Bone Fractures on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A bone fracture (abbreviated FRX or Fx, Fx, or #) is a medical condition in which there is a partial or complete break in the continuity of any
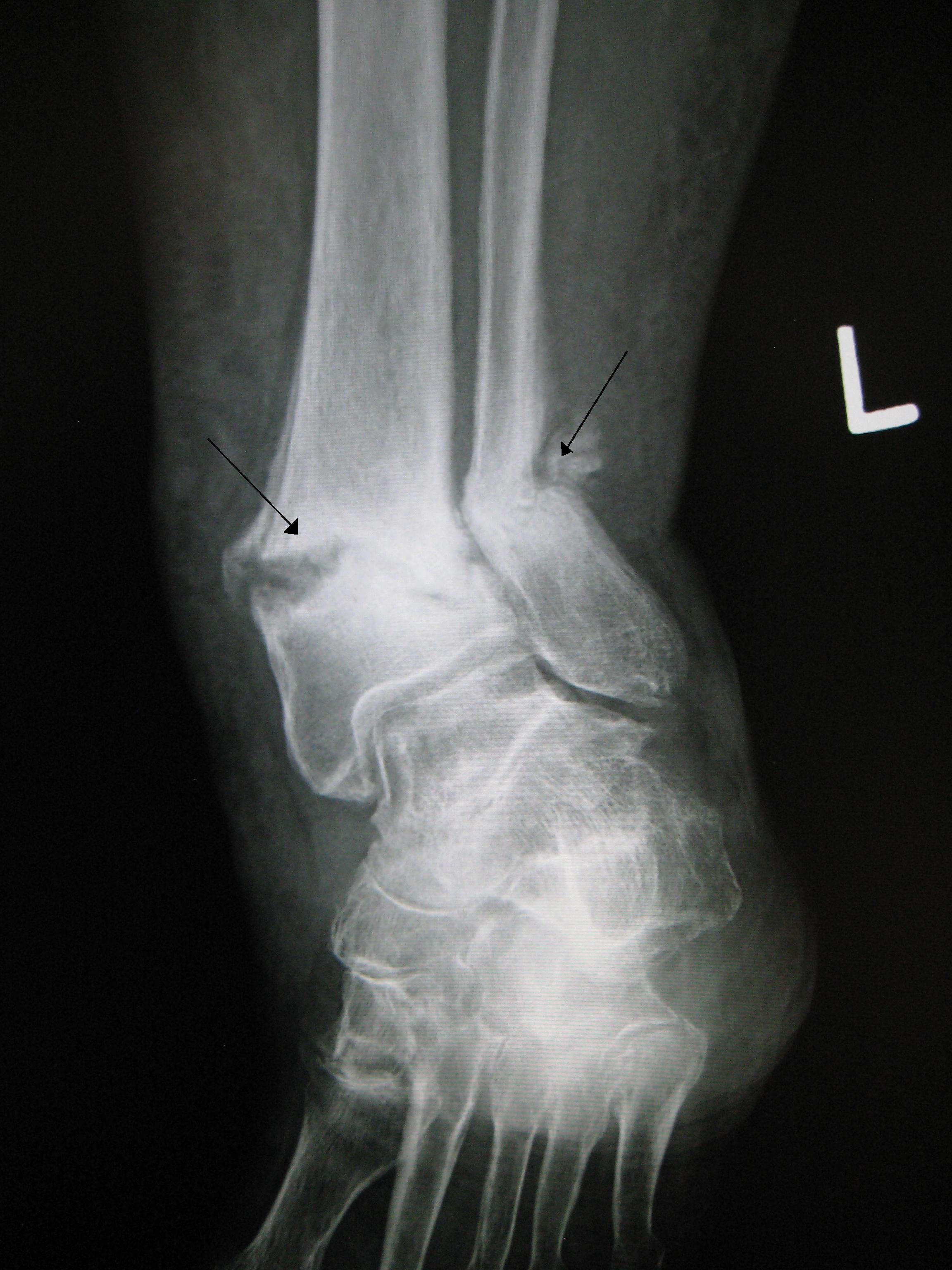 Some fractures may lead to serious complications including a condition known as
Some fractures may lead to serious complications including a condition known as
 The natural process of healing a fracture starts when the injured bone and surrounding tissues bleed, forming a fracture
The natural process of healing a fracture starts when the injured bone and surrounding tissues bleed, forming a fracture
 A bone fracture may be diagnosed based on the history given and the physical examination performed. Radiographic imaging often is performed to confirm the diagnosis. Under certain circumstances, radiographic examination of the nearby joints is indicated in order to exclude dislocations and fracture-dislocations. In situations where projectional radiography alone is insufficient, Computed Tomography (CT) or Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) may be indicated.
A bone fracture may be diagnosed based on the history given and the physical examination performed. Radiographic imaging often is performed to confirm the diagnosis. Under certain circumstances, radiographic examination of the nearby joints is indicated in order to exclude dislocations and fracture-dislocations. In situations where projectional radiography alone is insufficient, Computed Tomography (CT) or Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) may be indicated.
 In
In
at Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics online ****
 Treatment of bone fractures are broadly classified as surgical or conservative, the latter basically referring to any non-surgical procedure, such as pain management, immobilization or other non-surgical stabilization. A similar classification is ''open'' versus ''closed treatment'', in which ''open treatment'' refers to any treatment in which the fracture site is opened surgically, regardless of whether the fracture is an
Treatment of bone fractures are broadly classified as surgical or conservative, the latter basically referring to any non-surgical procedure, such as pain management, immobilization or other non-surgical stabilization. A similar classification is ''open'' versus ''closed treatment'', in which ''open treatment'' refers to any treatment in which the fracture site is opened surgically, regardless of whether the fracture is an
Authoritative information in orthopaedic surgery
American Association of Orthopedic Surgeons (AAOS)
Radiographic Atlas of Fracture
{{Authority control Acute pain
bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
in the body. In more severe cases, the bone may be broken into several fragments, known as a ''comminuted fracture''. An open fracture (or compound fracture) is a bone fracture where the broken bone breaks through the skin.
A bone fracture may be the result of high force impact or stress, or a minimal trauma injury as a result of certain medical conditions that weaken the bones, such as osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to more porous bone, and consequent increase in Bone fracture, fracture risk.
It is the most common reason f ...
, osteopenia
Osteopenia, known as "low bone mass" or "low bone density", is a condition in which bone mineral density is low. Because their bones are weaker, people with osteopenia may have a higher risk of fractures, and some people may go on to develop o ...
, bone cancer
A bone tumor is an neoplastic, abnormal growth of tissue in bone, traditionally classified as benign, noncancerous (benign) or malignant, cancerous (malignant). Cancerous bone tumors usually originate from a cancer in another part of the body su ...
, or osteogenesis imperfecta
Osteogenesis imperfecta (; OI), colloquially known as brittle bone disease, is a group of genetic disorders that all result in bones that bone fracture, break easily. The range of symptoms—on the skeleton as well as on the body's other Or ...
, where the fracture is then properly termed a pathologic fracture. Most bone fractures require urgent medical attention to prevent further injury.
Signs and symptoms
Although bone tissue contains no pain receptors, a bone fracture is painful for several reasons: * Breaking in the continuity of theperiosteum
The periosteum is a membrane that covers the outer surface of all bones, except at the articular surfaces (i.e. the parts within a joint space) of long bones. (At the joints of long bones the bone's outer surface is lined with "articular cartila ...
, with or without similar discontinuity in endosteum
The endosteum (: endostea) is a thin vascular membrane of connective tissue that lines the inner surface of the bony tissue that forms the medullary cavity of long bones.
This endosteal surface is usually resorbed during long periods of malnutr ...
, as both contain multiple pain receptors.
* Edema
Edema (American English), also spelled oedema (British English), and also known as fluid retention, swelling, dropsy and hydropsy, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue (biology), tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. S ...
and hematoma
A hematoma, also spelled haematoma, or blood suffusion is a localized bleeding outside of blood vessels, due to either disease or trauma including injury or surgery and may involve blood continuing to seep from broken capillaries. A hematoma is ...
of nearby soft tissues
Soft tissue connects and surrounds or supports internal organs and bones, and includes muscle, tendons, ligaments, fat, fibrous tissue, lymph and blood vessels, fasciae, and synovial membranes. Soft tissue is tissue in the body that is not ...
caused by ruptured bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It i ...
evokes pressure pain.
* Involuntary muscle spasms trying to hold bone fragments in place.
Damage to adjacent structures such as nerves, muscles or blood vessels, spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
, and nerve roots (for spine fractures), or cranial contents (for skull fractures) may cause other specific signs and symptoms.
Complications
compartment syndrome
Compartment syndrome is a serious medical condition in which increased pressure within a Fascial compartment, body compartment compromises blood flow and tissue function, potentially leading to permanent damage if not promptly treated. There are ...
. If not treated, eventually, compartment syndrome may require amputation
Amputation is the removal of a Limb (anatomy), limb or other body part by Physical trauma, trauma, medical illness, or surgery. As a surgical measure, it is used to control pain or a disease process in the affected limb, such as cancer, malign ...
of the affected limb. Other complications may include non-union, where the fractured bone fails to heal, or malunion, where the fractured bone heals in a deformed manner. One form of malunion is the malrotation of a bone, which is especially common after femoral and tibial fractures.
Complications of fractures may be classified into three broad groups, depending upon their time of occurrence. These are as follows –
# ''Immediate'' complications – occurs at the time of the fracture.
# ''Early'' complications – occurring in the initial few days after the fracture.
# ''Late'' complications – occurring a long time after the fracture.
Pathophysiology
 The natural process of healing a fracture starts when the injured bone and surrounding tissues bleed, forming a fracture
The natural process of healing a fracture starts when the injured bone and surrounding tissues bleed, forming a fracture hematoma
A hematoma, also spelled haematoma, or blood suffusion is a localized bleeding outside of blood vessels, due to either disease or trauma including injury or surgery and may involve blood continuing to seep from broken capillaries. A hematoma is ...
. The blood coagulates to form a blood clot
A thrombus ( thrombi) is a solid or semisolid aggregate from constituents of the blood (platelets, fibrin, red blood cells, white blood cells) within the circulatory system during life. A blood clot is the final product of the blood coagulatio ...
situated between the broken fragments. Within a few days, blood vessels grow into the jelly-like matrix of the blood clot. The new blood vessels bring phagocytes to the area, which gradually removes the non-viable material. The blood vessels also bring fibroblast
A fibroblast is a type of cell (biology), biological cell typically with a spindle shape that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework (Stroma (tissue), stroma) for animal Tissue (biology), tissues, and ...
s in the walls of the vessels and these multiply and produce collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix of the connective tissues of many animals. It is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up 25% to 35% of protein content. Amino acids are bound together to form a trip ...
fibres. In this way, the blood clot is replaced by a matrix of collagen. Collagen's rubbery consistency allows bone fragments to move only a small amount unless severe or persistent force is applied.
At this stage, some of the fibroblasts begin to lay down bone matrix in the form of collagen monomers. These monomers spontaneously assemble to form the bone matrix, for which bone crystals ( calcium hydroxyapatite) are deposited in amongst, in the form of insoluble crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macros ...
s. This mineralization of the collagen matrix stiffens it and transforms it into bone. In fact, bone ''is'' a mineralized collagen matrix; if the mineral is dissolved out of bone, it becomes rubbery. Healing bone callus
A callus (: calluses) is an area of thickened and sometimes hardened skin that forms as a response to repeated friction, pressure, or other irritation. Since repeated contact is required, calluses are most often found on the feet and hands, b ...
on average is sufficiently mineralized to show up on X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
within 6 weeks in adults and less in children. This initial "woven" bone does not have the strong mechanical properties of mature bone. By a process of remodelling, the woven bone is replaced by mature "lamellar" bone. The whole process may take up to 18 months, but in adults, the strength of the healing bone is usually 80% of normal by 3 months after the injury.
Several factors may help or hinder the bone healing process. For example, tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
smoking hinders the process of bone healing, and adequate nutrition (including calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ...
intake) will help the bone healing process. Weight-bearing stress on bone, after the bone has healed sufficiently to bear the weight, also builds bone strength.
Although there are theoretical concerns about NSAIDs slowing the rate of healing, there is not enough evidence to warrant withholding the use of this type analgesic in simple fractures.
Effects of smoking
Smokers generally have lower bone density than non-smokers, so they have a much higher risk of fractures. There is also evidence that smoking delays bone healing.Diagnosis
Classification
 In
In orthopedic
Orthopedic surgery or orthopedics ( alternative spelling orthopaedics) is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal ...
medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, ...
, fractures are classified in various ways. Historically they are named after the physician who first described the fracture conditions, however, there are more systematic classifications as well.
They may be divided into stable versus unstable depending on the likelihood that they may shift further.
Mechanism
* Traumatic fracture – a fracture due to sustained trauma. e.g., fractures caused by a fall, road traffic accident, fight, etc. * Pathologic fracture – a fracture through a bone that has been made weak by some underlying disease is called pathological fracture. e.g., a fracture through a bone weakened bymetastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spreading from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, ...
. Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to more porous bone, and consequent increase in Bone fracture, fracture risk.
It is the most common reason f ...
is the most common cause of pathological fracture.
* Periprosthetic fracture – a fracture at the point of mechanical weakness at the end of an implant.
Soft-tissue involvement
* Closed/simple fractures are those in which the overlying skin is intact * Open/compound fractures involve wounds that communicate with the fracture, or where fracturehematoma
A hematoma, also spelled haematoma, or blood suffusion is a localized bleeding outside of blood vessels, due to either disease or trauma including injury or surgery and may involve blood continuing to seep from broken capillaries. A hematoma is ...
is exposed, and may thus expose bone to contamination
Contamination is the presence of a constituent, impurity, or some other undesirable element that renders something unsuitable, unfit or harmful for the physical body, natural environment, workplace, etc.
Types of contamination
Within the scien ...
. Open injuries carry a higher risk of infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
. Reports indicate an incidence of infection after internal fixation of closed fracture of 1-2%, rising to 30% in open fractures.
** Clean fracture
** Contaminated fracture
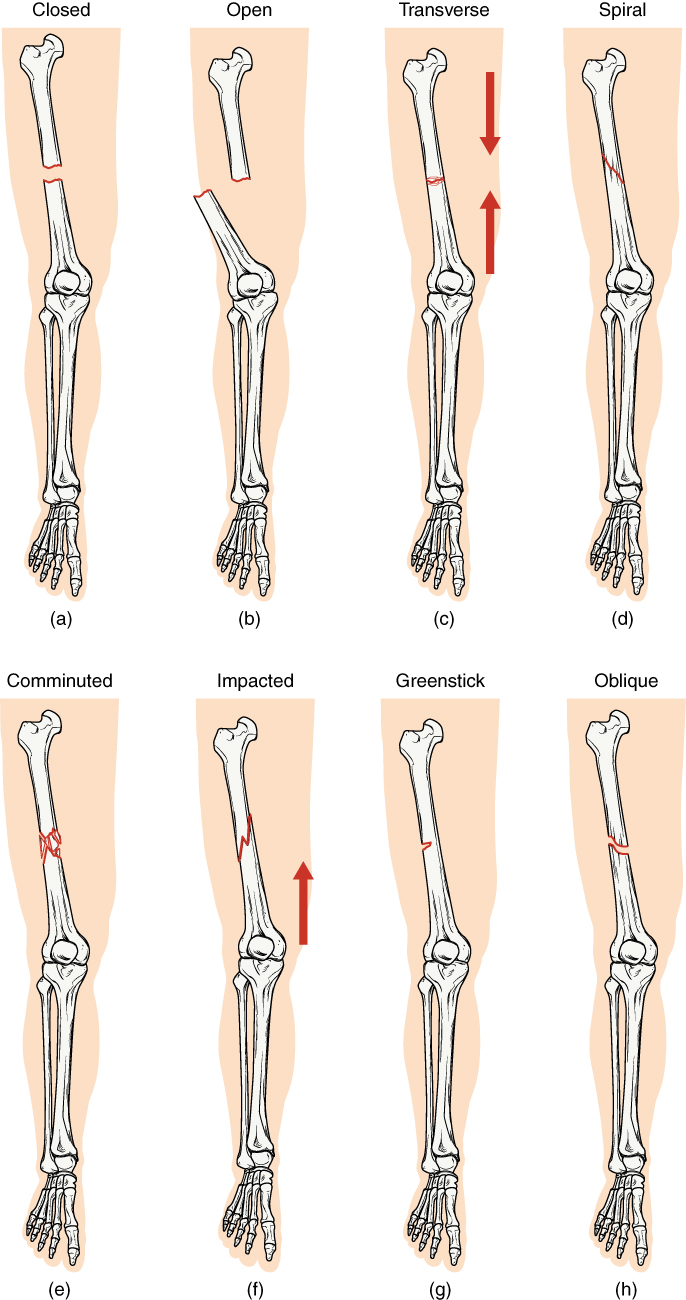
Displacement
* Non-displaced * Displaced ** Translated, or ''ad latus'', with sideways displacement. ** Angulated ** Rotated ** Shortened, a reduction in overall bone length when displaced fracture fragments overlapFracture pattern
* Linear fracture – a fracture that is parallel to the bone's long axis * Transverse fracture – a fracture that is at a right angle to the bone's long axis * Oblique fracture – a fracture that is diagonal to a bone's long axis (more than 30°) * Spiral fracture – a fracture where at least one part of the bone has been twisted * Compression fracture/ wedge fracture – usually occurs in the vertebrae, for example when the front portion of avertebra
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spina ...
in the spine collapses due to osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to more porous bone, and consequent increase in Bone fracture, fracture risk.
It is the most common reason f ...
(a medical condition which causes bones to become brittle and susceptible to fracture, with or without trauma)
* Impacted fracture – a fracture caused when bone fragments are driven into each other
* Avulsion fracture – a fracture where a fragment of bone is separated from the main mass
Fragments
* Incomplete fracture – a fracture in which the bone fragments are still partially joined, in such cases, there is a crack in the osseous tissue that does not completely traverse the width of the bone. * Complete fracture – a fracture in which bone fragments separate completely. * Comminuted fracture – a fracture in which the bone has broken into several pieces.Anatomical location
An anatomical classification may begin with specifying the involved body part, such as the head or arm, followed by more specific localization. Fractures that have additional definition criteria than merely localization often may be classified as subtypes of fractures, such as a Holstein-Lewis fracture being a subtype of a humerus fracture. Most typical examples in an orthopaedic classification given in the previous section cannot be classified appropriately into any specific part of an anatomical classification, however, as they may apply to multiple anatomical fracture sites. * Skull fracture ** Basilar skull fracture ** Blowout fracture – a fracture of the walls or floor of theorbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit (also known as orbital revolution) is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an ...
** Mandibular fracture
** Nasal fracture
A nasal fracture, commonly referred to as a broken nose, is a fracture of one of the bones of the nose. Symptoms may include bleeding, swelling, bruising, and an inability to breathe through the nose. They may be complicated by other facial fra ...
** Le Fort fracture of skull – facial fractures involving the maxillary bone and surrounding structures in a usually bilateral and either horizontal, pyramidal, or transverse way.
* Spinal fracture
A spinal fracture, also called a vertebral fracture or a broken back, is a bone fracture, fracture affecting the vertebrae of the spinal column. Most types of spinal fracture confer a significant risk of spinal cord injury. After the immediate tr ...
** Cervical fracture
*** Fracture of '' C1'', including Jefferson fracture
*** Fracture of '' C2'', including Hangman's fracture
*** Flexion teardrop fracture – a fracture of the anteroinferior aspect of a cervical vertebral
** Clay-shoveler fracture – fracture through the spinous process
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spina ...
of a vertebra
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spina ...
occurring at any of the lower cervical or upper thoracic vertebrae
** Burst fracture
A burst fracture is a type of traumatic spinal injury in which a vertebra breaks from a high-energy axial load (e.g., traffic collisions or falls from a great height or high speed, and some kinds of seizures), with shards of vertebra penetrating s ...
– in which a vertebra breaks from a high-energy axial load
** Compression fracture – a collapse of a vertebra, often in the form of wedge fractures due to larger compression anteriorly
** Chance fracture – compression injury to the anterior portion of a vertebral body with concomitant distraction injury to posterior elements
** Holdsworth fracture – an unstable fracture dislocation
In materials science, a dislocation or Taylor's dislocation is a linear crystallographic defect or irregularity within a crystal structure that contains an abrupt change in the arrangement of atoms. The movement of dislocations allow atoms to sli ...
of the thoraco lumbar junction of the spine
* Rib fracture
* Sternal fracture
* Shoulder fracture
** Clavicle fracture
** Scapular fracture
* Arm fracture
** Humerus fracture (fracture of upper arm)
*** Supracondylar fracture
*** Holstein-Lewis fracture – a fracture of the distal third of the humerus resulting in entrapment
Entrapment is a practice in which a law enforcement agent or an agent of the state induces a person to commit a crime that the person would have otherwise been unlikely or unwilling to commit.''Sloane'' (1990) 49 A Crim R 270. See also agent prov ...
of the radial nerve
The radial nerve is a nerve in the human body that supplies the posterior portion of the upper limb. It innervates the medial and lateral heads of the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, as well as all 12 muscles in the Posterior compartment of the ...
** Forearm fracture
*** Ulnar fracture
**** Monteggia fracture – a fracture of the proximal third of the ulna with the dislocation of the head of the radius
**** Hume fracture – a fracture of the olecranon
The olecranon (, ), is a large, thick, curved bony process on the proximal, posterior end of the ulna. It forms the protruding part of the elbow and is opposite to the cubital fossa or elbow pit (trochlear notch). The olecranon serves as a lever ...
with an associated anterior
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ...
dislocation
In materials science, a dislocation or Taylor's dislocation is a linear crystallographic defect or irregularity within a crystal structure that contains an abrupt change in the arrangement of atoms. The movement of dislocations allow atoms to sli ...
of the radial head
*** Radius fracture
**** Essex-Lopresti fracture – a fracture of the radial head with concomitant dislocation of the distal radio-ulnar joint with disruption of the interosseous membraneEssex Lopresti fractureat Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics online ****
Distal radius fracture
A distal radius fracture, also known as wrist fracture, is a fracture (bone), break of the part of the radius (bone), radius bone which is close to the wrist. Symptoms include pain, bruising, and rapid-onset swelling. The ulna bone may also be br ...
***** Galeazzi fracture – a fracture of the radius with dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint
***** Colles' fracture – a distal fracture of the radius with dorsal (posterior) displacement of the wrist and hand
***** Smith's fracture – a distal fracture of the radius with volar (ventral) displacement of the wrist and hand
***** Barton's fracture – an intra-articular fracture of the distal radius with dislocation of the radiocarpal joint
* Hand fracture
** Scaphoid fracture
** Rolando fracture – a comminuted intra-articular fracture
Fracture is the appearance of a crack or complete separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress (mechanics), stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacemen ...
through the base of the first metacarpal
In human anatomy, the metacarpal bones or metacarpus, also known as the "palm bones", are the appendicular bones that form the intermediate part of the hand between the phalanges (fingers) and the carpal bones ( wrist bones), which articulate ...
bone
** Bennett's fracture – a fracture of the base of the first metacarpal bone
The first metacarpal bone or the metacarpal bone of the thumb is the first bone proximal to the thumb. It is connected to the trapezium of the carpus at the first carpometacarpal joint and to the proximal thumb phalanx at the first metacarp ...
which extends into the carpometacarpal (CMC) joint
** Boxer's fracture – a fracture at the neck of a metacarpal
In human anatomy, the metacarpal bones or metacarpus, also known as the "palm bones", are the appendicular bones that form the intermediate part of the hand between the phalanges (fingers) and the carpal bones ( wrist bones), which articulate ...
* Broken finger – a fracture of the carpal phalanges
* Pelvic fracture
** Fracture of the hip bone
The hip bone (os coxae, innominate bone, pelvic bone or coxal bone) is a large flat bone, constricted in the center and expanded above and below. In some vertebrates (including humans before puberty) it is composed of three parts: the Ilium (bone) ...
** Duverney fracture – an isolated pelvic fracture involving only the iliac wing
* Femoral fracture
** Hip fracture
A hip fracture is a break that occurs in the upper part of the femur (thigh bone), at the femoral neck or (rarely) the femoral head. Symptoms may include pain around the hip, particularly with movement, and shortening of the leg. Usually ...
(anatomically a fracture of the femur
The femur (; : femurs or femora ), or thigh bone is the only long bone, bone in the thigh — the region of the lower limb between the hip and the knee. In many quadrupeds, four-legged animals the femur is the upper bone of the hindleg.
The Femo ...
bone and not the hip bone
The hip bone (os coxae, innominate bone, pelvic bone or coxal bone) is a large flat bone, constricted in the center and expanded above and below. In some vertebrates (including humans before puberty) it is composed of three parts: the Ilium (bone) ...
)
* Patella fracture
* Crus fracture
A crus fracture is a bone fracture, fracture of the Crus (lower leg), lower legs bones meaning either or both of the tibia and fibula.
Tibia fractures
* Pilon fracture
* Tibial plateau fracture
* Tibia shaft fracture
* Bumper fracture - a fractur ...
** Tibia fracture
*** Pilon fracture
*** Tibial plateau fracture
*** Bumper fracture – a fracture of the lateral
Lateral is a geometric term of location which may also refer to:
Biology and healthcare
* Lateral (anatomy), a term of location meaning "towards the side"
* Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle, an intrinsic muscle of the larynx
* Lateral release ( ...
tibia
The tibia (; : tibiae or tibias), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two Leg bones, bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outsi ...
l plateau caused by a forced valgus applied to the knee
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia (tibiofemoral joint), and one between the femur and patella (patellofemoral joint). It is the largest joint in the hu ...
*** Segond fracture – an avulsion fracture of the lateral tibial condyle
*** Gosselin fracture – a fractures of the tibial plafond into anterior and posterior fragments
*** Toddler's fracture – an undisplaced and spiral fracture of the distal third to distal half of the tibia
** Fibular fracture
*** Maisonneuve fracture
The Maisonneuve fracture is a spiral fracture of the proximal third of the fibula associated with a tear of the distal Inferior tibiofibular joint, tibiofibular syndesmosis and the interosseous membrane of the leg, interosseous membrane. There is ...
– a spiral fracture of the proximal third of the fibula associated with a tear of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis and the interosseous membrane
*** Le Fort fracture of ankle – a vertical fracture of the antero- medial part of the distal fibula with avulsion of the anterior tibiofibular ligament
The anterior ligament of the lateral malleolus (anterior tibiofibular ligament or anterior inferior ligament) is a flat, trapezoidal band of fibers, broader below than above, which extends obliquely downward and lateralward between the adjacent m ...
*** Bosworth fracture – a fracture with an associated fixed posterior dislocation
In materials science, a dislocation or Taylor's dislocation is a linear crystallographic defect or irregularity within a crystal structure that contains an abrupt change in the arrangement of atoms. The movement of dislocations allow atoms to sli ...
of the distal fibular fragment that becomes trapped behind the posterior tibial tubercle; the injury is caused by severe external rotation of the ankle
** Combined tibia and fibula fracture
The leg is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or buttock region. The major bones of the leg are the femur (thigh bone), tibia (shin bone), and adjacent fibula. There are 30 bones in ...
*** Trimalleolar fracture – involving the lateral malleolus, medial malleolus
A malleolus is the bony prominence on each side of the human ankle.
Each leg is supported by two bones, the tibia on the inner side (medial) of the leg and the fibula on the outer side (lateral) of the leg. The medial malleolus is the promin ...
, and the distal posterior aspect of the tibia
*** Bimalleolar fracture
A bimalleolar fracture is a fracture of the ankle that involves the lateral malleolus and the medial malleolus
A malleolus is the bony prominence on each side of the human ankle.
Each leg is supported by two bones, the tibia on the inner s ...
– involving the lateral malleolus and the medial malleolus
*** Pott's fracture
* Foot fracture
The foot (: feet) is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb (anatomy), limb which bears weight and allows animal locomotion, locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is an organ at the ter ...
** Lisfranc fracture – in which one or all of the metatarsal
The metatarsal bones or metatarsus (: metatarsi) are a group of five long bones in the midfoot, located between the tarsal bones (which form the heel and the ankle) and the phalanges ( toes). Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are ...
s are displaced from the tarsus
** Jones fracture
A Jones fracture is a broken bone in a specific part of the fifth metatarsal of the foot between the base and middle part that is known for its high rate of delayed healing or nonunion. It results in pain near the midportion of the foot on ...
– a fracture of the proximal end of the fifth metatarsal
** March fracture – a fracture of the distal third of one of the metatarsals occurring because of recurrent stress
** Cuneiform fracture – a fracture of one of the three cuneiform bones typically due to direct blow, axial load, or avulsion
** Calcaneal fracture – a fracture of the calcaneus (heel bone)
* Broken toe }
A broken toe is a type of bone fracture. Symptoms include pain when the toe is touched near the break point, or compressed along its length (as if gently stubbing the toe). There may be bruising, swelling, stiffness, or displacement of the broke ...
– a fracture of the pedal phalanges
OTA/AO classification
The Orthopaedic Trauma Association Committee for Coding and Classification published its classification system in 1996, adopting a similar system to the 1987AO Foundation
The AO Foundation is a nonprofit organization dedicated to improving the care of patients with musculoskeletal injuries or pathologies and their sequelae through research, development, and education of surgeons and operating room personnel. The AO ...
system. In 2007, they extended their system, unifying the two systems regarding wrist, hand, foot, and ankle fractures.
Classifications named after people
A number of classifications are named after the person (eponymous
An eponym is a noun after which or for which someone or something is, or is believed to be, named. Adjectives derived from the word ''eponym'' include ''eponymous'' and ''eponymic''.
Eponyms are commonly used for time periods, places, innovati ...
) who developed it.
* "Denis classification" for spinal fracture
A spinal fracture, also called a vertebral fracture or a broken back, is a bone fracture, fracture affecting the vertebrae of the spinal column. Most types of spinal fracture confer a significant risk of spinal cord injury. After the immediate tr ...
s
* " Frykman classification" for forearm fractures (fractures of radius and ulna)
* " Gustilo open fracture classification"
* "Letournel and Judet Classification" for Acetabular fractures
* "Neer classification" for humerus fractures
* Seinsheimer classification, Evans-Jensen classification, Pipkin classification, and Garden classification for hip fracture
A hip fracture is a break that occurs in the upper part of the femur (thigh bone), at the femoral neck or (rarely) the femoral head. Symptoms may include pain around the hip, particularly with movement, and shortening of the leg. Usually ...
s
Prevention
Both high- and low-force trauma can cause bone fracture injuries. Preventive efforts to reduce motor vehicle crashes, the most common cause of high-force trauma, include reducing distractions while driving. Common distractions are driving under the influence and texting or calling while driving, both of which lead to an approximate 6-fold increase in crashes. Wearing a seatbelt can also reduce the likelihood of injury in a collision. 30km/h
The kilometre per hour ( SI symbol: km/h; non-SI abbreviations: kph, kmph, km/hr) is a unit of speed, expressing the number of kilometres travelled in one hour.
History
Although the metre was formally defined in 1799, the term "kilometres per h ...
or 20 mph speed limit
Speed limits on road traffic, as used in most countries, set the legal maximum speed at which vehicles may travel on a given stretch of road. Speed limits are generally indicated on a traffic sign reflecting the maximum permitted speed, express ...
s (as opposed to the more common intracity 50 km/h / 30 mph) also drastically reduce the risk of accident, serious injury and even death in crashes between motor vehicles and humans. Vision Zero aims to reduce traffic deaths to zero through better traffic design and other measures and to drastically reduce traffic injuries which would prevent many bone fractures.
A common cause of low-force trauma is an at-home fall. When considering preventative efforts, the National Institute of Health
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in 1887 and is part of the United States Department of Health and Human Servic ...
(NIH) examines ways to reduce the likelihood of falling, the force of the fall, and bone fragility. To prevent at-home falls they suggest keeping cords out of high-traffic areas where someone could trip, installing handrails and keeping stairways well-lit, and installing an assistive bar near the bathtub in the washroom for support. To reduce the impact of a fall the NIH recommends to try falling straight down on your buttocks or onto your hands.
Some sports have a relatively high risk of bone fractures as a common sports injury
Sports injuries occur during participation in sports or exercise in general. Globally, around 40% of individuals engage in some form of regular exercise or organized sports, with upwards of 60% of US high school students participating in one or ...
. Preventive measures depend to some extent on the specific sport, but learning proper technique, wearing protective gear
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is protective clothing, helmets, goggles, or other garments or equipment designed to protect the wearer's body from injury or infection. The hazards addressed by protective equipment include physical, elect ...
and having a realistic estimation of one's own capabilities and limitations can all help reduce the risk of bone fracture. In contact sports
A contact sport is any sport where physical contact between competitors, or their environment, is an integral part of the game. For example, gridiron football. Contact may come about as the result of intentional or incidental actions by the playe ...
rules have been put in place to protect athlete health, such as the prohibition of unnecessary roughness in American football
American football, referred to simply as football in the United States and Canada and also known as gridiron football, is a team sport played by two teams of eleven players on a rectangular American football field, field with goalposts at e ...
.
Taking calcium and vitamin D supplements can help strengthen your bones. Vitamin D supplements combined with additional calcium marginally reduces the risk of hip fractures and other types of fracture in older adults; however, vitamin D supplementation alone did not reduce the risk of fractures. Taking vibration therapy can also help strengthening bones and reducing the risk of a fracture.
Patterns
Treatment
 Treatment of bone fractures are broadly classified as surgical or conservative, the latter basically referring to any non-surgical procedure, such as pain management, immobilization or other non-surgical stabilization. A similar classification is ''open'' versus ''closed treatment'', in which ''open treatment'' refers to any treatment in which the fracture site is opened surgically, regardless of whether the fracture is an
Treatment of bone fractures are broadly classified as surgical or conservative, the latter basically referring to any non-surgical procedure, such as pain management, immobilization or other non-surgical stabilization. A similar classification is ''open'' versus ''closed treatment'', in which ''open treatment'' refers to any treatment in which the fracture site is opened surgically, regardless of whether the fracture is an open
Open or OPEN may refer to:
Music
* Open (band), Australian pop/rock band
* The Open (band), English indie rock band
* ''Open'' (Blues Image album), 1969
* ''Open'' (Gerd Dudek, Buschi Niebergall, and Edward Vesala album), 1979
* ''Open'' (Go ...
or closed fracture.
Pain management
In arm fractures in children,ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used to relieve pain, fever, and inflammation. This includes dysmenorrhea, painful menstrual periods, migraines, and rheumatoid arthritis. It can be taken oral administration, ...
has been found to be as effective as a combination of paracetamol
Paracetamol, or acetaminophen, is a non-opioid analgesic and antipyretic agent used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. It is a widely available over-the-counter drug sold under various brand names, including Tylenol and Panadol.
Parac ...
and codeine. In the EMS setting it might be applicable to administer 1mg/kg of iv ketamine
Ketamine is a cyclohexanone-derived general anesthetic and NMDA receptor antagonist with analgesic and hallucinogenic properties, used medically for anesthesia, depression, and pain management. Ketamine exists as its S- (esketamine) a ...
to achieve a dissociated state.
Immobilization
Since bone healing is a natural process that will occur most often, fracture treatment aims to ensure the best possible ''function'' of the injured part after healing. Bone fractures typically are treated by restoring the fractured pieces of bone to their natural positions (if necessary), and maintaining those positions while the bone heals. Often, aligning the bone, called reduction, in a good position and verifying the improved alignment with an X-ray is all that is needed. This process is extremely painful withoutanaesthesia
Anesthesia (American English) or anaesthesia (British English) is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prev ...
, about as painful as breaking the bone itself. To this end, a fractured limb usually is immobilized with a plaster
Plaster is a building material used for the protective or decorative coating of walls and ceilings and for moulding and casting decorative elements. In English, "plaster" usually means a material used for the interiors of buildings, while "re ...
or fibreglass
Fiberglass (American English) or fibreglass ( Commonwealth English) is a common type of fiber-reinforced plastic using glass fiber. The fibers may be randomly arranged, flattened into a sheet called a chopped strand mat, or woven into glass c ...
cast
Cast may refer to:
Music
* Cast (band), an English alternative rock band
* Cast (Mexican band), a progressive Mexican rock band
* The Cast, a Scottish musical duo: Mairi Campbell and Dave Francis
* ''Cast'', a 2012 album by Trespassers William ...
or splint that holds the bones in position and immobilizes the joints above and below the fracture.
When the initial post-fracture oedema
Edema (American English), also spelled oedema (British English), and also known as fluid retention, swelling, dropsy and hydropsy, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may inclu ...
or swelling goes down, the fracture may be placed in a removable brace or orthosis. If being treated with surgery, surgical nails, screws, plates, and wires are used to hold the fractured bone together more directly. Alternatively, fractured bones may be treated by the Ilizarov method which is a form of an external fixator.
Occasionally smaller bones, such as phalanges of the toes and finger
A finger is a prominent digit (anatomy), digit on the forelimbs of most tetrapod vertebrate animals, especially those with prehensile extremities (i.e. hands) such as humans and other primates. Most tetrapods have five digits (dactyly, pentadact ...
s, may be treated without the cast, by buddy wrapping them, which serves a similar function to making a cast. A device called a Suzuki frame may be used in cases of deep, complex intra-articular digit fractures. By allowing only limited movement, immobilization helps preserve anatomical alignment while enabling callus
A callus (: calluses) is an area of thickened and sometimes hardened skin that forms as a response to repeated friction, pressure, or other irritation. Since repeated contact is required, calluses are most often found on the feet and hands, b ...
formation, toward the target of achieving union.
Splinting results in the same outcome as casting in children who have a distal radius fracture with little shifting.
Surgery
Surgical methods of treating fractures have their own risks and benefits, but usually, surgery is performed only if conservative treatment has failed, is very likely to fail, or is likely to result in a poor functional outcome. With some fractures such aship fracture
A hip fracture is a break that occurs in the upper part of the femur (thigh bone), at the femoral neck or (rarely) the femoral head. Symptoms may include pain around the hip, particularly with movement, and shortening of the leg. Usually ...
s (usually caused by osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to more porous bone, and consequent increase in Bone fracture, fracture risk.
It is the most common reason f ...
), surgery is offered routinely because non-operative treatment results in prolonged immobilisation, which commonly results in complications including chest infections, pressure sores, deconditioning, deep vein thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a type of venous thrombosis involving the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs or pelvis. A minority of DVTs occur in the arms. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, redness, and enl ...
(DVT), and pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an pulmonary artery, artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include dyspnea, shortness of breath, chest pain ...
, which are more dangerous than surgery. When a joint surface is damaged by a fracture
Fracture is the appearance of a crack or complete separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress (mechanics), stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacemen ...
, surgery is also commonly recommended to make an accurate anatomical reduction and restore the smoothness of the joint.
Infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
is especially dangerous in bones, due to the recrudescent nature of bone infections. Bone tissue is predominantly extracellular matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix (ICM), is a network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide structural and bio ...
, rather than living cells, and the few blood vessels
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the tissues of a body. They also take waste an ...
needed to support this low metabolism are only able to bring a limited number of immune cell
White blood cells (scientific name leukocytes), also called immune cells or immunocytes, are cell (biology), cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign entities. White blood c ...
s to an injury to fight infection. For this reason, open fractures and osteotomies call for very careful antiseptic
An antiseptic ( and ) is an antimicrobial substance or compound that is applied to living tissue to reduce the possibility of sepsis, infection, or putrefaction. Antiseptics are generally distinguished from ''antibiotics'' by the latter's abil ...
procedures and prophylactic use of antibiotics.
Occasionally, bone grafting is used to treat a fracture.
Sometimes bones are reinforced with metal. These implants must be designed and installed with care. ''Stress shielding
Stress shielding is the reduction in bone density ( osteopenia) as a result of removal of typical stress from the bone by an implant (for instance, the femoral component of a hip prosthesis). This is because by Wolff's law
Wolff's law, develop ...
'' occurs when plates or screws carry too large of a portion of the bone's load, causing atrophy
Atrophy is the partial or complete wasting away of a part of the body. Causes of atrophy include mutations (which can destroy the gene to build up the organ), malnutrition, poor nourishment, poor circulatory system, circulation, loss of hormone, ...
. This problem is reduced, but not eliminated, by the use of low- modulus materials, including titanium
Titanium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in ...
and its alloys. The heat generated by the friction of installing hardware can accumulate easily and damage bone tissue
A bone is a Stiffness, rigid Organ (biology), organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red blood cell, red and white blood cells, store minerals, provi ...
, reducing the strength of the connections. If dissimilar metals are installed in contact with one another (i.e., a titanium plate with cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. ...
-chromium
Chromium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6 element, group 6. It is a steely-grey, Luster (mineralogy), lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium ...
alloy or stainless steel
Stainless steel, also known as inox, corrosion-resistant steel (CRES), or rustless steel, is an iron-based alloy that contains chromium, making it resistant to rust and corrosion. Stainless steel's resistance to corrosion comes from its chromi ...
screws), galvanic corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engine ...
will result. The metal ions produced can damage the bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
locally and may cause systemic effects as well.
Bone stimulation
Bone stimulation with eitherelectromagnetic
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge via electromagnetic fields. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental forces of nature. It is the dominant force in the interacti ...
or ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply ...
waves may be suggested as an alternative to surgery to reduce the healing time for non-union fractures. The proposed mechanism of action is by stimulating osteoblasts and other proteins that form bones using these modalities. The evidence supporting the use of ultrasound and shockwave therapy for improving unions is very weak and it is likely that these approaches do not make a clinically significant difference for a delayed union or non-union.
Physical therapy
Physical therapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is a healthcare profession, as well as the care provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through patient education, physical intervention, disease preventio ...
exercises (either home-based or physiotherapist-led) to improve functional mobility and strength, gait training for hip fractures, and other physical exercise are also often suggested to help recover physical capacities after a fracture has healed.
Children
In children, whose bones are still developing, there are risks of either a growth plate injury or a greenstick fracture. * A greenstick fracture occurs due to mechanical failure on the tension side. That is since the bone is not so brittle as it would be in an adult, it does not completely fracture, but rather exhibits bowing without complete disruption of the bone'scortex
Cortex or cortical may refer to:
Biology
* Cortex (anatomy), the outermost layer of an organ
** Cerebral cortex, the outer layer of the vertebrate cerebrum, part of which is the ''forebrain''
*** Motor cortex, the regions of the cerebral cortex i ...
in the surface opposite the applied force.
* Growth plate injuries, as in Salter-Harris fractures, require careful treatment and accurate reduction to make sure that the bone continues to grow normally.
* Plastic deformation of the bone, in which the bone permanently bends, but does not break, also is possible in children. These injuries may require an osteotomy (bone cut) to realign the bone if it is fixed and cannot be realigned by closed methods.
* Certain fractures mainly occur in children, including fracture of the clavicle
The clavicle, collarbone, or keybone is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately long that serves as a strut between the scapula, shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on each side of the body. The clavic ...
and supracondylar fracture of the humerus.
See also
* Stress fracture * Distraction osteogenesis *Rickets
Rickets, scientific nomenclature: rachitis (from Greek , meaning 'in or of the spine'), is a condition that results in weak or soft bones in children and may have either dietary deficiency or genetic causes. Symptoms include bowed legs, stun ...
* Catagmatic
* H. Winnett Orr, U.S. Army surgeon who developed Orthopedic plaster casts
References
External links
Authoritative information in orthopaedic surgery
American Association of Orthopedic Surgeons (AAOS)
Radiographic Atlas of Fracture
{{Authority control Acute pain