
A sustainable food system is a type of
food system that provides
healthy food to people and creates
sustainable
Sustainability is a social goal for people to co-exist on Earth over a long period of time. Definitions of this term are disputed and have varied with literature, context, and time. Sustainability usually has three dimensions (or pillars): env ...
environmental, economic, and social systems that surround food. Sustainable food systems start with the development of
sustainable agricultural practices, development of more
sustainable food distribution systems, creation of
sustainable diets, and reduction of
food waste
The causes of food going uneaten are numerous and occur throughout the food system, during food production, production, food processing, processing, Food distribution, distribution, Grocery store, retail and food service sales, and Social clas ...
throughout the system. Sustainable food systems have been argued to be central to many or all
17 Sustainable Development Goals.
Moving to sustainable food systems, including via
shifting consumption to sustainable diets, is an important component of
addressing the
causes of climate change and
adapting to it. A 2020 review conducted for the European Union found that up to 37% of global greenhouse gas emissions could be attributed to the food system, including crop and livestock production, transportation, changing land use (including deforestation), and food loss and waste. Reduction of meat production, which
accounts for ~60% of greenhouse gas emissions and ~75% of agriculturally used land, is one major component of this change.
The
global
Global may refer to:
General
*Globe, a spherical model of celestial bodies
*Earth, the third planet from the Sun
Entertainment
* ''Global'' (Paul van Dyk album), 2003
* ''Global'' (Bunji Garlin album), 2007
* ''Global'' (Humanoid album), 198 ...
food
system
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its open system (systems theory), environment, is described by its boundaries, str ...
is facing major
interconnected challenges, including mitigating
food insecurity,
effects from climate change,
biodiversity loss
Biodiversity loss happens when plant or animal species disappear completely from Earth (extinction) or when there is a decrease or disappearance of species in a specific area. Biodiversity loss means that there is a reduction in Biodiversity, b ...
,
malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
, inequity,
soil degradation
Soil retrogression and degradation are two regressive evolution processes associated with the loss of equilibrium of a soil health, stable soil. Retrogression is primarily due to soil erosion and corresponds to a phenomenon where succession revert ...
,
pest outbreaks,
water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
and energy scarcity, economic and political crises,
natural resource depletion, and preventable ill-health.
The concept of sustainable food systems is frequently at the center of sustainability-focused policy programs, such as proposed
Green New Deal programs.
Definition
There are many different definitions of a sustainable food system.
From a global perspective, the
Food and Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; . (FAO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition and food security. Its Latin motto, , translates ...
of the United Nations describes a sustainable food system as follows:

The
American Public Health Association
The American Public Health Association (APHA) is a Washington, D.C.–based professional membership and advocacy organization for public health professionals in the United States. APHA is the largest professional organization of public health pr ...
(APHA) defines a sustainable food system as:
The
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
's
Scientific Advice Mechanism
The Scientific Advice Mechanism is a service created by the European Commission which provides independent science advice on request directly to European Commissioners.
The Mechanism consists of three parts: the Group of Chief Scientific Adviso ...
defines a sustainable food system as a system that:
Problems with conventional food systems
Industrial agriculture causes environmental impacts, as well as health problems associated with both
obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi ...
and
hunger
In politics, humanitarian aid, and the social sciences, hunger is defined as a condition in which a person does not have the physical or financial capability to eat sufficient food to meet basic nutritional needs for a sustained period. In t ...
.
This has generated a strong interest in healthy, sustainable eating as a major component of the overall movement toward
sustainability
Sustainability is a social goal for people to co-exist on Earth over a long period of time. Definitions of this term are disputed and have varied with literature, context, and time. Sustainability usually has three dimensions (or pillars): env ...
and
climate change mitigation
Climate change mitigation (or decarbonisation) is action to limit the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that cause climate change. Climate change mitigation actions include energy conservation, conserving energy and Fossil fuel phase-out, repl ...
.
Conventional food systems are largely based on the availability of inexpensive
fossil fuels
A fossil fuel is a flammable carbon compound- or hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the buried remains of prehistoric organisms (animals, plants or microplanktons), a process that occurs within geologica ...
, which is necessary for
mechanized agriculture, the manufacturing or collection of chemical
fertilizers
A fertilizer or fertiliser is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrition, plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from Liming (soil), liming materials or other non- ...
, the processing of food products, and the packaging of foods. Food processing began when the number of consumers started growing rapidly. The demand for cheap and efficient calories climbed, which resulted in nutrition decline. Since more than two billion people are suffering from malnutrition, in 2017, more than 11 million deaths were environmental malnutrition. In fact, during the last 50 - 70 years, environmental, genetic, and field soil dilution factors have decreased the nutritional density of fruits like apples, oranges, bananas, mangos, and vegetables like tomatoes and potatoes by 25-50%. Industrialized agriculture, due to its reliance on economies of scale to reduce production costs, often leads to the compromising of local, regional, or even global
ecosystems
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
through fertilizer runoff,
nonpoint source pollution,
deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal and destruction of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. Ab ...
, suboptimal mechanisms affecting
consumer product choice, and
greenhouse gas emissions.
Food and power
In the contemporary world, transnational corporations execute high levels of control over the food system. In this system, both farmers and consumers are disadvantaged and have little control; power is concentrated in the center of the supply chain, where corporations control how food moves from producers to consumers.
Disempowerment of consumers
People living in different areas face substantial inequality in their access to healthy food. Areas where affordable, healthy food, particularly fresh fruits and vegetables, is difficult to access are sometimes called
food deserts. This term has been particularly applied in the USA. In addition, conventional channels do not distribute food by emergency assistance or charity. Urban residents receive more sustainable food production from healthier and safer sources than low-income communities. Nonetheless, conventional channels are more sustainable than charitable or welfare food resources. Even though the
conventional food system provides easier access and lower prices, their food may not be the best for the environment nor consumer health.
People who live in food deserts are currently being overfed with fast food and ultra-processed foods, yet remain undernourished because they are consuming nutrient-poor diets. Both obesity and undernutrition are associated with poverty and marginalization. This has been referred to as the "double burden of malnutrition." In low-income areas, there may be abundant access to fast-food or small convenience stores and "corner" stores, but no supermarkets that sell a variety of healthy foods.
Disempowerment of producers
Small farms tend to be more sustainable than large farming operations, because of differences in their management and methods. Industrial agriculture replaces human labor using increased usage of fossil fuels, fertilizers, pesticides, and machinery and is heavily reliant on
monoculture
In agriculture, monoculture is the practice of growing one crop species in a field at a time. Monocultures increase ease and efficiency in planting, managing, and harvesting crops short-term, often with the help of machinery. However, monocultur ...
. However, if current trends continue, the number of operating farms in existence is expected to halve by 2100, as smallholders' farms are consolidated into larger operations. The percentage of people who work as farmers worldwide dropped from 44% to 26% between 1991 and 2020.
Small farmers worldwide are often trapped in poverty and have little agency in the global food system. Smallholder farms produce a greater diversity of crops as well as harboring more non-crop biodiversity, but in wealthy, industrialized countries, small farms have declined severely. For example, in the USA, 4% of the total number of farms operate 26% of all agricultural land.
Complications from globalization
The need to reduce production costs in an increasingly global market can cause production of foods to be moved to areas where economic costs (labor, taxes, etc.) are lower or environmental regulations are more lax, which are usually further from consumer markets. For example, the majority of salmon sold in the United States is raised off the coast of Chile, due in large part to less stringent Chilean standards regarding fish feed and regardless of the fact that salmon are not indigenous in Chilean coastal waters. The globalization of food production can result in the loss of traditional food systems in
less developed countries and have negative impacts on the
population health, ecosystems, and
cultures
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
in those countries.
Globalization of sustainable food systems has coincided the proliferation of
private standards in the agri-food sector where big food retailers have formed
multi-stakeholder initiatives (MSIs) with governance over
standard setting organizations (SSOs) who maintain the standards. One such MSI is the
Consumer Goods Forum(CGF). With CGF members openly using
lobbying
Lobbying is a form of advocacy, which lawfully attempts to directly influence legislators or government officials, such as regulatory agency, regulatory agencies or judiciary. Lobbying involves direct, face-to-face contact and is carried out by va ...
dollars to influence trade agreements for food systems which leads to creating barriers to competition. Concerns around corporate governance within food systems as a substitute for regulation were raised by the Institute for Multi-Stakeholder Initiative Integrity. The proliferation of
private standards resulted in
standard harmonization from organizations that include the
Global Food Safety Initiative
The Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI) is a private organization that works as a "coalition of action" from the Consumer Goods Forum (CGF) and brings together retailers and brand owners (manufacturers) from across the CGF membership. The GFSI ...
and
ISEAL Alliance. The unintended consequence of
standard harmonization was a
perverse incentive
The phrase "perverse incentive" is often used in economics to describe an incentive structure with undesirable results, particularly when those effects are unexpected and contrary to the intentions of its designers.
The results of a perverse in ...
because companies owning
private standards generate revenue from fees that other companies have to pay to implement the standards. This has led to more and more private standards entering the marketplace who are enticed to make money.
Systemic structures
Moreover, the existing conventional food system lacks the inherent framework necessary to foster sustainable models of food production and consumption. Within the decision-making processes associated with this system, the burden of responsibility primarily falls on consumers and private enterprises. This expectation places the onus on individuals to voluntarily and often without external incentives, expend effort to educate themselves about sustainable behaviours and specific product choices. This educational endeavour is reliant on the availability of public information. Subsequently, consumers are urged to alter their decision-making patterns concerning production and consumption, driven by prioritised ethical values and sometimes health benefits, even when significant drawbacks are prevalent. These drawbacks faced by consumers include elevated costs of
organic food
Organic food, also known as ecological or biological food, refers to foods and beverages produced using methods that comply with the standards of organic farming. Standards vary worldwide, but organic farming features practices that cycle resou ...
s, imbalanced monetary price differentials between animal-intensive diets and plant-based alternatives, and an absence of comprehensive consumer guidance aligned with contemporary valuations. In 2020, an analysis of
external climate costs of foods indicated that external greenhouse gas costs are typically
highest for animal-based products – conventional and organic to about the same extent within that
ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
subdomain – followed by conventional dairy products and lowest for
organic plant-based foods. It finds contemporary monetary evaluations to be "inadequate" and
policy
Policy is a deliberate system of guidelines to guide decisions and achieve rational outcomes. A policy is a statement of intent and is implemented as a procedure or protocol. Policies are generally adopted by a governance body within an or ...
-making that lead to reductions of these costs to be possible, appropriate and urgent.
Agricultural pollution
Sourcing sustainable food
At the global level the environmental impact of
agribusiness
Agribusiness is the industry, enterprises, and the field of study of value chains in agriculture and in the bio-economy,
in which case it is also called bio-business or bio-enterprise.
The primary goal of agribusiness is to maximize profit ...
is being addressed through
sustainable agriculture
Sustainable agriculture is agriculture, farming in sustainability, sustainable ways meeting society's present food and textile needs, without compromising the ability for current or future generations to meet their needs. It can be based on an ...
,
cellular agriculture and
organic farming
Organic farming, also known as organic agriculture or ecological farming or biological farming,Labelling, article 30 o''Regulation (EU) 2018/848 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 May 2024 on organic production and labelling of ...
.
Various alternatives to meat and novel classes of foods can substantially increase sustainability. There are large potential benefits of
marine algae-based aquaculture for the development of a future
healthy and sustainable food system.
Fungiculture
Fungiculture is the cultivation of fungi such as mushrooms. Cultivating fungi can yield foods (which include mostly mushrooms), medicine, construction materials and other products. A ''mushroom farm'' is involved in the business of growing fu ...
, another sector of a growing
bioeconomy besides algaculture, may also become a larger component of a sustainable food system. Consumption shares of various other ingredients for meat analogues such as protein from pulses may also rise substantially in a sustainable food system. The integration of
single-cell protein, which can be produced from captured CO
2.
Optimized dietary scenarios would also see changes in various other types of foods such as nuts, as well as pulses such as beans, which have favorable environmental and
health
Health has a variety of definitions, which have been used for different purposes over time. In general, it refers to physical and emotional well-being, especially that associated with normal functioning of the human body, absent of disease, p ...
profiles.
Complementary approaches under development include
vertical farming
Vertical farming is the practice of growing crops in vertically and horizontally stacked layers. It often incorporates controlled-environment agriculture, which aims to optimize plant growth, and soilless farming techniques such as hydroponics ...
of various types of foods and various agricultural technologies, often using
digital agriculture.
Sustainable seafood
Sustainable seafood is seafood from either fished or farmed sources that can maintain or increase production in the future without jeopardizing the ecosystems from which it was acquired. The sustainable seafood movement has gained momentum as more people become aware about both
overfishing
Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish (i.e. fishing) from a body of water at a rate greater than that the species can replenish its population naturally (i.e. the overexploitation of the fishery's existing Fish stocks, fish stock), resu ...
and environmentally destructive fishing methods. The goal of sustainable seafood practices is to ensure that
fish populations are able to continue to thrive, that marine habitats are protected, and that
fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment (Freshwater ecosystem, freshwater or Marine ecosystem, marine), but may also be caught from Fish stocking, stocked Body of water, ...
and aquaculture practices do not have negative impacts on local communities or economies.
There are several factors that go into determining whether a seafood product is sustainable or not. These include the method of
fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment (Freshwater ecosystem, freshwater or Marine ecosystem, marine), but may also be caught from Fish stocking, stocked Body of water, ...
or
farming
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
, the health of the fish population, the impact on the surrounding environment, and the social and economic implications of the seafood production. Some sustainable seafood practices include using methods that minimize
bycatch
Bycatch (or by-catch), in the fishing industry, is a fish or other marine species that is caught unintentionally while fishing for specific species or sizes of wildlife. Bycatch is either the wrong species, the wrong sex, or is undersized or juve ...
, implementing
season
A season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. On Earth, seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's axial tilt, tilted orbit around the Sun. In temperat ...
al or area closures to allow fish populations to recover, and using aquaculture methods that minimize the use of antibiotics or other chemicals. Organizations such as the
Marine Stewardship Council
The Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) is a non-profit organisation which aims to set standards for sustainable fishing. Fisheries that wish to demonstrate they are well-managed and sustainable compared to the MSC's standards are assessed by a tea ...
(MSC) and the
Aquaculture Stewardship Council
The Aquaculture Stewardship Council (ASC) is an independent non-profit organisation and labelling organization that establishes protocol on farmed seafood while ensuring sustainable aquaculture. The ASC provides producers with a certification of ...
(ASC) work to promote sustainable seafood practices and provide certification for products that meet their sustainability standards. In addition, many retailers and restaurants are now offering sustainable seafood options to their customers, often labeled with a sustainability certification logo to make it easier for consumers to make informed choices. Consumers can also play a role in promoting sustainable seafood by making conscious choices about the seafood they purchase and consume. This can include choosing seafood that is labeled as sustainably harvested or farmed, asking questions about the source and production methods of the seafood they purchase, and supporting restaurants and retailers that prioritize sustainability in their seafood offerings. By working together to promote sustainable seafood practices, we can help to ensure the health and sustainability of our oceans and the communities that depend on them.
Sustainable animal feed
A study suggests there would be large environmental benefits of using
insects
Insects (from Latin ') are hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs of jointed ...
for
animal feed
Animal feed is food given to domestic animals, especially livestock, in the course of animal husbandry. There are two basic types: fodder and forage. Used alone, the word ''feed'' more often refers to fodder. Animal feed is an important input ...
.When substituting mixed grain, which is currently the main animal feed, insect feed lowers water and land requirement and emits fewer greenhouse gas and ammonia.
Sustainable pet food
Recent studies show that vegan diets, which are more sustainable, would not have negative impact on the health of
pet dogs and cats if implemented appropriately. It aims to minimize the
ecological footprint
The ecological footprint measures human demand on natural capital, i.e. the quantity of nature it takes to support people and their economies. It tracks human demand on nature through an ecological accounting system. The accounts contrast the biolo ...
of pet food production while still providing the necessary nutrition for pets. Recent studies have explored the potential benefits of vegan diets for pets in terms of sustainability.
One example is the growing body of research indicating that properly formulated and balanced vegan diets can meet the nutritional needs of dogs and cats without compromising their health. These studies suggest that with appropriate planning and supplementation, pets can thrive on
plant-based diet
A plant-based diet is a diet consisting mostly or entirely of plant-based foods. It encompasses a wide range of dietary patterns that contain low amounts of animal products and high amounts of fiber-rich plant products such as vegetables ...
s. This is significant from a sustainability perspective as traditional pet food production heavily relies on animal-based ingredients, which contribute to
deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal and destruction of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. Ab ...
,
greenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide (), from burning fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate chan ...
, and
overfishing
Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish (i.e. fishing) from a body of water at a rate greater than that the species can replenish its population naturally (i.e. the overexploitation of the fishery's existing Fish stocks, fish stock), resu ...
.
By opting for sustainable pet food options, such as plant-based or
eco-friendly alternatives, pet owners can reduce their pets'
carbon footprint
A carbon footprint (or greenhouse gas footprint) is a calculated value or index that makes it possible to compare the total amount of greenhouse gases that an activity, product, company or country Greenhouse gas emissions, adds to the atmospher ...
and support more ethical and sustainable practices in the pet food industry. Additionally, sustainable pet food may also prioritize the use of responsibly sourced ingredients, organic farming practices, and minimal
packaging waste. It is important to note that when considering a vegan or alternative diet for pets, consultation with a veterinarian is crucial. Each pet has unique nutritional requirements, and a professional can help determine the most suitable diet plan to ensure all necessary nutrients are provided.
Substitution of meat and sustainable meat and dairy
Meat reduction strategies
Effects and combination of measures
"
Policy sequencing" to gradually extend regulations once established to other forest risk commodities (e.g. other than beef) and regions while coordinating with other importing countries could prevent ineffectiveness.
Meat and dairy
Despite meat from livestock such as beef and lamb being considered unsustainable, some
regenerative agriculture proponents suggest rearing livestock with a mixed farming system to restore organic matter in grasslands. Organizations such as the Canadian Roundtable for Sustainable Beef (CRSB) are looking for solutions to reduce the impact of meat production on the environment. In October 2021, 17% of beef sold in Canada was certified as sustainable beef by the CRSB. However, sustainable meat has led to criticism, as environmentalists point out that the
meat industry
The meat industry are the people and companies engaged in modern industrialized livestock agriculture for the production, packing, preservation and marketing of meat (in contrast to dairy products, wool, etc.). In economics, the meat industry is ...
excludes most of its emissions.
Important mitigation options for reducing the greenhouse gas emissions from livestock include genetic selection, introduction of
methanotrophic bacteria into the rumen, vaccines, feeds, toilet-training, diet modification and grazing management. Other options include shifting to
ruminant
Ruminants are herbivorous grazing or browsing artiodactyls belonging to the suborder Ruminantia that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through microb ...
-free alternatives, such as
milk substitute
A milk substitute is any substance that resembles milk and can be used in the same ways as milk. Such substances may be variously known as non-dairy beverage, nut milk, grain milk, legume milk, mock milk and alternative milk.
For adults, milk s ...
s and
meat analogues or poultry, which generates far fewer emissions.
Plant-based meat is proposed for sustainable alternatives to meat consumption.
Plant-based meat emits 30%–90% less greenhouse gas than conventional meat (kg--eq/kg-meat) and 72%–99% less water than conventional meat. Public company
Beyond Meat and privately held company
Impossible Foods are examples of plant-based food production. However, consulting firm
Sustainalytics
Sustainalytics is a company that rates the sustainability of listed companies based on their environmental, social and corporate governance (ESG) performance. The company was born of a merger between Toronto-based Jantzi Research, which was found ...
assured that these companies are not more sustainable than meat-processors competitors such as food processor
JBS, and they don't disclose all the emissions of their supply chain.
Beyond reducing negative impacts of meat production, facilitating shifts towards more sustainable meat, and facilitating reduced meat consumption (including via plant-based meat substitutes),
cultured meat
Cultured meat, also known as cultivated meat among other names, is a form of cellular agriculture wherein meat is produced by culturing animal cells ''in vitro''; thus growing animal flesh, molecularly identical to that of conventional meat, ou ...
may offer a potentially sustainable way to produce real meat without the associated negative environmental impacts.
Phase-outs, co-optimization and environmental standards

In regards to
deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal and destruction of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. Ab ...
, a study proposed kinds of "climate clubs" of "as many other states as possible taking similar measures and establishing uniform environmental standards". It suggested that "otherwise, global problems remain unsolvable, and shifting effects will occur" and that "border adjustments
..have to be introduced to target those states that do not participate—again, to avoid shifting effects with ecologically and economically detrimental consequences", with such "border adjustments or
eco-tariffs" incentivizing other countries to adjust their standards and domestic production to join the climate club. Identified potential barriers to sustainability initiatives may include contemporary trade-policy goals and
competition law
Competition law is the field of law that promotes or seeks to maintain market competition by regulating anti-competitive conduct by companies. Competition law is implemented through public and private enforcement. It is also known as antitrust ...
.
Greenhouse gas emissions for countries are often measured according to production, for imported goods that are produced in other countries than where they are consumed "
embedded emissions" refers to the emissions of the product. In cases where such products are and remain imported, eco-tariffs could over time adjust prices for specific categories of products – or for specific non-collaborative polluting origin countries – such as deforestation-associated meat, foods with intransparent supply-chain origin or foods with high embedded emissions.
Agricultural productivity and environmental efficiency
Agricultural productivity (including e.g. reliability of yields) is an important component of
food security
Food security is the state of having reliable access to a sufficient quantity of affordable, healthy Human food, food. The availability of food for people of any class, gender, ethnicity, or religion is another element of food protection. Simila ...
and increasing it sustainably (e.g. with high efficiency in terms of environmental impacts) could be a major way to decrease negative environmental impacts, such as by decreasing the amount of land needed for farming or reducing
environmental degradation
Environment most often refers to:
__NOTOC__
* Natural environment, referring respectively to all living and non-living things occurring naturally and the physical and biological factors along with their chemical interactions that affect an organism ...
like
deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal and destruction of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. Ab ...
.
Genetically engineered crops
There is research and development to engineer
genetically modified crops
Genetically modified crops (GM crops) are plants used in agriculture, the DNA of which has been modified using genetic engineering methods. Plant genomes can be engineered by physical methods or by use of '' Agrobacterium'' for the delivery of ...
with increased heat/drought/stress resistance, increased yields, lower water requirements, and overall lower environmental impacts, among other things.
Novel agricultural technologies
Organic food

Local food systems
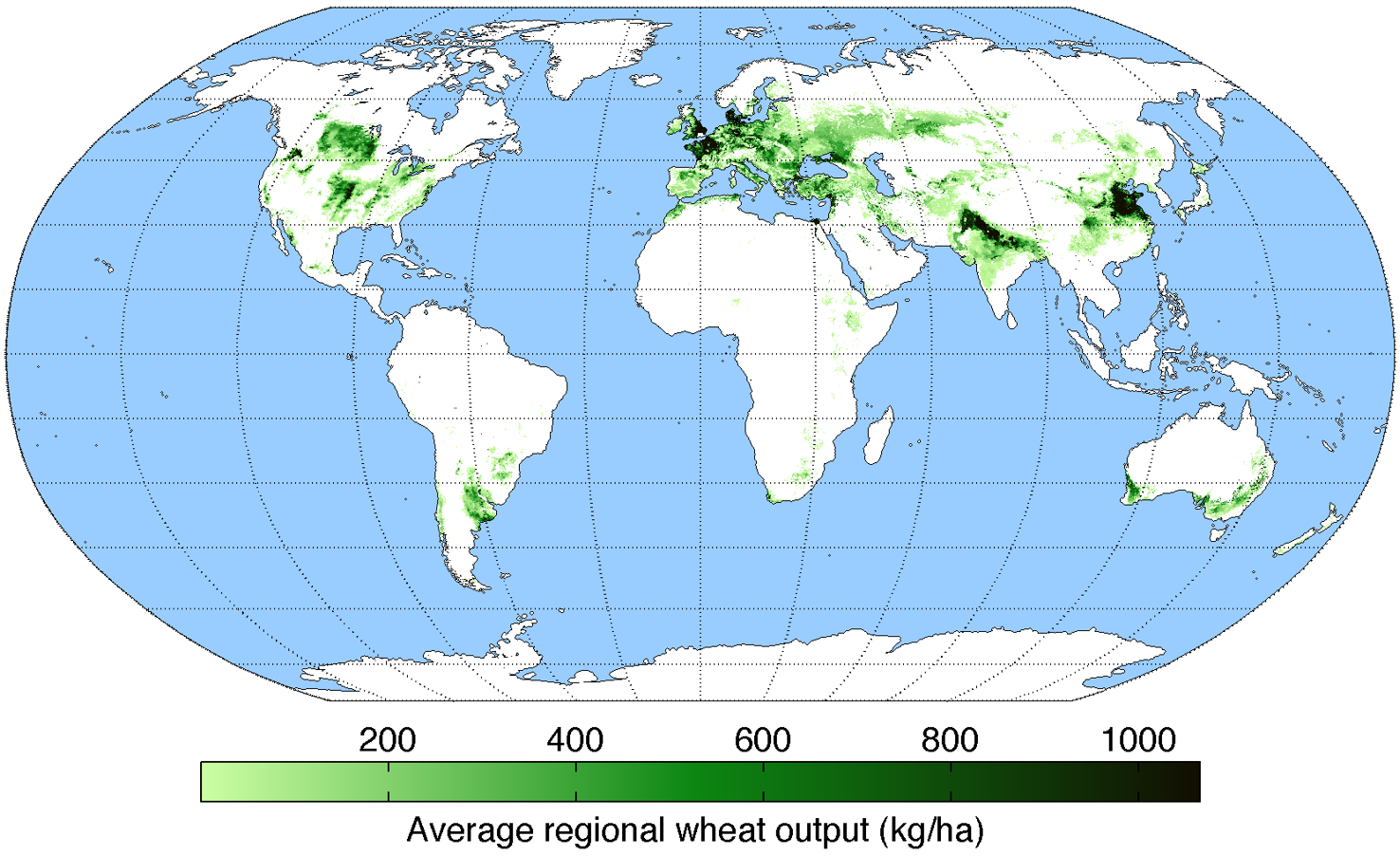
In
local and regional food systems, food is produced, distributed, and consumed locally. This type of system can be beneficial both to the consumer (by providing fresher and more sustainably grown product) and to the farmer (by fetching higher prices and giving more direct access to consumer feedback).
[O'Hara, Jeffrey K. "Description of Local Food Systems." Union of Concerned Scientists, 2011, pp. 6–13] Local and regional food systems can face challenges arising from inadequate institutions or programs, geographic limitations of producing certain crops, and seasonal fluctuations which can affect product demand within regions. In addition,
direct marketing
Direct marketing is a form of communicating an offer, where organizations communicate directly to a Target market, pre-selected customer and supply a method for a direct response. Among practitioners, it is also known as ''direct response ...
also faces challenges of accessibility, coordination, and awareness.
s, which have increased in number over the past two decades, are designed for supporting local farmers in selling their fresh products to consumers who are willing to buy.
Food hubs are also similar locations where farmers deliver products and consumers come to pick them up. Consumers who wish to have weekly produce delivered can buy shares through a system called
Community-Supported Agriculture
Community-supported agriculture (CSA model) or cropsharing is a system that connects producers and consumers within the food system closer by allowing the consumer to subscribe to the harvest of a certain farm or group of farms. It is an altern ...
(CSA).
However, these farmers' markets also face challenges with marketing needs such as starting up, advertisement, payments, processing, and regulations.
There are various movements working towards local food production, more productive use of urban wastelands and domestic gardens including
permaculture
Permaculture is an approach to land management and settlement design that adopts arrangements observed in flourishing natural ecosystems. It includes a set of design principles derived using Systems theory, whole-systems thinking. It applies t ...
,
guerilla gardening,
urban horticulture,
local food
Local food is food that is produced within a short distance of where it is consumed, often accompanied by a social structure and supply chain different from the large-scale supermarket Food system, system.
Local food (or locavore) movements ...
,
slow food,
sustainable gardening, and
organic gardening
Organic horticulture is the science and art of growing fruits, vegetables, flowers, or ornamental plants by following the essential principles of organic agriculture in soil building and conservation, pest management, and heirloom variety pres ...
.
Debates over local food system efficiency and sustainability have risen as these systems decrease transportation, which is a strategy for combating
environmental footprints and
climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
. A popular argument is that the less impactful footprint of food products from local markets on communities and environment.
Main factors behind climate change include land use practices and greenhouse emissions, as global food systems produce approximately 33% of theses emissions.
Compared to transportation in a local food system, a conventional system takes more fuel for energy and emits more pollution, such as carbon dioxide. This transportation also includes miles for agricultural products to help with agriculture and depends on factors such as transportation sizes, modes, and fuel types. Some airplane importations have shown to be more efficient than local food systems in some cases.
Overall, local food systems can often support better environmental practices.
Environmental impact of food miles
Studies found that
food miles are a relatively minor factor of carbon emissions; albeit increased food localization may also enable additional, more significant environmental benefits such as recycling of energy, water, and nutrients. For specific foods, regional differences in harvest seasons may make it more environmentally friendly to import from distant regions than more local production and storage or local production in greenhouses. This may vary depending on the environmental standards in the respective country, the distance of the respective countries and on a case-by-case basis for different foods.
However, a 2022 study suggests global food miles' emissions are 3.5–7.5 times higher than previously estimated, with transport accounting for about 19% of total food-system emissions,
though shifting towards plant-based diets remains substantially more important. The study concludes that "a shift towards plant-based foods must be coupled with more locally produced items, mainly in affluent countries".
Food distribution
In
food distribution
Food distribution is the process where a general population is supplied with food. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) considers food distribution as a subset of the Food systems, food system. The process and methodology behind food distri ...
, increasing food supply is a production problem, as it takes time for products to get marketed, and as they wait to get distributed the food goes to waste. Despite the fact that throughout all
food production an estimated 20-30% of food is wasted, there have been efforts to combat this issue, such as campaigns conducted to promote limiting food waste.
[Kling, William. "Food Waste in Distribution and Use." Journal of Farm Economics, vol. 25, no. 4, 1943, pp. 848–859.] However, due to insufficient facilities and practices as well as huge amounts of food going unmarketed or harvested due to prices or quality, food is wasted through each phase of its distribution.
Another factor for lack of sustainability within food distribution includes transportation in combination with inadequate methods for
food handling throughout the packing process. Additionally, poor or long conditions for food in storage and consumer waste add to this list of factors for inefficiency found in food distribution.
In 2019, though global production of calories kept pace with population growth, there are still more than 820 million people who have insufficient food and many more consume low-quality diets leading to micronutrient deficiencies.
Some modern tendencies in food distribution also create bounds in which problems are created and solutions must be formed. One factor includes growth of large-scale producing and selling units in bulk to
chain store
A chain store or retail chain is a retail outlet in which several locations share a brand, central management and standardized business practices. They have come to dominate many retail markets, dining markets, and service categories in many p ...
s which displays merchandising power from large scale market organizations as well as their mergence with
manufactures
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of the
secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer ...
.
[Pelz, V. H. "Modern Tendencies in Food Distribution." Journal of Farm Economics, vol. 12, no. 2, 1930, pp. 301–310.] In response to production, another factor includes large scale distribution and buying units among manufacturers in development of food distribution, which also affects producers, distributors, and consumers.
Another main factor involves protecting
public interest
In social science and economics, public interest is "the welfare or well-being of the general public" and society. While it has earlier philosophical roots and is considered to be at the core of democratic theories of government, often paired ...
, which means better adaptation for product and service, resulting in rapid development of food distribution.
A further factor revolves around
price maintenance, which creates pressure for lower prices, resulting in higher drive for lower cost throughout the whole food distribution process.
An additional factor comprises new changes and forms of newly invented technical processes such as developments of freezing food, discovered through experiments, to help with distribution efficiency. Another factor is new technical developments in distributing machinery to meet the influence of
consumer demand
In economics, demand is the quantity of a good that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices during a given time. In economics "demand" for a commodity is not the same thing as "desire" for it. It refers to both the desire to p ...
s and economic factors.
Lastly, one more factor includes government relation to businesses and those who petition against it in correlation with anti-trust laws due to large scale business organizations and the fear of monopoly contributing to changing public attitude.
Food security, nutrition and diet
The environmental effects of different dietary patterns depend on many factors, including the proportion of animal and plant foods consumed and the method of food production. At the same time, current and future food systems need to be provided with sufficient nutrition for not only the current population, but future population growth in light of a world affected by changing climate in the face of
global warming
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes ...
.
Nearly one in four households in the United States have experienced food insecurity in 2020–21. Even before the pandemic hit, some 13.7 million households, or 10.5% of all U.S. households, experienced food insecurity at some point during 2019, according to data from the U.S. Department of Agriculture. That works out to more than 35 million Americans who were either unable to acquire enough food to meet their needs, or uncertain of where their next meal might come from, last year.
The "global land squeeze" for agricultural land also has impacts on food security. Likewise,
effects of climate change on agriculture
There are numerous effects of climate change on agriculture, many of which are making it harder for agricultural activities to provide global food security. Rising temperatures and changing weather patterns often result in lower crop yields du ...
can result in lower crop yields and nutritional quality due to for example
drought
A drought is a period of drier-than-normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, ...
,
heat wave
A heat wave or heatwave, sometimes described as extreme heat, is a period of abnormally hot weather generally considered to be at least ''five consecutive days''. A heat wave is usually measured relative to the usual climate in the area and ...
s and
flood
A flood is an overflow of water (list of non-water floods, or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are of significant con ...
ing as well as increases in
water scarcity
Water scarcity (closely related to water stress or water crisis) is the lack of fresh water resources to meet the standard water demand. There are two types of water scarcity. One is ''physical.'' The other is ''economic water scarcity''. Physic ...
,
pests
PESTS was an anonymous American activist group formed in 1986 to critique racism, tokenism, and exclusion in the art world. PESTS produced newsletters, posters, and other print material highlighting examples of discrimination in gallery represent ...
and
plant diseases.
Soil conservation
Soil conservation is the prevention of loss of the topmost layer of the soil from erosion or prevention of reduced fertility caused by over usage, Soil acidification, acidification, salinization or other chemical soil contamination
Slash-and-b ...
may be important for food security as well. For sustainability and food security, the food system would need to adapt to such current and future problems.
According to one estimate, "just four corporations control 90% of the global
grain trade
The grain trade refers to the local and international trade in cereals such as wheat, barley, maize, rice, and other food grains. Grain is an important trade item because it is easily stored and transported with limited spoilage, unlike other agri ...
" and researchers have argued that the food system is too fragile due to various issues, such as "massive food producers" (i.e. market-mechanisms) having too much power and
nation
A nation is a type of social organization where a collective Identity (social science), identity, a national identity, has emerged from a combination of shared features across a given population, such as language, history, ethnicity, culture, t ...
s "polarising into super-importers and super-exporters". However the impact of market power on the food system is contested with other claiming more complex context dependent outcomes.
Production decision-making
In the food industry, especially in agriculture, there has been a rise in problems toward the production of some food products. For instance, growing vegetables and fruits has become more expensive. It is difficult to grow some agricultural crops because some have a preferable climate condition for developing. There has also been an incline on food shortages as production has decreased. Though the world still produces enough food for the population, not everyone receives good quality food because it is not accessible to them, since it depends on their location and/or income. In addition, the number of overweight people has increased, and there are about 2 billion people that are underfed worldwide. This shows how the global food system lacks quantity and quality according to the
food consumption patterns.
A study estimated that "relocating current croplands to
nvironmentally optimal locations, whilst allowing ecosystems in then-abandoned areas to regenerate, could simultaneously decrease the current carbon, biodiversity, and irrigation water footprint of global crop production by 71%, 87%, and 100%", with relocation only within national borders also having substantial potential.
Policies, including ones that affect consumption, may affect production-decisions such as which foods are produced to various degrees and in various indirect and direct ways. Individual studies have named several proposed options of such
and the restricted website
Project Drawdown has aggregated and preliminarily evaluated some of these measures.
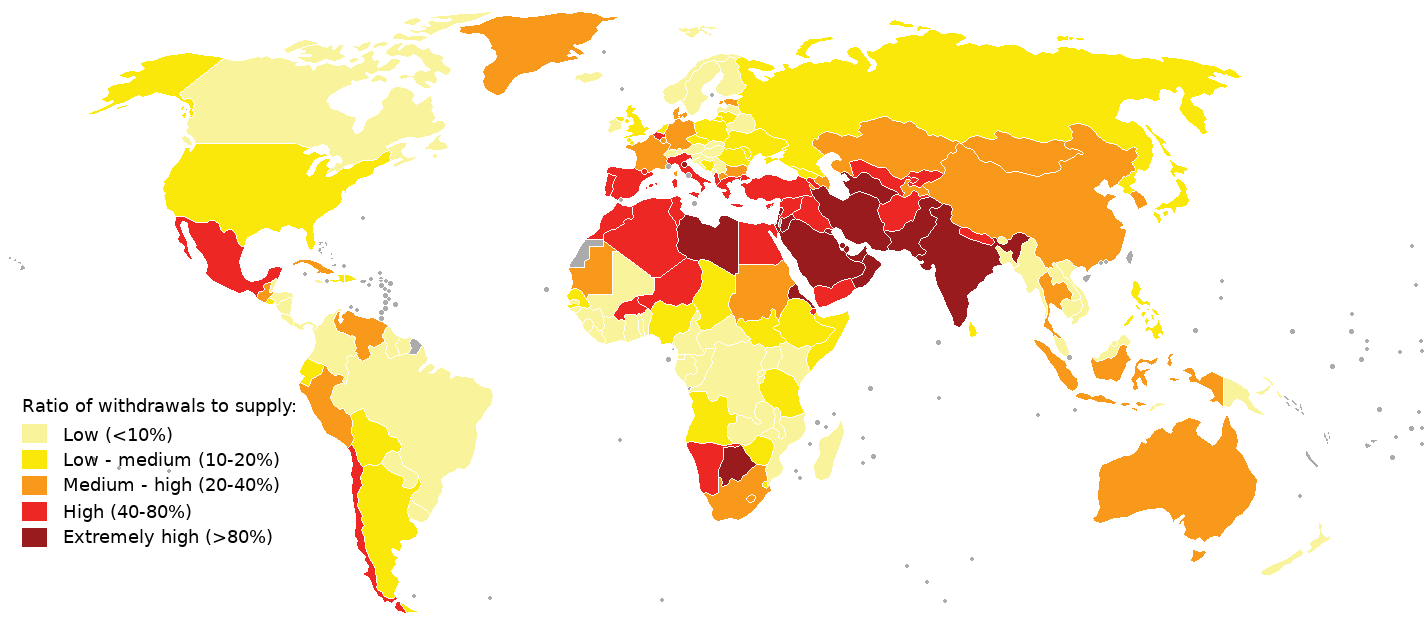
Climate change adaptation
Food waste
According to the
Food and Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; . (FAO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition and food security. Its Latin motto, , translates ...
(FAO), food waste is responsible for 8 percent of global human-made
greenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide (), from burning fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate chan ...
. The FAO concludes that nearly 30 percent of all available agricultural land in the world – 1.4 billion hectares – is used for produced but uneaten food. The global blue
water footprint of food waste is 250 km
3, the amount of water that flows annually through the
Volga
The Volga (, ) is the longest river in Europe and the longest endorheic basin river in the world. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchment ...
or three times
Lake Geneva
Lake Geneva is a deep lake on the north side of the Alps, shared between Switzerland and France. It is one of the List of largest lakes of Europe, largest lakes in Western Europe and the largest on the course of the Rhône. Sixty percent () ...
.
There are several factors that explain how
food waste
The causes of food going uneaten are numerous and occur throughout the food system, during food production, production, food processing, processing, Food distribution, distribution, Grocery store, retail and food service sales, and Social clas ...
has increased globally in food systems. The main factor is population, because as population increases more food is being made, but most food produced goes to waste. Especially, during COVID-19, food waste grew sharply due to the booming of food delivery services according to
2022 study In addition, not all countries have the same resources to provide the best quality of food. According to a study done in 2010, private households produce the largest amounts of food waste across the globe. Another major factor is overproduction; the rate of food production is significantly higher than the rate of consumption, leading to a surplus of food waste.
Throughout the world there are different ways that food is being processed. With different priorities, different choices are being made to meet their most important needs. Money is another big factor that determines how long the process will take and who is working, and it is treated differently in low income countries' food systems.
However, high income countries food systems still may deal with other issues such as
food security
Food security is the state of having reliable access to a sufficient quantity of affordable, healthy Human food, food. The availability of food for people of any class, gender, ethnicity, or religion is another element of food protection. Simila ...
. This demonstrates how all food systems have their weaknesses and strengths.
Climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
causes food waste to increase because the warm temperature causes crops to dry faster and creates a higher risk for fires. Food waste can occur any time throughout production. According to the ''World Wildlife Organization'', since most food produced goes to landfills, when it rots it causes methane to be produced. The
disposal of food has a big impact on our environment and health.
Academic Opportunities
The study of sustainable food applies
systems theory
Systems theory is the Transdisciplinarity, transdisciplinary study of systems, i.e. cohesive groups of interrelated, interdependent components that can be natural or artificial. Every system has causal boundaries, is influenced by its context, de ...
and methods of
sustainable design
Environmentally sustainable design (also called environmentally conscious design, eco-design, etc.) is the philosophy of designing physical objects, the built environment, and services to comply with the principles of ecological sustainability ...
towards
food systems
The term food system describes the interconnected systems and processes that influence nutrition, food, health, community development, and agriculture. A food system includes all processes and infrastructure involved in feeding a population: grow ...
. As an interdisciplinary field, the study of sustainable food systems has been growing in the last several decades. University programs focused on sustainable food systems include:
*
University of Colorado Boulder
The University of Colorado Boulder (CU Boulder, CU, or Colorado) is a public research university in Boulder, Colorado, United States. Founded in 1876, five months before Colorado became a state, it is the flagship university of the University o ...
*
Harvard
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher lear ...
Extension
*
University of Delaware
The University of Delaware (colloquially known as UD, UDel, or Delaware) is a Statutory college#Delaware, privately governed, state-assisted Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Newark, Delaware, United States. UD offers f ...
* Mesa Community College
*
University of California, Davis
The University of California, Davis (UC Davis, UCD, or Davis) is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Davis, California, United States. It is the northernmost of the ten campuses of the University ...
*
University of Vermont
The University of Vermont and State Agricultural College, commonly referred to as the University of Vermont (UVM), is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Burlington, Vermont, United States. Foun ...
*
Sterling College (Vermont)
*
University of Michigan
The University of Michigan (U-M, U of M, or Michigan) is a public university, public research university in Ann Arbor, Michigan, United States. Founded in 1817, it is the oldest institution of higher education in the state. The University of Mi ...
*
Portland State University
Portland State University (PSU) is a public research university in Portland, Oregon, United States. It was founded in 1946 as a post-secondary educational institution for World War II veterans. It evolved into a four-year college over the next ...
*
University of Sheffield
The University of Sheffield (informally Sheffield University or TUOS) is a public university, public research university in Sheffield, South Yorkshire, England. Its history traces back to the foundation of Sheffield Medical School in 1828, Fir ...
's Institute for Sustainable Food
*
University of Georgia
The University of Georgia (UGA or Georgia) is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university with its main campus in Athens, Georgia, United States. Chartered in 1785, it is the oldest public university in th ...
's Sustainable Food Systems Initiative
*
The Culinary Institute of America
The Culinary Institute of America (CIA) is a Private university, private culinary school with its main campus in Hyde Park, New York, and branch campuses in St. Helena, California, St. Helena and Napa, California; San Antonio, Texas; and Singa ...
's Master's in Sustainable Food Systems
*
University of Edinburgh
The University of Edinburgh (, ; abbreviated as ''Edin.'' in Post-nominal letters, post-nominals) is a Public university, public research university based in Edinburgh, Scotland. Founded by the City of Edinburgh Council, town council under th ...
's Global Academy of Agriculture and Food Systems
There is a debate about "establishing a body akin to the
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is an intergovernmental body of the United Nations. Its job is to "provide governments at all levels with scientific information that they can use to develop climate policies". The World Met ...
(IPCC) for food systems" which "would respond to questions from policymakers and produce advice based on a synthesis of the available evidence" while identifying "
gaps in the science that need addressing".
Public policy
European Union
Global
Asia
See also
*
Hemp juice
Hemp juice is a beverage derived from industrial hemp, made from the result of pressing the ''Cannabis sativa'' plant. The juice is obtained through a large-scale industrial Cold-pressed juice, cold-pressing procedure using the upper parts of ...
*
Standardization#Environmental protection
References
Cited sources
*
Further reading
{{Environmental technology
Food politics
Sustainability
 The
The  In regards to
In regards to 
 In local and regional food systems, food is produced, distributed, and consumed locally. This type of system can be beneficial both to the consumer (by providing fresher and more sustainably grown product) and to the farmer (by fetching higher prices and giving more direct access to consumer feedback).O'Hara, Jeffrey K. "Description of Local Food Systems." Union of Concerned Scientists, 2011, pp. 6–13 Local and regional food systems can face challenges arising from inadequate institutions or programs, geographic limitations of producing certain crops, and seasonal fluctuations which can affect product demand within regions. In addition,
In local and regional food systems, food is produced, distributed, and consumed locally. This type of system can be beneficial both to the consumer (by providing fresher and more sustainably grown product) and to the farmer (by fetching higher prices and giving more direct access to consumer feedback).O'Hara, Jeffrey K. "Description of Local Food Systems." Union of Concerned Scientists, 2011, pp. 6–13 Local and regional food systems can face challenges arising from inadequate institutions or programs, geographic limitations of producing certain crops, and seasonal fluctuations which can affect product demand within regions. In addition, 