|
Basal Plate (neural Tube)
In the developing nervous system, the basal plate is the region of the neural tube ventral to the sulcus limitans. It extends from the rostral mesencephalon to the end of the spinal cord and contains primarily motor neurons, whereas neurons found in the alar plate are primarily associated with sensory functions. The cell types of the basal plate include lower motor neurons and four types of interneuron. Initially, the left and right sides of the basal plate are continuous, but during neurulation they become separated by the floor plate, and this process is directed by the notochord The notochord is an elastic, rod-like structure found in chordates. In vertebrates the notochord is an embryonic structure that disintegrates, as the vertebrae develop, to become the nucleus pulposus in the intervertebral discs of the verteb .... Differentiation of neurons in the basal plate is under the influence of the protein Sonic hedgehog released by ventralizing structures, such as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nervous System
In biology, the nervous system is the complex system, highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its behavior, actions and sense, sensory information by transmitting action potential, signals to and from different parts of its body. The nervous system detects environmental changes that impact the body, then works in tandem with the endocrine system to respond to such events. Nervous tissue first arose in Ediacara biota, wormlike organisms about 550 to 600 million years ago. In Vertebrate, vertebrates, it consists of two main parts, the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord. The PNS consists mainly of nerves, which are enclosed bundles of the long fibers, or axons, that connect the CNS to every other part of the body. Nerves that transmit signals from the brain are called motor nerves (efferent), while those nerves that transmit information from the body to the CNS are called sensory nerves (aff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural network in the nervous system. They are located in the nervous system and help to receive and conduct impulses. Neurons communicate with other cells via synapses, which are specialized connections that commonly use minute amounts of chemical neurotransmitters to pass the electric signal from the presynaptic neuron to the target cell through the synaptic gap. Neurons are the main components of nervous tissue in all Animalia, animals except sponges and placozoans. Plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Molecular evidence suggests that the ability to generate electric signals first appeared in evolution some 700 to 800 million years ago, during the Tonian period. Predecessors of neurons were the peptidergic secretory cells. They eventually ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonic Hedgehog
Sonic hedgehog protein (SHH) is a major signaling molecule of embryonic development in humans and animals, encoded by the ''SHH'' gene. This signaling molecule is key in regulating embryonic morphogenesis in all animals. SHH controls organogenesis and the organization of the central nervous system, limbs, digits and many other parts of the body. Sonic hedgehog is a morphogen that patterns the developing embryo using a concentration gradient characterized by the French flag model. This model has a non-uniform distribution of SHH molecules which governs different cell fates according to concentration. Mutations in this gene can cause holoprosencephaly, a failure of splitting in the cerebral hemispheres, as demonstrated in an experiment using SHH knock-out mice in which the forebrain midline failed to develop and instead only a single fused telencephalic vesicle resulted. Sonic hedgehog still plays a role in differentiation, proliferation, and maintenance of adult tissues. Abno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Notochord
The notochord is an elastic, rod-like structure found in chordates. In vertebrates the notochord is an embryonic structure that disintegrates, as the vertebrae develop, to become the nucleus pulposus in the intervertebral discs of the vertebral column. In non-vertebrate chordates a notochord persists. The notochord is derived from the embryonic mesoderm and consists of an inner core of vacuolated cells filled with glycoproteins, covered by two helical collagen-elastin sheaths. It lies longitudinally along the rostral-caudal (head to tail) axis of the body, dorsal to the gut tube, and ventral to the dorsal nerve cord. Some chordate invertebrates, such as tunicates, develop a notochord during the larval stage but lose it through subsequent stages into adulthood. The notochord is important for signaling the dorso-ventral patterning of cells coming from the mesodermal progenitors. This helps form the precursors needed for certain organs and the embryo to develop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
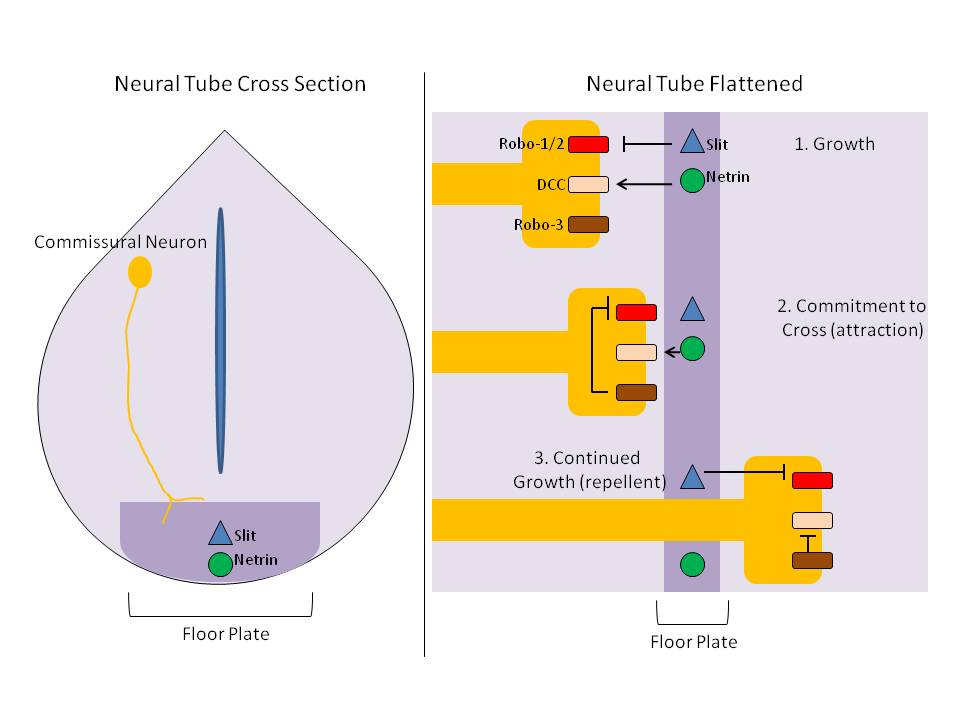
Floor Plate (biology)
The floor plate is a structure integral to the developing nervous system of vertebrate organisms. Located on the ventral midline of the embryonic neural tube, the floor plate is a specialized glial structure that spans the anteroposterior axis from the midbrain to the tail regions. It has been shown that the floor plate is conserved among vertebrates, such as zebrafish and mice, with homologous structures in invertebrates such as the fruit fly ''Drosophila'' and the nematode ''Caenorhabditis elegans, C. elegans''. Functionally, the structure serves as an organizer to ventralize tissues in the embryo as well as to guide neuronal positioning and differentiation along the dorsoventral axis of the neural tube. Induction Induction of the floor plate during embryogenesis of vertebrate embryos has been studied extensively in chick and zebrafish and occurs as a result of a complex signaling network among tissues, the details of which have yet to be fully refined. Currently there are s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurulation
Neurulation refers to the folding process in vertebrate embryos, which includes the transformation of the neural plate into the neural tube. The embryo at this stage is termed the neurula. The process begins when the notochord induces the formation of the central nervous system (CNS) by signaling the ectoderm germ layer above it to form the thick and flat neural plate. The neural plate folds in upon itself to form the neural tube, which will later differentiate into the spinal cord and the brain, eventually forming the central nervous system. Computer simulations found that cell wedging and differential proliferation are sufficient for mammalian neurulation. Different portions of the neural tube form by two different processes, called primary and secondary neurulation, in different species. * In primary neurulation, the neural plate creases inward until the edges come in contact and fuse. * In secondary neurulation, the tube forms by hollowing out of the interior of a solid precur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Motor Neuron
Lower motor neurons (LMNs) are motor neurons located in either the anterior grey column, anterior nerve roots (spinal lower motor neurons) or the cranial nerve nuclei of the brainstem and cranial nerves with motor function (cranial nerve lower motor neurons). Many voluntary movements rely on spinal lower motor neurons, which innervate skeletal muscle fibers and act as a link between upper motor neurons and muscles. Cranial nerve lower motor neurons also control some voluntary movements of the eyes, face and tongue, and contribute to chewing, swallowing and vocalization. Damage to lower motor neurons often leads to hypotonia, hyporeflexia, flaccid paralysis as well as muscle atrophy and fasciculations. Classification Lower motor neurons are classified based on the type of muscle fiber they innervate: * Alpha motor neurons (α-MNs) innervate extrafusal muscle fibers, the most numerous type of muscle fiber and the one involved in muscle contraction. * Beta motor neurons (β-M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alar Plate
The alar plate (or alar lamina) is a neural structure in the embryonic nervous system, part of the dorsal side of the neural tube, that involves the communication of general somatic and general visceral sensory impulses. The caudal part later becomes the sensory axon part of the spinal cord. The alar plate specifically later on becomes the dorsal gray of the spinal cord, and also develops into the sensory nuclei of cranial nerves V, VII, VIII, IX, and X. The inferior olivary nucleus The inferior olivary nucleus (ION) is a structure found in the medulla oblongata underneath the superior olivary nucleus.Gado, Thomas A. Woolsey; Joseph Hanaway; Mokhtar H. (2003). The brain atlas a visual guide to the human central nervous syste ..., mesencephalic nucleus of V, and main sensory nucleus of V are also developed from this plate. The cerebellum also develops from the alar plate, particularly from the rhombic lip. This is considered an exception to the general differentiation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal cord is hollow and contains a structure called the central canal, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The spinal cord is also covered by meninges and enclosed by the neural arches. Together, the brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system. In humans, the spinal cord is a continuation of the brainstem and anatomically begins at the occipital bone, passing out of the foramen magnum and then enters the spinal canal at the beginning of the cervical vertebrae. The spinal cord extends down to between the first and second lumbar vertebrae, where it tapers to become the cauda equina. The enclosing bony vertebral column protects the relatively shorter spinal cord. It is around long in adult men and around long in adult women. The diam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nervous System
In biology, the nervous system is the complex system, highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its behavior, actions and sense, sensory information by transmitting action potential, signals to and from different parts of its body. The nervous system detects environmental changes that impact the body, then works in tandem with the endocrine system to respond to such events. Nervous tissue first arose in Ediacara biota, wormlike organisms about 550 to 600 million years ago. In Vertebrate, vertebrates, it consists of two main parts, the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord. The PNS consists mainly of nerves, which are enclosed bundles of the long fibers, or axons, that connect the CNS to every other part of the body. Nerves that transmit signals from the brain are called motor nerves (efferent), while those nerves that transmit information from the body to the CNS are called sensory nerves (aff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesencephalon
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the uppermost portion of the brainstem connecting the diencephalon and cerebrum with the pons. It consists of the cerebral peduncles, tegmentum, and tectum. It is functionally associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation.Breedlove, Watson, & Rosenzweig. Biological Psychology, 6th Edition, 2010, pp. 45-46 The name ''mesencephalon'' comes from the Greek ''mesos'', "middle", and ''enkephalos'', "brain". Structure The midbrain is the shortest segment of the brainstem, measuring less than 2cm in length. It is situated mostly in the posterior cranial fossa, with its superior part extending above the tentorial notch. The principal regions of the midbrain are the tectum, the cerebral aqueduct, tegmentum, and the cerebral peduncles. Rostral and caudal, Rostrally the midbrain adjoins the diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, etc.), while Rostral and caudal, cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulcus Limitans (neural Tube)
A shallow, longitudinal groove separating the developing gray matter into a basal and alar plates along the length of the neural tube. The sulcus limitans extends the length of the spinal cord and through the mesencephalon The midbrain or mesencephalon is the uppermost portion of the brainstem connecting the diencephalon and cerebrum with the pons. It consists of the cerebral peduncles, tegmentum, and tectum. It is functionally associated with vision, hearing, mo .... References Embryology of nervous system {{Developmental-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |