ear canal. It gathers sound energy and focuses it on the eardrum ( tympanic membrane).
Structure
Auricle
The ...
(via the auricular branch, also known as Arnold's or Alderman's nerve) and part of the meninges
In anatomy, the meninges (; meninx ; ) are the three membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord. In mammals, the meninges are the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. Cerebrospinal fluid is located in the subarachnoid spac ...
. The vagus nerve is also responsible for regulating inflammation in the body, via the inflammatory reflex.
Efferent vagus nerve fibers innervating the pharynx and back of the throat are responsible for the gag reflex
The pharyngeal reflex or gag reflex is a reflex muscular contraction of the back of the throat, evoked by touching the roof of the mouth, back of the tongue, area around the tonsils, uvula, and back of the throat. It, along with other aerodigest ...
. In addition, 5-HT3 receptor-mediated afferent vagus stimulation in the gut due to gastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis, also known as infectious diarrhea, is an inflammation of the Human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract including the stomach and intestine. Symptoms may include diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Fever, lack of ...
is a cause of vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis, puking and throwing up) is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteritis, pre ...
. Stimulation of the vagus nerve in the cervix uteri (as in some medical procedures) can lead to a vasovagal response
Reflex syncope is a brief loss of consciousness due to a neurologically induced drop in blood pressure and/or a decrease in heart rate. Before an affected person passes out, there may be sweating, a decreased ability to see, or ringing ...
.
The vagus nerve also plays a role in satiation following food consumption. Knocking out vagal nerve receptors has been shown to cause hyperphagia (greatly increased food intake). Neuroscientist Ivan De Araujo
Ivan De Araujo is a director at the Max Planck Institute for Biological Cybernetics in Tübingen, Germany, along with Peter Dayan. He is known for his seminal investigations on sugar preference and on the reward functions of the gut-brain axis. ...
and colleagues have shown that the vagus nerve transmits reward signals from the body to the brain, potentially explaining how stimulation of the nerve leads to emotional changes.
Cardiac effects
 Parasympathetic innervation of the heart is partially controlled by the vagus nerve and is shared by the
Parasympathetic innervation of the heart is partially controlled by the vagus nerve and is shared by the thoracic ganglia
The thoracic ganglia are paravertebral ganglia. The thoracic portion of the sympathetic trunk typically has 12 thoracic ganglia. Emerging from the ganglia are thoracic splanchnic nerves (the cardiopulmonary, the greater, lesser, and least splanch ...
. Vagal and spinal ganglionic nerves mediate the lowering of the heart rate
Heart rate is the frequency of the cardiac cycle, heartbeat measured by the number of contractions of the heart per minute (''beats per minute'', or bpm). The heart rate varies according to the body's Human body, physical needs, including the nee ...
. The right vagus branch innervates the sinoatrial node
The sinoatrial node (also known as the sinuatrial node, SA node, sinus node or Keith–Flack node) is an ellipse, oval shaped region of special cardiac muscle in the upper back wall of the right atrium made up of Cell (biology), cells known as pa ...
. In healthy people, parasympathetic tone from these sources is well-matched to sympathetic tone. Hyperstimulation of parasympathetic influence promotes bradyarrhythmias. When hyperstimulated, the left vagal branch predisposes the heart to conduction block at the atrioventricular node
The atrioventricular node (AV node, or Aschoff-Tawara node) electrically connects the heart's atria and ventricles to coordinate beating in the top of the heart; it is part of the electrical conduction system of the heart. The AV node lies at the ...
.
At this location, neuroscientist Otto Loewi
Otto Loewi (; 3 June 1873 – 25 December 1961) was a Germany, German-born pharmacology, pharmacologist and psychobiologist who discovered the role of acetylcholine as an endogenous neurotransmitter. For this discovery, he was awarded the Nobel ...
first demonstrated that nerves secrete substances called neurotransmitters
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotransmitters are rele ...
, which have effects on receptors in target tissues. In his experiment, Loewi electrically stimulated the vagus nerve of a frog heart, which slowed the heart. Then he took the fluid from the heart and transferred it to a second frog heart without a vagus nerve. The second heart slowed without electrical stimulation. Loewi described the substance released by the vagus nerve as vagusstoff, which was later found to be acetylcholine
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic compound that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (including humans) as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Par ...
.
Drugs that inhibit the muscarinic receptor
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs) are acetylcholine receptors that form G protein-coupled receptor, G protein-coupled receptor complexes in the cell membranes of certain neurons and other Cell (biology), cells. They play several role ...
s (anticholinergic
Anticholinergics (anticholinergic agents) are substances that block the action of the acetylcholine (ACh) neurotransmitter at synapses in the central nervous system, central and peripheral nervous system.
These agents inhibit the parasympatheti ...
s) such as atropine
Atropine is a tropane alkaloid and anticholinergic medication used to treat certain types of nerve agent and pesticide poisonings as well as some types of slow heart rate, and to decrease saliva production during surgery. It is typically give ...
and scopolamine
Scopolamine, also known as hyoscine, or Devil's Breath, is a medication used to treat motion sickness and postoperative nausea and vomiting. It is also sometimes used before surgery to decrease saliva. When used by injection, effects begin a ...
, are called vagolytic because they inhibit the action of the vagus nerve on the heart, gastrointestinal tract, and other organs. Anticholinergic drugs increase heart rate and are used to treat bradycardia
Bradycardia, also called bradyarrhythmia, is a resting heart rate under 60 beats per minute (BPM). While bradycardia can result from various pathological processes, it is commonly a physiological response to cardiovascular conditioning or due ...
.
Urogenital and hormonal effects
Excessive activation of the vagal nerve duringemotional stress
In psychology, stress is a feeling of emotional strain and pressure. Stress is a form of psychological and mental discomfort. Small amounts of stress may be beneficial, as it can improve athletic performance, motivation and reaction to the env ...
, which is a parasympathetic overcompensation for a strong sympathetic nervous system
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS or SANS, sympathetic autonomic nervous system, to differentiate it from the somatic nervous system) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the parasympathetic nervous sy ...
response associated with stress, can also cause vasovagal syncope due to a sudden drop in cardiac output
In cardiac physiology, cardiac output (CO), also known as heart output and often denoted by the symbols Q, \dot Q, or \dot Q_ , edited by Catherine E. Williamson, Phillip Bennett is the volumetric flow rate of the heart's pumping output: tha ...
, causing cerebral hypoperfusion. Vasovagal syncope affects young children and women more than other groups. It can also lead to temporary loss of bladder control under moments of extreme fear.
Research has shown that women having had complete spinal cord injury
A spinal cord injury (SCI) is damage to the spinal cord that causes temporary or permanent changes in its function. It is a destructive neurological and pathological state that causes major motor, sensory and autonomic dysfunctions.
Symptoms of ...
can experience orgasm
Orgasm (from Greek , ; "excitement, swelling"), sexual climax, or simply climax, is the sudden release of accumulated sexual excitement during the sexual response cycle, characterized by intense sexual pleasure resulting in rhythmic, involu ...
s through the vagus nerve, which can go from the uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', : uteri or uteruses) or womb () is the hollow organ, organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans, that accommodates the embryonic development, embryonic and prenatal development, f ...
and cervix
The cervix (: cervices) or cervix uteri is a dynamic fibromuscular sexual organ of the female reproductive system that connects the vagina with the uterine cavity. The human female cervix has been documented anatomically since at least the time ...
to the brain.
Insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (''INS)'' gene. It is the main Anabolism, anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabol ...
signaling activates the adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleoside triphosphate that provides energy to drive and support many processes in living cell (biology), cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known ...
(ATP)-sensitive potassium (KATP) channels in the arcuate nucleus
The arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus (ARH), or ARC, is also known as the infundibular nucleus to distinguish it from the arcuate nucleus of the medulla oblongata in the brainstem. The arcuate nucleus is an aggregation of neurons in the medio ...
, decreases AgRP release, and through the vagus nerve, leads to decreased glucose production by the liver by decreasing gluconeogenic enzymes: phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (, PEPCK) is an enzyme in the lyase family used in the metabolic pathway of gluconeogenesis. It converts oxaloacetate into phosphoenolpyruvate and carbon dioxide.
It is found in two forms, cytosolic and mitoc ...
, glucose 6-phosphatase
The enzyme glucose 6-phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.9, G6Pase; systematic name D-glucose-6-phosphate phosphohydrolase) catalyzes the hydrolysis of glucose 6-phosphate, resulting in the creation of a phosphate group and free glucose:
: D-glucose 6-ph ...
.
Clinical significance
Stimulation
Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) therapy via aneurostimulator
Neurostimulation is the purposeful modulation of the nervous system's activity using invasive (e.g. microelectrodes) or non-invasive means (e.g. transcranial magnetic stimulation, transcranial electric stimulation such as tDCS or tACS). Neuro ...
implanted in the chest has been used to control seizure
A seizure is a sudden, brief disruption of brain activity caused by abnormal, excessive, or synchronous neuronal firing. Depending on the regions of the brain involved, seizures can lead to changes in movement, sensation, behavior, awareness, o ...
s in epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of Non-communicable disease, non-communicable Neurological disorder, neurological disorders characterized by a tendency for recurrent, unprovoked Seizure, seizures. A seizure is a sudden burst of abnormal electrical activit ...
patients and has been approved for treating drug-resistant clinical depression
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive low mood, low self-esteem, and loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities. Intro ...
. Several noninvasive VNS devices that stimulate an afferent branch of the vagus nerve are available. GammaCore is recommended by The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) for cluster headaches.
VNS may also be achieved by one of the ''vagal maneuver
A vagal maneuver is an action used to stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system by activating the vagus nerve. The vagus nerve is the longest nerve of the autonomic nervous system and helps regulate many critical aspects of human physiology, i ...
s'': holding the breath for 20 to 60 seconds, dipping the face in cold water, coughing, humming or singing, or tensing the stomach muscles as if to bear down to have a bowel movement. Patients with supraventricular tachycardia
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is an umbrella term for fast heart rhythms arising from the upper part of the heart. This is in contrast to the other group of fast heart rhythms – ventricular tachycardia, which start within the lower cham ...
, atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (AF, AFib or A-fib) is an Heart arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia) characterized by fibrillation, rapid and irregular beating of the Atrium (heart), atrial chambers of the heart. It often begins as short periods ...
, and other illnesses may be trained to perform vagal maneuvers (or find one or more on their own).
Vagus nerve blocking (VBLOC) therapy is similar to VNS but used only during the day. In a six-month open-label trial
An open-label trial, or open trial, is a type of clinical trial in which information is not withheld from trial participants. In particular, both the researchers and participants know which treatment is being administered. This contrasts with a d ...
involving three medical centers in Australia, Mexico, and Norway, vagus nerve blocking helped 31 obese participants lose an average of nearly 15 percent of their excess weight. , a yearlong double-blind
In a blind or blinded experiment, information which may influence the participants of the experiment is withheld until after the experiment is complete. Good blinding can reduce or eliminate experimental biases that arise from a participants' expec ...
, phase II trial had begun.
Vagotomy
Vagotomy (cutting of the vagus nerve) is a now obsolete therapy that was performed forpeptic ulcer disease
Peptic ulcer disease is when the inner part of the stomach's gastric mucosa (lining of the stomach), the first part of the small intestine, or sometimes the lower esophagus, gets damaged. An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer, while ...
and now superseded by oral medications, including H2 antagonists, proton pump inhibitors and antibiotics. Vagotomy is currently being researched as a less invasive alternative weight-loss procedure to gastric bypass surgery
Gastric bypass surgery refers to a technique in which the stomach is divided into a small upper pouch and a much larger lower "remnant" pouch, where the small intestine is rearranged to connect to both. Surgeons have developed several differen ...
. The procedure curbs the feeling of hunger and is sometimes performed in conjunction with putting bands on patients' stomachs, resulting in an average of 43% of excess weight loss at six months with diet and exercise.
One serious side effect of vagotomy is a vitamin B12 deficiency later in life – perhaps after about 10 years – that is similar to pernicious anemia
Pernicious anemia is a disease where not enough red blood cells are produced due to a deficiency of Vitamin B12, vitamin B12. Those affected often have a gradual onset. The most common initial symptoms are Fatigue, feeling tired and weak. Other ...
. The vagus normally stimulates the stomach's parietal cell
Parietal cells (also known as oxyntic cells) are epithelial cells in the stomach that secrete hydrochloric acid (HCl) and intrinsic factor. These cells are located in the gastric glands found in the lining of the fundus and body regions o ...
s to secrete acid and intrinsic factor. Intrinsic factor
Intrinsic factor (IF), also known as cobalamin binding intrinsic factor, or gastric intrinsic factor (GIF), is a glycoprotein produced by the parietal cells (in humans) or chief cells (in rodents) of the stomach. It is necessary for the absorp ...
is needed to absorb vitamin B12 from food. The vagotomy reduces this secretion and ultimately leads to deficiency, which, if left untreated, causes nerve damage, tiredness, dementia, paranoia, and ultimately death.
Researchers from Aarhus University
Aarhus University (, abbreviated AU) is a public research university. Its main campus is located in Aarhus, Denmark. It is the second largest and second oldest university in Denmark. The university is part of the Coimbra Group, the Guild, and Ut ...
and Aarhus University Hospital have demonstrated that vagotomy prevents (halves the risk of) the development of Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease primarily of the central nervous system, affecting both motor system, motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually and non-motor issues become ...
, suggesting that Parkinson's disease begins in the gastrointestinal tract and spreads via the vagus nerve to the brain. Or giving further evidence to the theory that dysregulated environmental stimuli, such as that received by the vagus nerve from the gut, may have a negative effect on the dopamine reward system of the substantia nigra
The substantia nigra (SN) is a basal ganglia structure located in the midbrain that plays an important role in reward and movement. ''Substantia nigra'' is Latin for "black substance", reflecting the fact that parts of the substantia nigra a ...
, thereby causing Parkinson's disease.
Vagus nerve pathology
The sympathetic and parasympathetic components of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) control and regulate the function of various organs, glands, and involuntary muscles throughout the body (e.g., vocalization, swallowing, heart rate, respiration, gastric secretion, and intestinal motility). Hence, most of the signs and symptoms of vagus nerve dysfunction, apart from vocalisation, are vague and non specific. Laryngeal nerve palsy results in paralysis of an ipsilateral vocal cord and is used as a pointer to diseases affecting the vagus nerve from its origin down to termination of its branch of the laryngeal nerve. * Sensory neuropathy The hypersensitivity of vagal afferent nerves causes refractory or idiopathic cough.Arnold's nerve
The auricular branch of the vagus nerve is often termed the Alderman's nerve ("a reference to the old Aldermen of the City of London and their practice of using rosewater bowls at ceremonial banquets, where attendees were encouraged to place a nap ...
ear-cough reflex, though uncommon, is a manifestation of a vagal sensory neuropathy and this is the cause of a refractory chronic cough that can be treated with gabapentin
Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropath ...
. The cough is triggered by mechanical stimulation of the external auditory meatus and accompanied by other neuropathic features such as throat irritation (laryngeal paresthesia) and cough triggered by exposure to nontussive triggers such as cold air and eating (termed allotussia). These features suggest a neuropathic origin to the cough.
* Motor neuropathy
Pathology of the vagus nerve proximal to the laryngeal nerve typically presents with symptom hoarse voice and physical sign of paralysed vocal cords. Although a large proportion of these are the result of idiopathic vocal cord palsy but tumours especially lung cancers are next common cause. Tumours at the apex of right lung and at the hilum of the left lung are the most common oncological causes of vocal cord palsy. Less common tumours causing vocal cord palsy includes thyroid and proximal oesophageal malignancy.
Etymology
TheLatin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
word ''vagus'' means literally "wandering" (the words ''vagrant
Vagrancy is the condition of wandering homelessness without regular employment or income. Vagrants usually live in poverty and support themselves by travelling while engaging in begging, scavenging, or petty theft. In Western countries, ...
'', '' vagabond'', '' vague'', and ''divagation'' come from the same root). Sometimes the right and left branches together are spoken of in the plural and are thus called vagi ( ). The vagus was also historically called the ''pneumogastric'' nerve since it innervates both the lungs and the stomach.
Additional illustrations
See also
*Porphyria
Porphyria ( or ) is a group of disorders in which substances called porphyrins build up in the body, adversely affecting the skin or nervous system. The types that affect the nervous system are also known as Porphyria#Acute porphyrias, acute p ...
– A rare disorder can cause seizures and damage to the vagal nerve.
* Vagovagal reflex
Vagovagal reflex refers to gastrointestinal tract reflex circuits where afferent and efferent fibers of the vagus nerve coordinate responses to gut stimuli via the dorsal vagal complex in the brain. The vagovagal reflex controls contraction o ...
* Inflammatory reflex
* Vagus ganglion
* Vagus nerve stimulation
* Vagusstoff
* Polyvagal theory
* Gastroparesis
Gastroparesis (gastro- from Ancient Greek – gaster, "stomach"; and -paresis, πάρεσις – "partial paralysis") is a medical disorder of ineffective neuromuscular contractions (peristalsis) of the stomach, resulting in food and l ...
* Reflex syncope
Reflex syncope is a brief loss of consciousness due to a neurologically induced drop in blood pressure and/or a decrease in heart rate. Before an affected person passes out, there may be sweating, a decreased ability to see, or ringing ...
– Vasovagal syncope is one of the major types of reflex syncope.
References
External links
* * * () {{DEFAULTSORT:Vagus Nerve Cranial nerves Autonomic nervous system Thorax (human anatomy) Abdomen Gustatory system Human head and neck Nervous system Nerves of the head and neck Innervation of the tongue