|
Hematoma
A hematoma, also spelled haematoma, or blood suffusion is a localized bleeding outside of blood vessels, due to either disease or trauma including injury or surgery and may involve blood continuing to seep from broken capillaries. A hematoma is benign and is initially in liquid form spread among the tissues including in sacs between tissues where it may coagulate and solidify before blood is reabsorbed into blood vessels. An ecchymosis is a hematoma of the skin larger than 10 mm. They may occur among and or within many areas such as skin and other organs, connective tissues, bone, joints and muscle. A collection of blood (or even a hemorrhage) may be aggravated by anticoagulant medication (blood thinner). Blood seepage and collection of blood may occur if heparin is given via an intramuscular route; to avoid this, heparin must be given intravenously or subcutaneously. Signs and symptoms Some hematomas are visible under the surface of the skin (commonly called bruise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subgaleal Hematoma
Subgaleal hemorrhage, also known as subgaleal hematoma, is bleeding in the potential space between the skull periosteum and the scalp galea aponeurosis (dense fibrous tissue surrounding the skull). Symptoms The diagnosis is generally clinical, with a fluctuant boggy mass developing over the scalp (especially over the occiput) with superficial skin bruising. The swelling develops gradually 12–72 hours after delivery, although it may be noted immediately after delivery in severe cases. Subgaleal hematoma growth is insidious, as it spreads across the whole calvaria and may not be recognized for hours to days. If enough blood accumulates, a visible fluid wave may be seen. Patients may develop periorbital ecchymosis (" raccoon eyes"). Patients with subgaleal hematoma may present with hemorrhagic shock given the volume of blood that can be lost into the potential space between the skull periosteum and the scalp galea aponeurosis, which has been found to be as high as 20-40% of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contusion
A bruise, also known as a contusion, is a type of hematoma of tissue, the most common cause being capillaries damaged by trauma, causing localized bleeding that extravasates into the surrounding interstitial tissues. Most bruises occur close enough to the epidermis such that the bleeding causes a visible discoloration. The bruise then remains visible until the blood is either absorbed by tissues or cleared by immune system action. Bruises which do not blanch under pressure can involve capillaries at the level of skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscle, or bone. Bruises are not to be confused with other similar-looking lesions. Such lesions include petechia (less than , resulting from numerous and diverse etiologies such as adverse reactions from medications such as warfarin, straining, asphyxiation, platelet disorders and diseases such as ''cytomegalovirus''); and purpura (), classified as palpable purpura or non-palpable purpura and indicating various pathologic conditions su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fracture (bone)
A bone fracture (abbreviated FRX or Fx, Fx, or #) is a medical condition in which there is a partial or complete break in the continuity of any bone in the body. In more severe cases, the bone may be broken into several fragments, known as a ''comminuted fracture''. An open fracture (or compound fracture) is a bone fracture where the broken bone breaks through the skin. A bone fracture may be the result of high force impact or stress, or a minimal trauma injury as a result of certain medical conditions that weaken the bones, such as osteoporosis, osteopenia, bone cancer, or osteogenesis imperfecta, where the fracture is then properly termed a pathologic fracture. Most bone fractures require urgent medical attention to prevent further injury. Signs and symptoms Although bone tissue contains no pain receptors, a bone fracture is painful for several reasons: * Breaking in the continuity of the periosteum, with or without similar discontinuity in endosteum, as both contain mult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intramuscular Injection
Intramuscular injection, often abbreviated IM, is the medical injection, injection of a substance into a muscle. In medicine, it is one of several methods for parenteral, parenteral administration of medications. Intramuscular injection may be preferred because muscles have larger and more numerous blood vessels than subcutaneous tissue, leading to faster absorption than subcutaneous injection, subcutaneous or intradermal injections. Medication administered via intramuscular injection is not subject to the first-pass metabolism effect which affects oral medications. Common sites for intramuscular injections include the deltoid muscle of the upper arm and the gluteal muscle of the buttock. In infants, the vastus lateralis muscle of the thigh is commonly used. The injection site must be cleaned before administering the injection, and the injection is then administered in a fast, darting motion to decrease the discomfort to the individual. The volume to be injected in the muscle is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcutaneous Injection
Subcutaneous administration is the insertion of medications beneath the skin either by injection or infusion. A subcutaneous injection is administered as a bolus (medicine), bolus into the subcutis, the layer of skin directly below the dermis and Epidermis (skin), epidermis, collectively referred to as the Cutis (anatomy), cutis. The instruments are usually a hypodermic needle and a syringe. Subcutaneous injections are highly effective in administering medications such as insulin, morphine, heroin, diacetylmorphine and goserelin. Subcutaneous administration may be List of medical abbreviations, abbreviated as SC, SQ, subcu, sub-Q, SubQ, or subcut. Subcut is the preferred abbreviation to reduce the risk of misunderstanding and potential errors. Subcutaneous tissue has few blood vessels and so drugs injected into it are intended for slow, sustained rates of absorption, often with some amount of depot injection, depot effect. Compared with other route of administration, routes of ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
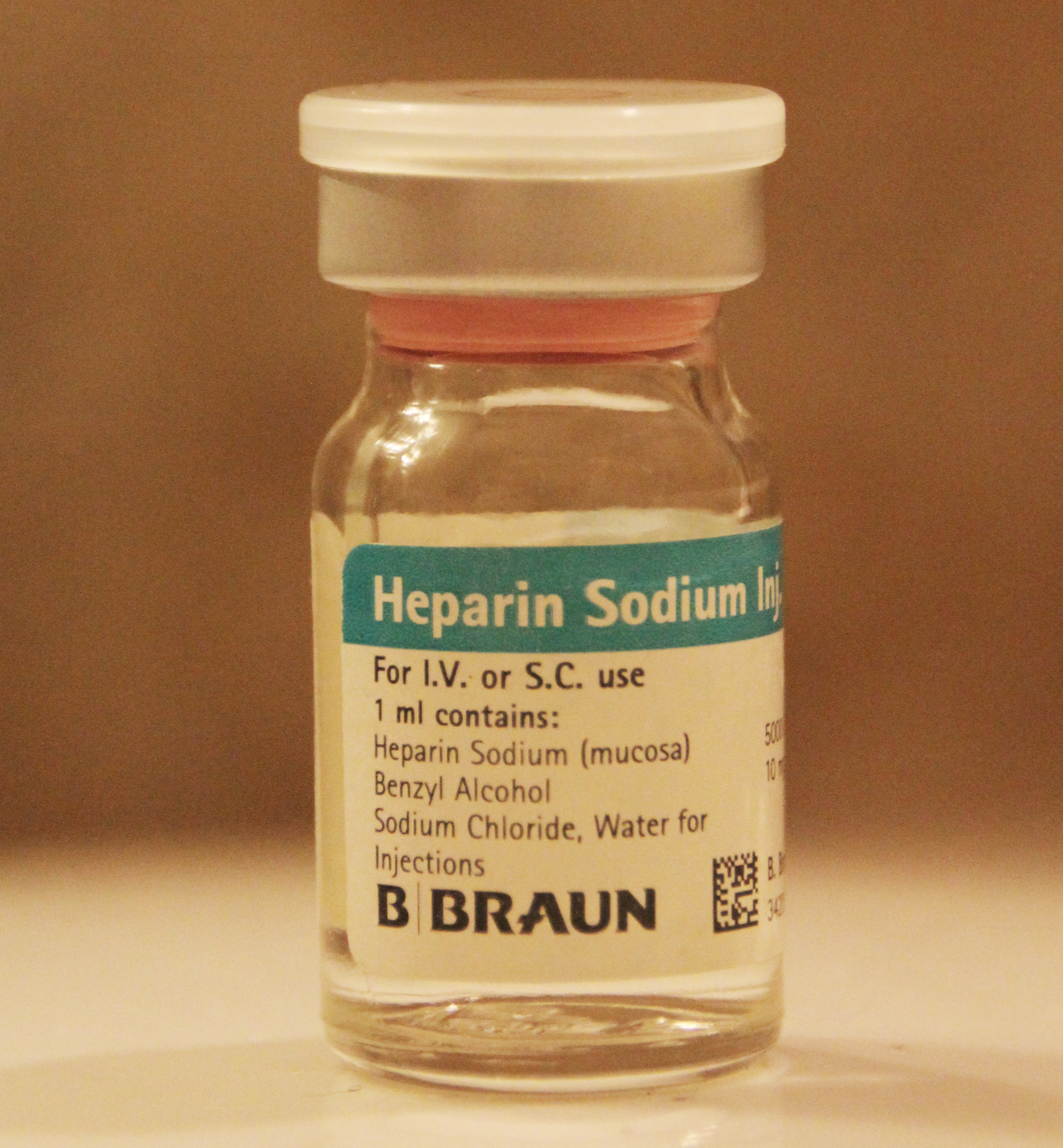
Heparin
Heparin, also known as unfractionated heparin (UFH), is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan. Heparin is a blood anticoagulant that increases the activity of antithrombin. It is used in the treatment of myocardial infarction, heart attacks and unstable angina. It can be given intravenously or by subcutaneous injection, injection under the skin. Its anticoagulant properties make it useful to prevent blood clotting in blood specimen test tubes and kidney dialysis machines. Common side effects include bleeding, pain at the injection site, and thrombocytopenia, low blood platelets. Serious side effects include heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Greater care is needed in those with poor kidney function. Heparin is contraindicated for suspected cases of Post-vaccination embolic and thrombotic events, vaccine-induced pro-thrombotic immune thrombocytopenia (VIPIT) secondary to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, as heparin may further increase the risk of bleeding in an anti-PF4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organ (biology)
In a multicellular organism, an organ is a collection of Tissue (biology), tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the biological organization, hierarchy of life, an organ lies between Tissue (biology), tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type Cell (biology), cells to act together in a function. Tissues of different types combine to form an organ which has a specific function. The Gastrointestinal tract, intestinal wall for example is formed by epithelial tissue and smooth muscle tissue. Two or more organs working together in the execution of a specific body function form an organ system, also called a biological system or body system. An organ's tissues can be broadly categorized as parenchyma, the functional tissue, and stroma (tissue), stroma, the structural tissue with supportive, connective, or ancillary functions. For example, the gland's tissue that makes the hormones is the parenchyma, whereas the stroma includes the nerve t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcutaneous Tissue
The subcutaneous tissue (), also called the hypodermis, hypoderm (), subcutis, or superficial fascia, is the lowermost layer of the integumentary system in vertebrates. The types of cells found in the layer are fibroblasts, adipose cells, and macrophages. The subcutaneous tissue is derived from the mesoderm, but unlike the dermis, it is not derived from the mesoderm's Dermatome (anatomy), dermatome region. It consists primarily of loose connective tissue and contains larger blood vessels and nerves than those found in the dermis. It is a major site of fat storage in the body. In arthropods, a hypodermis can refer to an epidermal layer of cells that secretes the chitinous cuticle. The term also refers to a layer of cells lying immediately below the Epidermis (botany), epidermis of plants. Structure * Fibrous bands anchoring the skin to the deep fascia * Collagen and elastin fibers attaching it to the dermis * Fat is absent from the eyelids, clitoris, penis, much of Pinna (anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bleeding
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vagina, or anus, or through a puncture in the skin. Hypovolemia is a massive decrease in blood volume, and death by excessive loss of blood is referred to as exsanguination. Typically, a healthy person can endure a loss of 10–15% of the total blood volume without serious medical difficulties (by comparison, blood donation typically takes 8–10% of the donor's blood volume). The stopping or controlling of bleeding is called hemostasis and is an important part of both first aid and surgery. Types * Upper head ** Intracranial hemorrhage — bleeding in the skull. ** Cerebral hemorrhage — a type of intracranial hemorrhage, bleeding within the brain tissue itself. ** Intracerebral hemorrhage — bleeding in the brain caused by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |