Rajasthan (other) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a
 The
The
 The
The
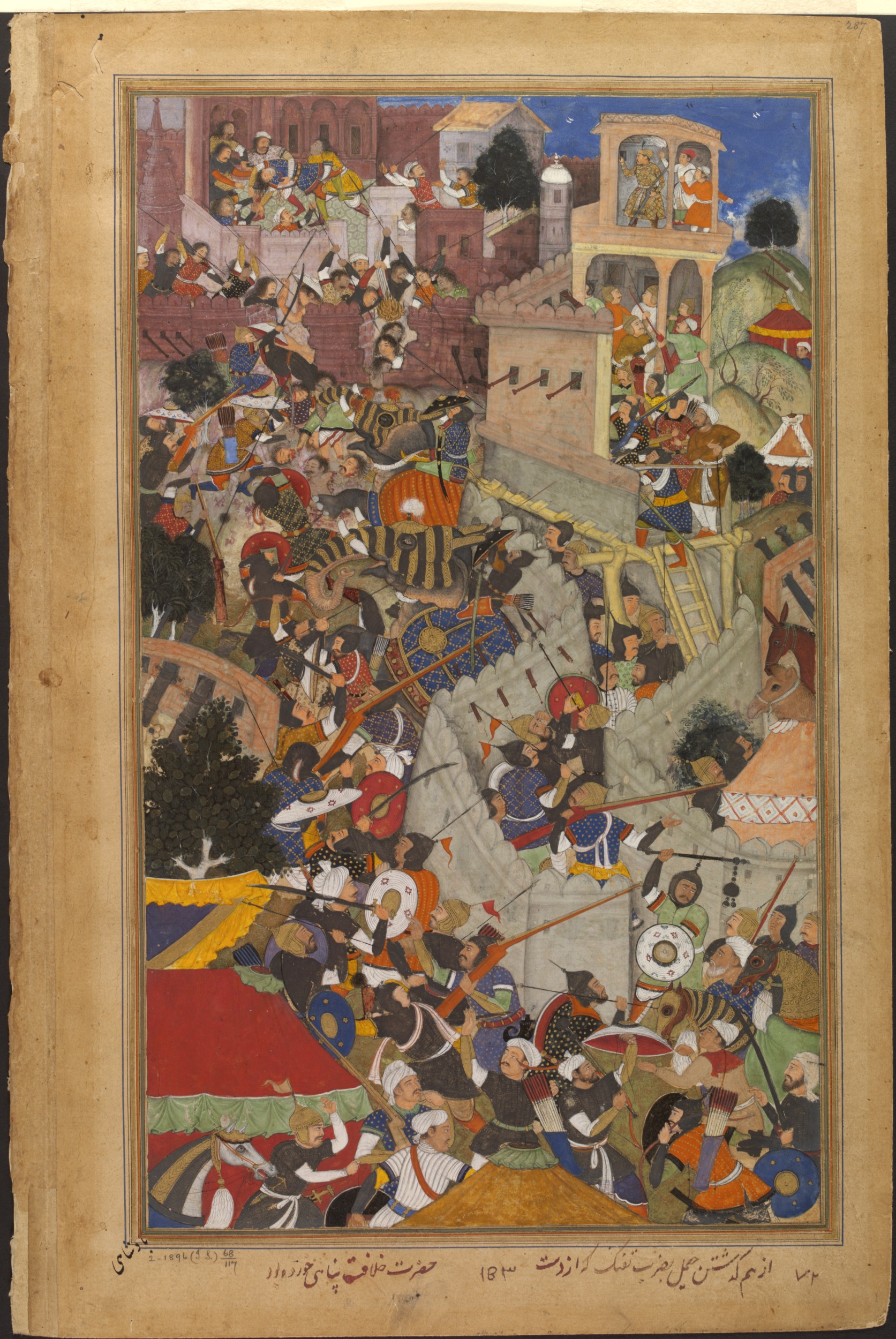 During
During
File:Maharana Kumbhakarna of Mewar.jpg,
 The Aravalli Range runs across the state from the southwest peak
The Aravalli Range runs across the state from the southwest peak
File:Mt. Abu.jpg,
 The
The
 The state is governed by a parliamentary system of representative democracy. The governor serves as the state's constitutional leader, whereas the
The state is governed by a parliamentary system of representative democracy. The governor serves as the state's constitutional leader, whereas the  Rajasthan has its High court Jodhpur which has its principal seat at
Rajasthan has its High court Jodhpur which has its principal seat at


 Rajasthan is composed of the following geographical, political and historical regions:
# Bagar
#
Rajasthan is composed of the following geographical, political and historical regions:
# Bagar
#
 The main industries are mineral based, agriculture-based, and
The main industries are mineral based, agriculture-based, and
File:Jaipur Airport.JPG,
 Rajasthani cooking was influenced by both the war-like lifestyles of its inhabitants and the availability of ingredients in this arid region. Food that could last for several days and could be eaten without heating was preferred. Thus, pickles of Rajasthan are quite famous for their tangy and spicy flavour. The ''Panchkuta'' delicacy is also a famous one – meaning 5 vegetables – a dish that lasts for several days, and is made out of certain weed plants that only grow in the wild desert. The scarcity of water and fresh green vegetables have all had their effect on cooking. It is known for its snacks like
Rajasthani cooking was influenced by both the war-like lifestyles of its inhabitants and the availability of ingredients in this arid region. Food that could last for several days and could be eaten without heating was preferred. Thus, pickles of Rajasthan are quite famous for their tangy and spicy flavour. The ''Panchkuta'' delicacy is also a famous one – meaning 5 vegetables – a dish that lasts for several days, and is made out of certain weed plants that only grow in the wild desert. The scarcity of water and fresh green vegetables have all had their effect on cooking. It is known for its snacks like 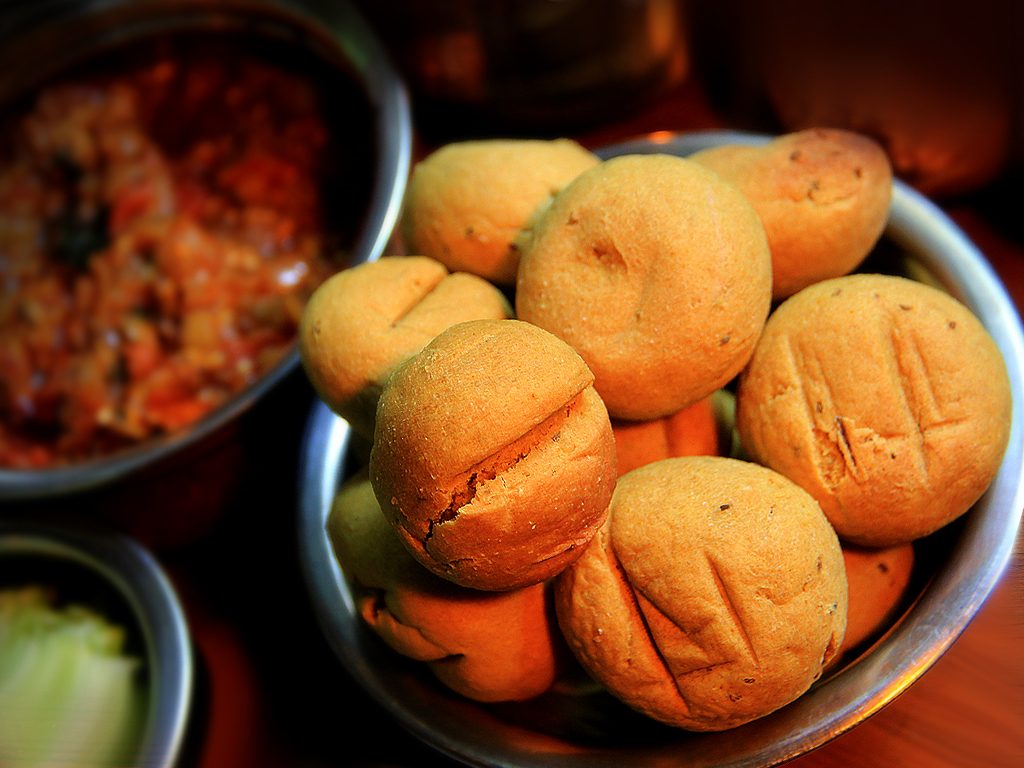 Dal-baati-churma is very popular in Rajasthan. The traditional way to serve it is to first coarsely mash the baati, and then pour pure ghee on top of it. It is served with daal (lentils) and spicy garlic chutney; it is also served with besan (gram flour) ki kadi. It is commonly served at all festivities, including religious occasions, wedding ceremonies, and birthday parties in Rajasthan.
Dal-baati-churma is very popular in Rajasthan. The traditional way to serve it is to first coarsely mash the baati, and then pour pure ghee on top of it. It is served with daal (lentils) and spicy garlic chutney; it is also served with besan (gram flour) ki kadi. It is commonly served at all festivities, including religious occasions, wedding ceremonies, and birthday parties in Rajasthan.
 In recent years, Rajasthan has worked on improving education. The state government has been making sustained efforts to raise the education standard.
Schools in the state are either managed by the government or by private trusts. The medium of instruction in most of the schools is mainly English, or Hindi. Under the
In recent years, Rajasthan has worked on improving education. The state government has been making sustained efforts to raise the education standard.
Schools in the state are either managed by the government or by private trusts. The medium of instruction in most of the schools is mainly English, or Hindi. Under the
 Rajasthan attracted a total of 45.9 million domestic and 1.6 million foreign tourists in 2017, which is the tenth highest in terms of domestic visitors and fifth highest in foreign tourists. The tourism industry in Rajasthan is growing effectively each year and is becoming one of the major income sources for the state government. Rajasthan is home to many attractions for domestic and foreign travellers, including the forts and palaces of
Rajasthan attracted a total of 45.9 million domestic and 1.6 million foreign tourists in 2017, which is the tenth highest in terms of domestic visitors and fifth highest in foreign tourists. The tourism industry in Rajasthan is growing effectively each year and is becoming one of the major income sources for the state government. Rajasthan is home to many attractions for domestic and foreign travellers, including the forts and palaces of
File:Camel rides in Thar desert.jpg, Camel rides in
Official Site of the Government of Rajasthan, India
Official Tourism Site of Rajasthan, India
state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
in northwestern India
Northwest India is a loosely defined region of India. In modern-day, it consists of north-western states of the Republic of India. In historical contexts, it refers to the northwestern Indian subcontinent.
In contemporary definition, it gene ...
. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern side, where it comprises most of the wide and inhospitable Thar Desert
The Thar Desert (), also known as the Great Indian Desert, is an arid region in the north-western part of the Indian subcontinent that covers an area of in India and Pakistan. It is the world's 18th-largest desert, and the world's 9th-large ...
(also known as the Great Indian Desert) and shares a border with the Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
i provinces of Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
to the northwest and Sindh
Sindh ( ; ; , ; abbr. SD, historically romanized as Sind (caliphal province), Sind or Scinde) is a Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Pakistan. Located in the Geography of Pakistan, southeastern region of the country, Sindh is t ...
to the west, along the Sutlej
The Sutlej River or the Satluj River is a major river in Asia, flowing through China, India and Pakistan, and is the longest of the five major rivers of the Punjab region. It is also known as ''Satadru''; and is the easternmost tributary of t ...
-Indus
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans- Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northwest through the dis ...
River valley. It is bordered by five other Indian states: Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
to the north; Haryana
Haryana () is a States and union territories of India, state located in the northern part of India. It was carved out after the linguistic reorganisation of Punjab, India, Punjab on 1 November 1966. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with les ...
and Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh ( ; UP) is a States and union territories of India, state in North India, northern India. With over 241 million inhabitants, it is the List of states and union territories of India by population, most populated state in In ...
to the northeast; Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (; ; ) is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal and the largest city is Indore, Indore. Other major cities includes Gwalior, Jabalpur, and Sagar, Madhya Pradesh, Sagar. Madhya Pradesh is the List of states and union te ...
to the southeast; and Gujarat
Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories ...
to the southwest. Its geographical location is 23°3' to 30°12' North latitude and 69°30' to 78°17' East longitude, with the Tropic of Cancer
The Tropic of Cancer, also known as the Northern Tropic, is the Earth's northernmost circle of latitude where the Sun can be seen directly overhead. This occurs on the June solstice, when the Northern Hemisphere is tilted toward the Sun ...
passing through its southernmost tip.
Its major features include the ruins of the Indus Valley civilisation
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation, was a Bronze Age civilisation in the Northwestern South Asia, northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 Common Era, BCE to 1300 BCE, and in i ...
at Kalibangan
Kalibangān is a town located at on the left or southern banks of the Ghaggar (Ghaggar-Hakra River) in Tehsil Pilibangān, between Suratgarh and Hanumangarh in Hanumangarh District, Rajasthan, India 205 km from Bikaner. It is also ident ...
and Balathal, the Dilwara Temples
The Dilwara Temples or Delvada Temples are a group of Śvētāmbara Jain temples located about kilometres from the Mount Abu settlement in Sirohi District, Rajasthan's only hill station. The earliest were built by Vimal Shah , a Jain mini ...
, a Jain pilgrimage site at Rajasthan's only hill station
A hill station is a touristic town located at a higher elevation than the nearby plain or valley. The English term was originally used mostly in Western imperialism in Asia, colonial Asia, but also in Africa (albeit rarely), for towns founded by ...
, Mount Abu
Mount Abu (), known as Arbudgiri in Jain tradition, is a hill station in the Aravalli Range in the Sirohi district of the state of Rajasthan in western India. Here, the mountain forms a rocky plateau 22 km long by 9 km wide. It is ref ...
, in the ancient Aravalli mountain range and eastern Rajasthan, the Keoladeo National Park
Keoladeo National Park, or Keoladeo Ghana National Park, is a national park in Rajasthan, India. The national park hosts thousands of native, resident and migratory birds, especially during the winter season, when many different species fly to t ...
of Bharatpur, a World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
known for its bird life. Rajasthan is also home to five national tiger
The tiger (''Panthera tigris'') is a large Felidae, cat and a member of the genus ''Panthera'' native to Asia. It has a powerful, muscular body with a large head and paws, a long tail and orange fur with black, mostly vertical stripes. It is ...
reserves, the Ranthambore National Park
Ranthambore National Park is a national park in the Indian state of Rajasthan. It covers a total area of . It is bounded to the north by the Banas River and to the south by the Chambal River. It is named after the historic Ranthambore Fort ...
in Sawai Madhopur
Sawai Madhopur (IAST: ''Savāī Mādhōpur'', IPA: əˈʋaːiː ˈmaːdʱoːpʊɾ is a city in the southeastern part of the Indian state of Rajasthan. It serves as the administrative headquarter of the Sawai Madhopur district, and forms a ...
, Sariska Tiger Reserve
Sariska Tiger Reserve is a tiger reserve in Alwar district, Rajasthan, India. It stretches over an core tiger habitat area of and 322.23 km² of buffer area making 1203.34 km² total area of tiger reserve. It is comprising scrub-thorn arid ...
in Alwar
Alwar ( Rajasthani Pronunciation: �lʋəɾ is a city located in India's National Capital Region (NCR) and the administrative headquarters of Alwar District in the state of Rajasthan. It is located 150 km south of Delhi and 150 km ...
, the Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve in Kota, Ramgarh Vishdhari Tiger reserve and Karauli Dholpur tiger reserve.
The State of Rajasthan was formed on 30 March 1949 when the states of the Rajputana Agency
The Rajputana Agency was a political office of the British Raj, British Indian Empire dealing with a collection of native states in Rajputana (now in Rajasthan, northwestern India), under the political charge of an Agent reporting directly to ...
of the erstwhile British Empire in India were merged into the new Indian Union. Its capital
Capital and its variations may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** Capital region, a metropolitan region containing the capital
** List of national capitals
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter
Econom ...
and largest city is Jaipur
Jaipur (; , ) is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and the List of cities and towns in Rajasthan, largest city of the north-western States and union territories of India, Indian state of Rajasthan. , the city had ...
. Other important cities are Jodhpur
Jodhpur () is the second-largest city of the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, after its capital Jaipur. As of 2023, the city has a population of 1.83 million. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Jodhpur district and ...
, Kota, Bikaner
Bikaner () is a city in the northwest of the States and territories of India, state of Rajasthan, India. It is located northwest of the state capital, Jaipur. It is the administrative headquarters of Bikaner District and Bikaner division.
Fo ...
, Ajmer
Ajmer () is a city in the north-western States and union territories of India, Indian state of Rajasthan. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Ajmer district and Ajmer division. It lies at the centre of Rajasthan, earning it the ...
, Bhilwara
Bhilwara () is a city and administrative headquarters in Bhilwara district of the Mewar region of Rajasthan, India. It has been termed as 'Textile city'.
History
Stone Age tools dating from 5,012 to 200,000 years were found in Bundi and ...
, Sawai Madhopur
Sawai Madhopur (IAST: ''Savāī Mādhōpur'', IPA: əˈʋaːiː ˈmaːdʱoːpʊɾ is a city in the southeastern part of the Indian state of Rajasthan. It serves as the administrative headquarter of the Sawai Madhopur district, and forms a ...
, Bharatpur and Udaipur
Udaipur (Hindi: , ) (ISO 15919: ''Udayapura'') is a city in the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, about south of the state capital Jaipur. It serves as the administrative headquarters of Udaipur district. It is the historic capital of t ...
. The economy of Rajasthan
Rajasthan is a mineral-rich state of India, with agriculture, mining and tourism as its main engines of growth. The state's mines produce gold, silver, sandstone, limestone, marble, rock phosphate, copper and lignite. It is the second-largest ...
is the seventh-largest state economy in India with in gross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the total market value of all the final goods and services produced and rendered in a specific time period by a country or countries. GDP is often used to measure the economic performanc ...
and a per capita GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the total market value of all the final goods and services produced and rendered in a specific time period by a country or countries. GDP is often used to measure the economic performance o ...
of . Rajasthan ranks 22nd among Indian states in human development index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistical composite index of life expectancy, Education Index, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income i ...
.
Etymology
Rajasthan means "The Land of Kings" and is aportmanteau
In linguistics, a blend—also known as a blend word, lexical blend, or portmanteau—is a word formed by combining the meanings, and parts of the sounds, of two or more words together.
of Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
"Rājā" ('King') and Sanskrit "Sthāna" ('Land') or Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
"St(h)ān", with the same meaning.'''' The oldest reference to ''Rajasthan'' is found in a stone inscription dated back to 625 CE. The first printed mention of the name ''Rajasthan'' appears in the 1829 publication ''Annals and Antiquities of Rajasthan or the Central and Western Rajpoot States of India'', while the earliest known record of ''Rajputana'' as a name for the region is in George Thomas's 1800 memoir ''Military Memories''. John Keay
John Stanley Melville Keay FRGS (born 1941) is a British historian, journalist, radio presenter and lecturer specialising in popular histories of India, the Far East and China, often with a particular focus on their colonisation and explora ...
, in his book ''India: A History'', stated that ''Rajputana'' was coined by the British in 1829, John Briggs, translating Ferishta
Firishta or Ferešte (), full name Muhammad Qasim Hindu Shah Astarabadi (), was a Persian historian, who later settled in India and served the Deccan Sultans as their court historian. He was born in 1570 and died between 1611 and 1623.
Life
F ...
's history of early Islamic India, used the phrase " Rajpoot (Rajput) princes" rather than "Indian princes".
History
Ancient times
Parts of what is now Rajasthan were partly part of the Vedic Civilisation and theIndus Valley civilisation
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation, was a Bronze Age civilisation in the Northwestern South Asia, northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 Common Era, BCE to 1300 BCE, and in i ...
. Kalibangan
Kalibangān is a town located at on the left or southern banks of the Ghaggar (Ghaggar-Hakra River) in Tehsil Pilibangān, between Suratgarh and Hanumangarh in Hanumangarh District, Rajasthan, India 205 km from Bikaner. It is also ident ...
, in Hanumangarh district, was a major provincial capital of the Indus Valley Civilisation. Topsfield writes that the Rajput
Rājpūt (, from Sanskrit ''rājaputra'' meaning "son of a king"), also called Thākur (), is a large multi-component cluster of castes, kin bodies, and local groups, sharing social status and ideology of genealogical descent originating fro ...
s first entered India from the north west in the first millennium A.D. They established kingdoms in western India in the region that is now known as Rajasthan.
An archaeological
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, ...
excavation at the Balathal site in Udaipur district shows a settlement contemporary with the Harrapan civilisation dating back to 3000–1500 BCE. Stone Age tools dating from 5,000 to 200,000 years were found in Bundi
Bundi is a town in the Hadoti region of Rajasthan state in northwest India.
Climate
The climate is hot semi arid (BSh), not having enough rainfall to qualify as a tropical savanna climate (Aw). The climate is quite warm, and most of the ra ...
and Bhilwara
Bhilwara () is a city and administrative headquarters in Bhilwara district of the Mewar region of Rajasthan, India. It has been termed as 'Textile city'.
History
Stone Age tools dating from 5,012 to 200,000 years were found in Bundi and ...
districts of the state.
 The
The Matsya kingdom
Matsya () was a Vedic kingdom and later became a part of sixteen Mahajanapadas, which also appears in Hindu Epic literature. The capital of Matsya was at Viratanagari (present-day Bairat, in Rajasthan) which is said to have been named after ...
of the Vedic civilisation of India is said to roughly corresponded to the former state of Jaipur
Jaipur (; , ) is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and the List of cities and towns in Rajasthan, largest city of the north-western States and union territories of India, Indian state of Rajasthan. , the city had ...
in Rajasthan and included the whole of Alwar with portions of Bharatpur. The capital of Matsya was at Viratanagar (modern Bairat), which is said to have been named after its founder King Virata
Virata (, IAST ''virāṭa'') was the King of Matsya, a prominent figure in the Indian epic ''Mahabharata'', and the titular character of the epic's fourth book, '' Virata Parva'', which recounts the Pandavas’ year of ajnatavasa—incognit ...
.
Bhargava identifies the two districts of Jhunjhunu
Jhunjhunu is a city and municipal council in the state of Rajasthan in India. It is the administrative headquarters of the Jhunjhunu district. It is also the largest city of the Shekhawati region, which includes Jhunjhunu, Churu and Sikar ...
and Sikar
Sikar is a city and municipal council in the Sikar district of the state of Rajasthan in India. It is the administrative headquarters of the Sikar district. It is largest city of the Shekhawati region, which consists of Sikar, Churu and Jhu ...
and parts of Jaipur
Jaipur (; , ) is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and the List of cities and towns in Rajasthan, largest city of the north-western States and union territories of India, Indian state of Rajasthan. , the city had ...
district along with Haryana districts of Mahendragarh
Mahendragarh is a city and a municipal committee in Mahendragarh district in the Indian state of Haryana. It is nearly from Gurgaon and comes under National Capital Region (India).
Etymology
Earlier earlier was known as Kanaud because i ...
and Rewari
Rewari is a city and a municipal council in Rewari district in the Indian state of Haryana. It is the district headquarters of Rewari district. It is located in south-west Haryana around 82 km from DelhiVedic
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas ( or ; ), sometimes collectively called the Veda, are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed ...
state of Brahmavarta
The literary text ''Manusmriti'' describes Brahmavarta () as the region between the rivers Sarasvati and Drishadvati in India. The text defines the area as a holy land, whose inhabitants set the standards for morality and conduct for the rest of ...
. Bhargava also locates the present day Sahibi River
The Sahibi river, also called the Sabi River, is an ephemeral, rain-fed river flowing through Rajasthan, Haryana (where its canalised portion is called the "Outfall Drain No 8") and Delhi states in India. It originates in the eastern slopes of t ...
as the Vedic Drishadwati
The Drishadvati River (IAST:, "She with many stones") is a river hypothesized by Indologists to identify the route of the Vedic river Saraswati and the state of '' Brahmavarta''. According to ''Manusmriti'', the ''Brahmavarta'', where the Rishis ...
River, which along with Saraswati River
The Sarasvati River () is a deified mythological river first mentioned in the Rigveda and later in Vedic and post-Vedic texts. It played an important role in the Vedic religion, appearing in all but the fourth book of the Rigveda.
As a phys ...
formed the borders of the Vedic state of Brahmavarta. Manu and Bhrigu
Bhrigu (, ) is a rishi in Hindu tradition. He is one of the seven great sages, the Saptarshis, and one of the many Prajapatis (the facilitators of creation) created by Brahma. He was the first compiler of predictive astrology and also the aut ...
narrated the Manusmriti
The ''Manusmṛti'' (), also known as the ''Mānava-Dharmaśāstra'' or the Laws of Manu, is one of the many legal texts and constitutions among the many ' of Hinduism.
Over fifty manuscripts of the ''Manusmriti'' are now known, but the earli ...
to a congregation of seers in this area. The ashrams of Vedic seers Bhrigu
Bhrigu (, ) is a rishi in Hindu tradition. He is one of the seven great sages, the Saptarshis, and one of the many Prajapatis (the facilitators of creation) created by Brahma. He was the first compiler of predictive astrology and also the aut ...
and his son Chayvan Rishi, for whom Chyawanprash
Chyavanprash (), originally Chayavanaprasham, is a cooked mixture of sugar, honey, ghee, Indian gooseberry ( amla) jam, sesame oil, berries and various herbs and spices. It is prepared as per the instructions suggested in Ayurvedic texts. Chyava ...
was formulated, were near Dhosi Hill
Dhosi Hill is an extinct volcano that stands alone at the north-west end of the Aravalli mountain range in southern Haryana, India. It was an important site during the Vedic period. Its rises 345 to 470 meters from the surrounding land and 740 ...
, part of which lies in Dhosi village of Jhunjhunu
Jhunjhunu is a city and municipal council in the state of Rajasthan in India. It is the administrative headquarters of the Jhunjhunu district. It is also the largest city of the Shekhawati region, which includes Jhunjhunu, Churu and Sikar ...
district of Rajasthan and part of which lies in Mahendragarh
Mahendragarh is a city and a municipal committee in Mahendragarh district in the Indian state of Haryana. It is nearly from Gurgaon and comes under National Capital Region (India).
Etymology
Earlier earlier was known as Kanaud because i ...
district of Haryana
Haryana () is a States and union territories of India, state located in the northern part of India. It was carved out after the linguistic reorganisation of Punjab, India, Punjab on 1 November 1966. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with les ...
.
The Western Kshatrapas
The Western Satraps, or Western Kshatrapas (Brahmi: , ''Mahakṣatrapa'', "Great Satraps") were Indo-Scythian (Saka) rulers of the western and central parts of India (extending from Saurashtra in the south and Malwa in the east, covering moder ...
(405–35 BCE), the Saka
The Saka, Old Chinese, old , Pinyin, mod. , ), Shaka (Sanskrit (Brāhmī): , , ; Sanskrit (Devanāgarī): , ), or Sacae (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples, Eastern Iranian peoples who lived in the Eurasian ...
rulers of the western part of India, were successors to the Indo-Scythians
The Indo-Scythians, also known as Indo-Sakas, were a group of nomadic people of Iranic Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into the present-day regions of Afghanistan, Eastern Iran and the northwestern Indian subcontinent: p ...
and were contemporaneous with the Kushans
The Kushan Empire (– CE) was a syncretic empire formed by the Yuezhi in the Bactrian territories in the early 1st century. It spread to encompass much of what is now Afghanistan, Eastern Iran, India, Pakistan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. Kus ...
, who ruled the northern part of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
. The Indo-Scythians invaded the area of Ujjain
Ujjain (, , old name Avantika, ) or Ujjayinī is a city in Ujjain district of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It is the fifth-largest city in Madhya Pradesh by population and is the administrative as well as religious centre of Ujjain ...
and established the Saka era
The Shaka era (IAST: Śaka, Śāka) is a historical Hindu calendar era (year numbering), the epoch (its year zero) of which corresponds to Julian year 78.
The era has been widely used in different regions of the Indian subcontinent as well a ...
(with their calendar
A calendar is a system of organizing days. This is done by giving names to periods of time, typically days, weeks, months and years. A calendar date, date is the designation of a single and specific day within such a system. A calendar is ...
), marking the beginning of the long-lived Saka Western Satraps
The Western Satraps, or Western Kshatrapas (Brahmi: , ''Mahakṣatrapa'', "Great Satraps") were Indo-Scythian (Saka) rulers of the western and central parts of India (extending from Saurashtra in the south and Malwa in the east, covering moder ...
state.
Classical era
Gurjara-Pratihara
 The
The Pratiharas
The Pratihara dynasty, also called the Gurjara-Pratiharas, the Pratiharas of Kannauj or the Imperial Pratiharas, was a prominent medieval Indian dynasty which ruled over the Kingdom of Kannauj. It initially ruled the Gurjaradesa until its vict ...
ruled for many dynasties in this part of the country; the region was known as ''Gurjaratra
Gurjaradesa, (, or Gurjaratra)*
* is a historical region in India comprising the southern Rajasthan and northern Gujarat during the period of 6th–12th century CE. The predominant power of the region, the Gurjara-Pratiharas eventually cont ...
''. Up to the 10th century CE, almost all of North India
North India is a geographical region, loosely defined as a cultural region comprising the northern part of India (or historically, the Indian subcontinent) wherein Indo-Aryans (speaking Indo-Aryan languages) form the prominent majority populati ...
acknowledged the supremacy of the Imperial Pratiharas, with their seat of power at Kannauj
Kannauj (Hindustani language, Hindustani pronunciation: ) is an ancient city, administrative headquarters and a municipal board or Nagar palika, Nagar Palika Parishad in Kannauj district in the Indian States and territories of India, state of Ut ...
.
The Gurjara Pratihar Empire acted as a barrier for Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
invaders from the 8th to the 11th century. The chief accomplishment of the Gurjara-Pratihara Empire lies in its successful resistance to foreign invasions from the west, starting in the days of Junaid. Historian R. C. Majumdar
Ramesh Chandra Majumdar (known as R. C. Majumdar; 4 December 1888 – 11 February 1980) was an Indian historian and professor known for promoting Hindu nationalist views. He principally studied the history of India.
Early life and education ...
says that this was openly acknowledged by the Arab writers. He further notes that historians of India have wondered at the slow progress of Muslim invaders in India, as compared with their rapid advance in other parts of the world. Now there seems little doubt that it was the power of the Pratihara army that effectively barred the progress of the Arabs beyond the confines of Sindh
Sindh ( ; ; , ; abbr. SD, historically romanized as Sind (caliphal province), Sind or Scinde) is a Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Pakistan. Located in the Geography of Pakistan, southeastern region of the country, Sindh is t ...
, their only conquest for nearly 300 years.
Medieval and early modern eras
TheGhurids
The Ghurid dynasty (also spelled Ghorids; ; self-designation: , ''Šansabānī'') was a Persianate dynasty of eastern Iranian Tajik origin, which ruled from the 8th-century in the region of Ghor, and became an Empire from 1175 to 1215. The G ...
had made an attempt to invade India through southern Rajasthan, however they were defeated in the Battle of Kasahrada
The Battle of Kasahrada, also known as Battle of Kayadara or Battle of Gadararaghatta was fought in 1178 at modern Kasahrada in Sirohi district near Mount Abu in present-day Rajasthan. It was fought between the Rajput Confederacy led by Mular ...
on 1178 by a confederacy of Rajputs under Mularaja II
Mularaja (), also known as ''Bala Mularaja'' (), was an Indian king from the Chaulukya dynasty of Gujarat. He ruled the present-day Gujarat and surrounding areas from his capital Anahilapataka (modern Patan). He ascended the throne as a child, ...
of the Kingdom of Gujarat. Prithviraj Chauhan
Prithviraja III (IAST: Pṛthvī-rāja; 22 May 1166 – February 1192), popularly known as Prithviraj Chauhan or Rai Pithora, was a king from the Chahamanas of Shakambhari, Chauhan (Chahamana) dynasty who ruled the territory of Sapadalaksha, w ...
led a confederacy of Rajput clans and defeated the invading Ghruids under Muhammad Ghori in the First Battle of Tarain
The First Battle of Tarain, also spelt as the First Battle of Taraori, was fought on 14 January 1191 between the invading Ghurid army led by Muhammad of Ghor and the Rajput Confederacy led by Prithviraj Chauhan, near Tarain (modern Taraori ...
in 1191. In 1192 CE, Muhammad Ghori decisively defeated Prithviraj at the Second Battle of Tarain
The Second Battle of Tarain was fought in 1192 between the Ghurid forces of Muhammad Ghuri and the Rajput Confederacy of Prithviraj Chauhan. It took place near Tarain (modern Taraori), which is , north of Delhi. The battle ended in a deci ...
. After the defeat of Chauhan in 1192 CE, a part of Rajasthan came under Muslim rulers. The principal centers of their powers were Nagaur
Nagaur (also Nagor and Nagore) is a city and municipal council in Nagaur district of the state of Rajasthan in India. It is the administrative headquarters of Nagaur District. The Nagaur city lies about midway between Jodhpur and Bikaner.
Na ...
and Ajmer. Ranthambhore was also under their suzerainty. At the beginning of the 13th century, the most prominent and powerful state of Rajasthan was Mewar
Mewar, also spelled as Mewad is a region in the south-central part of Rajasthan state of India. It includes the present-day districts of Bhilwara, Chittorgarh, Pratapgarh, Rajsamand, Udaipur, Pirawa Tehsil of Jhalawar District of Rajasth ...
. Since the invasion of the Muslim Turks from the 13th century onwards, the Rajputs resisted the Muslim incursions into India, and preserved Hindu culture
Hinduism () is an umbrella term for a range of Indian religious and spiritual traditions ( ''sampradaya''s) that are unified by adherence to the concept of ''dharma'', a cosmic order maintained by its followers through rituals and right ...
at their courts.
The Rajputs put up resistance to the Islamic invasions with their warfare and chivalry for centuries. The Ranas of Mewar led other kingdoms in their resistance to outside rule. Rana Hammir Singh
Maharana Hammir Singh (1302–1364), or Hammir, was a 14th-century ruler of Mewar in present-day Rajasthan, India. Hammir Singh, was a scion of the cadet branch Rana of the Guhila dynasty, who regained control of the region, re-established the ...
defeated the Tughlaq dynasty
The Tughlaq dynasty (also known as the Tughluq or Tughluk dynasty; ) was the third dynasty to rule over the Delhi Sultanate in medieval India. Its reign started in 1320 in Delhi when Ghazi Malik assumed the throne under the title of Ghiyath ...
and recovered a large portion of Rajasthan. The indomitable Rana Kumbha
Kumbhkaran Singh (1417–1468), popularly known as Maharana Kumbha, was the ruler of the Kingdom of Mewar in medieval India. He belonged to the Sisodia clan of Rajputs. It was during his reign that Mewar became one of the most powerful politic ...
defeated the Sultans of Malwa
Malwa () is a historical region, historical list of regions in India, region of west-central India occupying a plateau of volcanic origin. Geologically, the Malwa Plateau generally refers to the volcanic plateau, volcanic upland north of the ...
, Nagaur and Gujarat
Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories ...
and made Mewar the most powerful Rajput Kingdom in India. The ambitious Rana Sanga
Sangram Singh I (12 April 1482 – 30 January 1528), most commonly known as Rana Sanga, was the Rana of Mewar, Maharana of Mewar from 1509 to 1528. A member of the List of Ranas of Mewar, Sisodia dynasty, he controlled parts of present-day Ra ...
united the various Rajput clans, including the Muslim Khanzadas of Mewat under Raja Hasan Khan Mewati, and fought against the foreign powers in India. Rana Sanga defeated the Afghan Lodi Empire
The Lodi dynasty was an Afghan (ethnonym), Afghan dynasty, royal family that ruled Sultanate of Delhi from 1451 to 1526. It was the fifth and final dynasty of the Delhi Sultanate, and was founded by Bahlul Khan Lodi, Bahlul Lodi when he replaced ...
of Delhi and crushed the Turkic Sultanates of Malwa and Gujarat. Rana Sanga then tried to create an Indian empire but was defeated by the first Mughal
Mughal or Moghul may refer to:
Related to the Mughal Empire
* Mughal Empire of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries
* Mughal dynasty
* Mughal emperors
* Mughal people, a social group of Central and South Asia
* Mughal architecture
* Mug ...
Emperor Babur
Babur (; 14 February 148326 December 1530; born Zahīr ud-Dīn Muhammad) was the founder of the Mughal Empire in the Indian subcontinent. He was a descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan through his father and mother respectively. He was also ...
at Khanwa. The defeat was due to betrayal by the Tomar King Silhadi
Raja Shiladitya Tomar, also called Silhadi Tomar (died 6 May 1532), was a chieftain of northeast Malwa in the early decades of 16th century India. He become vassal of Sanga of Mewar and remained as an ally and Sanga helped him and Medini Rai in ...
of Raisen. After Rana Sanga
Sangram Singh I (12 April 1482 – 30 January 1528), most commonly known as Rana Sanga, was the Rana of Mewar, Maharana of Mewar from 1509 to 1528. A member of the List of Ranas of Mewar, Sisodia dynasty, he controlled parts of present-day Ra ...
's death, Marwar
Marwar (also called Jodhpur region) is a region of western Rajasthan state in North Western India. It lies partly in the Thar Desert. 'Maru' is a Sanskrit word for desert. The word 'wad' literally means fence in Rajasthani languages. Engl ...
rose as a power center in Rajasthan under Rao Maldeo Rathore
Rao Maldeo Rathore (5 December 1511 – 7 November 1562) was a king of the Rathore dynasty, who ruled the kingdom of Marwar in present day state of Rajasthan. Maldeo ascended the throne in 1531 CE, inheriting a small ancestral principality of Ra ...
. He conquered Jaisalmer, parts of Gujarat, Jalore, Nagaur, Ajmer, Sanchore, Bhinmal, Radhanpur, Bayana, Tonk, Toda and Nabhara. He expanded the territories of Marwar up to Sindh-Cholistan in west and his northern boundary was just fifty kilometres from Delhi. After defeating Humayun, Sher Shah came towards Rajputana. He defeated Chiefs of Rathore army by trickery in Battle of Sammel
The Battle of Sammel, also known as the Battle of Giri-Sumel, took place in 1544. It was fought near the villages of Giri and Sumel, between the Sur Empire under Sher Shah Suri and the Rathore army led by the commanders Jaita and Kumpa of Rao ...
and captured some territory of Marwar but it was recovered by Rathores in 1545.
Hem Chandra Vikramaditya
Hemu (; 1501 – 5 November 1556), also known as Hemu Vikramaditya and Hemchandra Vikramaditya, was an Indian king (maharaja) who previously served as a general and Wazir of Adil Shah Suri of the Sur Empire during a period in Indian history ...
, the Hindu emperor, was born in the village of Machheri in Alwar District
Alwar is a district in the States and territories of India, state of Rajasthan in northern India, whose district headquarters is Alwar, Alwar city. The district covers 8,337 km2. It is bound on the north by Rewari district of Haryana, on t ...
in 1501. He won 22 battles against Afghans, from Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
to Bengal
Bengal ( ) is a Historical geography, historical geographical, ethnolinguistic and cultural term referring to a region in the Eastern South Asia, eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. The region of Benga ...
including the states of Ajmer
Ajmer () is a city in the north-western States and union territories of India, Indian state of Rajasthan. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Ajmer district and Ajmer division. It lies at the centre of Rajasthan, earning it the ...
and Alwar
Alwar ( Rajasthani Pronunciation: �lʋəɾ is a city located in India's National Capital Region (NCR) and the administrative headquarters of Alwar District in the state of Rajasthan. It is located 150 km south of Delhi and 150 km ...
in Rajasthan, and defeated Akbar's forces twice, first at Agra
Agra ( ) is a city on the banks of the Yamuna river in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, about south-east of the national capital Delhi and 330 km west of the state capital Lucknow. With a population of roughly 1.6 million, Agra is the ...
and then at Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography ...
in 1556 at Battle of Delhi before acceding to the throne of Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography ...
and establishing the "Hindu Raj" in North India
North India is a geographical region, loosely defined as a cultural region comprising the northern part of India (or historically, the Indian subcontinent) wherein Indo-Aryans (speaking Indo-Aryan languages) form the prominent majority populati ...
, albeit for a short duration, from Purana Qila
Purana Qila () is one of the oldest forts in Delhi, India. It was built by the second Mughal Emperor Humayun and Surid Sultan Sher Shah Suri. The fort forms the inner citadel of the city of Dinpanah. It is located near the expansive Pragati ...
in Delhi. Hem Chandra was killed in the battlefield at Second Battle of Panipat
The Second Battle of Panipat was fought on 5 November 1556, between the Mughal Empire, Mughals under Akbar and emperor Hemu, titularly known as Hemu, Hemchandra Vikramaditya. Hemchandra had conquered Delhi and Agra a few weeks earlier by defeati ...
fighting against Mughals on 5 November 1556.
 During
During Akbar
Akbar (Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar, – ), popularly known as Akbar the Great, was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Humayun, under a regent, Bairam Khan, who helped the young emperor expa ...
's reign most of the Rajput kings accepted Mughal suzerainty, but the rulers of Mewar (Rana Udai Singh II
Udai Singh II (4 August 1522 – 28 February 1572) was the List of Ranas of Mewar, 12th Maharana of the Kingdom of Mewar and the founder of the city of Udaipur in the present-day state of Rajasthan, India. He was the fourth son of Rana SangaTo ...
) and Marwar (Rao Chandrasen Rathore
Rao Chandrasen (30 July 1541 – 11 January 1581) was a Rathore Rajput ruler of the Kingdom of Marwar. He was a younger son of Rao Maldev Rathore. He followed his father's policy and stayed hostile to the ruling foreign powers in north Indi ...
) refused to have any form of alliance with the Mughals. To teach the Rajputs a lesson Akbar attacked Udai Singh and killed Rajput commander Jaimal of Chitor and the citizens of Mewar in large numbers. Akbar killed 20,000–25,000 unarmed citizens in Chittor on the grounds that they had actively helped in the resistance.
Maharana Pratap
Pratap Singh I (9 May 1540 – 19 January 1597), popularly known as Maharana Pratap (), was king of the Kingdom of Mewar, in north-western India in the present-day state of Rajasthan, from 1572 until his death in 1597. He is notable for leadi ...
took an oath to avenge the citizens of Chittor; he fought the Mughal empire till his death and liberated most of Mewar apart from Chittor itself. Maharana Pratap
Pratap Singh I (9 May 1540 – 19 January 1597), popularly known as Maharana Pratap (), was king of the Kingdom of Mewar, in north-western India in the present-day state of Rajasthan, from 1572 until his death in 1597. He is notable for leadi ...
soon became the most celebrated warrior of Rajasthan and became famous all over India for his sporadic warfare and noble actions. According to Satish Chandra Satish Chandra is a given name of Hindu origin, and may refer to,
* Satish Chandra (politician), Indian National Congress leader
* Satish Chandra (historian), Indian academic
* Satish Chandra Agarwal, Indian politician
* Satish Chandra Basumata ...
, "Rana Pratap's defiance of the mighty Mughal empire, almost alone and unaided by the other Rajput states, constitutes a glorious saga of Rajput valor and the spirit of self-sacrifice for cherished principles. Rana Pratap's methods of sporadic warfare were later elaborated further by Malik Ambar, the Deccani general, and by Shivaji".
Rana Amar Singh I
Maharana Amar Singh I, the Maharana (ruler) of Mewar Kingdom (16 March 1559 – 26 January 1620), was the eldest son and successor of Maharana Pratap I. He was the 14th Rana of Mewar, ruling from 19 January 1597 until his death on 26 January ...
continued his ancestor's war against the Mughals under Jehangir
Nur-ud-din Muhammad Salim (31 August 1569 – 28 October 1627), known by his imperial name Jahangir (; ), was List of emperors of the Mughal Empire, Emperor of Hindustan from 1605 until his death in 1627, and the fourth Mughal emperors, Mughal ...
, he repelled the Mughal armies at Dewar. Later an expedition was again sent under the leadership of Prince Khurram, which caused much damage to life and property of Mewar
Mewar, also spelled as Mewad is a region in the south-central part of Rajasthan state of India. It includes the present-day districts of Bhilwara, Chittorgarh, Pratapgarh, Rajsamand, Udaipur, Pirawa Tehsil of Jhalawar District of Rajasth ...
. Many temples were destroyed, several villages were put on fire and women and children were captured and tortured to make Amar Singh accept surrender.
During Aurangzeb
Alamgir I (Muhi al-Din Muhammad; 3 November 1618 – 3 March 1707), commonly known by the title Aurangzeb, also called Aurangzeb the Conqueror, was the sixth Mughal emperors, Mughal emperor, reigning from 1658 until his death in 1707, becomi ...
's rule Rana Raj Singh I
Maharana Raj Singh I (24 September 1629 – 22 October 1680) was the Maharana of Mewar Kingdom (r. 1652–1680) and eldest son of Maharana Jagat Singh I. He fought against the Mughal Empire and annexed many Mughal territories. He participate ...
, Veer Durgadas Rathore
Durgadas Rathore (13 August 1638 – 22 November 1718) was a Rathore Rajput general of the Kingdom of Marwar. He is credited with having preserved the rule of the Rathore dynasty over Marwar (present-day Rajasthan), India, following th ...
and Patshah Akheraj Singh Rajpurohit were chief among those who defied the intolerant emperor of Delhi. They took advantage of the Aravalli hills and caused heavy damage to the Mughal armies that were trying to occupy Rajasthan.
After Aurangzeb's death Bahadur Shah I
Bahadur Shah I (Muhammad Mu'azzam; 14 October 1643 – 27 February 1712) or Shah Alam I, was the eighth Mughal Emperor from 1707 to 1712. He was the second son of the sixth Mughal emperor Aurangzeb, who he conspired to overthrow in his youth ...
tried to subjugate Rajasthan like his ancestors but his plan backfired when the three Rajput
Rājpūt (, from Sanskrit ''rājaputra'' meaning "son of a king"), also called Thākur (), is a large multi-component cluster of castes, kin bodies, and local groups, sharing social status and ideology of genealogical descent originating fro ...
Raja
Raja (; from , IAST ') is a noble or royal Sanskrit title historically used by some Indian subcontinent, Indian rulers and monarchs and highest-ranking nobles. The title was historically used in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia.
T ...
s of Amber
Amber is fossilized tree resin. Examples of it have been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since the Neolithic times, and worked as a gemstone since antiquity."Amber" (2004). In Maxine N. Lurie and Marc Mappen (eds.) ''Encyclopedia ...
, Udaipur
Udaipur (Hindi: , ) (ISO 15919: ''Udayapura'') is a city in the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, about south of the state capital Jaipur. It serves as the administrative headquarters of Udaipur district. It is the historic capital of t ...
, and Jodhpur
Jodhpur () is the second-largest city of the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, after its capital Jaipur. As of 2023, the city has a population of 1.83 million. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Jodhpur district and ...
made a joint resistance to the Mughals
The Mughal Empire was an early modern empire in South Asia. At its peak, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus River Basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to the highlands of pre ...
. The Rajputs first expelled the commandants of Jodhpur
Jodhpur () is the second-largest city of the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, after its capital Jaipur. As of 2023, the city has a population of 1.83 million. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Jodhpur district and ...
and Bayana
Bayana is a historical town and the headquarters of Bayana tehsil in the Bharatpur district of Rajasthan, India. Hindaun City is the nearest city to Bayana at just away. Bayana is also known as the "City of Bansasur". It was the site of the ...
and recovered Amer
Amer may refer to:
Places
* Amer (river), a river in the Dutch province of North Brabant
* Amer, Girona, a municipality in the province of Girona in Catalonia, Spain
* Amber, India (also known as Amer, India), former city of Rajasthan state
** Am ...
by a night attack. They next killed Sayyid Hussain Khan Barha, the commandant of Mewat
Mewat (; ) is a historical and cultural region which encompasses parts of the modern-day states of Haryana, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh in northwestern India.
Geography
The loose boundaries of the Mewat region generally include parts of th ...
and many other Mughal officers. Bahadur Shah I
Bahadur Shah I (Muhammad Mu'azzam; 14 October 1643 – 27 February 1712) or Shah Alam I, was the eighth Mughal Emperor from 1707 to 1712. He was the second son of the sixth Mughal emperor Aurangzeb, who he conspired to overthrow in his youth ...
, then in the Deccan
The Deccan is a plateau extending over an area of and occupies the majority of the Indian peninsula. It stretches from the Satpura and Vindhya Ranges in the north to the northern fringes of Tamil Nadu in the south. It is bound by the mount ...
was forced to patch up a truce with the Rajput Rajas. The Jats
The Jat people (, ), also spelt Jaat and Jatt, are a traditionally agricultural community in Northern India and Pakistan. Originally pastoralists in the lower Indus river-valley of Sindh, many Jats migrated north into the Punjab region in ...
, under Suraj Mal
Maharaja Suraj Mal (13 February 1707 – 25 December 1763), simply known as Suraj Mal, was a ruler of Bharatpur State in the present-day state of Rajasthan. Under him, Bharatpur State, a tributary of the House of Scindia, covered the present ...
, overran the Mughal garrison at Agra and plundered the city taking with them the two great silver doors of the entrance of the famous Taj Mahal
The Taj Mahal ( ; ; ) is an ivory-white marble mausoleum on the right bank of the river Yamuna in Agra, Uttar Pradesh, India. It was commissioned in 1631 by the fifth Mughal Empire, Mughal emperor, Shah Jahan () to house the tomb of his belo ...
which were then melted down by Suraj Mal in 1763.
Over the years, the Mughals began to have internal disputes which greatly distracted them at times. The Mughal Empire continued to weaken, and with the decline of the Mughal Empire in the late 18th century, Rajputana
Rājputana (), meaning Land of the Rajputs, was a region in the Indian subcontinent that included mainly the entire present-day States of India, Indian state of Rajasthan, parts of the neighboring states of Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat, and adjo ...
came under the influence of the Marathas
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern India, early modern polity in the Indian subcontinent. It comprised the realms of the Peshwa and four major independent List of Maratha dynasties and states, Ma ...
. The Maratha Empire, which had replaced the Mughal Empire as the overlord of the subcontinent, was finally replaced by the British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
in 1818.
In the 19th century, the Rajput kingdoms were exhausted, they had been drained financially and in manpower after continuous wars and due to heavy tributes exacted by the Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern India, early modern polity in the Indian subcontinent. It comprised the realms of the Peshwa and four major independent List of Maratha dynasties and states, Ma ...
. To save their kingdoms from instability, rebellions and banditry the Rajput kings concluded treaties with the British in the early 19th century, accepting British suzerainty
A suzerain (, from Old French "above" + "supreme, chief") is a person, state (polity)">state or polity who has supremacy and dominant influence over the foreign policy">polity.html" ;"title="state (polity)">state or polity">state (polity)">st ...
and control over their external affairs in return for internal autonomy.
Rana Kumbha
Kumbhkaran Singh (1417–1468), popularly known as Maharana Kumbha, was the ruler of the Kingdom of Mewar in medieval India. He belonged to the Sisodia clan of Rajputs. It was during his reign that Mewar became one of the most powerful politic ...
was the vanguard of the fifteenth century Rajput resurgence.
File:Maharaja Hemu Bhargava - Victor of Twenty Two Pitched Battles, 1910s.jpg, The emperor Hemu
Hemu (; 1501 – 5 November 1556), also known as Hemu Vikramaditya and Hemchandra Vikramaditya, was an Indian king (maharaja) who previously served as a general and Vizier, Wazir of Muhammad Adil Shah (died 1557), Adil Shah Suri of the Sur Emp ...
, who rose from obscurity and briefly established himself as ruler in northern India, from Punjab to Bengal, in defiance of the warring Sur and Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an Early modern period, early modern empire in South Asia. At its peak, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus River Basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to ...
s.
File:Durgadas Rathore painting.jpg, Durgadas Rathore, a Rathore Rajput warrior of Jodhpur
Jodhpur () is the second-largest city of the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, after its capital Jaipur. As of 2023, the city has a population of 1.83 million. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Jodhpur district and ...
who played an important role in protecting the Rathore dynasty
The Rathore dynasty is an Indian dynasty belonging to the Rathore (Rajput clan), Rathore clan of Rajput, Rajputs that has historically ruled over parts of Rajasthan, Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh. The Rathores trace their ancestry from the Solar dy ...
of Marwar
Marwar (also called Jodhpur region) is a region of western Rajasthan state in North Western India. It lies partly in the Thar Desert. 'Maru' is a Sanskrit word for desert. The word 'wad' literally means fence in Rajasthani languages. Engl ...
and for his rebellion against Aurangzeb
Alamgir I (Muhi al-Din Muhammad; 3 November 1618 – 3 March 1707), commonly known by the title Aurangzeb, also called Aurangzeb the Conqueror, was the sixth Mughal emperors, Mughal emperor, reigning from 1658 until his death in 1707, becomi ...
.
File:Akheraj rajpurohit.jpg, Patshah Akheraj Rajpurohit, Sewad warrior and Rajguru, along with Durgadas Rathore
Durgadas Rathore (13 August 1638 – 22 November 1718) was a Rathore Rajput general of the Kingdom of Marwar. He is credited with having preserved the rule of the Rathore dynasty over Marwar (present-day Rajasthan), India, following th ...
, protected Marwar, Ajit Singh of Marwar
Ajit Singh Rathore (19 February 1679 – 24 June 1724) was a ruler of Marwar region in the present-day Rajasthan and a son of Jaswant Singh Rathore. He also served as the Mughal Subahdar of Gujarat for two terms from 1715–1717 and 1719–172 ...
and rebelled against Aurangzeb
Alamgir I (Muhi al-Din Muhammad; 3 November 1618 – 3 March 1707), commonly known by the title Aurangzeb, also called Aurangzeb the Conqueror, was the sixth Mughal emperors, Mughal emperor, reigning from 1658 until his death in 1707, becomi ...
File:RajaRaviVarma MaharanaPratap.jpg, Maharana Pratap Singh, sixteenth-century Rajput ruler of Mewar
Mewar, also spelled as Mewad is a region in the south-central part of Rajasthan state of India. It includes the present-day districts of Bhilwara, Chittorgarh, Pratapgarh, Rajsamand, Udaipur, Pirawa Tehsil of Jhalawar District of Rajasth ...
, known for his defence of his realm against Mughal invasion.
File:Maharaja Suraj Mal.jpg, Suraj Mal
Maharaja Suraj Mal (13 February 1707 – 25 December 1763), simply known as Suraj Mal, was a ruler of Bharatpur State in the present-day state of Rajasthan. Under him, Bharatpur State, a tributary of the House of Scindia, covered the present ...
was ruler of Bharatpur. Some contemporary historians described him as "the Plato
Plato ( ; Greek language, Greek: , ; born BC, died 348/347 BC) was an ancient Greek philosopher of the Classical Greece, Classical period who is considered a foundational thinker in Western philosophy and an innovator of the writte ...
of the Jat people
The Jat people (, ), also spelt Jaat and Jatt, are a traditionally agricultural community in Northern India and Pakistan. Originally pastoralists in the lower Indus river-valley of Sindh, many Jats migrated north into the Punjab region in l ...
" and by a modern writer as the "Jat Odysseus
In Greek mythology, Greek and Roman mythology, Odysseus ( ; , ), also known by the Latin variant Ulysses ( , ; ), is a legendary Greeks, Greek king of Homeric Ithaca, Ithaca and the hero of Homer's Epic poetry, epic poem, the ''Odyssey''. Od ...
", because of his political sagacity, steady intellect and clear vision.
Modern era
The State of Rajasthan was formed on 30 March 1949 when the states of theRajputana Agency
The Rajputana Agency was a political office of the British Raj, British Indian Empire dealing with a collection of native states in Rajputana (now in Rajasthan, northwestern India), under the political charge of an Agent reporting directly to ...
of the erstwhile British Empire in India were merged into the new Indian Union. Modern Rajasthan includes most of Rajputana
Rājputana (), meaning Land of the Rajputs, was a region in the Indian subcontinent that included mainly the entire present-day States of India, Indian state of Rajasthan, parts of the neighboring states of Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat, and adjo ...
, which comprises the erstwhile nineteen princely states, three chiefships, and the British district of Ajmer-Merwara
Ajmer-Merwara (also known as Ajmir Province, and Ajmer-Merwara-Kekri) was a former province of British India in the historical Ajmer region. The territory was ceded to the British by Daulat Rao Sindhia by a treaty on 25 June 1818.
It was unde ...
. Jaisalmer
Jaisalmer , nicknamed ''The Golden city'', is a city in the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, located west of the state capital Jaipur, in the heart of the Thar Desert. It serves as the administrative headquarters of Jaisalmer district ...
, Marwar
Marwar (also called Jodhpur region) is a region of western Rajasthan state in North Western India. It lies partly in the Thar Desert. 'Maru' is a Sanskrit word for desert. The word 'wad' literally means fence in Rajasthani languages. Engl ...
(Jodhpur), Bikaner
Bikaner () is a city in the northwest of the States and territories of India, state of Rajasthan, India. It is located northwest of the state capital, Jaipur. It is the administrative headquarters of Bikaner District and Bikaner division.
Fo ...
, Mewar
Mewar, also spelled as Mewad is a region in the south-central part of Rajasthan state of India. It includes the present-day districts of Bhilwara, Chittorgarh, Pratapgarh, Rajsamand, Udaipur, Pirawa Tehsil of Jhalawar District of Rajasth ...
(Chittorgarh), Alwar
Alwar ( Rajasthani Pronunciation: �lʋəɾ is a city located in India's National Capital Region (NCR) and the administrative headquarters of Alwar District in the state of Rajasthan. It is located 150 km south of Delhi and 150 km ...
and Dhundhar
Dhundhar, also known as ''Jaipur region'', is a historical region of Rajasthan state in western India. It includes the districts of Jaipur, Neem ka Thana, Dantaramgarh part of Sikar District lying to the east of the Aravalli Range, Dausa, ...
(Jaipur) were some of the main Rajput princely states. Bharatpur and Dholpur
Dholpur is a city in the Dholpur district in Rajasthan state of India. It is situated on the left bank of the Chambal river. The city is the administrative headquarters of Dholpur district. Dholpur was established by King Dhaval Dev of the ...
were Jat princely states whereas Tonk was a princely state under Pathan
Pashtuns (, , ; ;), also known as Pakhtuns, or Pathans, are an Iranic ethnic group primarily residing in southern and eastern Afghanistan and northwestern Pakistan. They were historically also referred to as Afghans until 1964 after the ...
s. The three chiefships were Lawa, Neemrana and Kushalgarh.
Geography
The geographic features of Rajasthan are theThar Desert
The Thar Desert (), also known as the Great Indian Desert, is an arid region in the north-western part of the Indian subcontinent that covers an area of in India and Pakistan. It is the world's 18th-largest desert, and the world's 9th-large ...
and the Aravalli Range
The Aravalli Range (also spelled ''Aravali'') is a mountain range in North India, Northern-Western India, running approximately in a south-west direction, starting near Delhi, passing through southern Haryana and Rajasthan, and ending in Ahme ...
, which runs through the state from southwest to northeast, almost from one end to the other, for more than . Mount Abu
Mount Abu (), known as Arbudgiri in Jain tradition, is a hill station in the Aravalli Range in the Sirohi district of the state of Rajasthan in western India. Here, the mountain forms a rocky plateau 22 km long by 9 km wide. It is ref ...
lies at the southwestern end of the range, separated from the main ranges by the West Banas River
The West Banas is a river in western India. It originates from the southern Aravalli Range, in Sirohi District of the state of Rajasthan. It flows south, draining the valley between Mount Abu on the west and the easterly ridge of the Aravallis o ...
. Although a series of broken ridges continues into Haryana
Haryana () is a States and union territories of India, state located in the northern part of India. It was carved out after the linguistic reorganisation of Punjab, India, Punjab on 1 November 1966. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with les ...
in the direction of Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography ...
where it can be seen as outcrops in the form of the Raisina Hill
Raisina Hill (ISO: ''Rāyasīnā kī Pahāṛī''), often used as a metonym for the seat of the Government of India, is an area of New Delhi, housing India's most important government buildings, including Rashtrapati Bhavan, the official reside ...
and the ridges farther north. About three-fifths of Rajasthan lies northwest of the Aravallis, leaving two-fifths on the east and south direction.
 The Aravalli Range runs across the state from the southwest peak
The Aravalli Range runs across the state from the southwest peak Guru Shikhar
Guru Shikhar, a peak in the Arbuda Mountains of Sirohi district in Rajasthan, is the highest point of the Aravalli Range, Rajasthan, and Western India. It rises to an elevation of . It is 75 km from Sirohi, Sirohi city, the district headqu ...
(Mount Abu), which is in height, to Khetri
Khetri Nagar is a town in the Jhunjhunu district of Rajasthan in India. It is a part of the Shekhawati
Shekhawati is a region in the northern part of the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Rajasthan, comprising the d ...
in the northeast. This range divides the state into 60% in the northwest of the range and 40% in the southeast. The northwest tract is sandy and unproductive with little water but improves gradually from desert land in the far west and northwest to comparatively fertile and habitable land towards the east. The south-eastern area, higher in elevation (100 to 350 m above sea level) and more fertile, has a very diversified topography. In the south lies the hilly tract of Mewar. In the southeast, a large area within the districts of Kota and Bundi
Bundi is a town in the Hadoti region of Rajasthan state in northwest India.
Climate
The climate is hot semi arid (BSh), not having enough rainfall to qualify as a tropical savanna climate (Aw). The climate is quite warm, and most of the ra ...
forms a tableland. To the northeast of these districts is a rugged region (badlands) following the line of the Chambal River
The Chambal River is a tributary of the Yamuna River in Central India, Central and North India, Northern India, and thus forms part of the drainage system of the Ganges. The river flows north-northeast through Madhya Pradesh, running for a brie ...
. Farther north the country levels out; the flat plains of the northeastern Bharatpur district
Bharatpur District is a district in Rajasthan state in western India. The city of Bharatpur is the District Headquarters, Division Headquarters and Headquarters of Bharatpur
History Historical events
Bharatpur is a place of mythological imp ...
are part of an alluvial
Alluvium (, ) is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluvium is also sometimes called alluvial deposit. Alluvium is ...
basin. Merta City
Merta City is a city and a municipality located near Nagaur City in Nagaur district in the Indian state of Rajasthan. Merta is also known for its link with Mira Bai, the devotee of Lord Krishna. The Mira Mahal Museum houses memories related ...
lies in the geographical center of Rajasthan.
The Aravalli Range and the lands to the east and southeast of the range are generally more fertile and better watered. This region is home to the Khathiar-Gir dry deciduous forests ecoregion, with tropical dry broadleaf forests that include teak
Teak (''Tectona grandis'') is a tropical hardwood tree species in the family Lamiaceae. It is a large, deciduous tree that occurs in mixed hardwood forests. ''Tectona grandis'' has small, fragrant white flowers arranged in dense clusters (panic ...
, ''Acacia
''Acacia'', commonly known as wattles or acacias, is a genus of about of shrubs and trees in the subfamily Mimosoideae of the pea family Fabaceae. Initially, it comprised a group of plant species native to Africa, South America, and Austral ...
'', and other trees. The hilly Vagad
Vagad (also known as Vagar) is a region in southeastern Rajasthan state of western India. Its boundaries are roughly defined by those of the districts of Dungarpur and Banswara. Major cities of the region are Dungarpur and Banswara.
Geogra ...
region, home to the cities of Dungarpur
Dungarpur is a city in the southernmost part of Rajasthan, India.
History
Dungarpur is the seat of the elder branch of the Guhilot of Mewar family. The seat of the younger branch is that of the Maharana of Udaipur. The city was founded in ...
, Pratapgarh, and Banswara
Banswara is a city in the Banswara district in southern Rajasthan, India. The name, Banswara, came from king ‘Bansiya Bhil’.
Banswara is also known as "City of a Hundred Islands", "The Green City", which is often referred to as " Cherrap ...
lies in southernmost Rajasthan, on the border with Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (; ; ) is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal and the largest city is Indore, Indore. Other major cities includes Gwalior, Jabalpur, and Sagar, Madhya Pradesh, Sagar. Madhya Pradesh is the List of states and union te ...
. With the exception of Mount Abu, Vagad is the wettest region in Rajasthan, and the most heavily forested. North of Vagad lies the Mewar
Mewar, also spelled as Mewad is a region in the south-central part of Rajasthan state of India. It includes the present-day districts of Bhilwara, Chittorgarh, Pratapgarh, Rajsamand, Udaipur, Pirawa Tehsil of Jhalawar District of Rajasth ...
region, home to the cities of Udaipur
Udaipur (Hindi: , ) (ISO 15919: ''Udayapura'') is a city in the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, about south of the state capital Jaipur. It serves as the administrative headquarters of Udaipur district. It is the historic capital of t ...
and Chittaurgarh
Chittorgarh (; also Chitror or Chittor or Chittaurgarh) is a major city in the state of Rajasthan in western India. It lies on the Berach River, a tributary of the Banas, and is the administrative headquarters of Chittorgarh District. It wa ...
. The Hadoti
Hadoti is a region of Rajasthan state in western India, which was once called the Bundi Kingdom. The biggest cities are Jhalawar and Kota. It includes the districts of Bundi, Baran, Jhalawar and Kota and is bounded on the west by the Me ...
region lies to the southeast, on the border with Madhya Pradesh. North of Hadoti and Mewar lies the Dhundhar
Dhundhar, also known as ''Jaipur region'', is a historical region of Rajasthan state in western India. It includes the districts of Jaipur, Neem ka Thana, Dantaramgarh part of Sikar District lying to the east of the Aravalli Range, Dausa, ...
region, home to the state capital of Jaipur
Jaipur (; , ) is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and the List of cities and towns in Rajasthan, largest city of the north-western States and union territories of India, Indian state of Rajasthan. , the city had ...
. Mewat
Mewat (; ) is a historical and cultural region which encompasses parts of the modern-day states of Haryana, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh in northwestern India.
Geography
The loose boundaries of the Mewat region generally include parts of th ...
, the easternmost region of Rajasthan, borders Haryana
Haryana () is a States and union territories of India, state located in the northern part of India. It was carved out after the linguistic reorganisation of Punjab, India, Punjab on 1 November 1966. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with les ...
and Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh ( ; UP) is a States and union territories of India, state in North India, northern India. With over 241 million inhabitants, it is the List of states and union territories of India by population, most populated state in In ...
. Eastern and southeastern Rajasthan is drained by the Banas and Chambal rivers, tributaries of the Ganges
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary rive ...
.
The northwestern portion of Rajasthan is generally sandy and dry. Most of this region is covered by the Thar Desert
The Thar Desert (), also known as the Great Indian Desert, is an arid region in the north-western part of the Indian subcontinent that covers an area of in India and Pakistan. It is the world's 18th-largest desert, and the world's 9th-large ...
which extends into adjoining portions of Pakistan. The Aravalli Range does not intercept the moisture-giving southwest monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in Atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annu ...
winds off the Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea () is a region of sea in the northern Indian Ocean, bounded on the west by the Arabian Peninsula, Gulf of Aden and Guardafui Channel, on the northwest by Gulf of Oman and Iran, on the north by Pakistan, on the east by India, and ...
, as it lies in a direction parallel to that of the coming monsoon winds, leaving the northwestern region in a rain shadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.
Evaporated moisture from body of water, bodies of water (such as oceans and larg ...
. The Thar Desert is thinly populated; the City of Jodhpur
Jodhpur () is the second-largest city of the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, after its capital Jaipur. As of 2023, the city has a population of 1.83 million. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Jodhpur district and ...
is the largest city in the desert and a major metropolitan area of India which is known as the gateway of the Thar desert. The desert has some major districts like Jodhpur
Jodhpur () is the second-largest city of the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, after its capital Jaipur. As of 2023, the city has a population of 1.83 million. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Jodhpur district and ...
, Jaisalmer
Jaisalmer , nicknamed ''The Golden city'', is a city in the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, located west of the state capital Jaipur, in the heart of the Thar Desert. It serves as the administrative headquarters of Jaisalmer district ...
, Barmer, Bikaner
Bikaner () is a city in the northwest of the States and territories of India, state of Rajasthan, India. It is located northwest of the state capital, Jaipur. It is the administrative headquarters of Bikaner District and Bikaner division.
Fo ...
, and Nagaur
Nagaur (also Nagor and Nagore) is a city and municipal council in Nagaur district of the state of Rajasthan in India. It is the administrative headquarters of Nagaur District. The Nagaur city lies about midway between Jodhpur and Bikaner.
Na ...
. This area is also important from a defence point of view. Jodhpur
Jodhpur () is the second-largest city of the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, after its capital Jaipur. As of 2023, the city has a population of 1.83 million. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Jodhpur district and ...
airbase is one of the largest airbases in India, BSF and Military bases are also situated here. Currently four civil airports are located here: Jodhpur, Jaisalmer, Bikaner and Nagaur, of which Jodhpur is the major civil airport, being the 44th busiest airport in India and one of the oldest air strips of India, being built in the 1920s.
The Northwestern thorn scrub forests
The Aravalli West Thorn Scrub Forests, formerly known as Northwestern thorn scrub forests, is a xeric shrubland ecoregion of Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of ...
lie in a band around the Thar Desert, between the desert and the Aravallis. This region receives less than 400 mm of rain annually. Temperatures can sometimes exceed 45 °C in the summer months and drop below freezing point in the winter. The Godwar
Gorwar or Godwar, (in different periods also was called Chandravati Kingdom, Sirohi State) is a region of Rajasthan state in India, which lies in the southwest Rajasthan and borders with the state of Gujarat. Geography
Gorwar stretches along ...
, Marwar
Marwar (also called Jodhpur region) is a region of western Rajasthan state in North Western India. It lies partly in the Thar Desert. 'Maru' is a Sanskrit word for desert. The word 'wad' literally means fence in Rajasthani languages. Engl ...
, and Shekhawati
Shekhawati is a region in the northern part of the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Rajasthan, comprising the districts of Sikar, Jhunjhunu, and Churu district, Churu. The language of this region is also called Shekhawat ...
regions
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as areas, zones, lands or territories, are portions of the Earth's surface that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and ...
lie in the thorn scrub forest zone, along with the city of Jodhpur. The Luni River
The Luni is the largest river in the Thar Desert in Northwest India. It originates in Naga hills of the Pushkar valley of the Aravalli Range, near Ajmer, passes through the southeastern portion of the Thar Desert, and ends in the marshy lands of ...
and its tributaries are the major river system of Godwar and Marwar regions, draining the western slopes of the Aravallis and emptying southwest into the great Rann of Kutch
The Rann of Kutch is a large area of salt marshes that span the border between India and Pakistan. It is located mostly in the Kutch district of the Indian state of Gujarat, with a minor portion extending into the Sindh province of Pakistan. ...
wetland in neighbouring Gujarat
Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories ...
. This river is saline in the lower reaches and remains potable only up to Balotara in Barmer district
Barmer District is a district in Rajasthan state of India. It is located in the western part of Rajasthan state forming a part of the Thar Desert. Barmer was the third largest district by area in Rajasthan and fifth largest district in India, o ...
. The Ghaggar River
The Ghaggar-Hakra River () is an intermittent river in India and Pakistan that flows only during the monsoon season. The river is known as Ghaggar before the Ottu barrage at , and as Hakra downstream of the barrage in the Thar Desert. In pre- ...
, which originates in Haryana
Haryana () is a States and union territories of India, state located in the northern part of India. It was carved out after the linguistic reorganisation of Punjab, India, Punjab on 1 November 1966. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with les ...
, is an intermittent stream that disappears into the sands of the Thar Desert in the northern corner of the state and is seen as a remnant of the primitive Sarasvati river
The Sarasvati River () is a Apotheosis, deified myth, mythological Rigvedic rivers, river first mentioned in the Rigveda and later in Vedas, Vedic and post-Vedic texts. It played an important role in the Historical Vedic religion, Vedic religio ...
.
Mount Abu
Mount Abu (), known as Arbudgiri in Jain tradition, is a hill station in the Aravalli Range in the Sirohi district of the state of Rajasthan in western India. Here, the mountain forms a rocky plateau 22 km long by 9 km wide. It is ref ...
is a popular hill station in Rajasthan.
File: A sunset on the dunes of the Great Indian Thar Desert Rajasthan India.jpg, The Thar Desert
The Thar Desert (), also known as the Great Indian Desert, is an arid region in the north-western part of the Indian subcontinent that covers an area of in India and Pakistan. It is the world's 18th-largest desert, and the world's 9th-large ...
near Jaisalmer
Jaisalmer , nicknamed ''The Golden city'', is a city in the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, located west of the state capital Jaipur, in the heart of the Thar Desert. It serves as the administrative headquarters of Jaisalmer district ...
.
File: An aerial view of Udaipur and Aravali hills Rajasthan India 2012.jpg, Aerial view Udaipur and Aravali hills.
Flora and fauna
 The
The Desert National Park
Desert National Park is a national park in the Indian state of Rajasthan, near the towns of Jaisalmer and Barmer. It is one of the largest national parks, covering an area of in the Thar Desert. Sand dunes form around 44% of the park. The maj ...
in Jaisalmer
Jaisalmer , nicknamed ''The Golden city'', is a city in the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, located west of the state capital Jaipur, in the heart of the Thar Desert. It serves as the administrative headquarters of Jaisalmer district ...
, spread over an area of , is an excellent example of the ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
of the Thar Desert and its diverse fauna
Fauna (: faunae or faunas) is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding terms for plants and fungi are ''flora'' and '' funga'', respectively. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively ...
. Seashells and massive fossilised
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved i ...
tree trunks in this park record the geological history of the desert. The region is a haven for migratory and resident birds of the desert. One can see many eagle
Eagle is the common name for the golden eagle, bald eagle, and other birds of prey in the family of the Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of Genus, genera, some of which are closely related. True eagles comprise the genus ''Aquila ( ...
s, harriers, falcon
Falcons () are birds of prey in the genus ''Falco'', which includes about 40 species. Some small species of falcons with long, narrow wings are called hobbies, and some that hover while hunting are called kestrels. Falcons are widely distrib ...
s, buzzard
Buzzard is the common name of several species of birds of prey.
''Buteo'' species
* Archer's buzzard (''Buteo archeri'')
* Augur buzzard (''Buteo augur'')
* Broad-winged hawk (''Buteo platypterus'')
* Common buzzard (''Buteo buteo'')
* Easte ...
s, kestrel
The term kestrel (from , derivative from , i.e. ratchet) is the common name given to several species of predatory birds from the falcon genus ''Falco''. Kestrels are most easily distinguished by their typical hunting behaviour which is to hover ...
s and vulture
A vulture is a bird of prey that scavenges on carrion. There are 23 extant species of vulture (including condors). Old World vultures include 16 living species native to Europe, Africa, and Asia; New World vultures are restricted to Nort ...
s. Short-toed snake eagle
The short-toed snake eagle (''Circaetus gallicus''), also known as the short-toed eagle, is a medium-sized bird of prey in the family Accipitridae, which also includes many other diurnal raptors such as kites, buzzards and harriers. The genus n ...
s (''Circaetus gallicus''), tawny eagle
The tawny eagle (''Aquila rapax'') is a large bird of prey. Like all eagles, it belongs to the family ''Accipitridae''. Its heavily feathered legs mark it as a member of the subfamily Aquilinae, also known as booted eagles.Helbig, A. J., Kocum, ...
s (''Aquila rapax''), spotted eagle
''Clanga'' is a genus which contains the spotted eagles. The genus name is from Ancient Greek ''klangos'', "eagle".
Taxonomy
The genus ''Clanga'' was described in 1854 by the Polish naturalist Adam Ferdynand Adamowicz (1802-1881). The type spec ...
s (''Aquila clanga''), laggar falcon
The laggar falcon (''Falco jugger''), also known as the lugger falcon or jugger (from Hindi जग्गर — jaggar, "falcon"), is a mid-sized bird of prey which occurs in the Indian subcontinent from extreme southeastern Iran, southeastern ...
s (''Falco jugger'') and kestrels are some of the raptor species seen in Desert National Park. Road traffic inside the Park is, however, a threat to several wild species of the park with several species of amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals reported to have died as roadkill.
The Ranthambore National Park
Ranthambore National Park is a national park in the Indian state of Rajasthan. It covers a total area of . It is bounded to the north by the Banas River and to the south by the Chambal River. It is named after the historic Ranthambore Fort ...
located in Sawai Madhopur
Sawai Madhopur (IAST: ''Savāī Mādhōpur'', IPA: əˈʋaːiː ˈmaːdʱoːpʊɾ is a city in the southeastern part of the Indian state of Rajasthan. It serves as the administrative headquarter of the Sawai Madhopur district, and forms a ...
, one of the well known tiger reserves in the country, became a part of Project Tiger
Project Tiger is a wildlife conservation movement initiated in India to protect the endangered tiger. The project was initiated in 1973 by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change of the Government of India. As of March 2025, there ...
in 1973.
Tal Chhapar Sanctuary
Tal Chhapar Sanctuary is a sanctuary located in the Churu district of Northwestern Rajasthan, in the Shekhawati region of India. It is known for blackbucks and is also home to a variety of birds. The sanctuary is 210 km from Jaipur on the ...
is a very small sanctuary in Sujangarh, Churu District
Churu is a district of the northern Indian state of Rajasthan.
Churu lies in the Sekhawati region of northern Rajasthan and shares boundaries with the Hanumangarh District to the north, the Haryana state to the east, the Jhunjhunu and Sikar ...
, from Jaipur
Jaipur (; , ) is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and the List of cities and towns in Rajasthan, largest city of the north-western States and union territories of India, Indian state of Rajasthan. , the city had ...
in the Shekhawati
Shekhawati is a region in the northern part of the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Rajasthan, comprising the districts of Sikar, Jhunjhunu, and Churu district, Churu. The language of this region is also called Shekhawat ...
region. This sanctuary is home to a large population of blackbuck
The blackbuck (''Antilope cervicapra''), also known as the Indian antelope, is a medium-sized antelope native to India and Nepal. It inhabits grassy plains and lightly forested areas with perennial water sources.
It stands up to high at the sh ...
. Desert foxes and the caracal
The caracal (''Caracal caracal'') () is a medium-sized Felidae, wild cat native to Africa, the Middle East, Central Asia, and arid areas of Pakistan and northwestern India. It is characterised by a robust build, long legs, a short face, long ...
, an apex predator
An apex predator, also known as a top predator or superpredator, is a predator at the top of a food chain, without natural predators of its own.
Apex predators are usually defined in terms of trophic dynamics, meaning that they occupy the hig ...
, also known as the ''desert lynx'', can also be spotted, along with birds such as the partridge
A partridge is a medium-sized Galliformes, galliform bird in any of several genera, with a wide Indigenous (ecology), native distribution throughout parts of Europe, Asia and Africa. Several species have been introduced to the Americas. They ar ...
, harriers, eastern imperial eagle
The eastern imperial eagle (''Aquila heliaca'') is a large bird of prey that breeds in southeastern Europe and extensively through West and Central Asia. Most populations are migratory and winter in northeastern Africa, the Middle East and South a ...
, pale harrier, marsh harrier
The marsh harriers are bird of prey, birds of prey of the harrier (bird), harrier subfamily. They are medium-sized Bird of prey, raptors and the largest and broadest-winged harriers. Most of them are associated with marshland and dense reedbeds. ...
, short-toed eagle
The short-toed snake eagle (''Circaetus gallicus''), also known as the short-toed eagle, is a medium-sized bird of prey in the family Accipitridae, which also includes many other diurnal raptors such as kites, buzzards and harriers. The genus ...
, tawny eagle
The tawny eagle (''Aquila rapax'') is a large bird of prey. Like all eagles, it belongs to the family ''Accipitridae''. Its heavily feathered legs mark it as a member of the subfamily Aquilinae, also known as booted eagles.Helbig, A. J., Kocum, ...
, sparrow hawk, crested lark
The crested lark (''Galerida cristata'') is a species of lark widespread across Eurasia and North Africa, northern Africa. It is a non-migratory bird, but can occasionally be found as a Vagrancy (biology), vagrant in Great Britain.
Taxonomy and ...
, demoiselle crane
The demoiselle crane (''Grus virgo'') is a species of crane found in central Eurosiberia, ranging from the Black Sea to Mongolia and Northeast China. There is also a small breeding population in Turkey. These cranes are migratory birds. Birds f ...
, skylarks
''Skylarks'' is a 1936 British comedy film directed by Thornton Freeland and starring Jimmy Nervo, Teddy Knox and Nancy Burne.Low p.386 Nervo and Knox were a comic team, who became associated with the larger Crazy Gang (comedy group), Crazy Gang ...
, green bee-eater, brown dove
Brown doves are members of the genus ''Phapitreron'' in the Columbidae, pigeon family. Their common name refers to their overall brown coloration. They are Endemism, endemic to the Philippines. All brown doves are tree-dwellers, but the different ...
, black ibis, and sand grouse. The great Indian bustard
The great Indian bustard (''Ardeotis nigriceps'') or Indian bustard is a bustard occurring on the Indian subcontinent. It is a large bird with a horizontal body and long bare legs, and is among the heaviest of the flying birds. Once common on th ...
, known locally as the ''godavan'', and which is a state bird, has been classed as critically endangered since 2011.
Wildlife protection
Rajasthan is also noted for its national parks andwildlife
Wildlife refers to domestication, undomesticated animals and uncultivated plant species which can exist in their natural habitat, but has come to include all organisms that grow or live wilderness, wild in an area without being species, introdu ...
sanctuaries. There are four national parks and wildlife sanctuaries: Keoladeo National Park
Keoladeo National Park, or Keoladeo Ghana National Park, is a national park in Rajasthan, India. The national park hosts thousands of native, resident and migratory birds, especially during the winter season, when many different species fly to t ...
of Bharatpur, Sariska Tiger Reserve
Sariska Tiger Reserve is a tiger reserve in Alwar district, Rajasthan, India. It stretches over an core tiger habitat area of and 322.23 km² of buffer area making 1203.34 km² total area of tiger reserve. It is comprising scrub-thorn arid ...
of Alwar, Ranthambore National Park
Ranthambore National Park is a national park in the Indian state of Rajasthan. It covers a total area of . It is bounded to the north by the Banas River and to the south by the Chambal River. It is named after the historic Ranthambore Fort ...
of Sawai Madhopur
Sawai Madhopur (IAST: ''Savāī Mādhōpur'', IPA: əˈʋaːiː ˈmaːdʱoːpʊɾ is a city in the southeastern part of the Indian state of Rajasthan. It serves as the administrative headquarter of the Sawai Madhopur district, and forms a ...
, and Desert National Park
Desert National Park is a national park in the Indian state of Rajasthan, near the towns of Jaisalmer and Barmer. It is one of the largest national parks, covering an area of in the Thar Desert. Sand dunes form around 44% of the park. The maj ...
of Jaisalmer. A national-level institute, Arid Forest Research Institute
Arid Forest Research Institute (ICFRE-AFRI) is a research institute situated in Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India. The institute conducts scientific research in forestry in order to provide technologies to increase the Permanent vegetative cover, vege ...
(AFRI) an autonomous institute of the ministry of forestry is situated in Jodhpur and continuously works on desert flora and their conservation.
Ranthambore National Park
Ranthambore National Park is a national park in the Indian state of Rajasthan. It covers a total area of . It is bounded to the north by the Banas River and to the south by the Chambal River. It is named after the historic Ranthambore Fort ...
is 7 km from Sawai Madhopur
Sawai Madhopur (IAST: ''Savāī Mādhōpur'', IPA: əˈʋaːiː ˈmaːdʱoːpʊɾ is a city in the southeastern part of the Indian state of Rajasthan. It serves as the administrative headquarter of the Sawai Madhopur district, and forms a ...
Railway Station. It is known worldwide for its tiger population and is considered by both wilderness lovers and photographers as one of the best places in India to spot tigers. At one point, due to poaching and negligence, tigers became extinct at Sariska, but five tigers have been relocated there. Prominent among the wildlife sanctuaries are Mount Abu
Mount Abu (), known as Arbudgiri in Jain tradition, is a hill station in the Aravalli Range in the Sirohi district of the state of Rajasthan in western India. Here, the mountain forms a rocky plateau 22 km long by 9 km wide. It is ref ...
Sanctuary, Bhensrod Garh Sanctuary, Darrah Sanctuary, Jaisamand Sanctuary, Kumbhalgarh Wildlife Sanctuary, Jawahar Sagar Sanctuary, and Sita Mata Wildlife Sanctuary.
Governance and administration
 The state is governed by a parliamentary system of representative democracy. The governor serves as the state's constitutional leader, whereas the
The state is governed by a parliamentary system of representative democracy. The governor serves as the state's constitutional leader, whereas the chief minister
A chief minister is an elected or appointed head of government of – in most instances – a sub-national entity, for instance an administrative subdivision or federal constituent entity. Examples include a state (and sometimes a union ter ...
assumes the role of both the head of the government and the head of the council of ministers. The Legislative Assembly consists of 200 members who are elected for five-year terms. The state contributes 25 seats to Lok Sabha
The Lok Sabha, also known as the House of the People, is the lower house of Parliament of India which is Bicameralism, bicameral, where the upper house is Rajya Sabha. Member of Parliament, Lok Sabha, Members of the Lok Sabha are elected by a ...
, the lower house of the Indian Parliament, and 10 seats to Rajya Sabha
Rajya Sabha (Council of States) is the upper house of the Parliament of India and functions as the institutional representation of India’s federal units — the states and union territories.https://rajyasabha.nic.in/ It is a key component o ...
, the upper house.
The Government of Rajasthan
The Government of Rajasthan is the supreme governing authority of the Indian state of Rajasthan and its districts of Rajasthan, 41 districts. It consists of an executive branch, led by the governor of Rajasthan, as well as judiciary and legis ...
is a democratically elected body in India with the governor as its constitutional head. Governor
A governor is an politician, administrative leader and head of a polity or Region#Political regions, political region, in some cases, such as governor-general, governors-general, as the head of a state's official representative. Depending on the ...
is appointed by the President of India
The president of India (ISO 15919, ISO: ) is the head of state of the Republic of India. The president is the nominal head of the executive, the first citizen of the country, and the commander-in-chief, supreme commander of the Indian Armed ...
for a five-year term. The leader of the party or coalition with a majority in the Legislative Assembly is appointed as the chief minister by the governor, and the council of ministers are appointed by the governor on the advice of the chief minister
A chief minister is an elected or appointed head of government of – in most instances – a sub-national entity, for instance an administrative subdivision or federal constituent entity. Examples include a state (and sometimes a union ter ...
. The governor remains a ceremonial head of the state, while the chief minister and his council are responsible for day-to-day government functions. The council of ministers consists of Cabinet Ministers
A cabinet in governing is a group of people with the constitutional or legal task to rule a country or state, or advise a head of state, usually from the executive branch. Their members are known as ministers and secretaries and they are ...
, Ministers of State
Minister of state is a designation for a government minister, with varying meanings in different jurisdictions. In a number of European countries, the title is given as an honorific conferring a higher rank, often bestowed upon senior ministers ...
(MoS) and Deputy Ministers. The Secretariat headed by the Chief Secretary assists the council of ministers. The Chief Secretary is also the administrative head of the government. Each government department is headed by a minister, who is assisted by an Additional Chief Secretary
The Chief Secretary is the highest-ranking executive official and civil servant of the government of an Indian state. The Chief Secretary is the ''ex-officio'' head of the state Civil Services Board, the State Secretariat, the state cadre Indi ...
or a Principal Secretary, who is usually an officer of Indian Administrative Service
The Indian Administrative Service (IAS) is the Public administration, administrative arm of the All India Services of Government of India. The IAS is one of the three All India Services along with the Indian Police Service (IPS) and the Indian ...
(IAS), the Additional Chief Secretary/Principal Secretary serve as the administrative head of the department they are assigned to. Each department also has officers of the rank of Secretary, Special Secretary, Joint Secretary etc. assisting the Minister and the Additional Chief Secretary/Principal Secretary.
For the administration purpose, the state is divided into 07 divisions and 41 districts. Divisional Commissioner
A Divisional Commissioner, also known as Commissioner of division, is an Indian Administrative Service officer who serves as the administrator of a division of a state in India. The post is referred to as regional commissioner in Karnataka
...
, is the head of administration on the divisional level. The administration in each district is headed by a District Magistrate/District Collector, who is also an IAS officer, and is assisted by a number of officers belonging to Rajasthan Administrative Services. In Rajasthan, the police force is led by an IPS officer holding the position of Director General of Police. Each district is supervised by a Superintendent of Police
Superintendent (Supt) is a rank in the British police and in most English-speaking Commonwealth nations. In many Commonwealth countries, the full version is superintendent of police (SP). The rank is also used in most British Overseas Territori ...
, also an IPS officer, who is supported by officers from the Rajasthan Police Services. Their primary responsibility involves maintaining law and order and addressing relevant issues within their respective districts. The management of forests, environment, and wildlife in the district is overseen by the Divisional Forest Officer, who is a member of the Indian Forest Service
The Indian Forest Service (IFS) is the premier forest service of India. .The IFS is one of the three All India Services along with the Indian Administrative Service (IAS) & the Indian Police Service (IPS). It was constituted in the year 1966 un ...
. This responsibility is carried out with the assistance of officers from the Rajasthan Forest Service and Rajasthan Subordinate Service.
 Rajasthan has its High court Jodhpur which has its principal seat at
Rajasthan has its High court Jodhpur which has its principal seat at Jodhpur
Jodhpur () is the second-largest city of the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, after its capital Jaipur. As of 2023, the city has a population of 1.83 million. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Jodhpur district and ...
and a bench at Jaipur
Jaipur (; , ) is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and the List of cities and towns in Rajasthan, largest city of the north-western States and union territories of India, Indian state of Rajasthan. , the city had ...
, with district courts and session courts in each district or Sessions Division, and lower courts at the tehsil level. The president of India appoints the chief justice of the High Court of Rajasthan judiciary on the advice of the Chief Justice of the Supreme Court of India
The Supreme Court of India is the supreme judiciary of India, judicial authority and the supreme court, highest court of the Republic of India. It is the final Appellate court, court of appeal for all civil and criminal cases in India. It also ...
as well as the governor of Rajasthan. In Rajasthan, the Subordinate Judicial Service is an essential component of the state's judiciary, and it is divided into two categories: the Rajasthan Civil Judicial Services and the Rajasthan Higher Judicial Service. The former includes Civil Judges (Junior Division)/Judicial Magistrates and Civil Judges (Senior Division)/Chief Judicial Magistrate. On the other hand, the latter consists of Civil and Sessions Judges. The District Judge District Judge may refer to:
* A United States federal judge, appointed by the president and confirmed by the Senate
* A judge in a state court (United States), where the state is divided into judicial districts
*
* A judge in the district courts ...
has control over the Subordinate Judicial Service in Rajasthan.
The politics of Rajasthan has mainly been dominated mainly by the Bharatiya Janata Party
The Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP; , ) is a political party in India and one of the two major List of political parties in India, Indian political parties alongside the Indian National Congress. BJP emerged out from Syama Prasad Mukherjee's ...
and the Indian National Congress
The Indian National Congress (INC), colloquially the Congress Party, or simply the Congress, is a political parties in India, political party in India with deep roots in most regions of India. Founded on 28 December 1885, it was the first mo ...
.
Chief Secretary Of Rajasthan is Usha Sharma and Director General of Police or DGP of Rajasthan is Umesh Mishra.
Regions, divisions, districts and cities

 Rajasthan is composed of the following geographical, political and historical regions:
# Bagar
#
Rajasthan is composed of the following geographical, political and historical regions:
# Bagar
#Hadoti
Hadoti is a region of Rajasthan state in western India, which was once called the Bundi Kingdom. The biggest cities are Jhalawar and Kota. It includes the districts of Bundi, Baran, Jhalawar and Kota and is bounded on the west by the Me ...
#Dhundhar
Dhundhar, also known as ''Jaipur region'', is a historical region of Rajasthan state in western India. It includes the districts of Jaipur, Neem ka Thana, Dantaramgarh part of Sikar District lying to the east of the Aravalli Range, Dausa, ...
#Gorwar
Gorwar or Godwar, (in different periods also was called Chandravati Kingdom, Sirohi State) is a region of Rajasthan state in India, which lies in the southwest Rajasthan and borders with the state of Gujarat. Geography
Gorwar stretches along ...
#Shekhawati
Shekhawati is a region in the northern part of the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Rajasthan, comprising the districts of Sikar, Jhunjhunu, and Churu district, Churu. The language of this region is also called Shekhawat ...
#Mewar
Mewar, also spelled as Mewad is a region in the south-central part of Rajasthan state of India. It includes the present-day districts of Bhilwara, Chittorgarh, Pratapgarh, Rajsamand, Udaipur, Pirawa Tehsil of Jhalawar District of Rajasth ...
#Marwar
Marwar (also called Jodhpur region) is a region of western Rajasthan state in North Western India. It lies partly in the Thar Desert. 'Maru' is a Sanskrit word for desert. The word 'wad' literally means fence in Rajasthani languages. Engl ...
#Vagad
Vagad (also known as Vagar) is a region in southeastern Rajasthan state of western India. Its boundaries are roughly defined by those of the districts of Dungarpur and Banswara. Major cities of the region are Dungarpur and Banswara.
Geogra ...
#Mewat
Mewat (; ) is a historical and cultural region which encompasses parts of the modern-day states of Haryana, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh in northwestern India.
Geography
The loose boundaries of the Mewat region generally include parts of th ...
#Brij
Braj, also known as Vraj, Vraja, Brij or Brijbhumi, is a region in India on both sides of the Yamuna river with its centre at Mathura district, Mathura-Vrindavan in Uttar Pradesh state encompassing the area which also includes Palwal, Ballabh ...
#Merwara
Rajasthan is divided into 41 districts within 7 divisions
Division may refer to:
Mathematics
*Division (mathematics), the inverse of multiplication
* Division algorithm, a method for computing the result of mathematical division Military
*Division (military), a formation typically consisting of 10,000 t ...
:
A district collector
The district magistrate, also known as the district collector or deputy commissioner, is a career civil servant who serves as the executive head of a district's administration in India. The specific name depends on the state or union territo ...
or district magistrate
The district magistrate, also known as the district collector or deputy commissioner, is a career civil servant who serves as the executive head of a district's administration in India. The specific name depends on the state or union territo ...
, who is appointed by either the Indian Administrative Service
The Indian Administrative Service (IAS) is the Public administration, administrative arm of the All India Services of Government of India. The IAS is one of the three All India Services along with the Indian Police Service (IPS) and the Indian ...
or the Rajasthan Public Service Commission
The Rajasthan Public Service Commission (RPSC) is a government body of the Rajasthan, India, established by the Constitution of India, to select applicants for various state government jobs according to the merits of the applicants and the rule ...
, governs each district. Subdivisions (Tehsils) are responsible for governing districts and are overseen by sub-divisional magistrates. Additionally, districts are further divided into blocks. A block consists of panchayats (village councils) and town municipalities. Tehsils are intermediate level panchayat between the Zilla Parishad (district councils) at the district level and gram panchayat (village councils) at the lower level. Rajasthan has 5 cities with over one million population. The absolute urban population of the state is 17.4 million, which constitutes 24.87% of the total urban population of the state. There are 10 municipal corporation
Municipal corporation is the legal term for a local governing body, including (but not necessarily limited to) cities, counties, towns, townships, charter townships, villages, and boroughs. The term can also be used to describe municipally o ...
s, 34 municipal council
A municipal council is the legislative body of a municipality or local government area. Depending on the location and classification of the municipality it may be known as a city council, town council, town board, community council, borough cou ...
s and 172 municipal boards or nagar pachayats in the state. Jaipur
Jaipur (; , ) is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and the List of cities and towns in Rajasthan, largest city of the north-western States and union territories of India, Indian state of Rajasthan. , the city had ...
, Jodhpur
Jodhpur () is the second-largest city of the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, after its capital Jaipur. As of 2023, the city has a population of 1.83 million. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Jodhpur district and ...
, and Kota have two municipal corporations each since October 2019, as their populations have exceeded 1 million.
Communication
Major internet service provider (ISP) and telecom companies are present in Rajasthan includingVodafone Idea
Vodafone Idea is an Indian telecommunications company, headquartered in Gandhinagar. It is an all-India integrated GSM operator offering mobile telephony services.
As of 30 September 2024, Vi has a subscriber base of 212.45 million, making ...
, BSNL
Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (commonly known as BSNL) () is an Indian central public sector undertaking, under the ownership of Department of Telecommunications, which is part of the Ministry of Communications, Government of India with its he ...
, Airtel
Bharti Airtel Limited is an Indian multinational telecommunications company based in New Delhi. It operates in 18 countries across South Asia and Africa, as well as the Channel Islands. Currently, Airtel provides 5G, 4G and LTE Advanced ...
, Jio
Reliance Jio Infocomm Limited (d/b/a Jio) is an Indian telecommunications company and a subsidiary of Jio Platforms, headquartered in Navi Mumbai. It operates a national LTE (telecommunication), LTE network with coverage across all 22 telecom ...
, Data Infosys Limited
Data ( , ) are a collection of discrete or continuous values that convey information, describing the quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted formally ...
, RailTel Corporation of India, Software Technology Parks of India
Software Technology Parks of India (STPI) is an S&T autonomous society under Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) engaged in promoting IT/ ITES Industry, Innovation, R&D, Start-ups, Product/ IP creation in the fiel ...
(STPI). Data Infosys was the first ISP to bring the internet to Rajasthan in April 1999 and OASIS
In ecology, an oasis (; : oases ) is a fertile area of a desert or semi-desert environmentpastoral
The pastoral genre of literature, art, or music depicts an idealised form of the shepherd's lifestyle – herding livestock around open areas of land according to the seasons and the changing availability of water and pasture. The target au ...
. Wheat and barley
Barley (), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains; it was domesticated in the Fertile Crescent around 9000 BC, giving it nonshattering spikele ...
are cultivated over large areas, as are pulses
Legumes are plants in the pea family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seeds of such plants. When used as a dry grain for human consumption, the seeds are also called pulses. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consum ...
, sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fib ...
, and oilseed
Vegetable oils, or vegetable fats, are oils extracted from seeds or from other parts of edible plants. Like animal fats, vegetable fats are ''mixtures'' of triglycerides. Soybean oil, grape seed oil, and cocoa butter are examples of seed ...
s. Cotton and tobacco are the state's cash crops. Rajasthan is among the largest producers of edible oil
Cooking oil (also known as edible oil) is a plant or animal liquid fat used in frying, baking, and other types of cooking. Oil allows higher cooking temperatures than water, making cooking faster and more flavorful, while likewise distributing he ...
s in India and the second-largest producer of oilseeds
Vegetable oils, or vegetable fats, are oils extracted from seeds or from other parts of edible plants. Like animal fats, vegetable fats are ''mixtures'' of triglycerides. Soybean oil, grape seed oil, and cocoa butter are examples of seed o ...
. Rajasthan is also the biggest wool
Wool is the textile fiber obtained from sheep and other mammals, especially goats, rabbits, and camelids. The term may also refer to inorganic materials, such as mineral wool and glass wool, that have some properties similar to animal w ...
-producing state in India and the main opium
Opium (also known as poppy tears, or Lachryma papaveris) is the dried latex obtained from the seed Capsule (fruit), capsules of the opium poppy ''Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid mor ...
producer and consumer. There are mainly two crop seasons. The water for irrigation comes from wells and tanks. The Indira Gandhi Canal
The Indira Gandhi Canal (originally, Rajasthan Canal) project, with total length of to depending on how the length is calculated which either way includes the length of the Rajasthan Feeder Canal and the downstream length of main Indira Gan ...
irrigates northwestern Rajasthan.
 The main industries are mineral based, agriculture-based, and
The main industries are mineral based, agriculture-based, and textile
Textile is an Hyponymy and hypernymy, umbrella term that includes various Fiber, fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, Staple (textiles)#Filament fiber, filaments, Thread (yarn), threads, and different types of #Fabric, fabric. ...
based. Rajasthan is the second-largest producer of polyester
Polyester is a category of polymers that contain one or two ester linkages in every repeat unit of their main chain. As a specific material, it most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyesters include some natura ...
fibre in India. Several prominent chemical and engineering companies are located in the city of Kota, in southern Rajasthan. Rajasthan is pre-eminent in quarrying
A quarry is a type of open-pit mine in which dimension stone, rock, construction aggregate, riprap, sand, gravel, or slate is excavated from the ground. The operation of quarries is regulated in some jurisdictions to manage their s ...
and mining in India. The Taj Mahal
The Taj Mahal ( ; ; ) is an ivory-white marble mausoleum on the right bank of the river Yamuna in Agra, Uttar Pradesh, India. It was commissioned in 1631 by the fifth Mughal Empire, Mughal emperor, Shah Jahan () to house the tomb of his belo ...
was built from white marble which was mined from a town called Makrana
Makrana is an urban city located, near Kuchaman City, at the centre of state in Didwana-Kuchaman district in the Indian state of Rajasthan. Rajasthani language is widely spoken here. It also served as a tehsil headquarters, with 136 villa ...
. The state is the second-largest source of cement in India. It has rich salt deposits at Sambhar, copper mines at Khetri
Khetri Nagar is a town in the Jhunjhunu district of Rajasthan in India. It is a part of the Shekhawati
Shekhawati is a region in the northern part of the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Rajasthan, comprising the d ...
, Jhunjhunu
Jhunjhunu is a city and municipal council in the state of Rajasthan in India. It is the administrative headquarters of the Jhunjhunu district. It is also the largest city of the Shekhawati region, which includes Jhunjhunu, Churu and Sikar ...
, and zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
mines at Dariba, Zawar mines and Rampura Agucha (opencast) near Bhilwara
Bhilwara () is a city and administrative headquarters in Bhilwara district of the Mewar region of Rajasthan, India. It has been termed as 'Textile city'.
History
Stone Age tools dating from 5,012 to 200,000 years were found in Bundi and ...
. Dimensional stone mining is also undertaken in Rajasthan. Jodhpur sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sand ...
is mostly used in monuments, important buildings, and residential buildings. This stone is termed as ''Chittar Patthar''. Jodhpur leads in the handicraft
A handicraft is a traditional main sector of craft making and applies to a wide range of creative and design activities that are related to making things with one's hands and skill, including work with textiles, moldable and rigid material ...
and guar gum
Guar gum, also called guaran, is a galactomannan polysaccharide extracted from guar beans that has thickening and stabilizing properties useful in food, feed, and industrial applications. The guar seeds are mechanically dehusked, hydrated, mi ...
industries.
Rajasthan is also a part of the Mumbai-Delhi Industrial corridor set to benefit economically. The state gets 39% of the DMIC, with major districts of Jaipur, Alwar, Kota and Bhilwara benefiting.
Rajasthan also has reserves of low-silica limestone.
Rajasthan connected 100% of its population to electricity power in 2019 (raising the rate of electricity access from 71% of the population in 2015). The renewable energy sector plays the most important role in the increase of generation capacities, with the main focus on solar energy
Solar energy is the radiant energy from the Sun's sunlight, light and heat, which can be harnessed using a range of technologies such as solar electricity, solar thermal energy (including solar water heating) and solar architecture. It is a ...
. In 2020, Bhadla Solar Park
The Bhadla Solar Park is a solar power plant located in the Thar Desert of Rajasthan, India. It covers an area of 56 square kilometers and has a total installed capacity of 2,245 megawatts (MW), making it India's largest and the 11th-largest s ...
was recognised as the largest cluster of photovoltaic power plants in a single region in the world, with the installed power exceeding the 2.2 gigawatt peak.
Rajasthan is also a significant producer of silver. The state produced 679.172 tonnes of silver in 2018–19, 609.153 tonnes in 2019–20, and 705.676 tonnes in 2020–21.
Transportation
Rajasthan is connected by many national highways, the most renowned being NH 8, which is India's first 4–8 lane highway. Rajasthan also has an inter-city surface transport system both in terms of railways and bus network. All chief cities are connected by air, rail, and road.Air
Jaipur International Airport
Jaipur International Airport is an international airport serving Jaipur, the capital of Rajasthan. It is located in the southern suburb of Sanganer, located from the city centre. It is the List of the busiest airports in India, 13th-busiest a ...
(JAI) in Jaipur, is the state's largest, busiest and only international airport. Jaipur International Airport offers international service to Dubai
Dubai (Help:IPA/English, /duːˈbaɪ/ Help:Pronunciation respelling key, ''doo-BYE''; Modern Standard Arabic, Modern Standard Arabic: ; Emirati Arabic, Emirati Arabic: , Romanization of Arabic, romanized: Help:IPA/English, /diˈbej/) is the Lis ...
, Bangkok
Bangkok, officially known in Thai language, Thai as Krung Thep Maha Nakhon and colloquially as Krung Thep, is the capital and most populous city of Thailand. The city occupies in the Chao Phraya River delta in central Thailand and has an estim ...
, Sharjah
Sharjah (; ', Gulf Arabic: ''aš-Šārja'') is the List of cities in the United Arab Emirates, third-most populous city in the United Arab Emirates, after Dubai and Abu Dhabi. It is the capital of the Emirate of Sharjah and forms part of the D ...
and Muscat
Muscat (, ) is the capital and most populous city in Oman. It is the seat of the Governorate of Muscat. According to the National Centre for Statistics and Information (NCSI), the population of the Muscat Governorate in 2022 was 1.72 million. ...
. There are five civilian airports in Rajasthan including Jodhpur Airport
Jodhpur Airport is a domestic airport and an Indian Air Force base serving the city of Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India. It is operated by the Airports Authority of India (AAI) and shares its airside with the Jodhpur Air Force Station of the Indian A ...
, Udaipur Airport, Ajmer Airport, Bikaner Airport
Nal Air Force Station , also known as Bikaner Air Force Station and Civil Airport Bikaner, is a domestic airport and an Indian Air Force Station, which serves the city of Bikaner in Rajasthan, India. It is located at Nal, 13 km (8 mi ...
and Jaisalmer Airport
Jaisalmer Airport is a domestic airport serving Jaisalmer, Rajasthan, India. It is located from the city centre. The airport operates as a civil enclave on an Indian Air Force base.
The airport has a single runway of in length and in width ...
. Domestic airports are operated by the Airports Authority of India
The Airports Authority of India (AAI) is a statutory body under the ownership of the Ministry of Civil Aviation (India), Ministry of Civil Aviation, Government of India. It is responsible for creating, upgrading, maintaining, and managing civi ...
(AAI) and shares its airside with the Indian Air Force. These airports connect Rajasthan with the major cities of India such as Mumbai, Kolkata
Kolkata, also known as Calcutta ( its official name until 2001), is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of West Bengal. It lies on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River, west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary ...
, Hyderabad
Hyderabad is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Telangana. It occupies on the Deccan Plateau along the banks of the Musi River (India), Musi River, in the northern part of Southern India. With an average altitude of , much ...
, Chennai
Chennai, also known as Madras (List of renamed places in India#Tamil Nadu, its official name until 1996), is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Tamil Nadu by population, largest city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost states and ...
and Bangalore
Bengaluru, also known as Bangalore (List of renamed places in India#Karnataka, its official name until 1 November 2014), is the Capital city, capital and largest city of the southern States and union territories of India, Indian state of Kar ...
.Railway
Railways
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport using wheeled vehicles running in tracks, which usually consist of two parallel steel rails. Rail transport is one of the two primary means of land transport, next to roa ...
length in the state constitute 8.66 per cent of all India route length. Jaipur Junction is the headquarters of the North Western Railway
The North Western Railway (abbreviated NWR) is one of 19 railway zones in India. It is headquartered at Jaipur. It has a route length of more than across the states of Rajasthan, Gujarat, Punjab and Haryana. NWR operates international rail s ...
. Jaipur, Ajmer
Ajmer () is a city in the north-western States and union territories of India, Indian state of Rajasthan. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Ajmer district and Ajmer division. It lies at the centre of Rajasthan, earning it the ...
, Bikaner
Bikaner () is a city in the northwest of the States and territories of India, state of Rajasthan, India. It is located northwest of the state capital, Jaipur. It is the administrative headquarters of Bikaner District and Bikaner division.
Fo ...
are the busiest railway stations in the state. Kota is the only electrified section served by three Rajdhani Expresses and trains to all major cities of India. Jaipur Superfast Express, fastest train under Superfast category of trains; connects the finance capital of India Mumbai
Mumbai ( ; ), also known as Bombay ( ; its official name until 1995), is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra. Mumbai is the financial capital and the most populous city proper of India with an estimated population of 12 ...
to Jaipur. Luxury tourist train Maharajas' Express
The ''Maharajas' Express'' is a luxury tourist train owned and operated by The Indian Railway Catering and Tourism Corporation (IRCTC). It serves four routes across North-West and Central India, mainly centered on Rajasthan between the mont ...
runs across North-West and Central India, mainly centered on Rajasthan. There is also an international railway, the Thar Express
The ''Thar Express'' (, , Rajasthani languages, Rajasthani: थार एक्सप्रेस, Sindhi language, Sindhi: ٿر ايڪسپريس) was an international passenger train that ran between the a suburban area of Jodhpur in the India ...
from Jodhpur
Jodhpur () is the second-largest city of the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, after its capital Jaipur. As of 2023, the city has a population of 1.83 million. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Jodhpur district and ...
(India) to Karachi
Karachi is the capital city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Sindh, Pakistan. It is the List of cities in Pakistan by population, largest city in Pakistan and 12th List of largest cities, largest in the world, with a popul ...
(Pakistan). However, this is not open to foreign nationals. Jaipur Metro
The Jaipur Metro is a rapid transit system in the city of Jaipur, Rajasthan, India. Construction on the mostly elevated part of the first line, called Phase 1A, comprising of route from Mansarovar to Chandpole Bazaar, started in November 2010 ...
is the metro rail system in the city of Jaipur. It is the only metro rail system in Rajasthan and has been operational since 3 June 2015. It is the first metro in India to run on triple-storey elevated road and metro track.Road
The state is served by a substantial road network, providing links between urban centers, agricultural market-places and rural areas. There are 33national highways
National Highways (NH), formerly Highways England and before that the Highways Agency, is a State-owned enterprise, government-owned company charged with operating, maintaining and improving Roads in England, motorways and major A roads in Eng ...
(NH) in the state, covering a total distance of . The state has a total road length of . The Department of Public Works is responsible for maintaining and expanding the state highways
A state highway, state road, or state route (and the equivalent provincial highway, provincial road, or provincial route) is usually a road that is either Route number, numbered or maintained by a sub-national state or province. A road numbered ...
system and major district roads. Jaipur–Kishangarh Expressway forms a segment of the NH-8 which is a part of the Golden Quadrilateral
The Golden Quadrilateral (; abbreviated GQ) is a network of National Highway (India), national highways connecting major cities of India. It roughly forms a quadrilateral with major cities – Delhi (north), Kolkata (east), Mumbai (west) and ...
project. Rajasthan State Road Transport Corporation
Rajasthan State Road Transport Corporation (RSRTC) is a public transport company which provides bus services in the Indian state Rajasthan. It is headquartered in Jaipur, Rajasthan. The corporation was established by Government of Rajasthan on ...
(RSRTC) was established in 1964 to provide economical and reliable passenger road transport service in the state with connecting services to adjoining states. For travelling locally, the state, like most of the country, has auto rickshaw
An auto rickshaw is a motorized version of the pulled rickshaw or cycle rickshaw. Most have three wheels and do not tilt. They are known by many other terms in various countries, including three-wheeler, Adaidaita Sahu, Keke-napep, Maruwa, auto, ...
s and cycle rickshaw
The cycle rickshaw is a small-scale local means of transport. It is a type of tricycle designed to carry passengers on a vehicle for hire, for-hire basis. It is also known by a variety of other names such as bike taxi, velotaxi, pedicab, bi ...
s. Average speed on state highways varies between due to the heavy presence of vehicles; in villages and towns, speeds are as low as .
Jaipur International Airport
Jaipur International Airport is an international airport serving Jaipur, the capital of Rajasthan. It is located in the southern suburb of Sanganer, located from the city centre. It is the List of the busiest airports in India, 13th-busiest a ...
File:Maharajas' Express - Mayur Mahal, dining (4809207224).jpg, Maharajah's Express dining saloon
File:Jaipur 03-2016 34 Jaipur Metro.jpg, The Jaipur Metro
The Jaipur Metro is a rapid transit system in the city of Jaipur, Rajasthan, India. Construction on the mostly elevated part of the first line, called Phase 1A, comprising of route from Mansarovar to Chandpole Bazaar, started in November 2010 ...
is an important urban transportation link
File:National highway 841.jpg, NH 8 between Udaipur
Udaipur (Hindi: , ) (ISO 15919: ''Udayapura'') is a city in the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, about south of the state capital Jaipur. It serves as the administrative headquarters of Udaipur district. It is the historic capital of t ...
and Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad ( ), also spelled Amdavad (), is the most populous city in the Indian state of Gujarat. It is the administrative headquarters of the Ahmedabad district and the seat of the Gujarat High Court. Ahmedabad's population of 5,570,585 ...
Demographics
Population
According to the 2011 Census of India, Rajasthan has a total population of 68,548,437. The state contributes to 5.66% of India's population. The population density is 201 people per square kilometre. Thesex ratio
A sex ratio is the ratio of males to females in a population. As explained by Fisher's principle, for evolutionary reasons this is typically about 1:1 in species which reproduce sexually. However, many species deviate from an even sex ratio, ei ...
in 2011, at 928 women to 1000 men, was lower than the national figure of 943. The native Rajasthani people
Rajasthani people or Rajasthanis are a group of Indo-Aryan peoples native to Rajasthan ("the land of kings"), a states of India, state in Northern India. Their language, Rajasthani language, Rajasthani, is a part of the western group of Indo-Ar ...
make up the majority of the state's population. The state of Rajasthan is also populated by Sindhis
Sindhis are an Indo-Aryan ethnic group originating from and native to Sindh, a region of Pakistan, who share a common Sindhi culture, history, ancestry, and language. The historical homeland of Sindhis is bordered by southeastern Balochi ...
, who came to Rajasthan from Sindh province
Sindh ( ; ; , ; abbr. SD, historically romanized as Sind or Scinde) is a province of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest provin ...
(now in Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
) during the India-Pakistan separation in 1947.
Brahmins, according to ''Outlook
Outlook or The Outlook may refer to:
Computing
* Microsoft Outlook, also referred to as ''the classic Outlook'' an e-mail client and personal information management software product from Microsoft
* Outlook for Windows, also referred to as ''the ...
'' constituted 8% to 10% of the population of Rajasthan as per a 2003 report, but only 7% in a 2007 report. According to a 2007 ''DNA India
The ''Daily News and Analysis'', abbreviated as ''DNA'', is a Hindi-language news program on Zee news that was earlier an English-language newspaper with multiple local city editions across India. ''DNA'' was first launched as a broadsheet newspa ...
'' report, 12.5% of the state are Brahmins. According to a report by ''Moneycontrol.com
Network18 Media & Investments Limited, ( d/b/a Network18 Group) is an Indian media conglomerate owned by the Reliance Industries, headed by Mukesh Ambani. Rahul Joshi is the managing director, chief executive officer and group editor-in-chief, ...
'' at the time of 2018 Rajasthan Legislative Assembly election
Legislative Assembly elections were held in the Indian state of Rajasthan on 7 December 2018. The Indian National Congress became the single largest party with 100 seats, short of the majority by 1 seat. The Bharatiya Janata Party won 73 seats, ...
, the Scheduled Caste (SC) population was 18%, Scheduled Tribe (ST) was 13%, Jats
The Jat people (, ), also spelt Jaat and Jatt, are a traditionally agricultural community in Northern India and Pakistan. Originally pastoralists in the lower Indus river-valley of Sindh, many Jats migrated north into the Punjab region in ...
12%, Gurjars
The Gurjar (or Gujjar, Gujar, Gurjara) are an agricultural ethnic community, residing mainly in India, Pakistan, and Afghanistan, divided internally into various clan groups. They were traditionally involved in agriculture, pastoral and nomadic ...
and Rajputs
Rājpūt (, from Sanskrit ''rājaputra'' meaning "son of a king"), also called Thākur (), is a large multi-component cluster of castes, kin bodies, and local groups, sharing social status and ideology of genealogical descent originating fro ...
9% each, Brahmin
Brahmin (; ) is a ''Varna (Hinduism), varna'' (theoretical social classes) within Hindu society. The other three varnas are the ''Kshatriya'' (rulers and warriors), ''Vaishya'' (traders, merchants, and farmers), and ''Shudra'' (labourers). Th ...
s and Meena
Meena () is a tribe from northern and western India which is sometimes considered a sub-group of the Bhil community. It used to be claimed they speak Mina language, a
Spurious languages, spurious language. Its name is also transliterated as ' ...
s 7% each. A ''Hindustan Times
''Hindustan Times'' is an Indian English language, English-language daily newspaper based in Delhi. It is the flagship publication of HT Media Limited, an entity controlled by the Birla family, and is owned by Shobhana Bhartia, the daughter o ...
'' report from 2019 also agrees to the total ST population of 13%, of which Meenas
Meena () is a tribe from northern and western India which is sometimes considered a sub-group of the Bhil community. It used to be claimed they speak Mina language, a
spurious language. Its name is also transliterated as ''Meenanda'' or ''Mi ...
constitute the biggest group at 7%. According to a Deutsche Welle
(; "German Wave"), commonly shortened to DW (), is a German state-funded television network, state-owned international broadcaster funded by the Federal Government of Germany. The service is available in 32 languages. DW's satellite tele ...
report, the Jats constitute 12–15% of the population of Rajasthan, followed by Meenas with 10% and Gurjars with 6%. While as per a 2007 BBC Hindi
BBC News is an operational business division of the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) responsible for the gathering and broadcasting of news and current affairs in the UK and around the world. The department is the world's largest broadc ...
report, Meenas were 14% and Gurjars were 4% of the state's population.
Language
Hindi
Modern Standard Hindi (, ), commonly referred to as Hindi, is the Standard language, standardised variety of the Hindustani language written in the Devanagari script. It is an official language of India, official language of the Government ...
is the official language of the state, while English is the additional official language.
The languages of Rajasthan primarily belong to the Rajasthani group of Indo-Aryan languages
The Indo-Aryan languages, or sometimes Indic languages, are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. As of 2024, there are more than 1.5 billion speakers, primarily concentrated east ...
, which most people regard as their own language. In the north are dialects of Punjabi
Punjabi, or Panjabi, most often refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to Punjab, a region in India and Pakistan
* Punjabi language
* Punjabis, Punjabi people
* Punjabi dialects and languages
Punjabi may also refer to:
* Punjabi (horse), a ...
and Bagri, which is a transition between Rajasthani and Punjabi. In the northeast Shekhawati
Shekhawati is a region in the northern part of the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Rajasthan, comprising the districts of Sikar, Jhunjhunu, and Churu district, Churu. The language of this region is also called Shekhawat ...
and Dhundari
Dhundhari (ढूंढाड़ी), also known as Jaipuri, is a Indo-Aryan language variety of the Rajasthani languages group. It is spoken in the Dhundhar region of northeastern Rajasthan state, India. Dhundari-speaking people are found in ...
are spoken which gradually merge with Haryanvi
Haryanvi (हरियाणवी or हरयाणवी) is an Indo-Aryan language spoken primarily in the Indian state of Haryana and the territory of Delhi. Haryanvi is considered to be part of the dialect group of Western Hindi, which a ...
. In the east Mewati
Mewati ( Devanagri: मेवाती; Perso-Arabic: میواتی) is an Indo-Aryan language spoken predominantly by the Meo people. It has three million speakers in the Mewat Region with most speakers in Nuh district of Haryana. It is al ...
is spoken in the Mewat region, while in the far east Braj
Braj, also known as Vraj, Vraja, Brij or Brijbhumi, is a region in India on both sides of the Yamuna river with its centre at Mathura-Vrindavan in Uttar Pradesh state encompassing the area which also includes Palwal, Ballabhgarh and Nuh in ...
is spoken. To the southeast Haryanvi is spoken. To the west in the heart of the Thar Desert Marwari
Marwari may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the Marwar region of Rajasthan, India, largely in the Thar Desert
** Marwari people, an Indian ethnic group originating in the Marwar region
** Marwari language, the language of the Marwari ...
is spoken, which merges to Gujarati in the southwest. In the south, in the Mewar
Mewar, also spelled as Mewad is a region in the south-central part of Rajasthan state of India. It includes the present-day districts of Bhilwara, Chittorgarh, Pratapgarh, Rajsamand, Udaipur, Pirawa Tehsil of Jhalawar District of Rajasth ...
region, Mewari
Mewari is an Indo-Aryan language of the Rajasthani languages group. It is spoken by about five million speakers in Rajsamand, Bhilwara, Udaipur, Chittorgarh and Pratapgarh districts of Rajasthan state and Mandsaur, Neemuch districts of Madh ...
is spoken, while in the hills of Wagad, Wagdi, a Bhil language
The Bhil languages are a group of lects spoken by the Bhil that are classified as dialects of Indo-Aryan languages such as Gujarati and Rajasthani. They are spoken by around 10.4 million Bhils in western and central India as of 2011 and consti ...
, is spoken. Many speakers of Rajasthani languages refer to their language as Hindi, and Standard Hindi is the medium of education and is common in cities. Urdu
Urdu (; , , ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the Languages of Pakistan, national language and ''lingua franca'' of Pakistan. In India, it is an Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of Indi ...
is also common in cities although the vast majority of Muslims speak one of the Rajasthani languages as their first language. Sindhi is also common in the cities and along the border with Sindh in Pakistan where Dhatki
Dhatki (धाटकी; ڍاٽڪي), also known as Dhatti (धाटी; ڍاٽي), Thari (थारी; ٿَري), is a Indo-Aryan Language of the Indo-European language family. It is mainly spoken in Tharparkar and Umerkot districts of Sindh ...
, a transition between Marwari and Sindhi, is the main dialect on both sides of the border.
The languages taught under the three-language formula
The three-language formula is a language learning policy first formulated in 1968 by the Ministry of Education of the Government of India in consultation with the states.
History
The first recommendation for a three-language policy was made by the ...
are:
*First language: Hindi
*Second language: English
*Third language: Gujarati, Punjabi, Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
, Sindhi or Urdu
Religion
Rajasthan's residents are mainlyHindus
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
, who account for 88.49% of the population. Muslims
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
make up 9.07%, Sikhs
Sikhs (singular Sikh: or ; , ) are an ethnoreligious group who adhere to Sikhism, a religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ''Sikh'' ...
1.27% and Jains
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion whose three main pillars are nonviolence (), asceticism (), and a rejection of all simplistic and one-sided views of truth and reality (). Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and ...
0.91% of the population.
Culture
Food
 Rajasthani cooking was influenced by both the war-like lifestyles of its inhabitants and the availability of ingredients in this arid region. Food that could last for several days and could be eaten without heating was preferred. Thus, pickles of Rajasthan are quite famous for their tangy and spicy flavour. The ''Panchkuta'' delicacy is also a famous one – meaning 5 vegetables – a dish that lasts for several days, and is made out of certain weed plants that only grow in the wild desert. The scarcity of water and fresh green vegetables have all had their effect on cooking. It is known for its snacks like
Rajasthani cooking was influenced by both the war-like lifestyles of its inhabitants and the availability of ingredients in this arid region. Food that could last for several days and could be eaten without heating was preferred. Thus, pickles of Rajasthan are quite famous for their tangy and spicy flavour. The ''Panchkuta'' delicacy is also a famous one – meaning 5 vegetables – a dish that lasts for several days, and is made out of certain weed plants that only grow in the wild desert. The scarcity of water and fresh green vegetables have all had their effect on cooking. It is known for its snacks like Bikaneri Bhujia
Bikaneri bhujia, often simply called bhujia, is a crispy snack prepared by using '' Vigna aconitifolia'', gram flour and spices, originating from Bikaner, a city in the western state of Rajasthan in India. It is light yellow in colour. Bhujia ...
. Other famous dishes include ''bajre ki roti'' (millet bread) and ''lahsun ki chutney'' (hot garlic paste), ''mawa kachori'' Mirchi Bada
Mirchi Bada or Mirchi Vada is a vegetarian fast food dish native to Jodhpur in the Indian state of Rajasthan. The dish is made by stuffing a green chili with indian spices, mashed potato, and gram flour, then it is wrapped in besan batter a ...
, Pyaaj Kachori and ghevar
Ghevar or Ghewar is a disc-shaped Rajasthani sweet with a honeycomb-like texture, made from ghee, maida, and sugar syrup. It is traditionally associated with the month of Shraavana and the festivals of Teej and Raksha Bandhan. It is a part of ...
from Jodhpur, Alwar
Alwar ( Rajasthani Pronunciation: �lʋəɾ is a city located in India's National Capital Region (NCR) and the administrative headquarters of Alwar District in the state of Rajasthan. It is located 150 km south of Delhi and 150 km ...
ka Mawa (milk cake), ''Kadhi kachori'' from Ajmer, ''Malpua'' from Pushkar, Daal kachori
Kachori () is a deep-fried, spicy, stuffed pastry originating from the Marwar region of Rajasthan, India. It is made of maida filled with a stuffing of baked mixture of moong dal or onions (usually, depends on the variation), besan, coria ...
(Kota kachori) from Kota and rassgullas from Bikaner. Originating from the Marwar
Marwar (also called Jodhpur region) is a region of western Rajasthan state in North Western India. It lies partly in the Thar Desert. 'Maru' is a Sanskrit word for desert. The word 'wad' literally means fence in Rajasthani languages. Engl ...
region of the state is the concept of Marwari Bhojnalaya or vegetarian restaurants, today found in many parts of India, which offer vegetarian food popular among Marwari people
The Marwari or Marwadi (Devanagari: मारवाड़ी) are an Indo-Aryan ethno-linguistic group that originate from the Marwar region of Rajasthan, India. Their language, also called Marwari, comes under the umbrella of Rajasthani la ...
. Ghee is an essential ingredient in most Rajasthani cuisines, and dollops of ghee are poured over food as a welcoming gesture for guests. Dal-baati-churma is very popular in Rajasthan. The traditional way to serve it is to first coarsely mash the baati, and then pour pure ghee on top of it. It is served with daal (lentils) and spicy garlic chutney; it is also served with besan (gram flour) ki kadi. It is commonly served at all festivities, including religious occasions, wedding ceremonies, and birthday parties in Rajasthan.
Dal-baati-churma is very popular in Rajasthan. The traditional way to serve it is to first coarsely mash the baati, and then pour pure ghee on top of it. It is served with daal (lentils) and spicy garlic chutney; it is also served with besan (gram flour) ki kadi. It is commonly served at all festivities, including religious occasions, wedding ceremonies, and birthday parties in Rajasthan.
Music and dance
TheGhoomar
Ghoomar or ghumar is a traditional folk dance of Rajasthan. It was the Bhil tribe who performed it to worship Goddess Saraswati which was later embraced by Rajputs. The dance is chiefly performed by veiled women who wear flowing dresses called ...
dance from Jaipur, Jodhpur, and Kalbelia
The Kalbelia are a snake charming tribe from the Thar Desert in Rajasthan, India. The dance is an integral part of their culture and performed by men and women.
Kalbelia Tribes
Kalbelias are followers of Sage Kanifnath, who drank a bowl of ...
of the Kalbelia tribe has gained international recognition. Folk music is a large part of the Rajasthani culture. The Manganiyar
The Manganiar are a Muslim community found in the Thar Desert region of Rajasthan, India; mostly in the districts of Barmer and Jaisalmer, and in the districts of Tharparkar and Sanghar in the bordering province of Sindh in Pakistan.
They are k ...
, Meena
Meena () is a tribe from northern and western India which is sometimes considered a sub-group of the Bhil community. It used to be claimed they speak Mina language, a
Spurious languages, spurious language. Its name is also transliterated as ' ...
and Langa communities from Rajasthan are notable for their folk music. Kathputli, Bhopa
The Bhopa people are the priest-singers of the folk deities in the state of Rajasthan, India. They perform in front of a scroll, known as (''par'' in the Rajasthani language) that depicts the episodes of the narrative of the folk deity and func ...
, Chang, Teratali, Ghindr, Gair dance
Gair dance is one of the popular, famous folk dances from Rajasthan in India which is mostly performed by the Bhil community but found in all over Rajasthan.
It is alternatively referred to as ''Gair'' ''Ghalna'', ''Gair'' ''Ghumna'', ''Gair' ...
, Kachchhi Ghori, and Tejaji
Veer Tejaji (29 January 1074 - 28 August 1103) “ ''As per historians, he was born on Friday, Magha Shukla 14 samvat 1130 (29 January 1074)''. also known as Tejaji Maharaj, or simply Tejaji, was a great warrior, social reformer, cow protector ...
are examples of traditional Rajasthani culture. Folk songs are commonly ballads that relate heroic deeds and love stories; and religious or devotional songs known as ''bhajans'' and ''banis'' which are often accompanied by musical instruments like dholak
The ''dholak'' is a two-headed hand drum, a folk percussion instrument. The dholak is most commonly recognised in countries such as India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal and Sri Lanka, but can also be found amongst the Indo-Diaspora in countries s ...
, sitar
The sitar ( or ; ) is a plucked stringed instrument, originating from the Indian subcontinent, used in Hindustani classical music. The instrument was invented in the 18th century, and arrived at its present form in 19th-century India. Khusrau K ...
, and sarangi
The sārangī is a bowed, short-necked three-stringed instrument played in traditional music from South Asia – Punjabi folk music, Rajasthani folk music, Sindhi folk music, Haryanvi folk music, Braj folk music, and Boro folk music (the ...
are also sung.
Art
Rajasthan is known for its traditional, colourful art. The block prints, tie and dye prints, gota patti (main), Bagaru prints, Sanganer prints, andZari
Zari () is an even thread traditionally made of fine gold or silver used in traditional Indian, Bangladeshi and Pakistani garments, especially as brocade in saris etc. This thread is woven into fabrics, primarily silk, to make intricate pat ...
embroidery are major export products from Rajasthan. Handicraft items like wooden furniture and crafts, carpets, and blue pottery are commonly found here. Shopping reflects the colourful culture, Rajasthani clothes have a lot of mirror work and embroidery. Traditional Rajasthani dress for females consists of an ankle-length skirt and a short top, known as ''chaniya choli
Ghagra choli (also known as lehenga choli and chaniya choli) is a type of ethnic clothing for women from India, notably in the Indian states of Rajasthan, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Haryana, Punjab, India, Punjab, Himachal ...
''. A piece of cloth is used to cover the head, both for protection from heat and maintenance of modesty. Rajasthani dresses are usually designed in bright colours such as blue, yellow, and orange.
Education
 In recent years, Rajasthan has worked on improving education. The state government has been making sustained efforts to raise the education standard.
Schools in the state are either managed by the government or by private trusts. The medium of instruction in most of the schools is mainly English, or Hindi. Under the
In recent years, Rajasthan has worked on improving education. The state government has been making sustained efforts to raise the education standard.
Schools in the state are either managed by the government or by private trusts. The medium of instruction in most of the schools is mainly English, or Hindi. Under the 10+2+3 plan
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sp ...
, after completing secondary school, students typically enroll for two years in a junior college
A junior college is a type of post-secondary institution that offers vocational and academic training that is designed to prepare students for either skilled trades and technical occupations or support roles in professions such as engineering, a ...
, also known as pre-university, or in schools with a higher secondary facility affiliated with the Board of Secondary Education or any central board. Students choose from one of three streams, namely liberal arts
Liberal arts education () is a traditional academic course in Western higher education. ''Liberal arts'' takes the term ''skill, art'' in the sense of a learned skill rather than specifically the fine arts. ''Liberal arts education'' can refe ...
, commerce, or science. Upon completing the required coursework, students may enrol in general or professional degree programs. The secondary schools are affiliated with the Council for the Indian School Certificate Examinations
The Council for the Indian School Certificate Examinations (CISCE) is a non-governmental privately held national-level board of school education in India that conducts the Indian Certificate of Secondary Education (ICSE) Examination for Class ...
(CISCE), the Central Board for Secondary Education (CBSE), and the National Institute of Open School (NIOS).
Rajasthan has 52 universities, 26 state funded public universities, 7 deemed universities
Deemed university, or deemed-to-be-university, is an accreditation granted to higher educational institutions in India by the Department of Higher Education (India), Department of Higher Education. , the UGC lists 124 institutes which were granted ...
, an IIT in Jodhpur, an IIM in Udaipur
Udaipur (Hindi: , ) (ISO 15919: ''Udayapura'') is a city in the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, about south of the state capital Jaipur. It serves as the administrative headquarters of Udaipur district. It is the historic capital of t ...
, an NIT in Jaipur, a National Law University
National Law Universities (NLU) are law schools, public law schools in India, founded pursuant to the second-generation reforms for legal education sought to be implemented by the Bar Council of India. The first NLU was the National Law School ...
in Jodhpur, and one central and state-run university. Kota, is renowned for being a hub for training students in various national-level competitive exams that are necessary for securing admission to engineering and medical colleges across the country. In order to promote a reading culture among the rural population, the state has established new libraries up to the panchayat level and computerised all public libraries throughout the state, providing modern amenities to readers and subscriber.
Literacy
In recent decades theliteracy
Literacy is the ability to read and write, while illiteracy refers to an inability to read and write. Some researchers suggest that the study of "literacy" as a concept can be divided into two periods: the period before 1950, when literacy was ...
rate of Rajasthan has increased significantly. In 1991, the state's literacy rate was only 38.55% (54.99% male and 20.44% female). In 2001, the literacy rate increased to 60.41% (75.70% male and 43.85% female). This was the highest leap in the percentage of literacy recorded in India (the rise in female literacy being 23%). At the Census 2011, Rajasthan had a literacy rate of 67.06% (80.51% male and 52.66% female). Although Rajasthan's literacy rate is below the national average of 74.04% and although its female literacy rate is the lowest in the country, the state has been praised for its efforts and achievements in raising literacy rates.
In rural areas of Rajasthan, the literacy rate is 76.16% for males and 45.8% for females. This has been debated across all the party levels, when the governor of Rajasthan set a minimum educational qualification for the village panchayat elections.
Tourism
 Rajasthan attracted a total of 45.9 million domestic and 1.6 million foreign tourists in 2017, which is the tenth highest in terms of domestic visitors and fifth highest in foreign tourists. The tourism industry in Rajasthan is growing effectively each year and is becoming one of the major income sources for the state government. Rajasthan is home to many attractions for domestic and foreign travellers, including the forts and palaces of
Rajasthan attracted a total of 45.9 million domestic and 1.6 million foreign tourists in 2017, which is the tenth highest in terms of domestic visitors and fifth highest in foreign tourists. The tourism industry in Rajasthan is growing effectively each year and is becoming one of the major income sources for the state government. Rajasthan is home to many attractions for domestic and foreign travellers, including the forts and palaces of Jaipur
Jaipur (; , ) is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and the List of cities and towns in Rajasthan, largest city of the north-western States and union territories of India, Indian state of Rajasthan. , the city had ...
, the lakes of Udaipur
Udaipur (Hindi: , ) (ISO 15919: ''Udayapura'') is a city in the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, about south of the state capital Jaipur. It serves as the administrative headquarters of Udaipur district. It is the historic capital of t ...
, the temples of Rajsamand
Rajsamand is a city, located in Rajsamand Mewar district of Rajasthan, India. The city is named for Rajsamand Lake, an artificial lake created in the 17th century by Rana Raj Singh Rajsamand Udaipur of Mewar. It is the administrative head ...
and Pali
Pāli (, IAST: pāl̤i) is a Classical languages of India, classical Middle Indo-Aryan languages, Middle Indo-Aryan language of the Indian subcontinent. It is widely studied because it is the language of the Buddhist ''Pali Canon, Pāli Can ...
, sand dunes of Jaisalmer
Jaisalmer , nicknamed ''The Golden city'', is a city in the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, located west of the state capital Jaipur, in the heart of the Thar Desert. It serves as the administrative headquarters of Jaisalmer district ...
and Bikaner
Bikaner () is a city in the northwest of the States and territories of India, state of Rajasthan, India. It is located northwest of the state capital, Jaipur. It is the administrative headquarters of Bikaner District and Bikaner division.
Fo ...
, Havelis of Mandawa
Mandawa is a town located just 29 km from Jhunjhunu city in Jhunjhunu district of Rajasthan, India. It is part of Shekhawati region. Mandawa is located at . It has an average elevation of 316 metres (1036 ft). The nearest rail ...
and Fatehpur, the wildlife of Sawai Madhopur
Sawai Madhopur (IAST: ''Savāī Mādhōpur'', IPA: əˈʋaːiː ˈmaːdʱoːpʊɾ is a city in the southeastern part of the Indian state of Rajasthan. It serves as the administrative headquarter of the Sawai Madhopur district, and forms a ...
, the scenery of Mount Abu
Mount Abu (), known as Arbudgiri in Jain tradition, is a hill station in the Aravalli Range in the Sirohi district of the state of Rajasthan in western India. Here, the mountain forms a rocky plateau 22 km long by 9 km wide. It is ref ...
, the tribes of Dungarpur
Dungarpur is a city in the southernmost part of Rajasthan, India.
History
Dungarpur is the seat of the elder branch of the Guhilot of Mewar family. The seat of the younger branch is that of the Maharana of Udaipur. The city was founded in ...
and Banswara
Banswara is a city in the Banswara district in southern Rajasthan, India. The name, Banswara, came from king ‘Bansiya Bhil’.
Banswara is also known as "City of a Hundred Islands", "The Green City", which is often referred to as " Cherrap ...
, and the cattle fair of Pushkar
Pushkar is a temple town near Ajmer City and headquarters of Pushkar tehsil in the Ajmer district in the Indian state of Rajasthan. It is situated about northwest of Ajmer and about southwest of Jaipur.culture
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
, colours, majestic forts, and palaces, folk dances
A folk dance is a dance that reflects the life of the people of a certain country or region. Not all ethnic dances are folk dances. For example, ritual dances or dances of ritual origin are not considered to be folk dances. Ritual dances are usu ...
and music, local festivals, local food, sand dunes, carved temples and Haveli
A ''haveli'' is a traditional townhouse, mansion, or manor house, in the Indian subcontinent, usually one with historical and architectural significance, and located in a town or city. The word ''haveli'' is derived from Arabic ''hawali'', me ...
s. Rajasthan's Jaipur Jantar Mantar
A Jantar Mantar ( Hindustani pronunciation: ͡ʒən̪t̪ər mən̪t̪ər is an assembly of stone-built astronomical instruments, designed to be used with the naked eye. There were five Jantar Mantars in India. All were built at the comm ...
, Mehrangarh Fort
Mehrangarh is a historic fort located in Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India. It stands on a hilltop, rising about above the surrounding plains, and the complex spans 1,200 acres (486 hectares). It was initially built around 1459 by the Rajput ruler of ...
and Stepwell
Stepwells (also known as vav or baori) are wells, cisterns or ponds with a long corridor of steps that descend to the water level. Stepwells played a significant role in defining subterranean architecture in western India from the 7th to the ...
of Jodhpur
Jodhpur () is the second-largest city of the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, after its capital Jaipur. As of 2023, the city has a population of 1.83 million. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Jodhpur district and ...
, Dilwara Temples
The Dilwara Temples or Delvada Temples are a group of Śvētāmbara Jain temples located about kilometres from the Mount Abu settlement in Sirohi District, Rajasthan's only hill station. The earliest were built by Vimal Shah , a Jain mini ...
, Chittor Fort
Chittorgarh (literally Chittor Fort), also known as Chittod Fort, is one of the largest forts in India. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The fort was the capital of Mewar and is located in the present-day city of Chittorgarh. It sprawls ove ...
, Lake Palace
Lake Palace (formerly known as Jag Niwas Palace) is a former summer palace of the royal dynasty of Mewar, it is now turned into a hotel. The Lake Palace is located on the island of Jag Niwas in Lake Pichola, Udaipur, India, and its natural foun ...
, miniature paintings in Bundi
Bundi is a town in the Hadoti region of Rajasthan state in northwest India.
Climate
The climate is hot semi arid (BSh), not having enough rainfall to qualify as a tropical savanna climate (Aw). The climate is quite warm, and most of the ra ...
, and numerous city palaces and Havelis are part of the architectural heritage of India. Jaipur, the ''Pink City'', is noted for the ancient houses made of a type of sandstone dominated by a pink hue. In Jodhpur, most houses are painted blue. At Ajmer
Ajmer () is a city in the north-western States and union territories of India, Indian state of Rajasthan. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Ajmer district and Ajmer division. It lies at the centre of Rajasthan, earning it the ...
, there is white marble Bara-dari on the Anasagar lake and Soniji Ki Nasiyan
The Ajmer Jain temple, also known as Soniji Ki Nasiyan, is a Jain temple known for its architecture. It was built in the late nineteenth century. The main chamber, known as the Swarna Nagari "City of Gold", has several gold-plated wooden figure ...
. Jain Temples
A Jain temple, Derasar (Gujarati: દેરાસર) or Basadi (Kannada: ಬಸದಿ) is the place of worship for Jains, the followers of Jainism. Jain architecture is essentially restricted to temples and monasteries, and Jain buildings gen ...
dot Rajasthan from north to south and east to west. Dilwara Temples
The Dilwara Temples or Delvada Temples are a group of Śvētāmbara Jain temples located about kilometres from the Mount Abu settlement in Sirohi District, Rajasthan's only hill station. The earliest were built by Vimal Shah , a Jain mini ...
of Mount Abu, Shrinathji
Shrinathji is a form of Krishna, manifested as a seven-year-old child. The principal shrine of Shrinathji is the Shrinathji Temple in the temple city of Nathdwara, 48 kilometres north-east of Udaipur city in Rajasthan, India. Shrinathji is ...
Temple of Nathdwara, Ranakpur Jain temple
Ranakpur Jain temple or Chaturmukha Dharana Vihara is a Śvētāmbara Jain temple at Ranakpur dedicated to ''Tirthankara'' Rishabhanatha. The temple is located in the village of Ranakpur near Sadri in the Pali district of Rajasthan. It is a ...
dedicated to Lord Adinath in Pali District
Pali district is a district in Rajasthan, India. The city of Pali is its administrative headquarters.
Pali is also known as the Industrial/Textile City and has been a hub for merchant activities for centuries. It has a rich heritage and culture ...
, Jain temples in the fort complexes of Chittor
Chittorgarh (; also Chitror or Chittor or Chittaurgarh) is a major city in the state of Rajasthan in western India. It lies on the Berach River, a tributary of the Banas, and is the administrative headquarters of Chittorgarh District. It wa ...
, Jaisalmer and Kumbhalgarh
Kumbhalgarh (lit. "Kumbhal fort"), also known as the Great Wall of India, is a fortress on the westerly range of Aravalli Hills in Kumbhalgarh in the Rajsamand district of the Rajasthan state in India. Situated approximately from Rajsamand c ...
, Lodurva Jain temples, Mirpur Jain Temple of Sirohi
Sirohi is a town, located in Sirohi district in southern Rajasthan state in western India. It is the administrative headquarters of Sirohi District and was formerly the capital of the princely state of Sirohi ruled by Deora Chauhan Rajput
...
, Sarun Mata Temple at Kotputli
Kotputli is a city and municipal council in Kotputli-Behror district of Rajasthan, India, located between Jaipur city and New Delhi
New Delhi (; ) is the Capital city, capital of India and a part of the Delhi, National Capital Territo ...
, Bhandasar and Karni Mata Temple of Bikaner
Bikaner () is a city in the northwest of the States and territories of India, state of Rajasthan, India. It is located northwest of the state capital, Jaipur. It is the administrative headquarters of Bikaner District and Bikaner division.
Fo ...
and Mandore
Mandore is a suburb and historical town located 9 km north of Jodhpur city in the Jodhpur district of the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan.
History
Mandore is an ancient town, and was the seat of the Gurjar Pratiharas of Mandavy ...
of Jodhpur
Jodhpur () is the second-largest city of the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, after its capital Jaipur. As of 2023, the city has a population of 1.83 million. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Jodhpur district and ...
are some of the best examples. Keoladeo National Park
Keoladeo National Park, or Keoladeo Ghana National Park, is a national park in Rajasthan, India. The national park hosts thousands of native, resident and migratory birds, especially during the winter season, when many different species fly to t ...
, Ranthambore National Park
Ranthambore National Park is a national park in the Indian state of Rajasthan. It covers a total area of . It is bounded to the north by the Banas River and to the south by the Chambal River. It is named after the historic Ranthambore Fort ...
, Sariska Tiger Reserve
Sariska Tiger Reserve is a tiger reserve in Alwar district, Rajasthan, India. It stretches over an core tiger habitat area of and 322.23 km² of buffer area making 1203.34 km² total area of tiger reserve. It is comprising scrub-thorn arid ...
, Tal Chhapar Sanctuary
Tal Chhapar Sanctuary is a sanctuary located in the Churu district of Northwestern Rajasthan, in the Shekhawati region of India. It is known for blackbucks and is also home to a variety of birds. The sanctuary is 210 km from Jaipur on the ...
, are wildlife attractions of Rajasthan. Mewar festival of Udaipur, Teej festival and Gangaur
Gangaur (, ) is a Hindu festival celebrated in the Indian states of Rajasthan, Haryana, Fazilka District of Punjab, the regions of Malwa, Nimar ( Manawar, Barwani, Khargone, Khandwa) of Madhya Pradesh and the Braj and Bundelkhand regions o ...
festival in Jaipur, Desert festival
Jaisalmer , nicknamed ''The Golden city'', is a city in the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, located west of the state capital Jaipur, in the heart of the Thar Desert. It serves as the administrative headquarters of Jaisalmer district ...
of Jodhpur, Brij Holi of Bharatpur, Matsya festival of Alwar, Kite festival
The Bristol International Kite Festival, full name Bristol International Festival of Kites & Air Creations, used to be held annually during September in Bristol, England. It takes place at the Ashton Court estate, which is owned by Politics of B ...
of Jodhpur, Kolayat fair in Bikaner are some of the most popular fairs and festivals of Rajasthan.
Thar desert
The Thar Desert (), also known as the Great Indian Desert, is an arid region in the north-western part of the Indian subcontinent that covers an area of in India and Pakistan. It is the world's 18th-largest desert, and the world's 9th-large ...
File:Temples at Pushkar Lake.jpg, Pushkar Lake
Pushkar Lake or Pushkar Sarovar is located in the town of Pushkar near Ajmer, Ajmer city in Ajmer district of the Rajasthan state of western India. Pushkar Lake is a sacred lake of the Hindus. The Hindu scriptures describe it as "Tirtha (Hindui ...
and Ghat
File:Bhavai is a genre of folk dance popular in Rajasthan. The male or female performers balance a number of earthen pots while dancing.jpg, Kalbelia
The Kalbelia are a snake charming tribe from the Thar Desert in Rajasthan, India. The dance is an integral part of their culture and performed by men and women.
Kalbelia Tribes
Kalbelias are followers of Sage Kanifnath, who drank a bowl of ...
, a folk dance popular in Rajasthan
File:Demoiselle cranes in Khichan near Bikaner (Rajasthan).jpg, Demoiselle crane
The demoiselle crane (''Grus virgo'') is a species of crane found in central Eurosiberia, ranging from the Black Sea to Mongolia and Northeast China. There is also a small breeding population in Turkey. These cranes are migratory birds. Birds f ...
s in Khichan
Khichan village, and the eponymous adjacent Khichan Ramsar site wetland,Khichan Ramsar site
ramsar.org, accesse ...
near ramsar.org, accesse ...
Bikaner
Bikaner () is a city in the northwest of the States and territories of India, state of Rajasthan, India. It is located northwest of the state capital, Jaipur. It is the administrative headquarters of Bikaner District and Bikaner division.
Fo ...
File:Hawa Mahal 2011.jpg, Hawa Mahal
The Hawa Mahal is a palace in the city of Jaipur, Rajasthan, India. Built from red and pink sandstone, it is on the edge of the City Palace, Jaipur, and extends to the '' Zenana'', or women's chambers.
Hawa Mahal is known as the “palace of ...
, Jaipur
Jaipur (; , ) is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and the List of cities and towns in Rajasthan, largest city of the north-western States and union territories of India, Indian state of Rajasthan. , the city had ...
File:20191219 Fort Amber, Amer, Jaipur 0955 9481.jpg, Amber Fort
Amer Fort or Amber Fort is a fort located in Amer, Rajasthan, India. Amer is a town with an area of located from Jaipur, the capital of Rajasthan. Located high on a hill, it is the principal tourist attraction in Jaipur. Amer Fort is known f ...
as seen from the bank of Maotha Lake, Jaigarh Fort on the hills in the background
File:Nakki Lake during daytime.JPG, Nakki Lake
Nakki Lake is a lake situated in the Indian hill station of Mount Abu in Aravalli range.
History
It is believed to be a very ancient sacred Lake, according to the Hindu legend. It is called so because it is believed to be dug out from Nail ...
, Mount Abu
Mount Abu (), known as Arbudgiri in Jain tradition, is a hill station in the Aravalli Range in the Sirohi district of the state of Rajasthan in western India. Here, the mountain forms a rocky plateau 22 km long by 9 km wide. It is ref ...
File:Mehrangarh Fort.jpg, Mehrangarh Fort
Mehrangarh is a historic fort located in Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India. It stands on a hilltop, rising about above the surrounding plains, and the complex spans 1,200 acres (486 hectares). It was initially built around 1459 by the Rajput ruler of ...
File:Kalpavruksha page.jpg, Delicate marble carving at Dilwara Temples
The Dilwara Temples or Delvada Temples are a group of Śvētāmbara Jain temples located about kilometres from the Mount Abu settlement in Sirohi District, Rajasthan's only hill station. The earliest were built by Vimal Shah , a Jain mini ...
File:Lake Pichola (1580558921).jpg, Lake Palace
Lake Palace (formerly known as Jag Niwas Palace) is a former summer palace of the royal dynasty of Mewar, it is now turned into a hotel. The Lake Palace is located on the island of Jag Niwas in Lake Pichola, Udaipur, India, and its natural foun ...
, Udaipur
Udaipur (Hindi: , ) (ISO 15919: ''Udayapura'') is a city in the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, about south of the state capital Jaipur. It serves as the administrative headquarters of Udaipur district. It is the historic capital of t ...
File:Kirti Stambha of Fort of Chittaur -Chittaurgarh -Rajasthan -IMG 8307.jpg, Kirti Stambha of Chittor Fort
Chittorgarh (literally Chittor Fort), also known as Chittod Fort, is one of the largest forts in India. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The fort was the capital of Mewar and is located in the present-day city of Chittorgarh. It sprawls ove ...
File:A tiger in Ranthambore National Park (2016).jpg, Tiger at Ranthambore National Park
Ranthambore National Park is a national park in the Indian state of Rajasthan. It covers a total area of . It is bounded to the north by the Banas River and to the south by the Chambal River. It is named after the historic Ranthambore Fort ...
File:Jaipur 03-2016 39 Jal Mahal - Water Palace.jpg, Jal Mahal
Jal Mahal (meaning "Water Palace") is a palace in the middle of the Man Sagar Lake in Jaipur city, the capital of the state of Rajasthan, India. The palace was originally constructed around 1699; the building and the lake around it were later ...
, Jaipur
Jaipur (; , ) is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and the List of cities and towns in Rajasthan, largest city of the north-western States and union territories of India, Indian state of Rajasthan. , the city had ...
See also
* Jatan Sansthan (2001) * List of people from Rajasthan * Outline of RajasthanReferences
Further reading
* Bhattacharya, Manoshi. 2008. ''The Royal Rajputs: Strange Tales and Stranger Truths''. Rupa & Co, New Delhi. * Gahlot, Sukhvirsingh. 1992. ''RAJASTHAN: Historical & Cultural''. J. S. Gahlot Research Institute, Jodhpur. * Somani, Ram Vallabh. 1993. ''History of Rajasthan''. Jain Pustak Mandir, Jaipur. * Tod, James & Crooke, William. 1829. ''Annals and Antiquities of Rajasthan or the Central and Western Rajpoot States of India,''. Numerous reprints, including 3 Vols. Reprint: Low Price Publications, Delhi. 1990. (set of 3 vols.) * Mathur, P.C., 1995. ''Social and Economic Dynamics of Rajasthan Politics'' (Jaipur, Aaalekh)External links
Government
Official Site of the Government of Rajasthan, India
Official Tourism Site of Rajasthan, India
General information
* {{Authority control * States and union territories of India States and territories established in 1950 1950 establishments in India