Pharynx on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the
 The upper portion of the pharynx, the nasopharynx, extends from the base of the skull to the upper surface of the soft palate. It includes the space between the internal nares and the soft palate and lies above the oral cavity. The adenoids, also known as the pharyngeal tonsils, are lymphoid tissue structures located in the posterior wall of the nasopharynx. Waldeyer's tonsillar ring is an annular arrangement of lymphoid tissue in both the nasopharynx and oropharynx. The nasopharynx is lined by respiratory epithelium that is pseudostratified, columnar, and ciliated.
Polyps or mucus can obstruct the nasopharynx, as can congestion due to an upper respiratory infection. The
The upper portion of the pharynx, the nasopharynx, extends from the base of the skull to the upper surface of the soft palate. It includes the space between the internal nares and the soft palate and lies above the oral cavity. The adenoids, also known as the pharyngeal tonsils, are lymphoid tissue structures located in the posterior wall of the nasopharynx. Waldeyer's tonsillar ring is an annular arrangement of lymphoid tissue in both the nasopharynx and oropharynx. The nasopharynx is lined by respiratory epithelium that is pseudostratified, columnar, and ciliated.
Polyps or mucus can obstruct the nasopharynx, as can congestion due to an upper respiratory infection. The 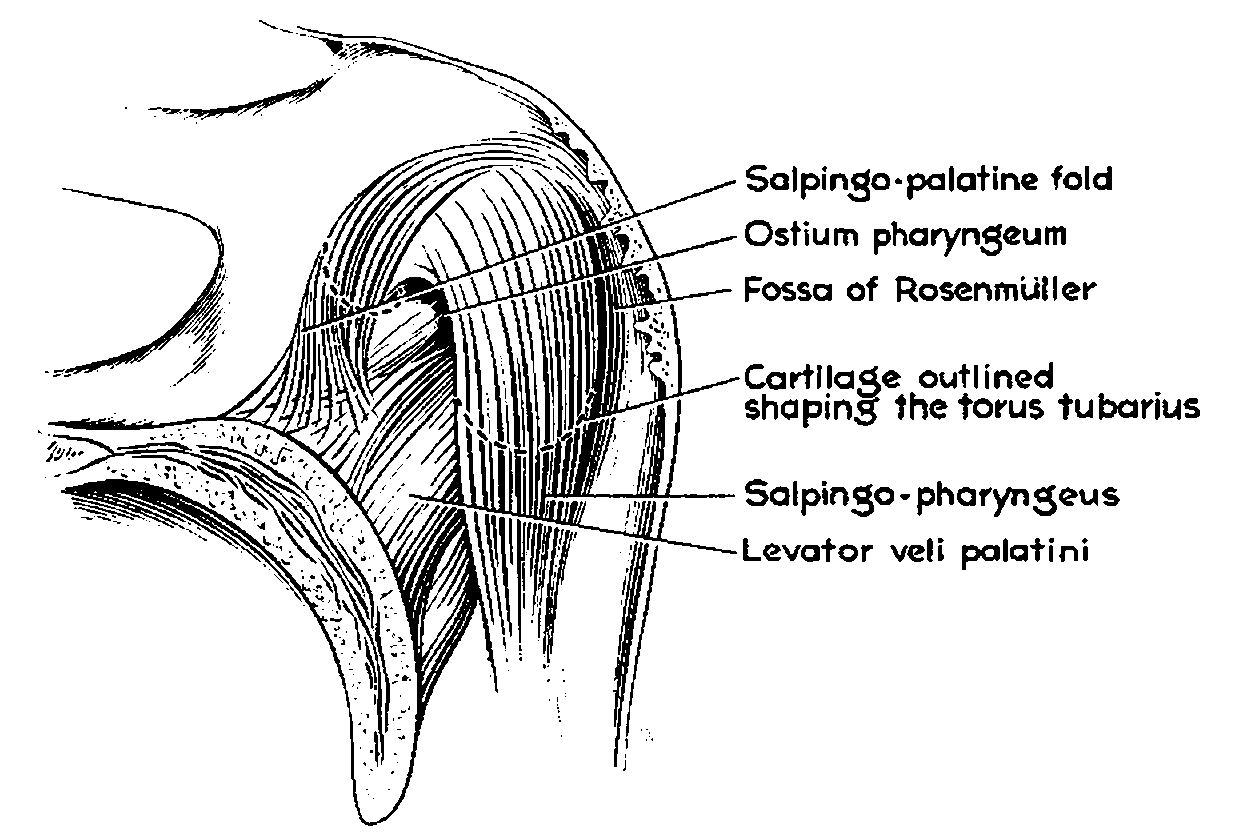 The anterior aspect of the nasopharynx communicates through the choanae with the nasal cavities. On its lateral wall is the pharyngeal opening of the auditory tube, somewhat triangular in shape and bounded behind by a firm prominence, the
The anterior aspect of the nasopharynx communicates through the choanae with the nasal cavities. On its lateral wall is the pharyngeal opening of the auditory tube, somewhat triangular in shape and bounded behind by a firm prominence, the

 Pharyngeal jaws are a "second set" of jaws contained within the pharynx of many species of fish, distinct from the primary (oral) jaws. Pharyngeal jaws have been studied in
Pharyngeal jaws are a "second set" of jaws contained within the pharynx of many species of fish, distinct from the primary (oral) jaws. Pharyngeal jaws have been studied in
File:Alitta virens pharynx (lateral).jpg, Everted pharynx of '' Alitta virens'' (also known as ''Nereis virens''), lateral view
File:Prorhynchus fontinalis pharynx.jpg, Pharynx of the flatworm '' Prorhynchus fontinalis''
File:Peerj-297-fig-5 Platydemus manokwari.png, Pharynx of the flatworm '' Platydemus manokwari'' visible as the worm feeds on a snail.
File:C elegans anatomy.png, Longitudinal section through the roundworm '' Caenorhabditis elegans'' showing the position of the pharynx in the animal body.
File:Lamprey Larva x sect pharynx labelled.png, Microscopic cross section through the pharynx of a larva from an unknown lamprey species.
Image:Illu nose nasal cavities.jpg, Nose and nasal
Image:Gray907.png, Coronal section of right ear, showing
Pharynx
Stedman's Online Medical Dictionary at Lippincott Williams and Wilkins * ''Human Anatomy and Physiology'' Elaine N. Marieb and Katja Hoehn, Seventh Edition. * ''TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours'' Sobin LH & Wittekind Ch (eds)Sixth edition UICC 2002
throat
In vertebrate anatomy, the throat is the front part of the neck, internally positioned in front of the vertebrae. It contains the Human pharynx, pharynx and larynx. An important section of it is the epiglottis, separating the esophagus from the t ...
behind the mouth
A mouth also referred to as the oral is the body orifice through which many animals ingest food and animal communication#Auditory, vocalize. The body cavity immediately behind the mouth opening, known as the oral cavity (or in Latin), is also t ...
and nasal cavity
The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nas ...
, and above the esophagus
The esophagus (American English), oesophagus (British English), or œsophagus (Œ, archaic spelling) (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, see spelling difference) all ; : ((o)e)(œ)sophagi or ((o)e)(œ)sophaguses), c ...
and trachea
The trachea (: tracheae or tracheas), also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all animals' lungs. The trachea extends from ...
(the tubes going down to the stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of Human, humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient Greek name for the stomach is ''gaster'' which is used as ''gastric'' in medical t ...
and the lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their ...
s respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its structure varies across species. The pharynx carries food to the esophagus and air to the larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ (anatomy), organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal ...
. The flap of cartilage called the epiglottis stops food from entering the larynx.
In humans, the pharynx is part of the digestive system
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller compone ...
and the conducting zone of the respiratory system
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies grea ...
. (The conducting zone—which also includes the nostrils of the nose, the larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ (anatomy), organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal ...
, trachea
The trachea (: tracheae or tracheas), also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all animals' lungs. The trachea extends from ...
, bronchi, and bronchioles—filters, warms, and moistens air and conducts it into the lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their ...
s). The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections: the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx (hypopharynx).
In humans, two sets of pharyngeal muscles form the pharynx and determine the shape of its lumen. They are arranged as an inner layer of longitudinal muscles and an outer circular layer.
Structure
Nasopharynx
 The upper portion of the pharynx, the nasopharynx, extends from the base of the skull to the upper surface of the soft palate. It includes the space between the internal nares and the soft palate and lies above the oral cavity. The adenoids, also known as the pharyngeal tonsils, are lymphoid tissue structures located in the posterior wall of the nasopharynx. Waldeyer's tonsillar ring is an annular arrangement of lymphoid tissue in both the nasopharynx and oropharynx. The nasopharynx is lined by respiratory epithelium that is pseudostratified, columnar, and ciliated.
Polyps or mucus can obstruct the nasopharynx, as can congestion due to an upper respiratory infection. The
The upper portion of the pharynx, the nasopharynx, extends from the base of the skull to the upper surface of the soft palate. It includes the space between the internal nares and the soft palate and lies above the oral cavity. The adenoids, also known as the pharyngeal tonsils, are lymphoid tissue structures located in the posterior wall of the nasopharynx. Waldeyer's tonsillar ring is an annular arrangement of lymphoid tissue in both the nasopharynx and oropharynx. The nasopharynx is lined by respiratory epithelium that is pseudostratified, columnar, and ciliated.
Polyps or mucus can obstruct the nasopharynx, as can congestion due to an upper respiratory infection. The auditory tube
The Eustachian tube (), also called the auditory tube or pharyngotympanic tube, is a tube that links the nasopharynx to the middle ear, of which it is also a part. In adult humans, the Eustachian tube is approximately long and in diameter. It ...
, which connects the middle ear to the pharynx, opens into the nasopharynx at the pharyngeal opening of the auditory tube. The opening and closing of the auditory tubes serves to equalize the barometric pressure in the middle ear with that of the ambient atmosphere.
 The anterior aspect of the nasopharynx communicates through the choanae with the nasal cavities. On its lateral wall is the pharyngeal opening of the auditory tube, somewhat triangular in shape and bounded behind by a firm prominence, the
The anterior aspect of the nasopharynx communicates through the choanae with the nasal cavities. On its lateral wall is the pharyngeal opening of the auditory tube, somewhat triangular in shape and bounded behind by a firm prominence, the torus tubarius
The torus tubarius (or torus of the auditory tube) is an elevation of the mucous membrane of the Pharynx#Nasopharynx, nasal part of the pharynx formed by the underlying base of the Eustachian tube, cartilaginous portion of the Eustachian tube, Eu ...
or cushion, caused by the medial end of the cartilage of the tube that elevates the mucous membrane.
Two folds arise from the cartilaginous opening:
* the salpingopharyngeal fold, a vertical fold of mucous membrane extending from the inferior part of the torus and containing the salpingopharyngeus muscle.
* the salpingopalatine fold, a smaller fold, in front of the salpingopharyngeal fold, extending from the superior part of the torus to the palate and containing the salpingopalatine muscle. The tensor veli palatini and levator veli palatini are lateral to the fold and do not contribute.
Oropharynx
The oropharynx lies behind the oral cavity, extending from the uvula to the level of the hyoid bone. It opens anteriorly, through the isthmus faucium, into the mouth, while in its lateral wall, between the palatoglossal arch and the palatopharyngeal arch, is thepalatine tonsil
Palatine tonsils, commonly called the tonsils and occasionally called the faucial tonsils, are tonsils located on the left and right sides at the back of the throat in humans and other mammals, which can often be seen as flesh-colored, pinkish ...
. The anterior wall consists of the base of the tongue and the epiglottic vallecula; the lateral wall is made up of the tonsil, tonsillar fossa, and tonsillar (faucial) pillars; the superior wall consists of the inferior surface of the soft palate and the uvula. Because both food and air pass through the pharynx, a flap of connective tissue called the epiglottis closes over the glottis when food is swallowed to prevent aspiration. The oropharynx is lined by non-keratinized squamous stratified epithelium.
The ''HACEK'' organisms ('' Haemophilus, Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, Cardiobacterium hominis, Eikenella corrodens, Kingella'') are part of the normal oropharyngeal flora, which grow slowly, prefer a carbon dioxide-enriched atmosphere, and share an enhanced capacity to produce endocardial infections, especially in young children. '' Fusobacterium'' is a pathogen.
Laryngopharynx
The laryngopharynx, (Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
: ''pars laryngea pharyngis''), also known as hypopharynx, is the caudal part of the pharynx; it is the part of the throat that connects to the esophagus. It lies inferior to the epiglottis and extends to the location where this common pathway diverges into the respiratory ( laryngeal) and digestive ( esophageal) pathways. At that point, the laryngopharynx is continuous with the esophagus posteriorly. The esophagus conducts food and fluids to the stomach; air enters the larynx anteriorly. During swallowing, food has the "right of way", and air passage temporarily stops. Corresponding roughly to the area located between the 4th and 6th cervical vertebrae
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In saurop ...
, the superior boundary of the laryngopharynx is at the level of the hyoid bone. The laryngopharynx includes three major sites: the pyriform sinus, postcricoid area, and the posterior pharyngeal wall. Like the oropharynx above it, the laryngopharynx serves as a passageway for food and air and is lined with a stratified squamous epithelium
A stratified squamous epithelium consists of squamous (flattened) epithelial cells arranged in layers upon a basal membrane. Only one layer is in contact with the basement membrane; the other layers adhere to one another to maintain structural ...
. It is innervated by the pharyngeal plexus and by the recurrent laryngeal nerve.
The vascular supply to the laryngopharynx includes the superior thyroid artery, the lingual artery and the ascending pharyngeal artery. The primary neural supply is from both the vagus and glossopharyngeal nerves. The vagus nerve provides an auricular branch also termed "Arnold's nerve" which also supplies the external auditory canal, thus laryngopharyngeal cancer can result in referred ear pain. This nerve is also responsible for the ear-cough reflex in which stimulation of the ear canal results in a person coughing.
Function
The pharynx moves food from the mouth to the esophagus. It also moves air from the nasal and oral cavities to thelarynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ (anatomy), organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal ...
. It is also used in human speech, as pharyngeal consonants are articulated here, and it acts as a resonating chamber during phonation.
Clinical significance

Inflammation
Inflammation of the pharynx, or pharyngitis, is the painful inflammation of the throat.Pharyngeal cancer
Pharyngeal cancer is a cancer that originates in the neck and/or throat.Waldeyer's tonsillar ring
Waldeyer's tonsillar ring is an anatomical term collectively describing the annular arrangement of lymphoid tissue in the pharynx. Waldeyer's ring circumscribes the naso and oropharynx, with some of its tonsillar tissue located above and some below the soft palate (and to the back of the oral cavity). It is believed that Waldeyer's ring prevents the invasion of microorganisms from going into the air and food passages and this helps in the defense mechanism of the respiratory and alimentary systems.Etymology
The word ''pharynx'' () is derived from the Greek φάρυγξ ''phárynx'', meaning "throat". Its plural form is ''pharynges'' or ''pharynxes'' , and its adjective form is ''pharyngeal'' ( or ).Other vertebrates
All vertebrates have a pharynx, used in both feeding and respiration. The pharynx arises during development in all vertebrates through a series of six or more outpocketings on the lateral sides of the head. These outpocketings are pharyngeal arches, and they give rise to a number of different structures in the skeletal, muscular, and circulatory systems. The structure of the pharynx varies across the vertebrates. It differs in dogs, horses, and ruminants. In dogs, a single duct connects the nasopharynx to the nasal cavity. The tonsils are a compact mass that points away from the lumen of the pharynx. In the horse, the auditory tube opens into the guttural pouch and the tonsils are diffuse and raised slightly. Horses are unable to breathe through the mouth as the free apex of the rostral epiglottis lies dorsal to the soft palate in a normal horse. Inruminant
Ruminants are herbivorous grazing or browsing artiodactyls belonging to the suborder Ruminantia that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through microb ...
s, the tonsils are a compact mass that points towards the lumen of the pharynx.
Pharyngeal arches
Pharyngeal arches are characteristic features of vertebrates whose origin can be traced back through chordates to basal deuterostomes who also share endodermal outpocketings of the pharyngeal apparatus. Similar patterns of gene expression can be detected in the developing pharynx of amphioxi and hemichordates. However, the vertebrate pharynx is unique in that it gives rise to endoskeletal support through the contribution of neural crest cells.Pharyngeal jaws
moray eel
Moray eels, or Muraenidae (), are a family (biology), family of eels whose members are found worldwide. There are approximately 200 species in 15 genera which are almost exclusively Marine (ocean), marine, but several species are regu ...
s where their specific action is noted. When the moray bites prey, it first bites normally with its oral jaws, capturing the prey. Immediately thereafter, the pharyngeal jaws are brought forward and bite down on the prey to grip it; they then retract, pulling the prey down the eel's esophagus, allowing it to be swallowed.
Invertebrates
Invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate s ...
s also have a pharynx. Invertebrates with a pharynx include the tardigrades, annelids and arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
s, and the priapulids (which have an eversible pharynx).
The "pharynx" of the nematode
The nematodes ( or ; ; ), roundworms or eelworms constitute the phylum Nematoda. Species in the phylum inhabit a broad range of environments. Most species are free-living, feeding on microorganisms, but many are parasitic. Parasitic worms (h ...
worm is a muscular food pump in the head, triangular in cross-section, that grinds food and transports it directly to the intestines. A one-way valve connects the pharynx to the excretory canal.
Additional images
auditory tube
The Eustachian tube (), also called the auditory tube or pharyngotympanic tube, is a tube that links the nasopharynx to the middle ear, of which it is also a part. In adult humans, the Eustachian tube is approximately long and in diameter. It ...
and levator veli palatini muscle
Image:Gray955.png, The entrance to the larynx, viewed from behind
File:Slide1kuku.JPG, Deep dissection of human larynx, pharynx and tongue seen from behind
File:Gray994.png, The nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx or larynx can be seen clearly in this sagittal section of the head and neck.
See also
* Cricopharyngeal ligament * Nasopharyngeal carcinoma * Pharyngeal aspiration * Pharyngeal consonant * Pharyngeal (disambiguation) * '' Saccopharynx'', a genus of deep-sea eel-like fishes with large mouths, distensible stomachs and long scaleless bodies * Salpinx in anatomy * Tonsil * Tornwaldt cystReferences
GeneralPharynx
Stedman's Online Medical Dictionary at Lippincott Williams and Wilkins * ''Human Anatomy and Physiology'' Elaine N. Marieb and Katja Hoehn, Seventh Edition. * ''TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours'' Sobin LH & Wittekind Ch (eds)Sixth edition UICC 2002
External links
* * * {{Portal bar, Anatomy Digestive system Human head and neck Human throat Human voice Animal anatomy Otorhinolaryngology