|
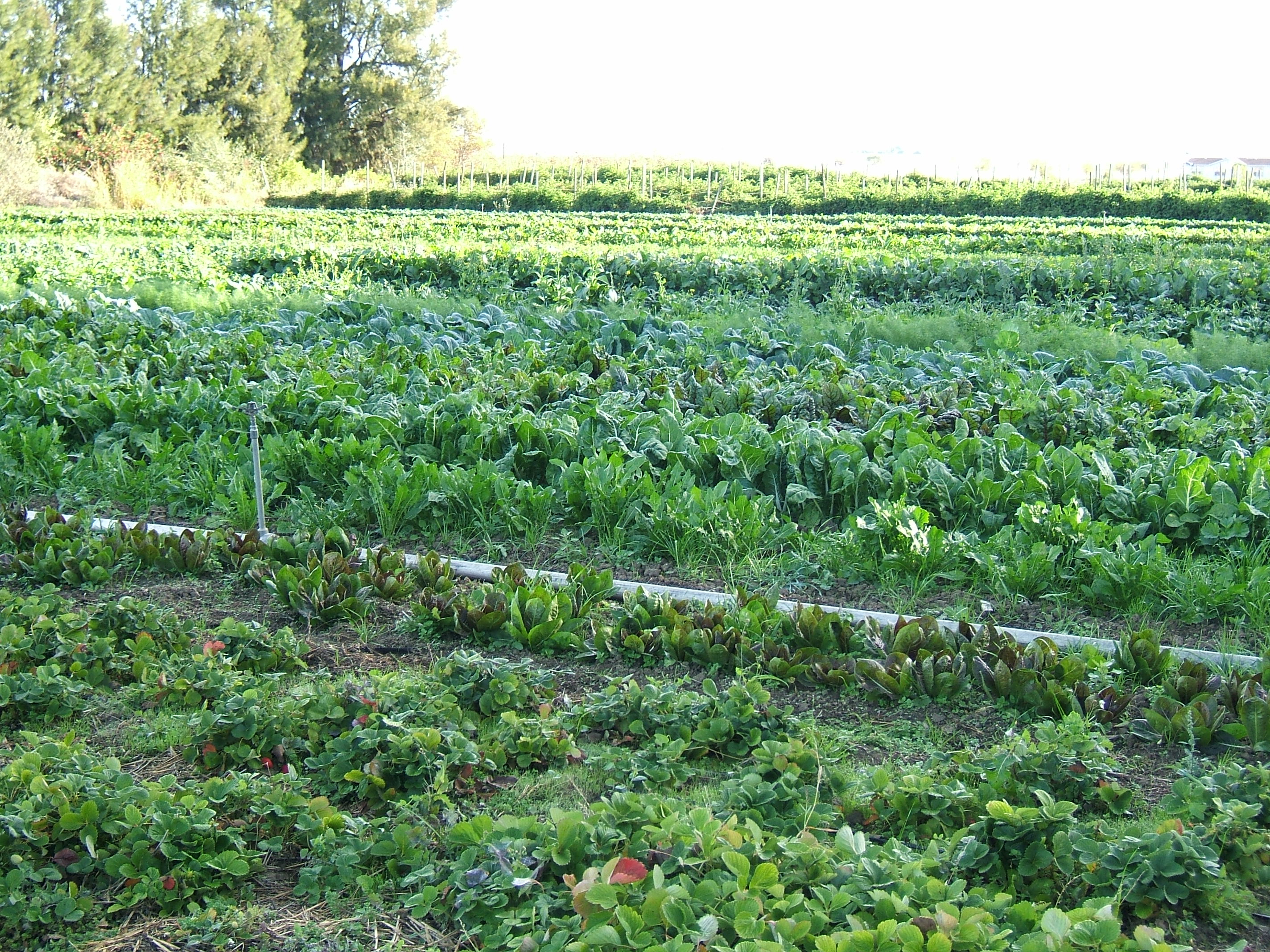
Organic Farming
Organic farming, also known as organic agriculture or ecological farming or biological farming,Labelling, article 30 o''Regulation (EU) 2018/848 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 May 2024 on organic production and labelling of organic products and repealing Council Regulation (EC) No 834/2007.''/ref> is an agricultural system that emphasizes the use of naturally occurring, non-synthetic inputs, such as compost manure, green manure, and bone meal and places emphasis on techniques such as crop rotation, companion planting, and mixed cropping. Biological pest control methods such as the fostering of insect predators are also encouraged. Organic agriculture can be defined as "an integrated farming system that strives for sustainability, the enhancement of soil fertility and biological diversity while, with rare exceptions, prohibiting synthetic pesticides, antibiotics, synthetic fertilizers, genetically modified organisms, and growth hormones". It originate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manure
Manure is organic matter that is used as organic fertilizer in agriculture. Most manure consists of animal feces; other sources include compost and green manure. Manures contribute to the fertility of soil by adding organic matter and nutrients, such as nitrogen, that are utilised by bacteria, fungi, and other organisms in the soil. Higher organisms then feed on the fungi and bacteria in a chain of life that comprises the soil food web. Types There are in the 21st century three main classes of manures used in soil management: Animal manure Most animal manure consists of feces. Common forms of animal manure include farmyard manure (or farm slurry ( liquid manure). Farmyard manure also contains plant material (often straw), which has been used as bedding for animals and has absorbed the feces and urine. Agricultural manure in liquid form, known as slurry, is produced by more intensive livestock rearing systems where concrete or slats are used instead of straw bedding. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrysanthemum
Chrysanthemums ( ), sometimes called mums or chrysanths, are flowering plants in the Asteraceae family. They are native to East Asia and northeastern Europe. Most species originate from East Asia, and the center of diversity is in China. Countless horticultural varieties and cultivars exist. Description The genus ''Chrysanthemum'' are perennial herbaceous flowering plants, sometimes subshrubs. The leaves are alternate, divided into leaflets and may be pinnatisect, lobed, or serrate (toothed) but rarely entire; they are connected to stalks with hairy bases. The compound inflorescence is an array of several flower heads, or sometimes a solitary head. The head has a base covered in layers of phyllaries. The simple row of ray florets is white, yellow, or red. The disc florets are yellow. Pollen grains are approximately 34 microns. The fruit is a ribbed achene. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific American
''Scientific American'', informally abbreviated ''SciAm'' or sometimes ''SA'', is an American popular science magazine. Many scientists, including Albert Einstein and Nikola Tesla, have contributed articles to it, with more than 150 Nobel Prize-winners being featured since its inception. In print since 1845, it is the oldest continuously published magazine in the United States. ''Scientific American'' is owned by Springer Nature, which is a subsidiary of Holtzbrinck Publishing Group. History ''Scientific American'' was founded by inventor and publisher Rufus Porter (painter), Rufus Porter in 1845 as a four-page weekly newspaper. The first issue of the large-format New York City newspaper was released on August 28, 1845. Throughout its early years, much emphasis was placed on reports of what was going on at the United States Patent and Trademark Office, U.S. Patent Office. It also reported on a broad range of inventions including perpetual motion machines, an 1860 devi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic Use In Livestock
The use of antibiotics in the husbandry of livestock includes treatment when ill (therapeutic), treatment of a group of animals when at least one is diagnosed with clinical infection (metaphylaxis), and preventative treatment (prophylaxis). Antibiotics are an important tool to treat animal as well as human disease, safeguard animal health and welfare, and support food safety. However, used irresponsibly, this may lead to antibiotic resistance which may impact human, animal and environmental health. While levels of use vary dramatically from country to country, for example some Northern European countries use very low quantities to treat animals compared with humans, worldwide an estimated 73% of antimicrobials (mainly antibiotics) are consumed by farm animals. Furthermore, a 2015 study also estimates that global agricultural antibiotic usage will increase by 67% from 2010 to 2030, mainly from increases in use in developing BRIC countries. Increased antibiotic use is a matter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hormone
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required for the normal development of animals, plants and fungi. Due to the broad definition of a hormone (as a signaling molecule that exerts its effects far from its site of production), numerous kinds of molecules can be classified as hormones. Among the substances that can be considered hormones, are eicosanoids (e.g. prostaglandins and thromboxanes), steroids (e.g. Estrogen, oestrogen and brassinosteroid), amino acid derivatives (e.g. epinephrine and auxin), protein or peptides (e.g. insulin and CLE peptides), and gases (e.g. ethylene and nitric oxide). Hormones are used to communicate between organ (anatomy), organs and Tissue (biology), tissues. In vertebrates, hormones are responsible for regulating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Growth Regulator
Plant hormones (or phytohormones) are signal molecules, produced within plants, that occur in extremely low concentrations. Plant hormones control all aspects of plant growth and development, including embryogenesis, the regulation of organ size, pathogen defense, stress tolerance and reproductive development. Unlike in animals (in which hormone production is restricted to specialized glands) each plant cell is capable of producing hormones. Went and Thimann coined the term "phytohormone" and used it in the title of their 1937 book. Phytohormones occur across the plant kingdom, and even in algae, where they have similar functions to those seen in vascular plants ("higher plants"). Some phytohormones also occur in microorganisms, such as unicellular fungi and bacteria, however in these cases they do not play a hormonal role and can better be regarded as secondary metabolites. Characteristics The word hormone is derived from Greek, meaning ''set in motion''. Plant hormon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sewage Sludge
Sewage sludge is the residual, semi-solid material that is produced as a by-product during sewage treatment of industrial or municipal wastewater. The term "septage" also refers to sludge from simple wastewater treatment but is connected to simple on-site sanitation systems, such as septic tanks. After treatment, and dependent upon the quality of sludge produced (for example with regards to heavy metal content), sewage sludge is most commonly either disposed of in landfills, dumped in the ocean or applied to land for its fertilizing properties, as pioneered by the product Milorganite. The term " Biosolids" is often used as an alternative to the term sewage sludge in the United States, particularly in conjunction with reuse of sewage sludge as fertilizer after sewage sludge treatment. Biosolids can be defined as organic wastewater solids that can be reused after stabilization processes such as anaerobic digestion and composting. Opponents of sewage sludge reuse reject this t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
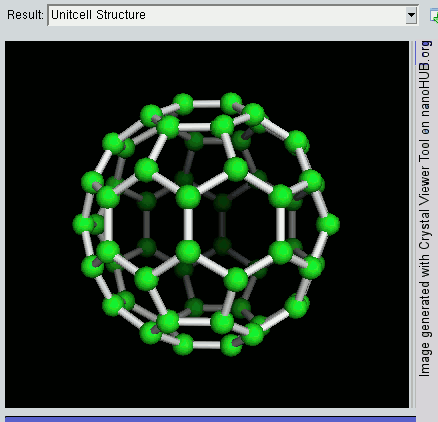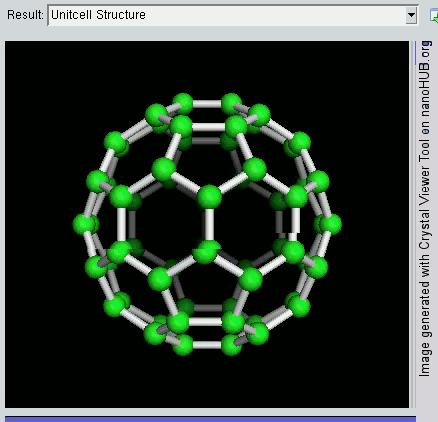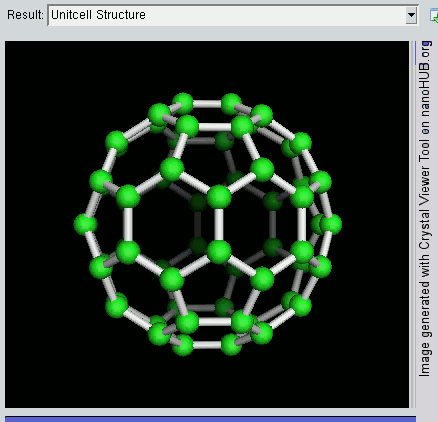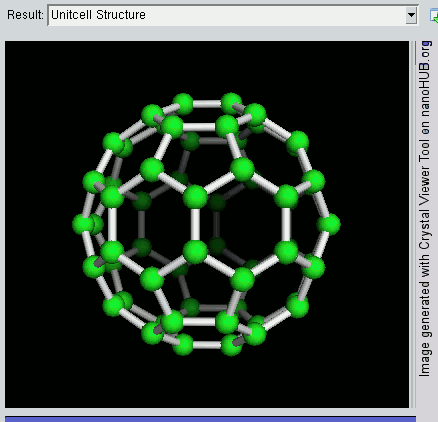
Nanomaterials
Nanomaterials describe, in principle, chemical substances or materials of which a single unit is sized (in at least one dimension) between 1 and 100 nm (the usual definition of nanoscale). Nanomaterials research takes a materials science-based approach to nanotechnology, leveraging advances in materials metrology and synthesis which have been developed in support of microfabrication research. Materials with structure at the nanoscale often have unique optical, electronic, thermo-physical or mechanical properties. Nanomaterials are slowly becoming commercialized and beginning to emerge as commodities. Definition In ISO/TS 80004, ''nanomaterial'' is defined as the "material with any external dimension in the nanoscale or having internal structure or surface structure in the nanoscale", with ''nanoscale'' defined as the "length range approximately from 1 nm to 100 nm". This includes both ''nano-objects'', which are discrete pieces of material, and ''nanostructu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetically Modified Organism
A genetically modified organism (GMO) is any organism whose genetic material has been altered using genetic engineering techniques. The exact definition of a genetically modified organism and what constitutes genetic engineering varies, with the most common being an organism altered in a way that "does not occur naturally by mating and/or natural Recombination (biology), recombination". A wide variety of organisms have been genetically modified (GM), including animals, plants, and microorganisms. Genetic modification can include the introduction of new genes or enhancing, altering, or Gene knockout, knocking out endogenous genes. In some genetic modifications, genes are transferred Cisgenesis, within the same species, across species (creating transgenic organisms), and even across Kingdom (biology), kingdoms. Creating a genetically modified organism is a multi-step process. Genetic engineers must isolate the gene they wish to insert into the host organism and combine it with o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veterinary Drug
An animal drug (also veterinary drug) refers to a drug intended for use in the diagnosis, cure, mitigation, treatment, or prevention of disease in animals. Regulation United States The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has the broad mandate under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (21 U.S.C. 321 et seq.) to assure the safety and effectiveness of animal drugs and their use in all animals, including farm animals. The division of the FDA responsible for this is the Center for Veterinary Medicine (CVM). The equivalents of the Investigational New Drug and New Drug Application are known as the Investigational New Animal Drug and New Animal Drug Application, respectively. The FDA enumerates veterinary drug approvals in the FDA Green Book. Drugs approved by the FDA for use in veterinary medicine are structurally similar to drugs approved for use in humans, owing to highly conserved physiology across species, and half of drugs approved for animals are separately approved fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur
Sulfur ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphur ( Commonwealth spelling) is a chemical element; it has symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with the chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystalline solid at room temperature. Sulfur is the tenth most abundant element by mass in the universe and the fifth most common on Earth. Though sometimes found in pure, native form, sulfur on Earth usually occurs as sulfide and sulfate minerals. Being abundant in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times, being mentioned for its uses in ancient India, ancient Greece, China, and ancient Egypt. Historically and in literature sulfur is also called brimstone, which means "burning stone". Almost all elemental sulfur is produced as a byproduct of removing sulfur-containing contaminants from natural gas and petroleum.. Downloahere Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper(II) Sulfate
Copper(II) sulfate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It forms hydrates , where ''n'' can range from 1 to 7. The pentahydrate (''n'' = 5), a bright blue crystal, is the most commonly encountered hydrate of copper(II) sulfate, while its anhydrous form is white. Older names for the pentahydrate include blue vitriol, bluestone, vitriol of copper,Antoine-François de Fourcroy, tr. by Robert Heron (1796) "Elements of Chemistry, and Natural History: To which is Prefixed the Philosophy of Chemistry". J. Murray and others, Edinburgh. Page 348. and Roman vitriol.Oxford University Press,Roman vitriol, Oxford Living Dictionaries. Accessed on 2016-11-13 It exothermically dissolves in water to give the aquo complex , which has octahedral molecular geometry. The structure of the solid pentahydrate reveals a polymeric structure wherein copper is again octahedral but bound to four water ligands. The centers are interconnected by sulfate anions to form chains. Preparation and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |