Torvosaurus Tanner DBi on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Torvosaurus'' () is a
 Fossilized remains of ''Torvosaurus'' have been found in
Fossilized remains of ''Torvosaurus'' have been found in
at
Theropods of Dry Mesa Quarry (Morrison Formation, Late Jurassic), Colorado, with emphasis on the osteology of ''Torvosaurus tanneri''
, ''Brigham Young University Geology Studies'' 37: 1–72 The In 1992, fossils of a large theropod found at
In 1992, fossils of a large theropod found at
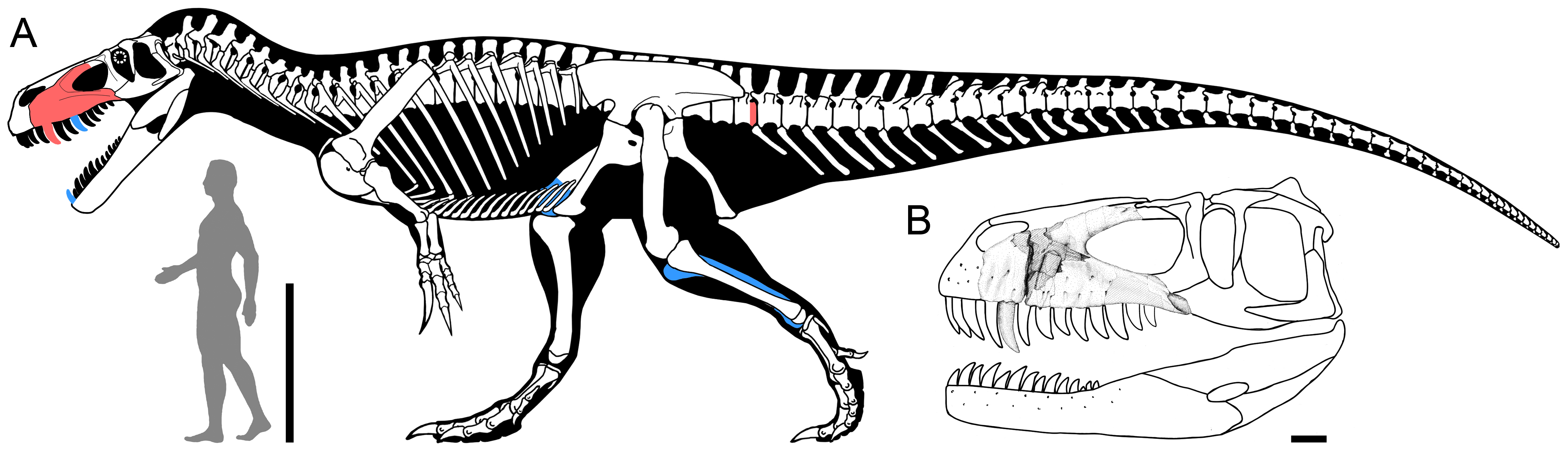
 ''Torvosaurus'' was a very large and robust predatory dinosaur. ''T. tanneri'' was initially described as long, but a detailed osteological description has revised its length estimate to . ''T. gurneyi'' was initially estimated around long, but its body length estimate was revised to in its specific description. Claims have been made indicating even larger sizes for the American species ''T. tanneri'', with estimates of up to in length and more than based on incomplete remains of ''Edmarka rex'' and "Brontoraptor". However, ''Edmarka rex'' and "Brontoraptor" lack detailed analyses to verify whether or not they actually belong to ''T. tanneri''. ''T. tanneri'' is estimated to have weighed approximately , while ''T. gurneyi'' is estimated to have weighed .
''Torvosaurus'' was a very large and robust predatory dinosaur. ''T. tanneri'' was initially described as long, but a detailed osteological description has revised its length estimate to . ''T. gurneyi'' was initially estimated around long, but its body length estimate was revised to in its specific description. Claims have been made indicating even larger sizes for the American species ''T. tanneri'', with estimates of up to in length and more than based on incomplete remains of ''Edmarka rex'' and "Brontoraptor". However, ''Edmarka rex'' and "Brontoraptor" lack detailed analyses to verify whether or not they actually belong to ''T. tanneri''. ''T. tanneri'' is estimated to have weighed approximately , while ''T. gurneyi'' is estimated to have weighed .
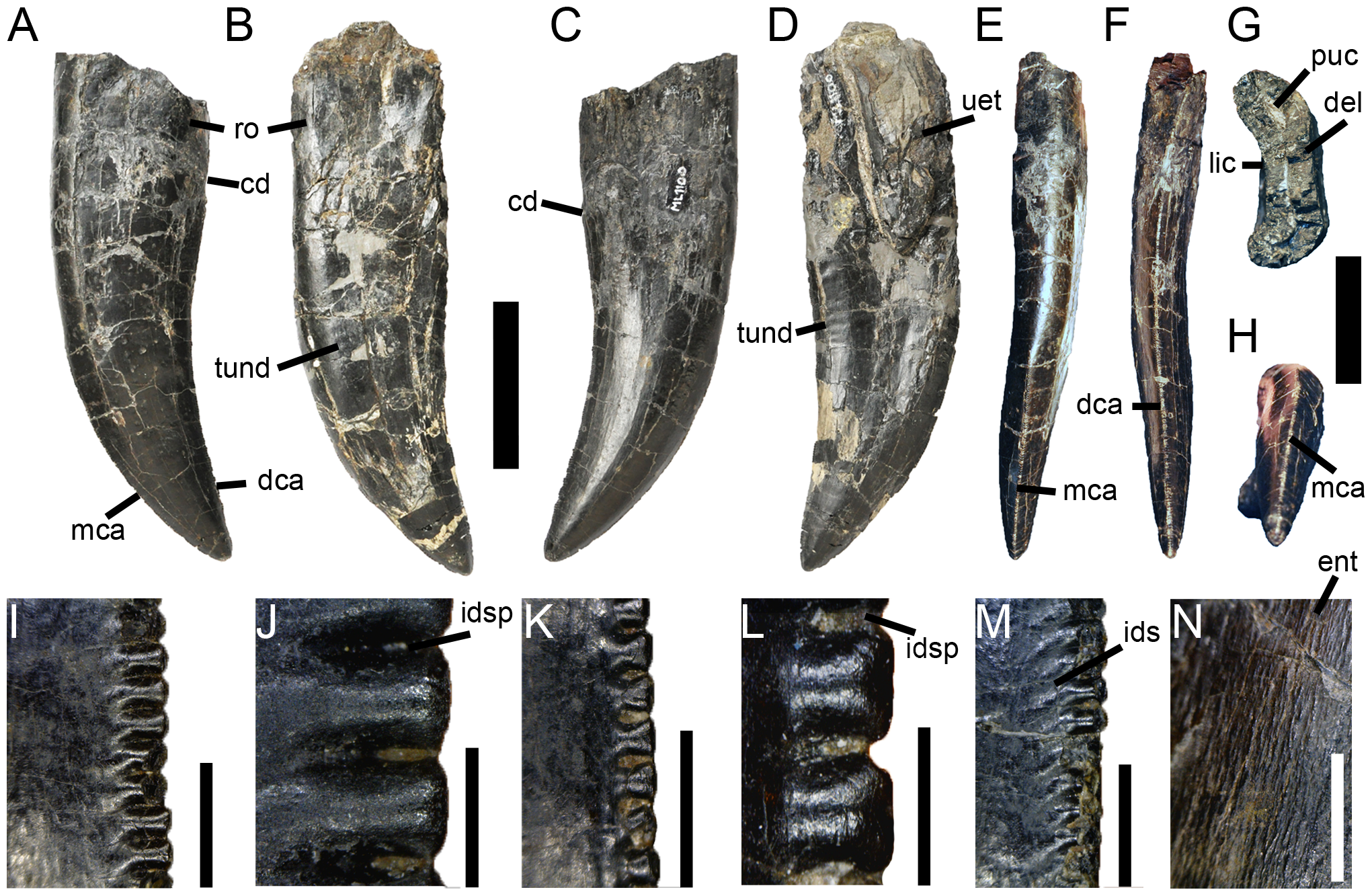
 Among the differentiating features originally recognized between ''T. gurneyi'' and ''T. tanneri'' are the number of teeth, alongside the size and shape of the mouth. While the upper jaw of ''T. tanneri'' has more than 11 teeth, that of ''T. gurneyi'' has less. However, later examination of a new right maxilla, probably belonging to the same individual as the holotype of ''T. gurneyi'', has determined that, while the two species can be distinguished based on the morphology of the maxillary medial wall and interdental plates, the supposedly lower number of maxillary teeth in the Portuguese form may be an artifact of preservation, since it is not possible to know the exact number of teeth in the complete maxilla at the moment.
The material from Germany is further distinguished by the other two species by a temporal difference of c. 10 Ma and a few morphological differences which indicate that it was the third species outside a sister taxon relationship between ''T. tanneri'' and ''T. gurneyi''. The material is only 10% smaller than the maxilla of ''T. tanneri'', although the ontogenetic stage of the specimen is unknown. This indicates that derived megalosaurines were already among the largest terrestrial predators of the late Middle Jurassic, with only a moderate increase in size in the genus by the Late Jurassic.
Among the differentiating features originally recognized between ''T. gurneyi'' and ''T. tanneri'' are the number of teeth, alongside the size and shape of the mouth. While the upper jaw of ''T. tanneri'' has more than 11 teeth, that of ''T. gurneyi'' has less. However, later examination of a new right maxilla, probably belonging to the same individual as the holotype of ''T. gurneyi'', has determined that, while the two species can be distinguished based on the morphology of the maxillary medial wall and interdental plates, the supposedly lower number of maxillary teeth in the Portuguese form may be an artifact of preservation, since it is not possible to know the exact number of teeth in the complete maxilla at the moment.
The material from Germany is further distinguished by the other two species by a temporal difference of c. 10 Ma and a few morphological differences which indicate that it was the third species outside a sister taxon relationship between ''T. tanneri'' and ''T. gurneyi''. The material is only 10% smaller than the maxilla of ''T. tanneri'', although the ontogenetic stage of the specimen is unknown. This indicates that derived megalosaurines were already among the largest terrestrial predators of the late Middle Jurassic, with only a moderate increase in size in the genus by the Late Jurassic. ''Torvosaurus'' had an elongated, narrow snout, with a kink in its profile just above the large nostrils. The frontmost snout bone, the
''Torvosaurus'' had an elongated, narrow snout, with a kink in its profile just above the large nostrils. The frontmost snout bone, the
 When first described in 1979 by Galton and Jensen,P. M. Galton and J. A. Jensen. 1979
When first described in 1979 by Galton and Jensen,P. M. Galton and J. A. Jensen. 1979
A new large theropod dinosaur from the Upper Jurassic of Colorado
. Brigham Young University Geology Studies 26(1):1–12 ''Torvosaurus'' was classified as a
 According to Carrano ''et al.'' (2012), ''Torvosaurus'' can be distinguished based on the following characteristics:
* The presence of a very shallow
According to Carrano ''et al.'' (2012), ''Torvosaurus'' can be distinguished based on the following characteristics:
* The presence of a very shallow
 The study of fossilized embryos of ''Torvosaurus'' provides researchers with information about the transformation of the embryo over time, the different developmental pathways present in dinosaur lineages, dinosaur reproductive behavior, and dinosaur parental care. In 2013, Araújo ''et al''. announced the discovery of specimen ML1188, a clutch of crushed dinosaur eggs and embryonic material attributed to ''Torvosaurus''. This discovery further supports the hypothesis that large theropods were oviparous, meaning that they laid eggs and hence that embryonic development occurred outside the body of female dinosaurs. This discovery was made in 2005 by the Dutch amateur fossil-hunter Aart Walen at the
The study of fossilized embryos of ''Torvosaurus'' provides researchers with information about the transformation of the embryo over time, the different developmental pathways present in dinosaur lineages, dinosaur reproductive behavior, and dinosaur parental care. In 2013, Araújo ''et al''. announced the discovery of specimen ML1188, a clutch of crushed dinosaur eggs and embryonic material attributed to ''Torvosaurus''. This discovery further supports the hypothesis that large theropods were oviparous, meaning that they laid eggs and hence that embryonic development occurred outside the body of female dinosaurs. This discovery was made in 2005 by the Dutch amateur fossil-hunter Aart Walen at the

 The Ornatenton Formation is a Callovian aged shallow marine deposit, within the formation ''Torvosaurus'' was
The Ornatenton Formation is a Callovian aged shallow marine deposit, within the formation ''Torvosaurus'' was
 Bite marks on ''
Bite marks on ''
''Largest Predatory Dinosaur in Europe Found'' at nationalgeographic
{{Taxonbar, from=Q131537 Megalosauridae Dinosaur genera Jurassic dinosaurs Morrison Formation Lourinhã Formation Taxa named by Peter Galton Taxa named by James A. Jensen Fossil taxa described in 1979 Dinosaurs of the United States Dinosaurs of Portugal
genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
of large megalosaurine theropod
Theropoda (; from ancient Greek , (''therion'') "wild beast"; , (''pous, podos'') "foot"">wiktionary:ποδός"> (''pous, podos'') "foot" is one of the three major groups (clades) of dinosaurs, alongside Ornithischia and Sauropodom ...
dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic Geological period, period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the #Evolutio ...
that lived approximately 165 to 148 million years ago
Million years ago, abbreviated as Mya, Myr (megayear) or Ma (megaannum), is a unit of time equal to (i.e. years), or approximately 31.6 teraseconds.
Usage
Myr is in common use in fields such as Earth science and cosmology. Myr is also used w ...
during the Callovian
In the geologic timescale, the Callovian is an age and stage in the Middle Jurassic, lasting between 165.3 ± 1.1 Ma (million years ago) and 161.5 ± 1.0 Ma. It is the last stage of the Middle Jurassic, following the Bathonian and preceding the ...
to Tithonian
In the geological timescale, the Tithonian is the latest age (geology), age of the Late Jurassic Epoch and the uppermost stage (stratigraphy), stage of the Upper Jurassic Series. It spans the time between 149.2 ±0.7 annum, Ma and 143.1 ±0.6 (mi ...
ages of the late Middle
Middle or The Middle may refer to:
* Centre (geometry), the point equally distant from the outer limits.
Places
* Middle (sheading), a subdivision of the Isle of Man
* Middle Bay (disambiguation)
* Middle Brook (disambiguation)
* Middle Creek ...
and Late Jurassic
The Late Jurassic is the third Epoch (geology), epoch of the Jurassic Period, and it spans the geologic time scale, geologic time from 161.5 ± 1.0 to 143.1 ± 0.8 million years ago (Ma), which is preserved in Upper Jurassic stratum, strata.Owen ...
period in what is now Colorado
Colorado is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States. It is one of the Mountain states, sharing the Four Corners region with Arizona, New Mexico, and Utah. It is also bordered by Wyoming to the north, Nebraska to the northeast, Kansas ...
, Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, and possibly England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
, Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
, Tanzania
Tanzania, officially the United Republic of Tanzania, is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It is bordered by Uganda to the northwest; Kenya to the northeast; the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to t ...
, and Uruguay
Uruguay, officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay, is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast, while bordering the Río de la Plata to the south and the A ...
. It contains two currently recognized species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
, ''Torvosaurus tanneri'' and ''Torvosaurus gurneyi'', plus a third unnamed species from Germany.
In 1979, the type species
In International_Code_of_Zoological_Nomenclature, zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the spe ...
''Torvosaurus tanneri'' was named. Measuring around long and weighing approximately , ''T. tanneri'' was among the largest terrestrial carnivore
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they ar ...
s in North America during the Late Jurassic. Specimens of ''Torvosaurus gurneyi'' were measured up to in length and in body mass, suggesting that it was much larger than ''T. tanneri'' and was the largest terrestrial carnivore in Europe during the Late Jurassic. Based on bone morphology, ''Torvosaurus'' is thought to have had very powerful short arms.
Discovery
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
, Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, and possibly in England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
, Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
, Tanzania
Tanzania, officially the United Republic of Tanzania, is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It is bordered by Uganda to the northwest; Kenya to the northeast; the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to t ...
, and Uruguay
Uruguay, officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay, is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast, while bordering the Río de la Plata to the south and the A ...
. The first discovered remains referable to ''Torvosaurus'' were discovered in 1899 by Elmer Riggs in the "Freeze-out Hills" of southeastern Wyoming
Wyoming ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States, Western United States. It borders Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho t ...
, northwest of Medicine Bow. The material consisted of part of the left foot and right hand and they were taken to the Field Museum of Natural History
The Field Museum of Natural History (FMNH), also known as The Field Museum, is a natural history museum in Chicago, Illinois, and is one of the largest such museums in the world. The museum is popular for the size and quality of its educationa ...
in Chicago
Chicago is the List of municipalities in Illinois, most populous city in the U.S. state of Illinois and in the Midwestern United States. With a population of 2,746,388, as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the List of Unite ...
, where they were stored until being re-discovered around 2010. The specimen was assigned to ''Torvosaurus tanneri'' after being described in 2014.Hanson, Michael; Makovicky, Peter J. "A new specimen of ''Torvosaurus tanneri'' originally collected by Elmer Riggs". ''Historical Biology, volume 26, issue 6 (2014).'' Pages 775-784. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/08912963.2013.853056?scroll=top&needAccess=true&journalCode=ghbi20 .
More remains of a large theropod
Theropoda (; from ancient Greek , (''therion'') "wild beast"; , (''pous, podos'') "foot"">wiktionary:ποδός"> (''pous, podos'') "foot" is one of the three major groups (clades) of dinosaurs, alongside Ornithischia and Sauropodom ...
that is now believed to have been ''Torvosaurus'' were discovered in the Tendaguru Formation
The Tendaguru Formation, or Tendaguru Beds are a highly List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Tanzania, fossiliferous Lithostratigraphy, formation and Lagerstätte located in the Lindi Region of southeastern Tanzania. The formation represe ...
of Tanzania
Tanzania, officially the United Republic of Tanzania, is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It is bordered by Uganda to the northwest; Kenya to the northeast; the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to t ...
and was named "''Megalosaurus
''Megalosaurus'' (meaning "great lizard", from Ancient Greek, Greek , ', meaning 'big', 'tall' or 'great' and , ', meaning 'lizard') is an extinct genus of large carnivorous theropod dinosaurs of the Middle Jurassic Epoch (Bathonian stage, 166 ...
''" ''ingens'' by Werner Janensch
Werner Ernst Martin Janensch (11 November 1878 – 20 October 1969) was a German paleontologist and geologist.
Biography
Janensch was born at Herzberg (Elster).
In addition to Friedrich von Huene, Janensch was probably Germany's most ...
in 1920, based on the specimen MB R 1050, a long tooth from German East Africa
German East Africa (GEA; ) was a German colonial empire, German colony in the African Great Lakes region, which included present-day Burundi, Rwanda, the Tanzania mainland, and the Kionga Triangle, a small region later incorporated into Portugu ...
(now Tanzania). It was eventually reclassified as a probable member of Carcharodontosauridae
Carcharodontosauridae (carcharodontosaurids; from the Greek καρχαροδοντόσαυρος, ''carcharodontósauros'': "shark-toothed lizards") is a group of carnivorous theropod dinosaurs. In 1931, Ernst Stromer named Carcharodontosaurida ...
before being reclassified as a probable member of the ''Torvosaurus'' genus in 2020. Although it was only referred to as ''Torvosaurus sp.'', one commentator has noted it could potentially be called ''Torvosaurus ingens''. Soto ''et al.'' described teeth of a member of the genus ''Torvosaurus'' from the Tacuarembó Formation
The Tacuarembó Formation is a Late Jurassic (Kimmeridgian
In the geologic timescale, the Kimmeridgian is an age in the Late Jurassic Epoch and a stage in the Upper Jurassic Series. It spans the time between 154.8 ±0.8 Ma and 149.2 ±0.7 Ma ...
of Uruguay
Uruguay, officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay, is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast, while bordering the Río de la Plata to the south and the A ...
. The authors noted that some of the specimens of “''Megalosaurus” ingens'' figured by Werner Janensch
Werner Ernst Martin Janensch (11 November 1878 – 20 October 1969) was a German paleontologist and geologist.
Biography
Janensch was born at Herzberg (Elster).
In addition to Friedrich von Huene, Janensch was probably Germany's most ...
share the features of the Uruguayan material and stated that the materials from Tanzania and Uruguay may represent the same taxon, due to geographical proximity, but ultimately concluded that, based on only teeth, they do not share any derived characteristics to distinguish them from the described species of the genus, ''T. tanneri'' and ''T. gurneyi''.Tacuarembó Formationat
Fossilworks
Fossilworks was a portal which provides query, download, and analysis tools to facilitate access to the Paleobiology Database, a large relational database assembled by hundreds of paleontologists from around the world.
History
Fossilworks was cr ...
.org However, Rauhut ''et al.'' consider the teeth to be undiagnostic, being coherent in size and shape with a variety of other theropods (including carcharodontosaurids), thus considering their attribution to the genus to be problematic.
In 1971, Vivian Jones of Delta, Colorado
Delta is a home rule municipality that is the county seat and the most populous municipality of Delta County, Colorado, United States. The town population was 9,035 at the 2020 United States census. The United States Forest Service headqua ...
, in the Calico Gulch Quarry in Moffat County, discovered a single gigantic thumb claw of a theropod. This was shown to James Alvin Jensen, a collector who was working for Brigham Young University
Brigham Young University (BYU) is a Private education, private research university in Provo, Utah, United States. It was founded in 1875 by religious leader Brigham Young and is the flagship university of the Church Educational System sponsore ...
. In an effort to discover comparable fossils, Vivian's husband Daniel Eddie Jones directed Jensen to the Dry Mesa Quarry, where abundant gigantic theropod bones, together with ''Supersaurus
''Supersaurus'' (meaning "super lizard") is a genus of diplodocid sauropod dinosaur that lived in North America during the Late Jurassic period. The type species, ''S. vivianae'', was first discovered by Vivian Jones of Delta, Colorado, in the ...
'' remains, proved present in rocks of the Morrison Formation
The Morrison Formation is a distinctive sequence of Upper Jurassic sedimentary rock found in the western United States which has been the most fertile source of dinosaur fossils in North America. It is composed of mudstone, sandstone, siltston ...
. From 1972 onward, the site was excavated by Jensen and Kenneth Stadtman. The type species
In International_Code_of_Zoological_Nomenclature, zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the spe ...
''Torvosaurus tanneri'' was named and described in 1979
Events
January
* January 1
** United Nations Secretary-General Kurt Waldheim heralds the start of the ''International Year of the Child''. Many musicians donate to the ''Music for UNICEF Concert'' fund, among them ABBA, who write the song ...
by Peter Malcolm Galton
Peter Malcolm Galton (born 14 March 1942 in London) is a British vertebrate paleontologist who has to date written or co-written about 190 papers in scientific journals or chapters in paleontology textbooks, especially on ornithischian and prosau ...
and Jensen. The genus name ''Torvosaurus'' derives from the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
word ''torvus'', meaning "savage", and the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
word ''sauros'' (σαυρος), meaning "lizard". The specific name Specific name may refer to:
* in Database management systems, a system-assigned name that is unique within a particular database
In taxonomy, either of these two meanings, each with its own set of rules:
* Specific name (botany), the two-part (bino ...
''tanneri'' comes from the, first counselor in the First Presidency
Among many churches in the Latter Day Saint movement, the First Presidency (also known as the Quorum of the Presidency of the Church) is the highest presiding or governing body. Present-day denominations of the movement led by a First Presidency ...
of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a Nontrinitarianism, nontrinitarian Restorationism, restorationist Christianity, Christian Christian denomination, denomination and the ...
, Nathan Eldon Tanner
Nathan Eldon Tanner (May 9, 1898 – November 27, 1982) was a Canadian politician and a leader of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church). He served in the Legislative Assembly of Alberta from 1935 to 1952 as a member of ...
.
In 1985, Jensen could report a considerable amount of additional material, among it being the first skull elements.Jensen, J.A., 1985, "Uncompahgre dinosaur fauna: A preliminary report", ''Great Basin Naturalist'', 45: 710–720 The fossils from Colorado were further described by Brooks Britt in 1991.Britt, B., 1991,Theropods of Dry Mesa Quarry (Morrison Formation, Late Jurassic), Colorado, with emphasis on the osteology of ''Torvosaurus tanneri''
, ''Brigham Young University Geology Studies'' 37: 1–72 The
holotype
A holotype (Latin: ''holotypus'') is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of s ...
, BYU 2002, originally consisted of upper and lower arm bones. The paratype
In zoology and botany, a paratype is a specimen of an organism that helps define what the scientific name of a species and other taxon actually represents, but it is not the holotype (and in botany is also neither an isotype (biology), isotype ...
s included some back bones, hip bones, and hand bones. When the material described in 1985 is added, the main missing elements are the shoulder girdle and the thighbone. The original thumb claw, specimen BYUVP 2020, was only provisionally referred, as it had been found in a site away from the Dry Mesa Quarry. The holotype and paratypes represented at least three individuals, these being two adults and a juvenile. In 1991, Britt concluded that there was no proof that the front limbs of the holotype were associated and chose the left humerus as the lectotype
In biology, a type is a particular specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally associated. In other words, a type is an example that serves to anchor or centralizes ...
. Several single bones and teeth found in other American sites have been referred to ''Torvosaurus''.
 In 1992, fossils of a large theropod found at
In 1992, fossils of a large theropod found at Como Bluff
Como Bluff is a long ridge extending east–west, located between the towns of Rock River and Medicine Bow, Wyoming. The ridge is an anticline, formed as a result of compressional geological folding. Three geological formations, the Sundance, ...
in Wyoming
Wyoming ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States, Western United States. It borders Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho t ...
contained skull, shoulder girdle, pelvic, and rib elements. They were named by Robert T. Bakker
Robert Thomas Bakker (born March 24, 1945) is an American paleontologist who helped reshape modern theories about dinosaurs, particularly by adding support to the theory that some dinosaurs were endothermic (warm-blooded). Along with his mentor ...
''et al.'' as the species ''Edmarka rex''. Bakker ''et al'' were impressed with the size of ''Edmarka'', noting that it "would rival '' T. rex'' in total length," and viewing this approximate size as "a natural ceiling for dinosaurian meat-eaters." This was often considered a junior synonym
In taxonomy, the scientific classification of living organisms, a synonym is an alternative scientific name for the accepted scientific name of a taxon. The botanical and zoological codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently.
...
of ''Torvosaurus'', but a detailed analysis has not been carried out yet. The same site has rendered comparable remains for which the ''nomen nudum
In Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy, a ''nomen nudum'' ('naked name'; plural ''nomina nuda'') is a designation which looks exactly like a scientific name of an organism, and may have originally been intended to be one, but it has not been published ...
'' ''Brontoraptor'' has been used.Siegwarth, J., Linbeck, R., Bakker, R. and Southwell, B. (1996). Giant carnivorous dinosaurs of the family Megalosauridae. ''Hunteria'' 3:1–77. Most researchers now regard both specimens as belonging to ''Torvosaurus tanneri''. However, ''Edmarka rex'' and ''Brontoraptor'' require reclassification to determine whether or not they actually belong to ''T. tanneri'', as all the specimens described prior to their discovery indicate that they reached their adult size and both incomplete specimens lack detailed osteological descriptions.
In 2012, a still undescribed, 55% complete specimen was discovered in Colorado in the Skull Creek Quarry, which is an exposure of the Morrison Formation. The specimen, nicknamed "Elvis", included the pelvic, spine, and hind limb bones, a complete, associated backbone, as well as cranial elements. It is the most complete specimen of ''Torvosaurus'' found to date. A mounted skeleton of the specimen, with missing parts reconstructed with casts from other ''Torvosaurus'' specimens, is currently on display in the Museum of Natural History & Science in Cincinnati.
In 2000, material from Portugal was referred to a ''Torvosaurus'' sp. by Octávio Mateus
Octávio Mateus (born 1975) is a Portugal, Portuguese dinosaur paleontologist and biologist Professor of Paleontology at the Faculdade de Ciências e Tecnologia da NOVA University Lisbon, Universidade Nova de Lisboa. He graduated in University of � ...
and Miguel Telles Antunes
Dr. Miguel Telles Antunes (born 11 January 1937) is a Portuguese academic, specializing in paleontology, zooarchaeology, and geology. Antunes is a ranking member of various institutions, including the Lisbon Academy of Sciences, Nova Universi ...
.Mateus, O., & Antunes, M. T. (2000). ''Torvosaurus'' sp.(Dinosauria: Theropoda) in the late Jurassic of Portugal. In I Congresso Ibérico de Paleontologia/XVI Jornadas de la Sociedad Española de Paleontología (pp. 115–117) In 2006, fossils from the Portuguese Lourinhã Formation
The Lourinhã Formation () is a fossil-rich geological formation in western Portugal, named for the municipality of Lourinhã. The formation is mostly Late Jurassic in age (Kimmeridgian/Tithonian), with the top of the formation extending into the ...
were referred to ''Torvosaurus tanneri''. In 2012, however, Matthew Carrano ''et al.'' concluded that this material could not be more precisely determined than a ''Torvosaurus'' sp. In 2013 and 2014, eggs with and without embryos were reported from Portugal and referred to ''Torvosaurus''. The species from Portugal was named ''T. gurneyi'' in honor of James Gurney
James Gurney (born June 14, 1958) is an American artist and author known for his illustrated book series '' Dinotopia'', which is presented in the form of a 19th-century explorer's
journal from an island utopia cohabited by humans and dinosaurs ...
in 2014, the creator of the ''Dinotopia
''Dinotopia'' is a series of illustrated fantasy books, created by author and illustrator James Gurney. It is set in the titular Dinotopia, an isolated island inhabited by shipwrecked humans and sapient dinosaurs who have learned to coexist p ...
'' series of books. It is the largest named theropod known from Europe, although an isolated anterior caudal vertebra from the Vega Formation in Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
, which may belong to ''Torvosaurus'' or a closely related taxon, is about 15% larger than the one found on ''T. gurneyi.'' It was the morphological distinctiveness of the holotype maxilla ML1100 that led to the naming of the Portuguese species. In 2017, a set of Portuguese cranial material assigned to ''Torvosaurus'' was described, including a specimen interpreted as belonging to the same individual as the holotype of ''Torvosaurus gurneyi''.
In 2020, Soto ''et al.'' described FC-DPV 2971, a tooth from Uruguay, as belonging to a new unnamed species of ''Torvosaurus''. They also assigned ''Megalosaurus
''Megalosaurus'' (meaning "great lizard", from Ancient Greek, Greek , ', meaning 'big', 'tall' or 'great' and , ', meaning 'lizard') is an extinct genus of large carnivorous theropod dinosaurs of the Middle Jurassic Epoch (Bathonian stage, 166 ...
''/''Ceratosaurus
''Ceratosaurus'' (from Greek 'horn' and 'lizard') is a genus of carnivorous theropod dinosaur that lived in the Late Jurassic period (Kimmeridgian to Tithonian ages). The genus was first described in 1884 by American paleontologist Othni ...
ingens'' (specimen MB R 1050) from Tanzania to ''Torvosaurus''. Also in 2020, a fragmentary maxilla referable to ''Torvosaurus'' was described from the middle Callovian
In the geologic timescale, the Callovian is an age and stage in the Middle Jurassic, lasting between 165.3 ± 1.1 Ma (million years ago) and 161.5 ± 1.0 Ma. It is the last stage of the Middle Jurassic, following the Bathonian and preceding the ...
Ornatenton Formation of Germany. This is the oldest record of the genus and suggests that megalosaurines originated in Europe, or at least that Europe was a biogeographical turntable for them from the Middle to the early Late Jurassic. Other possible ''Torvosaurus'' instances in Europe include fragmentary remains from the Kimmeridge Clay
The Kimmeridge Clay is a sedimentary rock, sedimentary deposit of fossiliferous marine clay which is of Late Jurassic to lowermost Cretaceous age and occurs in southern and eastern England and in the North Sea. This rock formation (geology), form ...
of England that possibly belong to the genus. These consist of a tibia (OUMNH J.29886) and a maxilla fragment that were collected separately from each other.
Description
 ''Torvosaurus'' was a very large and robust predatory dinosaur. ''T. tanneri'' was initially described as long, but a detailed osteological description has revised its length estimate to . ''T. gurneyi'' was initially estimated around long, but its body length estimate was revised to in its specific description. Claims have been made indicating even larger sizes for the American species ''T. tanneri'', with estimates of up to in length and more than based on incomplete remains of ''Edmarka rex'' and "Brontoraptor". However, ''Edmarka rex'' and "Brontoraptor" lack detailed analyses to verify whether or not they actually belong to ''T. tanneri''. ''T. tanneri'' is estimated to have weighed approximately , while ''T. gurneyi'' is estimated to have weighed .
''Torvosaurus'' was a very large and robust predatory dinosaur. ''T. tanneri'' was initially described as long, but a detailed osteological description has revised its length estimate to . ''T. gurneyi'' was initially estimated around long, but its body length estimate was revised to in its specific description. Claims have been made indicating even larger sizes for the American species ''T. tanneri'', with estimates of up to in length and more than based on incomplete remains of ''Edmarka rex'' and "Brontoraptor". However, ''Edmarka rex'' and "Brontoraptor" lack detailed analyses to verify whether or not they actually belong to ''T. tanneri''. ''T. tanneri'' is estimated to have weighed approximately , while ''T. gurneyi'' is estimated to have weighed .
 Among the differentiating features originally recognized between ''T. gurneyi'' and ''T. tanneri'' are the number of teeth, alongside the size and shape of the mouth. While the upper jaw of ''T. tanneri'' has more than 11 teeth, that of ''T. gurneyi'' has less. However, later examination of a new right maxilla, probably belonging to the same individual as the holotype of ''T. gurneyi'', has determined that, while the two species can be distinguished based on the morphology of the maxillary medial wall and interdental plates, the supposedly lower number of maxillary teeth in the Portuguese form may be an artifact of preservation, since it is not possible to know the exact number of teeth in the complete maxilla at the moment.
The material from Germany is further distinguished by the other two species by a temporal difference of c. 10 Ma and a few morphological differences which indicate that it was the third species outside a sister taxon relationship between ''T. tanneri'' and ''T. gurneyi''. The material is only 10% smaller than the maxilla of ''T. tanneri'', although the ontogenetic stage of the specimen is unknown. This indicates that derived megalosaurines were already among the largest terrestrial predators of the late Middle Jurassic, with only a moderate increase in size in the genus by the Late Jurassic.
Among the differentiating features originally recognized between ''T. gurneyi'' and ''T. tanneri'' are the number of teeth, alongside the size and shape of the mouth. While the upper jaw of ''T. tanneri'' has more than 11 teeth, that of ''T. gurneyi'' has less. However, later examination of a new right maxilla, probably belonging to the same individual as the holotype of ''T. gurneyi'', has determined that, while the two species can be distinguished based on the morphology of the maxillary medial wall and interdental plates, the supposedly lower number of maxillary teeth in the Portuguese form may be an artifact of preservation, since it is not possible to know the exact number of teeth in the complete maxilla at the moment.
The material from Germany is further distinguished by the other two species by a temporal difference of c. 10 Ma and a few morphological differences which indicate that it was the third species outside a sister taxon relationship between ''T. tanneri'' and ''T. gurneyi''. The material is only 10% smaller than the maxilla of ''T. tanneri'', although the ontogenetic stage of the specimen is unknown. This indicates that derived megalosaurines were already among the largest terrestrial predators of the late Middle Jurassic, with only a moderate increase in size in the genus by the Late Jurassic. ''Torvosaurus'' had an elongated, narrow snout, with a kink in its profile just above the large nostrils. The frontmost snout bone, the
''Torvosaurus'' had an elongated, narrow snout, with a kink in its profile just above the large nostrils. The frontmost snout bone, the premaxilla
The premaxilla (or praemaxilla) is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammals h ...
, bore three rather flat teeth oriented somewhat outwards with the front edge of the teeth crown overlapping the outer side of the rear edge of the preceding crown. The maxilla
In vertebrates, the maxilla (: maxillae ) is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxil ...
was tall and bore at least eleven rather long teeth. The antorbital fenestra
An antorbital fenestra (plural: fenestrae) is an opening in the skull that is in front of the eye sockets. This skull character is largely associated with Archosauriformes, archosauriforms, first appearing during the Triassic Period. Among Extant ...
was relatively short. The lacrimal bone
The lacrimal bones are two small and fragile bones of the facial skeleton; they are roughly the size of the little fingernail and situated at the front part of the medial wall of the orbit. They each have two surfaces and four borders. Several bon ...
had a distinctive lacrimal horn on top. Its lower end was broad in side view. The eye socket was tall with a pointed lower end. The jugal
The jugal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians and birds. In mammals, the jugal is often called the malar or zygomatic. It is connected to the quadratojugal and maxilla, as well as other bones, which may vary by species.
Anatomy ...
was long and transversely thin. The lower front side of the quadrate bone
The quadrate bone is a skull bone in most tetrapods, including amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, birds), and early synapsids.
In most tetrapods, the quadrate bone connects to the quadratojugal and squamosal bones in the skull, and forms up ...
was hollowed out by a tear-shaped depression, the contact surface with the quadratojugal The quadratojugal is a skull bone present in many vertebrates, including some living reptiles and amphibians.
Anatomy and function
In animals with a quadratojugal bone, it is typically found connected to the jugal (cheek) bone from the front and ...
. Both the neck vertebrae and the front dorsal vertebrae had relatively flexible ball-in-socket joints. The balls on the front side of the vertebral centra had a wide rim, a condition by Britt likened to a Derby hat
The bowler hat, also known as a Coke hat, billycock, bob hat, bombín (Spanish) or derby (United States), is a hard felt hat with a rounded crown, originally created by the London hat-makers Thomas and William Bowler in 1849 and commissioned by ...
. The tail base was stiffened in the vertical plane by high and in side view wide neural spines. The whole of the arm was very strong, but somewhat short. Whether the thumb claw was especially enlarged is uncertain. In the pelvis, the ilium resembled that of ''Megalosaurus'' and had a tall, short, front blade and a longer pointed rear blade. The pelvis as a whole was massively built, with the bone skirts between the pubic bone
In vertebrates, the pubis or pubic bone () forms the lower and anterior part of each side of the hip bone. The pubis is the most forward-facing (ventral and anterior) of the three bones that make up the hip bone. The left and right pubic bones ar ...
s and the ischia
Ischia ( , , ) is a volcanic island in the Tyrrhenian Sea. It lies at the northern end of the Gulf of Naples, about from the city of Naples. It is the largest of the Phlegrean Islands. Although inhabited since the Bronze Age, as a Ancient G ...
contacting each other and forming a vaulted closed underside.
Systematics and classification
 When first described in 1979 by Galton and Jensen,P. M. Galton and J. A. Jensen. 1979
When first described in 1979 by Galton and Jensen,P. M. Galton and J. A. Jensen. 1979A new large theropod dinosaur from the Upper Jurassic of Colorado
. Brigham Young University Geology Studies 26(1):1–12 ''Torvosaurus'' was classified as a
megalosaurid
Megalosauridae is a monophyletic family of carnivorous theropod dinosaurs within the group Megalosauroidea. Appearing in the Middle Jurassic, megalosaurids were among the first major radiation of large theropod dinosaurs. They were a relatively ...
, which is the current consensus. It was later assigned to Carnosauria
Carnosauria is an extinct group of carnivorous theropod dinosaurs that lived during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods.
While Carnosauria was historically considered largely synonymous with Allosauroidea, some recent studies have revived Ca ...
by Ralph Molnar
Ralph E. Molnar is a paleontologist who had been Curator of Mammals at the Queensland Museum and more recently associated with the Museum of Northern Arizona. He is also a research associate at the Texas Natural Science Centre. He co-authored descr ...
''et al.'' in 1990, then to a basal position in Spinosauroidea
Megalosauroidea (meaning 'great/big lizard forms') is a superfamily (or clade) of tetanuran theropod dinosaurs that lived from the Middle Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous period. The group is defined as ''Megalosaurus bucklandii'' and all taxa s ...
by Oliver Walter Mischa Rauhut in 2003, and to a very basal position in Tetanurae
Tetanurae (/ˌtɛtəˈnjuːriː/ or "stiff tails") is a clade that includes most Theropoda, theropod dinosaurs, including Megalosauroidea, megalosauroids, Allosauroidea, allosauroids, and Coelurosauria, coelurosaurs (which includes Tyrannosauroi ...
by Thomas Holtz in 1994. All these assignments are not supported by present phylogenetic analysis. In 1985, Jensen assigned ''Torvosaurus'' to a family of its own, Torvosauridae. Despite support for this concept by Paul Sereno
Paul Callistus Sereno (born October 11, 1957) is a professor of paleontology at the University of Chicago who has discovered several new dinosaur species on several continents, including at sites in Inner Mongolia, Argentina, Morocco and Niger. ...
and Mateus, it seems redundant because ''Torvosaurus'' is closely related to, and perhaps the sister species
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree.
Definition
The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram:
Taxon A and ...
of, the earlier ''Megalosaurus
''Megalosaurus'' (meaning "great lizard", from Ancient Greek, Greek , ', meaning 'big', 'tall' or 'great' and , ', meaning 'lizard') is an extinct genus of large carnivorous theropod dinosaurs of the Middle Jurassic Epoch (Bathonian stage, 166 ...
'' within Megalosaurinae
Megalosauridae is a monophyletic family of carnivorous theropod dinosaurs within the group Megalosauroidea. Appearing in the Middle Jurassic, megalosaurids were among the first major radiation of large theropod dinosaurs. They were a relatively ...
. However, Torvosauridae may be used as an alternative name for Megalosauridae if ''Megalosaurus'' is considered an indeterminable ''nomen dubium''. Though a close relative of ''Megalosaurus'', ''Torvosaurus'' is seemingly more advanced, or apomorphic. ''Torvosaurus''s larger clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach t ...
, Megalosauridae
Megalosauridae is a monophyletic Family (taxonomy), family of Carnivore, carnivorous theropod dinosaurs within the group Megalosauroidea. Appearing in the Middle Jurassic, megalosaurids were among the first major radiation of large theropod dino ...
, is most commonly held as a basal branch of Tetanurae
Tetanurae (/ˌtɛtəˈnjuːriː/ or "stiff tails") is a clade that includes most Theropoda, theropod dinosaurs, including Megalosauroidea, megalosauroids, Allosauroidea, allosauroids, and Coelurosauria, coelurosaurs (which includes Tyrannosauroi ...
, considered to be less derived than carnosaur
Carnosauria is an extinct group of carnivorous theropod dinosaurs that lived during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods.
While Carnosauria was historically considered largely synonymous with Allosauroidea, some recent studies have revived Carn ...
s or coelurosaur
Coelurosauria (; from Greek, meaning "hollow-tailed lizards") is the clade containing all theropod dinosaurs more closely related to birds than to carnosaurs.
Coelurosauria is a subgroup of theropod dinosaurs that includes compsognathids, ty ...
s and likely related to the spinosaurid
Spinosauridae (or spinosaurids) is a clade or Family (taxonomy), family of tetanuran theropod dinosaurs comprising ten to seventeen known genera. Spinosaurid fossils have been recovered worldwide, including Africa, Europe, South America, and Asia. ...
s.
The following is a cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an Phylogenetic tree, evolutionary tree because it does not s ...
based on the phylogenetic analysis conducted by Carrano, Benson, and Sampson (2012) showing the relationships of ''Torvosaurus'':Carrano, M. T.; Benson, R. B. J.; Sampson, S. D. (2012). "The phylogeny of Tetanurae (Dinosauria: Theropoda)". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology 10 (2): 211–300. doi:10.1080/14772019.2011.630927
Distinguishing anatomical features
 According to Carrano ''et al.'' (2012), ''Torvosaurus'' can be distinguished based on the following characteristics:
* The presence of a very shallow
According to Carrano ''et al.'' (2012), ''Torvosaurus'' can be distinguished based on the following characteristics:
* The presence of a very shallow maxilla
In vertebrates, the maxilla (: maxillae ) is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxil ...
ry fossa (it lacks a ''fenestra maxillaris'' piercing the bone wall)
* The presence of fused interdental plates
* The pneumatic fossae in the posterior dorsal and the anterior caudal vertebrae centra being expanded to form enlarged, deep openings
* The puboischiadic plate being highly ossified (the paired bony plates of both sides connect and close off the entire underside of the pelvis, a very basal trait that Galton & Jensen saw as an indication that Theropoda was polyphyletic
A polyphyletic group is an assemblage that includes organisms with mixed evolutionary origin but does not include their most recent common ancestor. The term is often applied to groups that share similar features known as Homoplasy, homoplasies ...
, with Carnosauria having independently evolved from carnivorous Prosauropoda
Sauropodomorpha ( ; from Greek, meaning "lizard-footed forms") is an extinct clade of long-necked, herbivorous, saurischian dinosaurs that includes the sauropods and their ancestral relatives. Sauropods generally grew to very large sizes, had lo ...
)
* A distal expansion of the ischium
The ischium (; : is ...
shaft with a prominent lateral midline crest and an ovalur outline when examined in lateral view
* The cervical vertebrae are opisthocoelous with a pronounced flat rim around the anterior ball (according to Rauhut, 2000)
* A transverse fenestra
A fenestra (fenestration; : fenestrae or fenestrations) is any small opening or pore, commonly used as a term in the biology, biological sciences. It is the Latin word for "window", and is used in various fields to describe a pore in an anatomy, ...
is situated in the neural arch of the dorsal vertebrae in front of the hyposphene (according to Rauhut, 2000)
Paleobiology
 The study of fossilized embryos of ''Torvosaurus'' provides researchers with information about the transformation of the embryo over time, the different developmental pathways present in dinosaur lineages, dinosaur reproductive behavior, and dinosaur parental care. In 2013, Araújo ''et al''. announced the discovery of specimen ML1188, a clutch of crushed dinosaur eggs and embryonic material attributed to ''Torvosaurus''. This discovery further supports the hypothesis that large theropods were oviparous, meaning that they laid eggs and hence that embryonic development occurred outside the body of female dinosaurs. This discovery was made in 2005 by the Dutch amateur fossil-hunter Aart Walen at the
The study of fossilized embryos of ''Torvosaurus'' provides researchers with information about the transformation of the embryo over time, the different developmental pathways present in dinosaur lineages, dinosaur reproductive behavior, and dinosaur parental care. In 2013, Araújo ''et al''. announced the discovery of specimen ML1188, a clutch of crushed dinosaur eggs and embryonic material attributed to ''Torvosaurus''. This discovery further supports the hypothesis that large theropods were oviparous, meaning that they laid eggs and hence that embryonic development occurred outside the body of female dinosaurs. This discovery was made in 2005 by the Dutch amateur fossil-hunter Aart Walen at the Lourinhã Formation
The Lourinhã Formation () is a fossil-rich geological formation in western Portugal, named for the municipality of Lourinhã. The formation is mostly Late Jurassic in age (Kimmeridgian/Tithonian), with the top of the formation extending into the ...
in Western Portugal in fluvial overbank sediments that are considered to be from the Tithonian age of the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. ...
, approximately 152 to 145 million years ago. This discovery is paleontologically significant for a number of reasons: (a) these are the most primitive dinosaur embryos known; (b) these are the only basal theropod embryos known; (c) fossilized eggs and embryos are rarely found together; (d) it represents the first evidence of a one-layered eggshell for theropod dinosaurs; and (e) it allows researchers to link a new eggshell morphology to the osteology of a particular group of theropod dinosaurs. The specimen is housed at the Museu da Lourinhã in Portugal. As the eggs were abandoned due to unknown circumstances, it is not known if ''Torvosaurus'' provided parental care to its eggs and young or abandoned them shortly after laying. However, the eggshells are highly porous, allowing efficient gaseous exchange between the external and internal media, thus indicating the eggs were buried for incubation within substrate in a manner similar to modern seaturtles. This is also corroborated by the undisturbed taphonomic setting and low-energy geological context.
All documented ''Torvosaurus'' specimens from the Morrison Formation
The Morrison Formation is a distinctive sequence of Upper Jurassic sedimentary rock found in the western United States which has been the most fertile source of dinosaur fossils in North America. It is composed of mudstone, sandstone, siltston ...
are from similarly sized, likely adult individuals and the lack of immature individuals may be explained by many factors, none of which are mutually exclusive. For one thing, the formation is known to preserve large vertebrates better than smaller ones. Immature individuals may also have occupied a different ecological niche from adults in habitats where their remains were likely to preserve as fossils and they may have been the prey of choice of larger predators as well. ''Torvosaurus'' may also have experienced Type B1 population survivorship, as has been found in other dinosaurs, with mortality increasing after sexual maturity was achieved, leading to an abundance of mature individuals in the fossil record. A final possibility is that immature ''Torvosaurus'' remains could be misidentified due to having different proportions compared to the very large and robust adults.
Paleoecology

Provenance and occurrence
Thetype specimen
In biology, a type is a particular wikt:en:specimen, specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally associated. In other words, a type is an example that serves to ancho ...
of ''Torvosaurus tanneri'', BYU 2002, was recovered in the Dry Mesa Quarry of the Brushy Basin Member of the Morrison Formation
The Morrison Formation is a distinctive sequence of Upper Jurassic sedimentary rock found in the western United States which has been the most fertile source of dinosaur fossils in North America. It is composed of mudstone, sandstone, siltston ...
in Montrose County, Colorado. The specimen was collected by James A. Jensen and Kenneth Stadtman in 1972 in medium-grained, coarse sandstone that was deposited during the Tithonian
In the geological timescale, the Tithonian is the latest age (geology), age of the Late Jurassic Epoch and the uppermost stage (stratigraphy), stage of the Upper Jurassic Series. It spans the time between 149.2 ±0.7 annum, Ma and 143.1 ±0.6 (mi ...
and Kimmeridgian
In the geologic timescale, the Kimmeridgian is an age in the Late Jurassic Epoch and a stage in the Upper Jurassic Series. It spans the time between 154.8 ±0.8 Ma and 149.2 ±0.7 Ma (million years ago). The Kimmeridgian follows the Oxfordian ...
ages of the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. ...
, approximately 153 to 148 million years ago. This specimen is housed in the collection of Brigham Young University
Brigham Young University (BYU) is a Private education, private research university in Provo, Utah, United States. It was founded in 1875 by religious leader Brigham Young and is the flagship university of the Church Educational System sponsore ...
in Provo, Utah
Provo ( ) is a city in and the county seat of Utah County, Utah, United States. It is south of Salt Lake City along the Wasatch Front, and lies between the cities of Orem, Utah, Orem to the north and Springville, Utah, Springville to the south ...
.
Fauna and habitat in North America
Studies suggest that thepaleoenvironment
Paleoecology (also spelled palaeoecology) is the study of interactions between organisms and/or interactions between organisms and their environments across geologic timescales. As a discipline, paleoecology interacts with, depends on and informs ...
of this section of the Morrison Formation included rivers that flowed from the west into a basin that contained a giant, saline alkaline lake and there were extensive wetlands in the vicinity. The Dry Mesa Dinosaur Quarry of western Colorado yields one of the most diverse Upper Jurassic vertebrate assemblages in the world. The Dry Mesa Quarry has produced the remains of the sauropods
Sauropoda (), whose members are known as sauropods (; from '' sauro-'' + '' -pod'', 'lizard-footed'), is a clade of saurischian ('lizard-hipped') dinosaurs. Sauropods had very long necks, long tails, small heads (relative to the rest of their b ...
''Apatosaurus
''Apatosaurus'' (; meaning "deceptive lizard") is a genus of herbivorous sauropod dinosaur that lived in North America during the Late Jurassic period. Othniel Charles Marsh described and named the first-known species, ''A. ajax'', in 1877, a ...
'', ''Brachiosaurus
''Brachiosaurus'' () is a genus of sauropod dinosaur that lived in North America during the Late Jurassic, about . It was first Species description, described by American paleontologist Elmer S. Riggs in 1903 in paleontology, 1903 from fossi ...
'', ''Diplodocus
''Diplodocus'' (, , or ) is an extinct genus of diplodocid sauropod dinosaurs known from the Late Jurassic of North America. The first fossils of ''Diplodocus'' were discovered in 1877 by S. W. Williston. The generic name, coined by Othnie ...
'', ''Barosaurus
''Barosaurus'' ( ) is a genus of giant, long-tailed, long-necked, herbivore, plant-eating Sauropoda, sauropod dinosaur closely related to the more familiar ''Diplodocus''. Remains have been found in the Morrison Formation from the Jurassic, Up ...
'', ''Supersaurus
''Supersaurus'' (meaning "super lizard") is a genus of diplodocid sauropod dinosaur that lived in North America during the Late Jurassic period. The type species, ''S. vivianae'', was first discovered by Vivian Jones of Delta, Colorado, in the ...
'', and ''Camarasaurus
''Camarasaurus'' ( ) is a genus of sauropod dinosaur that lived in North America during the Late Jurassic period. Its fossil remains have been found in the Morrison Formation, dating to the Kimmeridgian and Tithonian ages of the Jurassic, betwe ...
'', the iguanodonts
Ornithopoda () is a clade of ornithischian dinosaurs, called ornithopods (). They represent one of the most successful groups of herbivorous dinosaurs during the Cretaceous. The most primitive members of the group were bipedal and relatively sm ...
''Camptosaurus
''Camptosaurus'' ( ) is a genus of plant-eating, beaked ornithischian dinosaurs of the Late Jurassic Period (geology), period of western North America and possibly also Europe. The name means 'flexible lizard' (Ancient Greek, Greek (') meaning ...
'' and ''Dryosaurus
''Dryosaurus'' ( , meaning 'tree lizard', Greek ' () meaning 'tree, oak' and () meaning 'lizard', (the name reflects the forested habitat, not a vague oak-leaf shape of its cheek teeth as is sometimes assumed) is a genus of an ornithopod dinos ...
'', and the theropods
Theropoda (; from ancient Greek , (''therion'') "wild beast"; , (''pous, podos'') "foot"">wiktionary:ποδός"> (''pous, podos'') "foot" is one of the three major groups (clades) of dinosaurs, alongside Ornithischia and Sauropodom ...
''Allosaurus
''Allosaurus'' ( ) is an extinct genus of theropod dinosaur that lived 155 to 145 million years ago during the Late Jurassic period ( Kimmeridgian to late Tithonian ages). The first fossil remains that could definitively be ascribed to th ...
'', ''Tanycolagreus
''Tanycolagreus'' is a genus of coelurosaurian theropod from the Late Jurassic of North America.
Discovery and naming
In 1995 Western Paleontological Laboratories, Inc. uncovered the partial skeleton of a small theropod at the Bone Cabin Quarr ...
'', '' Koparion'', ''Stokesosaurus
''Stokesosaurus'' (meaning "Stokes' lizard") is a genus of small (around in length), carnivorous early tyrannosauroid theropod dinosaurs from the late Jurassic period of Utah, United States.
History
From 1960 onwards Utah geologist William ...
'', ''Ceratosaurus
''Ceratosaurus'' (from Greek 'horn' and 'lizard') is a genus of carnivorous theropod dinosaur that lived in the Late Jurassic period (Kimmeridgian to Tithonian ages). The genus was first described in 1884 by American paleontologist Othni ...
'', and ''Ornitholestes
''Ornitholestes'' (meaning "bird robber") is a small theropod dinosaur of the late Jurassic ( Brushy Basin Member of the Morrison Formation, middle Kimmeridgian age, about 154 million years agoTurner, C.E. and Peterson, F., (1999). "Biostratigrap ...
'', as well as ''Othnielosaurus
''Nanosaurus'' ("small or dwarf lizard") is an extinct genus of neornithischian dinosaur that lived about 155 to 148 million years ago, during the Late Jurassic in North America. Its fossils are known from the Morrison Formation of the south-we ...
'', ''Gargoyleosaurus
''Gargoyleosaurus'' (meaning "gargoyle lizard") is one of the earliest ankylosaurs known from reasonably complete fossil remains. The holotype was discovered in 1995 at the Bone Cabin Quarry West locality, in Albany County, Wyoming in exposures ...
'', and ''Stegosaurus
''Stegosaurus'' (; ) is a genus of herbivorous, four-legged, armored dinosaur from the Late Jurassic, characterized by the distinctive kite-shaped upright plates along their backs and spikes on their tails. Fossils of the genus have been fo ...
''.
The flora of the period has been revealed by fossils of green algae
The green algae (: green alga) are a group of chlorophyll-containing autotrophic eukaryotes consisting of the phylum Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister group that contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/ Streptophyta. The land plants ...
, fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
, moss
Mosses are small, non-vascular plant, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic phylum, division Bryophyta (, ) ''sensu stricto''. Bryophyta (''sensu lato'', Wilhelm Philippe Schimper, Schimp. 1879) may also refer to the parent group bryo ...
es, horsetails
''Equisetum'' (; horsetail) is the only living genus in Equisetaceae, a family of vascular plants that reproduce by spores rather than seeds.
''Equisetum'' is a "living fossil", the only living genus of the entire subclass Equisetidae, which f ...
, ferns
The ferns (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta) are a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. They differ from mosses by being vascular, i.e., having specialized tissue ...
, cycad
Cycads are seed plants that typically have a stout and woody (ligneous) trunk (botany), trunk with a crown (botany), crown of large, hard, stiff, evergreen and (usually) pinnate leaves. The species are dioecious, that is, individual plants o ...
s, ginkgo
''Ginkgo'' is a genus of non-flowering seed plants, assigned to the gymnosperms. The scientific name is also used as the English common name. The order to which the genus belongs, Ginkgoales, first appeared in the Permian, , and ''Ginkgo'' is n ...
es, and several families of conifer
Conifers () are a group of conifer cone, cone-bearing Spermatophyte, seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the phylum, division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a sin ...
s. Other animal fossils discovered include bivalve
Bivalvia () or bivalves, in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class (biology), class of aquatic animal, aquatic molluscs (marine and freshwater) that have laterally compressed soft bodies enclosed b ...
s, snail
A snail is a shelled gastropod. The name is most often applied to land snails, terrestrial molluscs, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod molluscs. However, the common name ''snail'' is also used for most of the members of the molluscan class Gas ...
s, ray-finned fishes
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fish or actinopterygians, is a class (biology), class of Osteichthyes, bony fish that comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species. They are so called because of their lightly built ...
, frog
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely semiaquatic group of short-bodied, tailless amphibian vertebrates composing the order (biology), order Anura (coming from the Ancient Greek , literally 'without tail'). Frog species with rough ski ...
s, salamander
Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by their lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All t ...
s, amphibian
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excl ...
s, turtle
Turtles are reptiles of the order (biology), order Testudines, characterized by a special turtle shell, shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Crypt ...
s, sphenodonts, lizard
Lizard is the common name used for all Squamata, squamate reptiles other than snakes (and to a lesser extent amphisbaenians), encompassing over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most Island#Oceanic isla ...
s, terrestrial (like '' Hoplosuchus'') and aquatic crocodylomorphs
Crocodylomorpha is a group of pseudosuchian archosaurs that includes the crocodilians and their extinct relatives. They were the only members of Pseudosuchia to survive the end-Triassic extinction. Extinct crocodylomorphs were considerably more ...
, cotylosaurs, several species of pterosaur
Pterosaurs are an extinct clade of flying reptiles in the order Pterosauria. They existed during most of the Mesozoic: from the Late Triassic to the end of the Cretaceous (228 million to 66 million years ago). Pterosaurs are the earli ...
s, like '' Harpactognathus'', and early mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s, such as multituberculates
Multituberculata (commonly known as multituberculates, named for the multiple tubercles of their teeth) is an extinct order of rodent-like mammals with a fossil record spanning over 130 million years. They first appeared in the Middle Jurassic, a ...
, symmetrodonts, and triconodonts.
Fauna and habitat in Europe
 The Ornatenton Formation is a Callovian aged shallow marine deposit, within the formation ''Torvosaurus'' was
The Ornatenton Formation is a Callovian aged shallow marine deposit, within the formation ''Torvosaurus'' was sympatric
In biology, two closely related species or populations are considered sympatric when they exist in the same geographic area and thus frequently encounter each other. An initially interbreeding population that splits into two or more distinct spe ...
with the closely related and also large ''Wiehenvenator
''Wiehenvenator'' is a genus of Megalosauridae, megalosaurid Theropoda, theropod dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic (Callovian) of north western Germany. The genus contains a single species, ''W. albati''.
Discovery and naming
In 1998, geologist ...
.'' The Lourinhã Formation is Kimmeridgian-Tithonian in age. The environment is coastal and therefore has a strong marine influence. Its flora and fauna are very similar to that of the Morrison. ''Torvosaurus'' appears to be the top predator here. It lived alongside the European species of ''Allosaurus'' (''A. europaeus''), ''Ceratosaurus'', ''Stegosaurus'', and presumably ''Camptosaurus
''Camptosaurus'' ( ) is a genus of plant-eating, beaked ornithischian dinosaurs of the Late Jurassic Period (geology), period of western North America and possibly also Europe. The name means 'flexible lizard' (Ancient Greek, Greek (') meaning ...
''. The theropod ''Lourinhanosaurus
''Lourinhanosaurus'' (meaning "Lourinhã lizard") was a genus of carnivorous theropod dinosaur that lived during the Late Jurassic Period ( Kimmeridgian/Tithonian) in Portugal. It is one of many large predators discovered at the Lourinhã Format ...
'' also stalked the area. ''Lusotitan
''Lusotitan'' is a genus of herbivorous brachiosaurid sauropod dinosaur from the Late Jurassic of Portugal and possibly Spain.
Discovery and naming
In 1947 Manuel de Matos, a member of the Geological Survey of Portugal, discovered large saur ...
'' was the largest sauropod in the region, while the diplodocids ''Dinheirosaurus
''Dinheirosaurus'' is a genus of diplodocid sauropod dinosaur that is known from fossils uncovered in modern-day Portugal. It may represent a species of ''Supersaurus''. The only species is ''Dinheirosaurus lourinhanensis'', first described by ...
'' and '' Lourinhasaurus'' were also present. ''Dacentrurus
''Dacentrurus'' (meaning "tail full of points"), originally known as ''Omosaurus'', is a genus of Stegosauria, stegosaurian dinosaur from the Late Jurassic and perhaps Early Cretaceous (154 - 140 mya (unit), mya) of Europe.
Its type species, ''Om ...
'' and ''Miragaia
Miragaia () is a former civil parish in the municipality of Porto, Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in contine ...
'' were both stegosaurs, while ''Dracopelta
''Dracopelta'' (meaning “dragon shield”) is a monospecific genus of ankylosaur dinosaur from Portugal that lived during the Late Jurassic (uppermost lower Tithonian-upper Tithonian, 152.1-145.0 Ma) in what is now the Lourinhã Formation. The ...
'' was an ankylosauria
Ankylosauria is a group of herbivorous dinosaurs of the clade Ornithischia. It includes the great majority of dinosaurs with armor in the form of bony osteoderms, similar to turtles. Ankylosaurs were bulky quadrupeds, with short, powerful limbs ...
n. ''Draconyx
''Draconyx'' (meaning "dragon claw") is a genus of dinosaur from the Late Jurassic. It was an Ornithopoda, ornithopod which lived in what is now Portugal and was a herbivore. It was found in the Lourinhã Formation in 1991, and described by Oct� ...
'' was an iguanodontid related to ''Camptosaurus''. Due to the marine nature of the Lourinhã Formation, sharks, plesiochelyid turtles, and teleosaurid crocodyliforms are also present.
Fauna and habitat in Africa
The small-scale trough and ripple cross-bedded fine-grained sandstone at the base of the Upper Dinosaur Member of theTendaguru Formation
The Tendaguru Formation, or Tendaguru Beds are a highly List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Tanzania, fossiliferous Lithostratigraphy, formation and Lagerstätte located in the Lindi Region of southeastern Tanzania. The formation represe ...
, of which possible ''Torvosaurus'' material is known from, is interpreted as tidal flat deposits. Stagnant water bodies, such as small lakes and ponds, were present and a freshwater depositional environment close to the sea was also probably present.
The possible unnamed ''Torvosaurus'' species from the Tendaguru Formation would have shared its habitat with many species of sauropod
Sauropoda (), whose members are known as sauropods (; from '' sauro-'' + '' -pod'', 'lizard-footed'), is a clade of saurischian ('lizard-hipped') dinosaurs. Sauropods had very long necks, long tails, small heads (relative to the rest of their b ...
s, such as ''Australodocus
''Australodocus'' (meaning "southern beam" from the Latin language, Latin ''australis'' "southern" and the Ancient Greek, Greek ''dokos''/δοκоς "beam") is a genus of sauropod dinosaur that lived during the Late Jurassic, Jurassic period, arou ...
'', ''Dicraeosaurus
''Dicraeosaurus'' (Gr. , ' "bifurcated, double-headed" + Gr. , ' "lizard") is a genus of diplodocoid sauropod dinosaur that lived in what is now Lindi Region, Tanzania during the late Jurassic period. The genus was named for the neural spines on ...
'', ''Giraffatitan
''Giraffatitan'' (name meaning "titanic giraffe") is a genus of sauropod dinosaur that lived during the late Jurassic Period (geology), Period (Kimmeridgian–Tithonian stages) in what is now Lindi Region, Tanzania. Only one species is known, ...
'', ''Janenschia
''Janenschia'' (named after Werner Janensch) is a large herbivorous sauropod dinosaur from the Late Jurassic Tendaguru Formation of Lindi Region, Tanzania around 155 million years ago.
Discovery and naming
''Janenschia'' has had a convoluted nom ...
'', ''Tornieria
''Tornieria'' ("for Gustav Tornier, Tornier") is a genus of diplodocid sauropod dinosaur from the Late Jurassic in Lindi Region of Tanzania. It has a convoluted taxonomy, taxonomic history.
Discovery and naming
In 1907, German paleontologist E ...
'', ''Wamweracaudia
''Wamweracaudia'' is a large herbivorous sauropod dinosaur from the Late Jurassic Tendaguru Formation of Tanzania, Africa, 155-145 million years ago.
Discovery and naming
During the German expeditions to the Tendaguru in German East Africa betwe ...
'', three unnamed species of diplodocine
Diplodocinae is an extinct subfamily of diplodocid sauropods that existed from the Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous of North America, Europe, Africa and South America, about 161.2 to 136.4 million years ago. Genera within the subfamily include ' ...
sauropods, an unnamed species of flagellicaudata
Diplodocoidea is a superfamily of sauropod dinosaurs, which included some of the longest animals of all time, including slender giants like '' Supersaurus'', ''Diplodocus'', ''Apatosaurus'', and ''Amphicoelias''. Most had very long necks and long ...
n, and "The Archbishop
"The Archbishop" is the third episode of the first series of the BBC sitcom ''Blackadder'' (''The Black Adder''). It is set in Kingdom of England, England in the late 15th century, and follows the exploits of the fictitious Prince Edmund (Blacka ...
". The theropods it coexisted with were '' Allosaurus tendagurensis'', '' Ceratosaurus roechlingi'', ''Elaphrosaurus
''Elaphrosaurus'' ( ) is a genus of ceratosaurian Theropoda, theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 154 to 150 million years ago during the Late Jurassic, Late Jurassic Period in what is now Tanzania in Africa. ''Elaphrosaurus'' was a medium- ...
'', '' Labrosaurus stechowi'', ''Ostafrikasaurus
''Ostafrikasaurus'' is a potentially nomen dubium, dubious genus of theropod dinosaur from the Late Jurassic Period (geologic time), period of what is now Lindi Region, Tanzania. It is known only from fossil teeth discovered sometime between 1909 ...
'', '' Veterupristisaurus'' (of which it would have possibly competed with to be top predator), a possible abelisauroid, and an indeterminate megalosauroid
Megalosauroidea (meaning 'great/big lizard forms') is a Taxonomic rank, superfamily (or clade) of Tetanurae, tetanuran theropod dinosaurs that lived from the Middle Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous period. The group is defined as ''Megalosaurus, M ...
, while the ornithischian
Ornithischia () is an extinct clade of mainly herbivorous dinosaurs characterized by a pelvic structure superficially similar to that of birds. The name ''Ornithischia'', or "bird-hipped", reflects this similarity and is derived from the Greek st ...
s it coexisted with were '' Dysalotosaurus'' and ''Kentrosaurus
''Kentrosaurus'' ( ; ) is a genus of stegosaurid dinosaur from the Late Jurassic in Lindi Region of Tanzania. The type species is ''K. aethiopicus'', named and described by German people, German Palaeontology, palaeontologist Edwin Hennig in 191 ...
''. As far as pterosaurs are concerned, it coexisted with '' Tendaguripterus'', an indeterminate archaeopterodactyloid, an indeterminate azhdarchid
Azhdarchidae (from the Persian word , , a dragon-like creature in Persian mythology) is a family of pterosaurs known primarily from the Late Cretaceous Period, though an isolated vertebra apparently from an azhdarchid is known from the Early Cre ...
, two indeterminate dsungaripteroids, an indeterminate rhamphorynchoid, and an indeterminate pterosaur of unknown classification. Due to the coastal environment of the Tendaguru Formation, crocodyliformes
Crocodyliformes is a clade of crurotarsan archosaurs, the group often traditionally referred to as "crocodilians". They are the first members of Crocodylomorpha to possess many of the features that define later relatives. They are the only pseu ...
, such as ''Bernissartia
''Bernissartia'' ('of Bernissart') is an extinct genus of neosuchian crocodyliform that lived in the Early Cretaceous, around 130 million years ago.
At only in length, ''Bernissartia'' is one of the smallest crocodyliforms that ever lived. It ...
'', amphibians
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excl ...
, including an unnamed lissamphibia
The Lissamphibia (from Greek λισσός (lissós, "smooth") + ἀμφίβια (amphíbia), meaning "smooth amphibians") is a group of tetrapods that includes all modern amphibians. Lissamphibians consist of three living groups: the Salientia ( ...
n, and shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch cartilaginous fish characterized by a ribless endoskeleton, dermal denticles, five to seven gill slits on each side, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the ...
s are also present.
Fauna and habitat in South America
Within South America, possible ''Torvosaurus'' remains are only present within theTacuarembó Formation
The Tacuarembó Formation is a Late Jurassic (Kimmeridgian
In the geologic timescale, the Kimmeridgian is an age in the Late Jurassic Epoch and a stage in the Upper Jurassic Series. It spans the time between 154.8 ±0.8 Ma and 149.2 ±0.7 Ma ...
of Uruguay. Because the formation was laid down in fluvial
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of its course if it ru ...
to lacustrine
A lake is often a naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on or near the Earth's surface. It is localized in a basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from t ...
sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sand ...
s, siltstone
Siltstone, also known as aleurolite, is a clastic sedimentary rock that is composed mostly of silt. It is a form of mudrock with a low clay mineral content, which can be distinguished from shale by its lack of fissility.
Although its permeabil ...
s, and mudstone
Mudstone, a type of mudrock, is a fine-grained sedimentary rock whose original constituents were clays or muds. Mudstone is distinguished from ''shale'' by its lack of fissility.Blatt, H., and R.J. Tracy, 1996, ''Petrology.'' New York, New York, ...
s, this indicates that the environment of the formation would have been dominated by river
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside Subterranean river, caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of ...
s, streams
A stream is a continuous body of surface water flowing within the bed and banks of a channel. Depending on its location or certain characteristics, a stream may be referred to by a variety of local or regional names. Long, large stream ...
, and lakes
A lake is often a naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on or near the Earth's surface. It is localized in a basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from t ...
.
If present, ''Torvosaurus'' would probably have been the apex predator
An apex predator, also known as a top predator or superpredator, is a predator at the top of a food chain, without natural predators of its own.
Apex predators are usually defined in terms of trophic dynamics, meaning that they occupy the hig ...
in the Tacuarembó Formation, although it may have been rivalled by ''cf.
The abbreviation cf. (short for either Latin or , both meaning 'compare') is generally used in writing to refer the reader to other material to make a comparison with the topic being discussed. However some sources offer differing or even contr ...
Ceratosaurus
''Ceratosaurus'' (from Greek 'horn' and 'lizard') is a genus of carnivorous theropod dinosaur that lived in the Late Jurassic period (Kimmeridgian to Tithonian ages). The genus was first described in 1884 by American paleontologist Othni ...
''. It shared its habitat with two unnamed theropod
Theropoda (; from ancient Greek , (''therion'') "wild beast"; , (''pous, podos'') "foot"">wiktionary:ποδός"> (''pous, podos'') "foot" is one of the three major groups (clades) of dinosaurs, alongside Ornithischia and Sauropodom ...
s, an unnamed coelurosaur
Coelurosauria (; from Greek, meaning "hollow-tailed lizards") is the clade containing all theropod dinosaurs more closely related to birds than to carnosaurs.
Coelurosauria is a subgroup of theropod dinosaurs that includes compsognathids, ty ...
, an unnamed sauropod
Sauropoda (), whose members are known as sauropods (; from '' sauro-'' + '' -pod'', 'lizard-footed'), is a clade of saurischian ('lizard-hipped') dinosaurs. Sauropods had very long necks, long tails, small heads (relative to the rest of their b ...
known solely from footprints, an unnamed ornithopod
Ornithopoda () is a clade of ornithischian dinosaurs, called ornithopods (). They represent one of the most successful groups of herbivorous dinosaurs during the Cretaceous. The most primitive members of the group were bipedal and relatively sm ...
also known from footprints, an indeterminate mesoeucrocodylia
Mesoeucrocodylia is the clade that includes Eusuchia and crocodyliforms formerly placed in the paraphyletic group Mesosuchia. The group appeared during the Early Jurassic, and continues to the present day.
Diagnosis
It was long known that Me ...
n, an indeterminate turtle
Turtles are reptiles of the order (biology), order Testudines, characterized by a special turtle shell, shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Crypt ...
species that lived alongside the named turtle species '' Tacuarembemys kusterae'', and the possible pholidosaur '' Meridiosaurus vallisparadisi''. Fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
, such as '' Arganodus tiguidiensis'', '' Asiatoceratodus cf. tiguidensis'', '' Neoceratodus africanus'', and '' Priohybodus arambourgi'', and bivalves
Bivalvia () or bivalves, in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class of aquatic molluscs (marine and freshwater) that have laterally compressed soft bodies enclosed by a calcified exoskeleton consis ...
, such as '' Diplodon'', are also present.
Coexistence with other large carnivores
''Torvosaurus'' coexisted with other large theropods such as ''Allosaurus
''Allosaurus'' ( ) is an extinct genus of theropod dinosaur that lived 155 to 145 million years ago during the Late Jurassic period ( Kimmeridgian to late Tithonian ages). The first fossil remains that could definitively be ascribed to th ...
'' and ''Ceratosaurus
''Ceratosaurus'' (from Greek 'horn' and 'lizard') is a genus of carnivorous theropod dinosaur that lived in the Late Jurassic period (Kimmeridgian to Tithonian ages). The genus was first described in 1884 by American paleontologist Othni ...
'' in the United States and Portugal, possibly '' Veterupristisaurus'' in Tanzania, and possibly ''cf.
The abbreviation cf. (short for either Latin or , both meaning 'compare') is generally used in writing to refer the reader to other material to make a comparison with the topic being discussed. However some sources offer differing or even contr ...
Ceratosaurus (?)'' in Uruguay. The three, possibly four, species appear to have had different ecological niche
In ecology, a niche is the match of a species to a specific environmental condition.
Three variants of ecological niche are described by
It describes how an organism or population responds to the distribution of Resource (biology), resources an ...
s, based on anatomy and the location of fossils. ''Torvosaurus'' and ''Ceratosaurus'' may have preferred to be active around waterways and had lower, more sinuous, bodies that would have given them an advantage in forest and underbrush terrains, whereas ''Allosaurus'' had shorter bodies, longer legs, were faster and less maneuverable, and seem to have preferred dry floodplains. Also, Rauhut et al. (2016) proposed that allosaurids and megalosaurids would have had different environmental preferences, the former being more common in inland areas, while the latter being dominant in marine and coastal environments.
On the other hand, the majority of ''Torvosaurus'' remains from the Morrison Formation have been found in localities preserving multiple taxa, including ''Allosaurus,'' with ''Torvosaurus'' itself being a minor component of the bonebeds. This pattern has been interpreted as indicative of ''Torvosaurus'' sharing habitats with other predators, most notably ''Allosaurus'', but at much lower abundances. The three may also have had different dietary preferences, with ''Allosaurus'' being more suited for bone slicing (thanks to its short and stout serrated teeth, deep and narrow skull, and powerful dorsoventral movement capacity of the neck), while ''Ceratosaurus,'' with its long and blade-like teeth and relatively straight neck, would have probably been incapable of doing so, instead concentrating on the deepest organs of a carcass. While probably capable of some bone consumption, ''Torvosaurus,'' with its large skull and teeth and large, powerful, and lithe body may have been specialized in opening up and dismembering exceptionally large sauropod carcasses. This would have allowed smaller theropods, like ''Allosaurus'', better access in a possible commensalism
Commensalism is a long-term biological interaction (symbiosis) in which members of one species gain benefits while those of the other species neither benefit nor are harmed. This is in contrast with mutualism, in which both organisms benefit fr ...
relationship.
''Allosaurus'' was itself a potential food item to other carnivores, as illustrated by an ''Allosaurus'' pubic foot marked by the teeth of another theropod, probably ''Ceratosaurus'' or ''Torvosaurus''. The location of the bone in the body (along the bottom margin of the torso and partially shielded by the legs) and the fact that it was among the most massive in the skeleton indicates that the ''Allosaurus'' was being scavenged.
Allosaurus
''Allosaurus'' ( ) is an extinct genus of theropod dinosaur that lived 155 to 145 million years ago during the Late Jurassic period ( Kimmeridgian to late Tithonian ages). The first fossil remains that could definitively be ascribed to th ...
'' and ''Mymoorapelta
''Mymoorapelta'' (Meaning "Shield from the Mygatt-Moore Quarry" after a combination of the names of the discoverers of the Mygatt-Moore Quarry that fossils were originally collected from, and the Greek word πέλτα, meaning "shield") is a Nod ...
'' remains were found among other bones with feeding traces in the Upper Jurassic Mygatt-Moore Quarry. Unlike the others, these have left striations that, when measured to determine denticle width, produced tooth and body size extrapolations greater than any known specimen of ''Allosaurus'' or ''Ceratosaurus
''Ceratosaurus'' (from Greek 'horn' and 'lizard') is a genus of carnivorous theropod dinosaur that lived in the Late Jurassic period (Kimmeridgian to Tithonian ages). The genus was first described in 1884 by American paleontologist Othni ...
'', the two large predators known for osteological remains from the quarry. The extrapolations are instead coherent, either with an unusually large specimen of ''Allosaurus'' or a separate large taxon like ''Torvosaurus'' which is not known from the quarry. The result either increases the known diversity of the site based on ichnological evidence alone or represents powerful evidence of cannibalism in ''Allosaurus''. Based on the position and nutrient value associated with the various skeletal elements with bite marks, it is predicted that while ''Mymoorapelta'' was either predated upon or scavenged shortly after death, ''Allosaurus'' was scavenged some time after death.
References
External links
''Largest Predatory Dinosaur in Europe Found'' at nationalgeographic
{{Taxonbar, from=Q131537 Megalosauridae Dinosaur genera Jurassic dinosaurs Morrison Formation Lourinhã Formation Taxa named by Peter Galton Taxa named by James A. Jensen Fossil taxa described in 1979 Dinosaurs of the United States Dinosaurs of Portugal