|
Spinal Trigeminal Nucleus
The spinal trigeminal nucleus is a nucleus in the medulla that receives information about deep/crude touch, pain, and temperature from the ipsilateral face. In addition to the trigeminal nerve (CN V), the facial (CN VII), glossopharyngeal (CN IX), and vagus nerves (CN X) also convey pain information from their areas to the spinal trigeminal nucleus. Thus the spinal trigeminal nucleus receives afferents from V, VII, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nucleus (neuroanatomy)
In neuroanatomy, a nucleus (: nuclei) is a cluster of neurons in the central nervous system, located deep within the cerebral hemispheres and brainstem. The neurons in one nucleus usually have roughly similar connections and functions. Nuclei are connected to other nuclei by tracts, the bundles (fascicles) of axons (nerve fibers) extending from the cell bodies. A nucleus is one of the two most common forms of nerve cell organization, the other being layered structures such as the cerebral cortex or cerebellar cortex. In anatomical sections, a nucleus shows up as a region of gray matter, often bordered by white matter. The vertebrate brain contains hundreds of distinguishable nuclei, varying widely in shape and size. A nucleus may itself have a complex internal structure, with multiple types of neurons arranged in clumps (subnuclei) or layers. The term "nucleus" is in some cases used rather loosely, to mean simply an identifiably distinct group of neurons, even if they are sprea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Principal Sensory Nucleus Of Trigeminal Nerve
The principal sensory nucleus of trigeminal nerve (or chief sensory nucleus of V, main trigeminal sensory nucleus) is a group of second-order neurons which have cell bodies in the caudal pons. It receives information about discriminative sensation and light touch of the face as well as conscious proprioception of the jaw via first order neurons of CN V. * Most of the sensory information crosses the midline and travels to the contralateral ventral posteromedial nucleus (VPM) of the thalamus via the anterior trigeminothalamic tract The ventral trigeminal tract, ventral trigeminothalamic tract, anterior trigeminal tract, or anterior trigeminothalamic tract, is a nerve tract, tract composed of second-order neuron, second-order neuronal axons. These afferent fibers carry sensor .... * However, information of the ''oral cavity'' travels to the ipsilateral VPM of the thalamus via the dorsal trigeminothalamic tract. {{Authority control Cranial nerve nuclei Trigeminal nerve Pon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Facial Nerve
The facial nerve, also known as the seventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve VII, or simply CN VII, is a cranial nerve that emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste sensations from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. The nerve typically travels from the pons through the facial canal in the temporal bone and exits the skull at the stylomastoid foramen. It arises from the brainstem from an area posterior to the cranial nerve VI (abducens nerve) and anterior to cranial nerve VIII (vestibulocochlear nerve). The facial nerve also supplies preganglionic parasympathetic fibers to several head and neck ganglia. The facial and intermediate nerves can be collectively referred to as the nervus intermediofacialis. The path of the facial nerve can be divided into six segments: # intracranial (cisternal) segment (from brainstem pons to internal auditory canal) # meatal (canalicular) segment (with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Medulla Oblongata
The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involuntary) functions, ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla contains the cardiovascular center, the respiratory center, vomiting and vasomotor centers, responsible for the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep–wake cycle. "Medulla" is from Latin, ‘pith or marrow’. And "oblongata" is from Latin, ‘lengthened or longish or elongated'. During embryonic development, the medulla oblongata develops from the myelencephalon. The myelencephalon is a secondary brain vesicle which forms during the maturation of the rhombencephalon, also referred to as the hindbrain. The bulb is an archaic term for the medulla oblongata. In modern clinical usage, the word bulbar (as in bulbar palsy) is r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cranial Nerve Nuclei
A cranial nerve nucleus is a collection of neuron cell bodies (gray matter) in the brain stem that is associated with one or more of the cranial nerves. Axons carrying information to and from the cranial nerves form a synapse first at these nuclei. Lesions occurring at these nuclei can lead to effects resembling those seen by the severing of nerve(s) they are associated with. All the nuclei except that of the trochlear nerve (CN IV) supply nerves of the same side of the body. Structure Motor and sensory In general, motor nuclei are closer to the front (ventral), and sensory nuclei and neurons are closer to the back (dorsal). This arrangement mirrors the arrangement of tracts in the spinal cord. * Close to the midline are the motor efferent nuclei, such as the oculomotor nucleus, which control skeletal muscle. Just lateral to this are the autonomic (or visceral) efferent nuclei. * There is a separation, called the sulcus limitans, and lateral to this are the sensory nuclei. Near ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Trigeminal Nerve Nuclei
The sensory trigeminal nerve nuclei are the largest of the cranial nerve nuclei, and extend through the whole of the midbrain, pons and medulla, and into the upper cervical spinal cord. The nucleus is divided into three parts, from rostral to caudal (top to bottom in humans): * The mesencephalic nucleus * The principal sensory nucleus * The spinal trigeminal nucleus ::The spinal trigeminal nucleus is further subdivided into three parts, from rostral to caudal: :* Pars oralis (from the Pons to the Hypoglossal nucleus) :* Pars interpolaris (from the Hypoglossal nucleus to the obex) :* Pars caudalis (from the obex to C2) There is also a distinct trigeminal motor nucleus that is medial to the principal sensory nucleus. See also * Photic sneeze reflex * Trigeminal nerve In neuroanatomy, the trigeminal nerve (literal translation, lit. ''triplet'' nerve), also known as the fifth cranial nerve, cranial nerve V, or simply CN V, is a cranial nerve responsible for Sense, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nucleus Of Tractus Solitarius
The solitary nucleus (SN) (nucleus of the solitary tract, nucleus solitarius, or nucleus tractus solitarii) is a series of neurons whose cell bodies form a roughly vertical column of grey matter in the medulla oblongata of the brainstem. Their axons form the bulk of the enclosed solitary tract. The solitary nucleus can be divided into different parts including dorsomedial, dorsolateral, and ventrolateral subnuclei. The solitary nucleus receives general visceral and special visceral inputs from the facial nerve (CN VII), glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) and vagus nerve (CN X); it receives and relays stimuli related to taste and visceral sensation. It sends outputs to various parts of the brain, such as the hypothalamus, thalamus, and reticular formation, forming circuits that contribute to autonomic regulation. Cells along the length of the SN are arranged roughly in accordance with function; for instance, cells involved in taste are located in the rostral part, while those recei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ventral Trigeminal Tract
The ventral trigeminal tract, ventral trigeminothalamic tract, anterior trigeminal tract, or anterior trigeminothalamic tract, is a tract composed of second-order neuronal axons. These afferent fibers carry sensory information about discriminative and crude touch, conscious proprioception, pain, and temperature from the head, face, and oral cavity. The ventral trigeminal tract connects the two major components of the brainstem trigeminal complex – the principal, or main sensory nucleus and the spinal trigeminal nucleus, to the ventral posteromedial nucleus of the thalamus. The ventral trigeminal tract is also called the anterior trigeminal lemniscus. Structure The first-order neurons from the trigeminal ganglion enter the pons and synapse in the principal (chief sensory) nucleus or spinal trigeminal nucleus. Axons of the second-order neurons cross the midline and terminate in the ventral posteromedial nucleus of the contralateral thalamus (as opposed to the ventral posterola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ventral Posteromedial Nucleus
The ventral posteromedial nucleus (VPM) is a nucleus within the ventral posterior nucleus of the thalamus and serves an analogous somatosensory relay role for the ascending trigeminothalamic tracts as its lateral neighbour the ventral posterolateral nucleus serves for dorsal column–medial lemniscus pathway 2nd-order neurons. The term "ventral posteromedial nucleus" was introduced by Le Gros Clark in 1930. Afferents and efferents Orofacial somatosensory The VPM receives second-order general somatic afferent fibers from the ventral trigeminal tract and the dorsal trigeminal tract which convey general somatic sensory information from the face and oral cavity (including touch, pressure, temperature, pain, and propriception). Proprioceptive synapses are situated anteriorly, ones mediating touch in the middle, and nociceptive ones posteriorly. Third-order neurons in turn project to the somatosensory cortex in the postcentral gyrus. Taste The VPM receives second-order tas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nociception
In physiology, nociception , also nocioception; ) is the Somatosensory system, sensory nervous system's process of encoding Noxious stimulus, noxious stimuli. It deals with a series of events and processes required for an organism to receive a painful stimulus, convert it to a molecular signal, and recognize and characterize the signal to trigger an appropriate defensive response. In nociception, intense chemical (e.g., capsaicin present in chili pepper or cayenne pepper), mechanical (e.g., cutting, crushing), or thermal (heat and cold) stimulation of sensory neurons called nociceptors produces a signal that travels along a chain of nerve fibers to the brain. Nociception triggers a variety of physiological and behavioral responses to protect the organism against an aggression, and usually results in a subjective experience, or perception, of pain in Sentience, sentient beings. Detection of noxious stimuli Potentially damaging mechanical, thermal, and chemical stimuli are detecte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dental Pain
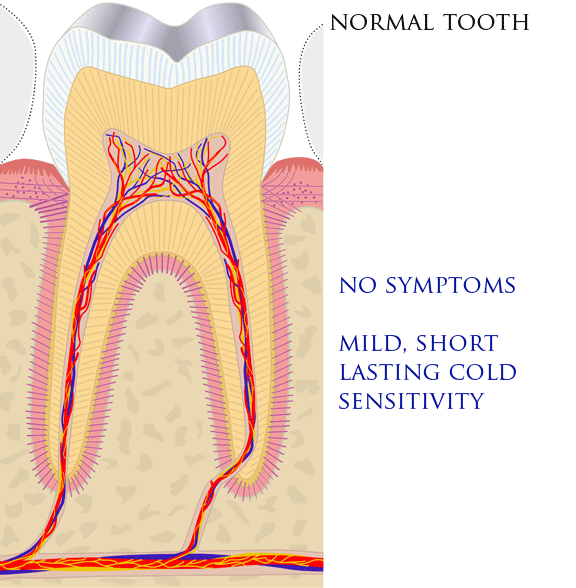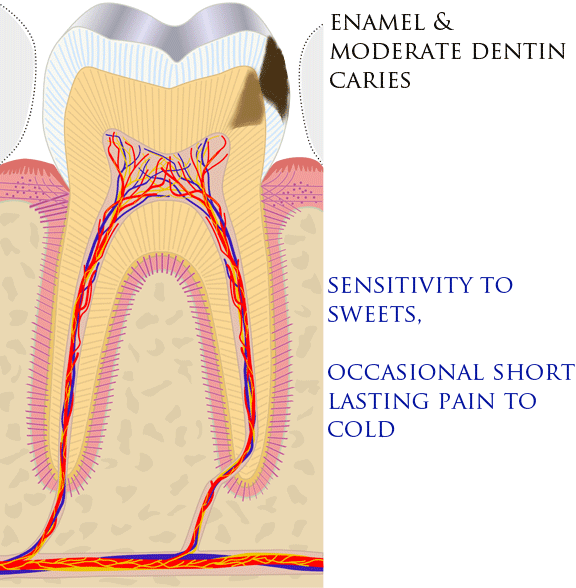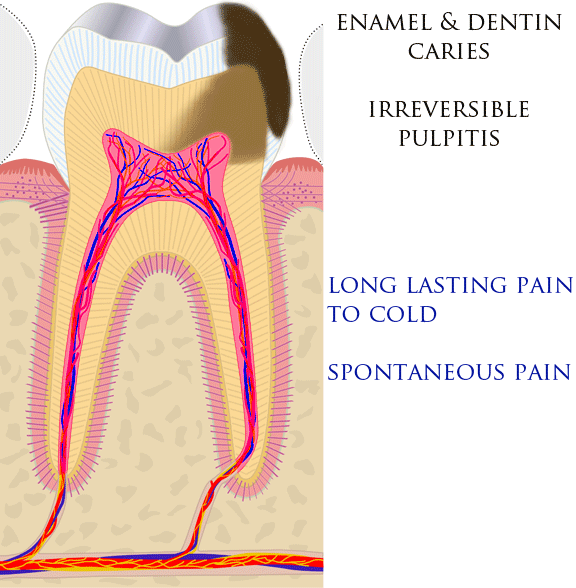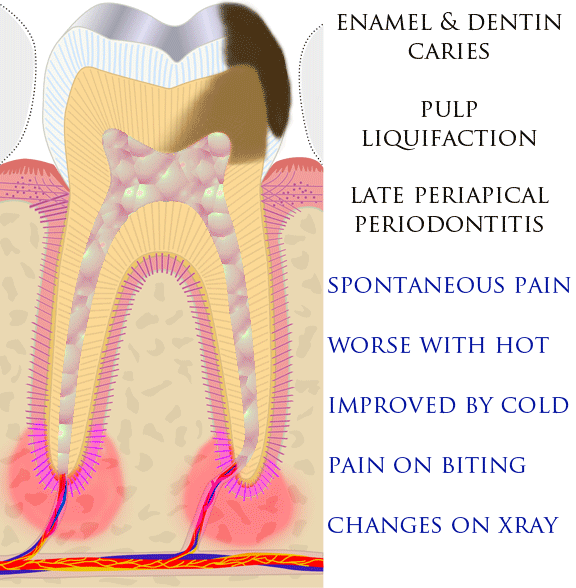
Toothaches, also known as dental pain or tooth pain,Segen JC. (2002). ''McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine''. The McGraw-Hill Companies. is pain in the teeth or their supporting structures, caused by dental diseases or pain referred to the teeth by non-dental diseases. When severe it may impact sleep, eating, and other daily activities. Common causes include inflammation of the pulp, (usually in response to tooth decay, dental trauma, or other factors), dentin hypersensitivity, apical periodontitis (inflammation of the periodontal ligament and alveolar bone around the root apex), dental abscesses (localized collections of pus), alveolar osteitis ("dry socket", a possible complication of tooth extraction), acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (a gum infection), and temporomandibular disorder. Pulpitis is reversible when the pain is mild to moderate and lasts for a short time after a stimulus (for instance cold); or irreversible when the pain is seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tactile Sense
Haptic perception ( "palpable", ''haptikόs'' "suitable for touch") means literally the ability "to grasp something", and is also known as stereognosis. Perception in this case is achieved through the active exploration of surfaces and objects by a moving subject, as opposed to passive contact by a static subject during ''tactile perception''.Weber, E. H. (1851). ''Die Lehre vom Tastsinne und Gemeingefühle auf Versuche gegründet''. Friedrich Vieweg und Sohn. Haptic perception involves the cutaneous receptors of touch, and proprioceptors that sense movement and body position. The inability for haptic perception is known as astereognosis. History The term ''haptik'' was coined by the German Psychologist Max Dessoir in 1892, when suggesting a name for academic research into the sense of touch in the style of that in "acoustics" and "optics". Gibson (1966) defined the haptic system as " e sensibility of the individual to the world adjacent to his body by use of his body". Gibson an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |