|
Gag Reflex
The pharyngeal reflex or gag reflex is a reflex muscular contraction of the back of the throat, evoked by touching the roof of the mouth, back of the tongue, area around the tonsils, uvula, and back of the throat. It, along with other aerodigestive reflexes such as reflexive pharyngeal swallowing, prevents objects in the oral cavity from entering the throat except as part of normal swallowing and helps prevent choking, and is a form of coughing. The pharyngeal reflex is different from the laryngeal spasm, which is a reflex muscular contraction of the vocal cords. Reflex arc In a reflex arc, a series of physiological steps occur very rapidly to produce a reflex. Generally, a sensory receptor receives an environmental stimulus, in this case from objects reaching nerves in the back of the throat, and sends a message via an afferent nerve to the central nervous system (CNS). The CNS receives this message and sends an appropriate response via an efferent nerve (also known as a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflex
In biology, a reflex, or reflex action, is an involuntary, unplanned sequence or action and nearly instantaneous response to a stimulus. Reflexes are found with varying levels of complexity in organisms with a nervous system. A reflex occurs via neural pathways in the nervous system called reflex arcs. A stimulus initiates a neural signal, which is carried to a synapse. The signal is then transferred across the synapse to a motor neuron, which evokes a target response. These neural signals do not always travel to the brain, so many reflexes are an automatic response to a stimulus that does not receive or need conscious thought. Many reflexes are fine-tuned to increase organism survival and self-defense. This is observed in reflexes such as the startle reflex, which provides an automatic response to an unexpected stimulus, and the feline righting reflex, which reorients a cat's body when falling to ensure safe landing. The simplest type of reflex, a short-latency reflex, has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vagus Nerve
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve (CN X), plays a crucial role in the autonomic nervous system, which is responsible for regulating involuntary functions within the human body. This nerve carries both sensory and motor fibers and serves as a major pathway that connects the brain to various organs, including the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. As a key part of the parasympathetic nervous system, the vagus nerve helps regulate essential involuntary functions like heart rate, breathing, and digestion. By controlling these processes, the vagus nerve contributes to the body's "rest and digest" response, helping to calm the body after stress, lower heart rate, improve digestion, and maintain homeostasis. The vagus nerve consists of two branches: the right and left vagus nerves. In the neck, the right vagus nerve contains approximately 105,000 fibers, while the left vagus nerve has about 87,000 fibers, according to one source. However, other sources report sl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the human mouth, mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its structure varies across species. The pharynx carries food to the esophagus and air to the larynx. The flap of cartilage called the epiglottis stops food from entering the larynx. In humans, the pharynx is part of the Digestion, digestive system and the conducting zone of the respiratory system. (The conducting zone—which also includes the nostrils of the Human nose, nose, the larynx, trachea, bronchus, bronchi, and bronchioles—filters, warms, and moistens air and conducts it into the lungs). The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections: the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx (hypopharynx). In humans, two sets of pharyngeal muscles form the pharynx and determine the shape of its lumen (anatomy), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ (anatomy), organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about 4–5 centimeters in diameter. The larynx houses the vocal cords, and manipulates pitch (music), pitch and sound pressure, volume, which is essential for phonation. It is situated just below where the tract of the pharynx splits into the trachea and the esophagus. The word 'larynx' (: larynges) comes from the Ancient Greek word ''lárunx'' ʻlarynx, gullet, throatʼ. Structure The triangle-shaped larynx consists largely of cartilages that are attached to one another, and to surrounding structures, by muscles or by fibrous and elastic tissue components. The larynx is lined by a respiratory epithelium, ciliated columnar epithelium except for the vocal folds. The laryngeal cavity, cavity of the larynx extends from its tria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain Death
Brain death is the permanent, irreversible, and complete loss of Electroencephalography, brain function, which may include cessation of involuntary activity (e.g., Control of ventilation#Control of respiratory rhythm, breathing) necessary to sustain life. It differs from persistent vegetative state, in which the person is alive and some autonomic functions remain. It is also distinct from comas as long as some brain and bodily activity and function remain, and it is also not the same as the condition locked-in syndrome. A differential diagnosis can medically distinguish these differing conditions. Brain death is used as an indicator of legal death in many jurisdictions, but it is Medical definition of death, defined inconsistently and often confused by the public. Various parts of the brain may keep functioning when others do not anymore, bringing questions about whether they should truly be considered dead. The term "brain death" has been used to refer to various combinations. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a form of alternative medicine and a component of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in which thin needles are inserted into the body. Acupuncture is a pseudoscience; the theories and practices of TCM are not based on scientific knowledge, and it has been characterized as quackery. There is a range of acupuncture technological variants that originated in different philosophies, and techniques vary depending on the country in which it is performed. However, it can be divided into two main foundational philosophical applications and approaches; the first being the modern standardized form called eight principles TCM and the second being an older system that is based on the ancient Daoist '' wuxing'', better known as the five elements or phases in the West. Acupuncture is most often used to attempt pain relief, though acupuncturists say that it can also be used for a wide range of other conditions. Acupuncture is typically used in combination with other forms o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acupressure
Acupressure is an alternative medicine technique often used in conjunction with acupuncture or reflexology. It is based on the concept of "life energy" (qi), which purportedly flows through "meridians" in the body. There is no scientific evidence for the existence of acupuncture points, meridians, or qi. Although some medical studies have suggested that acupressure may be effective at helping manage nausea and vomiting, insomnia, low back pain, migraines, and constipation, among other things, such studies have been found to have a high likelihood of bias. There is no reliable evidence for the effectiveness of acupressure. History and origin There are different theories as to the origin of acupressure. One theory posits that it originated in India and then was brought to China. Another theory posits that it originated in China. Indian theory Acupressure therapy was prevalent in India. After the Chinese Buddhism#Han Dynasty (206 BCE–220 CE), spread of Buddhism to China, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Anaesthetic
General anaesthetics (or anesthetics) are often defined as compounds that induce a loss of consciousness in humans or loss of righting reflex in animals. Clinical definitions are also extended to include an induced coma that causes lack of awareness to painful stimuli, sufficient to facilitate surgical applications in clinical and veterinary practice. General anaesthetics do not act as analgesics and should also not be confused with sedatives. General anaesthetics are a structurally diverse group of compounds whose mechanisms encompass multiple biological targets involved in the control of neuronal pathways. The precise workings are the subject of some debate and ongoing research. General anesthetics elicit a state of General anaesthesia, general anesthesia. It remains somewhat controversial regarding how this state should be defined. General anesthetics, however, typically elicit several key reversible effects: immobility, analgesia, amnesia, unconsciousness, and reduced autonomi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Anesthetic
A local anesthetic (LA) is a medication that causes absence of all sensation (including pain) in a specific body part without loss of consciousness, providing local anesthesia, as opposed to a general anesthetic, which eliminates all sensation in the entire body and causes unconsciousness. Local anesthetics are most commonly used to eliminate pain during or after surgery. When it is used on specific nerve pathways ( local anesthetic nerve block), paralysis (loss of muscle function) also can be induced. Classification LAs are of 2 types: *Clinical LAs: ** amino amide LAs ** amino ester LAs *Synthetic LAs **Cocaine derivatives Synthetic cocaine-derived LAs differ from cocaine because they have a much lower abuse potential and do not cause hypertension vasoconstriction (with few exceptions). The suffix "-caine" at the ends of these medication names is derived from the word "cocaine", because cocaine was formerly used as a local anesthetic. Examples Short Duration of Act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedative
A sedative or tranquilliser is a substance that induces sedation by reducing irritability or Psychomotor agitation, excitement. They are central nervous system (CNS) Depressant, depressants and interact with brain activity, causing its deceleration. Various kinds of sedatives can be distinguished, but the majority of them affect the neurotransmitter Gamma-Aminobutyric acid, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Most sedatives produce relaxing effects by increasing GABA activity. This group is related to hypnotics. The term ''sedative'' describes drugs that serve to calm or Anxiolytic, relieve anxiety, whereas the term ''hypnotic'' describes drugs whose main purpose is to initiate, sustain, or lengthen sleep. Because these two functions frequently overlap, and because drugs in this class generally produce dose-dependent effects (ranging from anxiolysis to loss of consciousness), they are often referred to collectively as ''sedative–hypnotic'' drugs. Terminology There is some overlap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-nausea
An antiemetic is a drug that is effective against vomiting and nausea. Antiemetics are typically used to treat motion sickness and the side effects of opioid analgesics, general anaesthetics, and chemotherapy directed against cancer. They may be used for severe cases of gastroenteritis, especially if the patient is dehydrated. Some antiemetics previously thought to cause birth defects appear safe for use by pregnant women in the treatment of morning sickness and the more serious hyperemesis gravidarum. __TOC__ Types * 5-HT3 receptor antagonists block serotonin receptors in the central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract. As such, they can be used to treat post-operative and cytotoxic drug nausea & vomiting. However, they can also cause constipation, dry mouth, and fatigue. ** Dolasetron (Anzemet) can be administered in tablet form or in an injection. ** Granisetron (Kytril, Sancuso) can be administered in tablet (Kytril), oral solution (Kytril), injection (Kytril), or i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
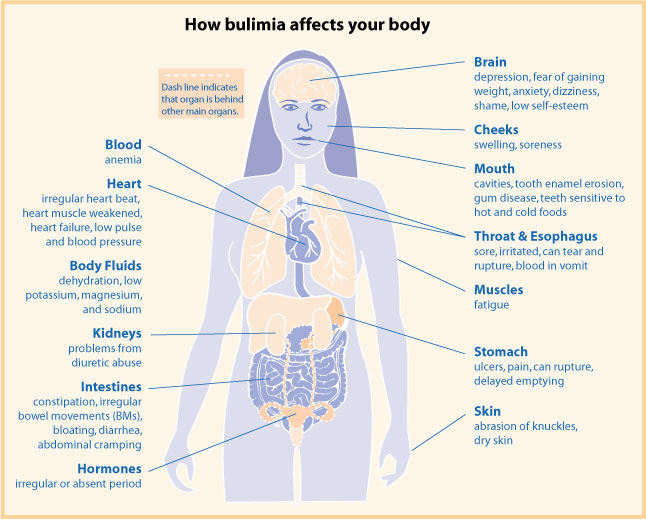
Bulimia Nervosa
Bulimia nervosa, also known simply as bulimia, is an eating disorder characterized by binge eating (eating large quantities of food in a short period of time, often feeling out of control) followed by compensatory behaviors, such as self-induced vomiting or fasting, to prevent weight gain. Other efforts to lose weight may include the use of diuretics, laxatives, stimulants, water fasting, or excessive exercise. Most people with bulimia are at normal weight and have higher risk for other mental disorders, such as depression, anxiety, borderline personality disorder, bipolar disorder, and problems with drugs to alcohol. There is also a higher risk of suicide and self-harm. Bulimia is more common among those who have a close relative with the condition. The percentage risk that is estimated to be due to genetics is between 30% and 80%. Other risk factors for the disease include psychological stress, cultural pressure to attain a certain body type, poor self-esteem, and obes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |