Rain shadow on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
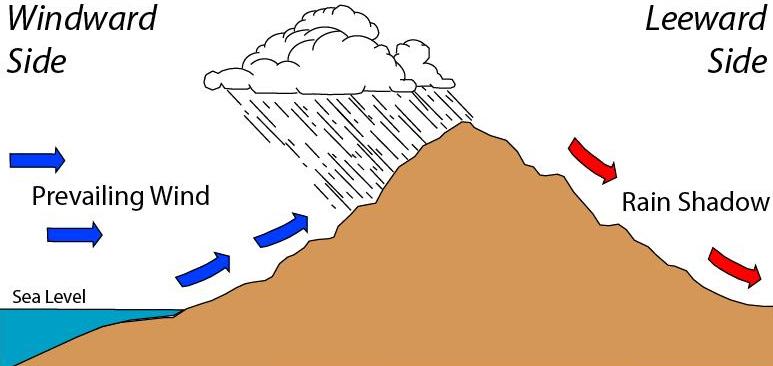
 A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced
 * The
* The
 * The windward side of the island of
* The windward side of the island of
 * The eastern side of the Sahyadri ranges on the
* The eastern side of the Sahyadri ranges on the
 On the largest scale, the entirety of the North American Interior Plains are shielded from the prevailing
On the largest scale, the entirety of the North American Interior Plains are shielded from the prevailing
 * The
* The
USA Today on rain shadows
Weather pages on rain shadows
{{DEFAULTSORT:Rain Shadow Land surface effects on climate Mountain meteorology Hydrology

 A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rain
Rain is a form of precipitation where water drop (liquid), droplets that have condensation, condensed from Water vapor#In Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric water vapor fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is res ...
fall behind a mountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher t ...
ous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds
In meteorology, prevailing wind in a region of the Earth's surface is a surface wind that blows predominantly from a particular Wind direction, direction. The dominant winds are the trends in direction of wind with the highest speed over a partic ...
, known as its leeward
In geography and seamanship, windward () and leeward () are directions relative to the wind. Windward is ''upwind'' from the point of reference, i.e., towards the direction from which the wind is coming; leeward is ''downwind'' from the point o ...
side.
Evaporated moisture
Moisture is the presence of a liquid, especially water, often in trace amounts. Moisture is defined as water in the adsorbed or absorbed phase. Small amounts of water may be found, for example, in the air (humidity), in foods, and in some comme ...
from bodies of water
A body of water or waterbody is any significant accumulation of water on the surface of Earth or another planet. The term most often refers to oceans, seas, and lakes, but it includes smaller pools of water such as ponds, wetlands, or more ra ...
(such as ocean
The ocean is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of Earth. The ocean is conventionally divided into large bodies of water, which are also referred to as ''oceans'' (the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian Ocean, Indian, Southern Ocean ...
s and large lake
A lake is often a naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on or near the Earth's surface. It is localized in a basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from ...
s) is carried by the prevailing onshore breezes towards the drier and hotter inland areas. When encountering elevated landform
A landform is a land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. They may be natural or may be anthropogenic (caused or influenced by human activity). Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement ...
s, the moist air is driven upslope towards the peak, where it expands, cools, and its moisture condenses and starts to precipitate. If the landforms are tall and wide enough, most of the humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation (meteorology), precipitation, dew, or fog t ...
will be lost to precipitation over the windward
In geography and seamanship, windward () and leeward () are directions relative to the wind. Windward is ''upwind'' from the point of reference, i.e., towards the direction from which the wind is coming; leeward is ''downwind'' from the point ...
side (also known as the ''rainward'' side) before ever making it past the top. As the air descends the leeward side of the landforms, it is compressed and heated, producing Foehn winds that ''absorb'' moisture downslope and cast a broad "shadow" of dry climate region behind the mountain crests. This climate typically takes the form of shrub–steppe, xeric shrublands, or desert
A desert is a landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions create unique biomes and ecosystems. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About one-third of the la ...
s.
The condition exists because warm moist air rises by orographic lifting to the top of a mountain range. As atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing altitude, the air has expanded and adiabatically cooled to the point that the air reaches its adiabatic dew point
The dew point is the temperature the air needs to be cooled to (at constant pressure) in order to produce a relative humidity of 100%. This temperature depends on the pressure and water content of the air. When the air at a temperature above the ...
(which is not the same as its constant pressure dew point commonly reported in weather forecasts). At the adiabatic dew point, moisture condenses onto the mountain and it precipitates on the top and windward
In geography and seamanship, windward () and leeward () are directions relative to the wind. Windward is ''upwind'' from the point of reference, i.e., towards the direction from which the wind is coming; leeward is ''downwind'' from the point ...
sides of the mountain. The air descends on the leeward side, but due to the precipitation it has lost much of its moisture. Typically, descending air also gets warmer because of adiabatic compression (as with foehn winds) down the leeward side of the mountain, which increases the amount of moisture that it can absorb and creates an arid region.
Notably affected regions
There are regular patterns ofprevailing winds
In meteorology, prevailing wind in a region of the Earth's surface is a surface wind that blows predominantly from a particular Wind direction, direction. The dominant winds are the trends in direction of wind with the highest speed over a partic ...
found in bands round Earth's equator
The equator is the circle of latitude that divides Earth into the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Southern Hemisphere, Southern Hemispheres of Earth, hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, about in circumferen ...
ial region. The zone designated the trade winds is the zone between about 30° N and 30° S, blowing predominantly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined by humans as being in the same celestial sphere, celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the Solar ...
and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisphere. The westerlies
The westerlies, anti-trades, or prevailing westerlies, are prevailing winds from the west toward the east in the middle latitudes between 30 and 60 degrees latitude. They originate from the high-pressure areas in the horse latitudes (about ...
are the prevailing winds in the middle latitudes
The middle latitudes, also called the mid-latitudes (sometimes spelled midlatitudes) or moderate latitudes, are spatial regions on either Hemispheres of Earth, hemisphere of Earth, located between the Tropic of Cancer (latitude ) and the Arctic ...
between 30 and 60 degrees latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at t ...
, blowing predominantly from the southwest in the Northern Hemisphere and from the northwest in the Southern Hemisphere. Some of the strongest westerly winds in the middle latitudes can come in the Roaring Forties of the Southern Hemisphere, between 30 and 50 degrees latitude.
Examples of notable rain shadowing include:
Africa
Northern Africa
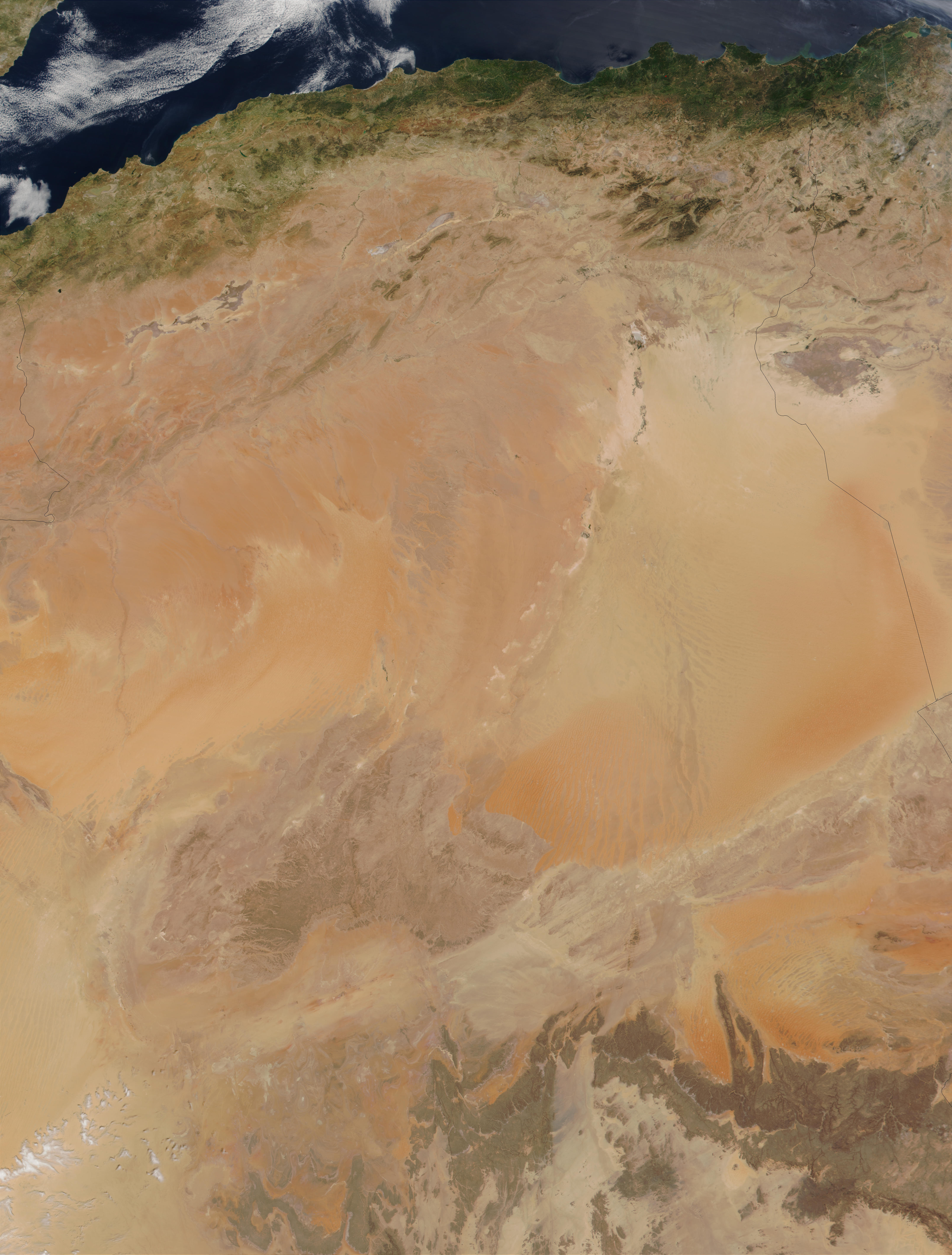
 * The
* The Sahara
The Sahara (, ) is a desert spanning across North Africa. With an area of , it is the largest hot desert in the world and the list of deserts by area, third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Ar ...
is made even drier because of a strong rain shadow effects caused by major mountain ranges (whose highest points can culminate up to more than 4,000 meters; 2½ miles high). To the northwest, the Atlas Mountains
The Atlas Mountains are a mountain range in the Maghreb in North Africa. They separate the Sahara Desert from the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean; the name "Atlantic" is derived from the mountain range, which stretches around through M ...
, covering the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
coast for Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
, Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
and Tunisia
Tunisia, officially the Republic of Tunisia, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered by Algeria to the west and southwest, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Tunisia also shares m ...
. On the windward
In geography and seamanship, windward () and leeward () are directions relative to the wind. Windward is ''upwind'' from the point of reference, i.e., towards the direction from which the wind is coming; leeward is ''downwind'' from the point ...
side of the Atlas Mountains
The Atlas Mountains are a mountain range in the Maghreb in North Africa. They separate the Sahara Desert from the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean; the name "Atlantic" is derived from the mountain range, which stretches around through M ...
, the warm, moist winds blowing from the northwest off the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
, which contain a lot of water vapor, are forced to rise, lift up and expand over the mountain range. This causes them to cool down, which causes an excess of moisture to condense into high clouds and results in heavy precipitation over the mountain range. This is known as orographic rainfall and after this process, the air is dry because it has lost most of its moisture over the Atlas Mountains
The Atlas Mountains are a mountain range in the Maghreb in North Africa. They separate the Sahara Desert from the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean; the name "Atlantic" is derived from the mountain range, which stretches around through M ...
. On the leeward
In geography and seamanship, windward () and leeward () are directions relative to the wind. Windward is ''upwind'' from the point of reference, i.e., towards the direction from which the wind is coming; leeward is ''downwind'' from the point o ...
side, the cold, dry air starts to descend and to sink and compress, making the winds warm up. This warming causes the moisture to evaporate, making clouds disappear. This prevents rainfall formation and creates desert conditions in the Sahara.
* Desert regions in the Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
(Ethiopia
Ethiopia, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country located in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east, Ken ...
, Eritrea
Eritrea, officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa, with its capital and largest city being Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia in the Eritrea–Ethiopia border, south, Sudan in the west, and Dj ...
, Somalia
Somalia, officially the Federal Republic of Somalia, is the easternmost country in continental Africa. The country is located in the Horn of Africa and is bordered by Ethiopia to the west, Djibouti to the northwest, Kenya to the southwest, th ...
and Djibouti
Djibouti, officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden to the east. The country has an area ...
) such as the Danakil Desert are all influenced by the air heating and drying produced by rain shadow effect of the Ethiopian Highlands
The Ethiopian Highlands (also called the Abyssinian Highlands) is a rugged mass of mountains in Ethiopia in Northeast Africa. It forms the largest continuous area of its elevation in the continent, with little of its surface falling below , whil ...
.
Southern Africa
 * The windward side of the island of
* The windward side of the island of Madagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
, which sees easterly on-shore winds, is wet tropical, while the western and southern sides of the island lie in the rain shadow of the central highlands and are home to thorn forests and deserts. The same is true for the island of Réunion
Réunion (; ; ; known as before 1848) is an island in the Indian Ocean that is an overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France. Part of the Mascarene Islands, it is located approximately east of the isl ...
.
* On Tristan da Cunha
Tristan da Cunha (), colloquially Tristan, is a remote group of volcano, volcanic islands in the South Atlantic Ocean. It is one of three constituent parts of the British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory of Saint Helena, Ascensi ...
, Sandy Point on the east coast is warmer and drier than the rainy, windswept settlement of Edinburgh of the Seven Seas in the west.
* In Western Cape Province, the Breede River Valley and the Karoo region lie in the rain shadow of the Cape Fold Mountains and are arid; whereas the wettest parts of the Cape Mountains can receive , Worcester receives only around and is useful only for grazing.
Asia
Central and Northern Asia
* TheHimalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya ( ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than list of h ...
and connecting ranges also contribute to arid conditions in Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
including Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by po ...
's Gobi desert, as well as the semi-arid steppes of Mongolia and north-central to north western China.
Eastern Asia
* TheOrdos Desert
The Ordos Desert () is a desert/ steppe region in Northwest China, administered under the prefecture of Ordos City in the Inner Mongolian Autonomous Region (centered ca. ). It extends over an area of approximately , and comprises two sub-de ...
is rain shadowed by mountain chains including the Kara-naryn-ula, the Sheitenula, and the Yin Mountains, which link on to the south end of the Great Khingan Mountains.
* The central region of Myanmar
Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and has ...
is in the rain shadow of the Arakan Mountains and is almost semi-arid with only of rain, versus up to on the Rakhine State
Rakhine State ( ; , ; ), formerly known as Arakan State, is a Administrative divisions of Myanmar, state in Myanmar (Burma). Situated on the western coast, it is bordered by Chin State to the north, Magway Region, Bago Region and Ayeyarwady Re ...
coast.
* The plains around Tokyo, Japan – known as Kanto plain – during winter experiences significantly less precipitation than the rest of the country by virtue of surrounding mountain ranges, including the Japanese Alps, blocking prevailing northwesterly winds originating in Siberia.
Southern Asia
 * The eastern side of the Sahyadri ranges on the
* The eastern side of the Sahyadri ranges on the Deccan Plateau
The Deccan is a plateau extending over an area of and occupies the majority of the Indian peninsula. It stretches from the Satpura Range, Satpura and Vindhya Ranges in the north to the northern fringes of Tamil Nadu in the south. It is bound ...
including: Vidarbha, North Karnataka, Rayalaseema and western Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is the southernmost States and union territories of India, state of India. The List of states and union territories of India by area, tenth largest Indian state by area and the List of states and union territories of Indi ...
.
* Gilgit
Gilgit (; Shina language, Shina: ; ) is a city in Pakistani-administered Gilgit-Baltistan, Gilgit–Baltistan in the disputed Kashmir region.The application of the term "administered" to the various regions of Kashmir and a mention of the Kas ...
and Chitral, Pakistan, are rainshadow areas.
* The Thar Desert is bounded and rain shadowed by the Aravalli ranges to the southeast, the Himalaya to the northeast, and the Kirthar and Sulaiman ranges to the west.
*The Central Highlands of Sri Lanka rain shadow the northeastern parts of the island, which experience much less severe summer monsoon rains and instead have precipitation peaks in autumn and winter.
Western Asia
* The peaks of the Caucasus Mountains to the west and Hindukush and Pamir to the east rain shadow the Karakum and Kyzyl Kum deserts east of theCaspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake and usually referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, ...
, as well as the semi-arid Kazakh Steppe
The Kazakh Steppe ( ), also known as the Great Steppe or Great Betpak-Dala, Dala ( ), is a vast region of open grassland in Central Asia, covering areas in northern Kazakhstan and adjacent areas of Russia. It lies east of the Pontic–Caspian step ...
. They also cause vast rainfall differences between coastal areas on the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
such as Rize, Batumi
Batumi (; ka, ბათუმი ), historically Batum or Batoum, is the List of cities and towns in Georgia (country), second-largest city of Georgia (country), Georgia and the capital of the Autonomous Republic of Adjara, located on the coast ...
and Sochi
Sochi ( rus, Сочи, p=ˈsotɕɪ, a=Ru-Сочи.ogg, from – ''seaside'') is the largest Resort town, resort city in Russia. The city is situated on the Sochi (river), Sochi River, along the Black Sea in the North Caucasus of Souther ...
contrasted with the dry lowlands of Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by ...
facing the Caspian Sea.
* The semi-arid Anatolian Plateau is rain shadowed by mountain chains, including the Pontic Mountains in the north and the Taurus Mountains
The Taurus Mountains (Turkish language, Turkish: ''Toros Dağları'' or ''Toroslar,'' Greek language, Greek'':'' Ταύρος) are a mountain range, mountain complex in southern Turkey, separating the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coastal reg ...
in the south.
* The High Peaks of Mount Lebanon
Mount Lebanon (, ; , ; ) is a mountain range in Lebanon. It is about long and averages above in elevation, with its peak at . The range provides a typical alpine climate year-round.
Mount Lebanon is well-known for its snow-covered mountains, ...
rain-shadow the northern parts of the Beqaa Valley and Anti-Lebanon Mountains.
* The Judaean Desert, the Dead Sea
The Dead Sea (; or ; ), also known by #Names, other names, is a landlocked salt lake bordered by Jordan to the east, the Israeli-occupied West Bank to the west and Israel to the southwest. It lies in the endorheic basin of the Jordan Rift Valle ...
and the western slopes of the Moab
Moab () was an ancient Levant, Levantine kingdom whose territory is today located in southern Jordan. The land is mountainous and lies alongside much of the eastern shore of the Dead Sea. The existence of the Kingdom of Moab is attested to by ...
Mountains on the opposite (Jordan
Jordan, officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is a country in the Southern Levant region of West Asia. Jordan is bordered by Syria to the north, Iraq to the east, Saudi Arabia to the south, and Israel and the occupied Palestinian ter ...
ian) side are rain-shadowed by the Judaean Mountains.
* The Dasht-i-Lut in Iran is in the rain shadow of the Elburz and Zagros Mountains and is one of the most lifeless areas on Earth.
* The peaks of the Zagros Mountains rain-shadow the northern half of the West Azerbaijan province
West Azerbaijan province () is one of the 31 provinces of Iran, whose capital and largest city is Urmia.
It is in the northwest of the country, bordered by Turkey ( Ağrı, Hakkâri, Iğdır and Van Provinces), Iraq ( Erbil and Sula ...
in Iranian Azerbaijan (above Urmia), as manifested by the province's dry winters relative to those in the windward part of the region (i.e. Kurdistan Region
Kurdistan Region (KRI) is a semi-autonomous Federal regions of Iraq, federal region of the Iraq, Republic of Iraq. It comprises four Kurds, Kurdish-majority governorates of Arabs, Arab-majority Iraq: Erbil Governorate, Sulaymaniyah Governorate ...
and Hakkâri Province
Hakkâri Province (, ; ), is a province in the southeast of Turkey. The administrative centre is the city of Hakkâri. Its area is 7,095 km2, and its population is 287,625 (2023). The current Governor is Ali Çelik. The province encompasses ...
in Turkey).
*Much of the Mesaoria Plain of Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
is in the rain shadow of the Troodos Mountains and is semi-arid.
Europe
Central Europe
* The Plains of Limagne andForez
Forez (; ) is a Provinces of France, former province of France, corresponding approximately to the central part of the modern Loire (department), Loire ''département in France, département'' and a part of the Haute-Loire and Puy-de-Dôme ''dépa ...
in the northern Massif Central, France are also relatively rainshadowed (mostly the plain of Limagne, shadowed by the Chaîne des Puys (up to 2000 mm; 80" of rain a year on the summits and below 600mm; 20" at Clermont-Ferrand
Clermont-Ferrand (, , ; or simply ; ) is a city and Communes of France, commune of France, in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes regions of France, region, with a population of 147,284 (2020). Its metropolitan area () had 504,157 inhabitants at the 2018 ...
, which is one of the driest places in the country).
* The Piedmont
Piedmont ( ; ; ) is one of the 20 regions of Italy, located in the northwest Italy, Northwest of the country. It borders the Liguria region to the south, the Lombardy and Emilia-Romagna regions to the east, and the Aosta Valley region to the ...
wine region of northern Italy is rainshadowed by the mountains that surround it on nearly every side: Asti
Asti ( , ; ; ) is a ''comune'' (municipality) of 74,348 inhabitants (1–1–2021) located in the Italy, Italian region of Piedmont, about east of Turin, in the plain of the Tanaro, Tanaro River. It is the capital of the province of Asti and ...
receives only of precipitation per year, making it one of the driest places in mainland Italy.
* Some valleys in the inner Alps
The Alps () are some of the highest and most extensive mountain ranges in Europe, stretching approximately across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): Monaco, France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Germany, Austria and Slovenia.
...
are also strongly rainshadowed by the high surrounding mountains: the areas of Gap and Briançon
Briançon (, ) is the sole Subprefectures in France, subprefecture of the Hautes-Alpes Departments of France, department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur Regions of France, region in Southeastern France. It is the highest city in France at an a ...
in France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, the district of Zernez
Zernez is a village and a municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in the Engiadina Bassa/Val Müstair Region in the Switzerland, Swiss Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Graubünden. On 1 January 2015 the former municipalities of Lavin and Susch ...
in Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
.
* The Kuyavia and the eastern part of the Greater Poland
Greater Poland, often known by its Polish name Wielkopolska (; ), is a Polish Polish historical regions, historical region of west-central Poland. Its chief and largest city is Poznań followed by Kalisz, the oldest city in Poland.
The bound ...
has an average rainfall of about because of rainshadowing by the slopes of the Kashubian Switzerland, making it one of the driest places in the North European Plain.
Northern Europe
* ThePennines
The Pennines (), also known as the Pennine Chain or Pennine Hills, are a range of highland, uplands mainly located in Northern England. Commonly described as the "Vertebral column, backbone of England" because of its length and position, the ra ...
of Northern England, the mountains of Wales
Wales ( ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by the Irish Sea to the north and west, England to the England–Wales border, east, the Bristol Channel to the south, and the Celtic ...
, the Lake District
The Lake District, also known as ''the Lakes'' or ''Lakeland'', is a mountainous region and National parks of the United Kingdom, national park in Cumbria, North West England. It is famous for its landscape, including its lakes, coast, and mou ...
and the Highlands of Scotland create a rain shadow that includes most of the eastern United Kingdom, due to the prevailing south-westerly winds. Manchester
Manchester () is a city and the metropolitan borough of Greater Manchester, England. It had an estimated population of in . Greater Manchester is the third-most populous metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, with a population of 2.92&nbs ...
and Glasgow
Glasgow is the Cities of Scotland, most populous city in Scotland, located on the banks of the River Clyde in Strathclyde, west central Scotland. It is the List of cities in the United Kingdom, third-most-populous city in the United Kingdom ...
, for example, receive around double the rainfall of Leeds
Leeds is a city in West Yorkshire, England. It is the largest settlement in Yorkshire and the administrative centre of the City of Leeds Metropolitan Borough, which is the second most populous district in the United Kingdom. It is built aro ...
and Edinburgh
Edinburgh is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. The city is located in southeast Scotland and is bounded to the north by the Firth of Forth and to the south by the Pentland Hills. Edinburgh ...
respectively (although there are no mountains between Edinburgh and Glasgow). The contrast is even stronger further north, where Aberdeen
Aberdeen ( ; ; ) is a port city in North East Scotland, and is the List of towns and cities in Scotland by population, third most populous Cities of Scotland, Scottish city. Historically, Aberdeen was within the historic county of Aberdeensh ...
gets around a third of the rainfall of Fort William or Skye. In Devon, rainfall at Princetown on Dartmoor is almost three times the amount received to the east at locations such as Exeter
Exeter ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and the county town of Devon in South West England. It is situated on the River Exe, approximately northeast of Plymouth and southwest of Bristol.
In Roman Britain, Exeter w ...
and Teignmouth
Teignmouth ( ) is a seaside town, fishing port and civil parishes in England, civil parish in the English county of Devon. It is on the north bank of the estuary mouth of the River Teign, about south of Exeter. The town had a population of 14 ...
. The Fens
The Fens or Fenlands in eastern England are a naturally marshy region supporting a rich ecology and numerous species. Most of the fens were drained centuries ago, resulting in a flat, dry, low-lying agricultural region supported by a system o ...
of East Anglia receive similar rainfall amounts to Seville
Seville ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Spain, Spanish autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the Guadalquivir, River Guadalquivir, ...
.
* Iceland
Iceland is a Nordic countries, Nordic island country between the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between North America and Europe. It is culturally and politically linked with Europe and is the regi ...
has plenty of microclimate
A microclimate (or micro-climate) is a local set of atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric conditions that differ from those in the surrounding areas, often slightly but sometimes substantially. The term may refer to areas as small as a few square m ...
s courtesy of the mountainous terrain. Akureyri
Akureyri (, ) is a town in northern Iceland, the country's fifth most populous Municipalities of Iceland, municipality (under the official name of Akureyrarbær , 'town of Akureyri') and the largest outside the Capital Region (Iceland), Capital R ...
on a northerly fiord receives about a third of the precipitation that the island of Vestmannaeyjar off the south coast gets. The smaller island is in the pathway of Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream is a warm and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida and up the eastern coastline of the United States, then veers east near 36°N latitude (North Carolin ...
rain fronts with mountains lining the southern coast of the mainland.
* The Scandinavian Mountains
The Scandinavian Mountains or the Scandes is a mountain range that runs through the Scandinavian Peninsula. The western sides of the mountains drop precipitously into the North Sea and Norwegian Sea, forming the fjords of Norway, whereas to th ...
create a rain shadow for lowland areas east of the mountain chain and prevents the Oceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate or maritime climate, is the temperate climate sub-type in Köppen climate classification, Köppen classification represented as ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of co ...
from penetrating further east; thus Bergen
Bergen (, ) is a city and municipalities of Norway, municipality in Vestland county on the Western Norway, west coast of Norway. Bergen is the list of towns and cities in Norway, second-largest city in Norway after the capital Oslo.
By May 20 ...
and a place like Brekke in Sogn, west of the mountains, receive an annual precipitation of , respectively, while Oslo
Oslo ( or ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Norway. It constitutes both a county and a municipality. The municipality of Oslo had a population of in 2022, while the city's greater urban area had a population of 1,064,235 in 2022 ...
receives only , and Skjåk Municipality, a municipality
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having municipal corporation, corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality' ...
situated in a deep valley, receives only . Further east, the partial influence of the Scandinavian Mountains contribute to areas in east-central Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
around Stockholm
Stockholm (; ) is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in Sweden by population, most populous city of Sweden, as well as the List of urban areas in the Nordic countries, largest urban area in the Nordic countries. Approximately ...
only receiving annually. In the north, the mountain range extending to the coast in around Narvik
() is the third-largest List of municipalities of Norway, municipality in Nordland Counties of Norway, county, Norway, by population. The administrative centre of the municipality is the Narvik (town), town of Narvik. Some of the notable villag ...
and Tromsø
Tromsø is a List of towns and cities in Norway, city in Tromsø Municipality in Troms county, Norway. The city is the administrative centre of the municipality as well as the administrative centre of Troms county. The city is located on the is ...
cause a lot higher precipitation there than in coastal areas further east facing north such as Alta or inland areas like Kiruna
(; ; ; ) is the northernmost Stad (Sweden), city in Sweden, situated in the province of Lapland, Sweden, Lapland. It had 17,002 inhabitants in 2016 and is the seat of Kiruna Municipality (population: 23,167 in 2016) in Norrbotten County. The c ...
across the Swedish border.
* The South Swedish highlands, although not rising more than , reduce precipitation and increase summer temperatures on the eastern side. Combined with the high pressure of the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
, this leads to some of the driest climates in the humid zones of Northern Europe being found in the triangle between the coastal areas in the counties of Kalmar, Östergötland and Södermanland
Södermanland ( ), locally Sörmland, sometimes referred to under its Latinisation of names, Latinized form Sudermannia or Sudermania, is a Provinces of Sweden, historical province (or ) on the south eastern coast of Sweden. It borders Österg� ...
along with the offshore island of Gotland
Gotland (; ; ''Gutland'' in Gutnish), also historically spelled Gottland or Gothland (), is Sweden's largest island. It is also a Provinces of Sweden, province/Counties of Sweden, county (Swedish län), Municipalities of Sweden, municipality, a ...
on the leeward side of the slopes. Coastal areas in this part of Sweden usually receive less precipitation than windward locations in Andalusia
Andalusia ( , ; , ) is the southernmost autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community in Peninsular Spain, located in the south of the Iberian Peninsula, in southwestern Europe. It is the most populous and the second-largest autonomou ...
in the south of Spain.
Southern Europe
* The Cantabrian Mountains form a sharp division between " Green Spain" to the north and the dry central plateau. The northern-facing slopes receive heavy rainfall from theBay of Biscay
The Bay of Biscay ( ) is a gulf of the northeast Atlantic Ocean located south of the Celtic Sea. It lies along the western coast of France from Point Penmarc'h to the Spanish border, and along the northern coast of Spain, extending westward ...
, but the southern slopes are in rain shadow. The other most evident effect on the Iberian Peninsula occurs in the Almería
Almería (, , ) is a city and municipalities in Spain, municipality of Spain, located in Andalusia. It is the capital of the province of Almería, province of the same name. It lies in southeastern Iberian Peninsula, Iberia on the Mediterranean S ...
, Murcia and Alicante
Alicante (, , ; ; ; officially: ''/'' ) is a city and municipalities of Spain, municipality in the Valencian Community, Spain. It is the capital of the province of Alicante and a historic Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean port. The population ...
areas, each with an average rainfall of , which are the driest spots in Europe (see Cabo de Gata) mostly a result of the mountain range running through their western side, which blocks the westerlies.
* The Norte Region in Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
has extreme differences in precipitation with values surpassing in the Peneda-Gerês National Park to values close to in the Douro Valley. Despite being only apart, Chaves has less than half the precipitation of Montalegre.
* The eastern part of the Pyrenean mountains in the south of France ( Cerdagne).
* In the Northern Apennines
The Apennines or Apennine Mountains ( ; or Ἀπέννινον ὄρος; or – a singular with plural meaning; )Latin ''Apenninus'' (Greek or ) has the form of an adjective, which would be segmented ''Apenn-inus'', often used with nouns s ...
of Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, Mediterranean city La Spezia
La Spezia (, or ; ; , in the local ) is the capital city of the province of La Spezia and is located at the head of the Gulf of La Spezia in the southern part of the Liguria region of Italy.
La Spezia is the second-largest city in the Liguria ...
receives twice the rainfall of Adriatic city Rimini
Rimini ( , ; or ; ) is a city in the Emilia-Romagna region of Northern Italy.
Sprawling along the Adriatic Sea, Rimini is situated at a strategically-important north-south passage along the coast at the southern tip of the Po Valley. It is ...
on the eastern side. This is also extended to the southern end of the Apennines that see vast rainfall differences between Naples
Naples ( ; ; ) is the Regions of Italy, regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 908,082 within the city's administrative limits as of 2025, while its Metropolitan City of N ...
with above on the Mediterranean side and Bari
Bari ( ; ; ; ) is the capital city of the Metropolitan City of Bari and of the Apulia Regions of Italy, region, on the Adriatic Sea in southern Italy. It is the first most important economic centre of mainland Southern Italy. It is a port and ...
with about on the Adriatic side.
* The valley of the Vardar River and south from Skopje
Skopje ( , ; ; , sq-definite, Shkupi) is the capital and largest city of North Macedonia. It lies in the northern part of the country, in the Skopje Basin, Skopje Valley along the Vardar River, and is the political, economic, and cultura ...
to Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
is in the rain shadow of the Accursed Mountains
The Accursed Mountains (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, Prokletije, Проклетије, separator=" / ", ; both translated as "Cursed Mountains"), also known as the Albanian Alps (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, Albanski Alpi, Албански Алпи, separator=" / ", li ...
and Pindus Mountains. On its windward side the Accursed Mountains has the highest rainfall in Europe at around with small glaciers even at mean annual temperatures well above , but the leeward side receives as little as .
Caribbean
* Throughout theGreater Antilles
The Greater Antilles is a grouping of the larger islands in the Caribbean Sea, including Cuba, Hispaniola, Puerto Rico, and Jamaica, together with Navassa Island and the Cayman Islands. Seven island states share the region of the Greater Antille ...
, the southwestern sides are in the rain shadow of the trade winds and can receive as little as per year as against over on the northeastern, windward sides and over over some highland areas. This is most apparent in Cuba
Cuba, officially the Republic of Cuba, is an island country, comprising the island of Cuba (largest island), Isla de la Juventud, and List of islands of Cuba, 4,195 islands, islets and cays surrounding the main island. It is located where the ...
, where this phenomenon leads to the Cuban cactus scrub ecoregion, and the island of Hispaniola
Hispaniola (, also ) is an island between Geography of Cuba, Cuba and Geography of Puerto Rico, Puerto Rico in the Greater Antilles of the Caribbean. Hispaniola is the most populous island in the West Indies, and the second-largest by List of C ...
(which contains the Caribbean's highest mountain ranges), which results in xeric semi-arid shrublands throughout the Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles of the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean. It shares a Maritime boundary, maritime border with Puerto Rico to the east and ...
and Haiti
Haiti, officially the Republic of Haiti, is a country on the island of Hispaniola in the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and south of the Bahamas. It occupies the western three-eighths of the island, which it shares with the Dominican ...
.
North American mainland
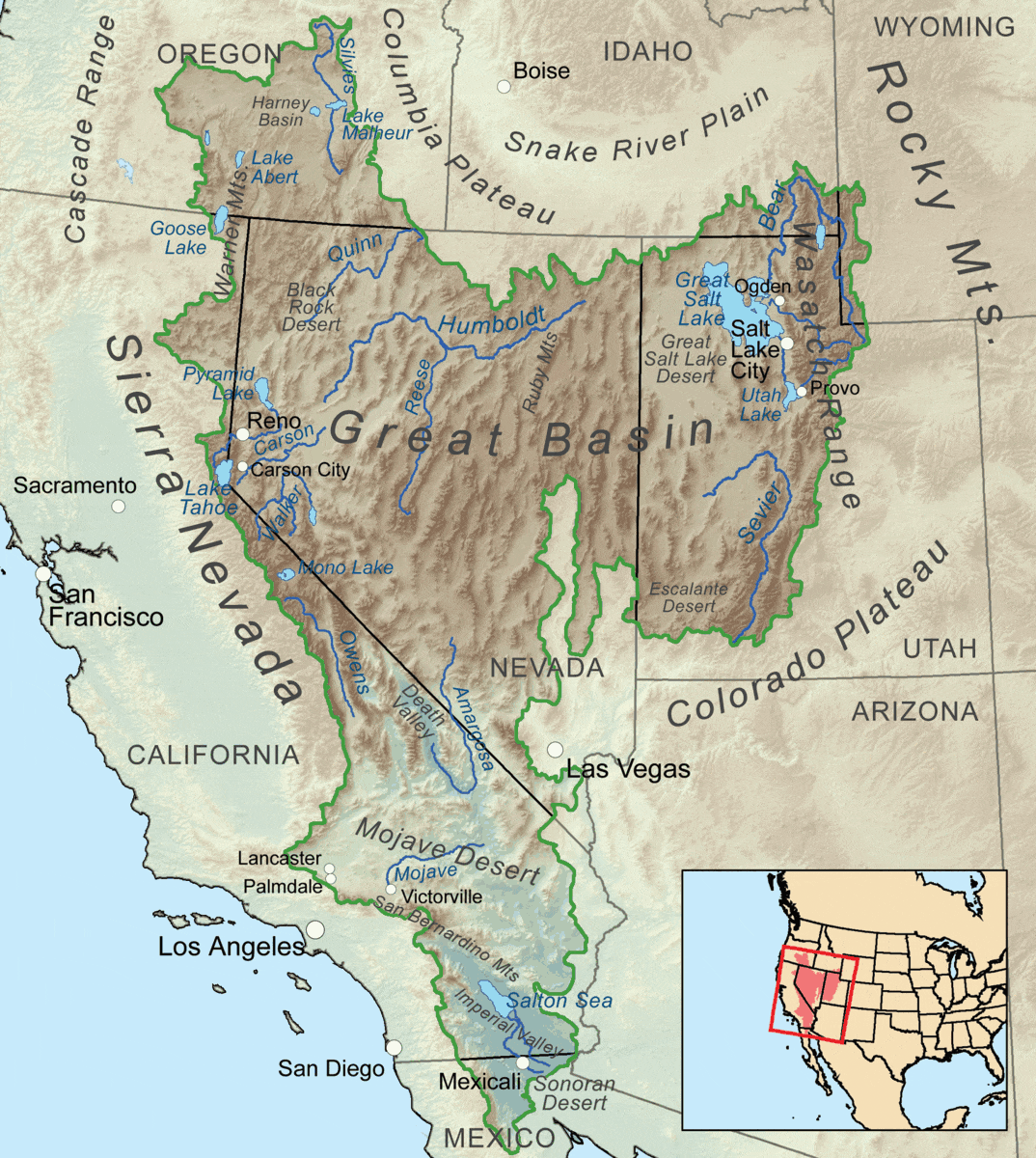
 On the largest scale, the entirety of the North American Interior Plains are shielded from the prevailing
On the largest scale, the entirety of the North American Interior Plains are shielded from the prevailing Westerlies
The westerlies, anti-trades, or prevailing westerlies, are prevailing winds from the west toward the east in the middle latitudes between 30 and 60 degrees latitude. They originate from the high-pressure areas in the horse latitudes (about ...
carrying moist Pacific weather by the North American Cordillera. More pronounced effects are observed, however, in particular valley regions within the Cordillera, in the direct lee of specific mountain ranges. This includes much of the Basin and Range Province in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
and Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
.
The Pacific Coast Ranges create rain shadows near the West Coast:
* The Dungeness Valley around Sequim and Port Angeles, Washington lies in the rain shadow of the Olympic Mountains. The area averages of rain per year. The rain shadow extends to the eastern Olympic Peninsula, Whidbey Island, parts of the San Juan Islands
The San Juan Islands is an archipelago in the Pacific Northwest of the United States between the U.S. state of Washington and Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. The San Juan Islands are part of Washington state, and form the core of ...
, and Victoria, British Columbia
Victoria is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of British Columbia, on the southern tip of Vancouver Island off Canada's Pacific Ocean, Pacific coast. The city has a population of 91,867, and the Gre ...
which receive between of precipitation each year. Seattle
Seattle ( ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Washington and in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. With a population of 780,995 in 2024, it is the 18th-most populous city in the United States. The city is the cou ...
is also affected by the rain shadow, albeit to a much lesser effect. By contrast, Aberdeen
Aberdeen ( ; ; ) is a port city in North East Scotland, and is the List of towns and cities in Scotland by population, third most populous Cities of Scotland, Scottish city. Historically, Aberdeen was within the historic county of Aberdeensh ...
, which is situated southwest of the Olympics, receives nearly of rain per year
* The east slopes of the Coast Ranges in central and southern California cut off the southern San Joaquin Valley
The San Joaquin Valley ( ; Spanish language in California, Spanish: ''Valle de San Joaquín'') is the southern half of California's Central Valley (California), Central Valley. Famed as a major breadbasket, the San Joaquin Valley is an importa ...
from enough precipitation to ensure desert-like conditions in areas around Bakersfield.
* San Jose, and adjacent cities are usually drier than the rest of the San Francisco Bay Area
The San Francisco Bay Area, commonly known as the Bay Area, is a List of regions of California, region of California surrounding and including San Francisco Bay, and anchored by the cities of Oakland, San Francisco, and San Jose, California, S ...
because of the rain shadow cast by the highest part of the Santa Cruz Mountains.
* The Sonoran Desert is bounded to the west by the Peninsular Ranges, but extends even along part of the east coast of the Gulf of California
The Gulf of California (), also known as the Sea of Cortés (''Mar de Cortés'') or Sea of Cortez, or less commonly as the Vermilion Sea (''Mar Vermejo''), is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean that separates the Baja California peninsula from ...
.
* The Sierra Madre Occidental in Mexico are west of the Chihuahuan Desert.
Most rain shadows in the western United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
are due to the Sierra Nevada
The Sierra Nevada ( ) is a mountain range in the Western United States, between the Central Valley of California and the Great Basin. The vast majority of the range lies in the state of California, although the Carson Range spur lies primari ...
mountains in California and Cascade Mountains, mostly in Oregon
Oregon ( , ) is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is a part of the Western U.S., with the Columbia River delineating much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while t ...
and Washington.
* The Cascades create a rain-shadowed Columbia Basin area of Eastern Washington and valleys in British Columbia, Canada - most notably the Thompson and Nicola Valleys which can receive less than of rain in parts, and the Okanagan Valley (particularly the south, nearest to the US border) which receives anywhere from 12 to 17 inches of rain annually.
* The endorheic
An endorheic basin ( ; also endoreic basin and endorreic basin) is a drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water (e.g. rivers and oceans); instead, the water drainage flows into permanent ...
Great Basin of Utah
Utah is a landlocked state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is one of the Four Corners states, sharing a border with Arizona, Colorado, and New Mexico. It also borders Wyoming to the northea ...
and Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a landlocked state in the Western United States. It borders Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the seventh-most extensive, th ...
is in the rain shadows of the Cascades and Sierra Nevada.
* The Mojave Desert
The Mojave Desert (; ; ) is a desert in the rain shadow of the southern Sierra Nevada mountains and Transverse Ranges in the Southwestern United States. Named for the Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous Mohave people, it is located pr ...
is rain-shadowed by the Sierra Nevada and the Transverse Ranges of southern California.
* The Black Rock Desert is in the rain shadows of the Cascades and Sierra Nevada.
* California's Owens Valley
Owens Valley (Mono language (California), Mono: ''Payahǖǖnadǖ'', meaning "place of flowing water") is an arid valley of the Owens River in eastern California in the United States. It is located to the east of the Sierra Nevada (U.S.), Sierra ...
is rain-shadowed by the Sierra Nevada.
* Death Valley
Death Valley is a desert valley in Eastern California, in the northern Mojave Desert, bordering the Great Basin Desert. It is thought to be the Highest temperature recorded on Earth, hottest place on Earth during summer.
Death Valley's Badwat ...
in the United States, behind both the Pacific Coast Ranges of California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
and the Sierra Nevada
The Sierra Nevada ( ) is a mountain range in the Western United States, between the Central Valley of California and the Great Basin. The vast majority of the range lies in the state of California, although the Carson Range spur lies primari ...
range, is the driest place in North America and one of the driest places on the planet. This is also due to its location well below sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an mean, average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal Body of water, bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical ...
which tends to cause high pressure and dry conditions to dominate due to the greater weight of the atmosphere above.
The Colorado Front Range is limited to precipitation that crosses over the Continental Divide. While many locations west of the Divide may receive as much as of precipitation per year, some places on the eastern side, notably the cities of Denver
Denver ( ) is a List of municipalities in Colorado#Consolidated city and county, consolidated city and county, the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Colorado, most populous city of the U.S. state of ...
and Pueblo, Colorado
Pueblo ( ) is a List of municipalities in Colorado#Home rule municipality, home rule municipality that is the county seat of and the List of municipalities in Colorado, most populous municipality in Pueblo County, Colorado, United States. The ...
, typically receive only about 12 to 19 inches. Thus, the Continental Divide acts as a barrier for precipitation. This effect applies only to storms traveling west-to-east. When low pressure systems skirt the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in great-circle distance, straight-line distance from the northernmost part of Western Can ...
and approach from the south, they can generate high precipitation on the eastern side and little or none on the western slope.
Further east:
* The Shenandoah Valley of Virginia, wedged between the Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians and the Blue Ridge Mountains
The Blue Ridge Mountains are a Physiographic regions of the United States, physiographic province of the larger Appalachian Highlands range. The mountain range is located in the Eastern United States and extends 550 miles southwest from southern ...
and partially shielded from moisture from the west and southeast, is much drier than the very humid remainder of Virginia and the American Southeast.
* Asheville, North Carolina sits in the rain shadow of the Balsam, Smoky, and Blue Ridge Mountains
The Blue Ridge Mountains are a Physiographic regions of the United States, physiographic province of the larger Appalachian Highlands range. The mountain range is located in the Eastern United States and extends 550 miles southwest from southern ...
. While the mountains surrounding Asheville contain the Appalachian temperate rainforests, with areas receiving over an annual average precipitation of , the city itself is the driest location in North Carolina, with an annual average precipitation of only .
* Ashcroft, British Columbia, the only true desert in Canada, sits in the rain shadow of the Coast Mountains of Canada.
* Yellowknife
Yellowknife is the capital, largest community, and the only city in the Northwest Territories, Canada. It is on the northern shore of Great Slave Lake, about south of the Arctic Circle, on the west side of Yellowknife Bay near the outlet of t ...
, the capital and most populous city in the Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories is a federal Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada. At a land area of approximately and a 2021 census population of 41,070, it is the second-largest and the most populous of Provinces and territorie ...
of Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
, is located in the rain shadow of the mountain ranges to the west of the city.
Oceania
Australia
* InNew South Wales
New South Wales (commonly abbreviated as NSW) is a States and territories of Australia, state on the Eastern states of Australia, east coast of :Australia. It borders Queensland to the north, Victoria (state), Victoria to the south, and South ...
and the Australian Capital Territory
The Australian Capital Territory (ACT), known as the Federal Capital Territory until 1938, is an internal States and territories of Australia, territory of Australia. Canberra, the capital city of Australia, is situated within the territory, an ...
, Monaro is shielded by both the Snowy Mountains to the northwest and coastal ranges to the southeast. Consequently, parts of it are as dry as the wheat-growing lands of those states. For comparison, Cooma receives of rain annually, whereas Batlow, on the western side of the ranges, receives of precipitation. Furthermore, Australia's capital Canberra
Canberra ( ; ) is the capital city of Australia. Founded following the Federation of Australia, federation of the colonies of Australia as the seat of government for the new nation, it is Australia's list of cities in Australia, largest in ...
is also protected from the west by the Brindabellas which create a strong rain shadow in Canberra's valleys, where it receives an annual rainfall of , compared to Adjungbilly's . In the cool season, the Great Dividing Range
The Great Dividing Range, also known as the East Australian Cordillera or the Eastern Highlands, is a cordillera system in eastern Australia consisting of an expansive collection of mountain ranges, plateaus and rolling hills. It runs roughl ...
also shields much of the southeast coast (i.e. Sydney
Sydney is the capital city of the States and territories of Australia, state of New South Wales and the List of cities in Australia by population, most populous city in Australia. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Syd ...
, the Central Coast, the Hunter Valley, Illawarra, the South Coast) from south-westerly polar blasts that originate from the Southern Ocean
The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean, comprises the southernmost waters of the world ocean, generally taken to be south of 60th parallel south, 60° S latitude and encircling Antarctica. With a size of , it is the seco ...
.
* In Queensland
Queensland ( , commonly abbreviated as Qld) is a States and territories of Australia, state in northeastern Australia, and is the second-largest and third-most populous state in Australia. It is bordered by the Northern Territory, South Austr ...
, the land west of Atherton Tableland in the Tablelands Region lies on a rain shadow and therefore would feature significantly lower annual rainfall averages than those in the Cairns Region. For comparison, Tully, which is on the eastern side of the tablelands, towards the coast, receives annual rainfall that exceeds , whereas Mareeba, which lies on the rain shadow of the Atherton Tableland, receives of rainfall annually.
* In Tasmania
Tasmania (; palawa kani: ''Lutruwita'') is an island States and territories of Australia, state of Australia. It is located to the south of the Mainland Australia, Australian mainland, and is separated from it by the Bass Strait. The sta ...
, the central Midlands region is in a strong rain shadow and receives only about a fifth as much rainfall as the highlands to the west.
* In Victoria, the western side of Port Phillip Bay is in the rain shadow of the Otway Ranges. The area between Geelong
Geelong ( ) (Wathawurrung language, Wathawurrung: ''Djilang''/''Djalang'') is a port city in Victoria, Australia, located at the eastern end of Corio Bay (the smaller western portion of Port Phillip Bay) and the left bank of Barwon River (Victo ...
and Werribee is the driest part of southern Victoria: the crest of the Otway Ranges receives of rain per year and has myrtle beech rainforests much further west than anywhere else, while the area around Little River receives as little as annually, which is as little as Nhill or Longreach and supports only grassland. Also in Victoria, Omeo is shielded by the surrounding Victorian Alps, where it receives around of annual rain, whereas other places nearby exceed .
* Western Australia
Western Australia (WA) is the westernmost state of Australia. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east, and South Australia to the south-east. Western Aust ...
's Wheatbelt and Great Southern regions are shielded by the Darling Range to the west: Mandurah, near the coast, receives about annually. Dwellingup, inland and in the heart of the ranges, receives over a year while Narrogin, further east, receives less than a year.
Pacific Islands
*Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
also has rain shadows, with some areas being desert. Orographic lifting produces the world's second-highest annual precipitation record, , on the island of Kauai
Kauai (), anglicized as Kauai ( or ), is one of the main Hawaiian Islands.
It has an area of 562.3 square miles (1,456.4 km2), making it the fourth-largest of the islands and the 21st-largest island in the United States. Kauai lies 73 m ...
; the leeward side is understandably rain-shadowed. The entire island of Kahoolawe lies in the rain shadow of Maui's East Maui Volcano.
* New Caledonia
New Caledonia ( ; ) is a group of islands in the southwest Pacific Ocean, southwest of Vanuatu and east of Australia. Located from Metropolitan France, it forms a Overseas France#Sui generis collectivity, ''sui generis'' collectivity of t ...
lies astride the Tropic of Capricorn, between 19° and 23° south latitude. The climate of the islands is tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the equator, where the sun may shine directly overhead. This contrasts with the temperate or polar regions of Earth, where the Sun can never be directly overhead. This is because of Earth's ax ...
, and rainfall is brought by trade winds from the east. The western side of the Grande Terre lies in the rain shadow of the central mountains, and rainfall averages are significantly lower.
* On the South Island
The South Island ( , 'the waters of Pounamu, Greenstone') is the largest of the three major islands of New Zealand by surface area, the others being the smaller but more populous North Island and Stewart Island. It is bordered to the north by ...
of New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
is found one of the most remarkable rain shadows anywhere on Earth. The Southern Alps intercept moisture coming off the Tasman Sea, precipitating about liquid water equivalent per year and creating large glacier
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires ...
s on the western side. To the east of the Southern Alps, scarcely from the snowy peaks, yearly rainfall drops to less than and some areas less than . (see Nor'west arch for more on this subject).
South America
 * The
* The Atacama Desert
The Atacama Desert () is a desert plateau located on the Pacific Ocean, Pacific coast of South America, in the north of Chile. Stretching over a strip of land west of the Andes Mountains, it covers an area of , which increases to if the barre ...
in Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes, Andes Mountains and the Paci ...
is the driest non-polar desert on Earth because it is blocked from moisture by the Andes Mountains
The Andes ( ), Andes Mountains or Andean Mountain Range (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long and wide (widest between 18°S ...
to the east while the Humboldt Current causes persistent atmospheric stability.
* Cuyo and Eastern Patagonia is rain shadowed from the prevailing westerly winds by the Andes
The Andes ( ), Andes Mountains or Andean Mountain Range (; ) are the List of longest mountain chains on Earth, longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range ...
range and is arid. The aridity of the lands next to eastern piedmont of the Andes decreases to the south due to a decrease in the height of the Andes with the consequence that the Patagonian Desert develop more fully at the Atlantic coast contributing to shaping the climatic pattern known as the Arid Diagonal. The Argentinian wine region of Cuyo and Northern Patagonia is almost completely dependent on irrigation, using water drawn from the many rivers that drain glacial ice from the Andes
The Andes ( ), Andes Mountains or Andean Mountain Range (; ) are the List of longest mountain chains on Earth, longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range ...
.
* The Guajira Peninsula in northern Colombia is in the rain shadow of the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta
The Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta (English: ''Snow-Covered Mountain Range of Saint Martha'') is an isolated mountain range in northern Colombia, separate from the Andes range that runs through the north of the country. Reaching an elevation of ...
and despite its tropical latitude is almost arid, receiving almost no rainfall for seven to eight months of the year and being incapable of cultivation without irrigation.
See also
*Lake-effect snow
Lake-effect snow is produced during cooler atmospheric conditions when a cold air mass moves across long expanses of warmer lake water. The lower layer of air, heated by the lake water, picks up water vapor from the lake and rises through colde ...
* Orographic precipitation
* Wind shadow
References
External links
USA Today on rain shadows
Weather pages on rain shadows
{{DEFAULTSORT:Rain Shadow Land surface effects on climate Mountain meteorology Hydrology